Off-Training Levels of Physical Activity and Sedentary Behavior in Young Athletes: Preliminary Results during a Typical Week
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Protocol
2.3. Measures
2.4. Data Analysis
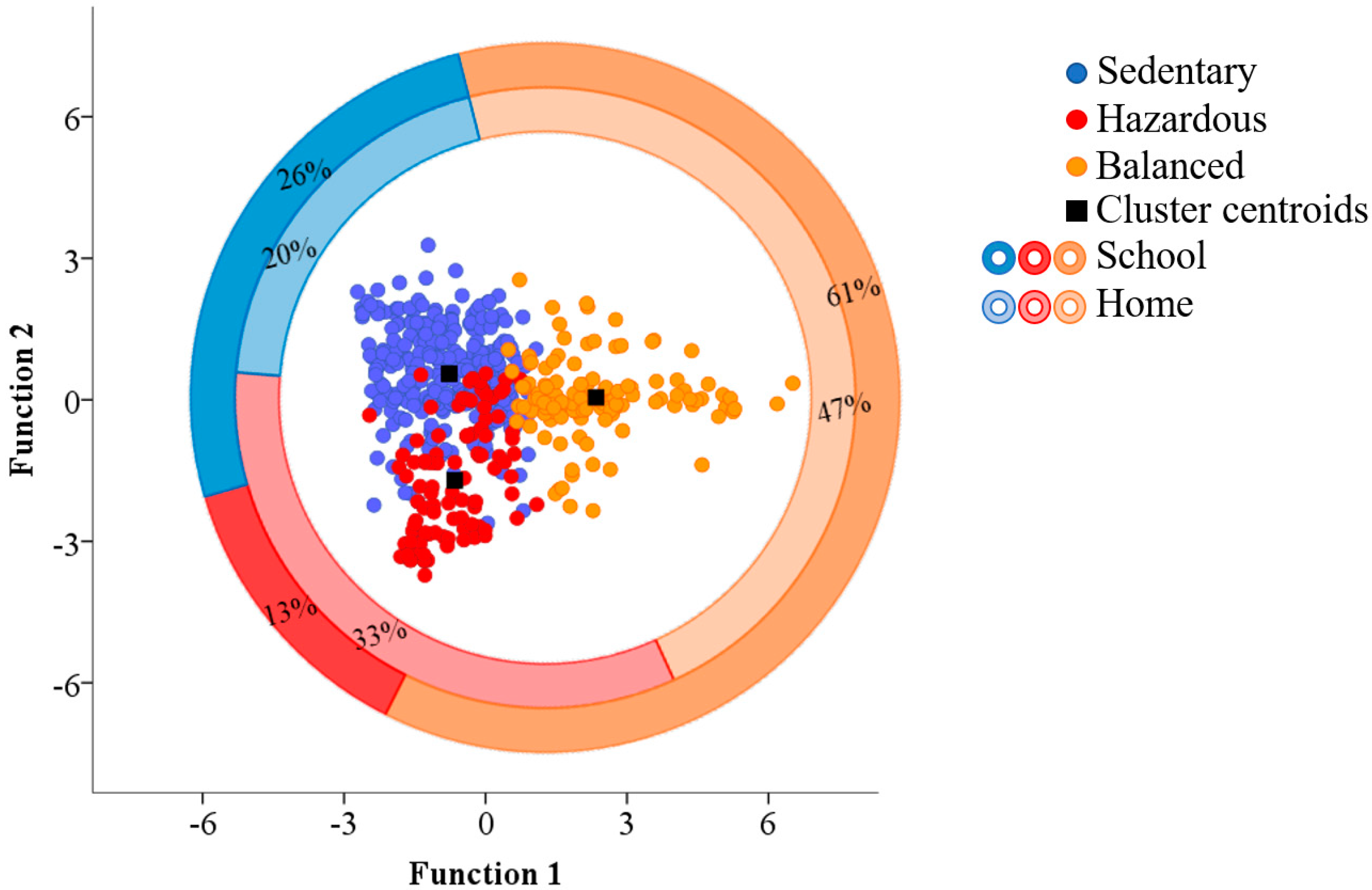
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Judice, P.B.; Silva, A.M.; Berria, J.; Petroski, E.L.; Ekelund, U.; Sardinha, L.B. Sedentary patterns, physical activity and health-related physical fitness in youth: A cross-sectional study. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2017, 14, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joensuu, L.; Syvaoja, H.; Kallio, J.; Kulmala, J.; Kujala, U.M.; Tammelin, T.H. Objectively measured physical activity, body composition and physical fitness: Cross-sectional associations in 9 to15 year-old children. Eur. J. Sport Sci. 2018, 18, 882–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, J.A.; Byun, W. Sedentary Behavior and Health Outcomes in Children and Adolescents. Am. J. Lifestyle Med. 2013, 8, 173–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, A.; Cooper, A.R.; Stamatakis, E.; Foster, L.J.; Crowne, E.C.; Sabin, M.; Shield, J.P. Physical activity patterns in nonobese and obese children assessed using minute-by-minute accelerometry. Int. J. Obes. 2005, 29, 1070–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godakanda, I.; Abeysena, C.; Lokubalasooriya, A. Sedentary behavior during leisure time, physical activity and dietary habits as risk factors of overweight among school children aged 14–15 years: Case control study. BMC Res. Notes 2018, 11, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steele, R.M.; van Sluijs, E.M.; Sharp, S.J.; Landsbaugh, J.R.; Ekelund, U.; Griffin, S.J. An investigation of patterns of children′s sedentary and vigorous physical activity throughout the week. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2010, 7, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ridgers, N.D.; Barnett, L.M.; Lubans, D.R.; Timperio, A.; Cerin, E.; Salmon, J. Potential moderators of day-to-day variability in children’s physical activity patterns. J. Sports Sci. 2018, 36, 637–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O′Donoghue, G.; Kennedy, A.; Puggina, A.; Aleksovska, K.; Buck, C.; Burns, C.; Cardon, G.; Carlin, A.; Ciarapica, D.; Colotto, M.; et al. Socio-economic determinants of physical activity across the life course: A “DEterminants of DIet and Physical ACtivity” (DEDIPAC) umbrella literature review. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0190737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Global Status Report on Noncommunicable Diseases 2010; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Craft, L.L.; Zderic, T.W.; Gapstur, S.M.; Vaniterson, E.H.; Thomas, D.M.; Siddique, J.; Hamilton, M.T. Evidence that women meeting physical activity guidelines do not sit less: An observational inclinometry study. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2012, 9, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Judice, P.B.; Silva, A.M.; Magalhaes, J.P.; Matias, C.N.; Sardinha, L.B. Sedentary behaviour and adiposity in elite athletes. J. Sports Sci. 2014, 32, 1760–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thorp, A.A.; Owen, N.; Neuhaus, M.; Dunstan, D.W. Sedentary behaviors and subsequent health outcomes in adults a systematic review of longitudinal studies, 1996–2011. Am. J. Prev. Med. 2011, 41, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armstrong, N. Young people are fit and active—Fact or fiction? J. Sport Health Sci. 2012, 1, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gidlow, C.J.; Cochrane, T.; Davey, R.; Smith, H. In-school and out-of-school physical activity in primary and secondary school children. J. Sports Sci. 2008, 26, 1411–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arundell, L.; Fletcher, E.; Salmon, J.; Veitch, J.; Hinkley, T. A systematic review of the prevalence of sedentary behavior during the after-school period among children aged 5–18 years. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2016, 13, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winsley, R.; Matos, N. Overtraining and elite young athletes. Med. Sport Sci. 2011, 56, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiler, R.; Aggio, D.; Hamer, M.; Taylor, T.; Kumar, B. Sedentary behaviour among elite professional footballers: Health and performance implications. BMJ Open Sport Exerc. Med. 2015, 1, e000023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sperlich, B.; Becker, M.; Hotho, A.; Wallmann-Sperlich, B.; Sareban, M.; Winkert, K.; Steinacker, J.M.; Treff, G. Sedentary Behavior among National Elite Rowers during Off-Training—A Pilot Study. Front. Physiol. 2017, 8, 655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venter, R.E. Perceptions of team athletes on the importance of recovery modalities. Eur. J. Sport Sci. 2014, 14 (Suppl. 1), S69–S76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourdon, P.C.; Cardinale, M.; Murray, A.; Gastin, P.; Kellmann, M.; Varley, M.C.; Gabbett, T.J.; Coutts, A.J.; Burgess, D.J.; Gregson, W.; et al. Monitoring Athlete Training Loads: Consensus Statement. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2017, 12, S2161–S2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monroe, C.M. Valuable steps ahead: Promoting physical activity with wearables and incentives. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2016, 4, 960–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balsalobre-Fernández, C.; Marchante, D.; Baz-Valle, E.; Alonso-Molero, I.; Jiménez, S.L.; Muñóz-López, M. Analysis of Wearable and Smartphone-Based Technologies for the Measurement of Barbell Velocity in Different Resistance Training Exercises. Front. Physiol. 2017, 8, 649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabbett, T.J.; Nassis, G.P.; Oetter, E.; Pretorius, J.; Johnston, N.; Medina, D.; Rodas, G.; Myslinski, T.; Howells, D.; Beard, A.; et al. The athlete monitoring cycle: A practical guide to interpreting and applying training monitoring data. Br. J. Sports Med. 2017, 51, 1451–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fagherazzi, G.; El Fatouhi, D.; Bellicha, A.; El Gareh, A.; Affret, A.; Dow, C.; Delrieu, L.; Vegreville, M.; Normand, A.; Oppert, J.-M.; et al. An International Study on the Determinants of Poor Sleep amongst 15,000 Users of Connected Devices. J. Med. Internet Res. 2017, 19, e363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrington, D.M.; Edwardson, C.L.; Henson, J.; Khunti, K.; Yates, T.; Davies, M.J. Moderate to vigorous physical activity, not sedentary time, is associated with total and regional adiposity in a sample of UK adults at risk of type 2 diabetes. Physiol. Meas. 2016, 37, 1862–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Exel, J.; Abrantes, C.; Gonçalves, B.; Mateus, N.; Sampaio, J. Different familiarity with running routes changes the complexity of kinematic and physiological responses: A pilot study on recreational middle-distance runners. In Proceedings of the Complex Systems in Sport, International Congress: Linking Theory and Practice, Barcelona, Spain, 5–6 October 2017; pp. 104–106. [Google Scholar]
