The Effects of Physical Education on Motor Competence in Children and Adolescents: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Eligibility Criteria
2.2. Data Sources
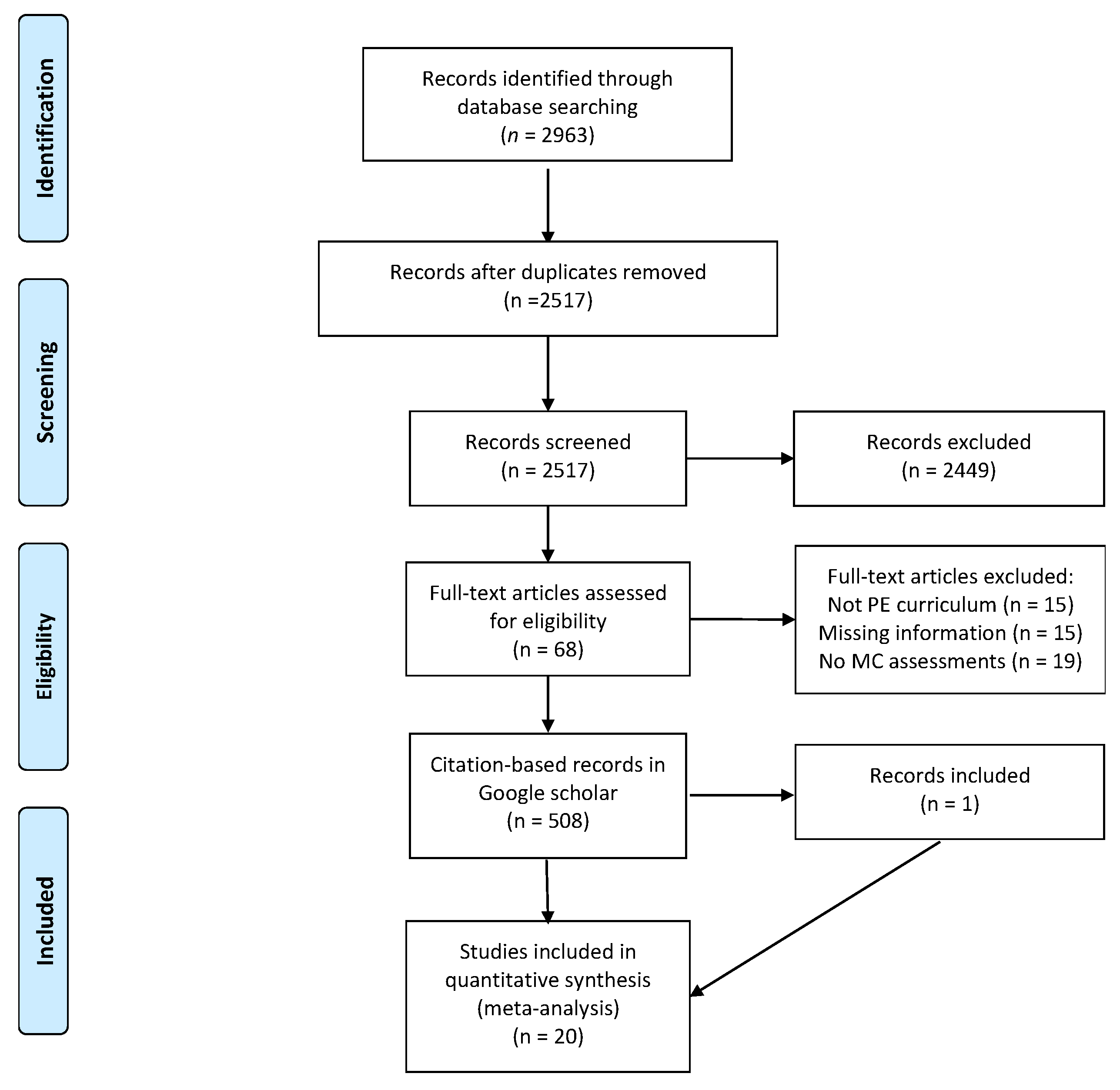
2.3. Study Selection and Data Abstraction
2.4. Calculation of Effect Size
2.5. Pooling of Effect Size
2.6. Heterogeneity, Inconsistency, and Small-Study Effects
2.7. Moderator Variables
3. Results
3.1. Overview of Included Studies
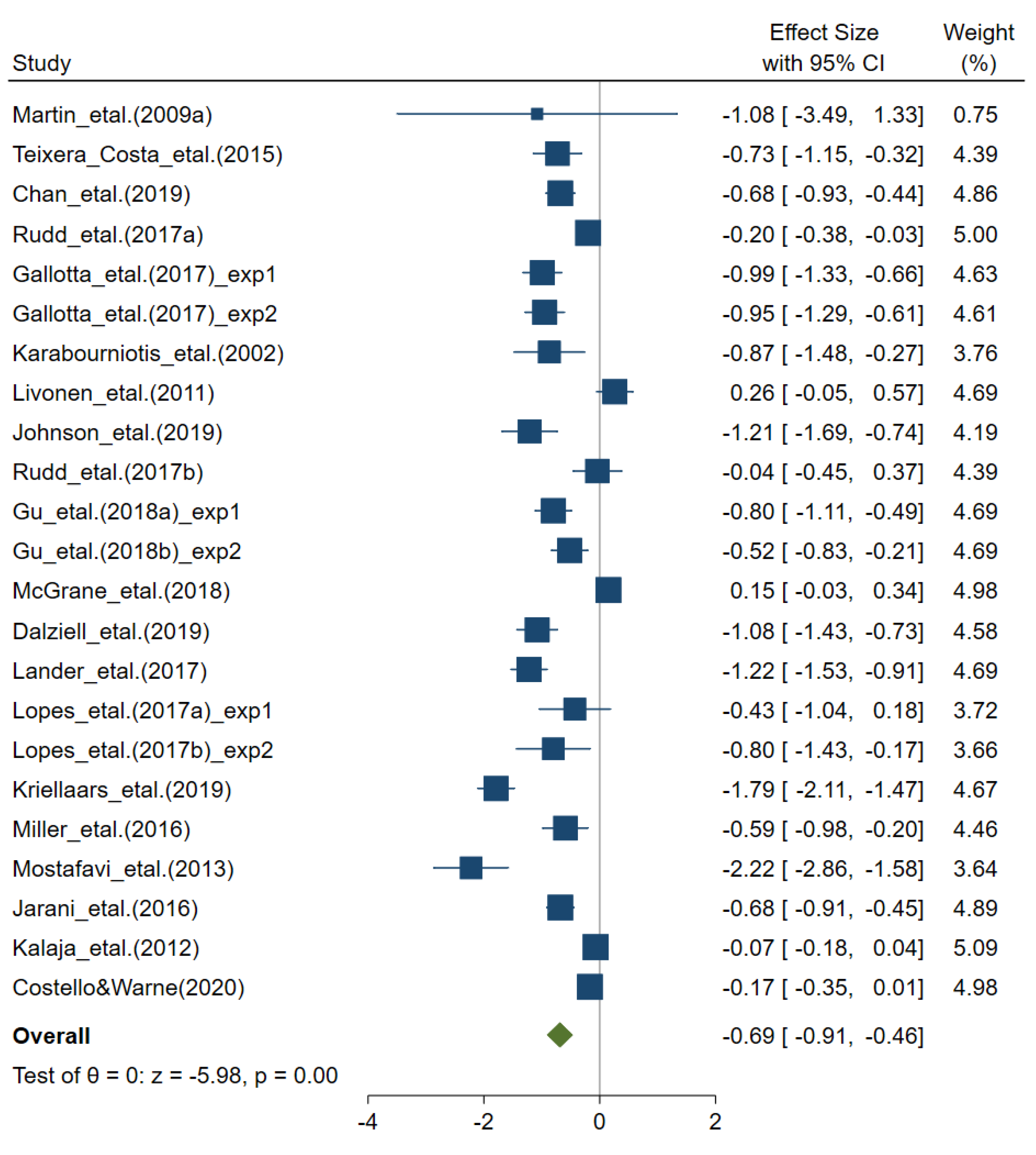
3.2. Effect of Physical Education on Overall Motor Competence
3.3. Heterogenity and Publication Bias
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cattuzzo, M.T.; Henrique, R.S.; Ré, A.H.N.; de Oliveira, I.S.; Melo, B.M.; Moura, M.D.S.; de Araújo, R.C.; Stodden, D.; Information, P.E.K.F.C. Motor competence and health related physical fitness in youth: A systematic review. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2016, 19, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnett, L.M.; Lai, S.K.; Veldman, S.L.; Hardy, L.L.; Cliff, D.P.; Morgan, P.J.; Zask, A.; Lubans, D.R.; Shultz, S.P.; Ridgers, N.D.; et al. Correlates of gross motor competence in children and adolescents: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sports Med. 2016, 46, 1663–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holfelder, B.; Schott, N. Relationship of fundamental movement skills and physical activity in children and adolescents: A systematic review. Psychol. Sport Exerc. 2014, 15, 382–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iivonen, S.; Sääkslahti, A. Preschool children’s fundamental motor skills: A review of significant determinants. Early Child Dev. Care 2013, 184, 1107–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, L.E.; Stodden, D.; Barnett, L.M.; Lopes, V.P.; Logan, S.W.; Rodrigues, L.P.; D’Hondt, E. Motor