Dynamic Recrystallization and Microstructural Evolution During Hot Deformation of Al-Cu-Mg Alloy
Abstract
1. Introduction
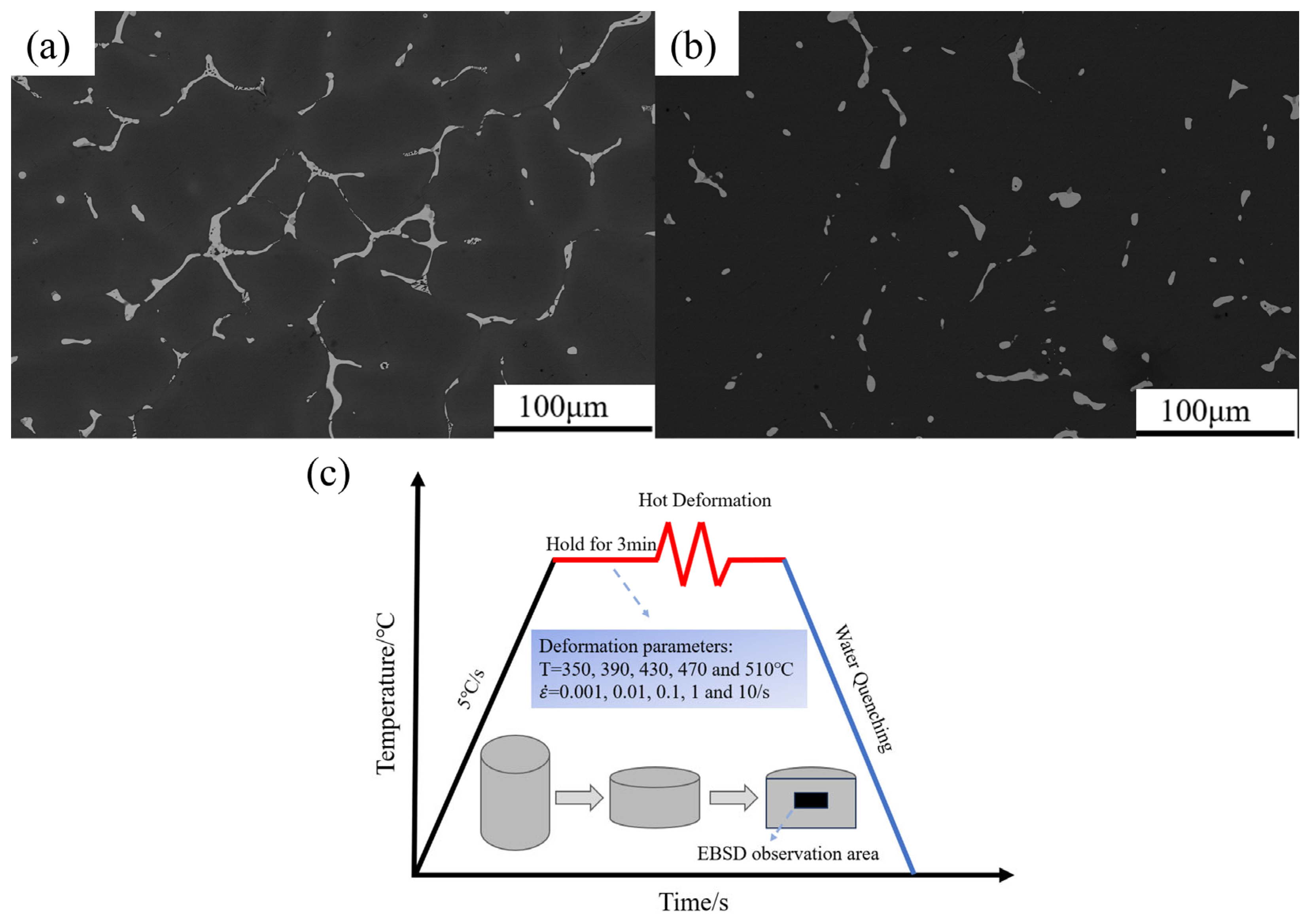
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
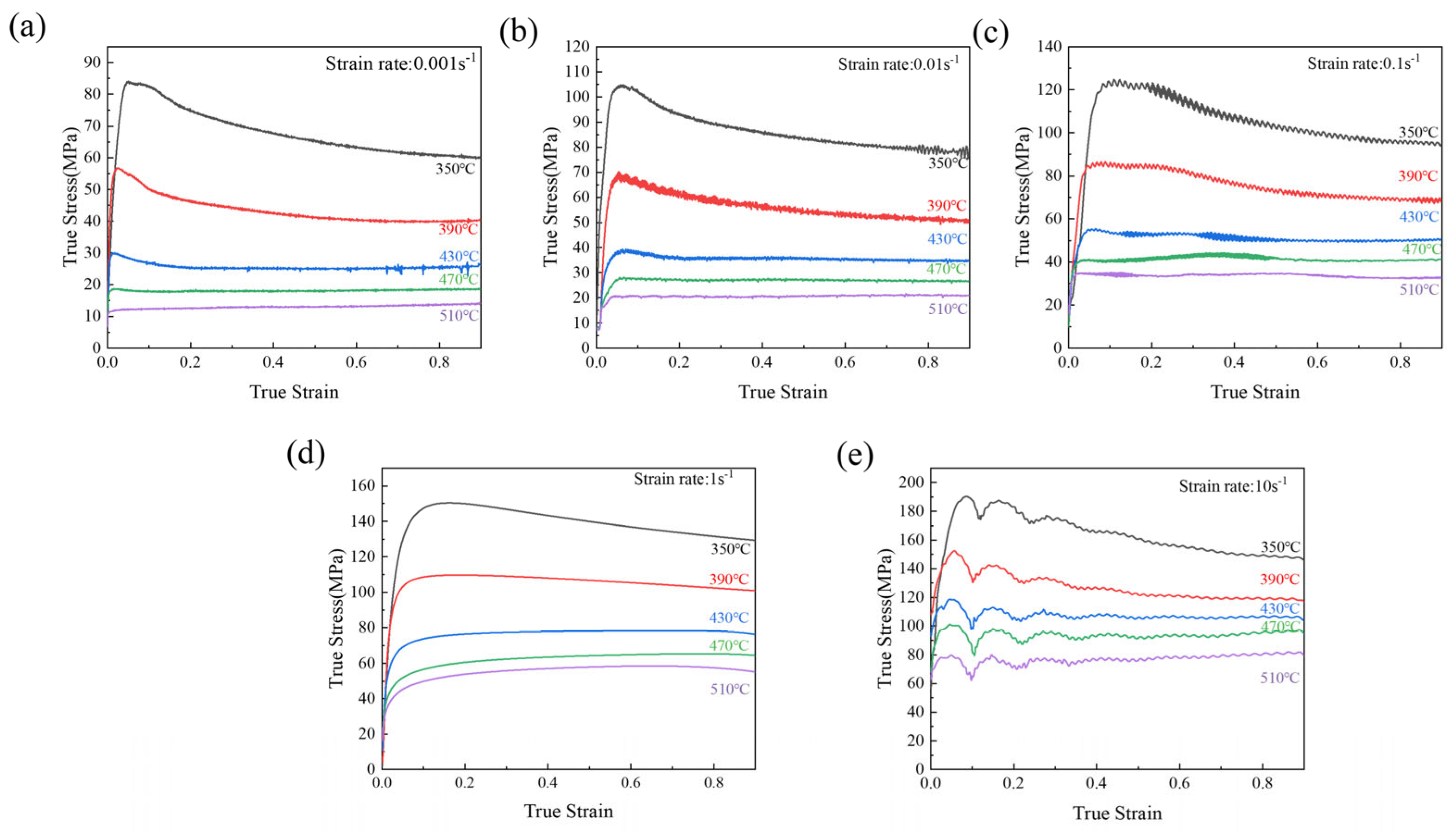
3.1. True Stress–Strain Curve
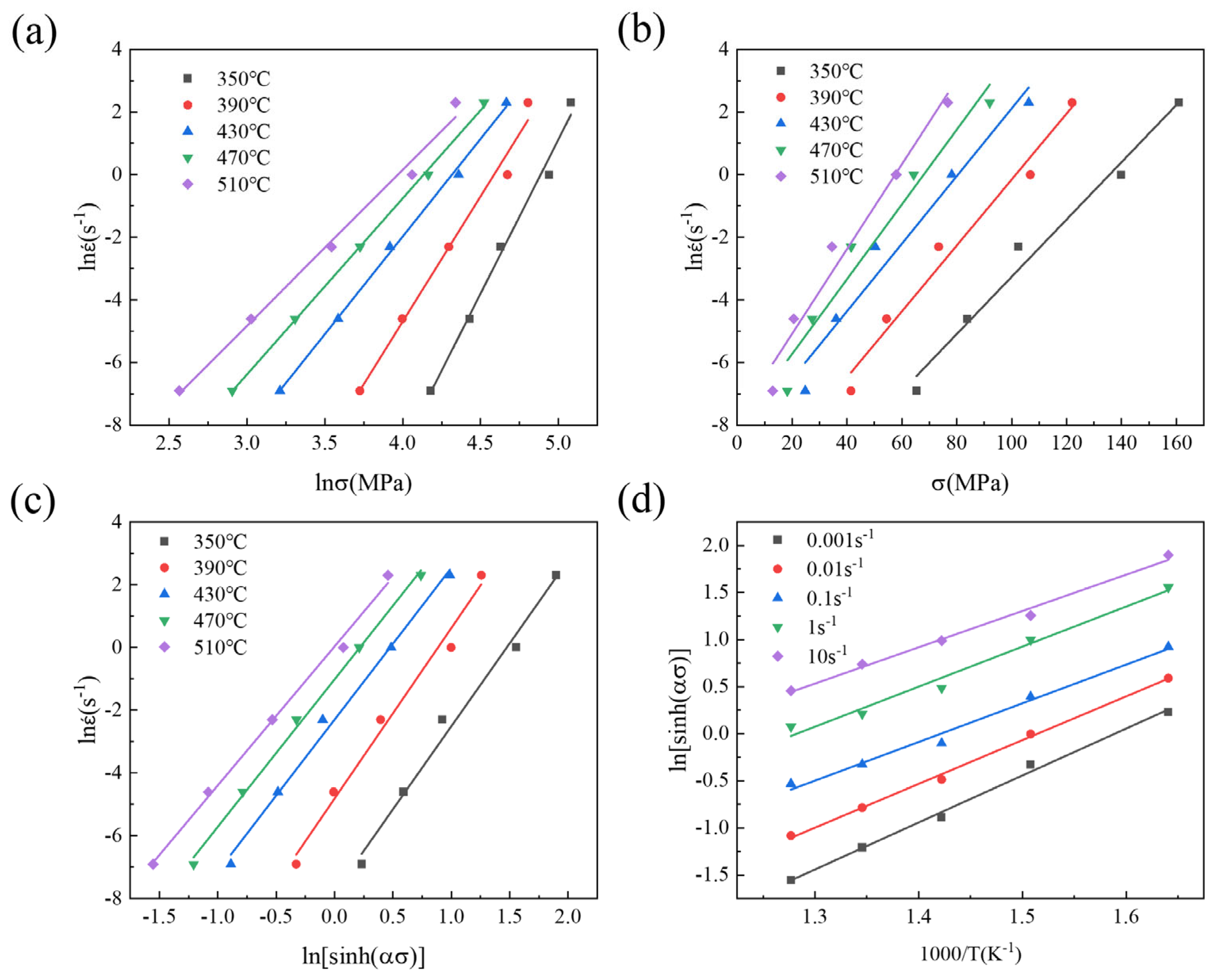
3.2. Establishing the Constitutive Equation of the Alloy
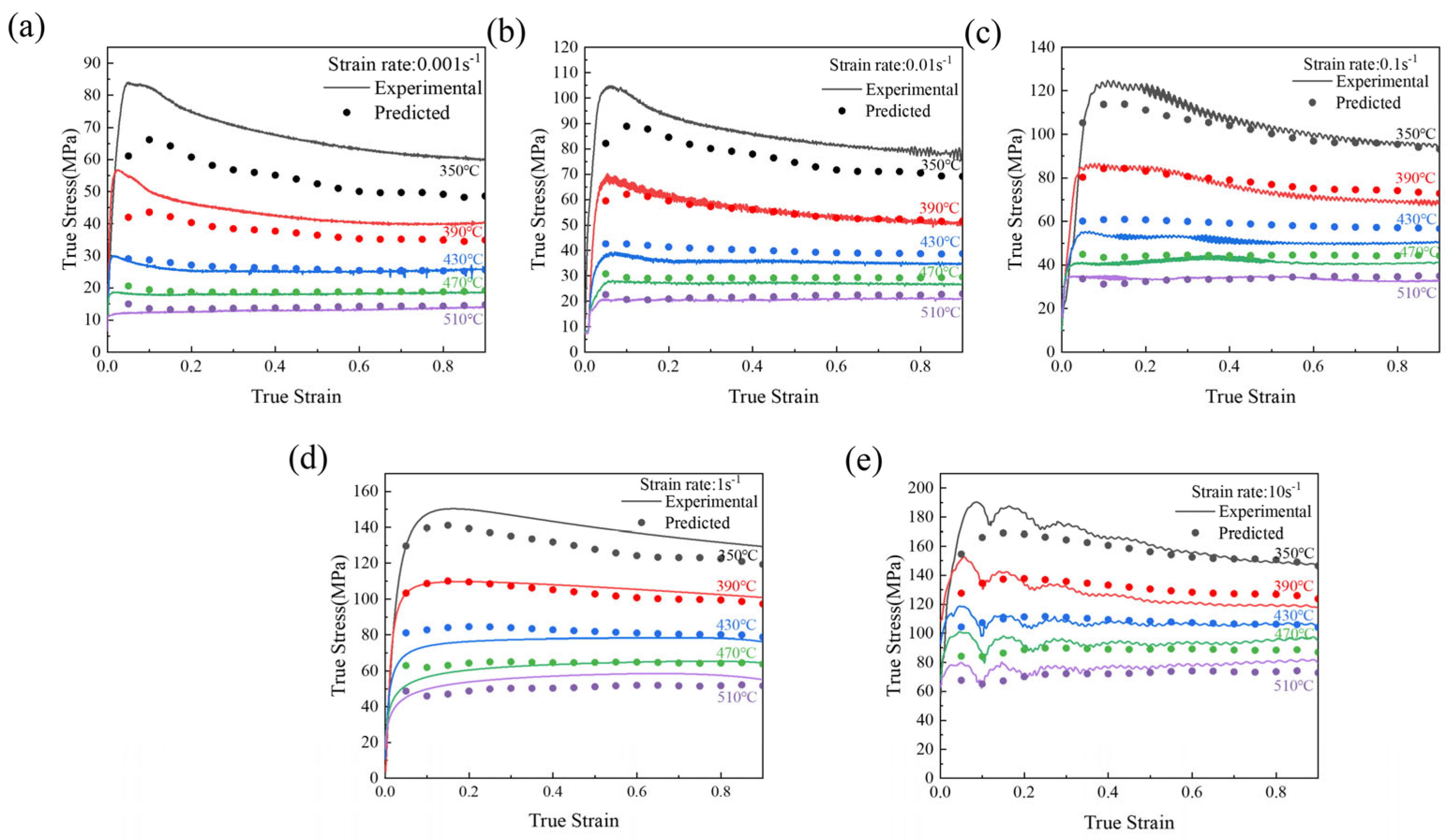
3.3. Verifying the Constitutive Equation of the Alloy
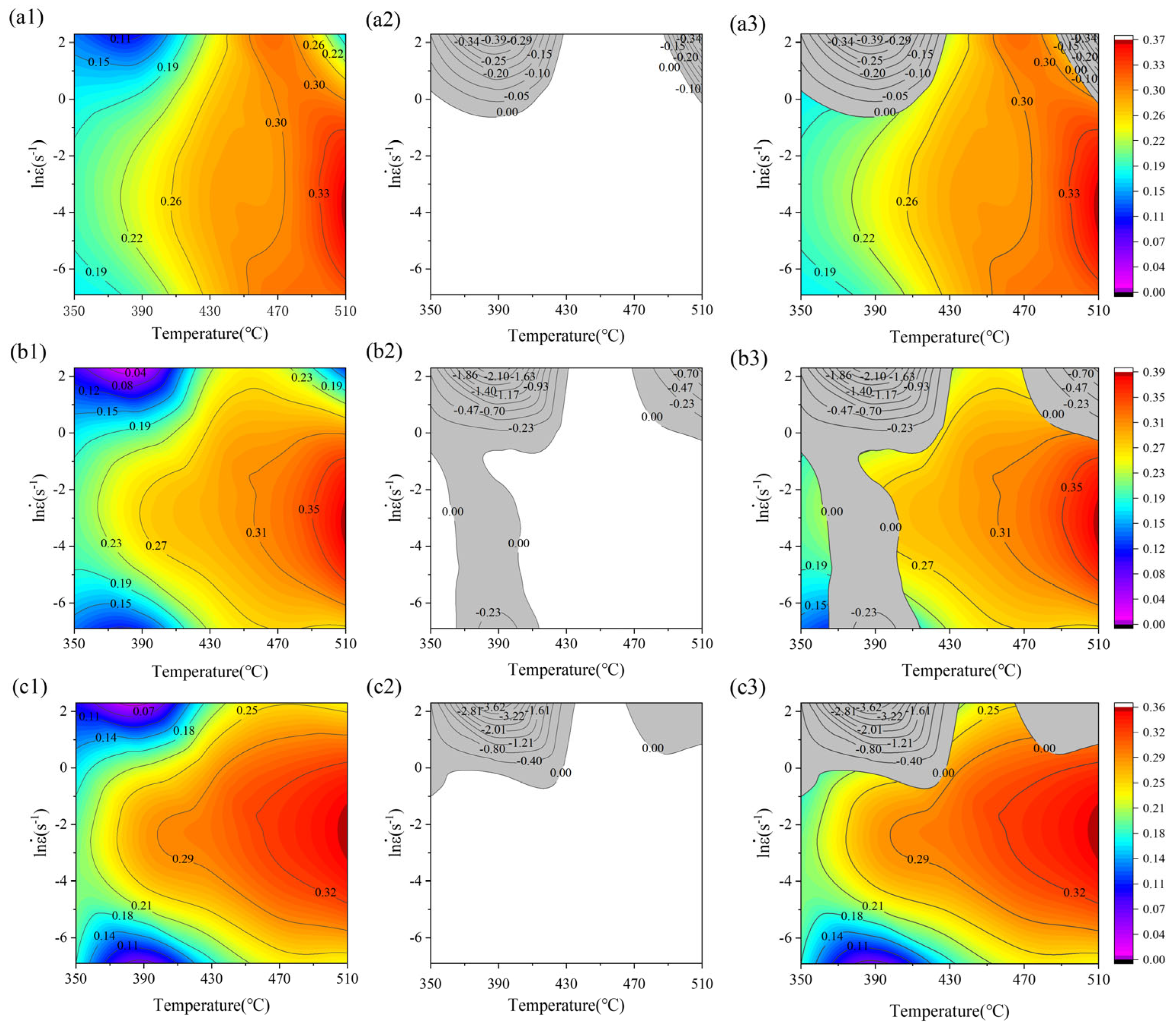
3.4. Hot Processing Maps
3.5. Microstructural Evolution
3.5.1. Effect of Deformation Temperature on Microstructure
Effect of Deformation Temperature on Microstructural Evolution at Strain Rate 0.001 s−1
Effect of Deformation Temperature on Microstructural Evolution at Strain Rate 10 s−1
3.5.2. Effect of Strain Rate on Alloy Microstructure
Effect of Strain Rate on Microstructural Evolution at 510 °C
Effect of Strain Rate on Microstructural Evolution at 350 °C
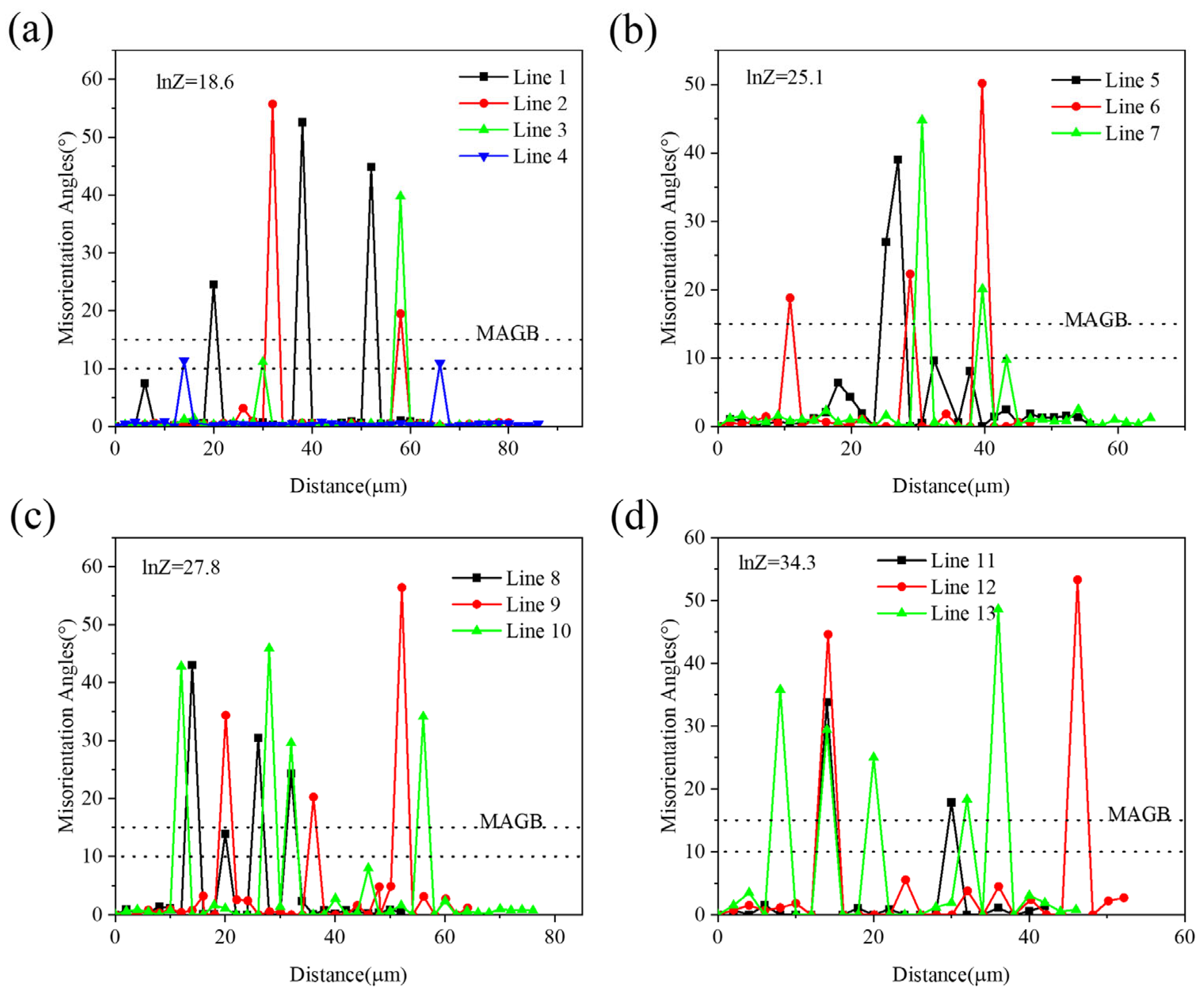
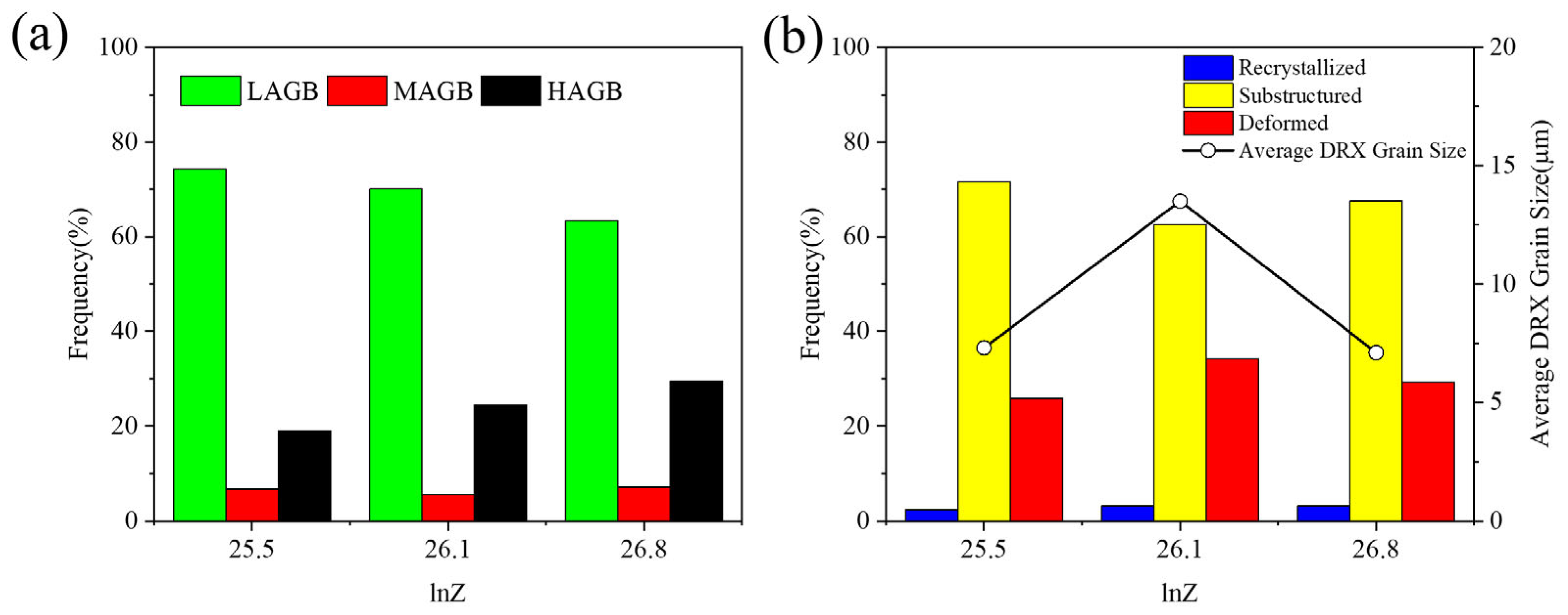
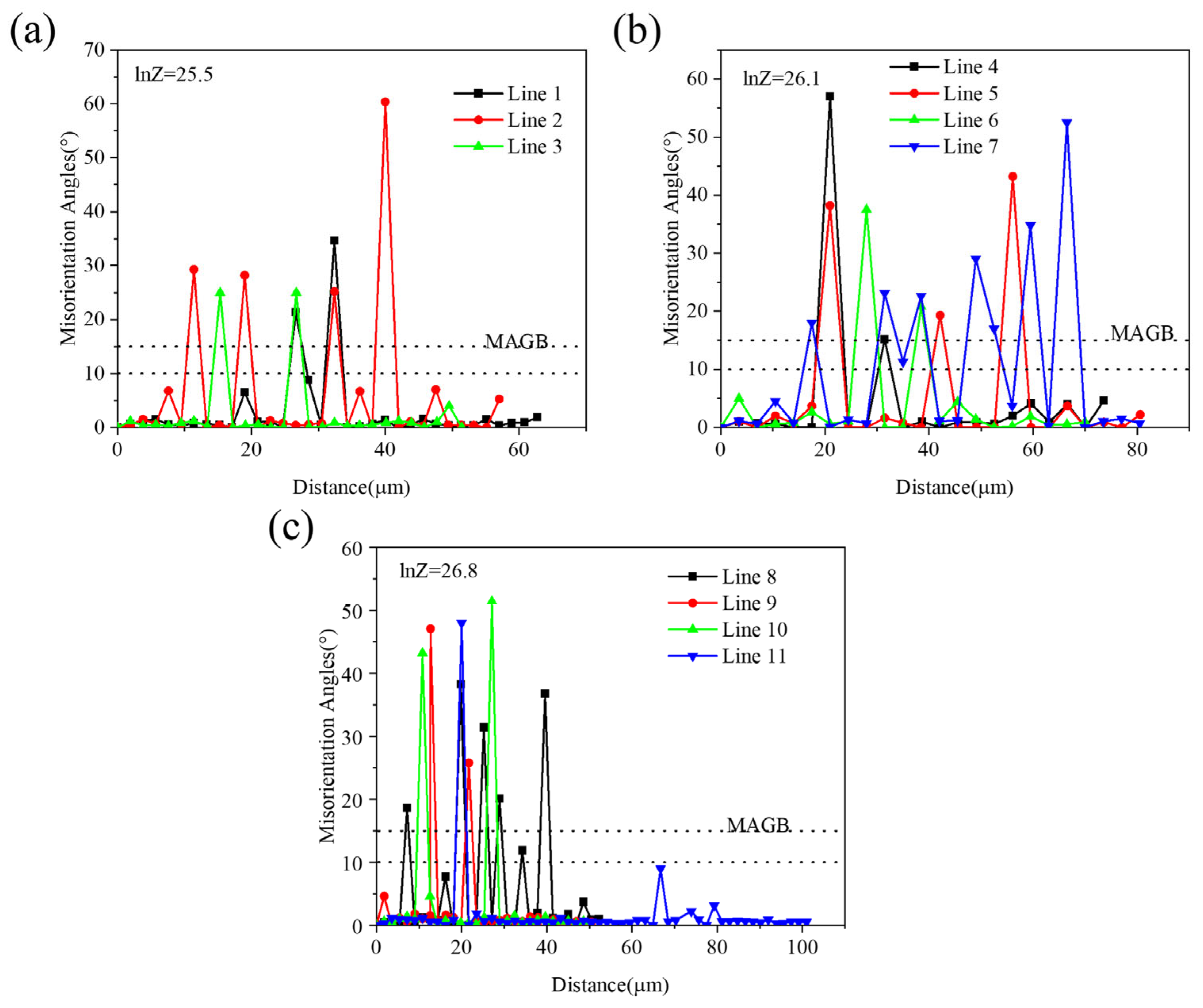
3.5.3. Effect of lnZ on Alloy Microstructure
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- The flow stress of the Al-4.8Cu-0.25Mg-0.32Mn-0.17Si alloy decreases with increasing deformation temperature but increases with strain rate. After the peak stress is reached, a dynamic equilibrium between work hardening, DRV, and DRX is established, maintaining a steady-state flow stress that exhibits gradual softening.
- (2)
- The flow behavior of the experimental alloy during hot deformation was accurately predicted by a strain-compensated Arrhenius constitutive model. The constitutive equation at ε = 0.9 is: , which shows excellent agreement with the experimental values (R = 0.979).
- (3)
- Based on the hot processing maps, the optimal hot processing parameters for the experimental alloy are determined to be 450–510 °C and 0.01–0.1 s−1. The lnZ analysis combined with microstructure characterization shows that superior workability is achieved at low lnZ values.
