The Role of La–Ti–Al–O Complex Inclusions in Microstructure Refinement and Toughness Enhancement of the Coarse-Grained Heat-Affected Zone in High-Heat-Input Welding
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Smelting and Composition of Experimental Steel
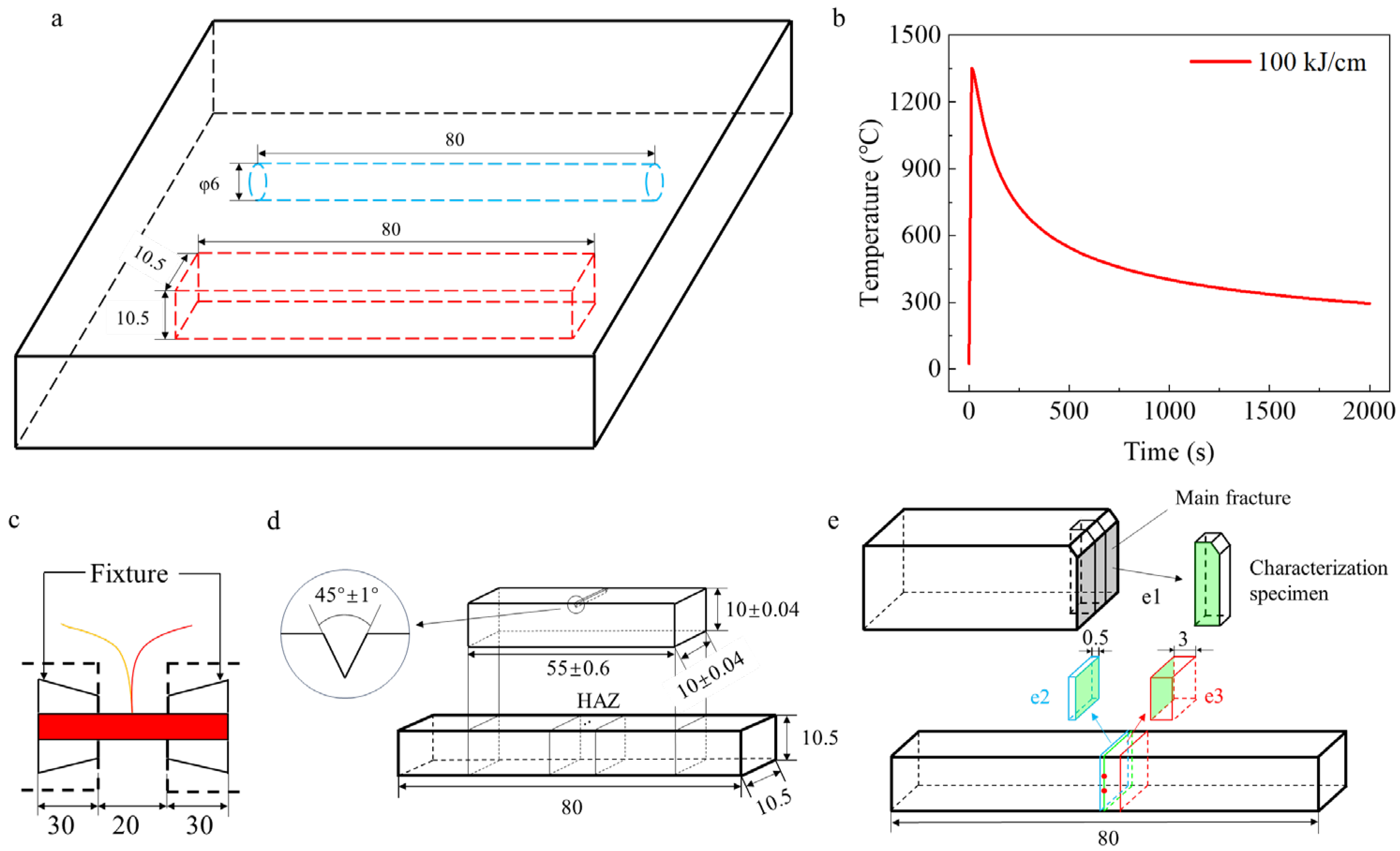
