Predictive Modeling of Shear Strength for Lotus-Type Porous Copper Bonded to Alumina
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
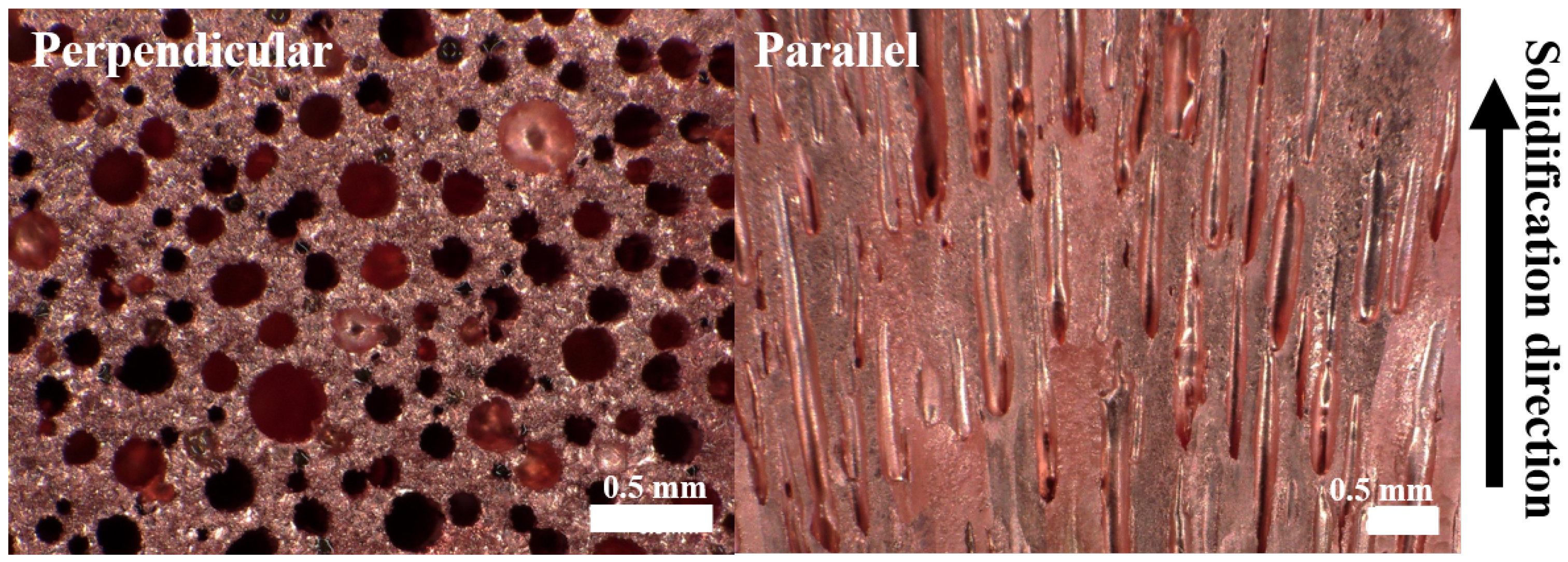
2.1. Preparation of Materials
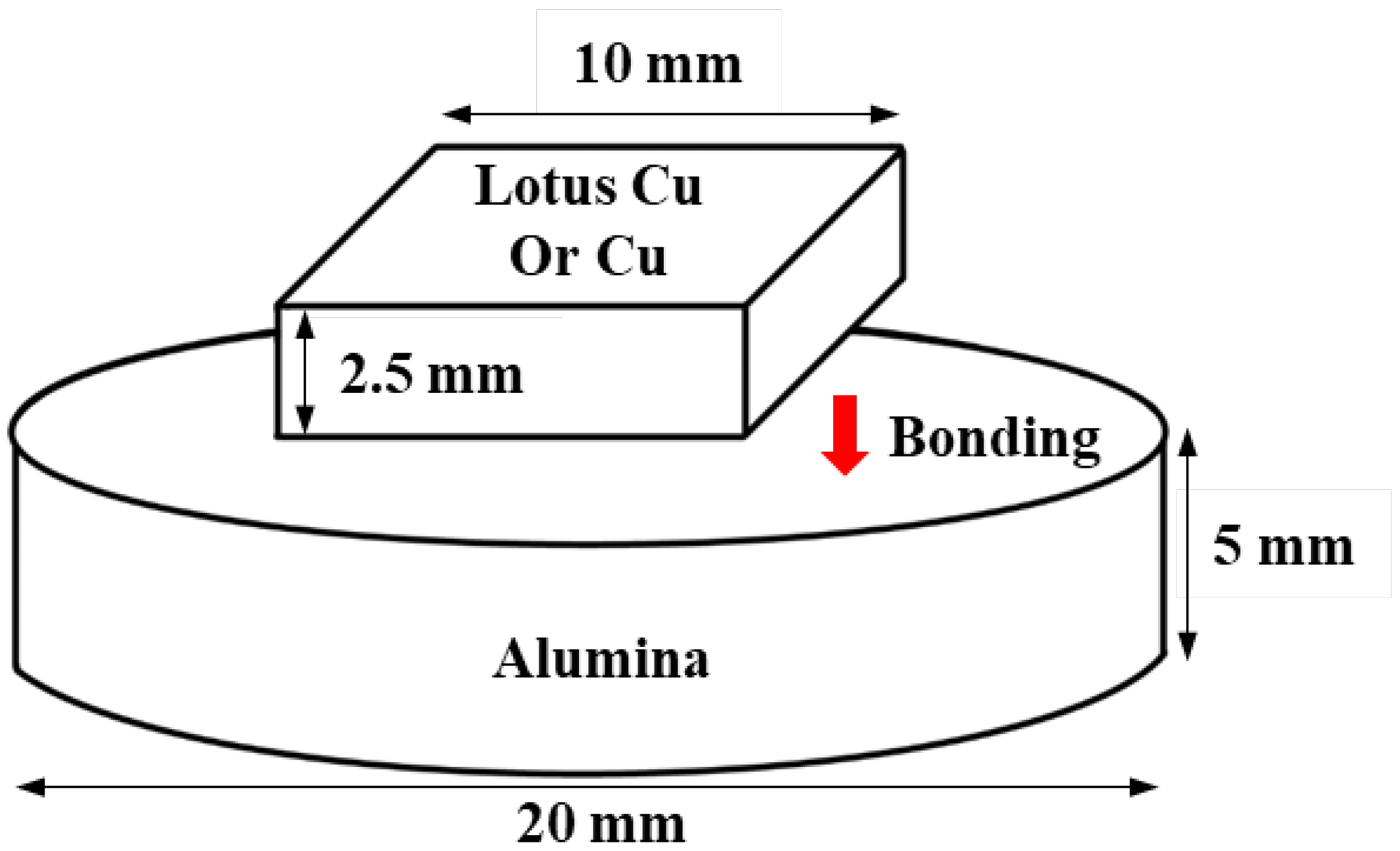
2.2. DBC Process and Experimental Design
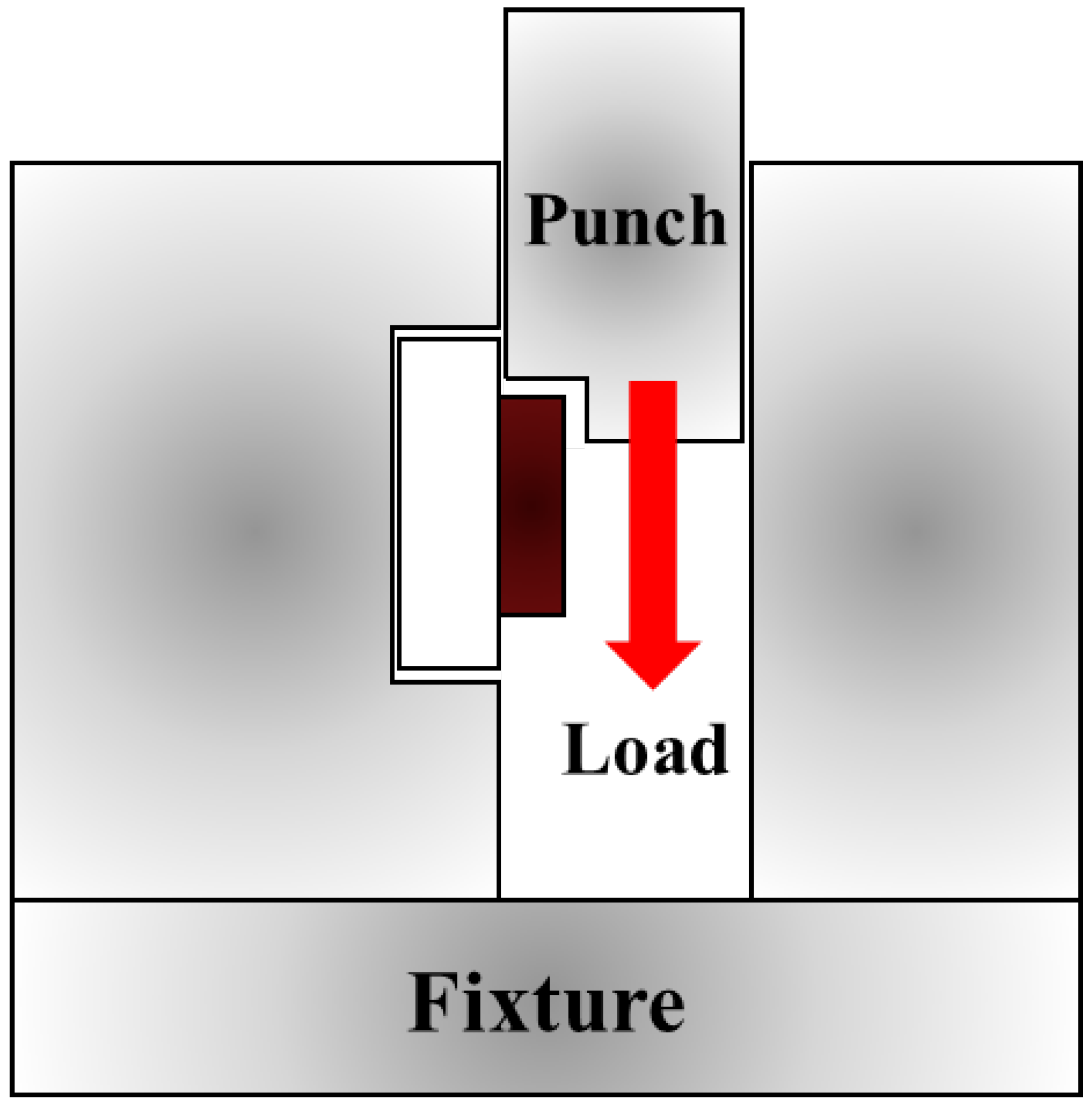
2.3. Shear Strength Test and Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
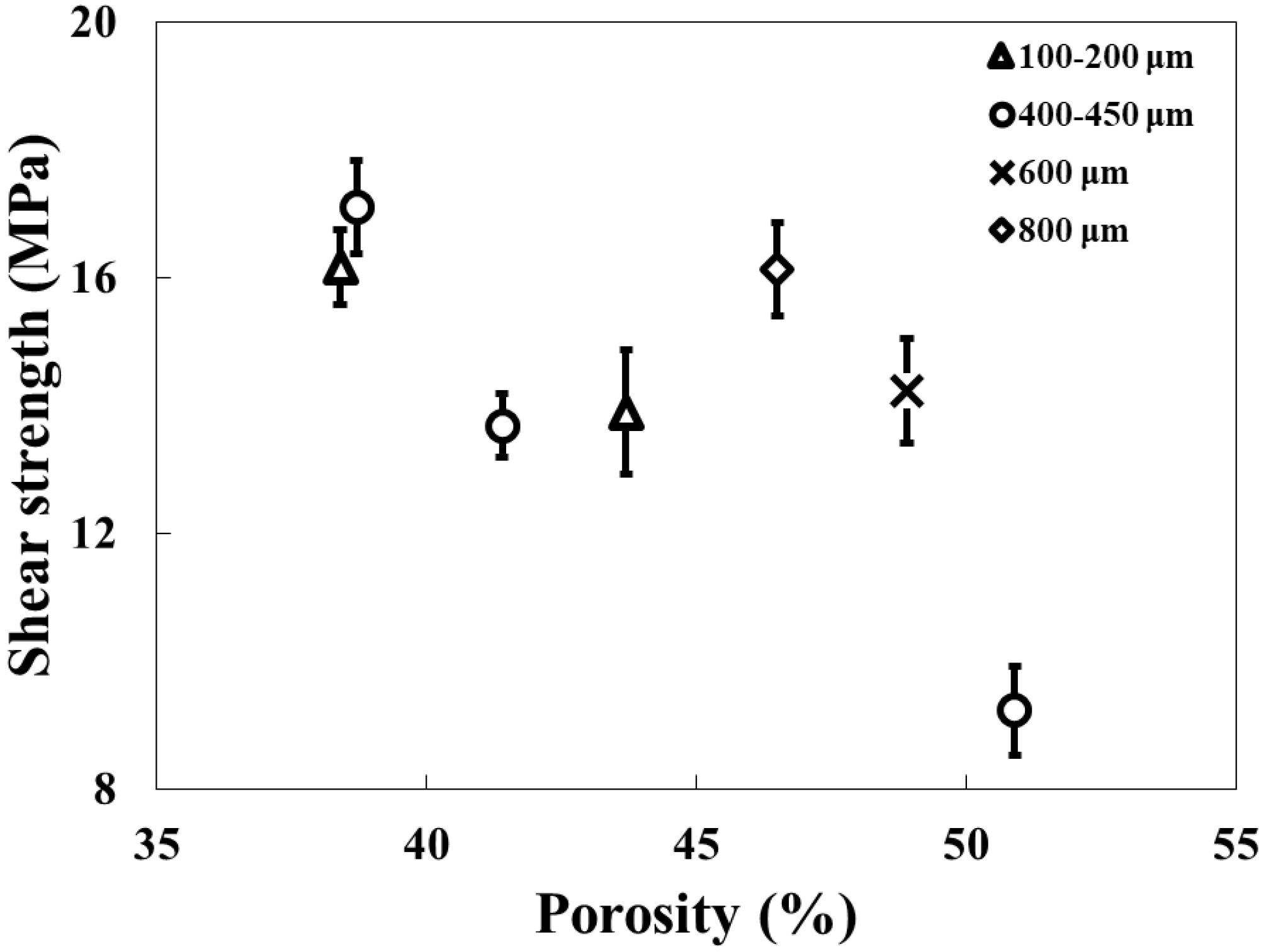
3.1. Shear Strength Test
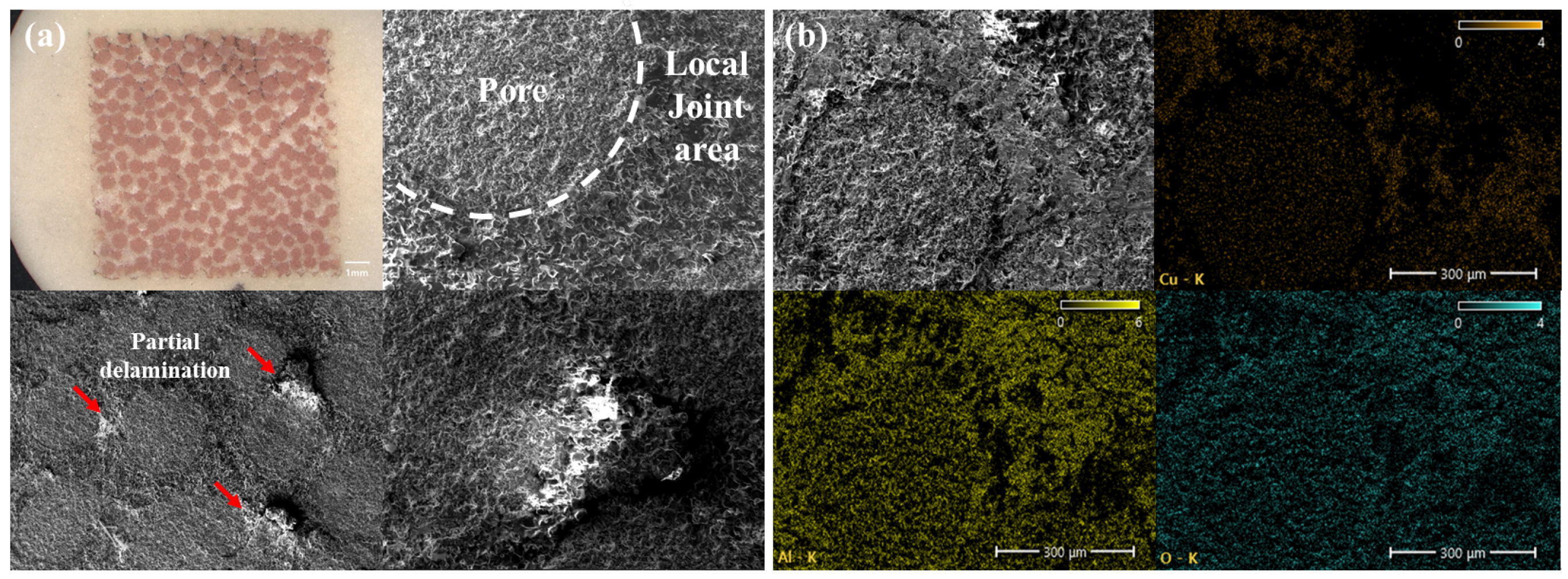
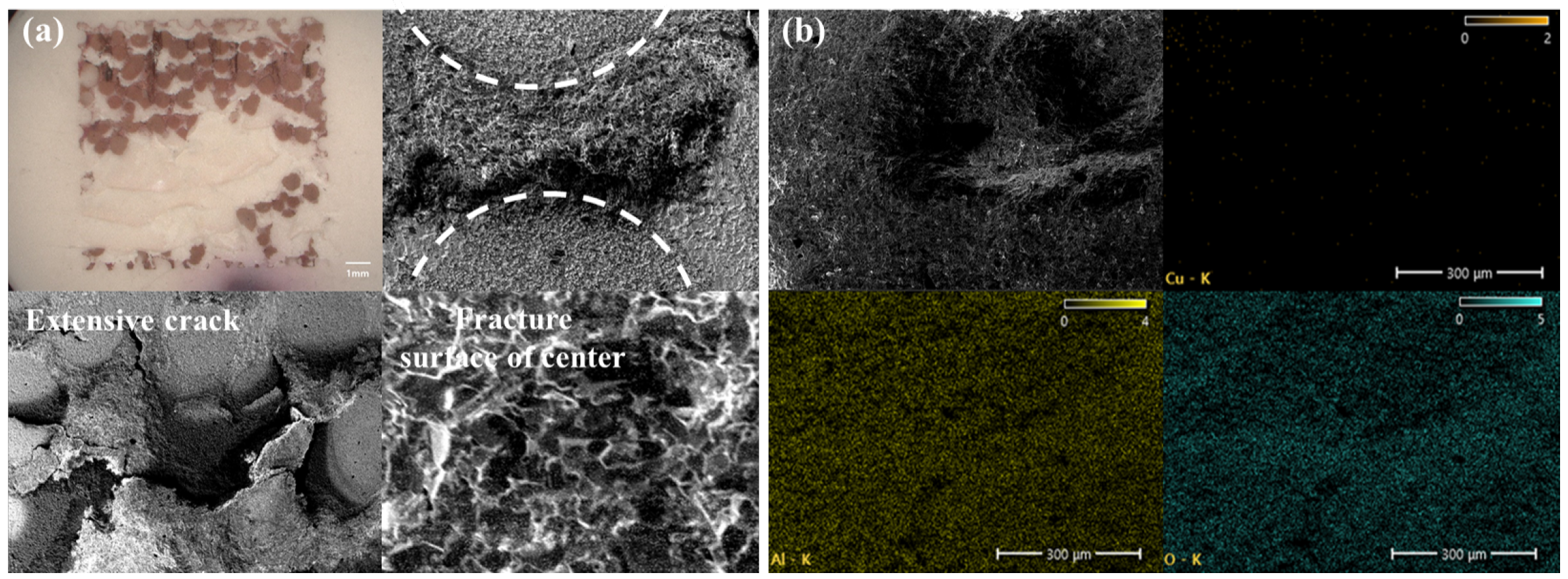
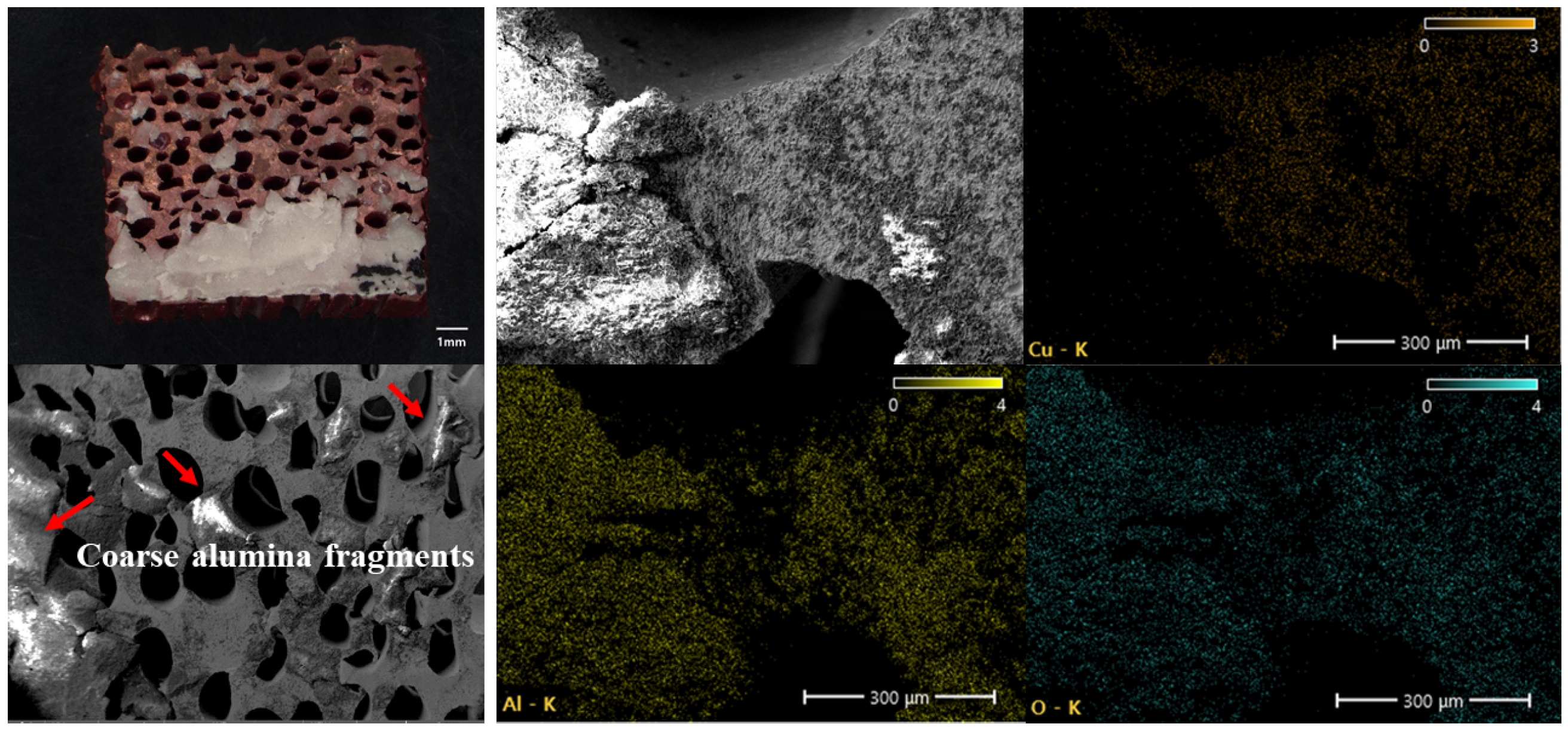
3.2. Analysis of Fracture Surfaces According to Pore Diameter
3.3. Modeling of Shear Strength Considering Porosity and Pore Diameter
4. Conclusions
- 1.
- Effect of Porosity and Pore Size: Shear strength of the DBC specimens decreased with increasing porosity. Conversely, larger pore sizes (600–800 μm) exhibited higher shear strength even at elevated porosities. Fractography revealed that the extent and depth of alumina fracture increased with pore size, indicating that larger copper ligaments between pores increase the fracture area.
- 2.
