The Exosome-Mediated Epigenome: Non-Coding RNA and mRNA-Coding Networks in Microbiome–Cellular Communication, Inflammation, and Tumorigenesis Along the Oral–Gut–Lung Axis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Transcriptomic Analysis of Overexpressed RNAs Related to Extracellular Exosomes from Circulating Whole Blood Plasma or Serum in Tumoral Diseases of the Gut–Lung Axis
2.2. Transcriptomic Analysis of Differentially Overexpressed Genes (DEGs) Related to Extracellular Exosomes in Gut and Lung Tumoral- and Inflammatory-Related Tissues
2.3. Non-Coding RNA and mRNA Transcriptional Regulators Related to Gut and Lung Extracellular Exosome Function in Tumoral and Inflammatory Diseases
2.4. Transcriptional Regulatory Networks (TRNs) Related to Gut and Lung Extracellular Exosomes
3. Discussion
3.1. Membrane Receptors of Gut–Lung Tumoral and Inflammatory Cells Transported by Exosomes for Host–Microbiota Interaction and Signaling Pathways Regulation
3.2. Transcriptional Regulators of Gut–Lung Tumoral and Inflammatory Cells Transported by Exosomes
3.3. The Whole Transcriptome Meta-Analysis of Lung, Gastric, and Colon Cancer Circulating Exosomes
4. Materials and Methods
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chang, X.; Wang, S.-L.; Zhao, S.-B.; Shi, Y.-H.; Pan, P.; Gu, L.; Yao, J.; Li, Z.-S.; Bai, Y. Extracellular Vesicles with Possible Roles in Gut Intestinal Tract Homeostasis and IBD. Mediat. Inflamm. 2020, 2020, 1945832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, M.; Wang, S.; Guo, X.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Qiu, W.; Gao, X.; Chen, Z.; Xu, J.; Zhao, R.; et al. Hypoxic Glioma-Derived Exosomes Deliver MicroRNA-1246 to Induce M2 Macrophage Polarization by Targeting TERF2IP via the STAT3 and NF-ΚB Pathways. Oncogene 2020, 39, 428–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Ma, N.; Wang, X.; Hu, J.; Ma, X.; Wang, J.; Cao, B. Exosomes Derived from 5-Fluorouracil-Resistant Colon Cancer Cells Are Enriched in GDF15 and Can Promote Angiogenesis. J. Cancer 2020, 11, 7116–7126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginini, L.; Billan, S.; Fridman, E.; Gil, Z. Insight into Extracellular Vesicle-Cell Communication: From Cell Recognition to Intracellular Fate. Cells 2022, 11, 1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Shi, K.; Chen, Y.; Wu, X.; Chen, Z.; Cao, K.; Tao, Y.; Chen, X.; Liao, J.; Zhou, J. Exosomes and Their Role in Cancer Progression. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 639159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Yang, L.; Baddour, J.; Achreja, A.; Bernard, V.; Moss, T.; Marini, J.C.; Tudawe, T.; Seviour, E.G.; San Lucas, F.A.; et al. Tumor Microenvironment Derived Exosomes Pleiotropically Modulate Cancer Cell Metabolism. eLife 2016, 5, e10250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, G.; Hoshino, A.; Kenific, C.M.; Matei, I.R.; Steiner, L.; Freitas, D.; Kim, H.S.; Oxley, P.R.; Scandariato, I.; Casanova-Salas, I.; et al. Tumour Exosomal CEMIP Protein Promotes Cancer Cell Colonization in Brain Metastasis. Nat. Cell Biol. 2019, 21, 1403–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bitto, N.J.; Cheng, L.; Johnston, E.L.; Pathirana, R.; Phan, T.K.; Poon, I.K.H.; O’Brien-Simpson, N.M.; Hill, A.F.; Stinear, T.P.; Kaparakis-Liaskos, M. Staphylococcus Aureus Membrane Vesicles Contain Immunostimulatory DNA, RNA and Peptidoglycan That Activate Innate Immune Receptors and Induce Autophagy. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2021, 10, e12080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Y.; Sun, F.; Zhao, B.; Kong, F.; Li, Z.; Kong, X. Bacteria Derived Extracellular Vesicles in the Pathogenesis and Treatment of Gastrointestinal Tumours. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 1103446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ullah, A.; Huang, Y.; Zhao, K.; Hua, Y.; Ullah, S.; Rahman, M.U.; Wang, J.; Wang, Q.; Hu, X.; Zheng, L. Characteristics and Potential Clinical Applications of the Extracellular Vesicles of Human Pathogenic Fungi. BMC Microbiol. 2023, 23, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moulin, C.; Crupi, M.J.F.; Ilkow, C.S.; Bell, J.C.; Boulton, S. Extracellular Vesicles and Viruses: Two Intertwined Entities. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gheitasi, H.; Sabbaghian, M.; Shekarchi, A.A.; Mirmazhary, A.A.; Poortahmasebi, V. Exosome-Mediated Regulation of Inflammatory Pathway during Respiratory Viral Disease. Virol. J. 2024, 21, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conti, M.; Minniti, M.; Tiné, M.; De Francesco, M.; Gaeta, R.; Nieri, D.; Semenzato, U.; Biondini, D.; Camera, M.; Cosio, M.G.; et al. Extracellular Vesicles in Pulmonary Hypertension: A Dangerous Liaison? Biology 2023, 12, 1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Li, M.; Li, H.; Ran, X.; Jin, F.; Tan, Q.; Chen, Z. Immune Cell-Derived Exosomes in Inflammatory Disease and Inflammatory Tumor Microenvironment: A Review. J. Inflamm. Res. 2024, 17, 301–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olejarz, W.; Kubiak-Tomaszewska, G.; Chrzanowska, A.; Lorenc, T. Exosomes in Angiogenesis and Anti-Angiogenic Therapy in Cancers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nail, H.M.; Chiu, C.C.; Leung, C.H.; Ahmed, M.M.M.; Wang, H.M.D. Exosomal MiRNA-Mediated Intercellular Communications and Immunomodulatory Effects in Tumor Microenvironments. J. Biomed. Sci. 2023, 30, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graner, M.W.; Schnell, S.; Olin, M.R. Tumor-Derived Exosomes, MicroRNAs, and Cancer Immune Suppression. Semin. Immunopathol. 2018, 40, 505–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, A.; Thakur, B.K.; Weiss, J.M.; Kim, H.S.; Peinado, H.; Lyden, D. Extracellular Vesicles in Cancer: Cell-to-Cell Mediators of Metastasis. Cancer Cell 2016, 30, 836–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.; He, X.; He, Y.; Ou, C.; Cao, P. Exosomal CircRNAs: Emerging Players in Tumor Metastasis. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 786224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nopora, A.; Weidle, U.H. CircRNAs as New Therapeutic Entities and Tools for Target Identification in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Cancer Genom. Proteom. 2024, 21, 118–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhao, L.; Bi, Y.; Zhao, J.; Gao, C.; Si, X.; Dai, H.; Asmamaw, M.D.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, W.; et al. The Role of LncRNAs and Exosomal LncRNAs in Cancer Metastasis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 165, 115207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Qi, Y.; Luo, Y.; Chen, X.; Liang, H. Exosomal Long Non-Coding RNA: Interaction Between Cancer Cells and Non-Cancer Cells. Front. Oncol. 2021, 10, 617837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paskeh, M.D.A.; Entezari, M.; Mirzaei, S.; Zabolian, A.; Saleki, H.; Naghdi, M.J.; Sabet, S.; Khoshbakht, M.A.; Hashemi, M.; Hushmandi, K.; et al. Emerging Role of Exosomes in Cancer Progression and Tumor Microenvironment Remodeling. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2022, 15, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.J.; Shin, K.J.; Chae, Y.C. Regulation of Cargo Selection in Exosome Biogenesis and Its Biomedical Applications in Cancer. Exp. Mol. Med. 2024, 56, 877–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otálora-Otálora, B.A.; Payán-Gómez, C.; López-Rivera, J.J.; Pedroza-Aconcha, N.B.; Arboleda-Mojica, S.L.; Aristizábal-Guzmán, C.; Isaza-Ruget, M.A.; Álvarez-Moreno, C.A. Interplay of Transcriptomic Regulation, Microbiota, and Signaling Pathways in Lung and Gut Inflammation-Induced Tumorigenesis. Cells 2024, 14, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otálora-Otálora, B.A.; Payán-Gómez, C.; López-Rivera, J.J.; Pedroza-Aconcha, N.B.; Aristizábal-Guzmán, C.; Isaza-Ruget, M.A.; Álvarez-Moreno, C.A. Global Transcriptomic Network Analysis of the Crosstalk between Microbiota and Cancer-Related Cells in the Oral-Gut-Lung Axis. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2024, 14, 1425388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizzagalli, M.D.; Bensimon, A.; Superti-Furga, G. A Guide to Plasma Membrane Solute Carrier Proteins. FEBS J. 2021, 288, 2784–2835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zou, W. Amino Acids and Their Transporters in T Cell Immunity and Cancer Therapy. Mol. Cell 2020, 80, 384–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, X.; Chen, R.; Cai, S.; Lu, S.; Zhang, Y. SLC1A4: A Powerful Prognostic Marker and Promising Therapeutic Target for HCC. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 650355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, X.; Yao, L.; Xu, L.; Ma, Q.; Huang, G.; Yang, M.; Gao, C.; Cheng, J.; Zhou, X.; Li, Q.; et al. Comprehensive Analysis of Potential Correlation Between Solute Carrier 1A (SLC1A) Family and Lung Adenocarcinoma. Int. J. Gen. Med. 2022, 15, 2101–2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavillette, D.; Marin, M.; Ruggieri, A.; Mallet, F.; Cosset, F.-L.; Kabat, D. The Envelope Glycoprotein of Human Endogenous Retrovirus Type W Uses a Divergent Family of Amino Acid Transporters/Cell Surface Receptors. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 6442–6452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, K.; Zhang, H.; Jia, X.; Li, X.; Sun, S.; Sun, D. Cell Death-Related Biomarker SLC2A1 Has a Significant Role in Prognosis Prediction and Immunotherapy Efficacy Evaluation in Pan-Cancer. Front. Genet. 2023, 13, 1068462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, Y.; Terasawa, H.; Tanaka, Y.; Mitsuura, C.; Nakashima, K.; Yusa, K.; Harada, S. Separate Cellular Localizations of Human T-Lymphotropic Virus 1 (HTLV-1) Env and Glucose Transporter Type 1 (GLUT1) Are Required for HTLV-1 Env-Mediated Fusion and Infection. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 502–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byerly, C.D.; Patterson, L.L.; Pittner, N.A.; Solomon, R.N.; Patel, J.G.; Rogan, M.R.; McBride, J.W. Ehrlichia Wnt Short Linear Motif Ligand Mimetic Deactivates the Hippo Pathway to Engage the Anti-Apoptotic Yap-GLUT1-BCL-XL axis. Infect. Immun. 2023, 91, e00085-23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.D.; Jawale, C.V.; Zhou, C.; Lin, L.; Trevejo-Nunez, G.J.; Rahman, S.A.; Mullet, S.J.; Das, J.; Wendell, S.G.; Delgoffe, G.M.; et al. Fungal Sensing Enhances Neutrophil Metabolic Fitness by Regulating Antifungal Glut1 Activity. Cell Host Microbe 2022, 30, 530–544.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Chen, S.; He, X.; Gong, S.; Sun, L.; Weng, L. SLC3A2 Promotes Tumor-Associated Macrophage Polarization through Metabolic Reprogramming in Lung Cancer. Cancer Sci. 2023, 114, 2306–2317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, N.N.T.; Lim, Y.S.; Nguyen, L.P.; Tran, S.C.; Luong, T.T.D.; Nguyen, T.T.T.; Pham, H.T.; Mai, H.N.; Choi, J.W.; Han, S.S.; et al. Hepatitis C Virus Modulates Solute Carrier Family 3 Member 2 for Viral Propagation. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 15486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malleret, B.; El Sahili, A.; Tay, M.Z.; Carissimo, G.; Ong, A.S.M.; Novera, W.; Lin, J.; Suwanarusk, R.; Kosaisavee, V.; Chu, T.T.T.; et al. Plasmodium Vivax Binds Host CD98hc (SLC3A2) to Enter Immature Red Blood Cells. Nat. Microbiol. 2021, 6, 991–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Li, Q. Pan-Cancer Analysis of the Oncogenic and Immunological Role of Solute Carrier Family 6 Member 8 (SLC6A8). Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 916439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ma, G.; Liu, J.; Zheng, H.; Huang, G.; Song, Q.; Pang, Z.; Du, J. SLC7A5 Is a Lung Adenocarcinoma-Specific Prognostic Biomarker and Participates in Forming Immunosuppressive Tumor Microenvironment. Heliyon 2022, 8, e10866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Nasser B Singab, A.; Lin, G.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, H.; Yang, G.; Chen, J.; Li, J.; Li, P.; Zhao, D.; et al. The Regulatory Role of Integrin in Gastric Cancer Tumor Microenvironment and Drug Resistance. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 2025, 195, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, A.; Nam, A.; Pozhitkov, A.; Yang, L.; Srivastava, S.; Nathan, A.; Wu, X.; Mambetsariev, I.; Nelson, M.; Subbalakshmi, A.R.; et al. A Non-Genetic Mechanism Involving the Integrin Β4/Paxillin Axis Contributes to Chemoresistance in Lung Cancer. iScience 2020, 23, 101496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, U.; Jung, D.B.; Jin, L.; Xiao, Y.; Dasari, S.; Bhattacharya, S.S.; Thirusangu, P.; Staub, J.K.; Roy, D.; Roy, B.; et al. Targeting LRRC15 Inhibits Metastatic Dissemination of Ovarian Cancer. Cancer Res. 2022, 82, 1038–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loo, L.; Waller, M.A.; Moreno, C.L.; Cole, A.J.; Stella, A.O.; Pop, O.T.; Jochum, A.K.; Ali, O.H.; Denes, C.E.; Hamoudi, Z.; et al. Fibroblast-Expressed LRRC15 Is a Receptor for SARS-CoV-2 Spike and Controls Antiviral and Antifibrotic Transcriptional Programs. PLoS Biol. 2023, 21, e3001967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Wang, G.; Zhu, H.; Xu, A. ITGA5 Is a Prognostic Biomarker and Correlated with Immune Infiltration in Gastrointestinal Tumors. BMC Cancer 2021, 21, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Chen, H.; Jiang, Z.; Lin, Y.; Wang, X.; Xiang, J.; Peng, J. Integrin Subunit Alpha V Promotes Growth, Migration, and Invasion of Gastric Cancer Cells. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2019, 215, 152531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, T.; Lin, Y.; Lai, X.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, Y.; Wang, X.; Liu, W.; Tang, Q.; Yang, T.; Feng, W.; et al. ITGB5 Facilitates Gastric Cancer Metastasis by Promoting TGFBR2 Endosomal Recycling. Cancer Lett. 2024, 592, 216953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeisel, M.B.; Fofana, I.; Fafi-Kremer, S.; Baumert, T.F. Hepatitis C Virus Entry into Hepatocytes: Molecular Mechanisms and Targets for Antiviral Therapies. J. Hepatol. 2011, 54, 566–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fénéant, L.; Levy, S.; Cocquerel, L. CD81 and Hepatitis C Virus (HCV) Infection. Viruses 2014, 6, 535–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, I.; Oshima, T. Claudins and Gastric Cancer: An Overview. Cancers 2022, 14, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, S.J.; Kim, M.S.; Na, C.H.; Jacobs-Lorena, M. Plasmodium Sporozoite Phospholipid Scramblase Interacts with Mammalian Carbamoyl-Phosphate Synthetase 1 to Infect Hepatocytes. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 6773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Yuan, L.; Yao, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, K.; Wu, X.; Wang, L.; Qin, L.; Li, W.; Xiang, Y.; et al. ITGB4 Deficiency in Airway Epithelium Aggravates RSV Infection and Increases HDM Sensitivity. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 912095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Liu, Y.; Tang, H.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, Q. ITGB5 Plays a Key Role in Escherichia Coli F4ac-Induced Diarrhea in Piglets. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siemens, N.; Patenge, N.; Otto, J.; Fiedler, T.; Kreikemeyer, B. Streptococcus Pyogenes M49 Plasminogen/Plasmin Binding Facilitates Keratinocyte Invasion via Integrin-Integrin-Linked Kinase (ILK) Pathways and Protects from Macrophage Killing. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 21612–21622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, N.-S.; Zeng, C.Q.-Y.; Hyser, J.M.; Utama, B.; Crawford, S.E.; Kim, K.J.; Höök, M.; Estes, M.K. Integrins A1β1 and A2β1 Are Receptors for the Rotavirus Enterotoxin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 8811–8818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolduc, G.R.; Madoff, L.C. The Group B Streptococcal Alpha C Protein Binds A1β1-Integrin through a Novel KTD Motif That Promotes Internalization of GBS within Human Epithelial Cells. Microbiology 2007, 153, 4039–4049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, Q.; Gong, L.; Liu, T.; Wang, P.; Yuan, Z.; Wang, W. The NF-ΚB-Regulated MiR-221/222/Syndecan-1 Axis and Intestinal Mucosal Barrier Function in Radiation Enteritis. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2022, 113, 166–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parimon, T.; Yao, C.; Habiel, D.M.; Ge, L.; Bora, S.A.; Brauer, R.; Evans, C.M.; Xie, T.; Alonso-Valenteen, F.; Medina-Kauwe, L.K.; et al. Syndecan-1 Promotes Lung Fibrosis by Regulating Epithelial Reprogramming through Extracellular Vesicles. JCI Insight 2019, 4, e129359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jinno, A.; Hayashida, A.; Jenkinson, H.F.; Park, P.W. Syndecan-1 Promotes Streptococcus Pneumoniae Corneal Infection by Facilitating the Assembly of Adhesive Fibronectin Fibrils. mBio 2020, 11, e01907–e01920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aquino, R.S.; Hayashida, A.; Park, P.W. Host Syndecan-1 Promotes Listeriosis by Inhibiting Intravascular Neutrophil Extracellular Traps. PLoS Pathog. 2020, 16, e1008497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, P.W.; Pier, G.B.; Hinkes, M.T.; Bernfield, M. Exploitation of Syndecan-1 Shedding by Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Enhances Virulence. Nature 2001, 411, 98–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, L.R.; Issa, R.; Albaldi, F.; Urwin, L.; Thompson, R.; Khalid, H.; Turner, C.E.; Ciani, B.; Partridge, L.J.; Monk, P.N. CD9 Co-Operation with Syndecan-1 Is Required for a Major Staphylococcal Adhesion Pathway. mBio 2023, 14, e0148223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayashida, A.; Amano, S.; Park, P.W. Syndecan-1 Promotes Staphylococcus Aureus Corneal Infection by Counteracting Neutrophil-Mediated Host Defense. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 3288–3297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashida, K.; Parks, W.C.; Pyong, W.P. Syndecan-1 Shedding Facilitates the Resolution of Neutrophilic Inflammation by Removing Sequestered CXC Chemokines. Blood 2009, 114, 3033–3043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malta, F.M.; Bruno, F.R.; Carvalho, K.I.; Nastri, A.C.S.S.; Kalil, J.; Carrilho, F.J.; Kallas, E.G.; Pinho, J.R.R. HCV Viremia Drives an Increment of CD86 Expression by Myeloid Dendritic Cells. J. Med. Virol. 2013, 85, 1919–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertaux-Skeirik, N.; Feng, R.; Schumacher, M.A.; Li, J.; Mahe, M.M.; Engevik, A.C.; Javier, J.E.; Peek, R.M.; Ottemann, K.; Orian-Rousseau, V.; et al. CD44 Plays a Functional Role in Helicobacter Pylori-Induced Epithelial Cell Proliferation. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1004663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wessels, M.R. Capsular Polysaccharide of Group A Streptococcus. Microbiol. Spectr. 2019, 7, 10.1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradimotlagh, A.; Chen, S.; Koohbor, S.; Moon, K.M.; Foster, L.J.; Reiner, N.; Nandan, D. Leishmania Infection Upregulates and Engages Host Macrophage Argonaute 1, and System-Wide Proteomics Reveals Argonaute 1-Dependent Host Response. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1287539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prieto-Fernández, E.; Egia-Mendikute, L.; Bosch, A.; García del Río, A.; Jimenez-Lasheras, B.; Antoñana-Vildosola, A.; Lee, S.Y.; Palazon, A. Hypoxia Promotes Syndecan-3 Expression in the Tumor Microenvironment. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 586977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumawat, K.; Gosens, R. WNT-5A: Signaling and Functions in Health and Disease. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2016, 73, 567–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Cai, H.; Zhang, C.; Yang, Z.; Niu, Y.; Wang, H.; Wei, X.; et al. MicroRNA-1253 Suppresses Cell Proliferation and Invasion of Non-Small-Cell Lung Carcinoma by Targeting WNT5A. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asem, M.S.; Buechler, S.; Wates, R.B.; Miller, D.L.; Stack, M.S. Wnt5a Signaling in Cancer. Cancers 2016, 8, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Xin, N.; Wang, W.; Zhao, C. Wnt/β-Catenin, an Oncogenic Pathway Targeted by H. Pylori in Gastric Carcinogenesis. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 35579–35588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Sztukowska, M.; Wang, Q.; Inaba, H.; Potempa, J.; Scott, D.A.; Wang, H.; Lamont, R.J. Noncanonical Activation of β-Catenin by Porphyromonas Gingivalis. Infect. Immun. 2015, 83, 3195–3203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui, T.M.; Wiesolek, H.L.; Sumagin, R. ICAM-1: A Master Regulator of Cellular Responses in Inflammation, Injury Resolution, and Tumorigenesis. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2020, 108, 787–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shukla, S.D.; Mahmood, M.Q.; Weston, S.; Latham, R.; Muller, H.K.; Sohal, S.S.; Walters, E.H. The Main Rhinovirus Respiratory Tract Adhesion Site (ICAM-1) Is Upregulated in Smokers and Patients with Chronic Airflow Limitation (CAL). Respir. Res. 2017, 18, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajan Raghavan, S.S.; Turner, L.; Jensen, R.W.; Johansen, N.T.; Jensen, D.S.; Gourdon, P.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Y.; Theander, T.G.; Wang, K.; et al. Endothelial Protein C Receptor Binding Induces Conformational Changes to Severe Malaria-Associated Group A PfEMP1. Structure 2023, 31, 1174–1183.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doulet, N.; Donnadieu, E.; Laran-Chich, M.P.; Niedergang, F.; Nassif, X.; Couraud, P.O.; Bourdoulous, S. Neisseria Meningitidis Infection of Human Endothelial Cells Interferes with Leukocyte Transmigration by Preventing the Formation of Endothelial Docking Structures. J. Cell Biol. 2006, 173, 627–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.C.; Chen, T.Y.; Liao, L.T.; Chen, T.; Li, Q.L.; Xu, J.X.; Hu, J.W.; Zhou, P.H.; Zhang, Y.Q. Neto2 Promotes Esophageal Cancer Progression by Inducing Proliferation and Metastasis via Pi3k/Akt and Erk Pathway. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 17, 259–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagattuta, K.A.; Kohlgruber, A.C.; Abdelfattah, N.S.; Nathan, A.; Rumker, L.; Birnbaum, M.E.; Elledge, S.J.; Raychaudhuri, S. The T Cell Receptor Sequence Influences the Likelihood of T Cell Memory Formation. Cell Rep. 2025, 44, 115098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashiro, Y.; Thang, B.Q.; Ramirez, K.; Shin, J.; Kohata, T.; Ohata, S.; Nguyen, A.V.; Ohtsuki, S.; Nagayama, K.; Yanagisawa, H. Matrix Mechanotransduction Mediated by Thrombospondin-1/Integrin/YAP in the Vascular Remodeling. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 9896–9905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, F.A.; Dhawan, S.; Singh, S.; Singh, B.; Gupta, P.; Pandey, A.; Mohmmed, A.; Gaur, D.; Chitnis, C.E. A Thrombospondin Structural Repeat Containing Rhoptry Protein from Plasmodium Falciparum Mediates Erythrocyte Invasion. Cell Microbiol. 