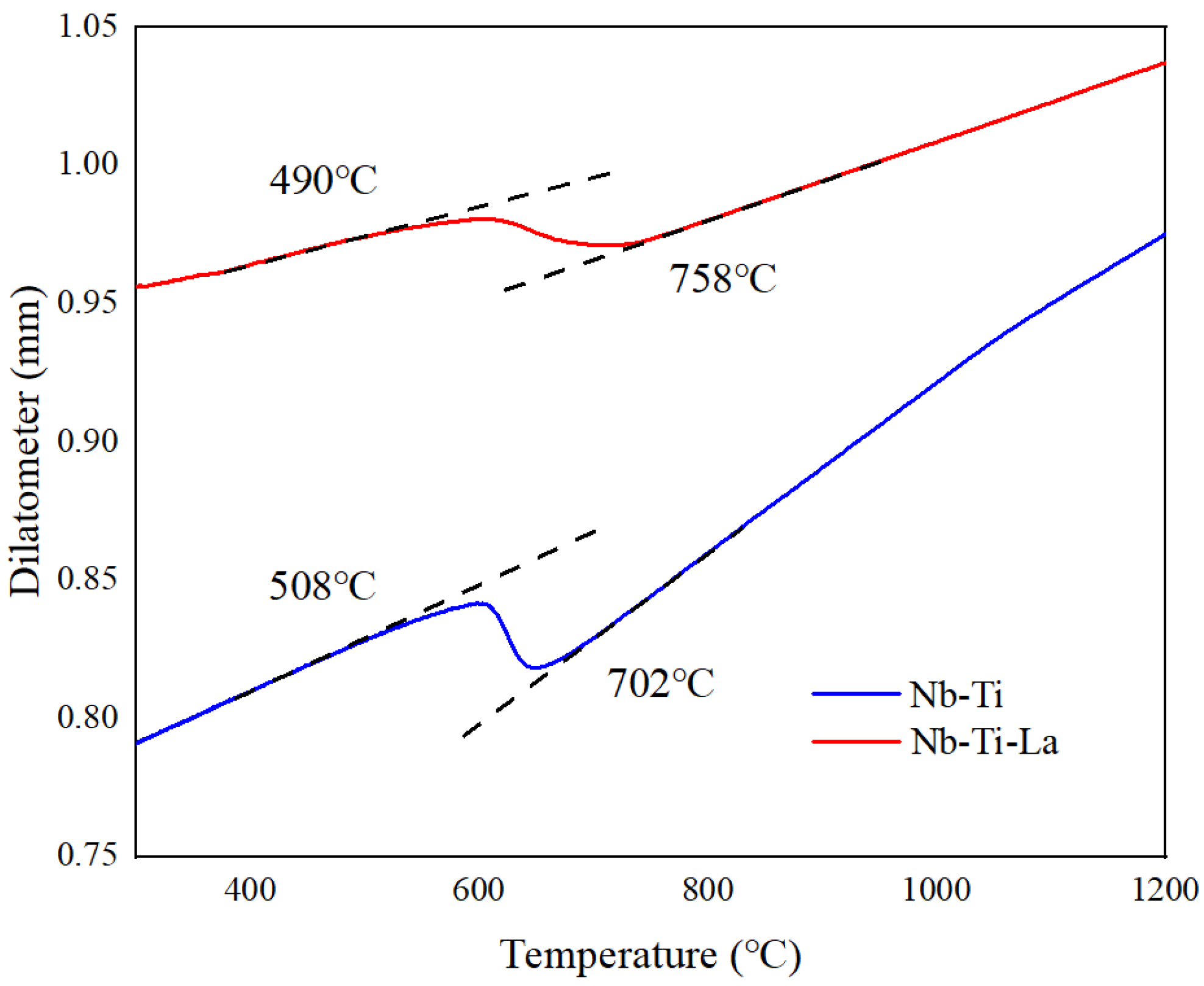
2.2. Welding Thermal Cycle Test
3. Results
3.1. Inclusions
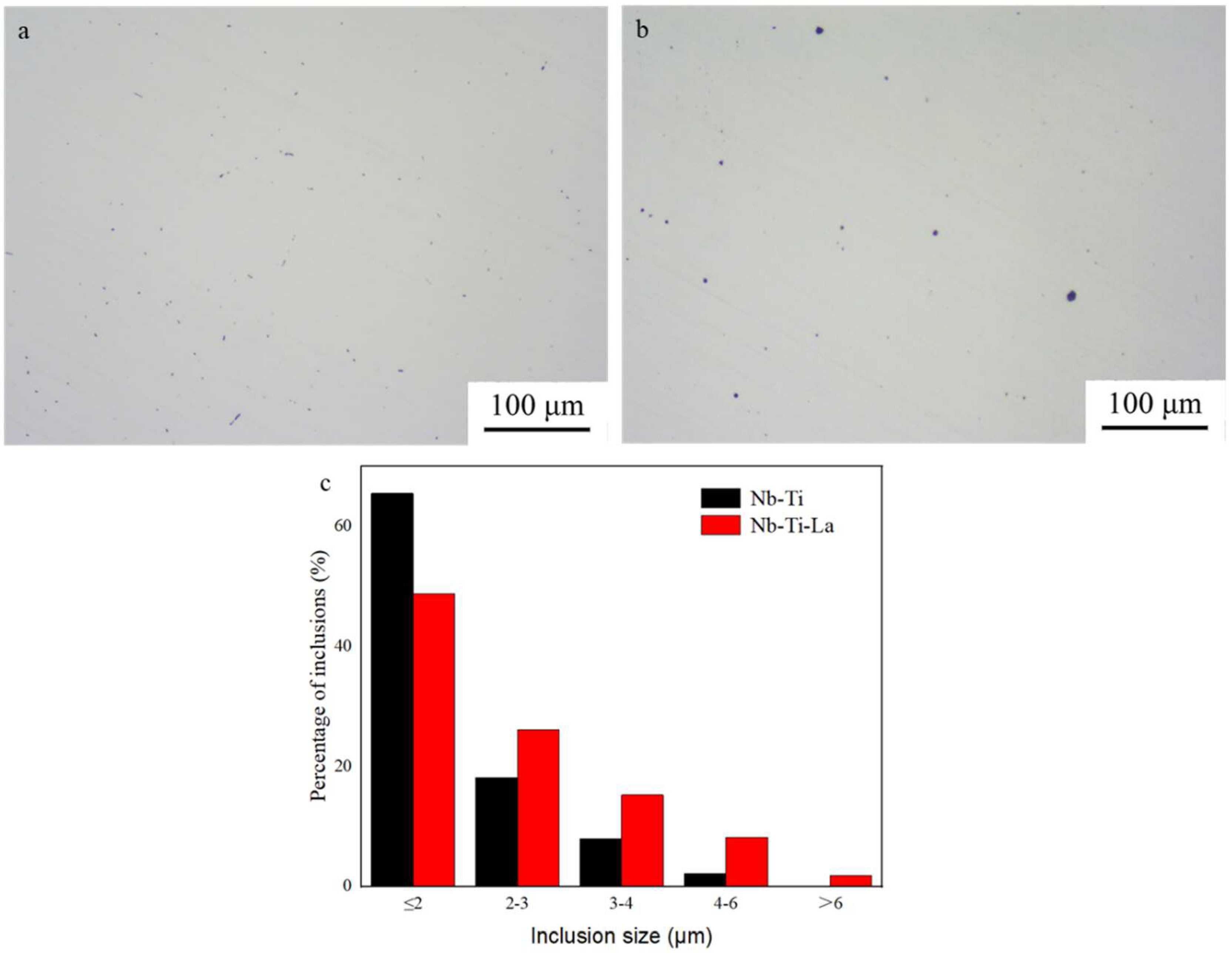
3.1.1. OM Observation and Statistical Analysis of Inclusions
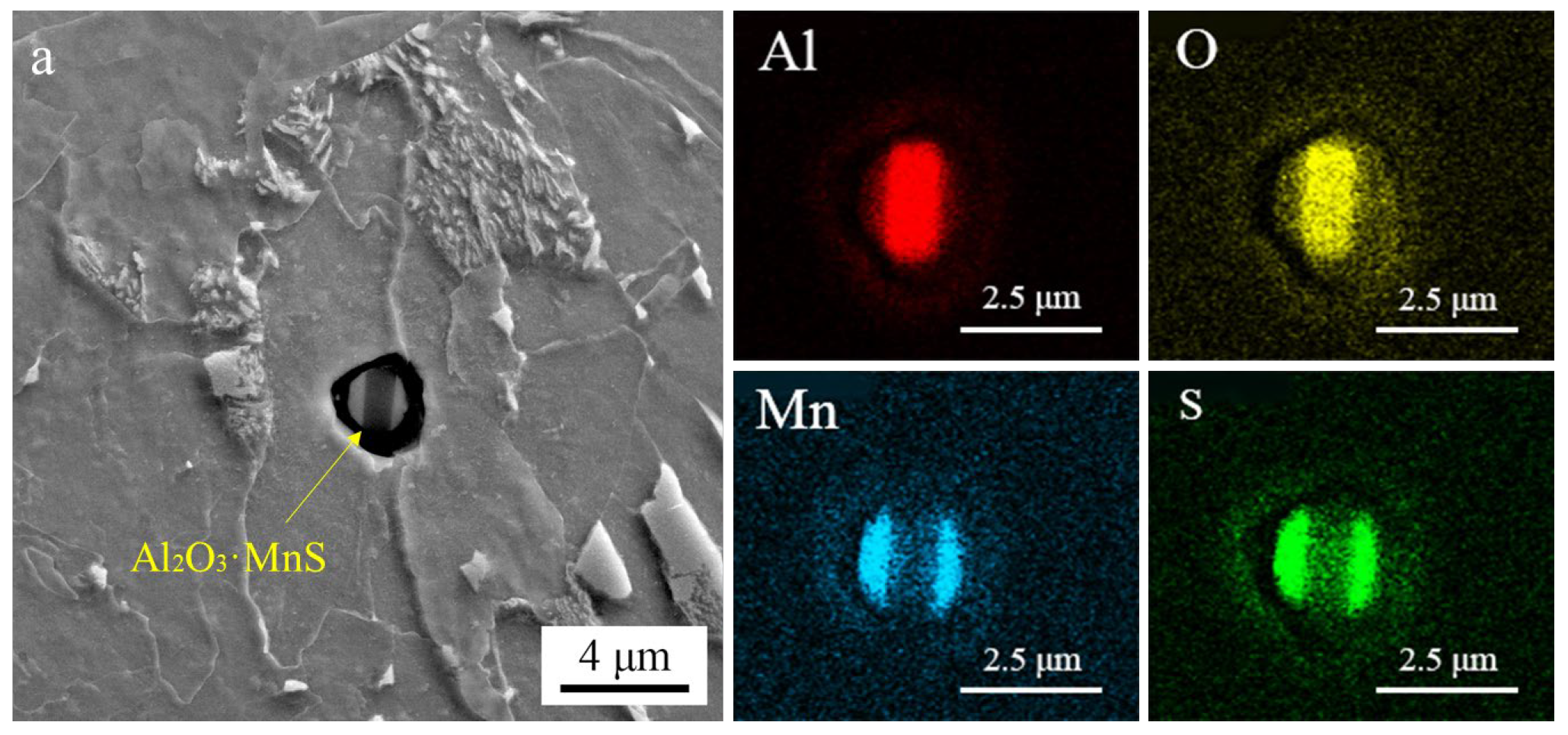
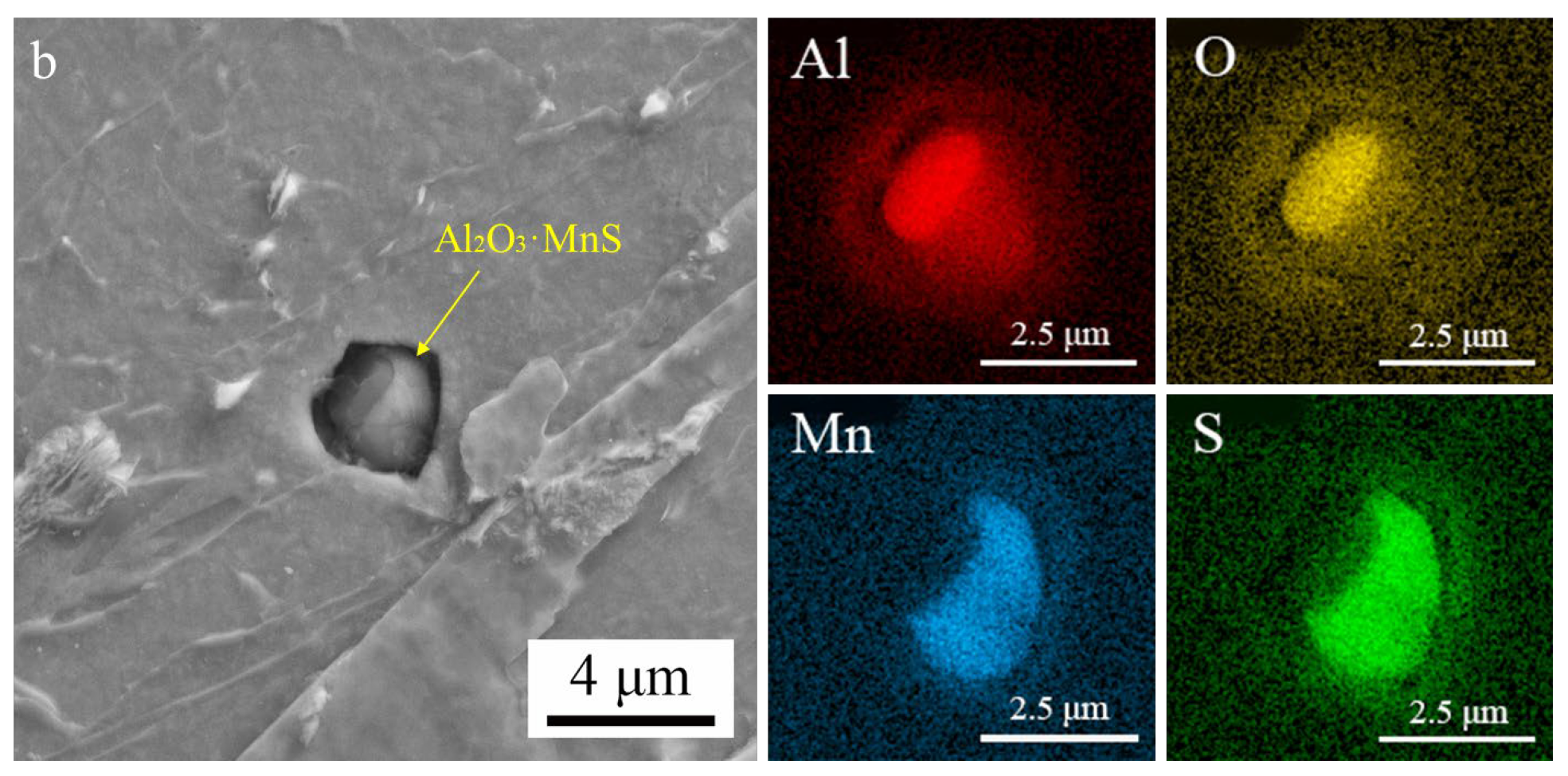
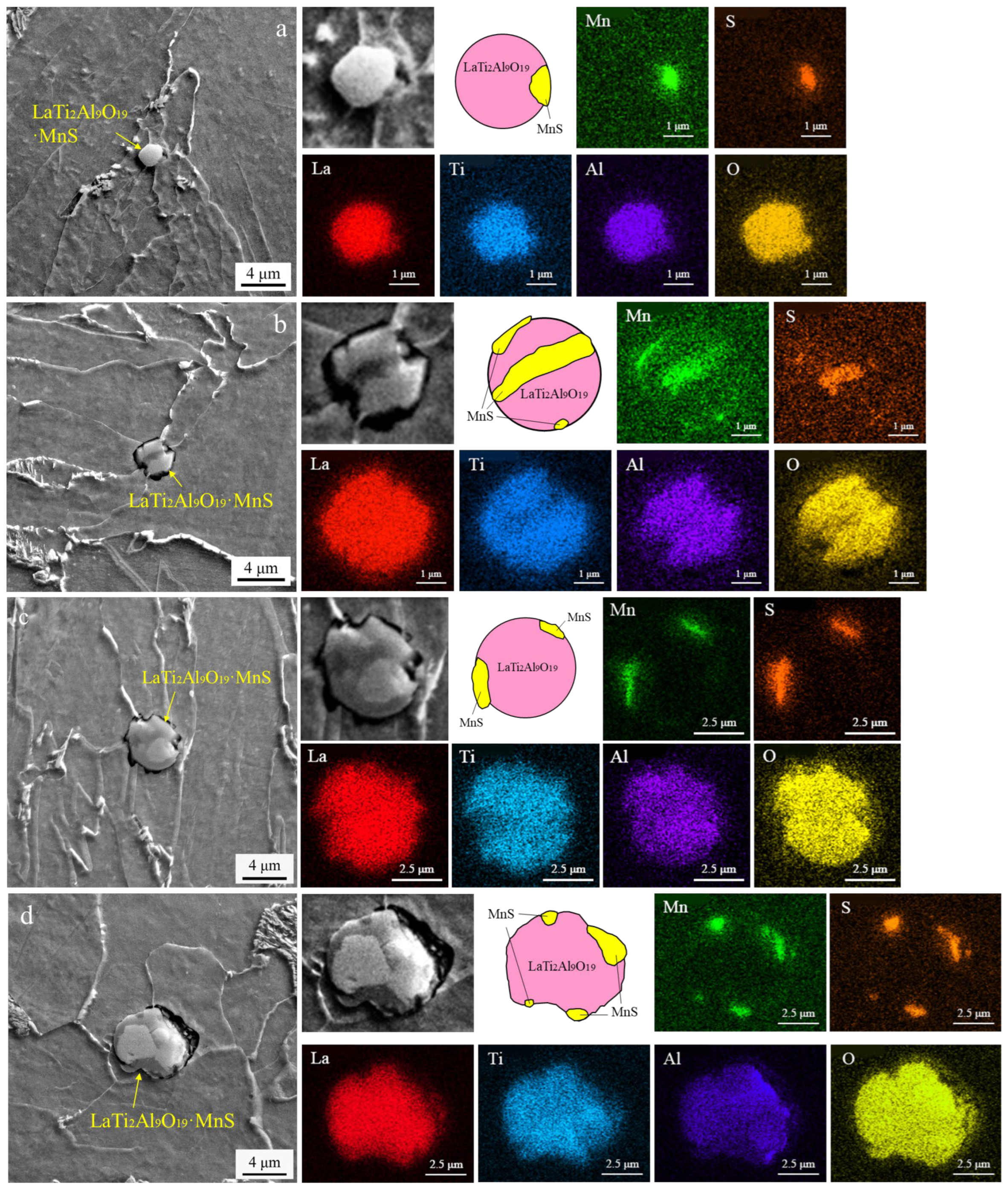
