Wear Behavior and Friction Mechanism of Titanium–Cerium Alloys: Influence of CeO2 Precipitate
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials Preparation
2.2. Material Characterization
2.3. Tribological Tests
3. Results and Discussion
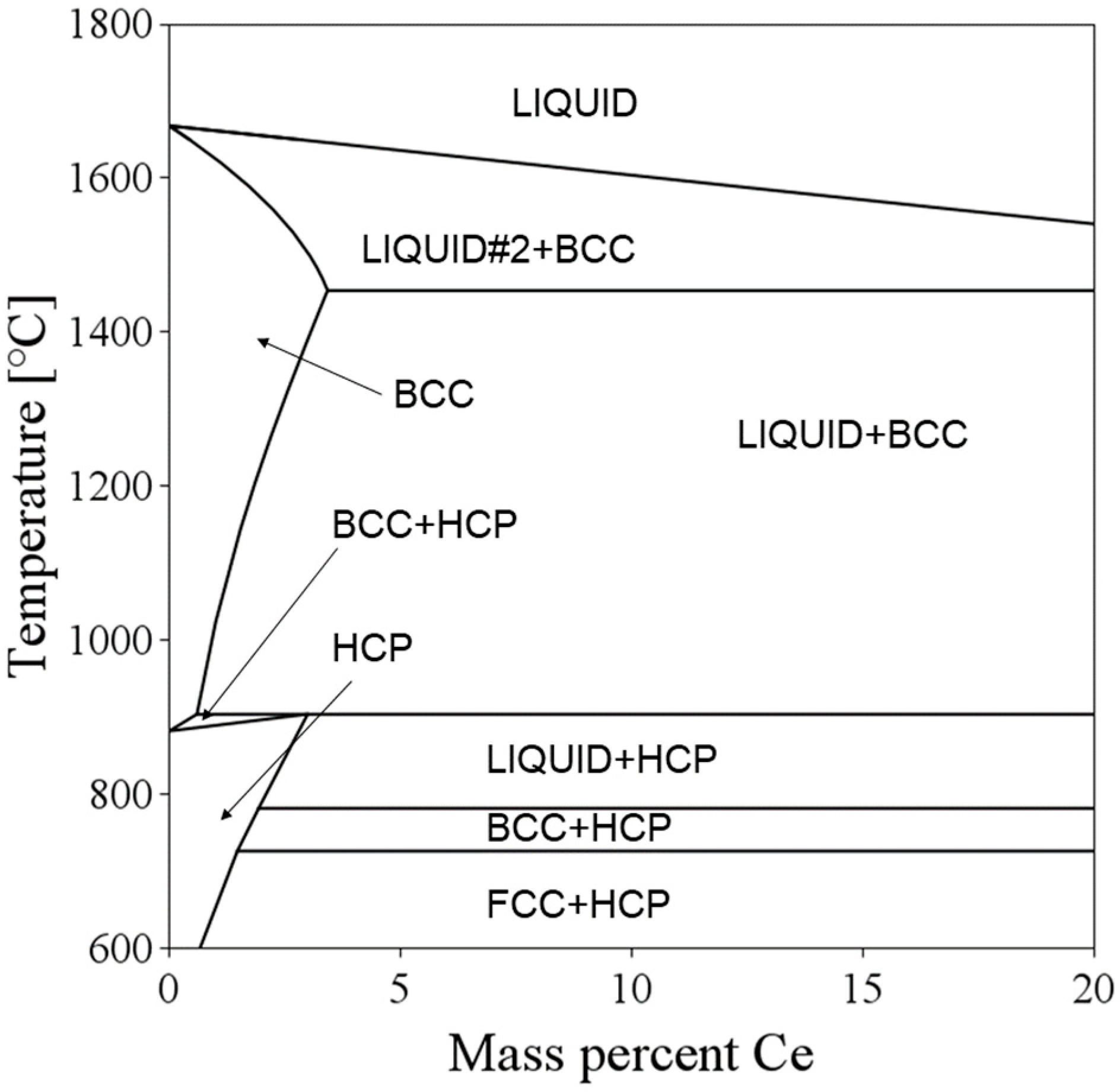
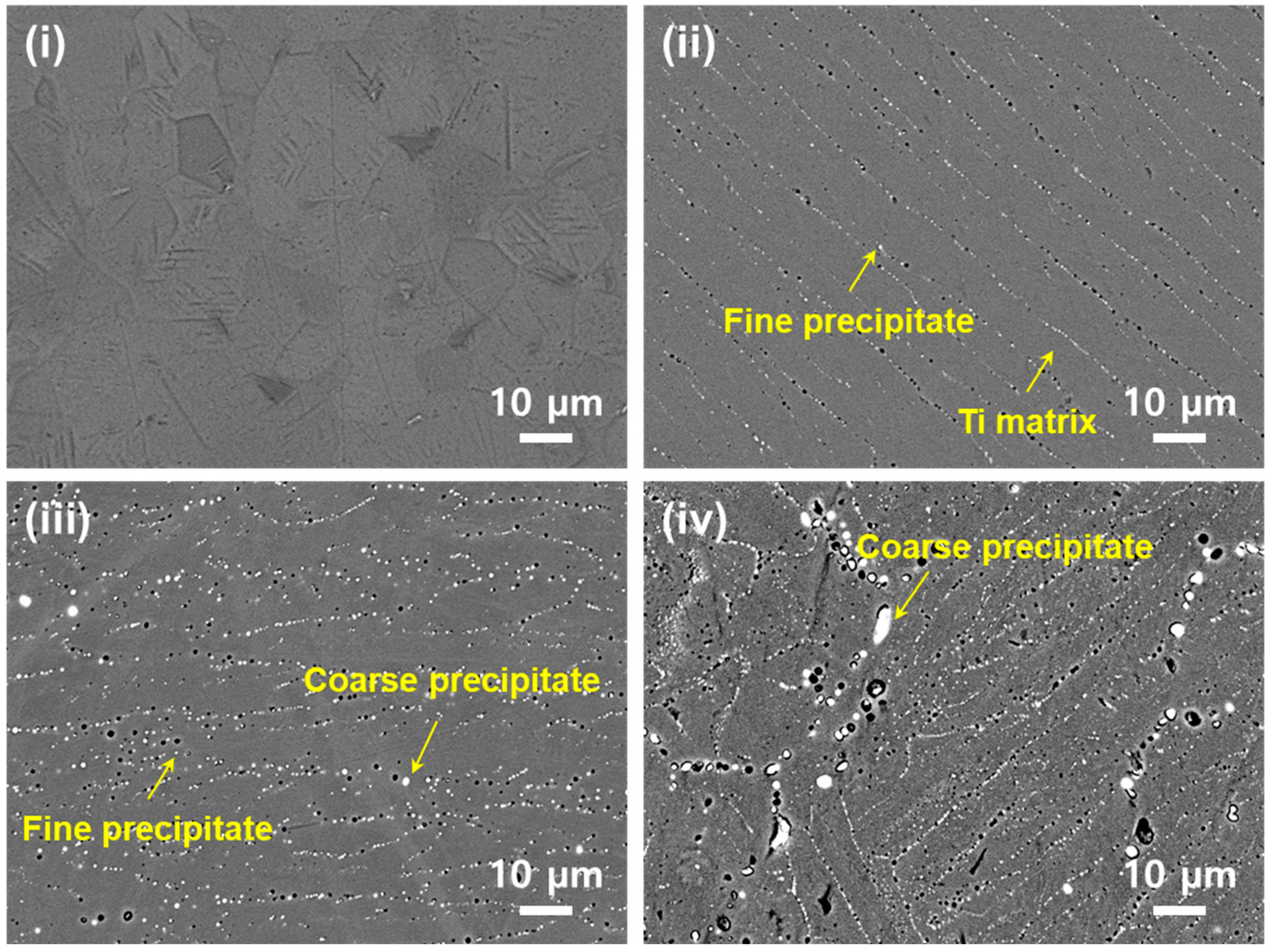
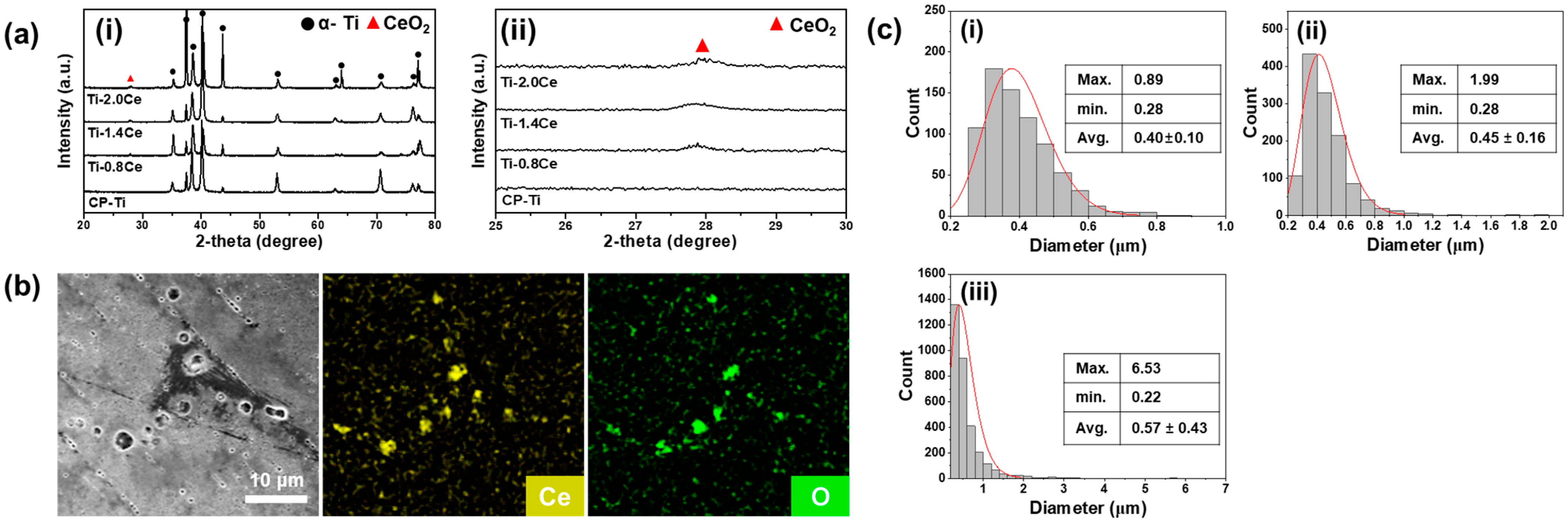
3.1. Microstructure and Phase Analysis
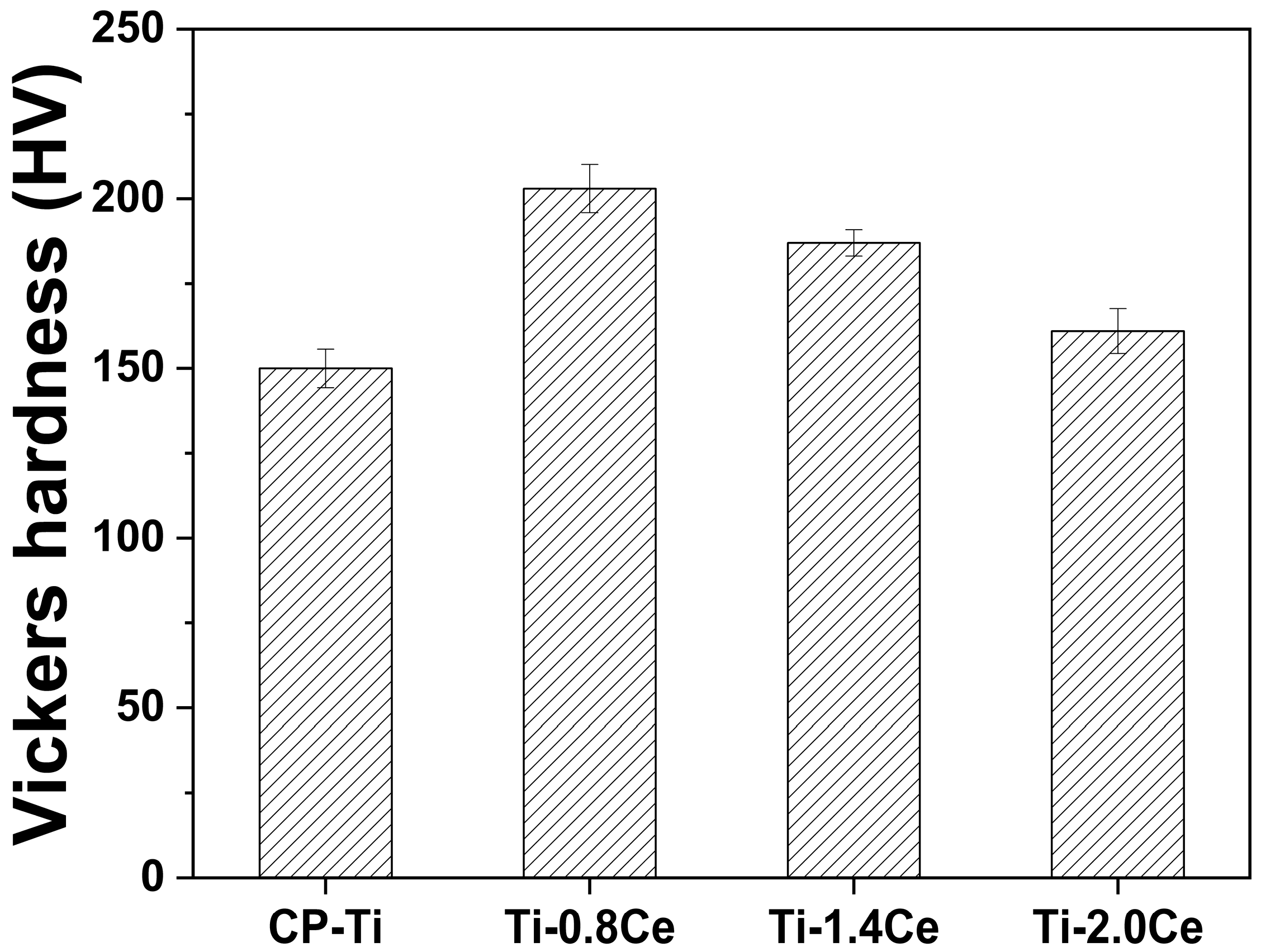
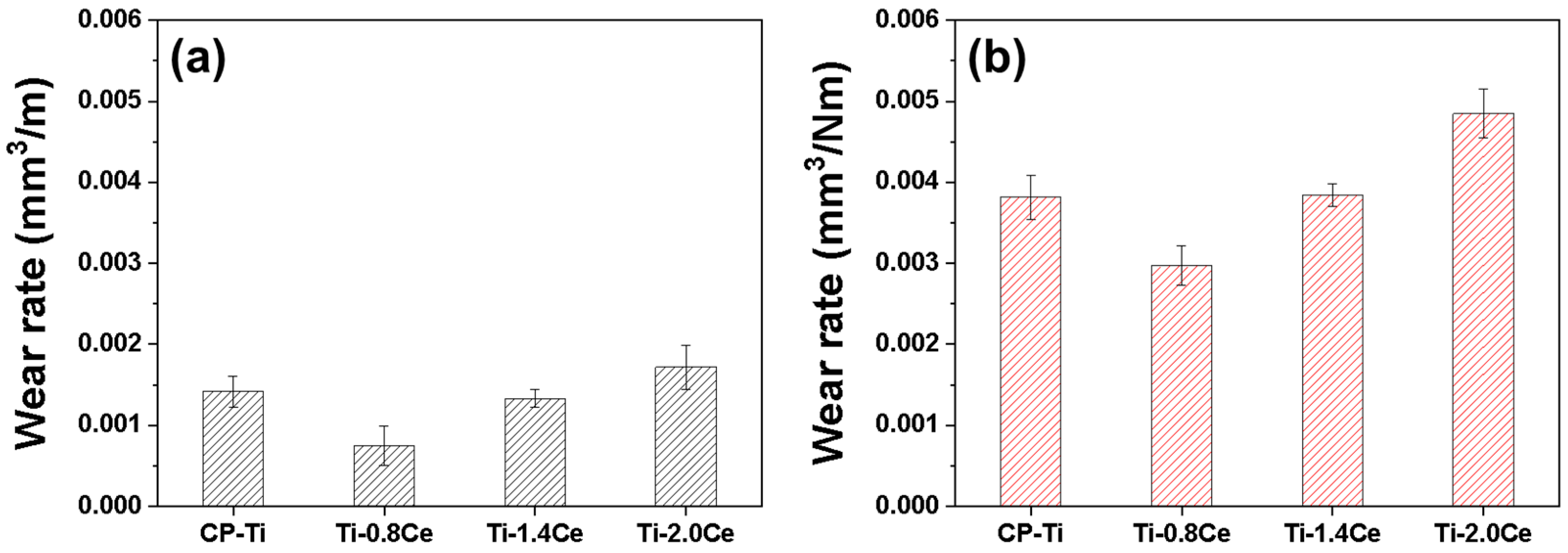
3.2. Wear Rate
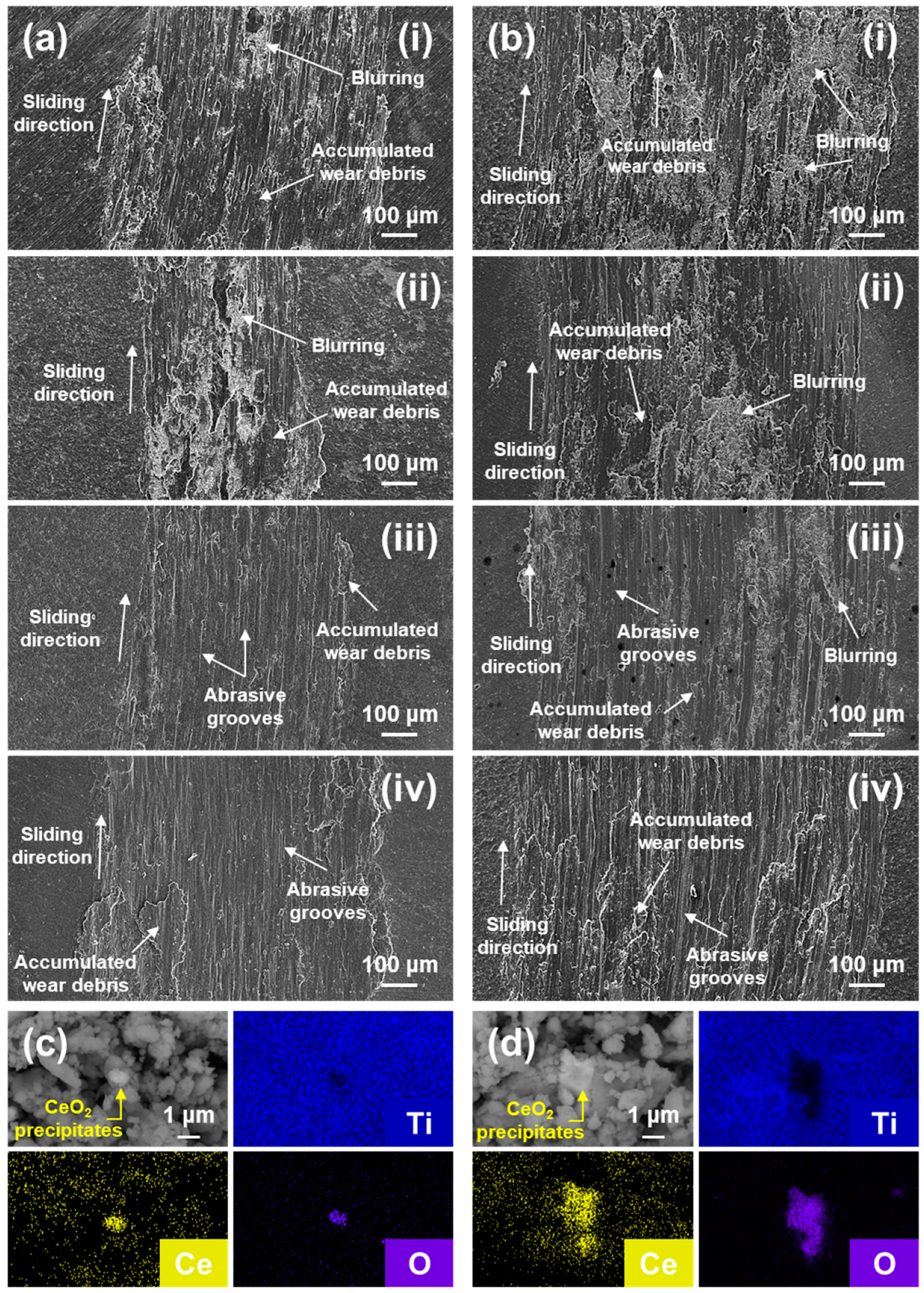
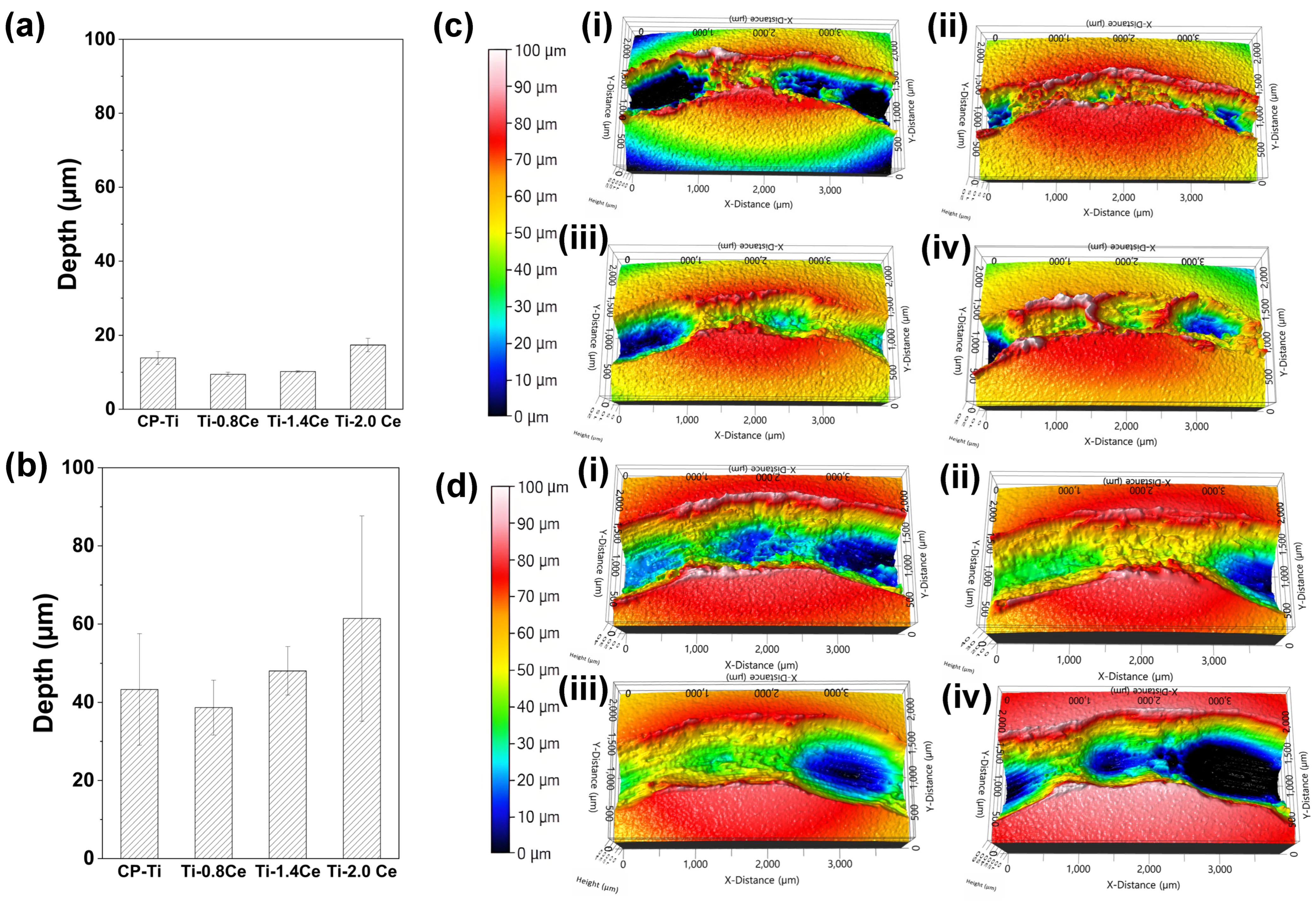
3.3. Wear Track and Debris
3.4. Friction
4. Conclusions
- The Ti-0.8Ce alloy showed the highest hardness and lowest wear rate, achieving reductions of 47.2% (1 N) and 22.2% (5 N) compared to CP-Ti improvements, which are attributed to the solid solution and precipitation strengthening effect of fine CeO2 precipitates.
- In the Ti-1.4Ce and Ti-2.0Ce, the formation of coarser CeO2 precipitates led to increased wear rates compared to Ti-0.8Ce, despite their higher hardness than CP-Ti. This is due to third-body abrasion and composite wear behavior induced by the hard precipitates.
- Although Ti-1.4Ce showed the lowest average friction coefficients (0.963 at 1 N, 0.776 at 5 N), this was a result of increased abrasive interaction with the precipitates rather than improved wear resistance. The elevated material removal due to this mechanism ultimately reduced wear performance.
