Microstructural Evolution and Oxidation Resistance of Fe-30Ni-15Cr Alloy for Internal Combustion Engine Valves Under Long-Term High-Temperature Exposure and Heat Treatment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Procedures
2.1. Material Processing
2.2. Microstructural Characterization
2.3. Heat-Treatment Methods and Long-Term Heat Exposure Tests
3. Results and Discussion
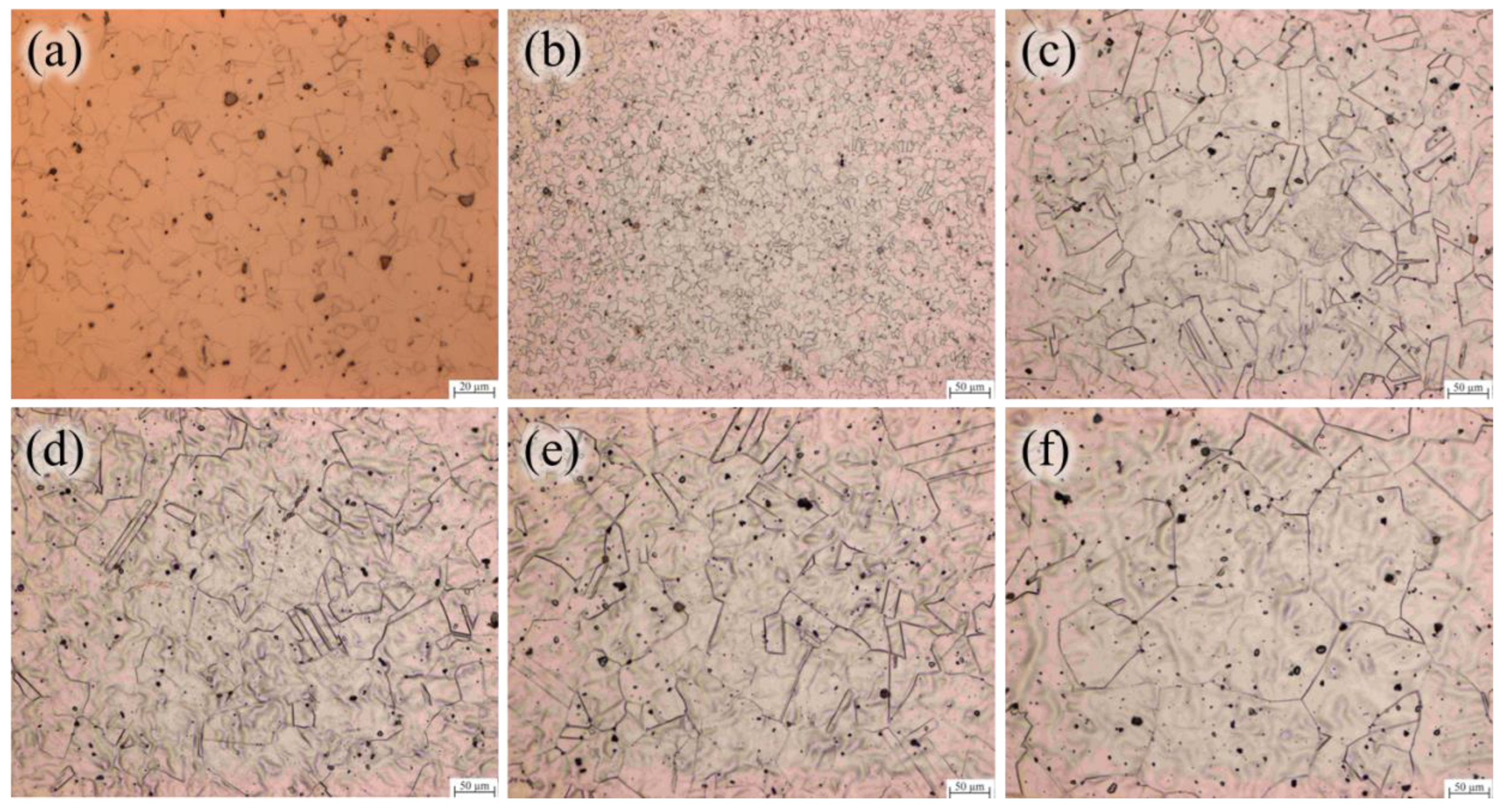
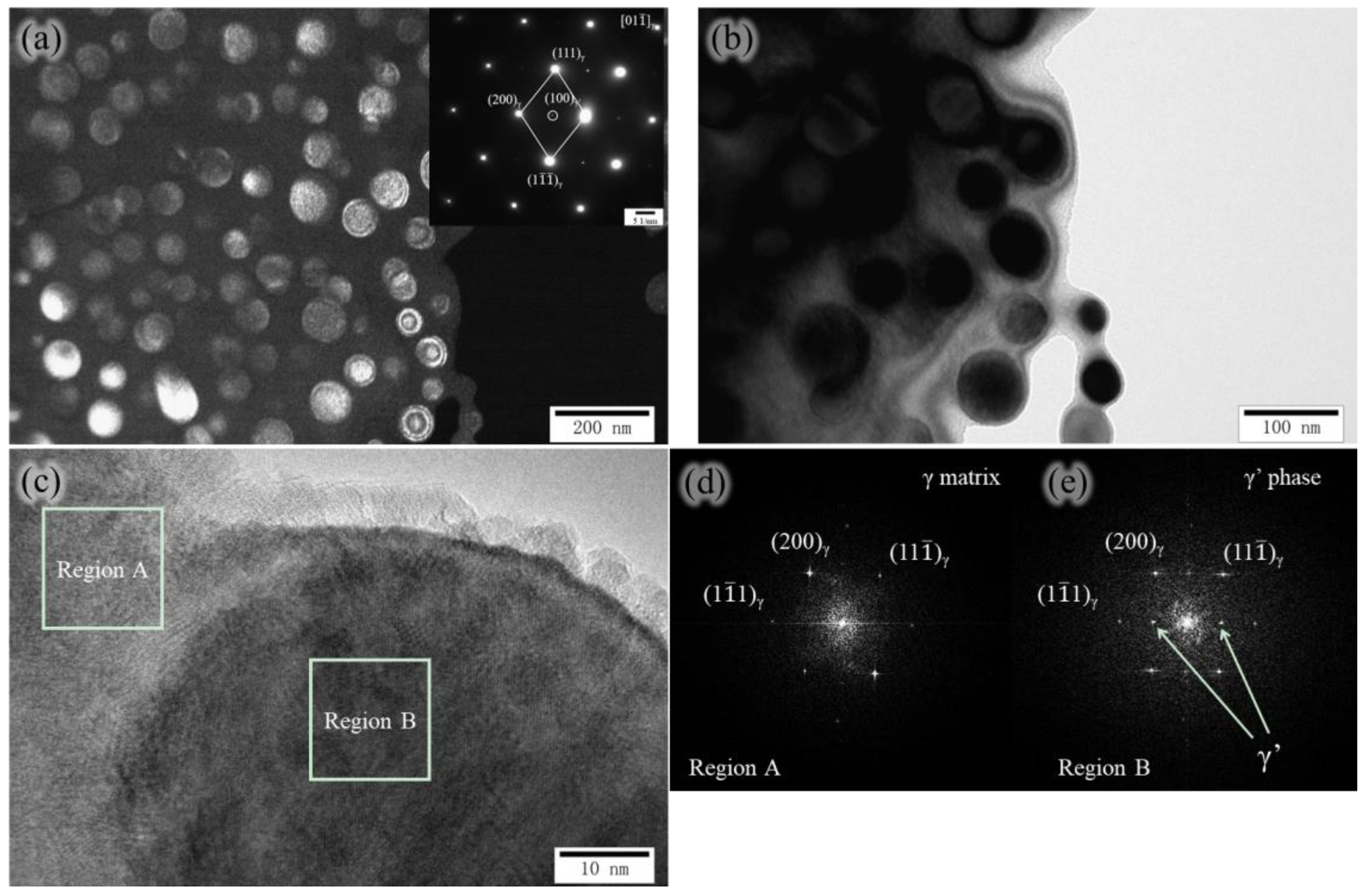
3.1. The Evolution of Microstructure and Mechanical Properties in Forged and Solution Heat Treated States
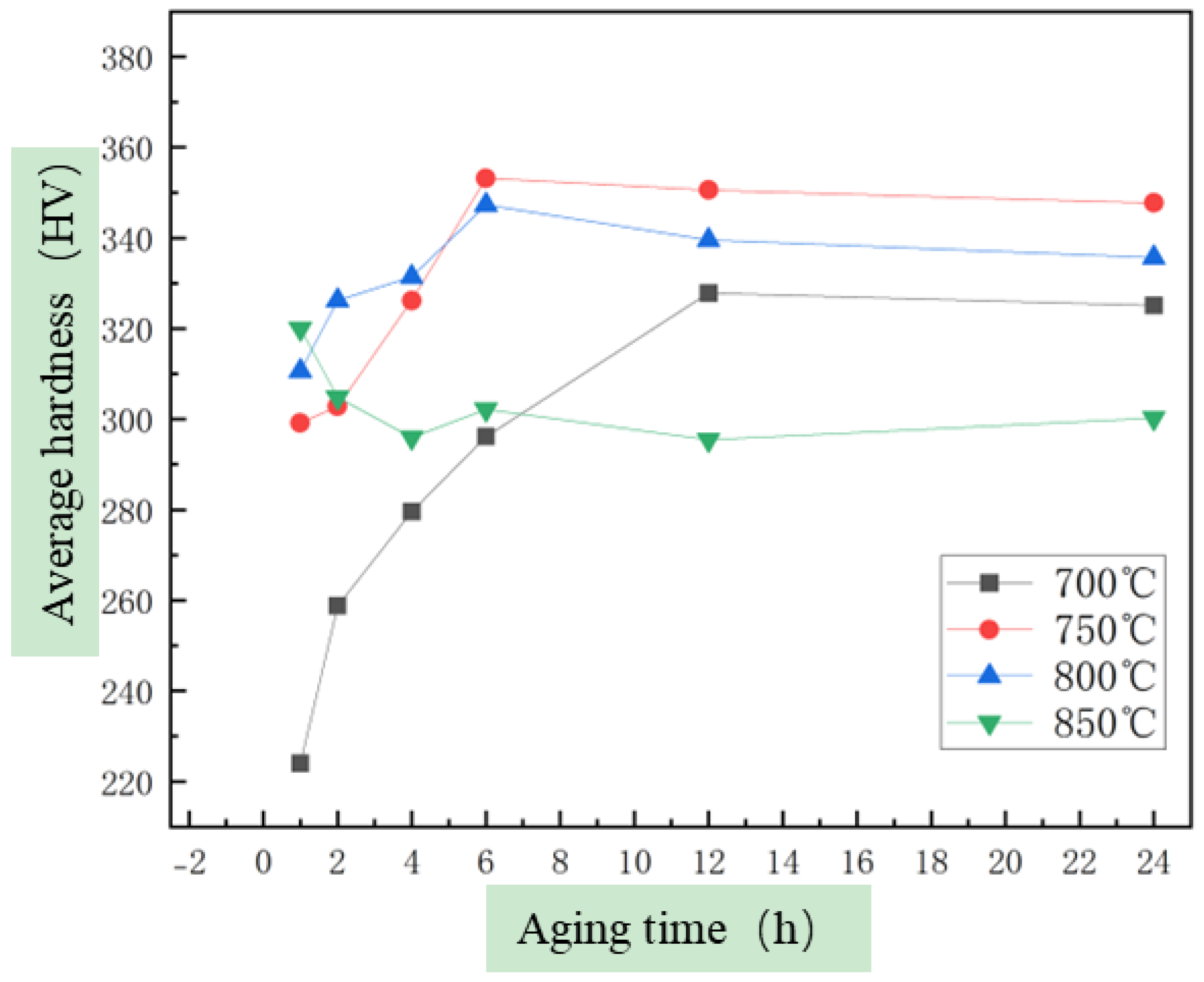
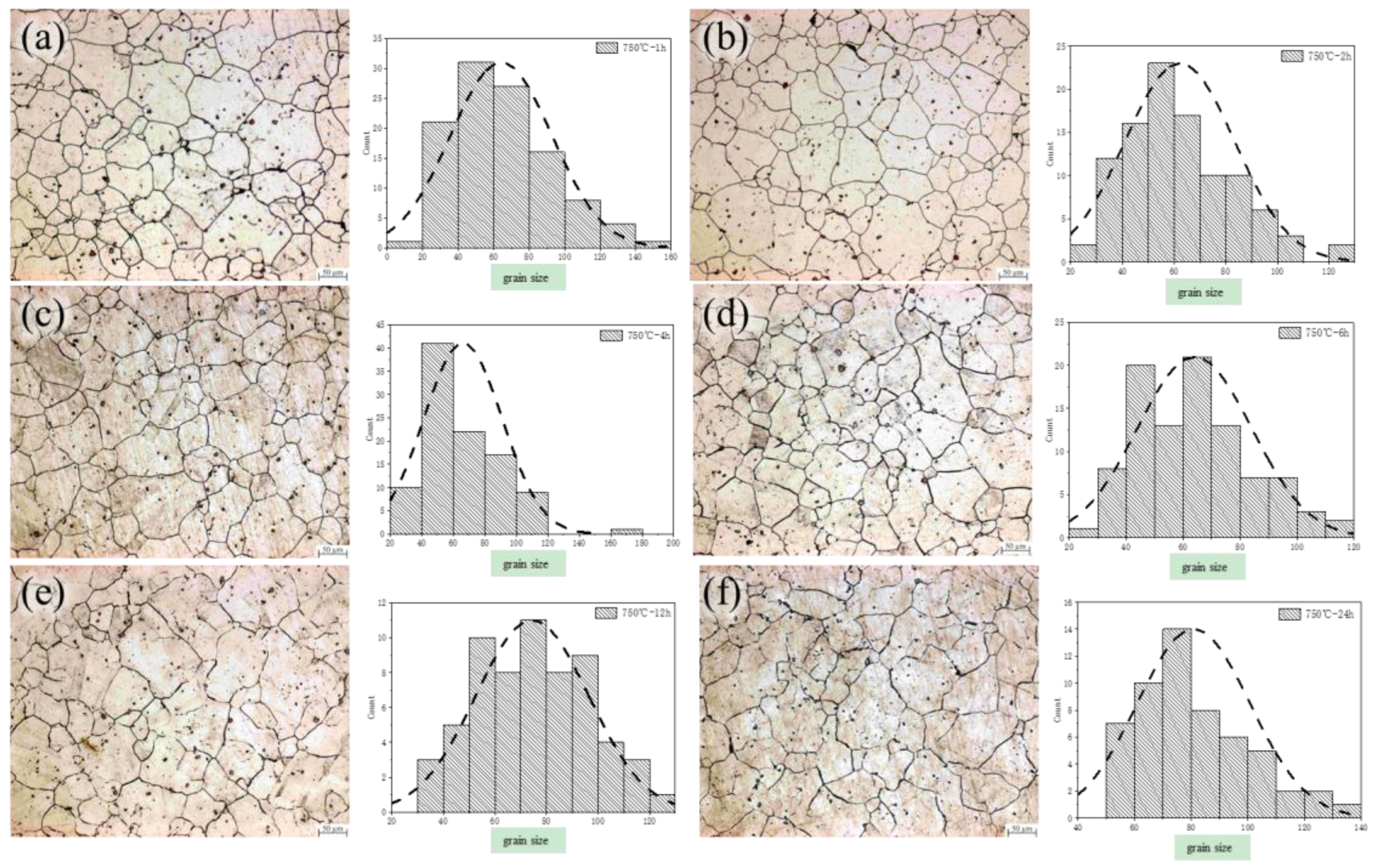
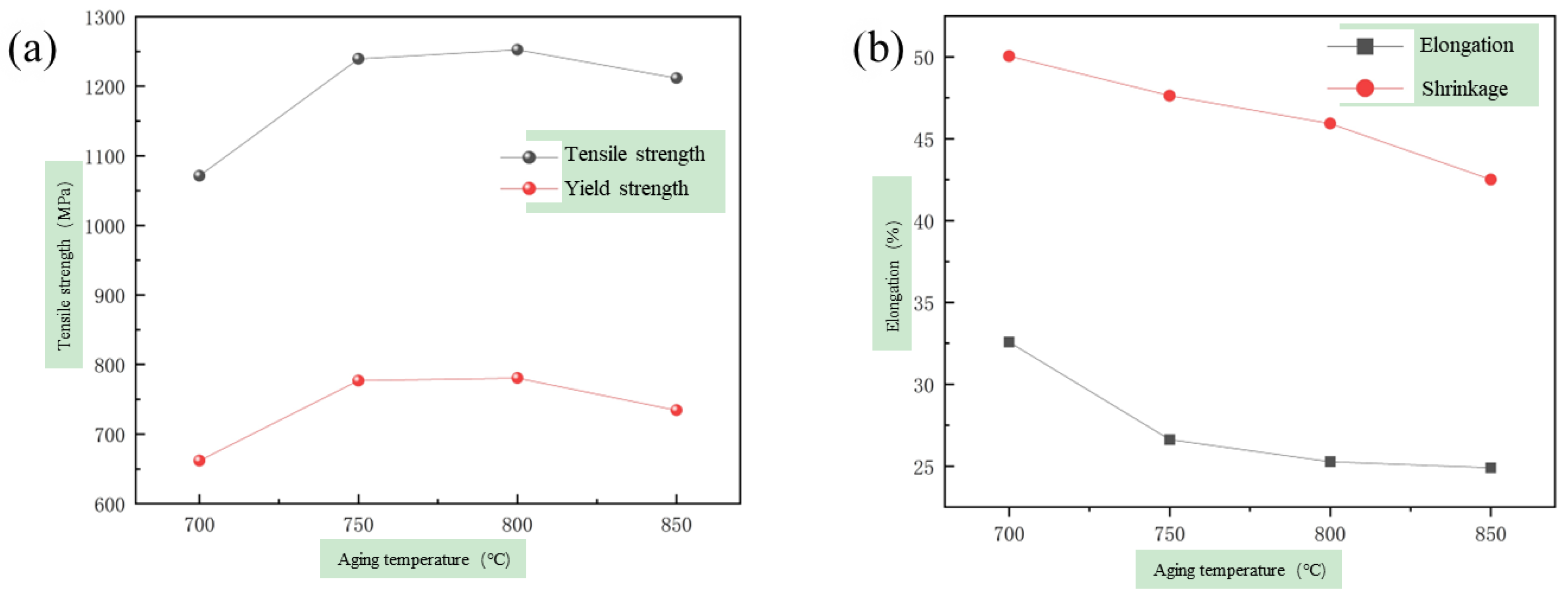