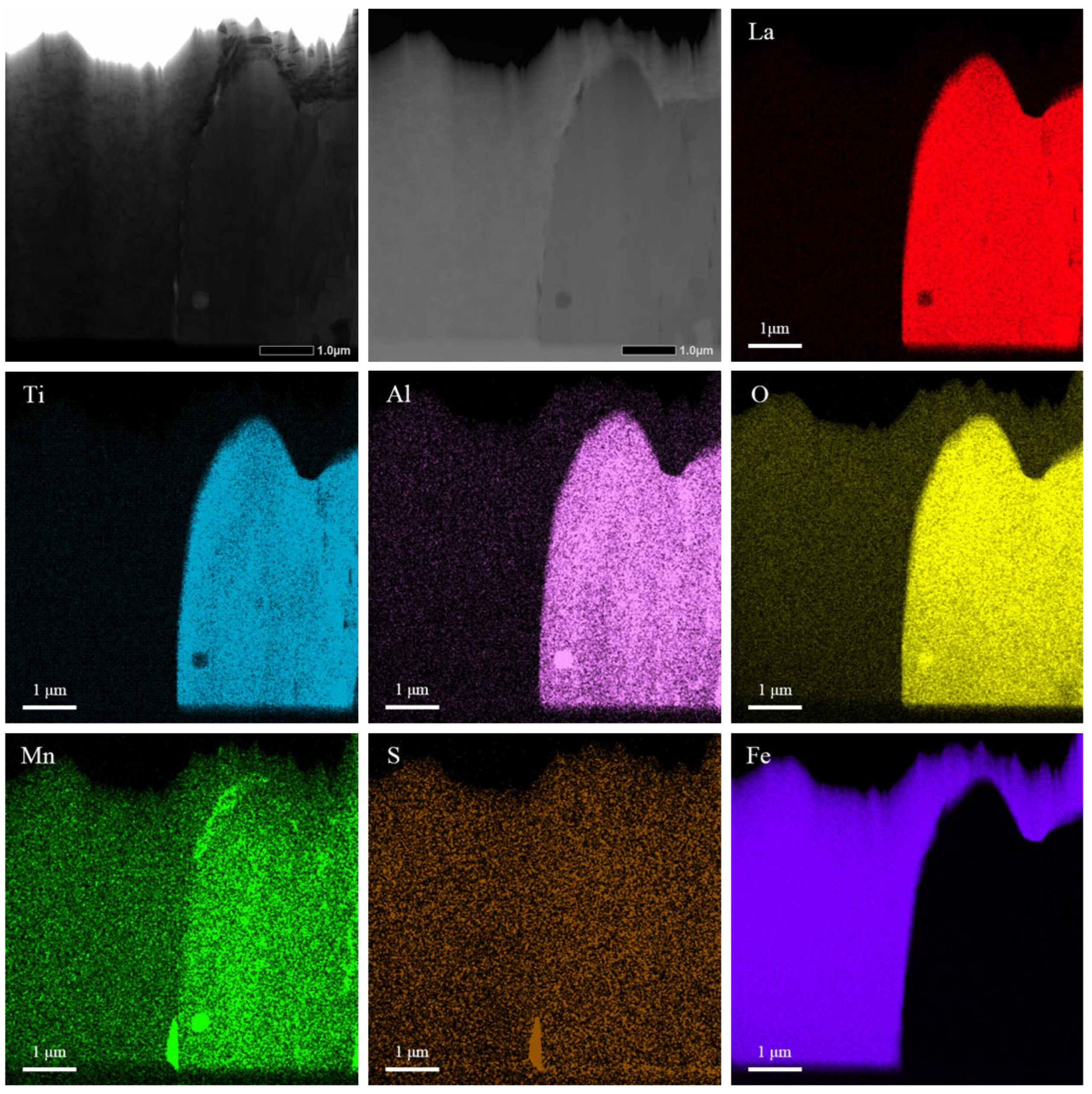
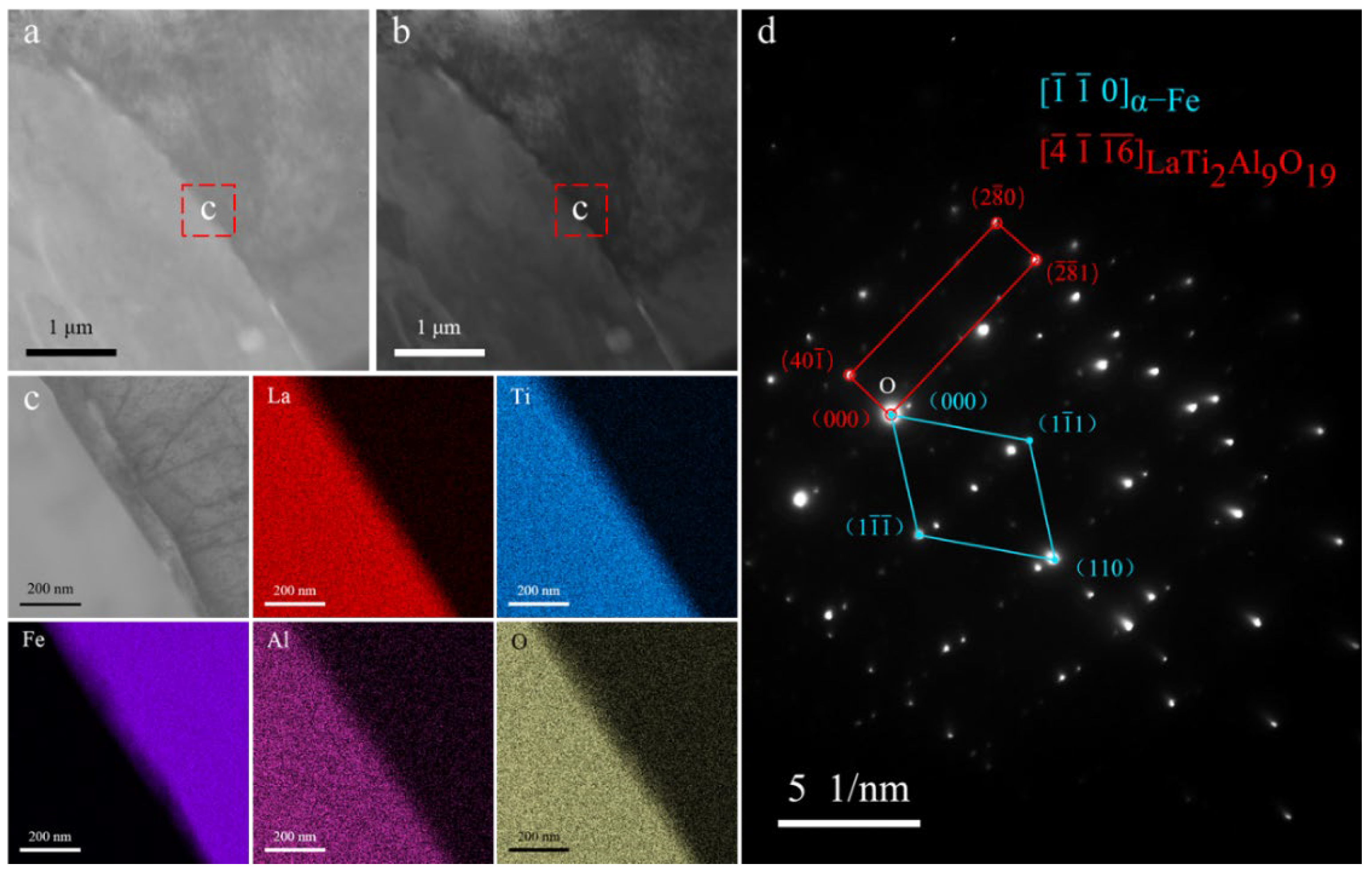
3.1.2. SEM Observation and EDX Analysis of Inclusions
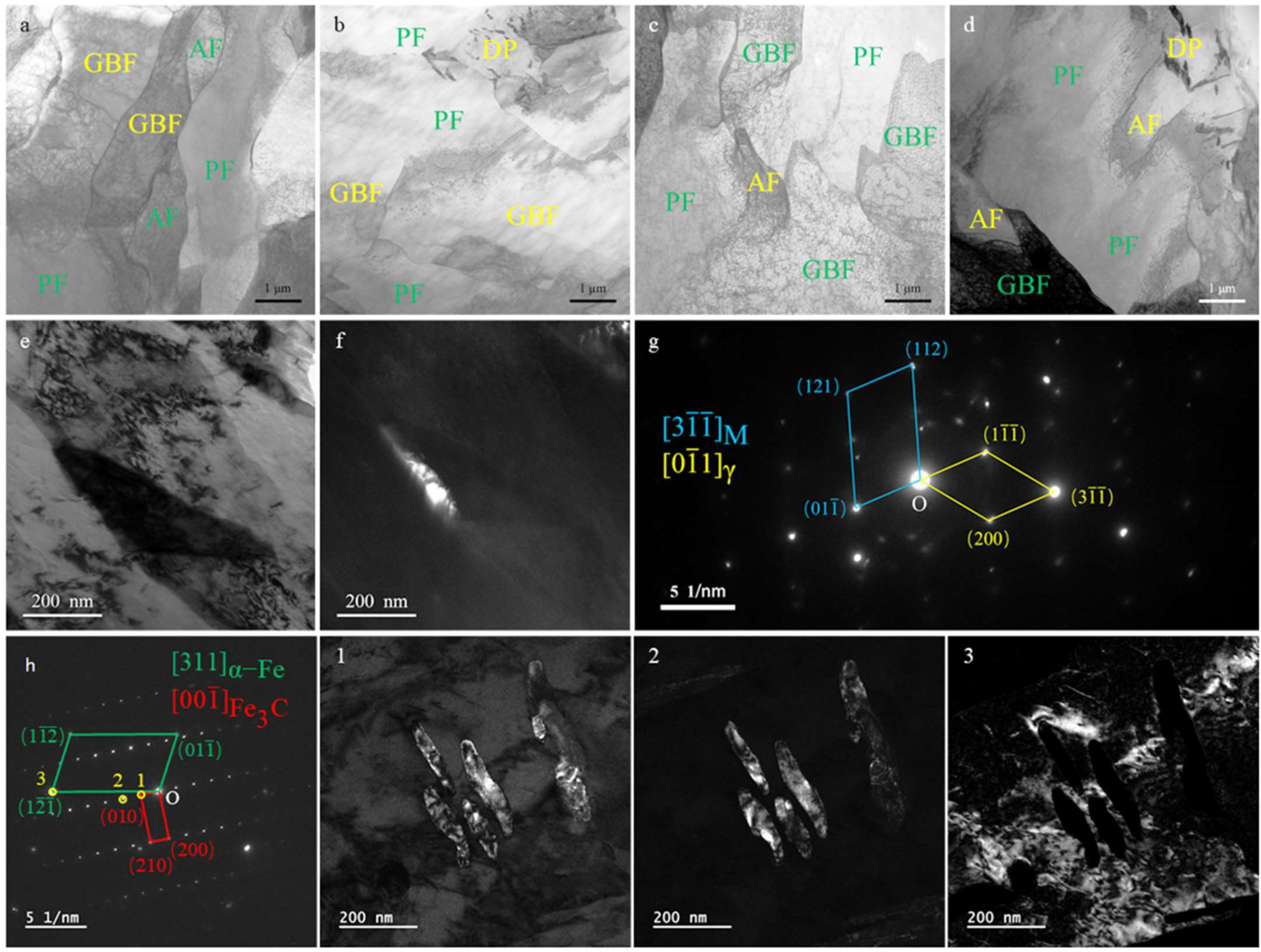
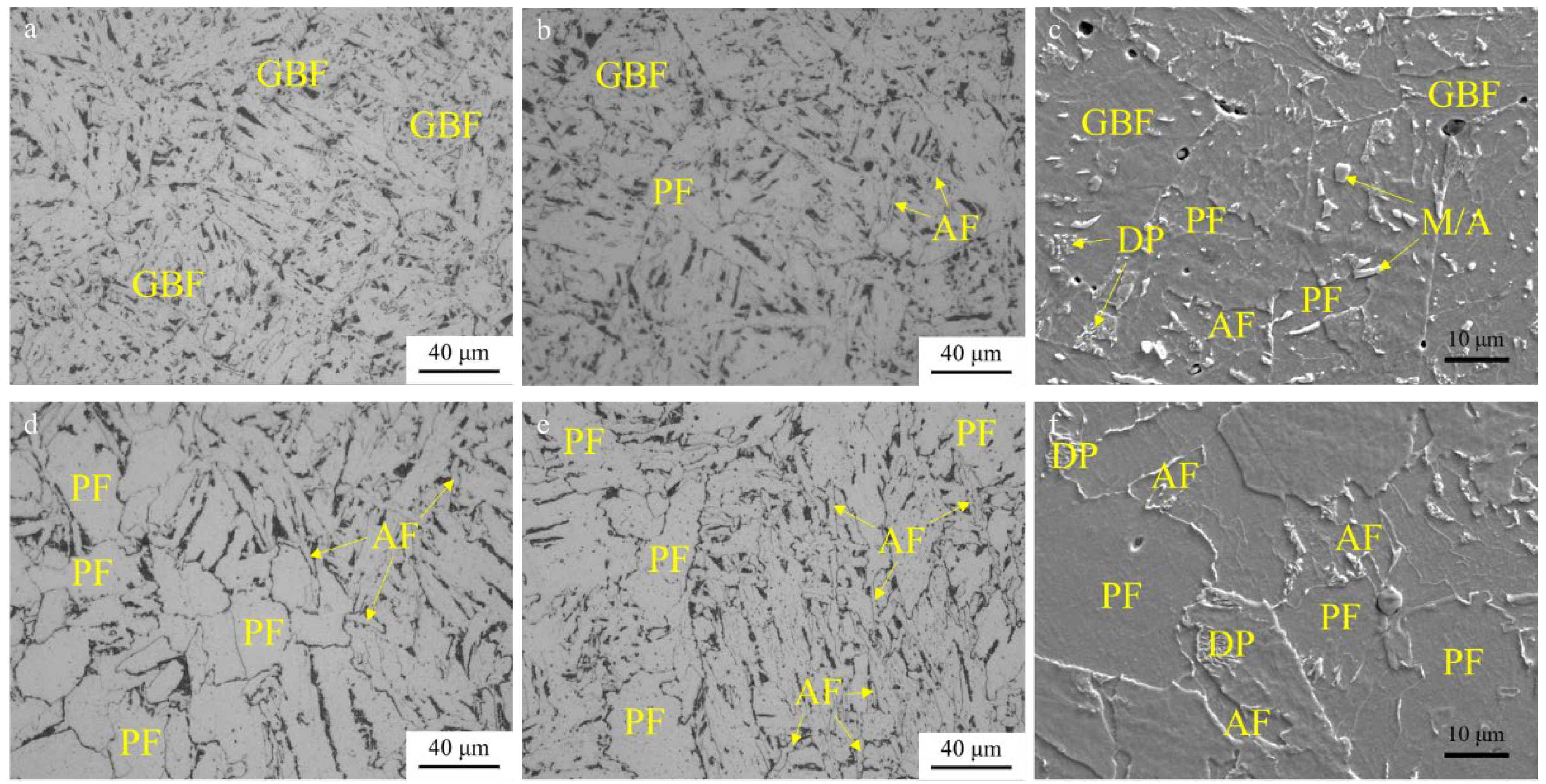
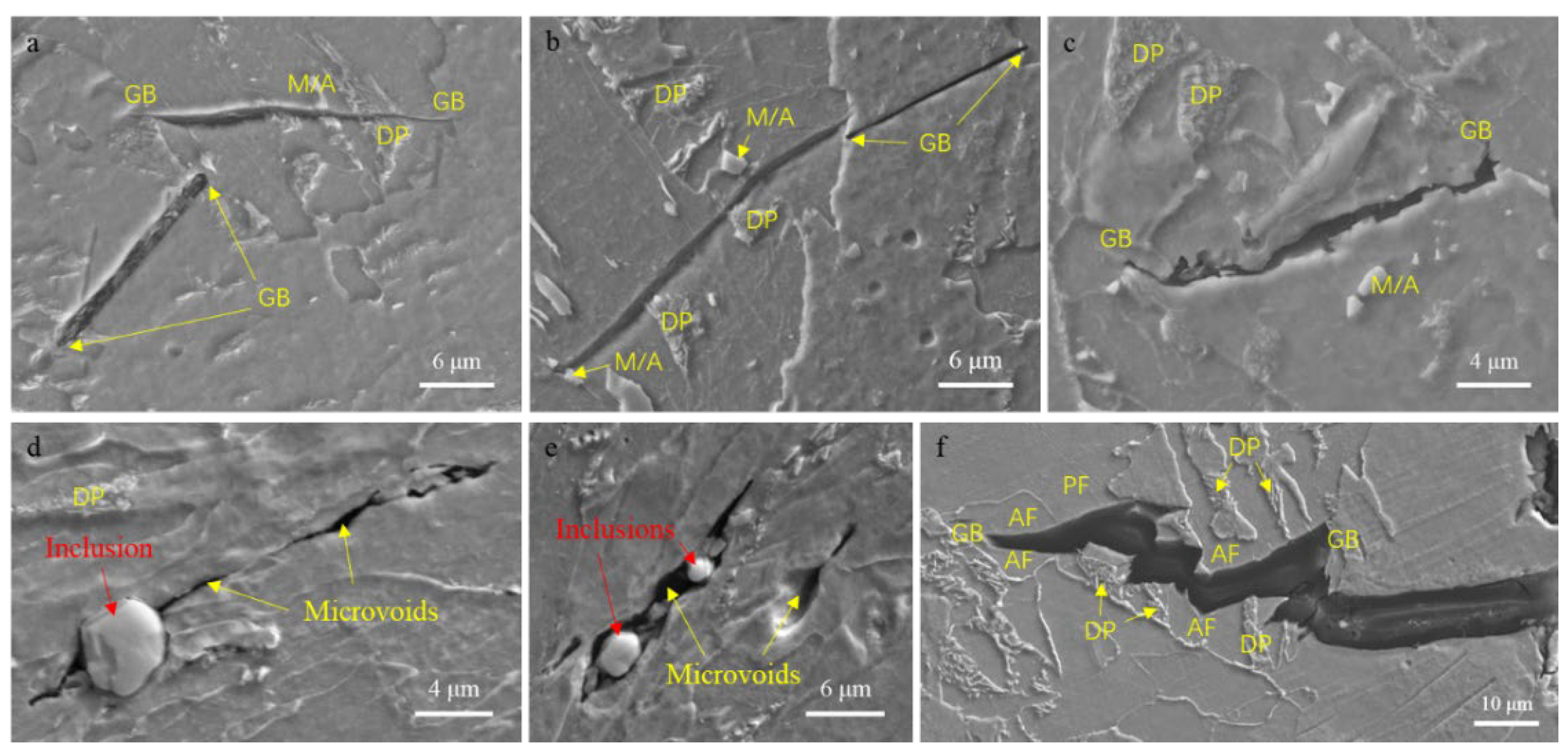
3.2. Microstructures
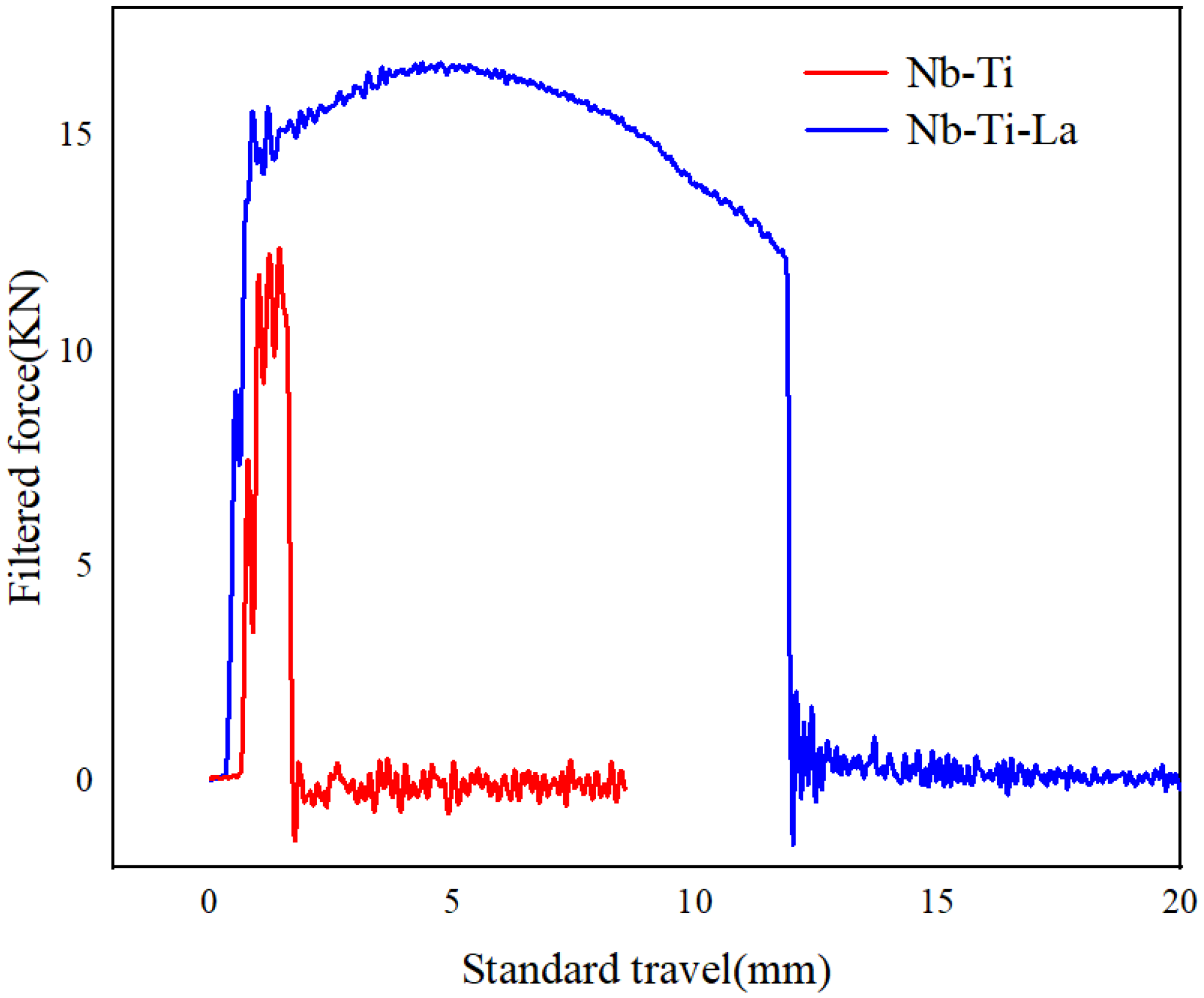
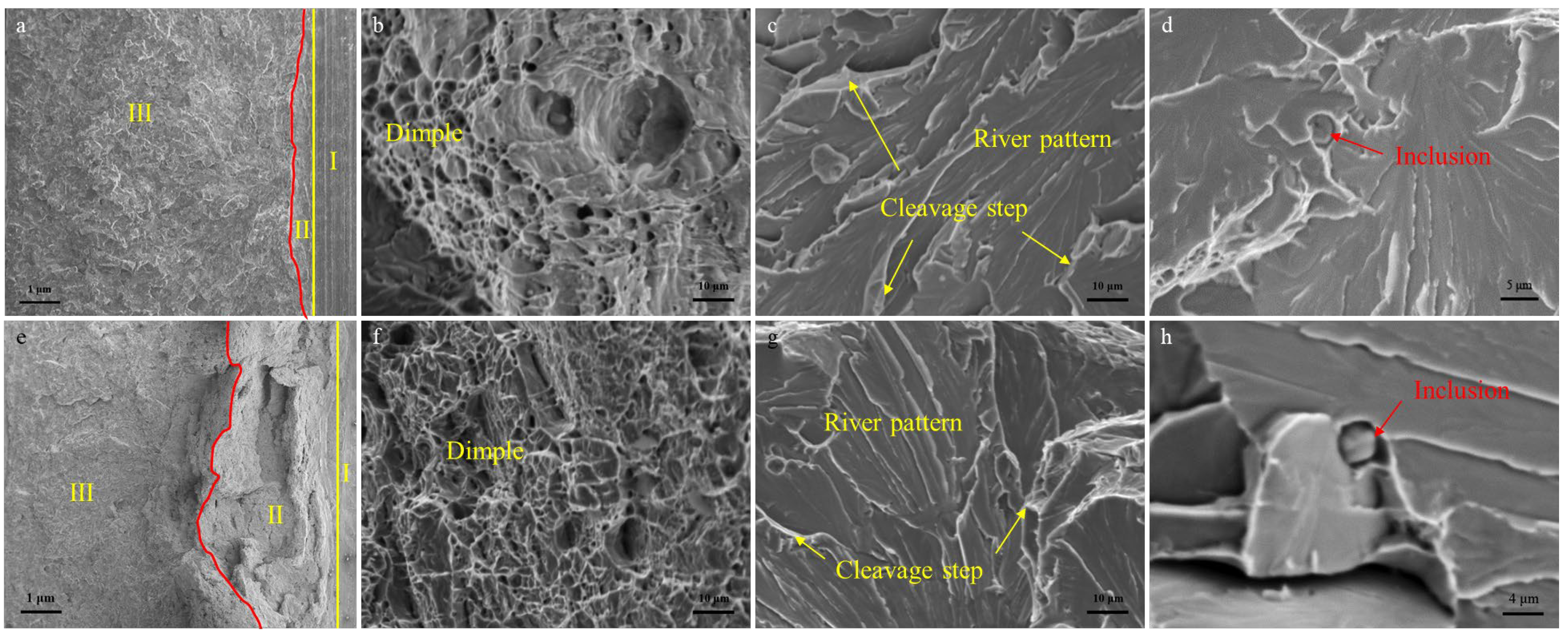
