Strain Rate Dependence of Hardness for PE and SME TiNi Alloys
Abstract
1. Introduction
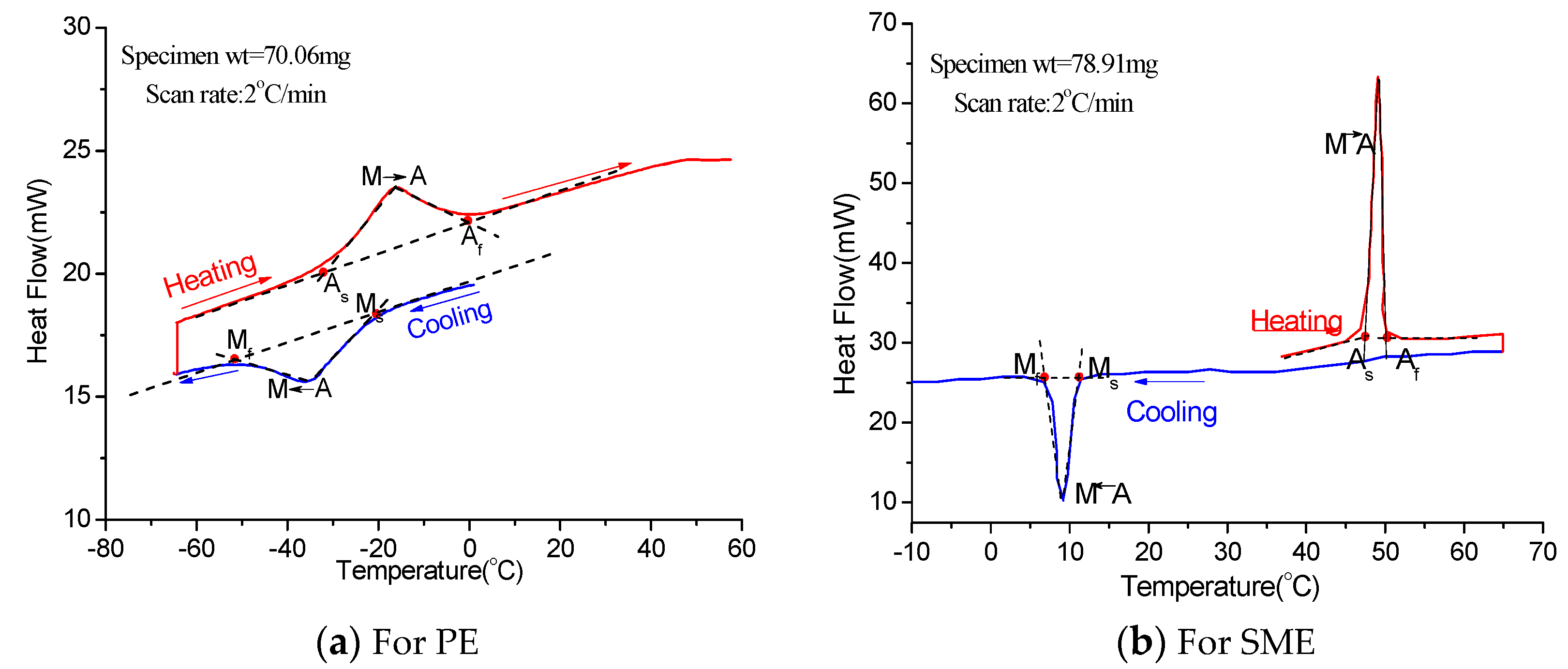
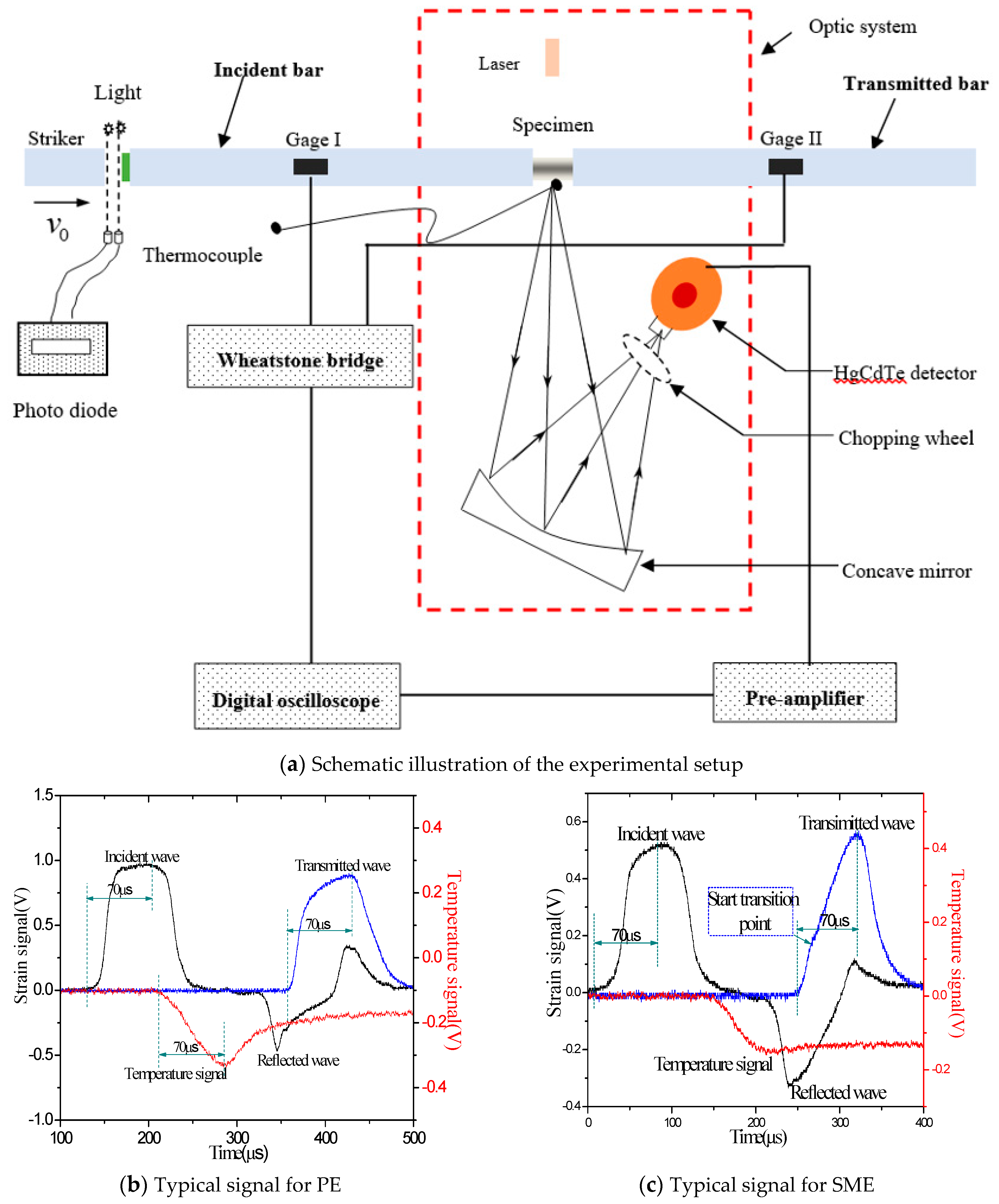
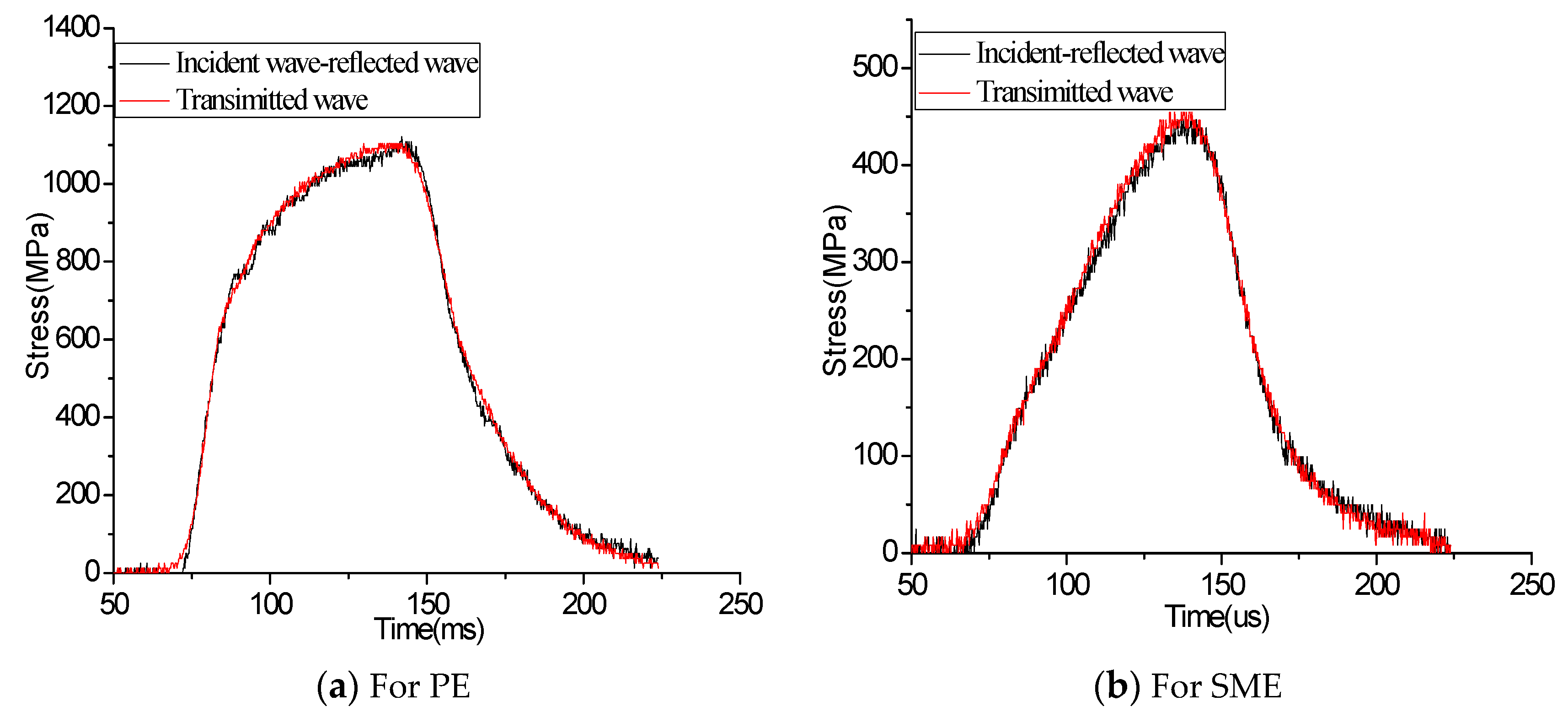
2. Material and Methodology
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Otsuka, K.; Wayman, C.M. Shape Memory Materials; Cambridge UniversityPress: Cambridge, UK, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Shaw, J.A.; Kyriakides, S. On the nucleation and propagation of phase transformation fronts in a NiTi alloy. Acta Mater. 1997, 45, 683–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruno, O.P.; Leo, P.H.; Reitich, F. Free Boundary Conditions at Austenite-Martensite Interfaces. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1995, 74, 746–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sittner, P.; Liu, Y.; Novak, V.J. On the origin of Luders-like deformation of NiTi shape memory alloys. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2005, 53, 1719–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.P.; Li, Z.Q. Phase transformation in superelastic NiTi polycrystalline micro-tubes under tension and torsion—from localization to homogeneous deformation. Int. J. Solids. Struct. 2002, 39, 3797–3809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.Q.; Sun, Q.P. The initiation and growth of macroscopic martensite band in nano-grained NiTi microtube under tension. Int. J. Plast. 