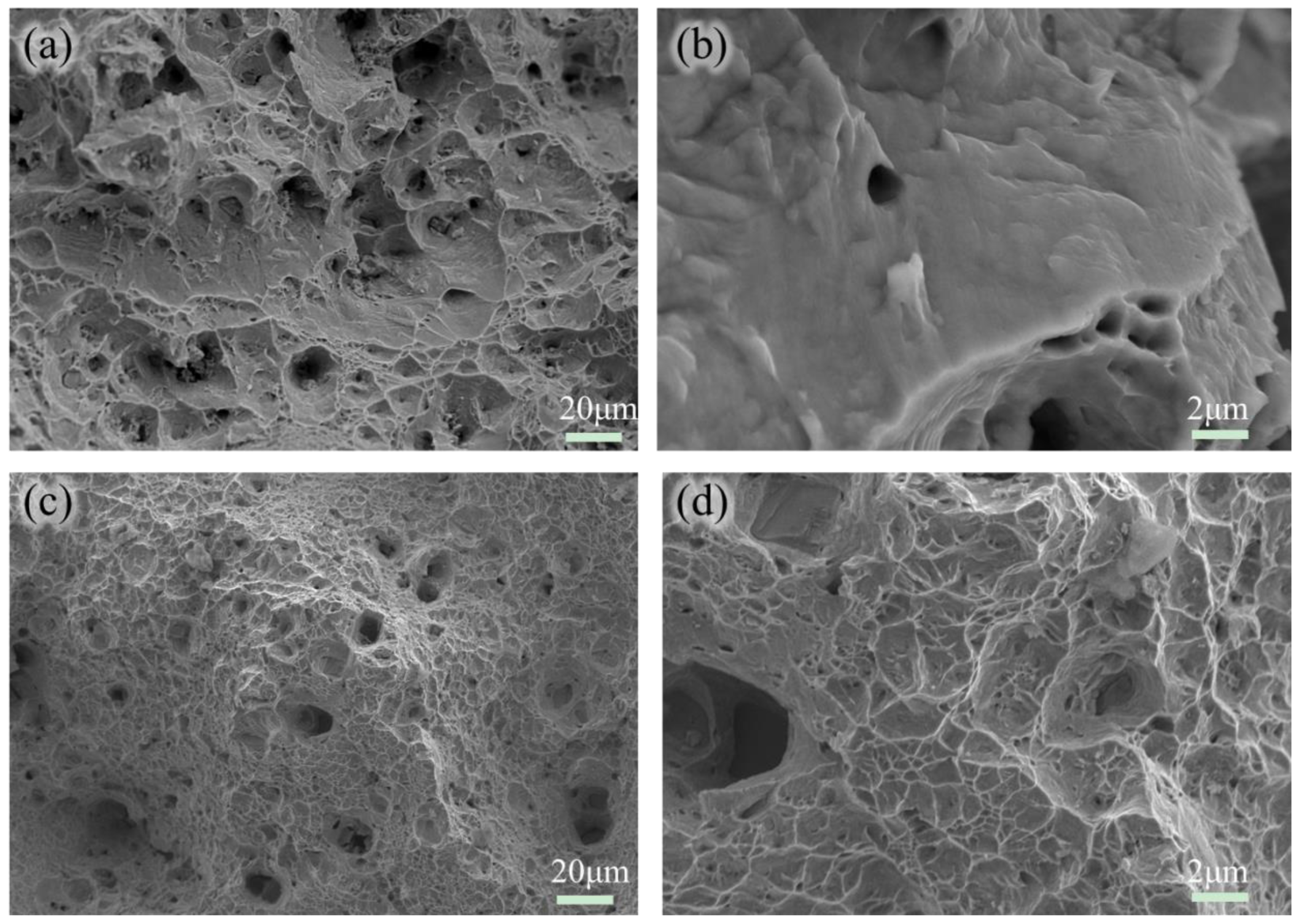
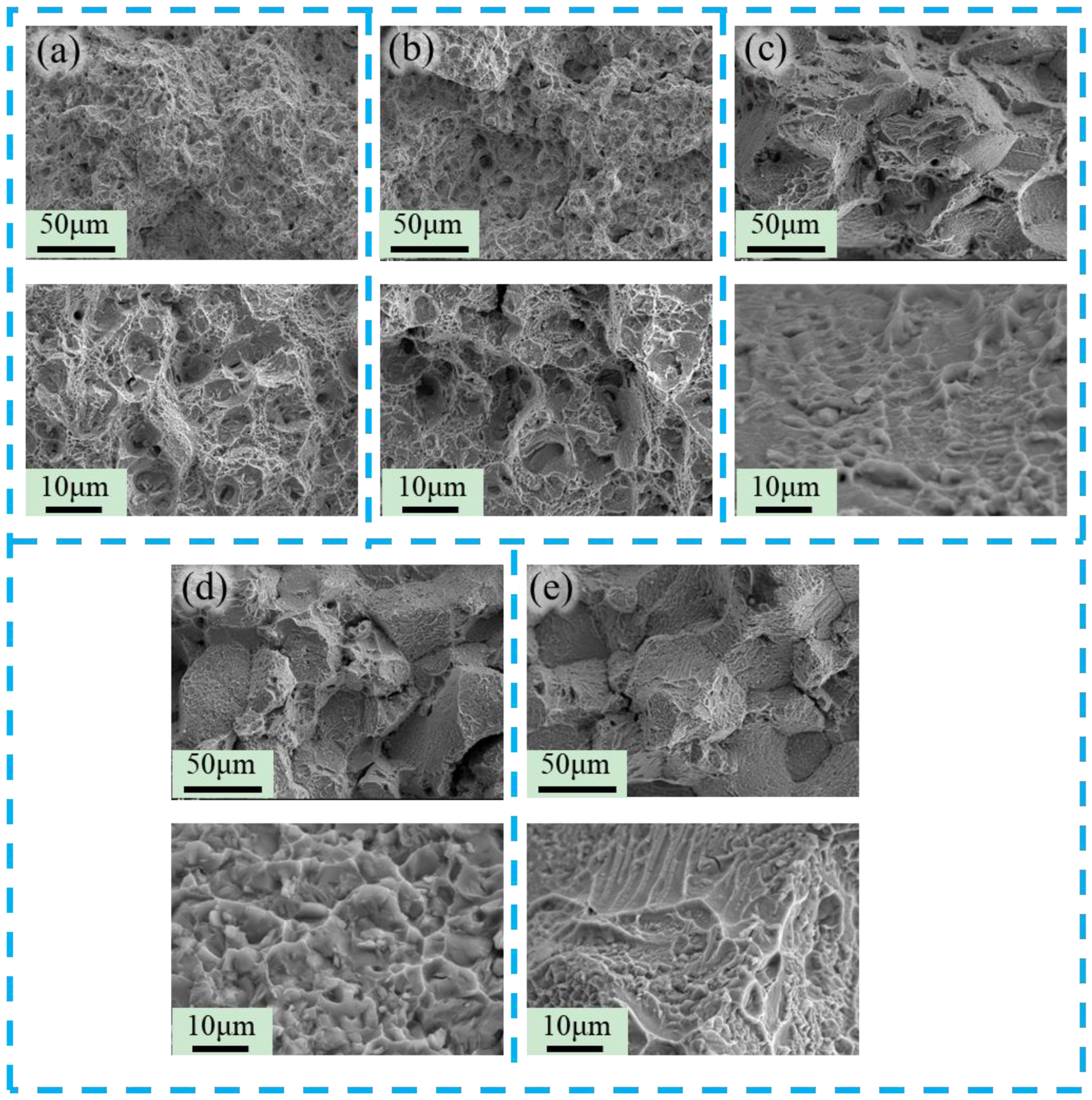
3.2. The Evolution of Microstructure and Mechanical Properties in Ultra-Long Term Aged Heat Treated
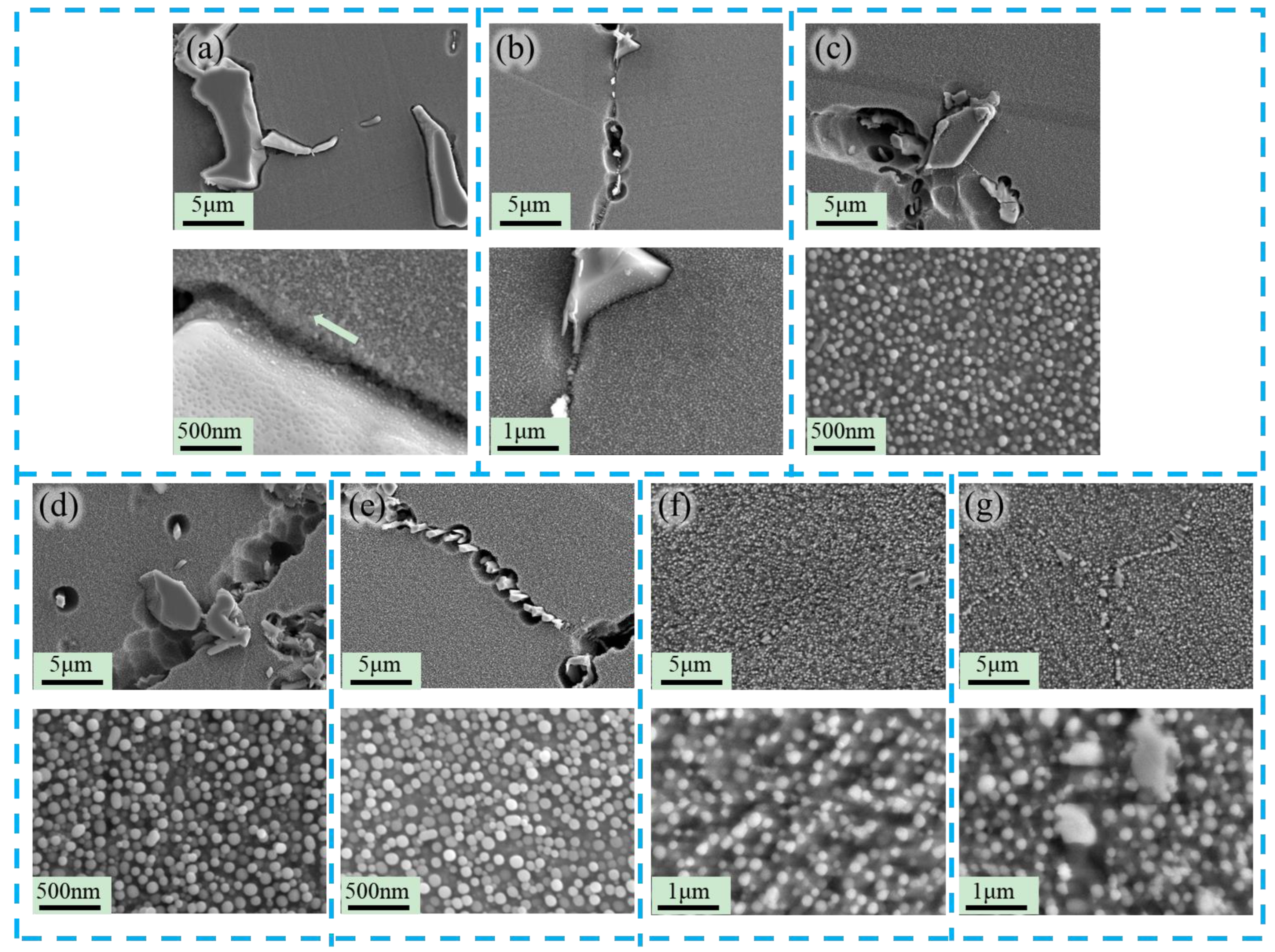
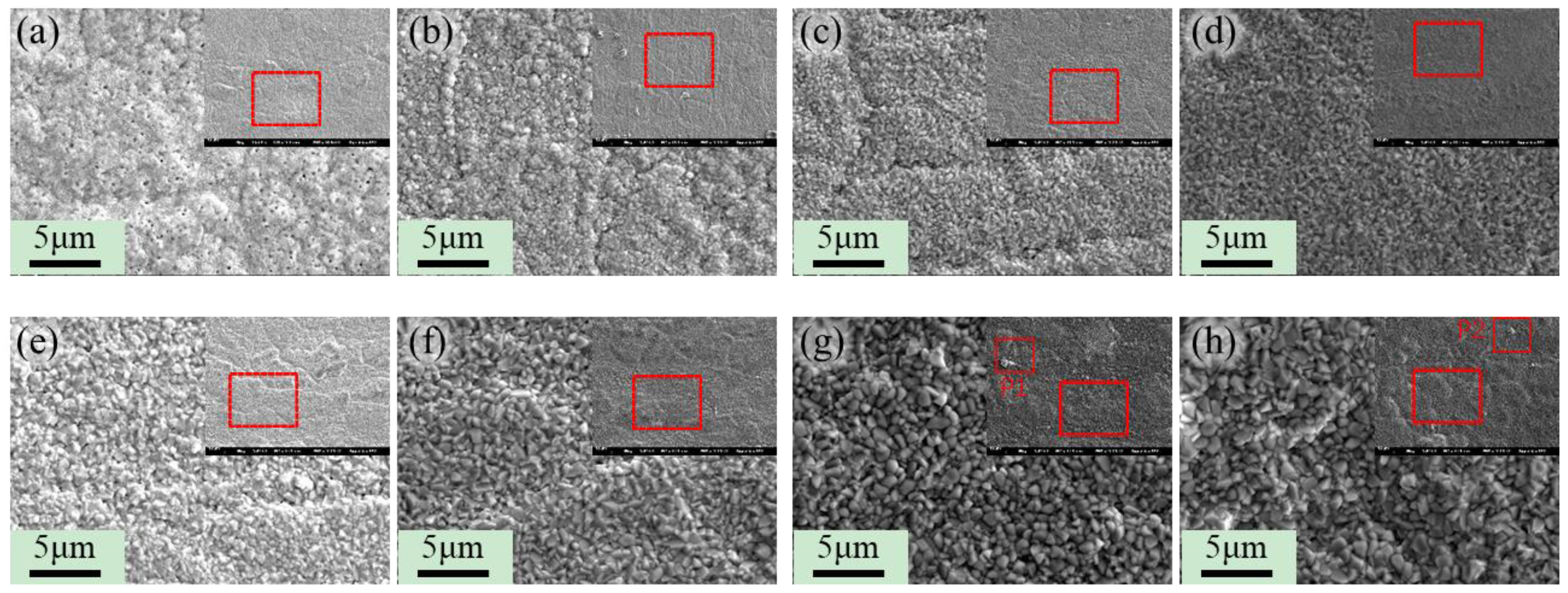
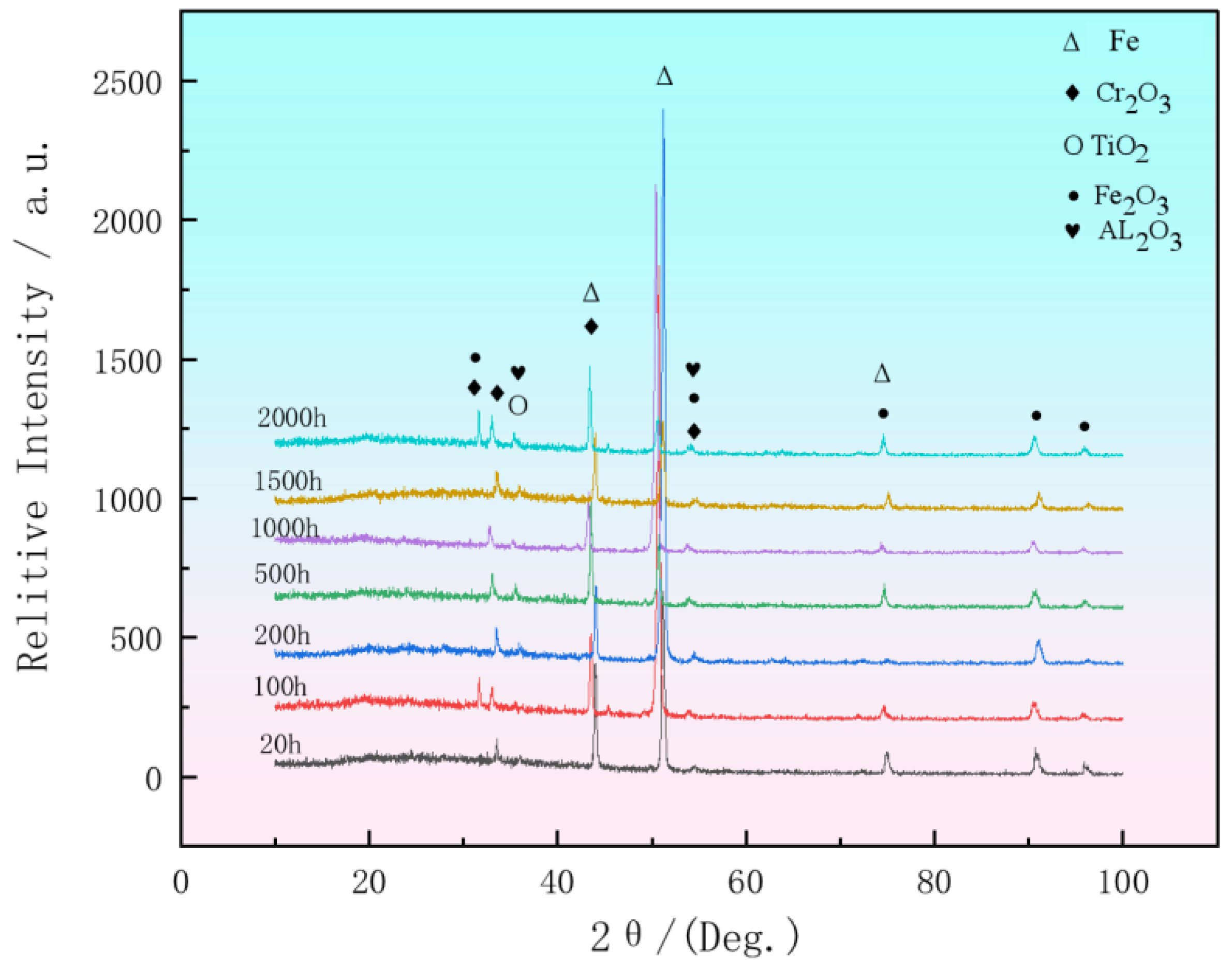
3.3. Research on Oxidation During Ultra-Long Term Aging Heat-Treatment Process
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Starr, F. Design and Development of Exhaust Valves for Internal Combustion engines from the Perspective of Modern Thinking: Part 2 1930–90. Int. J. Hist. Eng. Technol. 