Study on the Bath Smelting Reduction Reaction and Mechanism of Iron Ore: A Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Progress on the Thermal Decomposition Characteristics of Iron Ore during Smelting Reduction
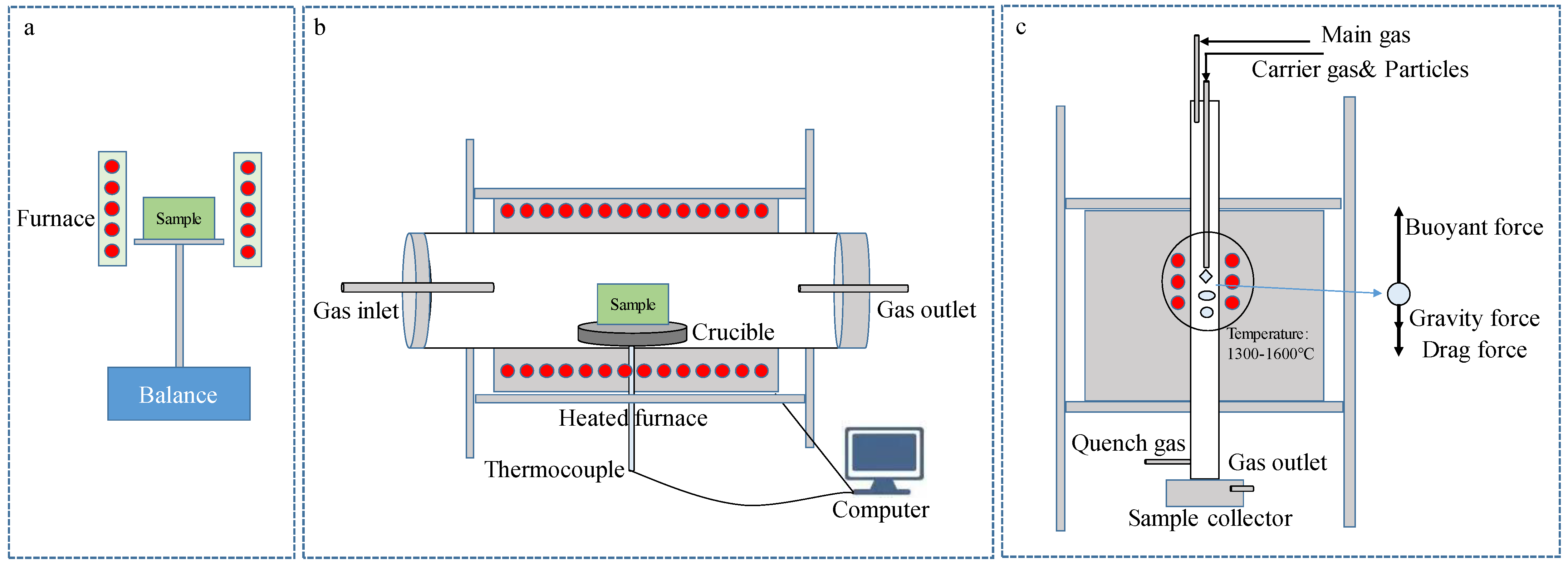
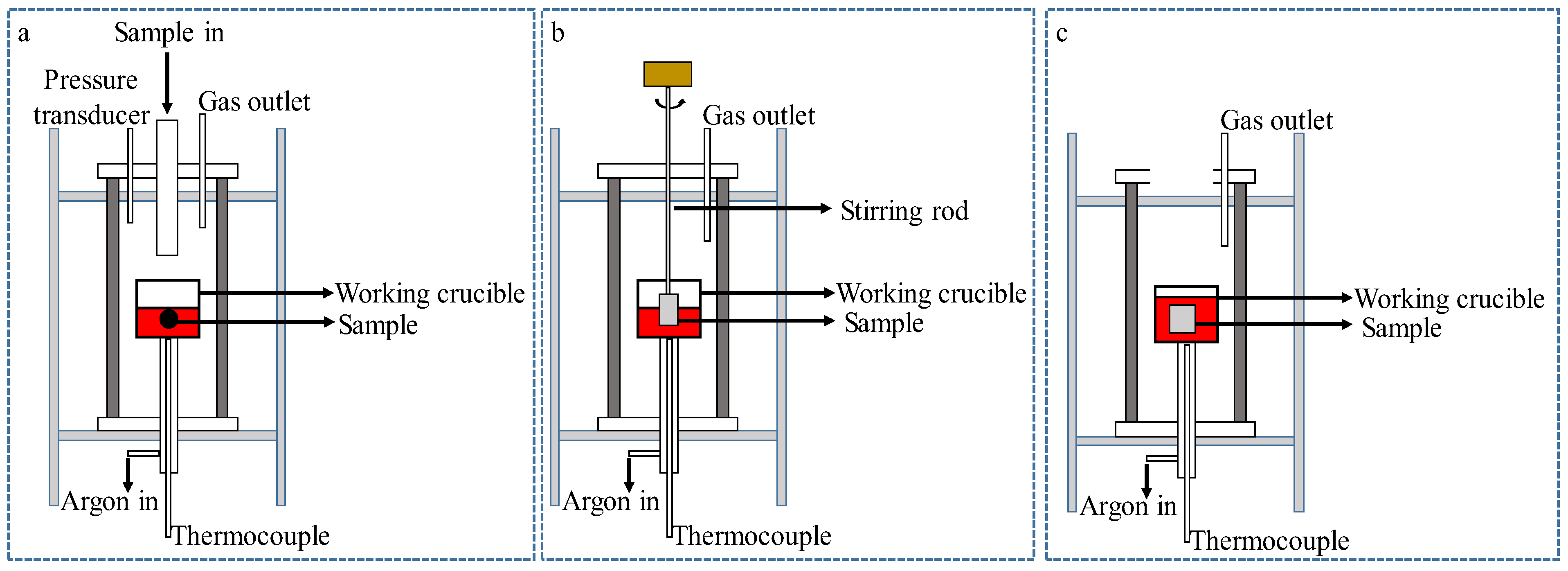
2.1. Research Progress of Experimental Methods
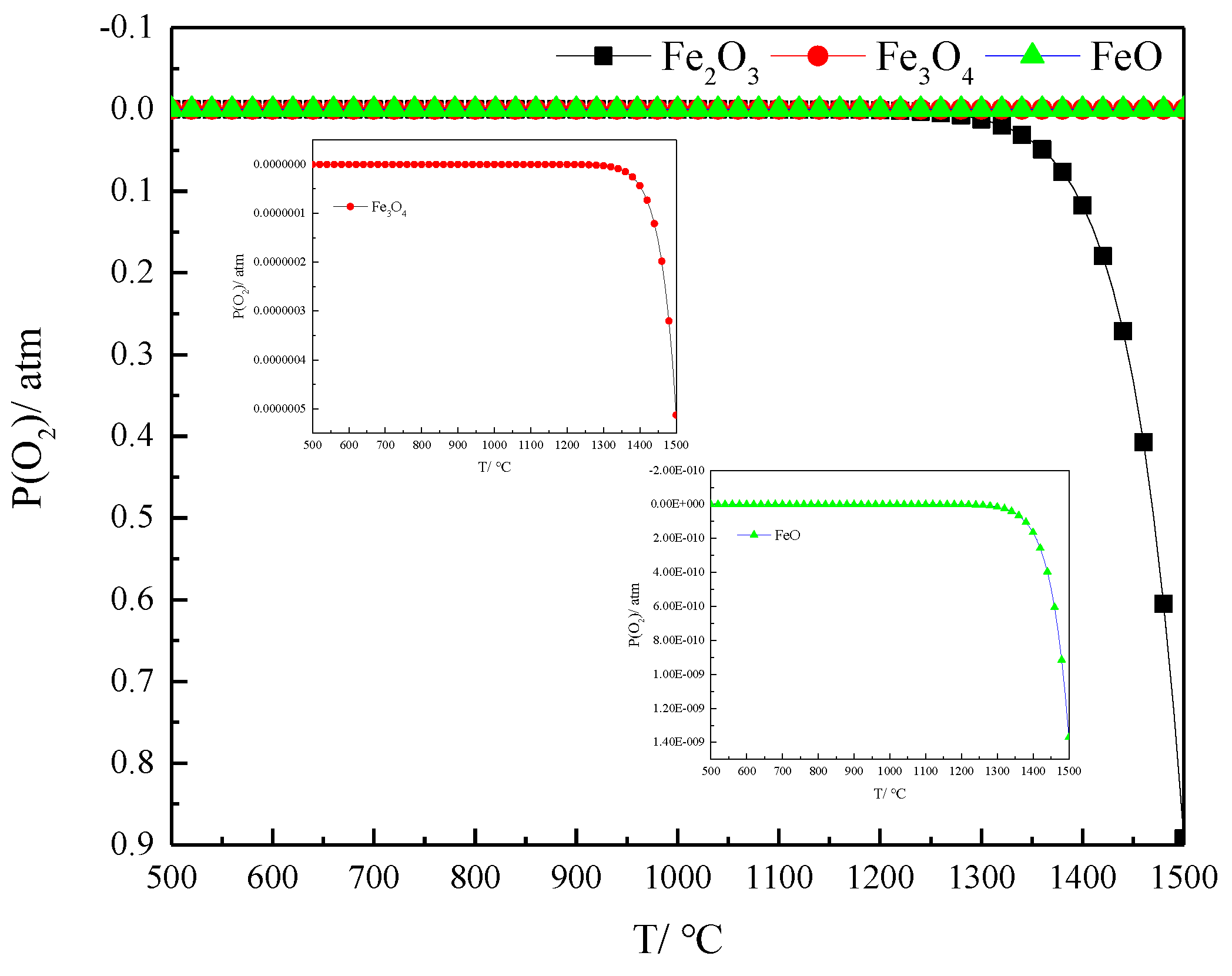
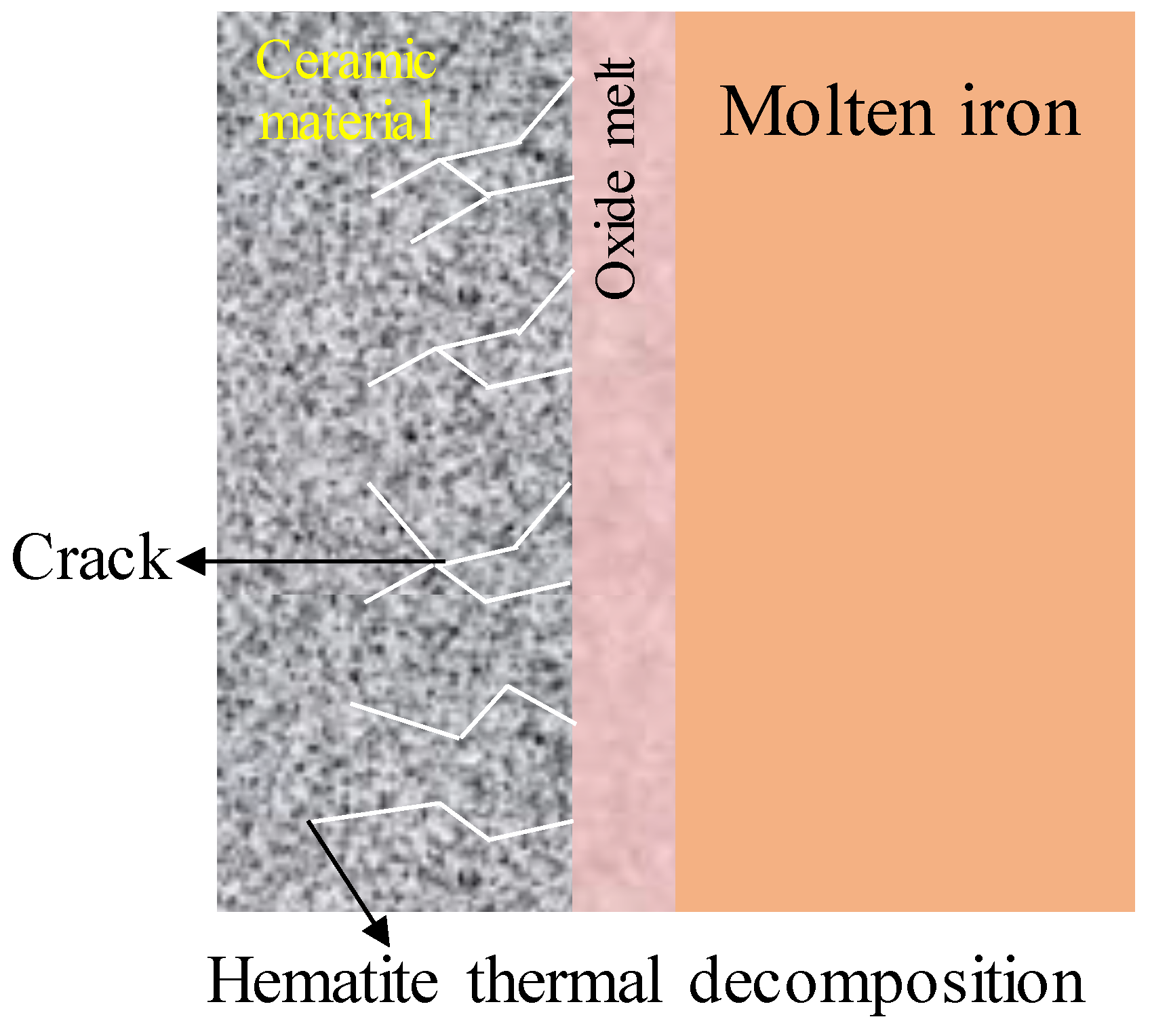
