Comparative Study of Two Intervention Programmes for Teaching Soccer to School-Age Students
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Design
2.2. Sample
2.3. Variables
2.4. Instruments
2.5. Procedure
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| DIS | ||||||||||||
| S1 | S2 | S3 | S4 | S5 | S6 | S7 | S8 | S9 | S10 | S11 | S12 | |
| Feedback | Descriptive/Prescriptive | Descriptive/Prescriptive | Descriptive/Prescriptive | Descriptive/Prescriptive | Descriptive/Prescriptive | Descriptive/Prescriptive | Descriptive/Prescriptive | Descriptive/Prescriptive | Descriptive/Prescriptive | Descriptive/Prescriptive | Descriptive/Prescriptive | Descriptive/Prescriptive |
| Presentation | Analytical | Analytical | Analytical | Analytical | Analytical | Analytical | Analytical | Analytical | Analytical -Global | Analytical -Global | Global | Global |
| Space | Static activ. Small | Small Medium Large | Static activ. Medium Small | Small Medium | Static activ. Small | Small Medium | Small | Small | Small | Small | Small Medium | Small Medium |
| Situation | 2 × 0, 3 × 0 | 1 × 0 | 1 × 0, 2 × 0, 3 × 0 | 1 × 0 | 1 × 0, 1 × 1, 1 × Large Group | 1 × 0 | 1 × 0, 2 × 0 | 1 × 0, 1 × 1 | 1 × 1, 2 × 1 | 1 × 0, 1 × 1, 2 × 1 | 1 × 1, 2 × 1, 2 × 2, N × N | 1 × 1, 2 × 1, 2 × 2, 5 × 5 |
| Means | Simple practical exercise | Simple practical exercise Complex practical exercise | Simple practical exercise Complex practical exercise | Simple practical exercise Complex practical exercise | Simple practical exercise Simple specific game | Simple practical exercise Complex practical exercise | Simple practical exercise Complex practical exercise | Simple practical exercise Simple specific game | Simple specific game | Simple practical exercise Simple specific game | Simple non-specific game Simple specific game | Simple specific game Adapted sport/SSG. |
| Game principles | Protect Progress | Protect Progress | Progress | Progress | Progress Reach goal | Progress Reach goal | Progress Reach goal | Recover | Recover Hinder progress | Recover Hinder progress | Reach goal Protect goal | Reach goal Protect goal |
| Specific content | Pass-control | Ball control: progression and protection | Progression with support of team mates | Dribbling on the run | Progression to goal to shoot | Dribbling past opponent to try to shoot | Review of attack contents | Interception: passes between opponents | Interception: passes between opponents/shot /entry | Review of defence contents | Situations played: attack and defence | Situations played: attack and defence |
| Phase | Attack | Attack | Attack | Attack | Attack | Attack | Attack | Attack | Defence | Defence | Mixed | Mixed |
| TGAS | ||||||||||||
| S1 | S2 | S3 | S4 | S5 | S6 | S7 | S8 | S9 | S10 | S11 | S12 | |
| Phase | Attack | Attack | Attack | Attack | Attack | Attack | Attack | Defence | Defence | Defence | Mixed | Mixed |
| Specific content | Pass-control | Ball control: progression and protection | Progression with support of team mates | Dribbling on the run | Progression to goal to shoot | Dribbling past opponent to try to shoot | Review of attack contents | Interception: passes between opponents | Interception: passes between opponents shot/entry | Review of defence contents | Situations played: attack and defence | Situations played: attack and defence |
| Game principles | Protect Progress | Protect Progress | Progress | Progress | Progress Reach goal | Progress Reach goal | Progress Reach goal | Recover | Recover Hinder progress | Recover Hinder progress | Reach goal Protect goal | Reach goal Protect goal |
| Means | Complex specific game | Simple non-specific game Simple specific game | Simple specific game Complex specific game | Simple non-specific game Simple specific game | Simple specific game | Simple specific game | Simple specific game Complex specific game | Simple specific game Complex specific game | Simple specific game Complex specific game | Simple specific game Complex specific game | Simple specific game Complex specific game Adapted sport/SSG. | Simple specific game Complex specific game Adapted sport/SSG. |