2014, 84, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezugwu, E.O.; Wang, Z.M.; Machado, A.R. The machinability of nickel-based alloys: A review. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 1999, 86, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akca, E.; Gursel, A. A Review on Superalloys and IN718 Nickel-Based INCONEL Superalloy. Period. Eng. Nat. Sci. 2015, 3, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Gupta, M.; Kumar, V. Parametric Optimization of WEDM Characteristics on Inconel 825 using Desirability Research. Int. J. Recent Technol. Eng. 2019, 8, 2277–3878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polzer, A.; Mouralova, K.; Benes, L.; Zahradnicek, R.; Fries, J. Comparison of machinability of nickel alloys using WEDM. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part B J. Eng. Manuf. 2022, 236, 1268–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, K.; Blackburn, T.; Magnussen, J.P.; Kerbstadt, M.; Ferreirós, P.A.; Pinomaa, T.; Hofer, C.; Hopkinson, D.G.; Day, S.J.; Bagot, P.A.; et al. Chromium-based bcc-superalloys strengthened by iron supplements. Acta Mater. 2023, 257, 119183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathi, N.; Kumar, P.; Gupta, A. Non-conventional machining of nickel based superalloys: A review. Mater. Today Proc. 2023, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamal, S.; Jayaganthan, R.; Prakash, S. Evaluation