2.2. The Thermal Decomposition Reaction Mechanism and Influencing Factors of Iron Ore
- (1)
- The influence of atmosphere
- (2)
- Particle size
- (3)
- Residence time/Heating rate
2.3. Study of the Kinetics of Iron Ore Thermal Decomposition
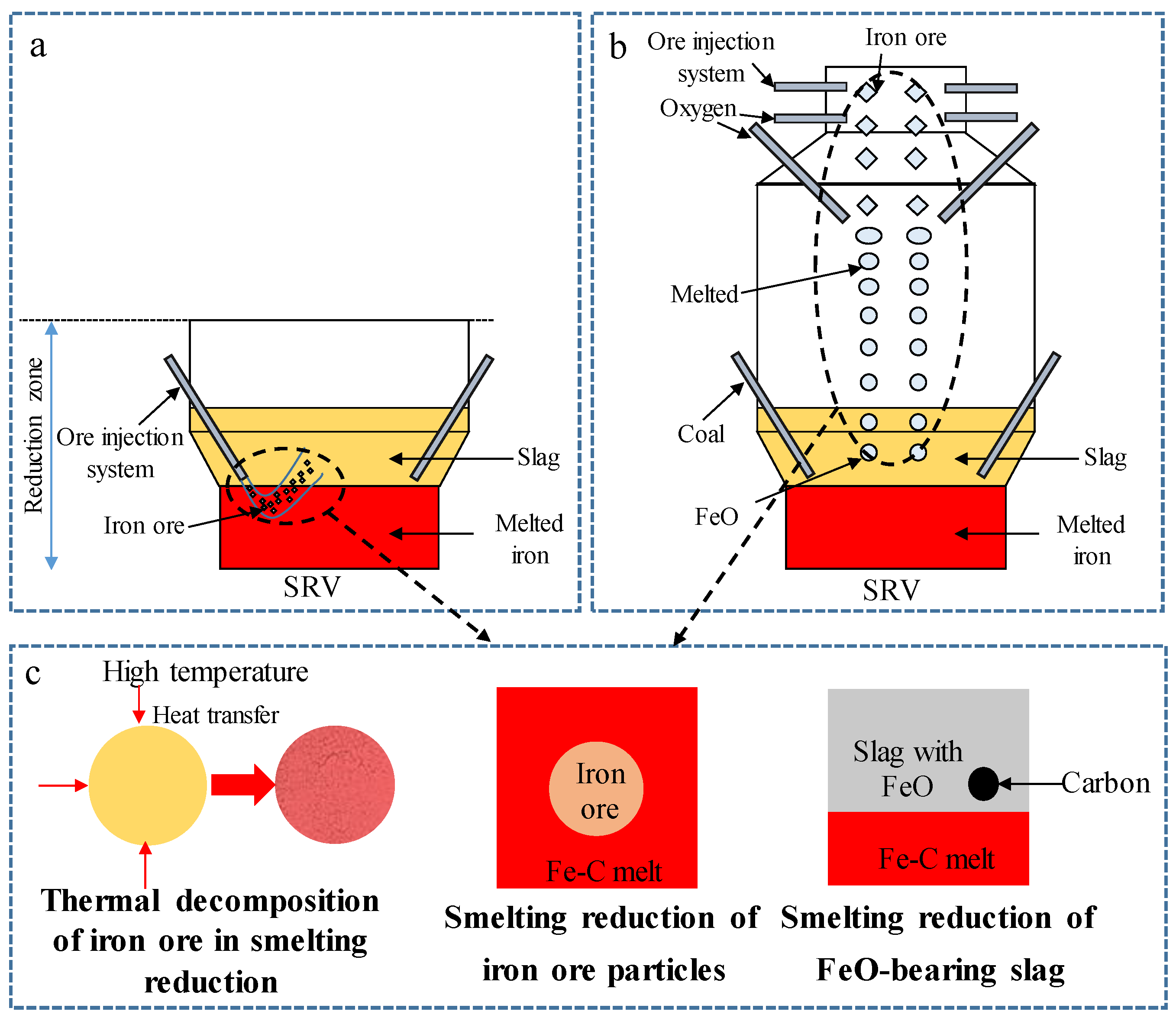
3. Progress on the Smelting Reduction of Iron-Ore Particles
3.1. Research Progress of Experimental Methods