- (4)
- The softening mechanisms of the experimental alloy are dominated by DRV and DRX. At high lnZ values (high strain rate and low deformation temperature), DDRX is the primary mechanism. At middle lnZ values (low strain rate or high deformation temperature), CDRX and DDRX become dominant. At low lnZ values (low strain rate and high deformation temperature), CDRX and GDRX become dominant. The DRX mechanisms are controlled by deformation temperature and strain rate.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhou, F.; Lu, Q.; Wang, J.; Xiao, N.; Li, X.; Chen, B.; Du, Y.; Li, K. Negative effect of nano-scale Al3(Sc, Zr) on strength of Sc-Zr micro-alloyed Al-Cu-Mg-Ag alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2025, 1028, 180597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Zhao, F.; Yong, W.; Jiang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Xie, J. A machine learning strategy to achieve dual-synchronous property improvement of aviation Al-Cu-Mg alloy. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2026, 244, 208–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starke, E.A.; Staley, J.T. Application of modern aluminum alloys to aircraft. Prog. Aeosp. Sci. 1996, 32, 131–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashkenazi, D. How aluminum changed the world: A metallurgical revolution through technological and cultural perspectives. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2019, 143, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Yi, Y.; He, H.; Huang, S.; Zhang, J.; Dong, F. Hot deformation behavior and microstructural evolution of the Al-Cu-Li alloy: A study with processing map. J. Alloys Compd. 2023, 934, 167755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wu, X.; Zhao, P.; Xiong, X.; Zheng, Z.; Gao, K.; Wen, S.; Wei, W.; Rong, L.; Huang, H.; et al. Characterization of η’ and T′ precipitates in Al-Zn-Mg-Zr alloy using transmission electron microscopy and atom probe tomography. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2025, 252, 206–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stachowicz, F. Influence of rolling speed on the temperature field during cold rolling of aluminum sheets. Acta Metall. Slovaca 2023, 29, 206–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.; Fan, X.G.; Li, H.W.; Zhan, M.; Li, S.H. Grain morphology related microstructural developments in bulk deformation of 2219 aluminum alloy sheet at elevated temperature. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2019, 760, 328–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Dong, P.; Zhang, P.; Wang, Y.; Li, F.; Zhu, C.; Meng, D.-A.; Fan, S.; Zhao, S. Deformation behavior and microstructure characterization of the radially forged 2A50 aluminum alloy at high-temperature solid and semi-solid states. J. Alloys Compd. 2024, 989, 174392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kareem, S.A.; Anaele, J.U.; Aikulola, E.O.; Olanrewaju, O.F.; Omiyale, B.O.; Falana, S.O.; Oke, S.R.; Bodunrin, M.O. Hot deformation behavior of aluminum alloys: A comprehensive review on deformation mechanism, processing maps analysis and constitutive model description. Mater. Today Commun. 2025, 44, 112004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.; Logé, R.E. A review of dynamic recrystallization phenomena in metallic materials. Mater. Des. 2016, 111, 548–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doherty, R.D.; Hughes, D.A.; Humphreys, F.J.; Jonas, J.J.; Jensen, D.J.; Kassner, M.E.; King, W.E.; McNelley, T.R.; McQueen, H.J.; Rollett, A.D. Current issues in recrystallization: A review. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 1997, 238, 219–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, L.; Zhao, K.; Gao, T.; Liu, G.; Sun, Q.; Liu, S.; Liu, X. Constitutive equation and microstructural evolution of one distinctive Al–based hybrid composite reinforced by nano–AlN and micro–TiC particles during hot compression. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2023, 888, 145830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cram, D.G.; Zurob, H.S.; Brechet, Y.J.M.; Hutchinson, C.R. Modelling discontinuous dynamic recrystallization using a physically based model for nucleation. Acta Mater. 2009, 57, 5218–5228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cram, D.G.; Fang, X.Y.; Zurob, H.S.; Bréchet, Y.J.M.; Hutchinson, C.R. The effect of solute on discontinuous dynamic recrystallization. Acta Mater. 2012, 60, 6390–6404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blum, W.; Zhu, Q.; Merkel, R.; McQueen, H.J. Geometric dynamic recrystallization in hot torsion of Al 5Mg 0.6Mn (AA5083). Mater. Sci. Eng. A 1996, 205, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Zhang, J.S.; Wang, W.; Tang, Y.T.; Jiang, J.; Reed, R.C.; Lin, J. Mechanistic insights and kinetics of continuous and geometric dynamic recrystallisation in hot deformed aluminium alloy. Acta Mater. 2025, 289, 120893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphreys, F.J. A unified theory of recovery, recrystallization and grain growth, based on the stability and growth of cellular microstructures—I. The basic model. Acta Mater. 1997, 45, 4231–4240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wu, X.; Cao, L.; Liao, B.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Q. Hot deformation and dynamic recrystallization in Al-Mg-Si alloy. Mater. Charact. 2021, 173, 110976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asgharzadeh, H.; Simchi, A.; Kim, H.S. Dynamic restoration and microstructural evolution during hot deformation of a P/M Al6063 alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2012, 542, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, Z.; Wu, X.; He, F.; Wen, S.; Xiong, X.; Gao, K.; Wei, W.; Huang, H.; Nie, Z. Hot deformation behavior, dynamic recrystallization and precipitation behavior of a novel Er, Zr-microalloyed Al–Cu–Mg alloy. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2025, 36, 5381–5395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellars, C.M.; McTegart, W.J. On the mechanism of hot deformation. Acta Metall. 