| Situation | 5 × 1, 5 × 4 | 1 × 1, 1 × Large Group | 1 × GG, 5 × 4, N × N, Combin. | 1 × 1 | 1 × 1 | 1 × 1 | 2 × 1, 3 × 2, 5 × 4 | 2 × 1, 3 × 1, 3 × 2, 4 × 2 | 1 × 1, 3 × 2, 4 × 2 | 1 × 1, 3 × 1, 3 × 2 | 2 × 1, 2 × 2, 3 × 2, 4 × 4 | 2 × 2, 3 × 2, 4 × 4, 5 × 5 |
| Space | Static activ. Medium | Medium | Medium Large | Small Medium | Small Medium | Small Medium | Small Medium | Small | Small | Small | SmallMedium | SmallMedium |
| Presentation | Global | Global | Global | Global | Global | Global | Global | Global | Global | Global | Global | Global |
| Feedback | Interrogative | Interrogative | Interrogative | Interrogative | Interrogative | Interrogative | Interrogative | Interrogative | Interrogative | Interrogative | Interrogative | Interrogative |
References
- Hernández, J. Análisis de las estructuras del juego deportivo; Inde: Barcelona, Spain, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- González-Víllora, S.; García, L.M.; Contreras, O.R.; Sánchez-Mora, D. El concepto de iniciación deportiva en la actualidad. Retos: Nuevas Tendencias en Educación Física, Deporte y Recreación 2009, 15, 14–20. [Google Scholar]
- Delgado, M.A. El papel del entrenador en el deporte durante la edad escolar. Deporte y actividad física para todos 2001, 2, 63–78. [Google Scholar]
- Castejón, F.J. La investigación en iniciación deportiva válida para el profesorado de educación física en ejercicio. Retos: Nuevas Tendencias en Educación Física, Deporte y Recreación 2015, 28, 263–269. [Google Scholar]
- González-Espinosa, S.; Ibáñez, S.J.; Feu, S. Diseño de dos programas de enseñanza del baloncesto basados en métodos de enseñanza-aprendizaje diferentes. E-balonmano.com: Revista de Ciencias del Deporte 2017, 13, 131–152. [Google Scholar]
- Del Valle, S.; García, M.J. Cómo programar en Educación Física paso a paso; Inde: Barcelona, Spain, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Fernández, E.; Cecchini, J.A.; Zagalaz, M.L. Didáctica de la educación física en la educación primaria; Síntesis: Madrid, Spain, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Viciana, J. Planificar en Educación Física (1ª ed.); Inde: Barcelona, Spain, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Ureña, N.; Alarcón, F.; Ureña, F. La realidad de los deportes colectivos en la Enseñanza Secundaria. Cómo planifican e intervienen los profesores de Murcia. Retos: Nuevas Tendencias en Educación Física, Deporte y Recreación 2009, 16, 9–15. [Google Scholar]
- Ibáñez, S.J. La planificación y el control del entrenamiento técnico-táctico en baloncesto. In Fisiología, entrenamiento y medicina del baloncesto; Terrados, N., Calleja, J., Eds.; Paidotribo: Barcelona, Spain, 2008; pp. 299–313. [Google Scholar]
- Ibáñez, S.J. La intervención del entrenador de baloncesto: Investigación e implicaciones prácticas. In Aportaciones teóricas y prácticas para el baloncesto del futuro; Lorenzo, A., Ibáñez, S.J., Ortega, E., Eds.; Wanceulen: Sevilla, Spain, 2009; pp. 11–30. [Google Scholar]
- Alarcón, F.; Cárdenas, D.; Miranda, M.T.; Ureña, N.; Piñar, M.I. La metodología de enseñanza en los deportes de equipo. Revista de Investigación en Educación 2010, 7, 91–103. [Google Scholar]
- Oslin, J.; Mitchell, S. Game-centered approaches to teaching physical education. In Handbook of Physical Education; Kirk, D., MacDonald, D., O’Sullivan, M., Eds.; Sage: London, UK, 2006; pp. 627–651. [Google Scholar]
- Light, R.L.; Harvey, S.; Mouchet, A. Improving ‘at-action’ decision-making in team sports through a holistic coaching approach. Sport Educ. Soc. 2014, 19, 258–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, S.; Fairclough, S. Observational analysis of student activity modes, lesson contexts and teacher interactions during games classes in high school (11–16 years) physical education. Eur. Phys. Educ. Rev. 2011, 17, 255–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, J.I.; McCahan, B.J. Teaching games for understanding as a curriculum model. In Teaching Games for Understanding: Theory, Research and Practice; Butler, J.I., Griffin, L.L., Eds.; Human Kinetics: Champaign, IL, USA, 2005; pp. 33–55. [Google Scholar]