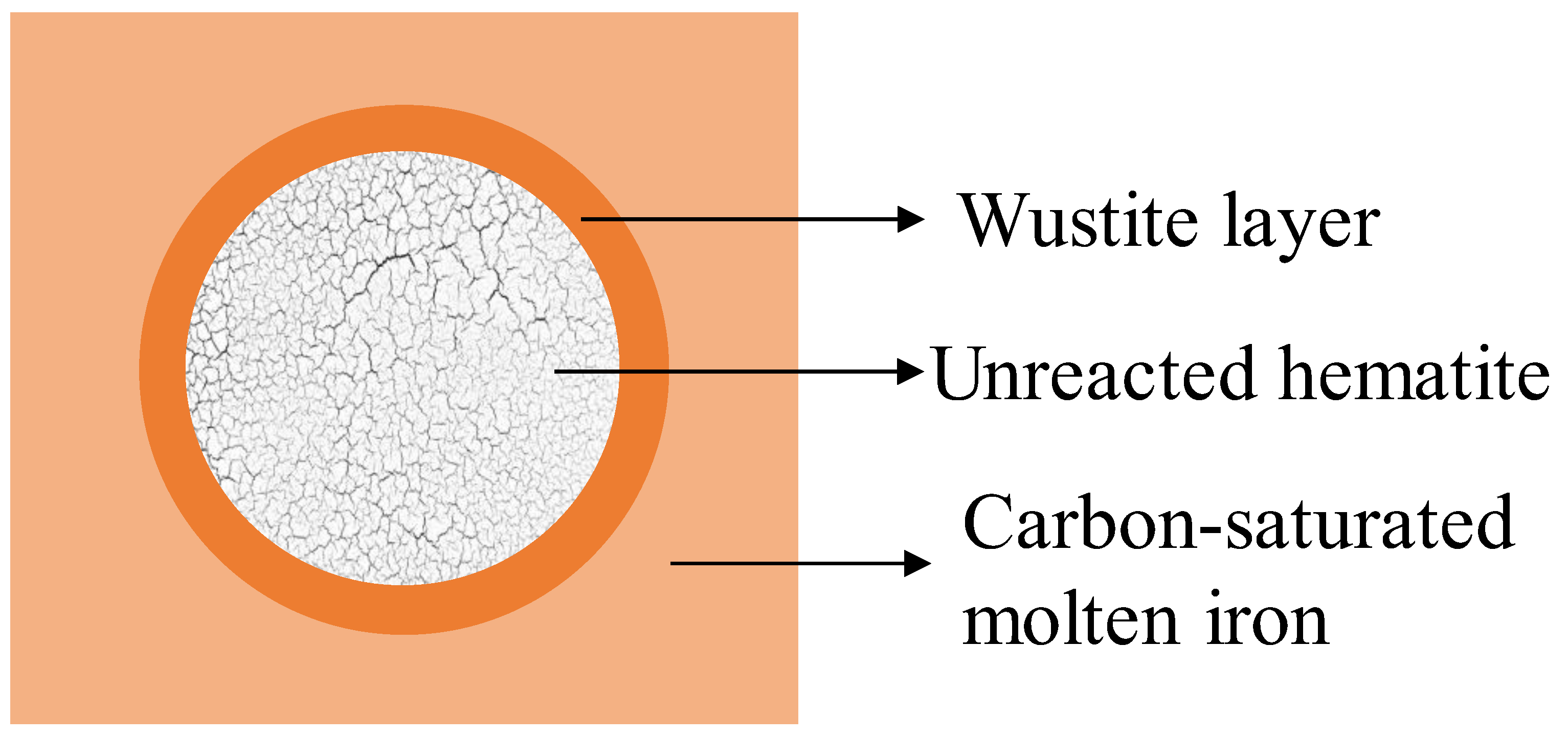
3.2. Solid Iron-Ore Smelting Reduction Mechanisms and Influencing Factors
- (1)
- Melt composition
- (2)
- Melt temperature
- (3)
- Particle size and mass of iron ore
3.3. Study of the Kinetic of Solid Iron Ore Smelting Reduction Reaction
4. Progress on the Smelting Reduction of FeO-Bearing Slags
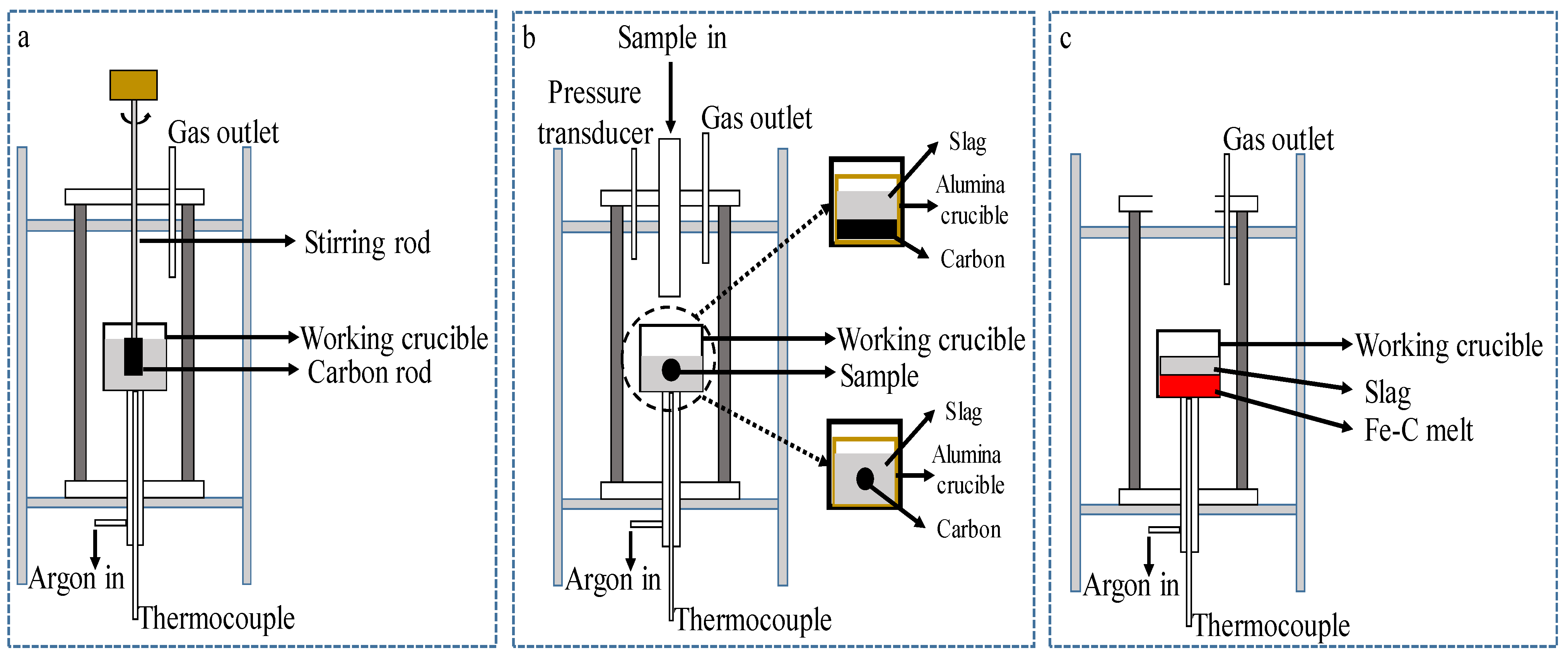
4.1. Research Progress of Experimental Methods