1966, 14, 1136–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi-Bani, A.; Zarei-Hanzaki, A.; Pishbin, M.H.; Haghdadi, N. A comparative study on the capability of Johnson–Cook and Arrhenius-type constitutive equations to describe the flow behavior of Mg–6Al–1Zn alloy. Mech. Mater. 2014, 71, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Cao, Z.; Wan, Z.; Hu, L.; Ye, W.; Li, N.; Fan, C. 3D processing map and hot deformation behavior of 6A02 aluminum alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 742, 356–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajadi, S.A.; Toroghinejad, M.R.; Rezaeian, A. Characterization of dynamic recrystallization and development of a processing map during hot deformation of FeCoCrNi high-entropy alloy. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2025, 37, 601–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, W.; Hou, J.; Qiang, F.; Liu, Y.; Huo, K.; Zheng, P.; Han, P.; Qiao, K.; et al. Dynamic precipitation behavior and recrystallization mechanism during hot deformation of 7E33 aluminum alloy. Mater. Charact. 2025, 227, 115328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.C.; Wu, H.L.; Cao, J.; Yin, Z.K. Modeling of continuous dynamic recrystallization of Al-Zn-Cu-Mg alloy during hot deformation based on the internal-state-variable (ISV) method. Int. J. Plast. 2018, 106, 73–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, L.; Gao, W.; Feng, Z.; Lu, Z.; Zhu, C. Hot deformation characterization of as-homogenized Al-Cu-Li X2A66 alloy through processing maps and microstructural evolution. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2019, 35, 2409–2421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, G.; Guan, Y.; Gao, A.; Sun, W. Constitutive equation and processing maps of an Al–Mg–Si aluminum alloy: Determination and application in simulating extrusion process of complex profiles. Mater. Des. 2016, 92, 983–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaneme, K.K.; Kareem, S.A.; Bodunrin, M.O. Hyperbolic–sine