- Baena, A. Bases teóricas y didácticas de la EF escolar; Gioconda: Granada, Spain, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Light, R.L.; Kentel, J.A. Soft pedagogy. In Boys’ Bodies; Kehlen, M., Atkinson, M., Eds.; Peter Lang Publishers: Oxford, UK, 2014; pp. 133–152. [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell, S.A.; Oslin, J.L.; Griffin, L.L. Teaching Sport Concepts and Skill—A Tactical Games Approach; Human Kinetics: Champaign, IL, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Memmert, D.; Harvey, S. Identification of non-specific tactical tasks in invasion games. Phys. Educ. Sport Pedagog. 2010, 15, 287–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, L.; Harvey, S.; Savory, L.; Fairclough, S.; Kozub, S.; Kerr, C. Physical activity levels and motivational responses of boys and girls: A comparison of direct instruction and tactical games models of games teaching in physical education. Eur. Phys. Educ. Rev. 2014, 21, 93–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill-Haas, S.V.; Dawson, B.; Impellizzeri, F.M.; Coutts, A.J. Physiology of Small-Sided Games Training in Football: A Systematic Review. Sports Med. 2011, 41, 199–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koklu, Y.; Ersoz, G.; Alemdaroglu, U.; Asci, A.; Ozkan, A. Physiological responses and time-motion characteristics of 4-a-side small-sided game in young soccer players: The influence of different team formation methods. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2012, 26, 3118–3123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casamichana, D.; San Román, J.; Calleja, J.; Castellano, J. Los juegos reducidos en el entrenamiento del fútbol; Fútbol de libro. Colección Fútbol Profesional: Barcelona, España, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Clemente, F.M. Associations between wellness and internal and external load variables in two intermittent small-sided soccer games. Physiol. Behav. 2018, 197, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez-Carmona, C.D.; Gamonales, J.M.; Pino-Ortega, J.; Ibáñez, S.J. Comparative Analysis of Load Profile between Small-Sided Games and Official Matches in Youth Soccer Players. Sports 2018, 6, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas-Inda, S. Análisis de carga interna y externa de futbolistas jóvenes en juegos reducidos/Analysis of Internal and External Load in Small Games in Young Football Players. Revista Internacional de Medicina y Ciencias de la Actividad Física y del Deporte 2018, 18, 463–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rovegno, I.; Nevett, M.; Brock, S.; Babiarz, M. Teaching and learning basic invasion-game tactics in 4th grade: A descriptive study from situated and constraints theoretical perspectives. J. Teach. Phys. Educ. 2001, 20, 370–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allison, S.; Thorpe, R. A comparison of the effectiveness of two approaches to teaching games within physical education. A skills approach versus games for understanding approach. Br. J. Phys. Educ. 1997, 28, 9–13. [Google Scholar]
- García, J.A.; Ruiz, L.M. Análisis comparativo de dos modelos de intervención en el aprendizaje del balonmano. Revista de Psicología del Deporte 2003, 12, 55–66. [Google Scholar]
- Mesquita, I.; Farias, C.; Hastie, P. The impact of a hybrid Sport Education-Invasion Games Competence Model soccer unit on students’ decision making, skill execution and overall game performance. Eur. Phys. Educ. Rev. 2012, 18, 205–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Espinosa, S.; Ibáñez, S.J.; Feu, S.; Galatti, L.R. Programas de intervención para la enseñanza deportiva en el contexto escolar, PETB y PEAB: Estudio preliminar. Retos: Nuevas Tendencias en Educación Física, Deporte y Recreación 2017, 31, 107–113. [Google Scholar]
