Improved Synaptic Device Properties of HfAlOx Dielectric on Highly Doped Silicon Substrate by Partial Reset Process
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
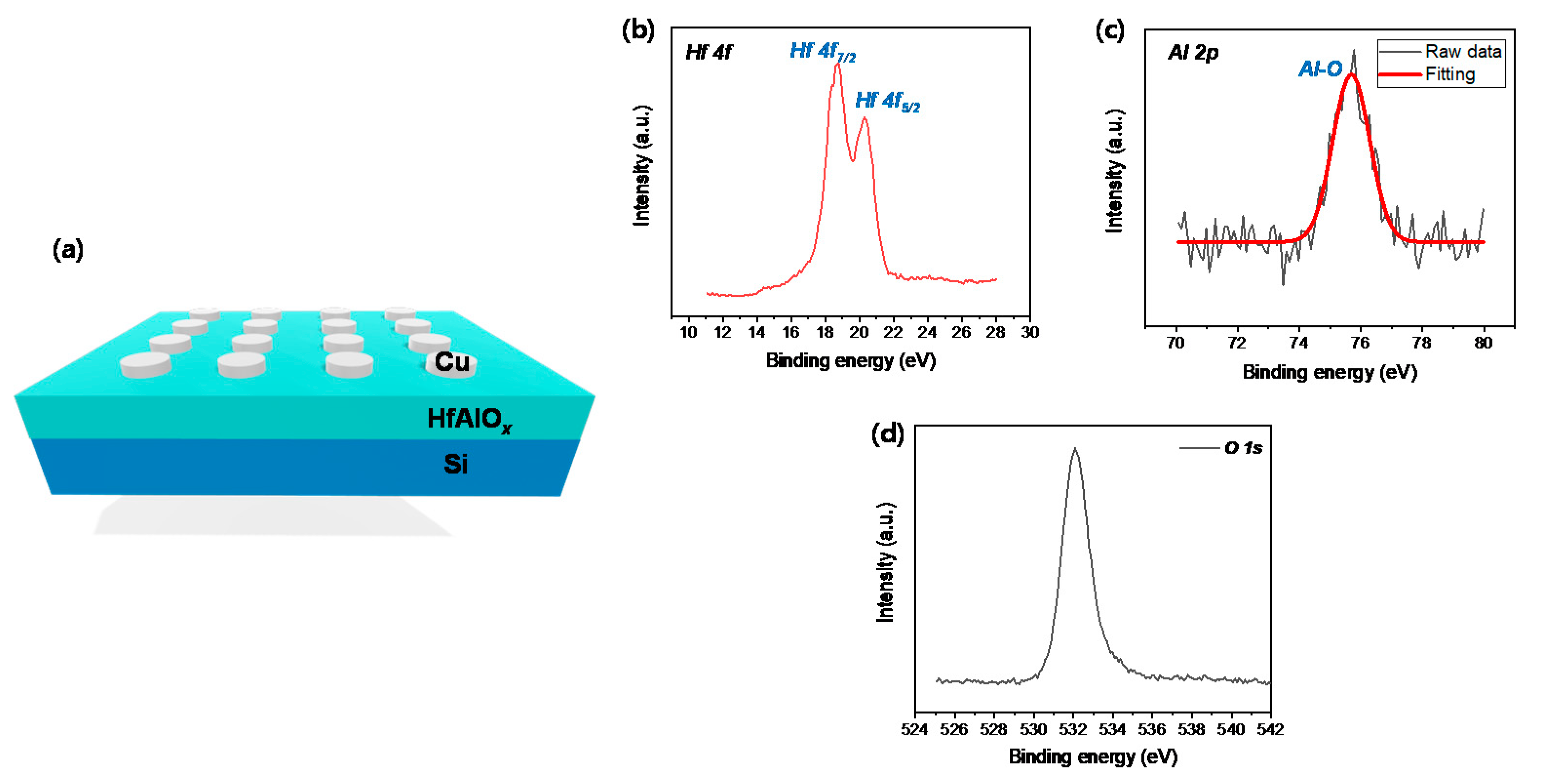
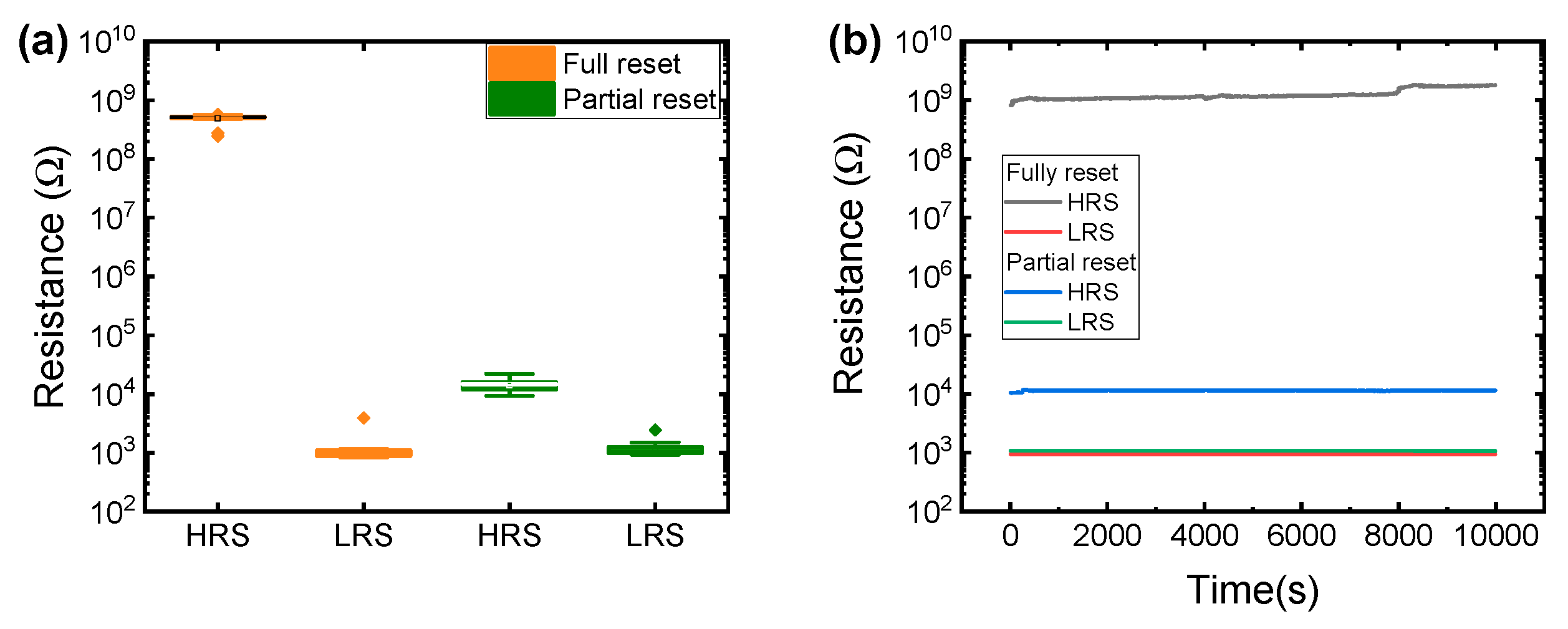
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sim, J.-M.; Kang, M.; Song, Y.-H. A New Read Scheme for Alleviating Cell-to-Cell Interference in Scaled-Down 3D NAND Flash Memory. Electronics 2020, 9, 1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J. Neuromorphic Computing Using Emerging Synaptic Devices: A Retrospective Summary and an Outlook. Electronics 2020, 9, 1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Ting, Y.; Chen, J.; Wu, W. Low Power Consumption Nanofilamentary ECM and VCM Cells in a Single Sidewall of High-Density VRRAM Arrays. Adv. Sci. 2019, 6, 1902363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Zhao, C.; Qi, Y.; Xu, W.; Liu, Y.; Mitrovic, I.Z.; Yang, L.; Zhao, C. Advances of RRAM Devices: Resistive Switching Mechanisms, Materials and Bionic Synaptic Application. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, W. Challenges and Applications of Emerging Nonvolatile Memory Devices. Electronics 2020, 9, 1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanza, M.; Wong, H.-S.P.; Pop, E.; Ielmini, D.; Strukov, D.; Regan, B.C.; Larcher, L.; Villena, M.A.; Yang, J.J.; Goux, L.; et al. Recommended Methods to Study Resistive Switching Devices. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2019, 5, 1800143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, F.; Gao, S.; Chen, C.; Song, C.; Zeng, F. Recent progress in resistive random access memories: Materials, switching mechanisms, and performance. Mater. Sci. Eng. R: Rep. 2014, 83, 1–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Wang, S.; Liu, H. Multi-Level Switching of Al-Doped HfO2 RRAM with a Single Voltage Amplitude Set Pulse. Electronics 2021, 10, 731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, E.; Ossorio, Ó.G.; Dueñas, S.; Castán, H.; García, H.; Wenger, C. Programming Pulse Width Assessment for Reliable and Low-Energy Endurance Performance in Al:HfO2-Based RRAM Arrays. Electronics 2020, 9, 864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, H.; Choi, J.; Kim, S. Voltage