- Murray, A. Managing the Training Load in Adolescent Athletes. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2017, 12, S242–S249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, M.S.; Asch, D.A.; Volpp, K.G. Wearable devices as facilitators, not drivers, of health behavior change. JAMA 2015, 313, 459–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clemente, F.M.; Nikolaidis, P.T.; Martins, F.M.; Mendes, R.S. Weekly physical activity patterns of university students: Are athletes more active than non-athletes? SpringerPlus 2016, 5, 1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clemente, F.M.; Nikolaidis, P.T.; Martins, F.M.; Mendes, R.S. Physical Activity Patterns in University Students: Do They Follow the Public Health Guidelines? PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0152516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aadland, E.; Ylvisaker, E. Reliability of Objectively Measured Sedentary Time and Physical Activity in Adults. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0133296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kellmann, M.; Beckmann, J. Sport, Recovery and Performance: Interdisciplinary Insights; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, C.-C.; Hsu, Y.-L. A Review of Accelerometry-Based Wearable Motion Detectors for Physical Activity Monitoring. Sensors 2010, 10, 7772–7788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Troiano, R.P.; Berrigan, D.; Dodd, K.W.; Masse, L.C.; Tilert, T.; McDowell, M. Physical activity in the United States measured by accelerometer. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2008, 40, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freedson, P.S.; Melanson, E.; Sirard, J. Calibration of the Computer Science and Applications, Inc. accelerometer. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 1998, 30, 777–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romanzini, M.; Petroski, E.L.; Ohara, D.; Dourado, A.C.; Reichert, F.F. Calibration of ActiGraph GT3X, Actical and RT3 accelerometers in adolescents. Eur. J. Sport Sci. 2014, 14, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leech, N.L.; Barrett, K.C.; Morgan, G.A. Logistic Regression and Discriminant Analysis. In IBM SPSS for Intermediate Statistics: Use and Interpretation; Leech, N.L., Barrett, K.C., Morgan, G.A., Eds.; Routledge: Abingdon, UK, 2014; pp. 167–187. [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman, L.; Rousseeuw, P.J. Finding Groups in Data: An Introduction to Cluster Analysis; John Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Pearson, N.; Braithwaite, R.E.; Biddle, S.J.; van Sluijs, E.M.; Atkin, A.J. Associations between sedentary behaviour and physical activity in children and adolescents: A meta-analysis. Obes. Rev. 2014, 15, 666–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swartz, A.M.; Miller, N.E.; Cho, Y.I.; Welch, W.A.; Strath, S.J. A prospective examination of the impact of high levels of exercise training on sedentary behaviour. Eur. J. Sport Sci. 2017, 17, 222–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kentta, G.; Hassmen, P. Overtraining and recovery. A conceptual model. Sports Med. 1998, 26, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Rezende, L.F.; Rodrigues Lopes, M.; Rey-Lopez, J.P.; Matsudo, V.K.; Luiz Odo, C. Sedentary behavior and health outcomes: An overview of systematic reviews. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e105620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tremblay, M. Letter to the editor: Standardized use of the terms “sedentary” and “sedentary behaviours”. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2012, 37, 540–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chau, J.Y.; Grunseit, A.C.; Chey, T.; Stamatakis, E.; Brown, W.J.; Matthews, C.E.; Bauman, A.E.; van der Ploeg, H.P. Daily Sitting Time and All-Cause Mortality: A Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ekelund, U.; Steene-Johannessen, J.; Brown, W.J.; Fagerland, M.W.; Owen, N.; Powell, K.E.; Bauman, A.; Lee, I.M.; Lancet Sedentary Behaviour Working Group. Does physical activity attenuate, or even eliminate, the detrimental association of sitting time with mortality? A harmonised meta-analysis of data from more than 1 million men and women. Lancet 2016, 388, 1302–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, B.H.; Anderssen, S.A.; Andersen, L.B.; Hildebrand, M.; Kolle, E.; Steene-Johannessen, J.; Kriemler, S.; Page, A.S.; Puder, J.J.; Reilly, J.J.; et al. Cross-Sectional Associations of Reallocating Time Between Sedentary and Active Behaviours on Cardiometabolic Risk Factors in Young People: An International Children′s Accelerometry Database (ICAD) Analysis. Sports Med. 2018, 48, 2401–2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skrede, T.; Stavnsbo, M.; Aadland, E.; Aadland, K.N.; Anderssen, S.A.; Resaland, G.K.; Ekelund, U. Moderate-to-vigorous physical activity, but not sedentary time, predicts changes in cardiometabolic risk factors in 10-year-old children: The Active Smarter Kids Study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 105, 1391–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolling, S.; Steinacker, J.M.; Endler, S.; Ferrauti, A.; Meyer, T.; Kellmann, M. The longer the better: Sleep-wake patterns during preparation of the World Rowing Junior Championships. Chronobiol. Int. 2016, 33, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tufano, J.J.; Brown, L.E.; Coburn, J.W.; Tsang, K.K.; Cazas, V.L.; LaPorta, J.W. Effect of aerobic recovery intensity on delayed-onset muscle soreness and strength. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2012, 26, 2777–2782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, R.S.; Leicht, A.S.; Bishop, D.; Barbero-Alvarez, J.C.; Nakamura, F.Y. Seasonal changes in physical performance and heart rate variability in high level futsal players. Int. J. Sports Med. 2013, 34, 424–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnold, A.; Thigpen, C.A.; Beattie, P.F.; Kissenberth, M.J.; Shanley, E. Overuse Physeal Injuries in Youth Athletes. Sports Health 2017, 9, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trilk, J.L.; Pate, R.R.; Pfeiffer, K.A.; Dowda, M.; Addy, C.L.; Ribisl, K.M.; Neumark-Sztainer, D.; Lytle, L.A. A cluster analysis of physical activity and sedentary behavior patterns in middle school girls. J. Adolesc. Health 2012, 51, 292–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammami, A.; Randers, M.B.; Kasmi, S.; Razgallah, M.; Tabka, Z.; Chamari, K.; Bouhlel, E. Effects