3.3. Impact Properties
4. Discussion
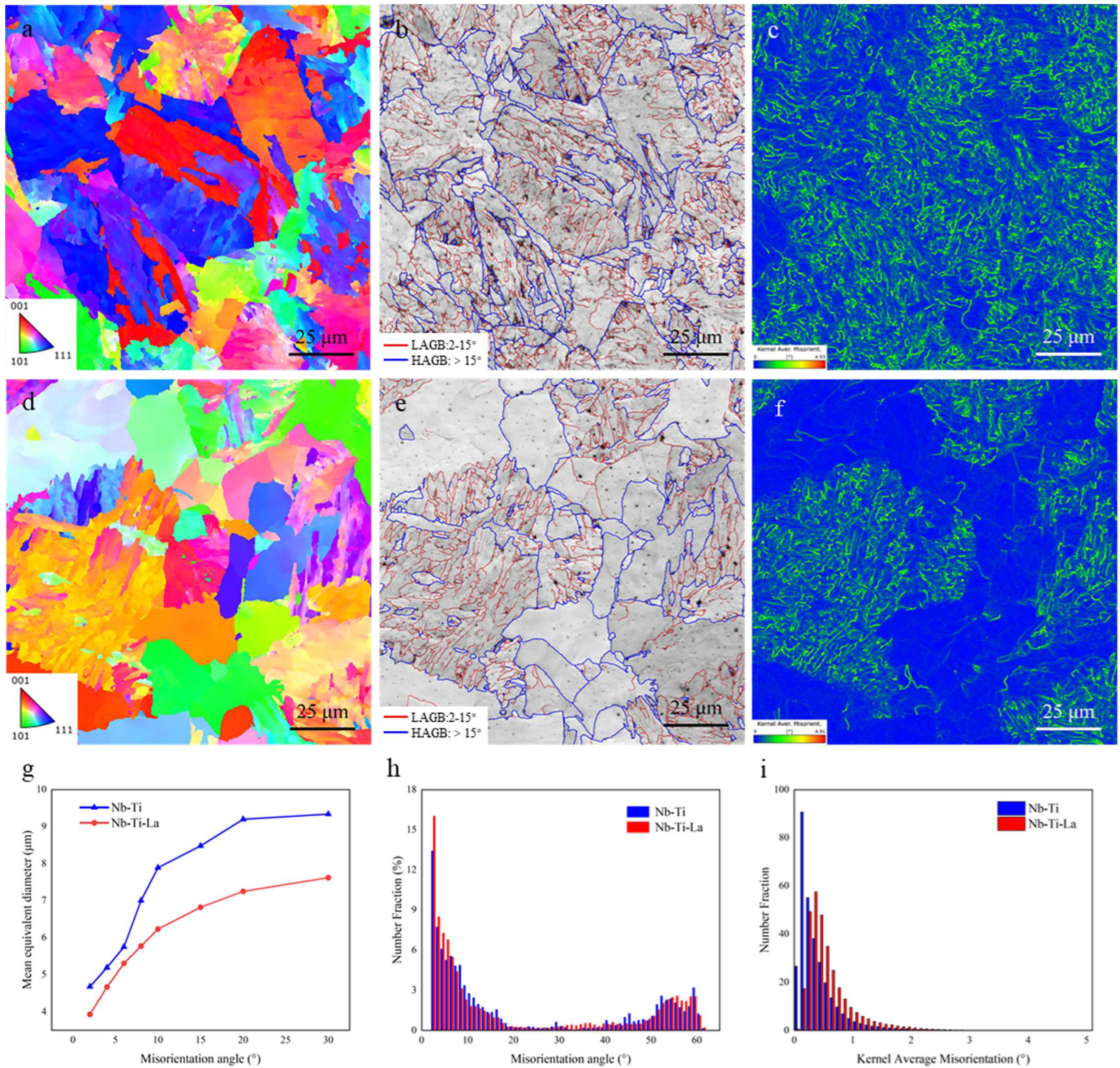
4.1. A Study on the Influence of Rare Earth La on the Microstructure of CGHAZs
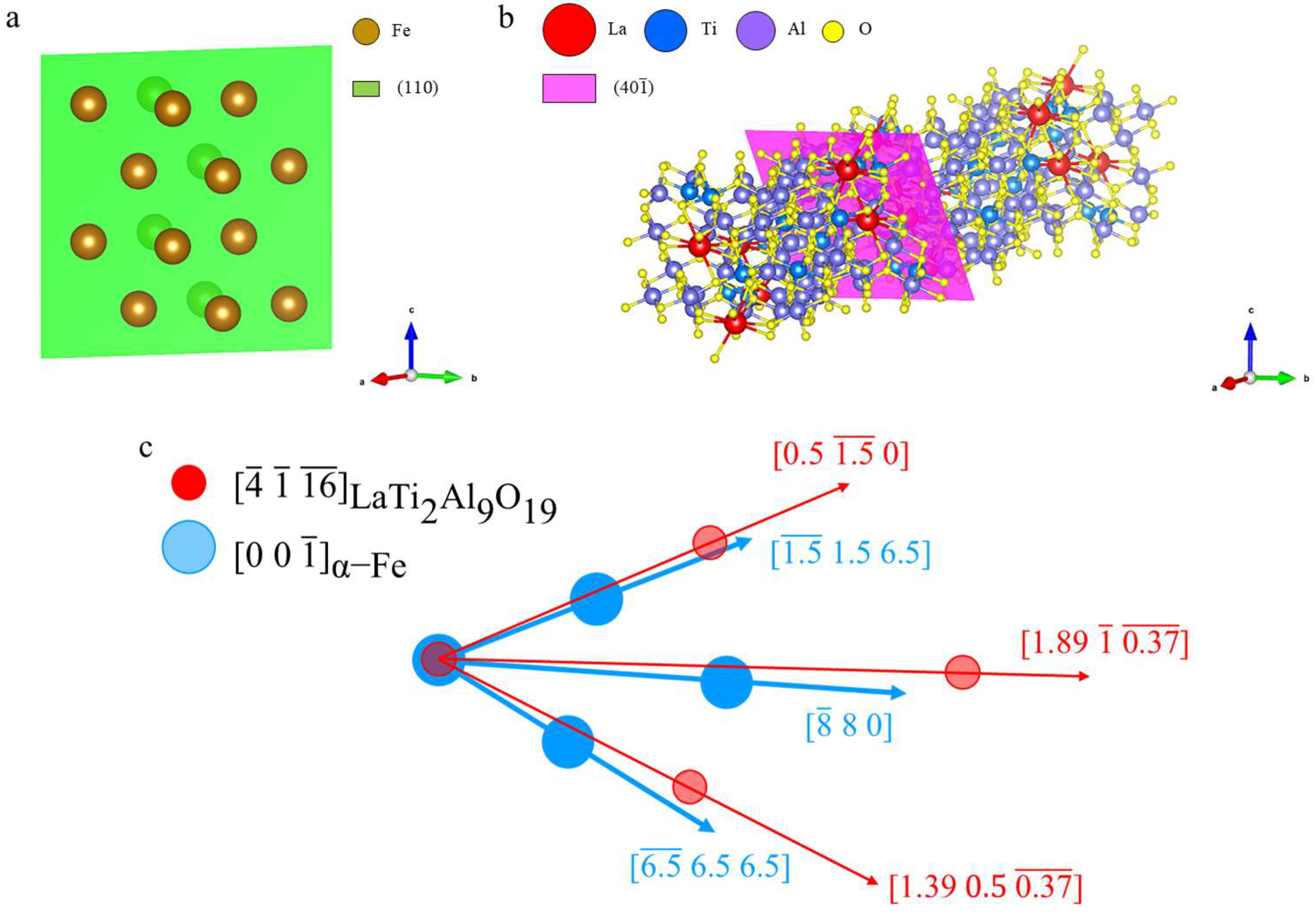
4.2. A Study on the Composition Distribution of La–Ti–Al–O Composite Inclusions and Their Effect on Acicular Ferrite Nucleation