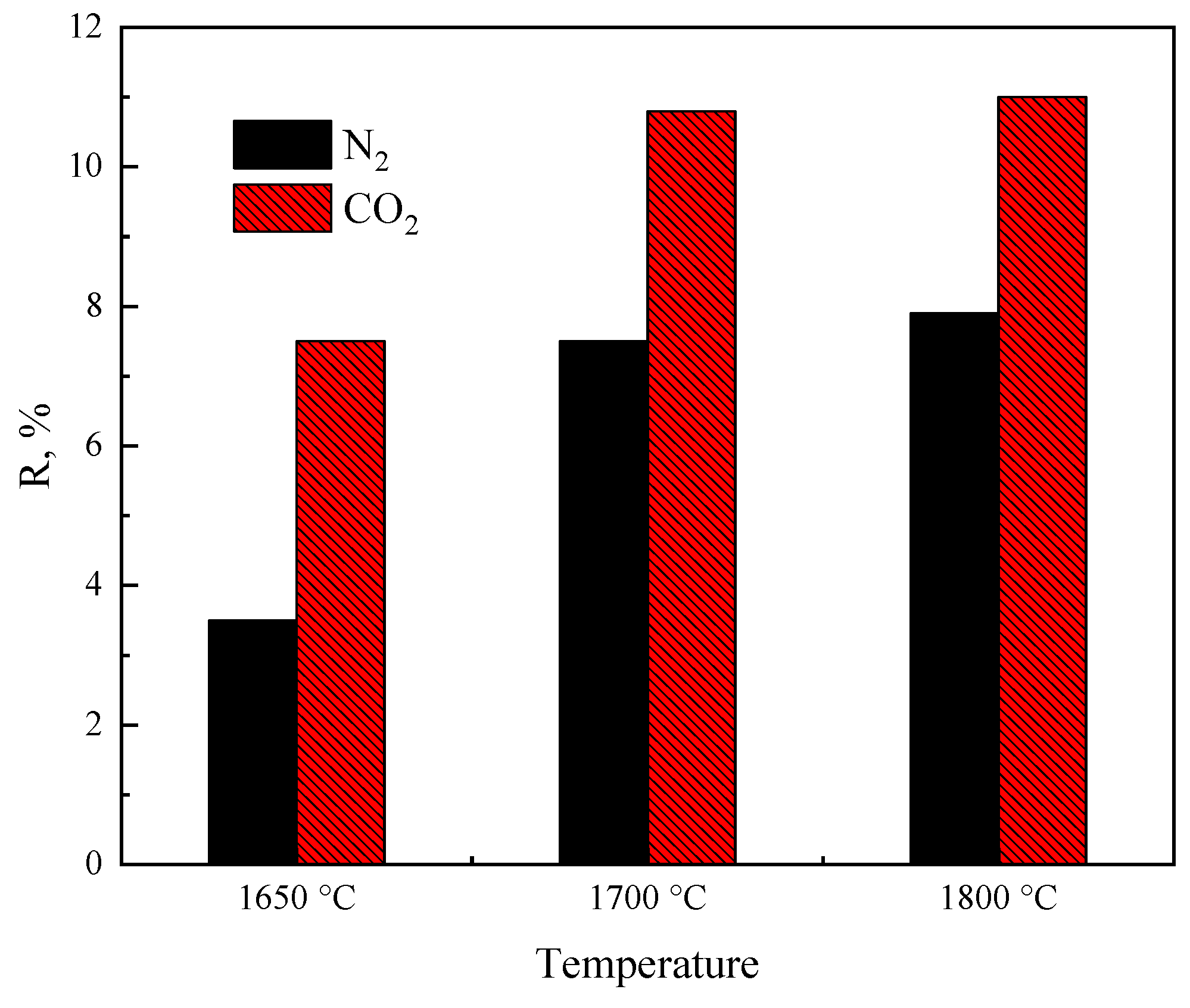
4.2. Smelting Reduction Reaction Mechanism of FeO-Containing Slag and Influencing Factors
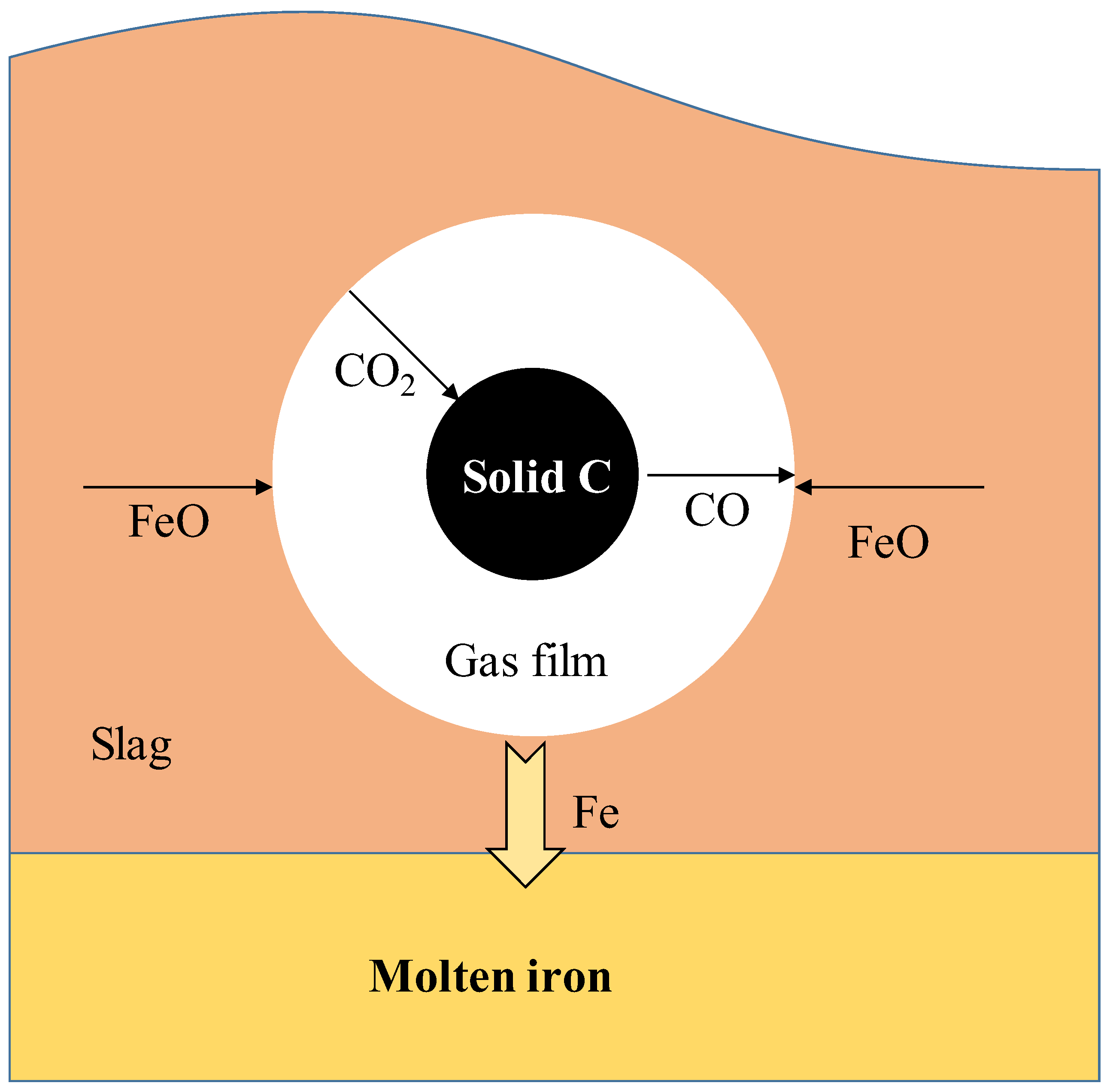
- Chemical reactions at the gas–slag interface, as shown in Equation (14):
- Chemical reactions at the gas–carbon interface, as shown in Equation (15):
- Diffusion of FeO from the slag to the gas–slag interface.
- Diffusion of CO2 into solid carbon through the gas halo.
- Diffusion of CO into gas–slag interface through the gas halo.
- [C] in the molten iron is transported to the gas–metal interface.
- Chemical Reaction (18) occurs at the gas–metal interface.
- Gas transfer from the gas–metal interface to the gas–slag interface.
- FeO in the slag is transported to the gas–slag interface.
- Chemical Reaction (17) occurs at the gas–slag interface.
