Larger Countermovement Increases the Jump Height of Countermovement Jump
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects
2.2. Procedures
2.3. Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
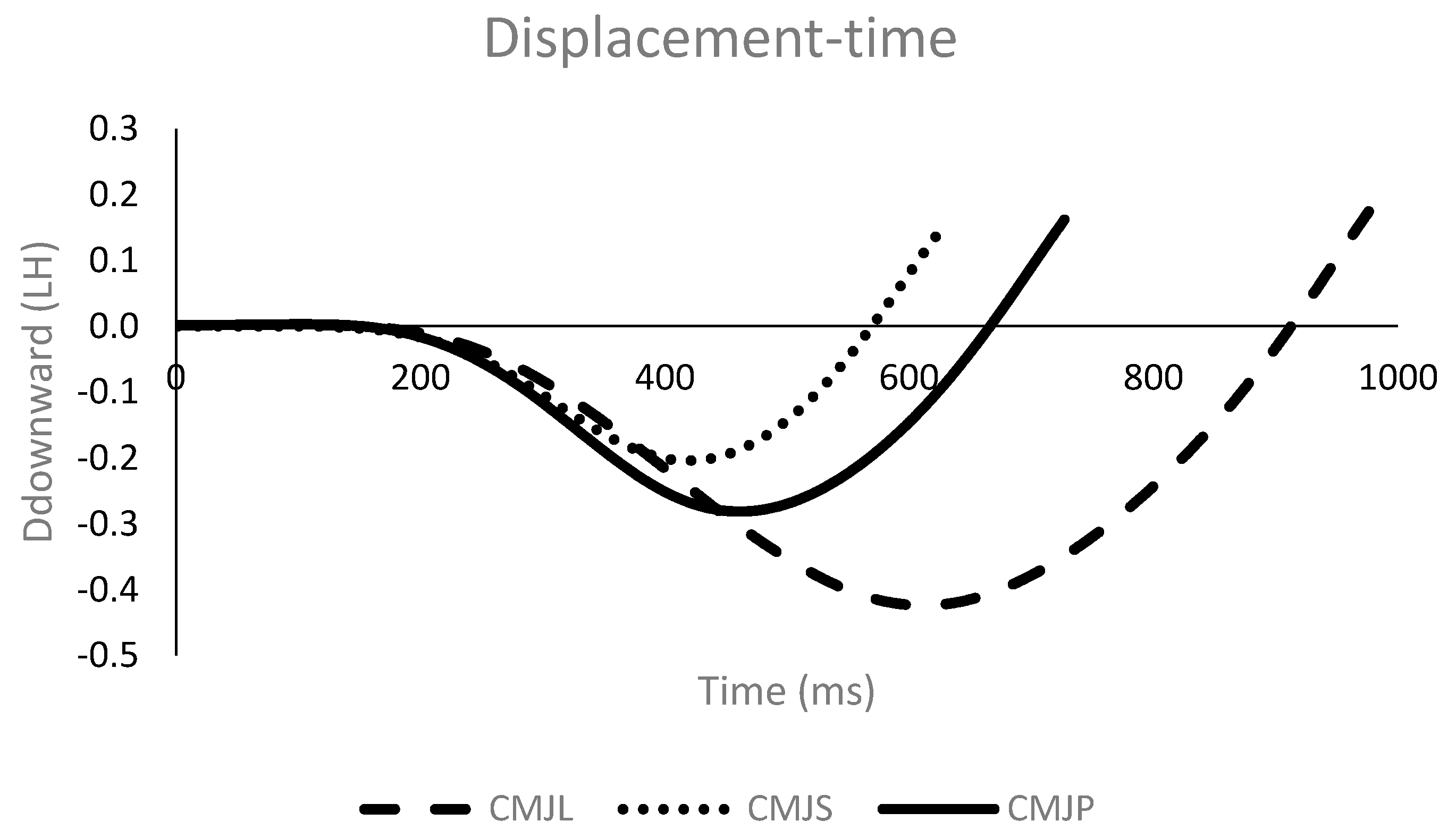
3.1. Center of Mass Displacement Variables
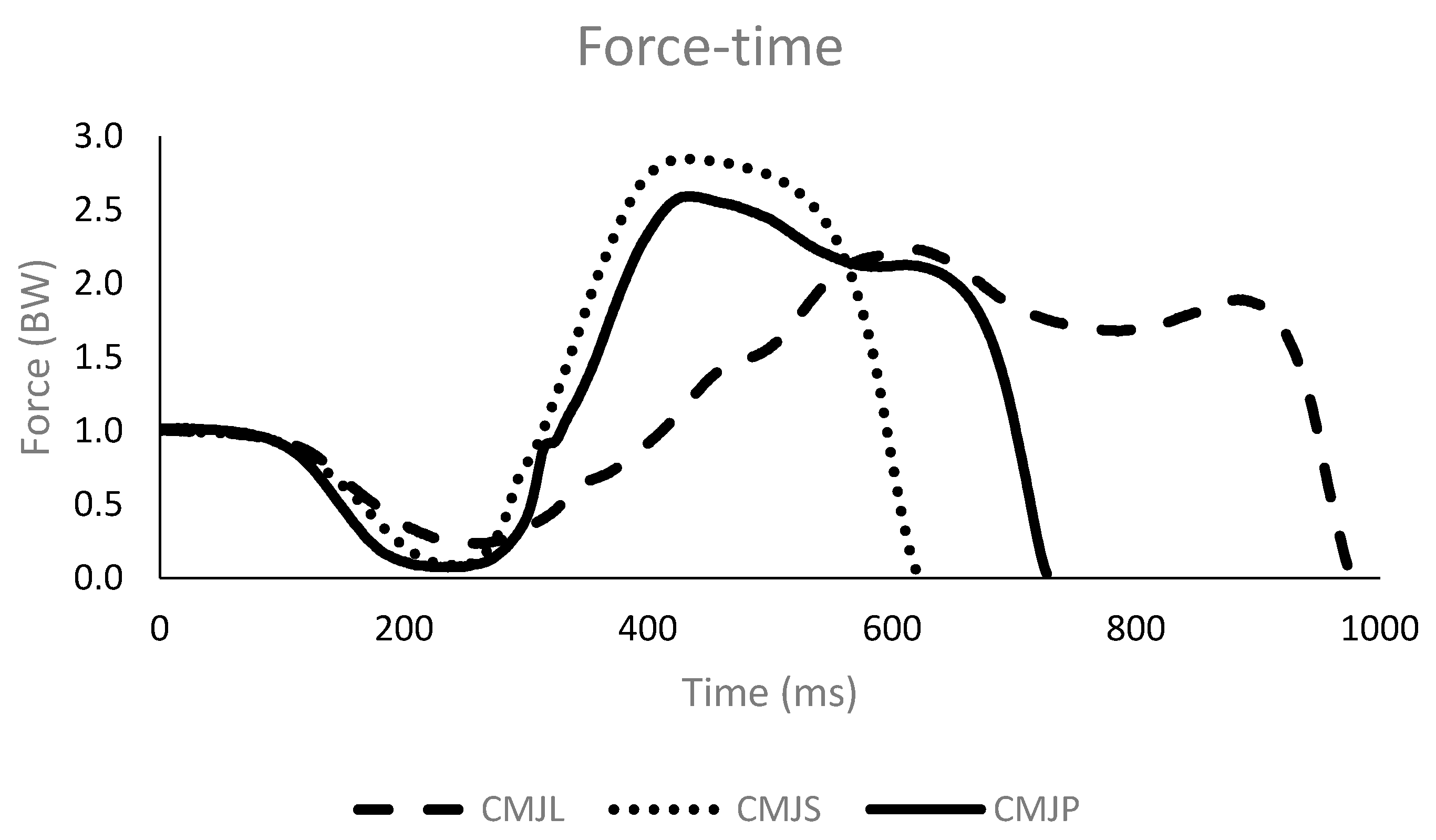
3.2. Force-Applied Variables
3.3. Velocity of Center of Mass Variables
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bobbert, M.F.; Casius, L.J.; Sijpkens, I.W.; Jaspers, R.T. Humans adjust control to initial squat depth in vertical squat jumping. J. Appl. Physiol. 2008, 105, 1428–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domire, Z.J.; Challis, J.H. The influence of squat depth on maximal vertical jump performance. J. Sports Sci. 2007, 25, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gheller, R.G.; Dal Pupo, J.; Ache-Dias, J.; Detanico, D.; Padulo, J.; Dos Santos, S.G. Effect of different knee starting angles on intersegmental coordination and performance in vertical jumps. Hum. Mov. Sci. 2015, 42, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Badillo, J.; Marques, M. Relationship between kinematic factors and countermovement jump height in trained track and field athletes. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2010, 24, 3443–3447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandic, R.; Jakovljevic, S.; Jaric, S. Effects of countermovement depth on kinematic and kinetic patterns of maximum vertical jumps. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2015, 25, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salles, A.S.; Baltzopoulos, V.; Rittweger, J. Differential effects of countermovement magnitude and volitional effort on vertical jumping. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2011, 111, 441–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirby, T.J.; McBride, J.M.; Haines, T.L.; Dayne, A.M. Relative net vertical impulse determines jumping performance. J. Appl. Biomech. 2011, 27, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McBride, J.M.; Kirby, T.J.; Haines, T.L.; Skinner, J. Relationship between relative net vertical impulse and jump height in jump squats performed to various squat depths and with various loads. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2010, 5, 484–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandic, R.; Knezevic, O.M.; Mirkov, D.M.; Jaric, S. Control strategy of maximum vertical jumps: The preferred countermovement depth may not be fully optimized for jump height. J. Hum. Kinet. 2016, 52, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markovic, S.; Mirkov, D.M.; Nedeljkovic, A.; Jaric, S. Body size and countermovement depth confound relationship between muscle power output and jumping performance. Hum. Mov. Sci. 2014, 33, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vetter, R.E. Effects of six warm-up protocols on sprint and jump performance. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2007, 21, 819–823. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Linthorne, N.P. Analysis of standing vertical jumps using a force platform. Am. J. Phys. 2001, 69, 1198–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Street, G.; McMillan, S.; Board, W.; Rasmussen, M.; Heneghan, J.M. Sources of error in determining countermovement jump height with the impulse method. J. Appl. Biomech. 2001, 17, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kibele, A. Possibilities and limitations in the biomechanical analysis of countermovement jumps: A methodological study. J. Appl. Biomech. 1998, 14, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, W.; Marshall, S.; Batterham, A.; Hanin, J. Progressive statistics for studies in sports medicine and exercise science. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2009, 41, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jidovtseff, B.; Quievre, J.; Nigel, H.; Cronin, J. Influence of jumping strategy on kinetic parameters. J. Sports Med. Phys. Fit. 2014, 54, 129–138. [Google Scholar]
- Kopper, B.; Ureczky, D.; Tihanyi, J. Trunk position influences joint activation pattern and physical performance during vertical jumping. Acta Physiol. Hung. 2012, 99, 194–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moran, K.A.; Wallace, E.S. Eccentric loading and range of knee joint motion effects on performance enhancement in vertical jumping. Hum. Mov. Sci. 2007, 26, 824–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toumi, H.; Best, T.M.; Martin, A.; F’Guyer, S.; Poumarat, G. Effects of eccentric phase velocity of plyometric training on the vertical jump. Int. J. Sports Med. 2004, 25, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Variables | CMJP | CMJS | CMJL | ES CMJP-CMJS | ES CMJP-CMJL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| hmax (LH) | 0.48 ± 0.08 | 0.45 ± 0.06 * | 0.50 ± 0.08 # | 0.55 | −0.50 |