of cyclic hot corrosion behaviour of detonation gun sprayed Cr3C2–25%NiCr coatings on nickel- and iron-based superalloys. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2009, 203, 1004–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Shen, X.; Song, W.; Shi, W.; Zhong, X.; Du, C.; Ma, H.; Li, X. High-temperature oxidation behavior of GH4169 and Inconel617 nickel-based superalloys in SOFC environment. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2024, 91, 414–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.; Xu, Y.; Xiao, H.; Li, S.; Song, L. Investigation of the Nb element segregation for laser additive manufacturing of nickel-based superalloys. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2021, 180, 121800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.G.; Wang, N.; Liu, J.D.; Xu, W. Influence of rare earth elements (Y, La and Ce) on the mechanical properties and oxidation resistance of nickel-based superalloys: A critical review. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2024, 195, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, K.; Ou, M.; Xing, W.; Ma, G.; Hao, X.; Wang, M.; Ma, Y. The formation of η-Ni3Ti phase microstructure in a cast nickel-based superalloy with high Ti/Al ratio. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 29, 764–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinharoy, S.; Narasimhan, S.L. Oxidation behavior of two nickel-base superalloys used as elevated temperature valves in spark ignited engines and diesel exhaust recirculation (EGR) applications. Superalloys 2004, 2004, 623–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikkelsen, L.P. High Temperature Oxidation of Iron-Chromium Alloys; Risø National Laboratory: Roskilde, Denmark, 2003; Available online: https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:135939374 (accessed on 2 January 2025).
- GB/228.1-2021; Metallic Materials—Tensile Testing—Part 1: Method of Test at Room Temperature. China Iron and Steel Association: Beijing, China, 2021.