- Chatzopoulos, D.; Tsormbatzoudis, H.; Drakou, A. Combinations of technique and games approaches: Effects on game performance and motivation. J. Hum. Mov. Stud. 2006, 50, 157–170. [Google Scholar]
- Práxedes, A.; García-González, L.; Cortés, A.M.; Arroyo, M.P.M.; Domínguez, A.M. Application of an intervention program to improve tactical understanding in indoor football: A study conducted in an educational context. Movimento 2016, 22, 51–62. [Google Scholar]
- Ato, M.; López, J.J.; Benavente, A. Un sistema de clasificación de los diseños de investigación en psicología. Anales de Psicología 2013, 29, 1038–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibáñez, S.J.; Feu, S.; Cañadas, M. Sistema integral para el análisis de las tareas de entrenamiento, SIATE, en deportes de invasión. E-balonmano.com: Revista de Ciencias del Deporte 2016, 12, 3–30. [Google Scholar]
- González-Víllora, S.; Gutiérrez, D.; Pastor-Vicedo, J.C.; Fernández, J.G. Análisis funcional de los deportes de invasión: Importancia del subsistema técnico-táctico en el juego. Concreción en el fútbol. Retos: Nuevas Tendencias en Educación Física, Deporte y Recreación 2007, 12, 18–28. [Google Scholar]
- Sáenz-López, P. La Educación Física y su Didáctica. Manual para el profesor; Wanceulen: Sevilla, Spain, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Ibáñez, S.J. Planificación de una temporada en la iniciación al baloncesto. In Táctica y técnica en la iniciación al baloncesto; Ortega, G., Jiménez, A.C., Eds.; Wanceulen: Sevilla, Spain, 2009; pp. 69–99. [Google Scholar]
- Aiken, L.R. Three coefficients for analyzing the reliability and validity of ratings. Educ. Psychol. Meas. 1985, 45, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cronbach, L.J. Essentials of Psychological Testing, 5th ed.; Harper & Row: New York, NY, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, C.; Wragg, C. Data Analysis and Research for Sport and Exercise Science. A Student Guide; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Field, A. Discovering Statistics Using SPSS; Sage publications: London, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Cubo, S.; Martín, B.; Ramos, J.L. Métodos de investigación y análisis de datos en ciencias sociales y de la salud; Pirámide: Madrid, Spain, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, J. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences (2a ed.); Erlbaum: Hillsdale, NJ, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Pardo, A.; Ruiz, M.A. Análisis de datos con SPSS 13 Base; McGraw Hill: Madrid, Spain, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Crewson, P. Applied Statistics Handbook. Version 1.2; AcaStat Software: Leesburg, VA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Cañadas, M.; Ibáñez, S.J.; García, J.; Parejo, I.; Feu, S. Estudio de las fases de juego a través del análisis del entrenamiento deportivo en categoría minibasket. Cuadernos de Psicología del Deporte 2012, 12, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abad, M.T.; Benito, P.J.; Giménez, F.J.; Robles, J. Fundamentos pedagógicos de la enseñanza comprensiva del deporte: Una revisión de la literatura. Cultura, Ciencia y Deporte 2013, 23, 137–146. [Google Scholar]
- Metzler, M.W. Instructional Models for Physical Education; Holocomb Hathaway: Scottsdale, AZ, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, A. Games Centered Approaches in Teaching Children & Adolescents: Systematic Review of Associated Student Outcomes. J. Teach. Phys. Educ. 2015, 34, 36–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Muñoz, J.; Yagüe, S.; Sánchez-Sánchez, J.M. El proceso de enseñanza-aprendizaje de los deportes colectivos; Wanceulen: Sevilla, Spain, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- González-Víllora, S.; García-López, L.M.; Contreras-Jordán, O.R. Evolución de la toma de decisiones y la habilidad técnica en fútbol/Decision making and skill development in youth football players. Revista Internacional de Medicina y Ciencias de la Actividad Fisica y del Deporte 2015, 15, 467–487. [Google Scholar]