| hflight (LH) | 0.36 ± 0.07 | 0.33 ± 0.06 * | 0.37 ± 0.06 # | 0.86 | −0.67 |
| htakeoff (LH) | 0.12 ± 0.03 | 0.12 ± 0.02 | 0.13 ± 0.02 | 0.03 | −0.09 |
| Ddownward (LH) | −0.32 ± 0.06 | −0.23 ± 0.05 * | −0.43 ± 0.06 # | −2.02 | 2.47 |
| Dupward (LH) | 0.45 ± 0.06 | 0.35 ± 0.05 * | 0.55 ± 0.06 # | 1.90 | −2.16 |
| Variables | CMJP | CMJS | CMJL | ES CMJP-CMJS | ES CMJP-CMJL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ImpulseNv (N/kg) | 2.53 ± 0.22 | 2.41 ± 0.23 | 2.59 ± 0.20 | 0.51 | −0.31 |
| Fmin (BW) | 0.36 ± 0.22 | 0.40 ± 0.23 | 0.36 ± 0.18 | −0.40 | 0.03 |
| Finitial (BW) | 2.35 ± 0.29 | 2.47 ± 0.35 * | 2.36 ± 0.31 | −0.46 | −0.05 |
| Fmax (BW) | 2.44 ± 0.23 | 2.81 ± 0.31 * | 2.38 ± 0.28 | −1.54 | 0.32 |
| Fav (BW) | 1.99 ± 0.16 | 2.23 ± 0.21 * | 1.84 ± 0.14 # | −1.77 | 1.81 |
| Variables | CMJP | CMJS | CMJL | ES CMJP-CMJS | ES CMJP-CMJL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vmin (m·s−1) | −1.15 ± 0.29 | −0.95 ± 0.27 * | −1.32 ± 0.28 # | −1.41 | 1.07 |
| Vmax (m·s−1) | 2.68 ± 0.20 | 2.58 ± 0.18 * | 2.73 ± 0.19 # | 0.95 | −0.76 |
| Vtakeoff (m·s−1) | 2.54 ± 0.22 | 2.44 ± 0.20 * | 2.59 ± 0.21 # | 0.87 | −0.67 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sánchez-Sixto, A.; Harrison, A.J.; Floría, P. Larger Countermovement Increases the Jump Height of Countermovement Jump. Sports 2018, 6, 131. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports6040131
Sánchez-Sixto A, Harrison AJ, Floría P. Larger Countermovement Increases the Jump Height of Countermovement Jump. Sports. 2018; 6(4):131. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports6040131
Chicago/Turabian StyleSánchez-Sixto, Alberto, Andrew J. Harrison, and Pablo Floría. 2018. "Larger Countermovement Increases the Jump Height of Countermovement Jump" Sports 6, no. 4: 131. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports6040131
APA StyleSánchez-Sixto, A., Harrison, A. J., & Floría, P. (2018). Larger Countermovement Increases the Jump Height of Countermovement Jump. Sports, 6(4), 131. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports6040131