2002, 18, 1481–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Yan, Y.; Huo, Y.; Sun, Q. Rate dependent damping of single crystal CuAlNi shape memory alloy. Mater. Lett. 2013, 109, 287–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.J.; Sun, Q.P. Rate-dependent domain spacing in a stretched NiTi strip. Int. J. Solids. Struct. 2010, 47, 2775–2783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.J.; Sun, Q.P. On non-monotonic rate dependence of stress hysteresis of superelastic shape memory alloy bars. Int. J. Solids. Struct. 2011, 48, 1688–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.H.; Feng, P.; He, Y.J.; Yu, T.X.; Sun, Q.P. Experimental study on rate dependence of macroscopic domain and stress hysteresis in NiTi shape memory alloy strips. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2010, 52, 1660–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morin, C.; Moumi, Z.; Zaki, W. Thermomechanical coupling in shape memory alloys under cyclic loadings: Experimental analysis and constitutive modeling. Int. J. Plast. 2011, 27, 1959–1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leo, P.H.; Shield, T.W.; Bruno, O.P. Transient heat transfer effects on the pseudoelastic behavior of shape-memory wires. Acta Metall. Materialia 1993, 41, 2477–2485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemat-Nasser, S.; Choi, J.Y.; Guo, W.G.; Isaacs, J.B. Very high strain-rate response of a NiTi shape-memory alloy. Mech. Mater. 