- (1)
- FeO content in slag
- (2)
- Carbonaceous materials
4.3. Study of the Kinetics of the Smelting Reduction Reaction of FeO-Bearing Slag
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- For the study of the thermal decomposition of iron ore in the smelting reduction process, the reaction mechanism of goethite and hematite decomposition was clearer. However, discrepancies in previous studies regarding the decomposition temperature, especially the influence of different factors (particle size, heating rate, and high temperature-residence time) on it, need to be further clarified. In addition, there are differences between the current experimental conditions and the actual process conditions of iron ore’s thermal decomposition, so the falling process of iron ore within SRV and the thermal decomposition within the molten iron need to be further investigated. The correlation between the internal cracking characteristics during thermal decomposition and the subsequent smelting reduction reaction was also analyzed.
- (2)
- Research was advanced on the smelting reduction of solid iron-ore particles within a melt: For the melt temperature, the composition and particle-size factors on the smelting reduction influence rule, the results of previous studies are more consistent. However, the effect of the particle size of the iron ore used in smelting reduction process on reduction rate needs to be further investigated. Previous studies clarified the existence of a liquid FeO layer between iron-ore particles and the melt in the reduction mechanism, but the specific smelting reduction mechanism and the phase evolution need to be further explored. In terms of kinetics, the study of the rate-controlling step of the reaction is still unclear, the values of the reaction activation energy derived vary greatly, and the limiting steps of the reaction and activation energy values need to be further clarified.
- (3)
- The mechanism of the FeO-bearing slag reduction with solid or dissolved [C] in SRV was more deeply studied. The effect of different factors on the reaction rate had been investigated, but the results need to be further refined to provide guidance on improving the reduction rate. Further studies on the activation energy of smelting reduction reaction are needed to obtain more consistent results.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BF | blast furnace |
| SRV | smelting reduction vessel |
| CCF | cyclone converter furnace |
| TGA | thermogravimetric analysis |
| DSC | differential scanning calorimetry |
References
- Bates, P.; Coad, A. HIsmelt, the Future in Ironmaking Technology. In Proceedings of the 4th European Coke and Ironmaking Congress, Paris, France, 19–21 June 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, C.; Meng, Y.; Yan, F.; Zhang, D.; Li, X.; Zhang, F. Analysis on Energy Efficiency and Optimization of HIsmelt Process. In Energy Technology 2019; Wang, T., Chen, X., Guillen, D.P., Zhang, L., Sun, Z., Wang, C., Haque, N., Howarter, J.A., Neelameggham, N.R., Ikhmayies, S., et al., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 3–11. [Google Scholar]
- Junjie, Y. Progress and Future of Breakthrough Low-Carbon Steelmaking Technology (ULCOS) of EU. Int. J. Mineral. Process. Extr. Metall. 2018, 3, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meijer, K.; Zeilstra, C.; Teerhuis, C.; Ouwehand, M.; van der Stel, J. Developments in Alternative Ironmaking. Trans. Indian. Inst. Met. 2013, 66, 475–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khasraw, D.; Yan, Z.; Hage, J.L.T.; Meijer, K.; Li, Z. Reduction of FeO in Molten Slag by Solid Carbonaceous Materials for HIsarna Alternative Ironmaking Process. Metall. Mater. Trans. B. 2022, 53, 3246–3261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delport, H.M.W. The Corex Process. Ironmak. Steelmak. (United Kingd.) 1992, 19, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.-C.; Shin, M.-K.; Joo, S.; Yoon, J.-K. The Effects of Operational Parameters on the Transport Phenomena in COREX Melter–Gasifier. ISIJ Int. 2000, 40, 1073–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.P.; Barman, S.C.; Reddy, B.M.; Sekhar, V.R. Raw Materials for Corex and Their Influence on Furnace Performance. Ironmak. Steelmak. 2009, 36, 87–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thaler, C.; Tappeiner, T.; Schenk, J.L.; Kepplinger, W.L.; Plaul, J.F.; Schuster, S. Integration of the Blast Furnace Route and the FINEX®-Process for Low CO2 Hot Metal Production. Steel Res. Int. 2012, 83, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, S.-J. System Dynamics Approach for the Impacts of FINEX Technology and Carbon Taxes on Steel Demand: Case Study of the POSCO. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf.-Green Technol. 2015, 2, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, S.-H.; Choi, M.-E.; Kim, D.-H.; Ko, C.-K.; Park, W.-I.; Kim, S.-Y. FINEX® as an Environmentally Sustainable Ironmaking Process. Ironmak. Steelmak. 2019, 46, 625–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowell, R.G. FINEX: A Probabilistic Expert System for Forensic Identification. Forensic Sci.Int. 2003, 134, 196–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Langen, J.; Meijer, K.; Corbett, M.; Corbett, G. The Cyclone Converter Furnace. Rev. Met. Paris. 1993, 90, 363–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meijer, H.K.A. The Engineering of a Cyclone Converter Furnace (CCF) Plant. Fuel Energy Abstr. 1998, 1, 52. [Google Scholar]
- Fukui, F. A Study on the New Iron Ore Smelting Reduction Processes. Tetsu-to-Hagane 1996, 82, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawada, T. The Start-Up of the DIOS Pilot Plant (DIOS Project); Iron and Steel Society, Inc.: Warrendale, PA, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Aukrust, E. AISI Direct Steelmaking Program; American Iron and Steel Institute: Washington, DC, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Aukrust, E. AISI Direct Steelmaking Program. Annual Technical Report, Year Ending November 30, 1992; American Iron and Steel Institute: Washington, DC, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Fruehan, R.J. Future Steelmaking Technologies and the Role of Basic Research. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 1997, 28, 1963–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romenets, V.A.; Valavin, V.S.; Pokhvisnev, Y.V. Technological Assessment of the Romelt Process in the Classic and Two-Zone Variants. Metallurgist 2014, 58, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaytsev, A.; Romenets, V.; Valavin, V.; Krivolapov, N.; Pokhvisnev, Y. The mechanism of iron reduction from molten slag in romelt process. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Slags, Fluxes and Molten Salts, Stockholm, Sweden and Helsinki, Finland, 12–17 June 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Romenets, V.A. The Romelt Process. Iron Steelmak. 1995, 22, 37–41. [Google Scholar]