constitutive model determined hot deformation mechanisms and workability response of Al–Zn/Cu and Al–Zn/SiC based composites. Results Eng. 2023, 19, 101255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, J.; Deng, L.; Jin, J.; Zhang, M.; Tang, X.; Gong, P.; Wang, X.; Xiao, G.; Xia, Q. Enhancing constitutive description and workability characterization of Mg alloy during hot deformation using machine learning-based Arrhenius-type model. J. Magnes. Alloys 2024, 12, 3003–3023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ren, L.; Le, Q.; Jin, P.; Cheng, C.; Wang, T.; Wang, P.; Zhou, X.; Chen, X.; Li, D. The hot deformation behavior, microstructure evolution and texture types of as-cast Mg–Li alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 831, 154868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karami, M.; Mahmudi, R. Hot shear deformation constitutive analysis of an extruded Mg–6Li–1Zn alloy. Mater. Lett. 2012, 81, 235–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zener, C.; Hollomon, J.H. Effect of strain rate upon plastic flow of steel. J. Appl. Phys. 1944, 15, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Huang, L.; Zhao, M.; Guo, S.; Su, Y.; Li, J. Characterization of hot workability of Ti-6Cr-5Mo-5V-4Al alloy based on hot processing map and microstructure evolution. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 905, 164161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Li, M. Constitutive model and optimal processing parameters of TC17 alloy with a transformed microstructure via kinetic analysis and processing maps. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2017, 698, 302–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, Y.V.R.K.; Gegel, H.L.; Doraivelu, S.M.; Malas, J.C.; Morgan, J.T.; Lark, K.A.; Barker, D.R. Modeling of dynamic material behavior in hot deformation: Forging of Ti-6242. Metall. Trans. A 1984, 15, 1883–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spišák, E.; Majerníková, J.; Mulidrán, P.; Hajduk, J.; Ruda, F. The simulation