2005, 37, 287–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Song, B. Temperature dependence of a NiTi shape memory alloy’s superelastic behavior at a high strain rate. J. Mech. Mater. Struct. 2006, 1, 339–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zurbitu, J.; Castillo, G.; Urrutibeascoa, I.; Aurrekoetxea, J. Low-energy tensile-impact behavior of superelastic NiTi shape memory alloy wires. Mech. Mater. 2009, 41, 1050–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.W.; Song, B. Split Hopkinson (Kolsky) Bar: Design, Testing and Applications; Springer Science &Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, L.; Liu, Y.; Shan, J. Experimental study on temperature evolutionof pseudoelasticity TiNi alloys during shock-inducedphase transformation. Arch. Mech. 2018, 70, 191–205. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.G.; Shen, L.Y.; Shan, J.F.; Hui, M.M. Experimental study on temperature evolution and strain rate effect on phase transformation of TiNi shape memory alloy under shock loading. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2019, 156, 342–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.Z.; Ruan, Q.C.; Zhu, S.X.; Wei, Q.; Chen, H.; Lu, J.; Hu, B.; Wu, X.; Li, Y.; Fang, D. Temperature Rise Associated with Adiabatic Shear Band: Causality Clarified. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2019, 122, 015503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pieczyska, E.A.; Gadaj, S.P.; Nowacki, W.K.; Tobushi, H. Phase-Transformation Fronts Evolution for Stress- and Strain-Controlled Tension Tests in TiNi Shape Memory Alloy. Exp. Mech. 2006, 46, 531–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, J.A.; Kyriakides, S. Initiation and propagation of localized deformation in elasto–plastic strips under uniaxial tension. Int. J. Plast. 1998, 13, 837–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieczyska, E.A.; Tobushi, H.; Kulasiński, K. Development of transformation bands in TiNi SMA for various stress and strain rates studied by a fast and sensitive infrared camera. Smart Mater. Struct. 2013, 22, 035007-1-8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shen, L.; Hui, M.; Liu, Y. Strain Rate Dependence of Hardness for PE and SME TiNi Alloys. Metals 2020, 10, 1157. https://doi.org/10.3390/met10091157
Shen L, Hui M, Liu Y. Strain Rate Dependence of Hardness for PE and SME TiNi Alloys. Metals. 2020; 10(9):1157. https://doi.org/10.3390/met10091157
Chicago/Turabian StyleShen, Lingyan, Mengmeng Hui, and Yonggui Liu. 2020. "Strain Rate Dependence of Hardness for PE and SME TiNi Alloys" Metals 10, no. 9: 1157. https://doi.org/10.3390/met10091157
APA StyleShen, L., Hui, M., & Liu, Y. (2020). Strain Rate Dependence of Hardness for PE and SME TiNi Alloys. Metals, 10(9), 1157. https://doi.org/10.3390/met10091157




