Abstract
Abdominal pressure is vital in protecting the lumbar spine and controlling postural balance. Dynamic balance is associated with movement stability, adaptation to load, and reduced injury risk. Although trunk stability has been examined using belts and braces, the effects of external abdominal pressure support (APS) on balance control remain unknown. In this study, we aimed to determine the effects of external APS on dynamic balance. Overall, 31 young adults participated in this randomized crossover study. External APS was provided using a device that could be pressurized and decompressed by inflating a cuff belt wrapped around the trunk. The modified Star Excursion Balance Test was performed under external APS and non-APS conditions. The maximum anterior, posterolateral, and posteromedial values normalized to the spinal malleolar distance and their respective composite values were compared between the two conditions with and without APS. Posterolateral, posteromedial, and composite values were significantly higher in the APS condition than in the non-APS condition (p < 0.001). The external APS was effective in immediately improving dynamic balance. Furthermore, APS was effective in dynamic balance control as it improved stability during anterior trunk tilt, which displaces the center of gravity forward.
1. Introduction
All movements and forces of the body are linked through the myofascia surrounding the trunk, pelvic area, and lower extremities [1,2]. These structures interact and act as stabilizers that play an important role in maximizing performance [1]. In particular, effective mobilization of the trunk muscles is associated with optimal generation of muscle strength and precise control of hip motion through the lumbar spine and pelvis [3,4]. Conversely, trunk muscle weakness may lead to poor physical and balance performance [5]. Among the trunk muscles, the roles of the abdominal muscles are well known [6]. Abdominal bracing maneuvers that increase intra-abdominal pressure (IAP) by voluntary isometric contraction of the abdominal muscles are effective in increasing spinal stability [7,8,9]. Increasing abdominal pressure (AP) is important for generating muscle strength during lifting movements [10]. Increased AP also occurs during exertion and execution of lower extremity muscle groups such as in walking [11], jumping [12], and deadlift [10,13] movements. This phenomenon enables smooth execution of the main lower limb movement by stiffening the trunk prior to the movement [12]. The important factor in exerting lower limb muscle group strength is that an increase in AP may improve trunk stiffness. Therefore, when AP is externally supported, it may be associated with performance maximization of the trunk to lower extremity muscle groups. However, to the best of our knowledge, lumbar braces and belts have limited effects on AP [14]. These devices focus on tightening the lumbopelvic region and providing support to the lower back and do not add direct pressure manipulation from the abdomen to the AP. Additionally, consensus regarding the effectiveness of lumbar braces and belts is limited [15,16,17].
Strength, endurance, agility, speed, or other physical ability tests are used as surrogate measures of functional movement and athletic performance to examine the importance of trunk stability or lumbopelvic control [18,19,20]. The Star Excursion Balance Test (SEBT) is a dynamic balance test that is suitable for physically active individuals and does not require special equipment [21]. The SEBT predicts the risk of lower extremity injury [22,23,24] and identifies dynamic balance impairments in patients with lower extremity diseases [21,22,25,26]. Reliable dynamic balance tests are used to determine the effectiveness of training programs in healthy participants and patients with lower extremity diseases [21,27]. Although some studies have shown that foot and knee muscle strength and mobility predict dynamic postural stability, the relationship between the trunk and dynamic postural stability remains unclear [28]. Abdominal muscles are predictably activated earlier and exhibit greater amplitude in response to the direction of limb movement [29,30,31]. Regulating abdominal pressure can stabilize the spine independent of the direction of movement and also counteract moments imposed on the trunk [32]. Increased abdominal pressure improves spinal stability against off-balance perturbations [33,34]. Moreover, trunk and lower extremity perturbations when performing the SEBT may be influenced by the presence or absence of external abdominal pressure support (APS).