of the anisotropy of aluminum alloy sheets by deep drawing: A crucial study for the automotive and materials engineering industries. Acta Metall. Slovaca 2024, 30, 90–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Yi, Y.; He, H.; Huang, S.; Mao, X.; Guo, W.; You, W.; Guo, Y.; Dong, F.; Tang, J. Kinetic model for describing continuous and discontinuous dynamic recrystallization behaviors of 2195 aluminum alloy during hot deformation. Mater. Charact. 2021, 181, 111492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Pan, Q.; Wang, W.; Li, A.; Song, W. Microstructural evolution and constitutive analysis combined with weight optimization method of Al-7.82Zn-1.96Mg-2.35Cu-0.11Zr alloy during hot deformation. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 732, 902–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, C.; Wang, Q.; Ebrahimi, M.; Li, D.; Tang, H.; Zhang, N.; Cai, H. Hot Deformation Behavior and Processing Maps of an As-Cast Al-5Mg-3Zn-1Cu (wt%) Alloy. Materials 2023, 16, 4093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Huang, Y.; Liu, Y. Dynamic recrystallization mechanisms of as-forged Al–Zn–Mg-(Cu) aluminum alloy during hot compression deformation. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2023, 878, 145236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, Q.; Yu, H.; Lee, Y.-S.; Kim, M.-S.; Kim, H.-W. Hot deformation behavior and microstructure evolution of annealed Al-7.9Zn-2.7Mg-2.0Cu (wt%) alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 763, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassner, M.E.; Barrabes, S.R. New developments in geometric dynamic recrystallization. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2005, 410–411, 152–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Element | Cu | Mg | Mn | Si | Al |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| - | 4.80 | 0.25 | 0.32 | 0.17 | Bal. |
| lnZ | 350 °C | 390 °C | 430 °C | 470 °C | 510 °C |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| = 0.001 s−1 | 27.0 | 25.0 | 23.2 | 21.5 | 20.1 |