4.3. A Study on the Influence of La on Impact Toughness
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- The 0.0135 wt.% La created LaTi2Al9O19 · MnS complex inclusions in the Nb–Ti–La steel CGHAZ, contrasting with Al2O3 · MnS complex inclusions in the La-free Nb–Ti steel CGHAZ, and the 1.68% two-dimensional lattice mismatch for enabled effective AF plate nucleation.
- (2)
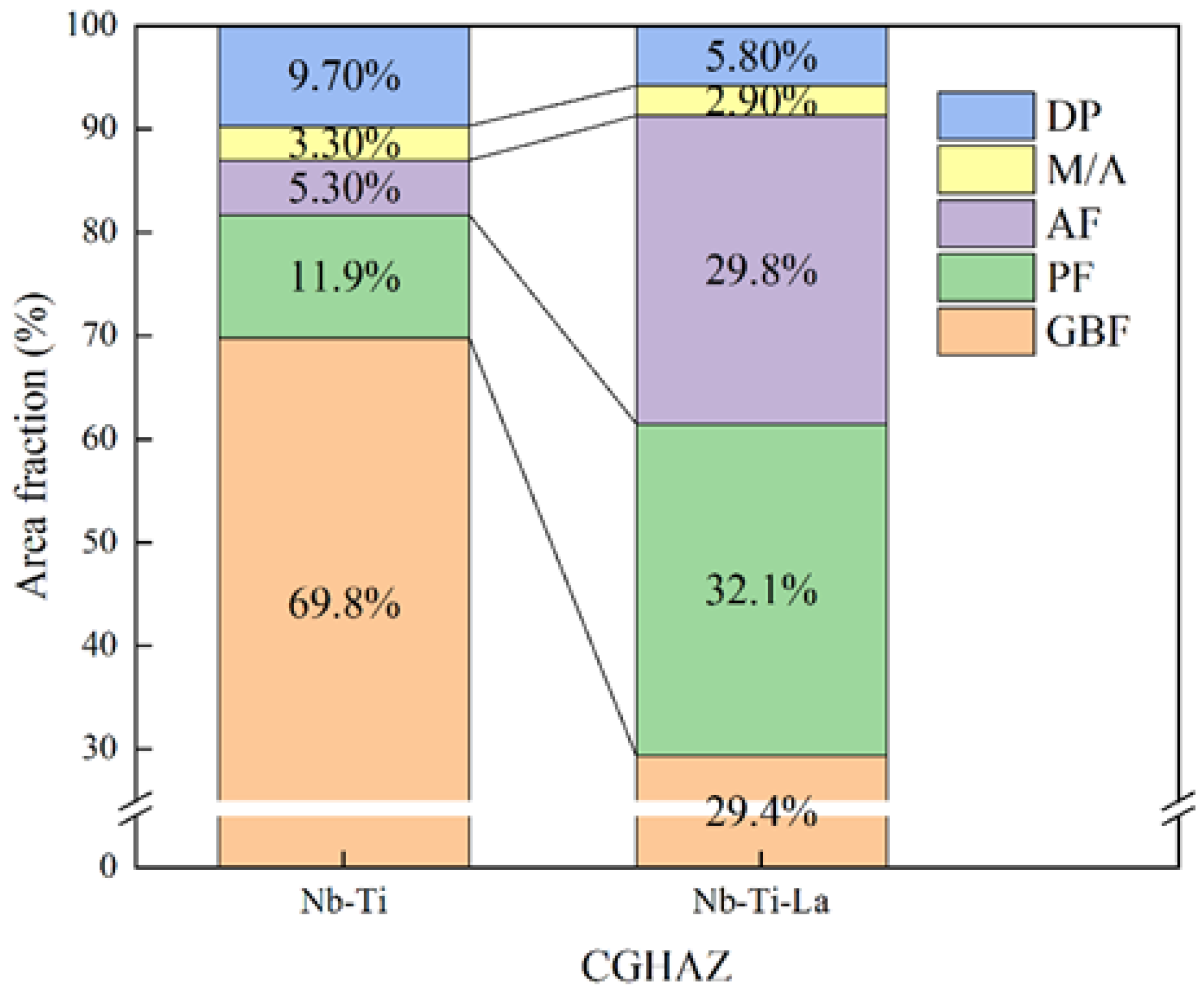
- La, as the main component of LaTi2Al9O19 · MnS core inclusions, has a strong adsorption capacity for small-sized non-metallic inclusions in steel, thereby increasing the average size of inclusions (increased from 1.76 μm to 2.63 μm). The precipitation position of La-containing composite inclusions gradually approached the interior of the crystal, creating conditions for AF/PF nucleation while significantly increasing the proportion of AF/PF in the microstructure of the CGHAZ (AF: from 5.3% to 29.8%; PF: from 11.9% to 32.1%).