- González-Víllora, S. Revisión sobre la formación específica en fútbol: Programaciones de enseñanza-aprendizaje desde la perspectiva vertical. Train. Fútbol 2009, 156, 26–46. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, A.; Martin, R.; Sun, H.C.; Ennis, C.D. Is in-class physical activity at risk in constructivist physical education? Res. Q. Exerc. Sport 2007, 78, 500–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguilar, M.; Botelho, G.; Lago, C.; Maçãs, V.; Sampaio, J. A Review on the Effects of Soccer Small-Sided Games. J. Hum. Kinet. 2012, 33, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casamichana, D.; Castellano, J. Time-motion, heart rate, perceptual and motor behaviour demands in small-sides soccer games: Effects of pitch size. J. Sports Sci. 2010, 28, 1615–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, D.A.; Drust, B. The effect of pitch dimensions on heart rate responses and technical demands of small-sided soccer games in elite players. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2009, 12, 475–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owen, A.L.; Wong, D.P.; Paul, D.; Dellal, A. Physical and Technical Comparisons between Various-Sided Games within Professional Soccer. Int. J. Sports Med. 2014, 35, 286–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rampinini, E.; Impellizzeri, F.M.; Castagna, C.; Abt, G.; Chamari, K.; Sassi, A.; Marcora, S.M. Factors influencing physiological responses to small-sided soccer games. J. Sports Sci. 2007, 25, 659–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rábano Muñoz, A.; Torres-Pacheco, M.; Asián-Clemente, J.A. Carga externa e interna de tres formatos de juegos reducidos basados en la periodización táctica. Revista de Preparación Física en el Fútbol 2017, 23, 40–50. [Google Scholar]
- Gracia, F.; García, J.; Cañadas, M.; Ibáñez, S.J. Heart rate differences in small sided games in formative basketball. E-balonmano.com: J. Sport Sci. 2014, 10, 23–30. [Google Scholar]
- Reina, M.; Mancha, D.; Feu, S.; Ibáñez, S.J. ¿Se entrena cómo se compite? Análisis de la carga en baloncesto femenino. Revista de Psicología del Deporte 2017, 26, 9–13. [Google Scholar]
- Lima, C.O.; Matías, C.J.; Greco, P.J. O conhecimento tático produto de métodos de ensino combinados e aplicados em sequências inversas no voleibol. Revista Brasileira de Educação Física e Esporte 2012, 26, 129–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serra, J.; García-López, L.M.; Sánchez-Mora, D. El juego modificado, recurso metodológico en el fútbol de iniciación. Retos: Nuevas Tendencias en Educación Física, Deporte y Recreación 2011, 20, 37–42. [Google Scholar]
- Chatzipanteli, A.; Digelidis, N.; Karatzoglidis, C.; Dean, R. A tactical-game approach and enhancement of metacognitive behaviour in elementary school students. Phys. Educ. Sport Pedagog. 2014, 21, 169–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sans, A.; Frattarola, C. Manual para la organización y el entrenamiento en las escuelas de fútbol; Paidotribo: Barcelona, Spain, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Stolz, S.; Pill, S. Teaching games and sport for understanding: Exploring and reconsidering its relevance in physical education. Eur. Phys. Educ. Rev. 2014, 20, 36–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacheco, R. La enseñanza y entrenamiento del fútbol 7. Un juego de iniciación al fútbol 11; Paidotribo: Barcelona, Spain, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, R.J.A.; Marshall, S.; Peters, D.M. Can we play a game now? The intrinsic value of TGfU. Eur. J. Phys. Health Educ. 2010, 4, 57–63. [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong, N.; Welsman, J.R. The physical activity patterns of European youth with reference to methods of assessment. Sports Med. 2006, 36, 1067–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harvey, S.; Song, Y.; Baek, J.