- Fracture Mechanism: Initial deformation occurred within the porous copper, with localized plastic strain concentrating around pore regions. Progressive separation of narrow copper ligaments led to detachment of alumina particles and eventual complete fracture. SEM and EDS analyses confirmed copper residues and alumina detachment consistent with the observed fracture process.
- 3.
- Predictive Modeling: The Ryshkewitch–Duckworth (R–D) model provided reasonable predictions for smaller pore sizes but showed limited accuracy for larger pore sizes when only porosity was considered. The model incorporating pore size demonstrated significantly improved predictive performance, with the prediction error decreasing from 12.3% to 7.5% and the coefficient of determination (R2) increasing from 0.43 to 0.74.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sanchez, J.L. State of the art and trends in power integration. In Proceedings of the 1999 International Conference on Modeling and Simulation of Microsystems (MCM), San Juan, Puerto Rico, 19–21 April 1999; pp. 20–29. [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez, J.L.; Bourennane, A.; Breil, M.; Austin, P.; Brunet, M.; Laur, J.P. Evolution of the classical functional integration towards a 3D heterogeneous functional integration. In Proceedings of the 2007 14th International Conference on Mixed Design of Integrated Circuits and Systems, Ciechocinek, Poland, 21–23 June 2007; pp. 23–34. [Google Scholar]