To our knowledge, no studies have investigated the effects of external APS on trunk stability during the SEBT. Therefore, we aimed to investigate the immediate effects of adding external APS during the SEBT on dynamic balance. The hypothesis was that the external APS would positively affect dynamic balance. This could be valid for external APS in rehabilitation, labor tasks, or various lifting activities. This study may provide insights into the future development of new lumbar orthoses and belts.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
This study’s sample size was calculated based on reports on the effectiveness of lumbar stabilization exercises with a hollowing strategy for trunk flexor muscle strength [35]. A power analysis conducted using G* Power 3.1.9 (University of Kiel, Kiel, Germany) with a d of 0.53, α of 0.05, and power of 0.80, revealed that at least 30 participants were required for this study. Recruitment was conducted from February 2023 to April 2023 through announcements to students on the social network services of one engineering university and one healthcare professional school in Kirishima, Japan. The population consisted of approximately 240 students (85% male) in one grade at the university and 160 students (40% male) in one grade at the school, all aged between 18 and 22. In total, 34 students who were active and willing to voluntarily participate were included. This study was conducted in the order in which the schedules were matched. Inclusion criteria were the following: no trunk or lower extremity injury within the past 6 months, no trunk or lower extremity surgery in the past 2 years, no trunk or lower extremity pain, and no history of neurological disease. In addition, they had to have had previous experience in competitive sports. After excluding 3 persons with no previous competitive sports experience, a total of 31 young adults (19 male and 12 female participants; age, 20.0 ± 0.9 years; height, 166.5 ± 8.6 cm; body mass, 57.9 ± 8.1 kg) were enrolled.
2.2. Ethics
This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Daiichi Institute of Technology (R4-003) and conducted in accordance with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki [36]. The study was explained orally and in writing and written informed consent was obtained from all participants.
2.3. Study Design and Procedures
This was a randomized crossover study in which measurements with and without APS were performed on two separate days. All 31 participants were evaluated under both conditions on separate days with a washout period of at least 48 h [37]. The order was randomized using a random number table. Prior to the measurements, the participants performed a 5 min walk as a warm-up, 1 round trip up and down 50 stairs, and 5 repetitions of trunk flexion, extension, right and left rotation, and right and left lateral flexion exercises [38,39]. Three abdominal bracing repetitions were performed as a warm-up for the trunk muscles, with arms crossed in front of the chest in an upright position. A modified version of the SEBT (mSEBT) was used to measure dynamic balance [21]. The immediate effects of the presence or absence of APS were tested.
2.4. Measurement Methods
Body mass and height were measured prior to the study. Body mass was measured using a digital scale (MC-780MA; Tanita®, Tokyo, Japan), barefoot, with light clothing and accessories removed. Body height was measured using a height scale (seca213; seca®, Chiba, Japan), with the participants barefoot and in an upright posture. Measurements were taken to the nearest ±0.1 kg and ±0.1 cm, respectively.
In the SEBT, the participants maintained their balance on one leg while extending the opposite leg maximally in eight directions. A farther reach indicated better dynamic postural control. The mSEBT uses only three directions (anterior, posterolateral, and posteromedial) and has been validated for a shorter time on the task [21,23,25]. Therefore, the mSEBT was used in this study (Figure 1). In the questionnaire, the leg with which the participant could normally kick the ball harder was used as the dominant leg, and that leg was used as the static leg during the mSEBT [40]. The mSEBT was performed after four practice trials, followed by a 1 min break and three measurement trials [27,41,42], and the maximum value was adopted. A participant failed to complete the test and was retested if he/she (1) put weight on the reaching leg; (2) lost balance and could not return the extended leg to the starting position; (3) dropped their hands off their waist; (4) could not keep the standing leg in the same place; or (5) could not keep the forefoot or heel of the standing leg on the floor [21]. The maximum values in each of the three directions of the mSEBT and the means of their sum (composite) were normalized and expressed as percentages based on the spinal malleolar distance for comparison [43].
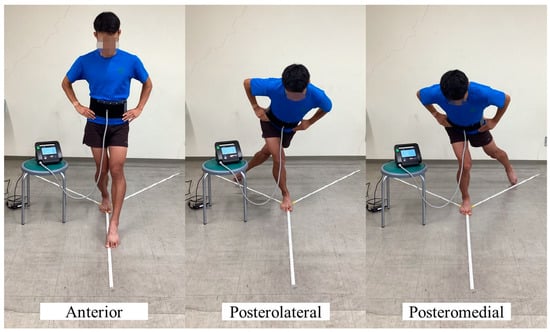
Figure 1.