Competence and its Effect on Positive Developmental Trajectories of Health. Sports Med. 2015, 45, 1273–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stodden, D.; Goodway, J.D.; Langendorfer, S.J.; Roberton, M.A.; Rudisill, M.E.; Garcia, C.; García, L.E. A Developmental Perspective on the Role of Motor Skill Competence in Physical Activity: An Emergent Relationship. Quest 2008, 60, 290–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, S.S.D. The Movement Assessment Battery for Children; The Psychological Corporation: London, UK, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Hardy, L.L.; Reinten-Reynolds, T.; Espinel, P.; Zask, A.; Okely, A.D. Prevalence and Correlates of Low Fundamental Movement Skill Competency in Children. Pediatrics 2012, 130, e390–e398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaul, D.; Issartel, J. Fine motor skill proficiency in typically developing children: On or off the maturation track? Hum. Mov. Sci. 2016, 46, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, W.; Belton, S.; Issartel, J. Fundamental movement skill proficiency amongst adolescent youth. Phys. Educ. Sport Pedagog. 2015, 21, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheehan, D.; Lienhard, K. Gross Motor Competence and Peak Height Velocity in 10- to 14-Year-Old Canadian Youth: A Longitudinal Study. Meas. Phys. Educ. Exerc. Sci. 2018, 23, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigmundsson, H.; Trana, L.; Polman, R.; Haga, M. What is Trained Develops! Theoretical Perspective on Skill Learning. Sports 2017, 5, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Logan, S.W.; Robinson, L.E.; Lucas, W.A.; Wilson, A.E. Getting the fundamentals of