- Jaromír, D.; Eva, C.; Črtomir, D. Laves phase evolution in 10Cr-3W-3Co steel during thermal exposure and creep. Mater. Lett. 2023, 348, 134656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Q.; Wu, Y.; Li, J.; Cai, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, J.; Liu, T. Effects of intermediate temperature on the grain boundary and γ’ precipitates of nickel-based powder superalloy under interrupted cooling. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 922, 166310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Q.; Zhang, W.; Du, J.; Lu, T.; Liu, Y.; Liu, X.; Li, H.; Wang, K. Growth and dissolution behavior and morphology evolution of γ′ precipitates in GH4742 nickel-based superalloy. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 32, 4198–4211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Liu, X.; Zhu, M.; Guo, Y.; Qin, H.; Tian, Q. Precipitation characteristics of γ’ precipitates of the GH4742 nickel-based superalloy at a slow cooling rate. J. Alloys Compd. 2023, 941, 169013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Huang, H.; Xin, D.; Qu, J.; Zhang, H.; Ruan, J.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, S.; Jiang, L. The evolution behavior and mechanism of γ’ particles during hot deformation in a new P/M nickel-based superalloy. Mater. Charact. 2024, 217, 114359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphreys, F.J.; Hatherly, M. Recrystallization and Related Annealing Phenomena; Elsevier Ltd.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, D.M.; Conduit, B.D.; Stone, H.J.; Hardy, M.C.; Conduit, G.J.; Mitchell, R.J. Grain growth behaviour during near y’ solvus thermal exposures in a polycrystalline nickel-base superalloy. Acta Mater. 2013, 61, 3378–3391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuriy, S.; Frantisek, K. Microstructural aspects of grain growth kinetics in non-oriented electrical steels. Mater. Charact. 2005, 55, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zhao, H.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, J.; Liu, T. An innovative approach towards forming the serrated grain boundaries and refining the γ′ precipitates in nickel-based superalloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 908, 164570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Li, G.; Wei, X.; Ma, B.; Huang, C.; Chen, W.; Zhao, P.; Wang, L.; Zeng, Q. Long-term aging behavior and mechanism of CMSX-4 nickel-based single crystal superalloy at 950 °C and 1050 °C. J. Alloys Compd. 1004, 2024, 175763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, K.; Wang, M.; Ou, M.; Li, H.; Hao, X.; Ma, Y.; Liu, K. Effects of microstructure evolution on the deformation mechanisms and tensile properties of a new Ni-base superalloy during aging at 800 °C. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2021, 68, 40–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Wang, L. Precipitation behavior of γ′ precipitates in 21Cr-32Fe-41Ni heat-resistant alloy at different aging temperatures. J. Alloys Compd. 2023, 958, 170405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayata, F.; Alpas, A.T. The high temperature wear mechanisms of iron-nickel steel (NCF 3015) and nickel based superalloy (inconel 751) engine valves. Wear 2021, 480, 203943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, W.; Lei, Y.; Wang, X.; Ma, Q.; Hu, L.; Xie, H.; Yin, X. Interface characteristics and mechanical properties of wire-arc depositing Inconel 625 superalloy on ductile cast iron. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2022, 440, 128493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sims, C.T.; Stoloff, N.S.; Hagel, W.C. Superalloys II: High-Temperature Materials for Aerospace and Industrial Power; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1987; ISBN 0471011479/9780471011477. [Google Scholar]
- Greene, G.A.; Finfrock, C.C. Oxidation of Inconel 718 in Air at High Temperatures. Oxid. Met. 2001, 55, 505–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.H.; Rogers, P.M.; Little, J.A. Oxidation behavior of several chromia-forming commercial nickel-base superalloys. Oxid. Met. 1997, 47, 381–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, L.; Venkataramani, R.; Sundararaman, M.; Mukhopadhyay, P.; Garg, S.P. Studies on the oxidation behavior of Inconel 625 between 873 and 1523 K. Oxid. Met. 1996, 45, 221–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.J.; Ye, F.X.; Lu, G.X.; Liu, C.; Hao, L.J. Residual stress evolution of thermally grown oxide in thermal barrier coatings deposited onto nickel-base superalloy and iron-base alloy with thermal exposure ageing. J. Alloys Compd. 2014, 584, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Alloy | Composition | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | Si | Mn | P | S | Cr | Ni | Al | Cu | Ti | Mo | Nb | B | Fe | |
| Ni30 | 0.04–0.07 | ≤0.20 | ≤0.30 | ≤0.014 | ≤0.010 | 14.20–15.00 | 30.50–31.50 | 1.85–2.05 | ≤0.1 | 2.55–2.75 | 0.65–0.80 | 0.65–0.80 | 0.002–0.004 | bal |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | Elongation (%) | Yield Strength (MPa) | Hardness (HV) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| As-forged | 1183 | 32.9 | 781 | 292 |
| Solution and aging treatment | 1252.47 | 29.2 | 780.64 | 353.2 |
| Time/h | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Elongation (%) | Yield Strength (MPa) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1130 | 29.2 | 763 |
| 100 | 1270 | 22.6 | 820 |
| 200 | 1260 | 19.2 | 840 |
| 500 | 1240 | 16.8 | 823 |
| 1000 | 1230 | 15.6 | 821 |
| 1500 | 1210 | 13.1 | 819 |
| 2000 | 1200 | 10.4 | 790 |
| 3000 | 1135.3 | 12.9 | 754.9 |
| 4000 | 1135.7 | 11.6 | 723.8 |
| Elements (wt%) and Time (h) | 100 | 500 | 1000 | 1500 | 2000 | 3000 | 4000 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | 15.09 | 14.46 | 11.42 | 13.29 | 13.63 | 17.19 | 26.47 |
| O | 4.67 | 9.4 | 7.05 | 11.75 | 14.19 | 6.43 | 18.6 |
| Al | 2.51 | 2.59 | 3.59 | 2.16 | 1.91 | 1.07 | 0.99 |
| Ti | 2.21 | 1.93 | 2.02 | 2.2 | 1.9 | 2.13 | 1.51 |
| Cr | 12.28 | 12.64 | 11.62 | 11.27 | 11.08 | 11.79 | 10.49 |
| Fe | 37.88 | 37.22 | 38.78 | 36.04 | 35.58 | 37.36 | 27 |
| Ni | 25.36 | 21.4 | 25.07 | 22.75 | 21.35 | 24.04 | 14.93 |
| Si | ~ | ~ | 0.31 | ~ | 0.37 | ~ | ~ |
| Mn | ~ | 0.36 | 0.14 | 0.53 | ~ | ~ | ~ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tu, Y.; Xiao, X.; Zhu, Z.; Zhou, L. Microstructural Evolution and Oxidation Resistance of Fe-30Ni-15Cr Alloy for Internal Combustion Engine Valves Under Long-Term High-Temperature Exposure and Heat Treatment. Metals 2025, 15, 61. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15010061
Tu Y, Xiao X, Zhu Z, Zhou L. Microstructural Evolution and Oxidation Resistance of Fe-30Ni-15Cr Alloy for Internal Combustion Engine Valves Under Long-Term High-Temperature Exposure and Heat Treatment. Metals. 2025; 15(1):61. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15010061
Chicago/Turabian StyleTu, Yuguo, Xueshan Xiao, Zhiyuan Zhu, and Linzhen Zhou. 2025. "Microstructural Evolution and Oxidation Resistance of Fe-30Ni-15Cr Alloy for Internal Combustion Engine Valves Under Long-Term High-Temperature Exposure and Heat Treatment" Metals 15, no. 1: 61. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15010061
APA StyleTu, Y., Xiao, X., Zhu, Z., & Zhou, L. (2025). Microstructural Evolution and Oxidation Resistance of Fe-30Ni-15Cr Alloy for Internal Combustion Engine Valves Under Long-Term High-Temperature Exposure and Heat Treatment. Metals, 15(1), 61. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15010061