- (3)
- La addition increased the AF fraction and HAGB proportion and reduced the MED, enhancing crack propagation energy (4 J to 100 J). The 0.0135 wt.% La addition thus enhanced CGHAZ low-temperature toughness for 100 kJ/cm high-heat-input welding.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, X.L.; Xie, Z.J.; Wang, Z.Q.; Yu, Y.S.; Wu, L.Q.; Shang, C.J. Crystallographic Study on Microstructure and Impact Toughness of Coarse Grained Heat Affected Zone of Ultra-High Strength Steel. Mater. Lett. 2022, 323, 132552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, X.; Xie, Z.; Shang, C.; Liu, Z. Crystallographic Study on Microstructure Evolution and Mechanical Properties of Coarse Grained Heat Affected Zone of a 500 MPa Grade Wind Power Steel. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 31, 3921–3934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Yang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, H.; Hu, P.; Xu, L. Deterioration Mechanism of Impact Toughness in the Coarse-Grained Heat-Affected Zone of Ca-Treated Shipbuilding Steel Plate with High-Cr Content. J. Alloys Compd. 2025, 1024, 180194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, J.; Kim, S.-J.; Lee, C. Effect of Thermo-Mechanical Cycling on the Microstructure and Strength of Lath Martensite in the Weld CGHAZ of HSLA Steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2011, 528, 7658–7662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Fei, J.; Xin, P.; Wang, R.; Jing, H.; Zhao, L.; Xu, L. Microstructure and Properties of Intercritically Reheated Coarse-Grained Heat Affected Zone in Pipeline Steel after Secondary Thermal Cycle. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2021, 46, 26445–26456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Deva, A.; Chattopadhyay, K. Effect of Addition of Rare Earth Element Cerium on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Microalloyed Peritectic Grade Steel. Trans. Indian. Inst. Met. 2024, 77, 3751–3758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henschel, S.; Gleinig, J.; Lippmann, T.; Dudczig, S.; Aneziris, C.G.; Biermann, H.; Krüger, L.; Weidner, A. Effect of Crucible Material for Ingot Casting on Detrimental Non-Metallic Inclusions and the Resulting Mechanical Properties of 18CrNiMo7-6 Steel. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2017, 19, 1700199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-Cruz, E.U.; Vargas-Ramírez, M.; Lobo-Guerrero, A.; Cruz-Ramírez, A.; Colin-García, E.; Sánchez-Alvarado, R.G.; Gutiérrez-Pérez, V.H.; Martínez-Vázquez, J.M. Effect of Low Aluminum Additions in the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Hot Forged High-Manganese Steels. J. Min. Met. B Met. 2023, 59, 77–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, G.; Wang, H.; Wan, X.; Hu, M.; Meng, Q. The Effect of Non-Metallic Inclusions in Refining Microstructure and Improving Cryogenic Toughness of Novel High-Mn Steel Weld Metals for LNG Tanks. Weld. World 2022, 66, 2281–2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xu, X.; Ning, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wang, C.; Liu, C.; Li, Y. Effect of Non-Metallic Inclusions on Hydrogen-Induced Cracking in Pipeline Steels: A Focused Review. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2025, 180, 109875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Ye, Z.; Wang, J.; Wang, W.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, L. Control of Non-Metallic Inclusions and Micro-Structure of an Al-Killed Steel through Adjusting Titanium Content. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2025, 35, 5629–5636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Jia, X.; Ma, Y.; Wang, P.; Zhu, F. Effect of Nb on Inclusions and Phase Transformation in Simulated High Heat Input Coarse-Grain HAZ of Nb/Ti Low Carbon Microalloyed Steel. Mater. Charact. 2022, 189, 111966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Zhai, G.; Wu, J.; Chen, X.; Zhai, Q. Evolution Mechanism of Inclusions and Microstructure in Low-Alloy Cast Steel with Cerium Addition. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 33, 929–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Yang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Xu, L.; Li, R. Inclusions and Microstructures in Coarse-Grained Heat-Affected Zone of Al–Ti–Ca Deoxidized Shipbuilding Steels with Different Al Contents after High-Heat Input Welding. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 30, 174–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, F.; Yang, C.; Su, H.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, Z. Effect of Magnesium on Inclusion Formation in Ti-Killed Steels and Microstructural Evolution in Welding Induced Coarse-Grained Heat Affected Zone. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 2009, 16, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.; Song, B.; Zhang, S.; Yang, Z.; Xue, Z.; Song, S.; Xu, R.; Tong, Z. Effect of Heat Input on Microstructure and Toughness of Rare Earth-Contained C–Mn Steel. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 2018, 25, 1033–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.; Xie, Y.; Song, B.; Xue, Z.; Nie, N.; Hu, C.; Xu, R. The Microstructure and Property of the Heat Affected Zone in C–Mn Steel Treated by Rare Earth. High. Temp. Mater. Process. 2019, 38, 362–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Duan, S.; Zhang, L. Effect of La Content on Inclusions, Grain Refinement, and Impact Toughness in Low Alloy Wear-Resistant Steel: In-Situ Tensile Testing and EBSD Orientation Analysis of Inclusions. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2025, 944, 148867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.; Song, B.; Zhang, S.; Xue, Z.; Yang, Z.; Xu, R. Role of Lanthanum Addition on Acicular Ferrite Transformation in C–Mn Steel. ISIJ Int. 2017, 57, 1261–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrison, W.M.; Maloney, J.L. Lanthanum Additions and the Toughness of Ultra-High Strength Steels and the Determination of Appropriate Lanthanum Additions. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2005, 403, 299–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, N.; Yang, W.; Chen, D.; Lu, W.; Zhang, X.; Chen, S.; Xu, M.; Pan, B.; Han, L.; Zhang, X.; et al. Effect of Lanthanum Addition on Formation Behaviors of Inclusions in Q355B Weathering Steel. Materials 2022, 15, 7952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Cai, Z.; Zhu, M. Effect of La Treatment and Al–La Composite Treatment on Sulfur-Containing Peritectic Steel. Met. Mater. Trans. B 2025, 56, 4114–4124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traore, M.; Gong, A.; Wang, Y.; Qiu, L.; Bai, Y.; Zhao, W.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wu, H.; et al. Research Progress of Rare Earth Separation Methods and Technologies. J. Rare Earths 2023, 41, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal Filho, W.; Kotter, R.; Özuyar, P.G.; Abubakar, I.R.; Eustachio, J.H.P.P.; Matandirotya, N.R. Understanding Rare Earth Elements as Critical Raw Materials. Sustainability 2023, 15, 1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Chen, Z.; Kou, D.; Li, Y.; Ma, Y.; Li, Y. Evolution of Microstructure in Reheated Coarse-Grained Zone of G115 Novel Martensitic Heat-Resistant Steel. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 2022, 29, 327–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Kou, D.; Chen, Z.; Yang, F.; Ma, Y.; Li, Y. Evolution of Microstructure in Welding Heat-Affected Zone of G115 Steel with the Different Content of Boron. Materials 2022, 15, 2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, C.; Cheng, L.; Cheng, S.; Wang, Z.; Hu, S.-E.; Liu, Z.; Luo, D.; Xiao, D.; Jin, X.; Liu, H.; et al. Simulated Coarse Grain Heat-Affected Zone Transformation Behavior of Newly Developed Zr–Ti–RE Deoxidized High-Strength Low-Alloy Steels with Extremely High Impact Toughness. Steel Res. int. 2023, 94, 2200343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bramfitt, B.L. The Effect of Carbide and Nitride Additions on the Heterogeneous Nucleation Behavior of Liquid Iron. Met. Trans. 1970, 1, 1987–1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Xiao, X.; Wang, Y.; Liu, C.; Ni, H. Effect of Sulfur Content on Precipitation Behaviour of MnS-Containing Inclusions in X70 Pipeline Steel. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 27, 5868–5880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Sun, M.; Ma, S.; Mao, Y.; Ma, Y.; Li, T.; Nie, D.; Yang, R. Effect of Zr on Inclusions and Microstructure of Non-Quenched and Tempered Steel F38MnVS. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2025, 35, 2075–2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-K.; Pan, Y.-C.; Su, Y.-H.F.; Lin, G.-R.; Hwang, W.-S.; Kuo, J.-C. Effects of Mg–Al–O–Mn–S Inclusion on the Nucleation of Acicular Ferrite in Magnesium-Containing Low-Carbon Steel. Mater. Charact. 2018, 141, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, E.; Wang, Q.; Guo, Z.; Wang, L.; Chang, X.; Zheng, Y.; Ma, C.; Chen, Z.; Wang, B.; Zhu, L. Nucleation and Growth Mechanisms of Ferrite on Mg–Ti–Oxide Surfaces: First-Principles Investigation. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 24, 6968–6981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Elements | C | Si | Mn | P | S | Nb | Ti | La | Al | O | N |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nb–Ti steel | 0.065 | 0.21 | 1.55 | 0.006 | 0.002 | 0.026 | 0.012 | 0 | 0.020 | 0.0025 | 0.0028 |
| Nb–Ti–La steel | 0.068 | 0.19 | 1.57 | 0.005 | 0.002 | 0.024 | 0.010 | 0.0135 | 0.023 | 0.0029 | 0.0027 |
| Total Impact Absorbed Energy (Et/J) | Crack Initiation Energy (Ei/J) | Crack Propagation Energy (Ep/J) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nb–Ti CGHAZ | 23 ± 5 | 19 ± 3 | 4 ± 2 |
| Nb–Ti–La CGHAZ | 137 ± 15 | 37 ± 9 | 100 ± 7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Q.; He, J.; Wang, Q.; Liu, R. The Role of La–Ti–Al–O Complex Inclusions in Microstructure Refinement and Toughness Enhancement of the Coarse-Grained Heat-Affected Zone in High-Heat-Input Welding. Metals 2025, 15, 1105. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15101105
Wang Q, He J, Wang Q, Liu R. The Role of La–Ti–Al–O Complex Inclusions in Microstructure Refinement and Toughness Enhancement of the Coarse-Grained Heat-Affected Zone in High-Heat-Input Welding. Metals. 2025; 15(10):1105. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15101105
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Qiuming, Jiangli He, Qingfeng Wang, and Riping Liu. 2025. "The Role of La–Ti–Al–O Complex Inclusions in Microstructure Refinement and Toughness Enhancement of the Coarse-Grained Heat-Affected Zone in High-Heat-Input Welding" Metals 15, no. 10: 1105. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15101105
APA StyleWang, Q., He, J., Wang, Q., & Liu, R. (2025). The Role of La–Ti–Al–O Complex Inclusions in Microstructure Refinement and Toughness Enhancement of the Coarse-Grained Heat-Affected Zone in High-Heat-Input Welding. Metals, 15(10), 1105. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15101105