of soccer training on health-related physical fitness measures in male adolescents. J. Sport Health Sci. 2018, 7, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herzog, W. Do recreational team sports provide fitness and health benefits? J. Sport Health Sci. 2018, 7, 127–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olds, T.; Wake, M.; Patton, G.; Ridley, K.; Waters, E.; Williams, J.; Hesketh, K. How do school-day activity patterns differ with age and gender across adolescence? J. Adolesc. Health 2009, 44, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Variables | Sedentary | Hazardous | Balanced | Totals | Function 1 | Function 2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Energy expenditure (kcals) | 22.52 [20.52–24.53] | 15.11 [12.94–17.28] | 73.48 [65.96–81.00] | 29.66 [27.33–31.99] | 0.69 * | 0.17 |
| MET | 1.06 [1.05–1.07] | 1.09 [1.06–1.12] | 1.22 [1.18–1.27] | 1.10 [1.09–1.11] | 0.32 * | −0.07 |
| Sedentary PA (min) | 37.37 [36.45–38.29] | 12.63 [11.12–14.14] | 17.20 [15.86–18.55] | 32.02 [30.93–33.10] | n/a | n/a |
| Light PA (min) | 11.43 [10.80–12.06] | 9.21 [7.22–11.19] | 13.06 [12.02–14.09] | 9.78 [9.31–10.26] | 0.10 | 0.16 * |
| Moderate PA (min) | 2.25 [2.03–2.46] | 2.31 [1.88–2.74] | 4.64 [4.15–5.13] | 2.46 [2.29–2.62] | 0.36 * | 0.01 |
| Vigorous PA (min) | 7.82 [7.23–8.41] | 6.36 [5.53–7.19] | 23.98 [22.46–25.49] | 9.99 [9.36–10.63] | 0.90 * | 0.16 |
| Total MVPA (min) | 10.07 [9.41–10.73] | 8.67 [7.64–9.70] | 28.61 [27.16–30.07] | 12.45 [11.75–13.16] | n/a | n/a |
| Step counts | 303.06 [279.05–327.06] | 210.34 [178.46–242.22] | 912.80 [843.90–981.69] | 389.00 [360.65–417.35] | 0.80 * | 0.20 |
| Standing (min) | 10.33 [9.56–11.10] | 8.26 [6.98–9.55] | 25.00 [22.95–27.04] | 11.73 [11.03–12.44] | 0.61 * | 0.15 |
| Sitting (min) | 5.24 [4.19–6.28] | 1.83 [1.06–2.60] | 2.00 [1.22–2.79] | 5.14 [4.45–5.84] | −0.11 | 0.20 * |
| Lying (min) | 37.70 [35.81–39.60] | 17.87 [14.61–21.13] | 25.59 [23.36–27.82] | 31.20 [29.88–32.51] | −0.16 | 0.56 * |
| Sedentary breaks over 30 min (min) | 47.18 [46.03–48.32] | 57.24 [56.09–58.38] | 56.57 [55.35–57.78] | 51.37 [50.52–52.20] | 0.27 | −0.51 * |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Exel, J.; Mateus, N.; Travassos, B.; Gonçalves, B.; Gomes, I.; Leite, N.; Sampaio, J. Off-Training Levels of Physical Activity and Sedentary Behavior in Young Athletes: Preliminary Results during a Typical Week. Sports 2018, 6, 141. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports6040141
Exel J, Mateus N, Travassos B, Gonçalves B, Gomes I, Leite N, Sampaio J. Off-Training Levels of Physical Activity and Sedentary Behavior in Young Athletes: Preliminary Results during a Typical Week. Sports. 2018; 6(4):141. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports6040141
Chicago/Turabian StyleExel, Juliana, Nuno Mateus, Bruno Travassos, Bruno Gonçalves, Isabel Gomes, Nuno Leite, and Jaime Sampaio. 2018. "Off-Training Levels of Physical Activity and Sedentary Behavior in Young Athletes: Preliminary Results during a Typical Week" Sports 6, no. 4: 141. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports6040141
APA StyleExel, J., Mateus, N., Travassos, B., Gonçalves, B., Gomes, I., Leite, N., & Sampaio, J. (2018). Off-Training Levels of Physical Activity and Sedentary Behavior in Young Athletes: Preliminary Results during a Typical Week. Sports, 6(4), 141. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports6040141