The mSEBT in the abdominal pressure measurement support setting. mSEBT, modified Star Excursion Balance Test.
External APS was provided using an abdominal trunk muscle strength-measuring device (RECORE®; Sigmax, Tokyo, Japan), which can be pressurized and decompressed by wrapping a 15 cm-wide cuff belt around the trunk and inflating it using air [44]. Initially, the abdominal pressure of all participants was measured three times while they were in the standing position, and the maximum value was defined as the maximum abdominal pressure (Figure 2). A biomechanical model simulation of the spine and its muscle structure was used to set and analyze a base pressure of 5 kPa corresponding to various movements [45]. This corresponded to approximately 30% of the mean maximum abdominal pressure among male participants in this study. As a pressure of 4 kPa corresponds to approximately 30% of the mean maximum abdominal pressure in female adults, the APS conditions during the mSEBT were set to 5 and 4 kPa for male and female participants, respectively. The non-APS condition was defined as simple wrapping of the cuff belt (0 kPa). The center of the cuff belt was 2.5 cm below the umbilicus, targeting the lower abdomen. The cuff belt was applied before the mSEBT trial, and the external APS was adjusted to the set value at the time of resting expiration, just before the commencement of the test. The application and setting of the APS system were performed by a physical therapist with sufficient experience.

Figure 2.
A participant wearing the abdominal trunk muscle strength-measuring device measuring their maximal abdominal pressure. AP, abdominal pressure.
2.5. Statistical Analysis
The reproducibility of the mSEBT measurements with and without APS was determined by calculating the intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC) (1, 3) using data from 13 young adults who had been assessed three times, each by one examiner prior to the study. The ICC of the mSEBT with the three-directional APS was 0.929–0.968 (0.824–0.989), whereas the ICC without APS was 0.946–0.981 (0.866–0.994). External abdominal pressure fluctuations during the mSEBT were also identified. The increase in abdominal pressure was confirmed by the difference between the maximum value of abdominal pressure during posterolateral implementation, which was assumed to cause trunk flexion, and the set value at the beginning of the measurement. The maximum values of three trials were used. The increases in the abdominal pressure were 4.92 ± 2.48 and 0.28 ± 0.19 with and without APS starting from set values of 5 and 0 kPa, respectively.
Data for each mSEBT item are presented as means and standard deviations. The data distribution for each item was determined to follow a normal distribution using the Shapiro–Wilk test. The effects of the presence or absence of APS on the mSEBT were compared using a paired t-test. SPSS version 28.0 (IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, USA) was used for all statistical analyses, and the significance level was set at p < 0.05. The effect size, d, calculated for comparison corresponded to the following criteria: trivial (<0.200), small (0.200–0.500), medium (0.500–0.800), and large (>0.800) [46].
3. Results
The participants’ characteristics are presented in Table 1. When comparing the mSEBT results with and without APS, no significant differences were present in the anterior direction (non-APS, 88.8 ± 6.0%; APS, 89.6 ± 7.2%; d = 0.19, trivial; p = 0.290). The values of the posterolateral (non-APS, 100.6 ± 9.4%; APS, 105.7 ± 7.7%; d = 0.74, medium), posteromedial (non-APS, 108.6 ± 7.5%; APS, 112.6 ± 7.9%; d = 0.70, medium), and composite of the directions (non-APS, 99.3 ± 6.6%; APS, 102.7 ± 6.3%; d = 0.73, medium) were significantly higher in the APS than in the non-APS settings (p < 0.001) (Figure 3).

Table 1.
Participants’ characteristics.
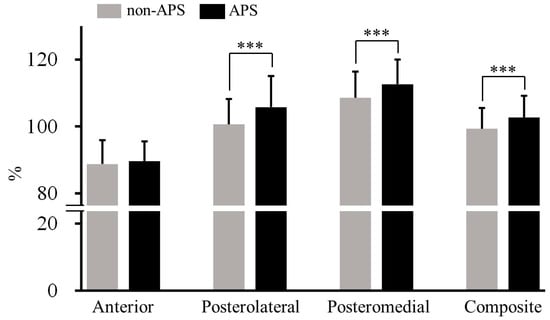
Figure 3.