- Schulz-Harder, J. Advantages and new development of direct bonded copper substrates. Microelectron. Reliab. 2003, 43, 359–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y. Power Electronic Packaging: Design, Assembly Process, Reliability and Modeling; Publishing House: Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Smet, V.; Forest, F.; Huselstein, J.J.; Richardeau, F.; Khatir, Z.; Lefebvre, S.; Berkani, M. Ageing and failure modes of IGBT modules in high-temperature power cycling. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2011, 58, 4931–4941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCluskey, P. Reliability of power electronics under thermal loading. In Proceedings of the 2012 7th International Conference on Integrated Power Electronics Systems (CIPS), Nuremberg, Germany, 6–8 March 2012; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Squiller, D.; Greve, H.; Mengotti, E.; McCluskey, F.P. Physics-of-failure assessment methodology for power electronic systems. Microelectron. Reliab. 2014, 54, 1680–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karageorgiou, V.; Kaplan, D. Porosity of 3D biomaterial scaffolds and osteogenesis. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 5474–5491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodall, R.; Mortensen, A. Porous metals. In Physical Metallurgy; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 2399–2595. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.W.; Hyun, S.K.; Kim, M.S.; Kim, M.G.; Ide, T.; Nakajima, H. Ductility improvement of intermetallic compound NiAl by unidirectional pores. Mater. Lett. 2012, 74, 213–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Fu, C.; Li, T.; Shi, C. Relationship between tensile strength and porosity for high porosity metals. Sci. China Ser. E Technol. Sci. 1999, 42, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.I.E. Effects of porosity on tensile mechanical properties of porous FeAl intermetallics. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2020, 30, 2757–2763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryshkewitch, E. Compression strength of porous sintered alumina and zirconia: 9th communication to ceramography. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1953, 36, 65–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duckworth, W. Discussion of ryshkewitch paper by winston duckworth. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1953, 36, 68–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajima, H. Mechanical, thermal and electrical properties of lotus-type porous metals. Mater. Sci. Appl. 2018, 9, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, A.J.; Breitenbach, M.; Zipprich, J.; Klingler, M.; Nowottnick, M. Nonconchoidal