movement: A meta? Analysis of the effectiveness of motor skill interventions in children. Child Care Health Dev. 2011, 38, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgan, P.; Barnett, L.M.; Cliff, D.; Okely, A.D.; Scott, H.A.; Cohen, K.E.; Lubans, D.R. Fundamental Movement Skill Interventions in Youth: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Pediatrics 2013, 132, e1361–e1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riethmuller, A.M.; Jones, R.A.; Okely, A.D. Efficacy of Interventions to Improve Motor Development in Young Children: A Systematic Review. Pediatrics 2009, 124, 782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dudley, D.; Okely, A.D.; Pearson, P.; Cotton, W. A systematic review of the effectiveness of physical education and school sport interventions targeting physical activity, movement skills and enjoyment of physical activity. Eur. Phys. Educ. Rev. 2011, 17, 353–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, S.K.; Costigan, S.A.; Morgan, P.; Lubans, D.R.; Stodden, D.; Salmon, J.; Barnett, L.M. Do School-Based Interventions Focusing on Physical Activity, Fitness, or Fundamental Movement Skill Competency Produce a Sustained Impact in These Outcomes in Children and Adolescents? A Systematic Review of Follow-Up Studies. Sports Med. 2013, 44, 67–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Australian National Curriculum in Physical Education. Available online: https://www.australiancurriculum.edu.au/f-10-curriculum/health-and-physical-education/ (accessed on 15 May 2020).
- England National Curriculum in Physical Education. Available online: https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/national-curriculum-in-england-physical-education-programmes-of-study (accessed on 15 May 2020).