- Ti-2.0Ce, containing coarse and irregular precipitates, exhibited the highest wear rate and deepest wear track, indicating a deterioration of wear resistance with excessive Ce addition.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Geetha, M.; Singh, A.K.; Asokamani, R.; Gogia, A.K. Ti based biomaterials, the ultimate choice for orthopaedic implants—A review. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2009, 54, 397–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niemeyer, T.C.; Grandini, C.R.; Pinto, L.M.C.; Angelo, A.C.D.; Schneider, S.G. Corrosion behavior of Ti-13Nb–13Zr alloy used as a biomaterial. J. Alloys Compd. 2009, 476, 172–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.L.; Niinomi, M.; Akahori, T.; Fukui, H.; Toda, H. Corrosion resistance and biocompatibility of Ti-Ta alloys for biomedical applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2005, 398, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budinski, K.G. Tribological properties of titanium alloys. Wear 1991, 151, 203–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Bell, T. Enhanced wear resistance of titanium surfaces by a new thermal oxidation treatment. Wear 2000, 238, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.O.; Haseeb, A. Response of Ti-6Al–4V and Ti-24Al–11Nb alloys to dry sliding wear against hardened steel. Tribol. Int. 2002, 35, 357–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasz, M.L.; Brotzen, F.R.; McLellan, R.B.; Griffin, A.J. Effect of oxygen and hydrogen on mechanical properties of commercial purity titanium. Int. Mater. Rev. 1996, 41, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.Y.; McMahon, C.J.; Pope, D.P.; Williams, J.C. The effect of oxygen on the structure and mechanical behavior of Aged Ti-8 Wt pct Al. Metall. Trans. A 1976, 7, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Liu, W.; Hou, H.; Liu, F. Pinning effect of coherent particles on moving planar grain boundary: Theoretical models and molecular dynamics simulations. Materialia 2019, 5, 100225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vega, M.; Medina, S.; Quispe, A.; Gómez, M.; Gómez, P. Recrystallisation driving forces against pinning forces in hot rolling of Ti-microalloyed steels. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2006, 423, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.F.; Luo, S.; Schaffer, G.; Qian, M. Impurity scavenging, microstructural refinement and mechanical properties of powder metallurgy titanium and titanium alloys by a small addition of cerium silicide. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2013, 573, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Liu, Y.; Liu, X.; Wu, X.; Zhou, S.; Zhang, L.; Li, W.; Zhang, W. Simultaneous strength-ductility enhancement in as-cast Ti6Al4V alloy by trace Ce. Mater. Des. 2022, 215, 110491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, W.; Biesiekierski, A.; Lin, J.; Li, Y.; Wen, C. Impact of rare earth elements on nanohardness and nanowear properties of beta-type Ti-24Nb-38Zr-2Mo alloy for medical applications. Materialia 2020, 12, 100772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Xue, R.; Xie, B.; Wang, K.; Xiao, G.; Yuan, Z.; Xu, X.; Zhang, L.; Liu, L. Influence of scandium and yttrium on mechanical properties, corrosion behavior, and martensitic transformation of near-β titanium alloys. J. Rare Earths, 2025; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Won, J.W.; Oh, J.M.; Kim, W.C.; Park, C.H.; Park, I.; Hyun, Y.