| = 0.01 s−1 | 29.3 | 27.3 | 25.5 | 23.8 | 22.4 |
| = 0.1 s−1 | 31.6 | 29.6 | 27.8 | 26.1 | 24.7 |
| = 1 s−1 | 33.9 | 31.9 | 30.1 | 28.4 | 27.0 |
| = 10 s−1 | 36.2 | 34.2 | 32.4 | 30.8 | 29.3 |
| Parameter | n | lnA | Q | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B0 | 0.1256 | 0.0178 | 5.195 | 13.840 | 101.351 |
| B1 | 0.2997 | −0.0235 | 10.286 | 650.020 | 3780.730 |
| B2 | −5.3564 | 0.1195 | −164.793 | −6477.686 | −37,912.653 |
| B3 | 29.5086 | −0.4113 | 917.328 | 29,714.088 | 174,077.607 |
| B4 | −78.8058 | 1.0309 | −2522.628 | −73,046.500 | −427,680.377 |
| B5 | 111.8490 | −1.5753 | 3692.808 | 98,856.678 | 578,173.082 |
| B6 | −81.2223 | 1.2430 | −2755.284 | −69,337.586 | −405,073.637 |
| B7 | 23.7708 | −0.3849 | 824.156 | 19,680.374 | 114,859.791 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
He, F.; Wu, X.; Rong, Z.; Zhang, X.; Xiong, X.; Wen, S.; Gao, K.; Wei, W.; Rong, L.; Huang, H.; et al. Dynamic Recrystallization and Microstructural Evolution During Hot Deformation of Al-Cu-Mg Alloy. Metals 2025, 15, 1100. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15101100
He F, Wu X, Rong Z, Zhang X, Xiong X, Wen S, Gao K, Wei W, Rong L, Huang H, et al. Dynamic Recrystallization and Microstructural Evolution During Hot Deformation of Al-Cu-Mg Alloy. Metals. 2025; 15(10):1100. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15101100
Chicago/Turabian StyleHe, Fangyan, Xiaolan Wu, Zhizheng Rong, Xueqin Zhang, Xiangyuan Xiong, Shengping Wen, Kunyuan Gao, Wu Wei, Li Rong, Hui Huang, and et al. 2025. "Dynamic Recrystallization and Microstructural Evolution During Hot Deformation of Al-Cu-Mg Alloy" Metals 15, no. 10: 1100. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15101100
APA StyleHe, F., Wu, X., Rong, Z., Zhang, X., Xiong, X., Wen, S., Gao, K., Wei, W., Rong, L., Huang, H., & Nie, Z. (2025). Dynamic Recrystallization and Microstructural Evolution During Hot Deformation of Al-Cu-Mg Alloy. Metals, 15(10), 1100. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15101100