Comparison of each mSEBT score with and without APS. *** p < 0.001. APS, abdominal pressure support; mSEBT, modified Star Excursion Balance Test.
4. Discussion
In this study, we examined the immediate effects of external APS on dynamic balance using the mSEBT. APS improved posterolateral performance by 5.1%, posteromedial performance by 3.7%, and composite performance by 3.4%. These results suggest that external APS may be effective for supporting dynamic balance in young adults. However, factors such as lower extremity muscle strength, range of motion, intrinsic receptivity, and neuromuscular control were not evaluated, so their associations with these factors are not known.
Lumbar belts and braces support spinal stability by tightening the abdominal wall and increasing the IAP, which reduces the load on the spine [47,48]. Simultaneous contraction of trunk flexors and extensors increases the IAP, and the longitudinal moments acting on the pelvis and diaphragm reportedly increase trunk stiffness and reduce intervertebral pressure [45,47,49]. This mechanism of action is similar to that of abdominal bracing, which induces higher activation of deep abdominal muscles, such as the internal oblique muscles [50]. These trunk-stabilizing muscles are constantly activated before the activation of the limbs [51]. This is thought to assist force or power generation of the limbs during kinetic chain activity [52,53]. A strong and stable trunk and its rapid activation are potentially the foundation for limb force generation and achieving improved sports performance [1]. A 4 kPa increase in the IAP results in a 25% improvement in spinal stability [54]. Furthermore, trunk muscle-strengthening exercises enhance spinal stability and postural control in patients with lower back pain (LBP) [55]. We previously confirmed that APS increased the AP by an average of 4.9 kPa during movements in the posterolateral direction. In contrast, in the non-APS setting, in which the cuff belt was simply wrapped around the trunk, the AP increased by 0.28 kPa during movements in the same posterolateral direction. This suggests that APS may have improved spinal stability during the mSEBT.
Spinal somatosensory acuity has been reported to influence changes in the trunk muscles and postural control [16,56]. Lumbar somatosensory dysfunction has been observed in patients with LBP [57]. However, the lumbar belt may partially provide somatosensory information to the lower back of patients with LBP [58]. APS may not only tighten, but the air pressure supporting the lower abdomen may also directly stimulate somatosensory sensation and promote AP activation. Considering these factors, a significant improvement in dynamic balance may have been observed with APS during movements in the posterolateral direction. The same reason could explain the same trunk flexion movements during the movements in the posteromedial direction. Thus, in the current study, APS would have provided immediate support for trunk stability in young adults during movements in the posterolateral and posteromedial directions and would have shown an overall improvement in dynamic balance scores.
In this study, when assessing the effectiveness of APS, we observed improvements in scores for the posterolateral and posteromedial directions, whereas no significant differences in scores for the anterior direction were present. Posture is controlled by activating the transversus abdominis muscle under the influence of different body positions and loading styles [32,59]. Wearing a belt or brace increases the hip flexion angle during lifting movements, in which the center of gravity shifts forward [60], and increases muscle activity in the internal oblique and rectus abdominis muscles [61,62]. In addition, an appropriate increase in IAP enhances the maximum voluntary contractile torque of hip extension [63]. Compared with movements in the posterolateral and posteromedial directions, which exhibit an anterior trunk tilt, movements in the anterior direction did not require a lumbar extension moment and required less lumbar stability. Lumbar shear load is strongly influenced by the lumbar flexion angle [64]. Thus, APS provided adequate support and improved dynamic balance when lumbar spine stability was needed during posterolateral and posteromedial movements when the hip flexion angle increased and the center of gravity moved forward due to the anterior tilt of the trunk. In the anterior direction, on the other hand, the need for lumbar spine stability was low because the lumbar spine was not flexed, so the APS was not needed as much and was not effective. Nevertheless, APS was beneficial during posterolateral and posteromedial movements, during which the center of gravity shifted forward, improving stability during anterior trunk tilt, which suggests its effectiveness for dynamic balance control and postural maintenance. Personalized lumbar orthoses that change shape using actuators or bands are currently available [65,66]. APS features focus on abdominal pressure and its effect on postural changes, not just tightness. As this design provides support using pneumatic pressure, changes can be easily personalized according to the individual’s movement; furthermore, the absence of pillars reduces concerns related to problems caused by contact. The results of this study may lead to the development of an autonomously modifiable lumbar brace with built-in software that allows air pressure to vary according to posture.