-H.; van der Mars, H. Two sides of the same coin: Student physical activity levels during a game-centred soccer unit. Eur. Phys. Educ. Rev. 2016, 22, 411–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, A.; Christensen, E.; Eather, N.; Gray, S.; Sproule, J.; Keay, J.; Lubans, D. Can physical education and physical activity outcomes be developed simultaneously using a game-centered approach? Eur. Phys. Educ. Rev. 2016, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, S.; Pill, S. Comparisons of Academic Researchers’ and Physical Education Teachers’ Perspectives on the Utilization of the Tactical Games Model. J. Teach. Phys. Educ. 2016, 35, 313–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, S.; Pill, S. Comparison of Researchers and Physical Education Teachers’ Perspectives on the Utilization of the Tactical Games Model. Res. Q. Exerc. Sport 2016, 87, S88–S89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Pedagogical Variables | Description |
| GS | Groups of players that the teachers and coaches design for each of the tasks (e.g. 2 × 1; 2 being the number of attackers and 1 the number of defenders). |
| POG | Presence of goalkeeper in the task. |
| GP | Game phase on which the task objective is mainly focused. |
| CONT-G | The contents (attack and defence) are grouped in individual, group and team contents, as well as tactical behaviours and technical moves. |
| CONT-S | Specific contents for each sports discipline. |
| TM | Sports motor activities that serve to develop technical and tactical contents. |
| LO | Level of opposition in the task design. |
| eTL Variables | Description |
| DO | Degree of opposition based on the number of opponents in the task. |
| DT | Indicates subjectively the intensity with which the task is developed. |
| PSP | Indicates the level of participation of the players during the task. |
| CL | Refers to the emotional and psychological load that the players bear when they have to carry out a task under pressure to achieve a result. |
| GS | The space in which the players have to carry out the proposed tasks. |
| CI | Refers to the tactical load, i.e. the attention that the player has to give to team mates and opponents. |
| eTL task load | Obtained by adding the value assigned to each of the six eTL variables (1 to 5 points). GO + DT + PES + CC + EJ + IC=quantification of eTL. |
| eTL × Time | Calculated by multiplying eTL by the useful time that the players have been practising measured in seconds. |
| DIS | |||||||||||
| S1 | S2 | S3 | S4 | S5 | S6 | S7 | S8 | S9 | S10 | S11 | S12 |
| DI10 | DI8 | DI10 | DI12 | DI15 | DI16 | DI19 | DI24 | DI26 | DI26 | DI28 | DI29 |
| DI3 | DI7 | DI9 | DI11 | DI14 | DI15 | DI18 | DI23 | DI25 | DI25 | DI27 | DI28 |
| DI2 | DI6 | DI8 | DI8 | DI13 | DI12 | DI17 | DI22 | DI24 | DI23 | DI20 | DI27 |
| DI1 | DI5 | DI2 | DI5 | DI5 | DI11 | DI16 | DI21 | DI21 | DI22 | DI4 | DI20 |
| TGAS | |||||||||||
| S1 | S2 | S3 | S4 | S5 | S6 | S7 | S8 | S9 | S10 | S11 | S12 |
| TG1 | TG5 | TG2 | TG6 | TG6 | TG11 | TG4 | TG21 | TG23 | TG22 | TG19 | TG20 |
| TG2 | TG6 | TG8 | TG7 | TG13 | TG12 | TG17 | TG22 | TG24 | TG23 | TG20 | TG27 |
| TG3 | TG7 | TG9 | TG11 | TG14 | TG13 | TG18 | TG23 | TG25 | TG25 | TG27 | TG28 |
| TG4 | TG8 | TG10 | TG12 | TG15 | TG16 | TG19 | TG24 | TG26 | TG26 | TG28 | TG29 |
| Variable | Category | DIS | TGAS | ||||||
| n | % | ASR | n | % | ASR | ||||
| GS | 0 vs. 1 | 1 | 3.4 | 1.0 | 0 | 0 | −1.0 | ||
| 1 vs. 0 | 8 | 27.6 | 3.0 | * | 0 | 0 | −3.0 | * | |
| 1 vs. 1 | 6 | 20.7 | −1.2 | 10 | 34.5 | 1.2 | |||
| 2 vs. 0 | 7 | 24.1 | 2.8 | * | 0 | 0 | −2.8 | * | |
| 2 vs. 1 | 2 | 6.9 | −0.5 | 3 | 10.3 | 0.5 | |||
| 2 vs. 2 | 1 | 3.4 | 0.0 | 1 | 3.4 | 0.0 | |||
| 3 vs. 0 | 1 | 3.4 | 1.0 | 0 | 0 | −1.0 | |||