fracture in power electronics substrates due to delamination in baseplate solder joints. In Proceedings of the 2018 7th Electronic System-Integration Technology Conference (ESTC), Dresden, Germany, 18–21 September 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, N.; Ola, O.; Xia, Y.; Zhu, Y. Porous ceramics: Light in weight but heavy in energy and environment technologies. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 2021, 143, 100589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Hu, P.; Zhao, X.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Y. Modelling and experimental investigation of pore-like flaw-strength response in structural ceramics. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 14431–14438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijaya, A.; Wagner, J.; Sartory, B.; Brunner, R. Analyzing microstructure relationships in porous copper using a multi-method machine learning-based approach. Commun. Mater. 2024, 5, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borwornpiyawat, P.; Juntasaro, E.; Aueviriyavit, S.; Juntasaro, V.; Sripumkhai, W.; Pattamang, P.; Jeamsaksiri, W. Effects of porous size and membrane pattern on shear stress characteristic in gut-on-a-chip with peristalsis motion. Micromachines 2022, 14, 22. [Google Scholar]
- Duckworth, W. Statistical effects of pore features on mechanical properties and fracture behaviors of heterogeneous random porous materials by phase-field modeling. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2023, 264, 112098. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, Z.; Jia, Q.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Y.; Ma, L.; Zou, G.; Guo, F. Review on shear strength and reliability of nanoparticle sintered joints for power electronics packaging. J. Electron. Mater. 2024, 53, 2703–2726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.W.; Eagar, T.W. Strain energy release in ceramic-to-metal joints with patterned interlayers. Scr. Mater. 2004, 50, 555–559. [Google Scholar]
- Paret, P. Power Electronics Materials and Bonded Interfaces-Reliability and Lifetime; No. NREL/PR-5400-76672; National Renewable Energy Lab. (NREL): Golden, CO, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Du, X.; Chen, J.; Wu, Y. Thermal fatigue failure of micro-solder joints in electronic packaging devices: A review. Materials 2024, 17, 2365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, M.; Anderko, K. Constitution of Binary Alloys; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1958. [Google Scholar]