This study had some limitations. First, the participants were healthy young adults with a history of competitive sports; older adults or patients with comorbidities were not included. Therefore, these results may not be generalizable to other groups. Second, dynamic balance tasks require consideration of lower extremity muscle strength, range of motion, intrinsic receptivity, and neuromuscular control [23,26,67,68]. As these factors were not assessed in the present study, their relevance remains unclear. Third, it remains unclear which APS strategies changed because of the lack of an objective assessment of joint parameters and muscle activity during movement. Finally, the equivalence of IAP and AP has not been rigorously investigated. Further studies on the sustained effects in various populations are required to thoroughly understand the mechanisms underlying the improvement of dynamic balance.
5. Conclusions
This study examined the immediate effects of external APS on dynamic balance during the mSEBT for healthy young adults. External APS resulted in immediate improvements in dynamic balance, primarily during anterior trunk tilt. These results suggest that external APS may be an effective way to support dynamic balance during forward bending movements such as picking up objects and lifting.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.N.; data curation, Y.N. and R.K.; formal analysis, Y.N., Y.T. and M.K.; investigation, T.K., Y.T., S.A. and T.M.; methodology, Y.N., T.K., Y.T., S.A. and T.M.; project administration, Y.N.; writing—original draft, Y.N. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by JKA and promotional funds were provided by the KEIRIN RACE. The article processing charges were also funded by JKA and its promotional funds from the KEIRIN RACE.
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Ethics Committee of Daiichi Institute of Technology (protocol code R4-003, 31 March 2023).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all participants involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the laboratory personnel for their administrative support.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Kibler, W.B.; Press, J.; Sciascia, A. The role of core stability in athletic function. Sports Med. 2006, 36, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vleeming, A.; Schuenke, M.D.; Danneels, L.; Willard, F.H. The functional coupling of the deep abdominal and paraspinal muscles: The effects of simulated paraspinal muscle contraction on force transfer to the middle and posterior layer of the thoracolumbar fascia. J. Anat. 2014, 225, 447–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willson, J.D.; Dougherty, C.P.; Ireland, M.L.; Davis, I.M. Core stability and its relationship to lower extremity function and injury. J. Am. Acad. Orthop. Surg. 2005, 13, 316–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akuthota, V.; Ferreiro, A.; Moore, T.; Fredericson, M. Core stability exercise principles. Curr. Sports Med. Rep. 2008, 7, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hicks, G.E.; Simonsick, E.M.; Harris, T.B.; Newman, A.B.; Weiner, D.K.; Nevitt, M.A.; Tylavsky, F.A. Cross-sectional associations between trunk muscle composition, back pain, and physical function in the health, aging and body composition study. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2005, 60, 882–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, N. Therapeutic exercise for spinal segmental stabilization in low back pain: Scientific basis and clinical approach. Phys. Ther. Rev. 2012, 5, 247–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monfort-Pañego, M.; Vera-García, F.J.; Sánchez-Zuriaga, D.; Sarti-Martínez, M.A. Electromyographic studies in abdominal exercises: A literature synthesis. J. Manip. Physiol. Ther. 2009, 32, 232–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essendrop, M.; Schibye, B. Intra-abdominal pressure and activation of abdominal muscles in highly trained participants during sudden heavy trunk loadings. Spine 2004, 29, 2445–2451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essendrop, M.; Andersen, T.B.; Schibye, B. Increase in spinal stability obtained at levels of intra-abdominal pressure and back muscle activity realistic to work situations. Appl. Ergon. 2002, 33, 471–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawabata, M.; Shima, N.; Hamada, H.; Nakamura, I.; Nishizono, H. Changes in intra-abdominal pressure and spontaneous breath volume by magnitude of lifting effort: Highly trained athletes versus healthy men. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2010, 109, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grillner, S.; Nilsson, J.; Thorstensson, A. Intra-abdominal pressure changes during natural movements in man. Acta Physiol. Scand. 1978, 103, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harman, E.A.; Frykman, P.N.; Clagett, E.R.; Kraemer, W.J. Intra-abdominal and intra-thoracic pressures during lifting and jumping. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 1988, 20, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harman, E.A.; Rosenstein, R.M.; Frykman, P.N.; Nigro, G.A. Effects of a belt on intra-abdominal pressure during weght lifting. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 1989, 21, 186–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azadinia, F.; Ebrahimi, E.; Kamyab, M.; Parnianpour, M.; Cholewicki, J.; Maroufi, N. Can lumbosacral orthoses cause trunk muscle weakness? A systematic review of literature. Spine J. 2017, 17, 589–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takasaki, H.; Miki, T. The impact of continuous use of lumbosacral orthoses on trunk motor performance: A systematic review with meta-analysis. Spine J. 2017, 17, 889–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Duijvenbode, I.C.D.; Jellema, P.; van Poppel, M.N.M.; van Tulder, M.W. Lumbar supports for prevention and treatment of low back pain. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2008, 2008, CD001823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerillo, J.L.; Becsey, A.N.; Sanghadia, C.P.; Root, K.T.; Lucke-Wold, B. Spine bracing: When to utilize-a narrative review. Biomechanics 2023, 3, 136–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozmen, T. Relationship between core stability, dynamic balance and jumping performance in soccer players. Turk. J. Sport Exe. 2016, 18, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Bruin, M.; Coetzee, D.; Schall, R. The relationship between core stability and athletic performance in female university athletes. S. Afr. J. Sports Med. 2021, 33, v33i1a10825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesser, T.W.; Huxel, K.C.; Tincher, J.L.; Okada, T. The relationship between core stability and performance in division I football players. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2008, 22, 1750–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gribble, P.A.; Hertel, J.; Plisky, P. Using the star excursion balance test to assess dynamic postural-control deficits and outcomes in lower extremity injury: A literature and systematic review. J. Athl. Train. 2012, 47, 339–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gribble, P.A.; Tucker, W.S.; White, P.A. Time-of-day influences on static and dynamic postural control. J. Athl. Train. 2007, 42, 35–41. [Google Scholar]
- Plisky, P.J.; Rauh, M.J.; Kaminski, T.W.; Underwood, F.B. Star excursion balance test as a predictor of lower extremity injury in high school basketball players. J. Orthop. Sports Phys. Ther. 2006, 36, 911–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stiffler, M.R.; Bell, D.R.; Sanfilippo, J.L.; Hetzel, S.J.; Pickett, K.A.; Heiderscheit, B.C. Star excursion balance test anterior asymmetry is associated with injury status in division I collegiate athletes. J. Orthop. Sports Phys. Ther. 2017, 47, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hertel, J.; Braham, R.A.; Hale, S.A.; Olmsted-Kramer, L.C. Simplifying the Star Excursion Balance Test: Analyses of subjects with and without chronic ankle instability. J. Orthop. Sports Phys. Ther. 2006, 36, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olmsted, L.C.; Carcia, C.R.; Hertel, J.; Shultz, S.J. Efficacy of the star excursion balance tests in detecting reach deficits in subjects with chronic ankle instability. J. Athl. Train. 2002, 37, 501–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munro, A.G.; Herrington, L.C. Between-session reliability of the star excursion balance test. Phys. Ther. Sport 2010, 11, 128–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, V.J.; Nagai, T.; Sell, T.C.; Abt, J.P.; Rowe, R.S.; McGrail, M.A.; Lephart, S.M. Prediction of dynamic postural stability during single-leg jump landings by ankle and knee flexibility and strength. J. Sport Rehabil. 2016, 25, 266–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aruin, A.S.; Latash, M.L. Directional specificity of postural muscles in feed-forward postural reactions during fast voluntary arm movements. Exp. Brain Res. 1995, 103, 323–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hodges, P.; Cresswell, A.; Thorstensson, A. Preparatory trunk motion accompanies rapid upper limb movement. Exp. Brain Res. 1999, 124, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakai, Y.; Kawada, M.; Miyazaki, T.; Kiyama, R. Trunk muscle activity during trunk stabilizing exercise with isometric hip rotation using electromyography and ultrasound. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2019, 49, 102357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crommert, M.E.; Ekblom, M.M.; Thorstensson, A. Activation of transversus abdominis varies with postural demand in standing. Gait Posture 2011, 33, 473–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vera-Garcia, F.J.; Elvira, J.L.L.; Brown, S.H.M.; McGill, S.M. Effects of abdominal stabilization maneuvers on the control of spine motion and stability against sudden trunk perturbations. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2007, 17, 556–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGill, S.M.; Grenier, S.; Kavcic, N.; Cholewicki, J. Coordination of muscle activity to assure stability of the lumbar spine. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2003, 13, 353–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.; Kim, M.; Oh, S.; Yoon, B. The effectiveness of hollowing and bracing strategies with lumbar stabilization exercise in older adult women with nonspecific low back pain: A quasi-experimental study on a community-based rehabilitation. J. Manip. Physiol. Ther. 2018, 41, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Medical Association World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki: Ethical principles for medical research involving human subjects. JAMA 2013, 310, 2191–2194. [CrossRef]
- Cornell, D.J.; Ebersole, K.T. Influence of an acute bout of self-myofascial release on knee extension force output and electro-mechanical activation of the quadriceps. Int. J. Sports Phys. Ther. 2020, 15, 732–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonta, M.; Tsepis, E.; Fousekis, K.; Mandalidis, D. Acute effects of static self-stretching exercises and foam roller self-massaging on the trunk range of motions and strength of the trunk extensors. Sports 2021, 9, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, K.-K.; Chai, H.-M.; Chen, Y.-J.; Wang, C.-L.; Shau, Y.-W.; Wang, S.-F. Mechanical deformation of posterior thoracolumbar fascia after myofascial release in healthy men: A study of dynamic ultrasound imaging. Musculoskelet. Sci. Pract. 2017, 27, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffman, M.; Schrader, J.; Applegate, T.; Koceja, D. Unilateral postural control of the functionally dominant and nondominant extremities of healthy subjects. J. Athl. Train. 1998, 33, 319–322. [Google Scholar]
- Hertel, J.; Miller, S.J.; Denegar, C.R. Intratester and intertester reliability during the star excursion balance tests. J. Sport Rehabil. 2000, 9, 104–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, R.H.; Gribble, P.A. Support for a reduction in the number of trials needed for the star excursion balance test. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2008, 89, 364–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gribble, P.A.; Hertel, J. Considerations for normalizing measures of the star excursion balance test. Meas. Phys. Educ. Exerc. Sci. 2003, 7, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakai, Y.; Oe, K.; Matsuno, R.; Kiyama, R.; Kawada, M.; Takeshita, Y.; Miyazaki, T.; Araki, S. Effect of self-myofascial release of the lower back on myofascial gliding, lumbar flexibility, and abdominal trunk muscle strength: A crossover study. Sports 2023, 11, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stokes, I.A.F.; Gardner-Morse, M.G.; Henry, S.M. Intra-abdominal pressure and abdominal wall muscular function: Spinal unloading mechanism. Clin. Biomech. 2010, 25, 859–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences; Routledge: London, UK, 1988; ISBN 9781134742707. [Google Scholar]
- Cholewicki, J.; Juluru, K.; Radebold, A.; Panjabi, M.M.; McGill, S.M. Lumbar spine stability can be augmented with an abdominal belt and/or increased intra-abdominal pressure. Eur. Spine J. 1999, 8, 388–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anders, C.; Hübner, A. Influence of elastic lumbar support belts on trunk muscle function in patients with non-specific acute lumbar back pain. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0211042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cholewicki, J.; Ivancic, P.C.; Radebold, A. Can increased intra-abdominal pressure in humans be decoupled from trunk muscle co-contraction during steady state isometric exertions? Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2002, 87, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeo, S.; Takahashi, T.; Takai, Y.; Kanehisa, H. Trunk muscle activities during abdominal bracing: Comparison among muscles and exercises. J. Sports Sci. Med. 2013, 12, 467–474. [Google Scholar]