-T. Simultaneous high tensile strength and high ductility in cast Ce-alloyed Ti. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2024, 918, 147487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.S.; Oh, J.M.; Park, C.H.; Lee, W.J.; Park, Y.H.; Won, J.W. Development of Highly Machinable Ti Alloy with Exceptional Tensile Properties by Er Alloying Element Addition. Korean J. Met. Mater. 2024, 62, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, N.Y.; Lee, W.; Park, C.H. Effect of Ce Addition on the Machinability of Ti-6Al-4V Alloy. Korean J. Met. Mater. 2025, 63, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handbook, A. Alloy phase diagrams. ASM Int. 1992, 3, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Lütjering, G.; Williams, J.; Gysler, A. Microstructure and mechanical properties of titanium alloys. In Microstructure and Properties of Materials; Technical University Hamburg-Harburg: Hamburg, Germany, 2000; Volume 2, pp. 1–77. [Google Scholar]
- Welsch, G.; Boyer, R.; Collings, E.W. Materials Properties Handbook: Titanium Alloys; ASM international: Materials Park, OH, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Gao, L.; Hou, Q.; Wu, P.; Zhou, Y.; Ding, Z. Enhanced oxygen storage capacity of porous CeO2 by rare earth doping. Molecules 2023, 28, 6005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Zhu, X.; Jiang, Z.; Chen, H.; Wang, N. Effect of rare earth Ce addition on microstructure and mechanical properties of titanium alloy Ti-6Al-4V. Mater. Lett. 2023, 330, 133244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, M.; Talib, I.; Rana, A.M.; Akbar, T.; Jabeen, S.; Lee, J.; Kim, S. Effect of bilayer CeO2−x/ZnO and ZnO/CeO2−x heterostructures and electroforming polarity on switching properties of non-volatile memory. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Bao, Y.; Duan, C.; Lu, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Q. Effect of rare earth Ce on deep stamping properties of high-strength interstitial-free steel containing phosphorus. Materials 2020, 13, 1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asanuma, H.; Polcik, P.; Kolozsvari, S.; Klimashin, F.; Riedl, H.; Mayrhofer, P. Cerium doping of Ti-Al-N coatings for excellent thermal stability and oxidation resistance. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2017, 326, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.F.; Luo, S.; Qian, M. The effect of lanthanum boride on the sintering, sintered microstructure and mechanical properties of titanium and titanium alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2014, 618, 447–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.; Wu, S.Q.; Ping, D.H.; Murakami, H.; Yamabe-Mitarai, Y. Effects of Sc addition on the microstructure and tensile properties of Ti-6.6 Al–5.5 Sn–1.8 Zr alloy. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2012, 136, 1015–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archard, J. Contact and rubbing of flat surfaces. J. Appl. Phys. 1953, 24, 981–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Song, H.; Sandfeld, S.; Liu, X.; Wei, Y. Breakdown of Archard law due to transition of wear mechanism from plasticity to fracture. Tribol. Int. 2022, 173, 107660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Choi, Y.; Matsugi, K. Effect of C content on the microstructure and properties of in-situ synthesized TiC particles reinforced Ti composites. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 22206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yildirim, M.; Özyürek, D.; Gürü, M. The effects of precipitate size on the hardness and wear behaviors of aged 7075 aluminum alloys produced by powder metallurgy route. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2016, 41, 4273–4281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singhal, V.; Shelly, D.; Babbar, A.; Lee, S.-Y.; Park, S.-J. Review of Wear and Mechanical Characteristics of Al-Si Alloy Matrix Composites Reinforced with Natural Minerals. Lubricants 2024, 12, 350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hesterberg, W.G.; Donahue, R.J.; Cleary, T.M. Evaporable Foam Casting System Utilizing a Hypereutectic Aluminum-Silicon Alloy. U.S. Patent No. 4,966,220, 30 October 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Jiang, J.; Yang, Z.; Zhao, Q.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, Y. The effect of copper content on the mechanical and tribological properties of hypo-, hyper-and eutectoid Ti-Cu alloys. Materials 2020, 13, 3411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, P.; Holladay, J. Friction and wear properties of titanium. Wear 1958, 2, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigney, D. Transfer, mixing and associated chemical and mechanical processes during the sliding of ductile materials. Wear 2000, 245, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fillot, N.; Iordanoff, I.; Berthier, Y. Wear modeling and the third body concept. Wear 2007, 262, 949–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gahr, K.