| 3 vs. 1 | 0 | 0 | −1.0 | 1 | 3.4 | 1.0 | |||
| 3 vs. 2 | 0 | 0 | −1.8 | 3 | 10.3 | 1.8 | |||
| 4 vs. 2 | 0 | 0 | −1.0 | 1 | 3.4 | 1.0 | |||
| 4 vs. 4 | 0 | 0 | −1.0 | 1 | 3.4 | 1.0 | |||
| 5 vs. 1 | 0 | 0 | −1.0 | 1 | 3.4 | 1.0 | |||
| 5 vs. 4 | 0 | 0 | −1.8 | 3 | 10.3 | 1.8 | |||
| 5 vs. 5 | 1 | 3.4 | 0.0 | 1 | 3.4 | 0.0 | |||
| N vs. N | 1 | 3.4 | 0.0 | 1 | 3.4 | 0.0 | |||
| 1 vs. Large group | 1 | 3.4 | −0.6 | 2 | 6.9 | 0.6 | |||
| Combined situation | 0 | 0 | −1.0 | 1 | 3.4 | 1.0 | |||
| POG | With goalkeeper | 1 | 3.4 | 1.0 | 0 | 0 | −1.0 | ||
| Without goalkeeper | 28 | 96.6 | −1.0 | 29 | 100 | 1.0 | |||
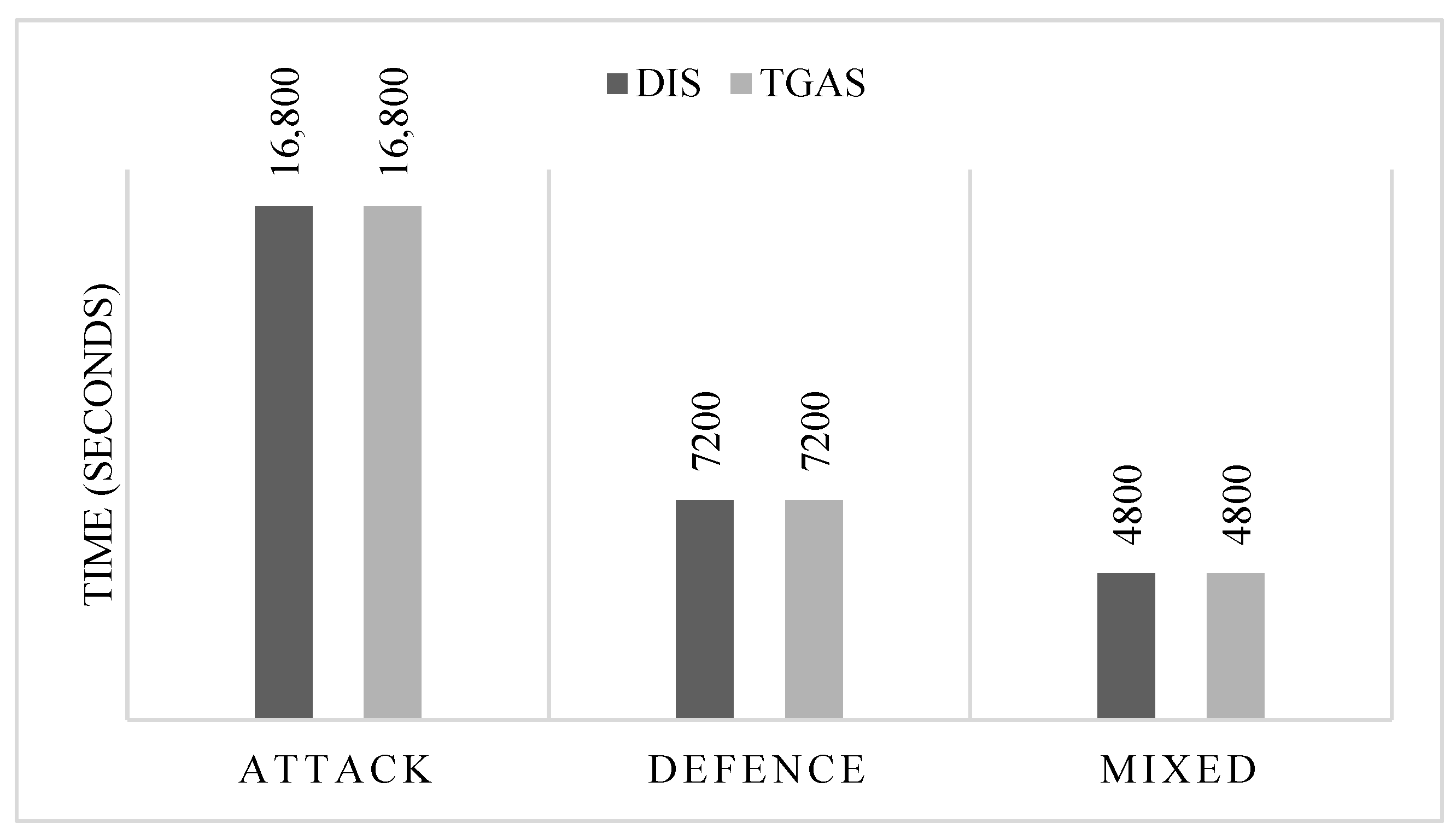
| GP | Attack | 19 | 65.5 | 0.0 | 19 | 65.5 | 0.0 | ||
| Defence | 6 | 20.7 | 0.0 | 6 | 20.7 | 0.0 | |||
| Mixed | 4 | 13.8 | 0.0 | 4 | 13.8 | 0.0 | |||
| CONT-G | AITTB | 1 | 3.4 | −3.2 | * | 11 | 37.9 | 3.2 | * |
| DITTB | 0 | 0 | −2.1 | * | 4 | 13.8 | 2.1 | * | |
| AITTM | 10 | 34.5 | 3.5 | * | 0 | 0 | −3.5 | * | |
| DITTM | 6 | 20.7 | 2.6 | * | 0 | 0 | −2.6 | * | |
| AGTTB | 3 | 10.3 | −1.4 | 7 | 24.1 | 1.4 | |||
| DGTTB | 0 | 0 | −1.4 | 2 | 6.9 | 1.4 | |||
| AGTTM | 8 | 27.6 | 3.0 | * | 0 | 0 | −3.0 | * | |
| ATTTB | 1 | 3.4 | −1.7 | 5 | 17.2 | 1.7 | |||
| CONT-G 2 1 | CTTID | 2 | 6.9 | 1.6 | 0 | 0 | −1.6 | ||
| CTTGD | 1 | 3.4 | −1.4 | 3 | 10.3 | 1.4 | |||
| CTTED | 1 | 3.4 | 0.0 | 1 | 3.4 | 0.0 | |||
| CONT-S | Pass-control | 5 | 17.2 | 0.4 | 4 | 13.8 | −0.4 | ||
| Ball control: progression | 2 | 6.9 | −0.5 | 3 | 10.3 | 0.5 | |||
| Ball control: protection | 2 | 6.9 | 0.0 | 2 | 6.9 | 0.0 | |||
| Progression with support | 1 | 3.4 | 0.0 | 1 | 3.4 | 0.0 | |||
| Shot at goal | 2 | 6.9 | 1.4 | 0 | 0 | −1.4 | |||
| Progression to shoot at goal | 1 | 3.4 | −1.0 | 3 | 10.3 | 1.0 | |||
| Progression through passes to score at goal | 3 | 10.3 | 0.0 | 3 | 10.3 | 0.0 | |||
| Dribbling on the run | 2 | 6.9 | 0.0 | 2 | 6.9 | 0.0 | |||
| Dribbling past opponent to shoot | 1 | 3.4 | 0.0 | 1 | 3.4 | 0.0 | |||
| Interception: Shot at goal or approach | 2 | 6.9 | 0.0 | 2 | 6.9 | 0.0 | |||
| Interception: passes between opponents | 4 | 13.8 | 0.0 | 4 | 13.8 | 0.0 | |||
| Situations played: attack and defence | 4 | 13.8 | 0.0 | 4 | 13.8 | 0.0 | |||
| TM | SPE | 12 | 41.4 | 3.9 | * | 0 | 0 | −3.9 | * |
| CPE | 5 | 17.2 | 2.3 | * | 0 | 0 | −2.3 | * | |
| SNSG | 1 | 3.4 | −0.6 | 2 | 6.9 | 0.6 | |||
| SSG | 10 | 34.5 | −1.6 | 16 | 55.2 | 1.6 | |||
| CSG | 0 | 0 | −3.5 | * | 10 | 34.5 | 3.5 | * | |
| Adapted sport/SSG | 1 | 3.4 | 0.0 | 1 | 3.4 | 0.0 | |||
| LO | Without opposition | 10 | 34.5 | 3.0 | * | 1 | 3.4 | −3.0 | * |
| Static obstacles | 7 | 24.1 | 2.8 | * | 0 | 0 | −2.8 | * | |
| Dynamic obstacles | 2 | 6.9 | 1.4 | 0 | 0 | −1.4 | |||
| With opposition | 10 | 34.5 | −5.0 | * | 28 | 96.6 | 5.0 | * | |
| Variable | Category | DIS | TGAS | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | % | ASR | n | % | ASR | ||||
| DO | Without opposition | 18 | 62.1 | 5.1 | * | 0 | 0 | −5.1 | * |
| Numerical superiority of 3 or + students | 1 | 3.4 | −1.0 | 3 | 10.3 | 1.0 | |||
| Numerical superiority of 2 students | 0 | 0 | −1.4 | 2 | 6.9 | 1.4 | |||
| Numerical superiority of 1 student | 2 | 6.9 | −2.3 | * | 9 | 31.0 | 2.3 | * | |
| Numerical equality | 8 | 27.6 | −1.9 | 15 | 51.7 | 1.9 | |||
| DT | Walking | 5 | 17.2 | 2.3 | * | 0 | 0 | −2.3 | * |
| Gentle pace | 13 | 44.8 | 4.1 | * | 0 | 0 | −4.1 | * | |
| Intensity with rest | 8 | 27.6 | −1.9 | 15 | 51.7 | 1.9 | |||
| Intensity without rest | 2 | 6.9 | −3.1 | * | 12 | 41.4 | 3.1 | * | |
| High intensity without rest | 1 | 3.4 | −0.6 | 2 | 6.9 | 0.6 | |||
| PSP | <20% | 10 | 34.5 | 1.5 | 5 | 17.2 | −1.5 | ||
| 21–40% | 4 | 13.8 | −0.4 | 5 | 17.2 | 0.4 | |||
| 41–60% | 0 | 0 | −1.0 | 1 | 3.4 | 1.0 | |||
| 61–80% | 0 | 0 | - | 0 | 0 | - | |||
| >81% | 15 | 51.7 | −0.8 | 18 | 62.1 | 0.8 | |||
| CL | Activity in technical moves | 19 | 65.5 | 5.3 | * | 0 | 0 | −5.3 | * |