Amplitude-Controlled Synaptic Plasticity from Complementary Resistive Switching in Alloying HfOx with AlOx-Based RRAM. Metals 2020, 10, 1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikhaylov, A.; Belov, A.; Korolev, D.; Antonov, I.; Kotomina, V.; Kotina, A.; Gryaznov, E.; Sharapov, A.; Koryazhkina, M.; Kryukov, R.; et al. Multilayer Metal-Oxide Memristive Device with Stabilized Resistive Switching. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2020, 5, 1900607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, H.; Kim, S. Self-Rectifying Resistive Switching and Short-Term Memory Characteristics in Pt/HfO2/TaOx/TiN Artificial Synaptic Device. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu., H.; Kim, S. Pseudo-Interface Switching of a Two-Terminal TaOx/HfO2 Synaptic Device for Neuromorphic Applications. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Chen, J.; Chen, Y.-C.; Kim, M.-H.; Kim, H.; Kwon, M.-W.; Hwang, S.; Ismail, M.; Li, Y.; Miao, X.-S.; et al. Neuronal dynamics in HfO x/AlOy-based homeothermic synaptic memristors with low-power and homogeneous resistive switching. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.-H.; Nili, H.; Kim, M.-H.; Min, K.K.; Park, B.-G.; Kim, H. Reset-voltage-dependent precise tuning operation of TiOx/Al2O3 memristive crossbar array. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2020, 117, 152103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waser, R.; Dittmann, R.; Staikov, G.; Szot, K. Redox-Based Resistive Switching Memories - Nanoionic Mechanisms, Prospects, and Challenges. Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 2632–2663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurlia, T.; Zeng, K.; Kivilahti, J. Failure mechanism of Ta diffusion abrrier between Cu and Si. J. Appl. Phys. 2000, 88, 3377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, J.Y.; Shin, Y.-H. Direct observation of conducting filaments on resistive switching of NiO thin films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008, 92, 222106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroeder, H.; Jeong, D.S. Resistive switching in a Pt/TiO2/Pt thin film stack–a candidate for a non-volatile ReRAM. Microelectron. Eng. 2007, 84, 1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simanjuntak, F.M.; Ohno, T.; Chandrasekaran, C.; Tseng, T.Y.; Samukawa, S. Neutral oxygen irradiation enhanced forming-less ZnO-based transparent analog memristor devices for neuromorphic computing applications. Nanotechnology 2020, 31, 26LT01. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlos, E.; Branquinho, R.; Martins, R.; Kiazadeh, A.; Fortunato, E. Recent Progress in Solution-Based Metal Oxide Resistive Switching Devices. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, e2004328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simanjuntak, F.M.; Ohno, T.; Samukawa, S. Film-Nanostructure-Controlled Inerasable-to-Erasable Switching Transition in ZnO-Based Transparent Memristor Devices: Sputtering-Pressure Dependency. ACS Appl. Electron. Mater. 2019, 11, 2184–2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, H.; Kim, S. Synaptic Characteristics from Homogeneous Resistive Switching in Pt/Al2O3/TiN Stack. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simanjuntak, F.M.; Ohno, T.; Samukawa, S. Neutral Oxygen Beam Treated ZnO-Based Resistive Switching Memory Device. ACS Appl. Electron. Mater. 2019, 1, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, H.; Kim, S. Gradually Tunable Conductance in TiO2/Al2O3 Bilayer Resistors for Synaptic Device. Metals 2021, 11, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simanjuntak, F.M.; Chandrasekaran, S.; Lin, C.-C.; Tseng, T.-Y. Switching Failure Mechanism in Zinc Peroxide-Based Programmable Metallization Cell. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryu, H.; Kim, S. Irregular Resistive Switching Behaviors of Al2O3-Based Resistor with Cu Electrode. Metals 2021, 11, 653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, A. Memory selector devices and crossbar array design: A modeling-based assessment. J. Comput. Electron. 2017, 16, 1186–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahata, C.; Kim, S. Modified resistive switching performance by increasing Al concentration in HfO2 on transparent indium tin oxide electrode. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 1199–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokolov, A.; Som, S.K.; Han, H.H.; Jeon, Y.R.; Lee, J.H.; Choi, C. Comparative study of Al2O3, HfO2, and HfAlOx for improved self-compliance bipolar resistive switching. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2017, 100, 5638–5648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tien, T.-C.; Lin, L.-C.; Lee, L.-S.; Hwang, C.-J.; Maikap, S.; Shulga, Y.M. Analysis of weakly bonded oxygen in HfO2/SiO2/Si stacks by using HRBS and ARXPS. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2010, 21, 475–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, K.; Biswas, K. Cryomilling: An environment friendly approach of preparation large quantity ultra refined pure aluminium nanoparticles. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2019, 8, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.; Kim, J.-G.; Kim, D.-H.; Kim, T.-W. Characterization of Al Incorporation into HfO2 Dielectric by Atomic Layer Deposition. Micromachines 2019, 10, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.; Kim, S. Short-Term Memory Dynamics of TiN/Ti/TiO2/SiOx/Si Resistive Random Access Memory. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryu, J.-H.; Kim, B.; Hussain, F.; Mahata, C.; Ismail, M.; Kim, Y.; Kim, S. Bio-inspired synaptic functions from a transparent zinc-tin-oxide-based memristor for neuromorphic engineering. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2021, 544, 148796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, S.; Kwon, O.; Ryu, H.; Kim, S. Improved Synaptic Device Properties of HfAlOx Dielectric on Highly Doped Silicon Substrate by Partial Reset Process. Metals 2021, 11, 772. https://doi.org/10.3390/met11050772
Kim S, Kwon O, Ryu H, Kim S. Improved Synaptic Device Properties of HfAlOx Dielectric on Highly Doped Silicon Substrate by Partial Reset Process. Metals. 2021; 11(5):772. https://doi.org/10.3390/met11050772
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Seunghyun, Osung Kwon, Hojeong Ryu, and Sungjun Kim. 2021. "Improved Synaptic Device Properties of HfAlOx Dielectric on Highly Doped Silicon Substrate by Partial Reset Process" Metals 11, no. 5: 772. https://doi.org/10.3390/met11050772
APA StyleKim, S., Kwon, O., Ryu, H., & Kim, S. (2021). Improved Synaptic Device Properties of HfAlOx Dielectric on Highly Doped Silicon Substrate by Partial Reset Process. Metals, 11(5), 772. https://doi.org/10.3390/met11050772