- Hodges, P.W.; Richardson, C.A. Feedforward contraction of transversus abdominis is not influenced by the direction of arm movement. Exp. Brain Res. 1997, 114, 362–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamison, S.T.; McNeilan, R.J.; Young, G.S.; Givens, D.L.; Best, T.M.; Chaudhari, A.M.W. Randomized controlled trial of the effects of a trunk stabilization program on trunk control and knee loading. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2012, 44, 1924–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butcher, S.J.; Craven, B.R.; Chilibeck, P.D.; Spink, K.S.; Grona, S.L.; Sprigings, E.J. The effect of trunk stability training on vertical takeoff velocity. J. Orthop. Sports Phys. Ther. 2007, 37, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Bojairami, I.; Driscoll, M. Coordination between trunk muscles, thoracolumbar fascia, and intra-abdominal pressure toward static spine stability. Spine 2022, 47, E423–E431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Dieën, J.H.; Selen, L.P.J.; Cholewicki, J. Trunk muscle activation in low-back pain patients, an analysis of the literature. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2003, 13, 333–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brumagne, S.; Janssens, L.; Knapen, S.; Claeys, K.; Suuden-Johanson, E. Persons with recurrent low back pain exhibit a rigid postural control strategy. Eur. Spine J. 2008, 17, 1177–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Sullivan, P.B.; Burnett, A.; Floyd, A.N.; Gadsdon, K.; Logiudice, J.; Miller, D.; Quirke, H. Lumbar repositioning deficit in a specific low back pain population. Spine 2003, 28, 1074–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newcomer, K.; Laskowski, E.R.; Yu, B.; Johnson, J.C.; An, K.N. The effects of a lumbar support on repositioning error in subjects with low back pain. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2001, 82, 906–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eriksson Crommert, A.E.M.; Thorstensson, A. Trunk muscle reactions to sudden unexpected and expected perturbations in the absence of upright postural demand. Exp. Brain Res. 2009, 196, 385–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marras, W.S.; Jorgensen, M.J.; Davis, K.G. Effect of foot movement and an elastic lumbar back support on spinal loading during free-dynamic symmetric and asymmetric lifting exertions. Ergonomics 2000, 43, 653–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granata, K.P.; Marras, W.S.; Davis, K.G. Biomechanical assessment of lifting dynamics, muscle activity and spinal loads while using three different styles of lifting belt. Clin. Biomech. 1997, 12, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyamoto, K.; Iinuma, N.; Maeda, M.; Wada, E.; Shimizu, K. Effects of abdominal belts on intra-abdominal pressure, intra-muscular pressure in the erector spinae muscles and myoelectrical activities of trunk muscles. Clin. Biomech. 1999, 14, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tayashiki, K.; Mizuno, F.; Kanehisa, H.; Miyamoto, N. Causal effect of intra-abdominal pressure on maximal voluntary isometric hip extension torque. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2018, 118, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potvin, J.R.; McGill, S.M.; Norman, R.W. Trunk muscle and lumbar ligament contributions to dynamic lifts with varying degrees of trunk flexion. Spine 1991, 16, 1099–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-H.; Stegall, P.R.; Roye, D.P.; Agrawal, S.K. Robotic Spine Exoskeleton (RoSE): Characterizing the 3-D stiffness of the human torso in the treatment of spine deformity. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2018, 26, 1026–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, A.; Fontanari, V.; Fontana, M.; Schmölz, W. Spinal deformities and advancement in corrective orthoses. Bioengineering 2020, 8, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoch, M.C.; Staton, G.S.; McKeon, P.O. Dorsiflexion range of motion significantly influences dynamic balance. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2011, 14, 90–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hubbard, T.J.; Kramer, L.C.; Denegar, C.R.; Hertel, J. Correlations among multiple measures of functional and mechanical instability in subjects with chronic ankle instability. J. Athl. Train. 2007, 42, 361–366. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).