| Opposition not counted | 9 | 31.0 | −3.2 | * | 21 | 72.4 | 3.2 | * | |
| Opposition counted | 0 | 0 | −2.8 | * | 7 | 24.1 | 2.8 | * | |
| Matches of all kinds | 1 | 3.4 | 0.0 | 1 | 3.4 | 0.0 | |||
| GS | Static activity | 5 | 17.2 | 1.7 | 1 | 3.4 | −1.7 | ||
| Small spaces | 16 | 55.2 | 0.0 | 16 | 55.2 | 0.0 | |||
| Medium spaces | 7 | 24.1 | −1.1 | 11 | 37.9 | 1.1 | |||
| Large spaces | 1 | 3.4 | 1.0 | 0 | 0 | −1.0 | |||
| Repetition of spaces | 0 | 0 | −1.0 | 1 | 3.4 | 1.0 | |||
| CI | Individual intervention | 10 | 34.5 | 3.5 | * | 0 | 0 | −3.5 | * |
| Intervention of 2 students | 16 | 55.2 | 0.0 | 16 | 55.2 | 0.0 | |||
| Intervention of 3 students | 1 | 3.4 | −1.7 | 5 | 17.2 | 1.7 | |||
| Intervention of 4 students | 0 | 0 | −1.4 | 2 | 6.9 | 1.4 | |||
| Intervention of all the students | 2 | 6.9 | −1.5 | 6 | 20.7 | 1.5 | |||
| Variable | IP | M ± DT | min | max |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| eTL | DIS | 14.34 ± 5.01 | 8 | 28 |
| TGAS | 20.21 ± 3.72 | 16 | 28 | |
| eTL × Time | DIS | 6885.52 ± 2404.37 | 3840.00 | 13,440.00 |
| TGAS | 9699.31 ± 1783.95 | 7680.00 | 13,440.00 |
| Variable | IP | M ± DT | x2 | gl | p | VC | p | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GS | DIS | 27.25 ± 19.15 | 29.533 | 16 | 0.021 | * | 0.714 | 0.021 | * |
| TGAS | 38.25 ± 14.34 | ||||||||
| POG1 | DIS | 1.96 ± 1.86 | 1.018 | 1 | 0.313 | 0.132 | 0.313 | ||
| TGAS | 2.00 ± 0.00 | ||||||||
| GP | DIS | 1.48 ± 0.74 | 0.000 | 2 | 1.000 | 0.000 | 1.000 | ||
| TGAS | 1.48 ± 0.74 | ||||||||
| CONT-G | DIS | 5.00 ± 3.27 | 42.600 | 7 | 0.000 | * | 0.857 | 0.000 | * |
| TGAS | 6.00 ± 2.00 | ||||||||
| CONT-G 22 | DIS | 5.00 ± 3.83 | 3.000 | 2 | 0.223 | 0.612 | 0.223 | ||
| TGAS | 7.00 ± 2.00 | ||||||||
| CONT-S3 | DIS | - | 5.311 | 13 | 0.968 | 0.303 | 0.968 | ||
| TGAS | - | ||||||||
| TM | DIS | 4.75 ± 1.50 | 28.718 | 5 | 0.000 | * | 0.704 | 0.000 | * |
| TGAS | 5.75 ± 1.26 | ||||||||
| LO | DIS | 2.76 ± 1.74 | 24.890 | 3 | 0.000 | * | 0.655 | 0.000 | * |
| TGAS | 4.86 ± 0.74 |
| Variable | IP | M ± DT | U | p | d | VC | p | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DO | DIS | 2.34 ± 1.84 | 192.500 | 0.000 | * | 1.052 | 0.690 | 0.000 | * |
| TGAS | 4.24 ± 0.99 | ||||||||
| DT | DIS | 2.34 ± 0.97 | 130.000 | 0.000 | * | 1.474 | 0.690 | 0.000 | * |
| TGAS | 3.55 ± 0.63 | ||||||||
| PSP | DIS | 3.21 ± 1.92 | 355.000 | 0.253 | 0.270 | 0.229 | 0.384 | ||
| TGAS | 3.72 ± 1.71 | ||||||||
| CL | DIS | 2.41 ± 0.68 | 123.000 | 0.000 | * | 1.530 | 0.729 | 0.000 | * |
| TGAS | 3.31 ± 0.54 | ||||||||
| GS | DIS | 2.14 ± 0.74 | 332.000 | 0.124 | 0.367 | 0.309 | 0.235 | ||
| TGAS | 2.45 ± 0.74 | ||||||||
| CI | DIS | 1.90 ± 1.01 | 198.500 | 0.000 | * | 1.017 | 0.536 | 0.002 | * |
| TGAS | 2.93 ± 1.22 | ||||||||
| eTL | DIS | 14.34 ± 5.01 | 145.500 | 0.000 | * | 1.357 | 0.793 | 0.004 | * |
| TGAS | 20.21 ± 3.72 | ||||||||
| eTL × Time | DIS | 6885.52 ± 2404.37 | 145.500 | 0.000 | * | 1.357 | 0.793 | 0.004 | * |
| TGAS | 9699.31 ± 1783.95 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
García-Ceberino, J.M.; Feu, S.; Ibáñez, S.J. Comparative Study of Two Intervention Programmes for Teaching Soccer to School-Age Students. Sports 2019, 7, 74. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports7030074
García-Ceberino JM, Feu S, Ibáñez SJ. Comparative Study of Two Intervention Programmes for Teaching Soccer to School-Age Students. Sports. 2019; 7(3):74. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports7030074
Chicago/Turabian StyleGarcía-Ceberino, Juan M., Sebastián Feu, and Sergio J. Ibáñez. 2019. "Comparative Study of Two Intervention Programmes for Teaching Soccer to School-Age Students" Sports 7, no. 3: 74. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports7030074
APA StyleGarcía-Ceberino, J. M., Feu, S., & Ibáñez, S. J. (2019). Comparative Study of Two Intervention Programmes for Teaching Soccer to School-Age Students. Sports, 7(3), 74. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports7030074