- Romenets, V.; Valavin, V.; Pokhvisnev, Y.; Vandariev, S. Processing Industrial Wastes with the Liquid-Phase Reduction Romelt Process. JOM 1999, 51, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zeilstra, C.; van der Stel, J.; Sietsma, J.; Yang, Y. Review and Data Evaluation for High-Temperature Reduction of Iron Oxide Particles in Suspension. Ironmak. Steelmak. 2020, 47, 741–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zou, Z.; Zeilstra, C.; Meijer, K.; Boom, R. Thermal Decomposition Behaviour of Fine Iron Ore Particles. ISIJ Int. 2014, 54, 2196–2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolska, E. Relations between the Existence of Hydroxyl Ions in the Anionic Sublattice of Hematite and Its Infrared and X-Ray Characteristics. Solid. State Ion. 1988, 28–30, 1349–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watari, F.; Delavignette, P.; Amelinckx, S. Electron Microscopic Study of Dehydration Transformations. II. The Formation of “Superstructures” on the Dehydration of Goethite and Diaspore. J. Solid. State Chem. 1979, 29, 417–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goss, C.J. The Kinetics and Reaction Mechanism of the Goethite to Hematite Transformation. Mineral. Mag. 1987, 51, 437–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, L.; Qu, Y.; Wang, C.; Shao, L.; Zou, Z.; Song, W. Kinetic Study on Thermal Decomposition Behavior of Hematite Ore Fines at High Temperature. Metall. Mater. Trans. B. 2020, 51, 395–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorescu, M.; Xu, T. Particle Size Effects on the Thermal Behavior of Hematite. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2012, 107, 463–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmani, M.; Alamdari, E.K.; Firoozi, S. Isoconversional Analysis of Thermal Dissociation Kinetics of Hematite in Air and Inert Atmospheres. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2017, 128, 1385–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darken, L.S.; Gurry, R.W. The System Iron—Oxygen. II. Equilibrium and Thermodynamics of Liquid Oxide and Other Phases. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1946, 68, 798–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, S.; Siguin, D.; Garcia, F. Thermal Analysis of Sintering of Magnetite Pellets. Ironmak. Steelmak 1994, 21, 119–123. [Google Scholar]
- Beuria, P.C.; Biswal, S.K.; Mishra, B.K.; Roy, G.G. Kinetics Study on Removal of LOI by Thermal Decomposition of Hydrated Minerals Associated in Hematite Ore. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2016, 126, 1231–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Przepiera, K.; Przepiera, A. Kinetics of Thermal Transformations of Precipitated Magnetite and Goethite. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2004, 65, 497–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diamandescu, L.; Mihãilã-Tãrãbãşanu, D.; Calogero, S. Mössbauer Study of the Solid Phase Transformation α-FeOOH → Fe2O3. Mater. Chem. Phys. 1997, 48, 170–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grygar, T.; Ruan, I.H.D.; Gilkes, R.J. Re-Examination of the Kinetics of the Thermal Dehydroxylation of Goethite. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 1999, 55, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, F.; Ramirez, M.; Pons, J.; López-Delgado, A.; Alguacil, F. Kinetic Study of the Thermal Decomposition of Low-Grade Nickeliferous Laterite Ores. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2008, 94, 517–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima-de-Faria, J. Dehydration of Goethite and Diaspore. Z. Für Krist. 1963, 119, 176–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollack, J.B.; Pitman, D.; Khare, B.N.; Sagan, C. Goethite on Mars: A Laboratory Study of Physically and Chemically Bound Water in Ferric Oxides. J. Geophys. Res. (1896–1977) 1970, 75, 7480–7490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thrierr-Sorel, A.; Larpin, J.-P.; Mougin, G. Etude Cinétique de La Transformation de La Goethite Alpha-FeOOH En Hematite Alpha-Fe2O3. Annal. Chim. 1978, 3, 305–315. [Google Scholar]
- Prasad, P.S.R.; Shiva Prasad, K.; Krishna Chaitanya, V.; Babu, E.V.S.S.K.; Sreedhar, B.; Ramana Murthy, S. In Situ FTIR Study on the Dehydration of Natural Goethite. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2006, 27, 503–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zeilstra, C.; Van Der Stel, J.; Sietsma, J.; Yang, Y. Thermal Decomposition Reaction Kinetics of Hematite Ore. ISIJ Int. 2020, 60, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Santos, D.M.; Mourão, M.B. High-Temperature Reduction of Iron Oxides by Solid Carbon or Carbon Dissolved in Liquid Iron–Carbon Alloy. Scand. J. Metall. 2004, 33, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mourão, M.B. Kinetics and mechanism of reactions between iron oxides and iron-carbon melts. Steel Res. 2000, 71, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.L.; Merchant, A.J. Kinetics and Mechanism of Smelting Reduction of Fluxed Chromite Part 1 Carbon–Chromite–Flux Composite Pellets in Fe–Cr–C–Si Melts. Ironmak. Steelmak. 1999, 26, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.L.; Merchant, A.J. Kinetics and Mechanism of Smelting Reduction of Fluxed Chromite Part 2 Chromite–Flux Pellets in Fe–C–Si Melts. Ironmak. Steelmak. 1999, 26, 254–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demir, O.; Eric, R.H. Reduction of Chromite in Liquid Fe-Cr-C-Si Alloys. MMTB 1994, 25, 549–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vardar, E.; Eric, R.H. Smelting of Iron Ore in Fe–Cr–C–Si Melts. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2008, 23, 764–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Jiang, M.-F.; Wang, D.-Y.; Xu, L.-X. Dissolution Kinetics of Chromium Ore in Slag System for Stainless Steelmaking. Can. Metall. Q. 2012, 51, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, A.; Nakagawa, R.; Yoshimatsu, S.; Fukuzawa, A.; Ozaki, T.; Kasahara, K.; Fukuzawa, Y.; Mitsui, T. Melting Rate of Directly Reduced Iron Pellets into Iron Melt. ISIJ Int. 1979, 19, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Deng, H.; Wang, N.; Zhang, G. Limestone Dissolution in Converter Slag: Kinetics and Influence of Decomposition Reaction. ISIJ Int. 2018, 58, 2271–2279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udalov, Y.P.; Mikhailov, M.N.; Smirnov, V.V.; Sharov, D.Y. Interaction of Molten Iron with Materials Containing Hematite. Glass Phys. Chem. 2008, 34, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udalov, Y.P.; Lavrov, B.A.; Smirnov, V.V.; Sharov, D.Y.; Sidorov, A.S. Interaction of Molten Iron with Ceramics Based on Iron and Aluminum Oxides. Glass Phys. Chem. 2004, 30, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhussein, A.; Scheller, P.R.; Yang, W. Reaction between MgO-SiO2 Refractory Material and Fe-Al Alloy. Metall. Res. Technol. 