- Singapore National Curriculum in Physical Education. Available online: https://www.moe.gov.sg/docs/default-source/document/education/syllabuses/physical-sports-education/files/physical_education_syllabus_2014.pdf (accessed on 15 May 2020).
- Renshaw, I.; Chow, J.Y. A constraint-led approach to sport and physical education pedagogy. Phys. Educ. Sport Pedagog. 2018, 24, 103–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, S.; Pill, S.; Almond, L. Old wine in new bottles: A response to claims that teaching games for understanding was not developed as a theoretically based pedagogical framework. Phys. Educ. Sport Pedagog. 2017, 23, 166–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grissmer, D.; Grimm, K.J.; Aiyer, S.M.; Murrah, W.M.; Steele, J.S. Fine motor skills and early comprehension of the world: Two new school readiness indicators. Dev. Psychol. 2010, 46, 1008–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suggate, S.P.; Pufke, E.; Stoeger, H. Children’s fine motor skills in kindergarten predict reading in grade 1. Early Child. Res. Q. 2019, 47, 248–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitchford, N.J.; Papini, C.; Outhwaite, L.A.; Gulliford, A. Fine Motor Skills Predict Maths Ability Better than They Predict Reading Ability in the Early Primary School Years. Front. Psychol. 2016, 7, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whittle, H.D. Effects of Elementary School Physical Education upon Aspects of Physical, Motor, and Personality Development. Res. Quarterly. Am. Assoc. Health Phys. Educ. Recreat. 1961, 32, 249–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, T.L. Self-Concepts and Movement Skills of Third Grade Children after Physical Education Programs. Percept. Mot. Ski. 1982, 54, 1145–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- di Cesare, M.; Sorić, M.; Bovet, P.; Miranda, J.J.; Bhutta, Z.; A Stevens, G.; Laxmaiah, A.; Kengne, A.-P.; Bentham, J. The epidemiological burden of obesity in childhood: A worldwide epidemic requiring urgent action. BMC Med. 2019, 17, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Capelle, A.; Broderick, C.R.; van Doorn, N.; Ward, R.E.; Parmenter, B.J. Interventions to improve fundamental motor skills in pre-school aged children: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2017, 20, 658–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wick, K.; Leeger-Aschmann, C.S.; Monn, N.D.; Radtke, T.; Ott, L.V.; Rebholz, C.E.; Cruz, S.; Gerber, N.; Schmutz, E.A.; Puder, J.J.; et al. Interventions to Promote Fundamental Movement Skills in Childcare and Kindergarten: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Sports Med. 2017, 47, 2045–2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Díaz, J.; Chaves-Castro, K.; Salazar, W. Effects of Different Movement Programs on Motor Competence: A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis. J. Phys. Act. Health 2019, 16, 657–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. Ann. Internal Med. 2009, 151, 264–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rysstad, A.L.; Pedersen, A.V. Brief Report: Non-Right-Handedness Within the Autism Spectrum Disorder. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2015, 46, 1110–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedges, L.V. Distribution theory for Glass’s estimator of effect size and related estimators. J. Educat. Stat. 1981, 6, 107–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- der Simonian, R.; Laird, N. Meta-analysis in clinical trials. Controll. Clin. Trials 1986, 7, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borenstein, M.; Hedges, L.; Higgins, J.P.T.; Rothstein, H. Introduction to Meta-Analysis; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Higgins, J.P.T.; Thompson, S.G.; Deeks, J.; Altman, U.G. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ 2003, 327, 557–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egger, M.; Smith, G.D.; Schneider, M.; Minder, C. Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ 1997, 315, 629–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawyer, S.M.; Azzopardi, P.S.; Wickremarathne, D.; Patton, G.C. The age of adolescence. Lancet Child Adolesc. Health 2018, 2, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulrich, D.A. Test of Gross Motor Development; ProEd: Austin, TX, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Iivonen, S.; Sääkslahti, A.; Laukkanen, A. A review of studies using the Korperkoordinationstest fur Kinder (KTK). Eur. J. Adapt. Phys. Act. 2015, 8, 18–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logan, S.W.; Ross, S.M.; Chee, K.; Stodden, D.; Robinson, L.E. Fundamental motor skills: A systematic review of terminology. J. Sports Sci. 2017, 36, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, L.C.; Bryant, A.S.; Keegan, R.; Morgan, K.; Jones, A.M. Definitions, Foundations and Associations of Physical Literacy: A Systematic Review. Sports Med. 2017, 47, 113–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karabourniotis, D. Curriculum Enrichment with Self-Testing Activities in Development of Fundamental Movement Skills of First-Grade Children in Greece. Percept. Mot. Skills 2002, 94, 1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, E.H.; Rudisill, M.E.; Hastie, P.A. Motivational climate, and fundamental motor skill performance in a naturalistic physical education setting. Phys. Educ. Sport Pedagog. 2009, 14, 227–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iivonen, S.; Sääkslahti, A.; Nissinen, K. The development of fundamental motor skills of four- to five-year-old preschool children and the effects of a preschool physical education curriculum. Early Child Dev. Care 2011, 181, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalaja, S.P.; Jaakkola, T.; Liukkonen, J.O.; Digelidis, N. Development of junior high school students’ fundamental movement skills and physical activity in a naturalistic physical education setting. Phys. Educ. Sport Pedagog. 2012, 17, 411–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafavi, R.; Ziaee, V.; Akbari, H.; Haji-Hosseini, S. The Effects of SPARK Physical Education Program on Fundamental Motor Skills in 4–6-Year-Old Children. Iran. J. Pediatr. 2013, 23, 216–219. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Costa, H.J.T.; Barcala-Furelos, R.; Abelairas-Gómez, C.; Giráldez, V.A. The Influence of a Structured Physical Education Plan on Preschool Children’s Psychomotor Development Profiles. Australas. J. Early Child. 2015, 40, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, A.; Christensen, E.; Eather, N.; Gray, S.; Sproule, J.; Keay, J.; Lubans, D.R. Can physical education and physical activity outcomes be developed simultaneously using a game-centered approach? Eur. Phys. Educ. Rev. 2015, 22, 113–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarani, J.; Grøntved, A.; Muca, F.; Spahi, A.; Qefalia, D.; Ushtelenca, K.; Kása, A.; Caporossi, D.; Gallotta, M.C. Effects of two physical education programmes on health- and skill-related physical fitness of Albanian children. J. Sports Sci. 2015, 34, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallotta, M.C.; Emerenziani, G.P.; Iazzoni, S.; Iasevoli, L.; Guidetti, L.; Baldari, C. Effects of different physical education programmes on children’s skill- and health-related outcomes: A pilot randomised controlled trial. J. Sports Sci. 2016, 35, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudd, J.R.; Barnett, L.M.; Farrow, D.; Berry, J.; Borkoles, E.; Polman, R. Effectiveness of a 16-week gymnastics curriculum at developing movement competence in children. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2017, 20, 164–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudd, J.R.; Barnett, L.M.; Farrow, D.; Berry, J.; Borkoles, E.; Polman, R. The Impact of Gymnastics on Children’s Physical Self-Concept and Movement Skill Development in Primary Schools. Meas. Phys. Educ. Exerc. Sci. 2017, 9, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lander, N.; Morgan, P.; Salmon, J.; Barnett, L.M. Improving Early Adolescent Girls’ Motor Skill. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2017, 49, 2498–2505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, V.P.; Stodden, D.; Rodrigues, L.P. Effectiveness of physical education to promote motor competence in primary school children. Phys. Educ. Sport Pedagog. 2017, 22, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Chen, Y.-L.; Jackson, A.W.; Zhang, T. Impact of a pedometer-based goal-setting intervention on children?s motivation, motor competence, and physical activity in physical education. Phys. Educ. Sport Pedagog. 2017, 23, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGrane, B.; Belton, S.; Fairclough, S.J.; Powell, D.; Issartel, J. Outcomes of the Y-PATH Randomized Controlled Trial: Can a School-Based Intervention Improve Fundamental Movement Skill Proficiency in Adolescent Youth? J. Phys. Act. Health 2018, 15, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, C.H.; Ha, A.S.; Ng, J.Y.Y.; Lubans, D.R. The A+FMS cluster randomized controlled trial: An assessment-based intervention on fundamental movement skills and psychosocial outcomes in primary schoolchildren. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2019, 22, 935–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, J.L.; Rusidill, M.E.; Hastie, P.; Wadsworth, D.; Strunk, K.; Venezia, A.; Sassi, J.; Morris, M.; Merritt, M. Changes in Fundamental Motor-Skill Performance Following a Nine-Month Mastery Motivational Climate Intervention. Res. Q. Exerc. Sport 2019, 90, 517–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalziell, A.; Booth, J.N.; Boyle, J.; Mutrie, N. Better Movers and Thinkers: An evaluation of how a novel approach to teaching physical education can impact children’s physical activity, coordination, and cognition. Br. Educ. Res. J. 2019, 45, 576–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kriellaars, D.J.; Cairney, J.; Bortoleto, M.A.; Kiez, T.K.; Dudley, D.; Aubertin, P. The Impact of Circus Arts Instruction in Physical Education on the Physical Literacy of Children in Grades 4 and 5. J. Teach. Phys. Educ. 2019, 38, 162–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costello, K.; Warne, J. A four-week fundamental motor skill intervention improves motor skills in eight to 10-year-old Irish primary school children. Cogent Soc. Sci. 2020, 6, 1724065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J. A power primer. Psychol. Bull. 1992, 112, 155–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, C.J. An effect size primer: A guide for clinicians and researchers. Prof. Psychol. Res. Pr. 2009, 40, 532–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hattie, J. Visible Learning: A Synthesis of Over 800 Meta-Analyses Relating to Achievement; Routledge: London, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson, L. Statistical methods in psychology journals: Guidelines and explanations. Am. Psychol. 1999, 54, 594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dallolio, L.; Ceciliani, A.; Sanna, T.; Garulli, A.; Leoni, E. Proposal for an Enhanced Physical Education Program in the Primary School: Evaluation of Feasibility and Effectiveness in Improving Physical Skills and Fitness. J. Phys. Act. Health 2016, 13, 1025–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rexen, C.T.; Ersbøll, A.K.; Wedderkopp, N.; Andersen, L. Longitudinal influence of musculo-skeletal injuries and extra physical education on physical fitness in schoolchildren. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2015, 26, 1470–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chow, J.Y.; Davids, K.; Hristovski, R.; Araújo, D.; Passos, P. Nonlinear pedagogy: Learning design for self-organizing neurobiological systems. New Ideas Psychol. 2011, 29, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cumpston, M.; Li, T.; Page, M.J.; Chandler, J.; A Welch, V.; Higgins, J.P.; Thomas, J. Updated guidance for trusted systematic reviews: A new edition of the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2019, 10, ED000142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smart, N.A.; Waldron, M.; Ismail, H.; Giallauria, F.; Vigorito, C.; Cornelissen, V.; Dieberg, G. Validation of a new tool for the assessment of study quality and reporting in exercise training studies. Int. J. Evid.-Based Health 2015, 13, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maher, C.G.; Sherrington, C.; Herbert, R.D.; Moseley, A.M.; Elkins, M.R. Reliability of the PEDro Scale for Rating Quality of Randomized Controlled Trials. Phys. Ther. 2003, 83, 713–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hallal, P.; Andersen, L.B.; Bull, F.C.; Guthold, R.; Haskell, W.; Ekelund, U. Global physical activity levels: Surveillance progress, pitfalls, and prospects. Lancet 2012, 380, 247–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crane, J.; Temple, V. A systematic review of dropout from organized sport among children and youth. Eur. Phys. Educ. Rev. 2014, 21, 114–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sallis, J.F.; Cerin, E.; Conway, T.L.; Adams, M.A.; Frank, L.D.; Pratt, M.; Salvo, D.; Schipperijn, J.; Smith, G.; Cain, K.; et al. Physical activity in relation to urban environments in 14 cities worldwide: A cross-sectional study. Lancet 2016, 387, 2207–2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Østergaard, L.; Kolle, E.; Steene-Johannessen, J.; Anderssen, S.A.; Andersen, L.B. Cross sectional analysis of the association between mode of school transportation and physical fitness in children and adolescents. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2013, 10, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eddy, L.H.; Wood, M.; Shire, K.; Bingham, D.D.; Bonnick, E.; Creaser, A.; Mon-Williams, M.; Hill, L.J.B. A systematic review of randomized and case-controlled trials investigating the effectiveness of school-based motor skill interventions in 3- to 12-year-old children. Child Care Health Dev. 2019, 45, 773–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taverna, L.; Tremolada, M.; Dozza, L.; Scaratti, R.Z.; Ulrike, D.; Lallo, C.; Tosetto, B. Who Benefits from An Intervention Program on Foundational Skills for Handwriting Addressed to Kindergarten Children and First Graders? Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smits-Engelsman, B.C.M.; Blank, R.; Polatajko, H.J.; Wilson, P.H.; van der Kaay, A.-C.; der Meijs, R.M.-V.; Brand, E.V.-V.D. Efficacy of interventions to improve motor performance in children with developmental coordination disorder: A combined systematic review and meta-analysis. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2012, 55, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Study | Sample Size (n) | Age (Years) | Total PE (h) | Intervention Group PE | Control Group | Assessment of Motor Competence |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Karabouniotis et al. (2002) [44] | 45 | 6 | 16 | Movement skill curriculum | Standard PE curriculum | TGMD |
| Martin et al. (2009) [45] | 54 | 6 | 10 | High autonomy PE | Low autonomy PE | TGMD-2 |
| Livonen et al. (2011) [46] | 84 | 5 | 36 | Movement literacy curriculum | Standard PE curriculum | FMS |
| Kalaja et al. (2012) [47] | 446 | 13 | 50 | FMS curriculum | Standard PE curriculum | FMS |
| Mostafavi et al. (2013) [48] | 60 | 5 | na | SPARK | Standard PE curriculum | TGMD-2 |
| Teixera Costa et al. (2015) [49] | 95 | 3 | 36 | Structured PE | No PE lessons | PMD |
| Miller et al. (2016) [50] | 107 | 11 | 6 | Game-centered curriculum | Wait-list | FMS |
| Jarani et al. (2016) [51] | 509 | 8 | 30 | Exercise or games-based | Standard PE curriculum | KTK |
| Gallotta et al. (2017) [52] | 230 | 10 | 40 | Fitness or coordination | Standard PE curriculum | KTK |
| Rudd et al. (2017) [53] | 310 | 8 | 32 | Gymnastics | Standard PE curriculum | TGMD-2, KTK |
| Rudd et al. (2017) [54] | 98 | 9 | 16 | Gymnastics | Standard PE curriculum | TGMD-2, KTK |
| Lander et al. (2017) [55] | 190 | 12 | 18 | FMS curriculum | Standard PE curriculum | FMS |
| Lopes et al. (2017) [56] | 60 | 9 | 48 and 73 | FMS curriculum | No PE lessons | FMS |
| Gu et al. (2018) [57] | 273 | 11 | 18 | Pedometer-based goal setting | Standard PE curriculum | PE Metrics TM |
| McGrane et al. (2018) [58] | 460 | 13 | 37 | PA towards health | Standard PE curriculum | TGMD-2 |
| Chan et al. (2019) [59] | 276 | 8 | 19 | AfL + FMS | Standard PE curriculum | TGMD-3 |
| Johnson et al. (2019) [60] | 96 | 4 | 15 | Mastery motivational climate | Standard PE curriculum | TGMD-3 |
| Dalziell et al. (2019) [61] | 143 | 11 | 32 | Better Movers and Thinkers | Standard PE curriculum | FLS |
| Kriellaars et al. (2019) [62] | 211 | 10 | 66 | Circus arts instruction | Standard PE curriculum | PLAY |
| Costello and Warne (2020) [63] | 100 | 9 | 4 | Movement literacy | Standard PE curriculum | FMS |
© 2020 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lorås, H. The Effects of Physical Education on Motor Competence in Children and Adolescents: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Sports 2020, 8, 88. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports8060088
Lorås H. The Effects of Physical Education on Motor Competence in Children and Adolescents: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Sports. 2020; 8(6):88. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports8060088
Chicago/Turabian StyleLorås, Håvard. 2020. "The Effects of Physical Education on Motor Competence in Children and Adolescents: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" Sports 8, no. 6: 88. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports8060088
APA StyleLorås, H. (2020). The Effects of Physical Education on Motor Competence in Children and Adolescents: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Sports, 8(6), 88. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports8060088