-H. Microstructure and Wear of Materials; P.O. Box 211, 1000 AE; Elsevier Science Publishers: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, Z.; Timokhina, I.; Pereloma, E. Clustering, nano-scale precipitation and strengthening of steels. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2021, 118, 100764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torgerson, T.; Mantri, S.; Banerjee, R.; Scharf, T. Room and elevated temperature sliding wear behavior and mechanisms of additively manufactured novel precipitation strengthened metallic composites. Wear 2019, 426, 942–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stachowiak, G.; Batchelor, A.W. Batchelor, Engineering Tribology; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Blau, P.J. Interpretations of the friction and wear break-in behavior of metals in sliding contact. Wear 1981, 71, 29–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, M.; Rack, H. Friction and surface behavior of selected titanium alloys during reciprocating-sliding motion. Wear 2001, 249, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Samples | Chemical Composition (wt.%) | True Density (g/cm3) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ti | N | C | O | Ce | ||
| CP–Ti Grade 1 | Bal. | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.09 | - | 4.501 |
| Ti-0.8Ce | Bal. | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.09 | 0.79 | 4.519 |
| Ti-1.4Ce | Bal. | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.09 | 1.37 | 4.528 |
| Ti-2.0Ce | Bal. | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.10 | 2.02 | 4.537 |