2018, 115, 512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udalov, Y.P.; Mikhailov, M.N.; Fil’chakov, I.F. Interaction of a Ceramic Material Based on Hematite with Molten Iron Produced by an Aluminothermic Reaction. Glass Phys. Chem. 2007, 33, 174–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarma, B.; Cramb, A.W.; Fruehan, R.J. Reduction of FeO in Smelting Slags by Solid Carbon: Experimental Results. Metall. Mater. Trans. B. 1996, 27, 717–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, A.; Deo, B.; Sathyamurthy, N. Kinetic model for reduction of iron oxide in molten slags by iron-carbon melt. Steel Res. 1994, 65, 414–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teasdale, S.L.; Hayes, P.C. Observations of the Reduction of FeO from Slag by Graphite, Coke and Coal Char. ISIJ Int. 2005, 45, 634–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamieson, B.J.; Barati, M.; Coley, K.S. Kinetics of the Carbothermic Reduction of Manganese Oxide from Slag. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2019, 50, 2733–2746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Lucas, J.A.; Evans, G.M.; Ratchey, I.P.; Belton, G.R. Rate of Interfacial Reaction between Liquid Iron Oxide and CO-CO2. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2000, 31, 1049–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, D.J.; Han, J.W.; Chung, W.S. A Study of the Reduction Rate of FeO in Slag by Solid Carbon. Metall. Mater. Trans. B. 1999, 30, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, S.-M.; Do, Y.-J. Reduction Behaviour of BOF Slags by Carbon in Iron. Steel Res. Int. 2006, 77, 312–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Story, S.R.; Sarma, B.; Fruehan, R.J.; Cramb, A.W.; Belton, G.R. Reduction of FeO in Smelting Slags by Solid Carbon: Re-Examination of the Influence of the Gas-Carbon Reaction. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 1998, 29, 929–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, K.; Fruehan, R.J. Reduction of FeO in Slag with Coal Char. ISIJ Int. 2000, 40, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bafghi, M.S.; Kurimoto, H.; Sano, M. Effect of Slag Foaming on the Reduction of Iron Oxide in Molten Slag by Graphite. ISIJ Int. 1992, 32, 1084–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R.H.; Fruehan, R.J. The effect of carbon content on the rate of reduction of FeO in slag relevant to iron smelting. Steel Res. 1999, 70, 283–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloyd, G.; Dr, Y.; La, B. Reaction of iron oxide with iron-carbon melts. Ironmak. Steelmakig. 1975, 2, 49–55. [Google Scholar]
- Sato, A.; Aragane, G.; Hirose, F.; Nakagawa, R.; Yoshimatsu, S. Reducing Rate of Iron Oxide in Molten Slag by Carbon in Molten Iron. Trans. Iron Steel Inst. Jpn. 1984, 24, 808–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Process | Illustrative Figure | Type | Iron-Bearing Raw Material | Time | R&D Unit | Distribution |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HIsmelt [1,2] |  | Fluidized ned/rotary kiln + smelting reduction vessel (SRV) | Iron-ore fine | 1981 | CRA | China |
| HIsarna [3,4,5] |  | Cyclone converter furnace (CCF) and SRV | Fine/complex iron ore | 2004 | ULCOS | Netherlands |
| Corex [6,7,8] |  | Reduction shaft Furnace and melter–gasifier | Plump/pellet | 1989 | VAI | South Africa, India, China |
| Finex [9,10,11,12] |  | Fluidized bed and melter–gasifier | Iron-ore fine | 1992 | POSCO | Republic of Korea |
| CFF [13,14] | - | CFF | Fine ores | 1989 | Hoogovens, British Steel and Ilva/CSM | - |
| DIOS [15,16] | - | SRV | Iron ore fine | 1988 | Japan Iron and Steel Federation | - |
| AISI [17,18,19] | - | Reduction shaft furnace and SRV | Iron-ore fine | 1988 | DOE | - |
| Romelt [20,21,22,23] | - | SRV | Iron-ore fine | 1985 | Novolipeski | - |
| Rate Controlling Process | Kinetic Equation | Differential Form |
|---|---|---|
| Random nucleation, two dimensional | ||
| Random nucleation, three-dimensional | ||
| Random nucleation, first-order decay law |
| No. | References | Activation Energy/kJ·mol−1 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Lopez [38] | 114.4 |
| 2 | Lima-de-Faria [39] | 82.8 |
| 3 | Pollack [40] | 121 ± 13 |
| 4 | Thrierr-Sorel [41] | 88 |
| 5 | Keller [34] | 96–167 |
| 6 | Goss [28] | 154 ± 15 |
| 7 | Prasad [42] | 85 |
| 8 | Beuria [34] | 70 |
| No. | FeO in Slag | Limiting Step |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Low FeO content (<5 wt %) | Mass transport in slag |
| 2 | Medium FeO content | Mixed rate limiting step |
| 3 | High FeO content (>30 wt %) | Chemical reaction of carbon/gas |
| Reductants | Oxide | Temperature (°C) | Reduction Rates (mol-FeO/cm2·s) | Activation Energies (kJ/mol) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Graphite | FeO–CaO–SiO2 (10 wt % FeO) | 1480 | 3.04 × 10−6 | 251.2 | Min [62] |
| Molten iron (Csat) 100 g | Slag 70 g | 1600 | 5.70 × 10−5 | Jung [63] | |
| Molten iron (3~4.5 wt % C) 1.5kg | Molten FeO 50 g | 1470 | 1.19 × 10−4 | 184.1 | Sato [51] |
| 1520 | 1.73 × 10−4 | ||||
| 1620 | 3.30 × 10−4 | ||||
| Molten iron (4.15 wt % C) 200 g | Fe2O3 0.7 g | 1400 | 7.94 × 10−4 | 234.3 | Lloyd [68] |
| 1600 | 5.01 × 10−3 | ||||
| Molten iron (Csat) 1.5 kg | FeO 20 g | 1420 | 3.55 × 10−4 | 175.7 | Sato [69] |
| 1520 | 5.18 × 10−4 | ||||
| 1620 | 8.58 × 10−4 | ||||
| Fe3O4 30 g | 1420 | 5.41 × 10−4 | 96.2 | ||
| 1520 | 8.35 × 10−4 | ||||
| 1620 | 1.05 × 10−3 | ||||
| Fe2O3 15 g | 1420 | 5.82 × 10−4 | 96.2 | ||
| 1520 | 8.13 × 10−4 | ||||
| 1620 | 1.17 × 10−3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, G.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Y.; Tan, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhang, B.; Liu, Z. Study on the Bath Smelting Reduction Reaction and Mechanism of Iron Ore: A Review. Metals 2023, 13, 672. https://doi.org/10.3390/met13040672
Wang G, Zhang J, Wang Y, Tan Y, Li Z, Zhang B, Liu Z. Study on the Bath Smelting Reduction Reaction and Mechanism of Iron Ore: A Review. Metals. 2023; 13(4):672. https://doi.org/10.3390/met13040672
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Guilin, Jianliang Zhang, Yaozu Wang, Yubo Tan, Zhen Li, Bo Zhang, and Zhengjian Liu. 2023. "Study on the Bath Smelting Reduction Reaction and Mechanism of Iron Ore: A Review" Metals 13, no. 4: 672. https://doi.org/10.3390/met13040672
APA StyleWang, G., Zhang, J., Wang, Y., Tan, Y., Li, Z., Zhang, B., & Liu, Z. (2023). Study on the Bath Smelting Reduction Reaction and Mechanism of Iron Ore: A Review. Metals, 13(4), 672. https://doi.org/10.3390/met13040672