- Honjo, G. Electron diffraction studies on oxide films formed on metals and alloys part 1. Oxidation of pure copper. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 1949, 4, 330–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeffes, J.H.E. Ellingham diagrams. In Encyclopedia of Materials, Science and Technology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2001; pp. 2751–2753. [Google Scholar]
- Griffith, A.A., VI. The phenomena of rupture and flow in solids. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. 1921, 221, 163–198. [Google Scholar]
- Sbaizero, O.; Pezzotti, G.; Nishida, T. Fracture energy and R-curve behavior of Al2O3/Mo composites. Acta Mater. 1998, 46, 681–687. [Google Scholar]
- Hoepfner, T.P.; Case, E.D. The influence of the microstructure on the hardness of sintered hydroxyapatite. Ceram. Int. 2003, 29, 699–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datta, S.K.; Mukhopadhyay, A.K.; Chakraborty, D. Porosity Dependence of Strength of Si3N4 Ceramics. J. Mech. Behav. Mater. 1990, 3, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hattiangadi, A.; Bandyopadhyay, A. Strength degradation of nonrandom porous ceramic structures under uniaxial compressive loading. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2010, 83, 2730–2736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, V.; Hinton, G.E. Rectified linear units improve restricted boltzmann machines. In Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on Machine Learning, Haifa, Israel, 21–24 June 2010; pp. 807–814. [Google Scholar]