| Testing Conditions | Value |
|---|---|
| Sliding distance | 300 m |
| Linear speed | 0.1 m/s |
| Wear radius | 5 mm |
| Wear load | 1 N, 5 N |
| Counterpart material | AISI 52100 steel ball (diameter = 5.556 mm) |
| Testing temperature | 25 °C ± 2 °C |
| Samples | Max. (μm) | Min. (μm) | Avg. (μm) | Area (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ti-0.8Ce | 0.89 | 0.28 | 0.40 ± 0.10 | 0.44 |
| Ti-1.4Ce | 1.99 | 0.28 | 0.45 ± 0.16 | 1.37 |
| Ti-2.0Ce | 6.53 | 0.22 | 0.57 ± 0.43 | 2.42 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yun, S.; Shin, D.; Bae, K.; Park, N.; Won, J.W.; Park, C.H.; Lee, J. Wear Behavior and Friction Mechanism of Titanium–Cerium Alloys: Influence of CeO2 Precipitate. Metals 2025, 15, 1094. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15101094
Yun S, Shin D, Bae K, Park N, Won JW, Park CH, Lee J. Wear Behavior and Friction Mechanism of Titanium–Cerium Alloys: Influence of CeO2 Precipitate. Metals. 2025; 15(10):1094. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15101094
Chicago/Turabian StyleYun, Sohee, Dongmin Shin, Kichang Bae, Narim Park, Jong Woo Won, Chan Hee Park, and Junghoon Lee. 2025. "Wear Behavior and Friction Mechanism of Titanium–Cerium Alloys: Influence of CeO2 Precipitate" Metals 15, no. 10: 1094. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15101094
APA StyleYun, S., Shin, D., Bae, K., Park, N., Won, J. W., Park, C. H., & Lee, J. (2025). Wear Behavior and Friction Mechanism of Titanium–Cerium Alloys: Influence of CeO2 Precipitate. Metals, 15(10), 1094. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15101094