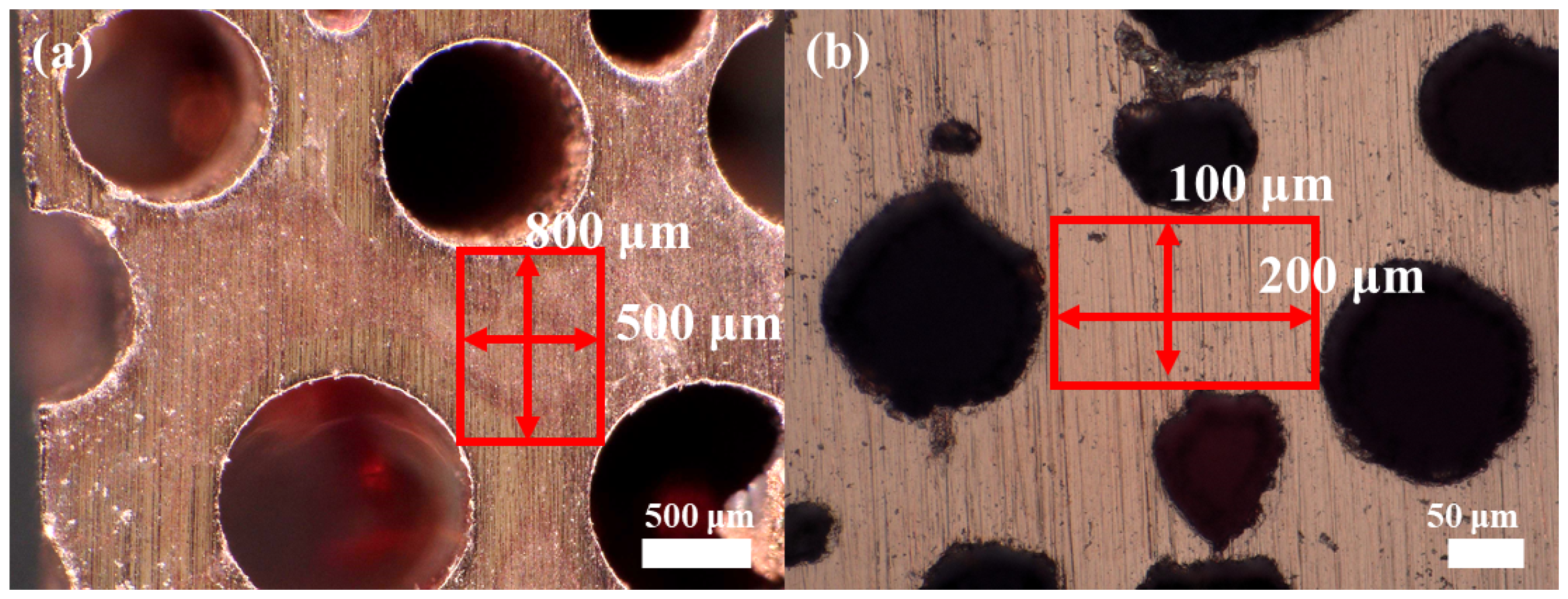



| Pore diameter (μm) | 160 | 137 | 443 | 425 | 413 | 583 | 811 |
| Porosity (%) | 43.5 | 39.0 | 38.7 | 41.4 | 50.9 | 48.9 | 46.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Choi, S.-G.; Kim, S.; Lee, J.; Kim, K.-S.; Hyun, S. Predictive Modeling of Shear Strength for Lotus-Type Porous Copper Bonded to Alumina. Metals 2025, 15, 1103. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15101103
Choi S-G, Kim S, Lee J, Kim K-S, Hyun S. Predictive Modeling of Shear Strength for Lotus-Type Porous Copper Bonded to Alumina. Metals. 2025; 15(10):1103. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15101103
Chicago/Turabian StyleChoi, Sang-Gyu, Sangwook Kim, Jinkwan Lee, Keun-Soo Kim, and Soongkeun Hyun. 2025. "Predictive Modeling of Shear Strength for Lotus-Type Porous Copper Bonded to Alumina" Metals 15, no. 10: 1103. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15101103
APA StyleChoi, S.-G., Kim, S., Lee, J., Kim, K.-S., & Hyun, S. (2025). Predictive Modeling of Shear Strength for Lotus-Type Porous Copper Bonded to Alumina. Metals, 15(10), 1103. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15101103