2013, 15, 1341–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabello, F.C.; Godfrey, H.P.; Newman, S.A. Hidden in Plain Sight: Borrelia Burgdorferi and the Extracellular Matrix. Trends Microbiol. 2007, 15, 350–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angabo, S.; Pandi, K.; David, K.; Steinmetz, O.; Makkawi, H.; Farhat, M.; Eli-Berchoer, L.; Darawshi, N.; Kawasaki, H.; Nussbaum, G. CD47 and Thrombospondin-1 Contribute to Immune Evasion by Porphyromonas Gingivalis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2024, 121, e2405534121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tal, M.C.; Dulgeroff, L.B.T.; Myers, L.; Cham, L.B.; Mayer-Barber, K.D.; Bohrer, A.C.; Castro, E.; Yiu, Y.Y.; Angel, C.L.; Pham, E.; et al. Upregulation of CD47 Is a Host Checkpoint Response to Pathogen Recognition. mBio 2020, 11, e01293-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novikov, A.; Cardone, M.; Thompson, R.; Shenderov, K.; Kirschman, K.D.; Mayer-Barber, K.D.; Myers, T.G.; Rabin, R.L.; Trinchieri, G.; Sher, A.; et al. Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Triggers Host Type I IFN Signaling To Regulate IL-1β Production in Human Macrophages. J. Immunol. 2011, 187, 2540–2547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veiga, E.; Cossart, P. Listeria InlB Takes a Different Route to Met. Cell 2007, 130, 218–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Junker, F.; Gordon, J.; Qureshi, O. Fc Gamma Receptors and Their Role in Antigen Uptake, Presentation, and T Cell Activation. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cormier, E.G.; Tsamis, F.; Kajumo, F.; Durso, R.J.; Gardner, J.P.; Dragic, T. CD81 Is an Entry Coreceptor for Hepatitis C Virus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 7270–7274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, G.H.; Cui, Y.; Yu, H.; Cui, X. Profiling Analysis of FOX Gene Family Members Identified FOXE1 as Potential Regulator of NSCLC Development. Cell Mol. Biol. 2016, 62, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Liu, Z.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Y. High Serum HDGF Levels Are Predictive of Bone Metastasis and Unfavorable Prognosis in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Tohoku J. Exp. Med. 2017, 242, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Sun, Y.; Wang, W.; Ren, J.; Wang, D. BHLHE40-Mediated Transcriptional Activation of GRIN2D in Gastric Cancer Is Involved in Metabolic Reprogramming. Funct. Integr. Genom. 2024, 24, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiss, Z.; Mudryj, M.; Ghosh, P.M. Non-Circadian Aspects of BHLHE40 Cellular Function in Cancer. Genes Cancer 2020, 11, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Regalo, G.; Förster, S.; Resende, C.; Bauer, B.; Fleige, B.; Kemmner, W.; Schlag, P.M.; Meyer, T.F.; Machado, J.C.; Leutz, A. C/EBPβ Regulates Homeostatic and Oncogenic Gastric Cell Proliferation. J. Mol. Med. 2016, 94, 1385–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Xie, X.; Yang, M.; Wang, Y.; Wu, H.; Deng, T.; Weng, X.; Wen, W.; Nie, G. YBX3 Mediates the Metastasis of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma via PI3K/AKT Signaling. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 617621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, X.; Huang, J.; Yu, K.; Chen, X.; He, Y.; Qi, D.; Wu, Y. YB-1 Transferred by Gastric Cancer Exosomes Promotes Angiogenesis via Enhancing the Expression of Angiogenic Factors in Vascular Endothelial Cells. BMC Cancer 2020, 20, 996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Sun, G.; Peng, C.; Chen, J.; Quan, J.; Wu, C.; Lian, X.; Tang, W.; Xiang, D. ZEB1 Promotes Colorectal Cancer Cell Invasion and Disease Progression by Enhanced LOXL2 Transcription. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2021, 14, 9–23. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Tabarestani, F.O.; Akbari, A.; Karizi, S.Z.; Ematalahi, F.S. Regulation of Long Non-Coding RNAs XIST and ROR Induced by Homeodomain Protein TGIF2LX in Colorectal Cancer. J. Cancer Res. Ther. 2022, 18, S359–S366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avendaño-Felix, M.; Aguilar-Medina, M.; Romero-Quintana, J.G.; Ayala-Ham, A.; Beltran, A.S.; Olivares-Quintero, J.F.; López-Camarillo, C.; Pérez-Plasencia, C.; Bermúdez, M.; Lizárraga-Verdugo, E.; et al. SOX9 Knockout Decreases Stemness Properties in Colorectal Cancer Cells. J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2023, 14, 1735–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhanasekaran, R.; Deutzmann, A.; Mahauad-Fernandez, W.D.; Hansen, A.S.; Gouw, A.M.; Felsher, D.W. The MYC Oncogene —The Grand Orchestrator of Cancer Growth and Immune Evasion. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 19, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Tan, Y.; Jia, Q.Y.; Tang, F.Q. Transcriptional Factor III A Promotes Colorectal Cancer Progression by Upregulating Cystatin A. World J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2022, 14, 1918–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Pang, J.; Wang, L.; Dong, Q.; Jin, D. CEBPB Regulates the Bile Acid Receptor FXR to Accelerate Colon Cancer Progression by Modulating Aerobic Glycolysis. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2022, 36, e24703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeda, K.; Kinoshita, I.; Shimizu, Y.; Ohba, Y.; Itoh, T.; Matsuno, Y.; Shichinohe, T.; Dosaka-Akita, H. Clinicopathological Significance of Expression of P-c-Jun, TCF4 and Beta-Catenin in Colorectal Tumors. BMC Cancer 2008, 8, 328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.; Wu, H.; Jin, S.; Li, D.; Tan, S.; Zhu, X. Roles of Myc-Associated Zinc Finger Protein in Malignant Tumors. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 18, 506–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, X.; Duronio, G.N.; Yang, Y.; Bala, P.; Hebbar, P.; Spisak, S.; Sahgal, P.; Singh, H.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, Y.; et al. An Enhancer-Driven Stem Cell–Like Program Mediated by SOX9 Blocks Intestinal Differentiation in Colorectal Cancer. Gastroenterology 2022, 162, 209–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, Y.; Wang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Ou, R.; Zhu, Z.; Ou, Y.; Chen, X.; Liang, X.; Ding, Y.; Song, L.; et al. Jade Family PHD Finger 3 (JADE3) Increases Cancer Stem Cell-like Properties and Tumorigenicity in Colon Cancer. Cancer Lett. 2018, 428, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saliba, J.; Coutaud, B.; Makhani, K.; Epstein Roth, N.; Jackson, J.; Park, J.Y.; Gagnon, N.; Costa, P.; Jeyakumar, T.; Bury, M.; et al. Loss of NFE2L3 Protects against Inflammation-Induced Colorectal Cancer through Modulation of the Tumor Microenvironment. Oncogene 2022, 41, 1563–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bury, M.; Le Calvé, B.; Lessard, F.; Dal Maso, T.; Saliba, J.; Michiels, C.; Ferbeyre, G.; Blank, V. NFE2L3 Controls Colon Cancer Cell Growth through Regulation of DUX4, a CDK1 Inhibitor. Cell Rep. 2019, 29, 1469–1481.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, G.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Sun, L.; Wang, L.; Yao, B.; Liu, R.; Chen, T.; Niu, Y.; Liu, Q. ZNF503 Accelerates Aggressiveness of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells by Down-Regulation of GATA3 Expression and Regulated by MicroRNA-495. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2019, 11, 3426–3437. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Chen, Y.J.; Li, Y.; Guo, X.; Huo, B.; Chen, Y.; He, Y.; Xiao, R.; Zhu, X.H.; Jiang, D.S.; Wei, X. Upregulation of IRF9 Contributes to Pulmonary Artery Smooth Muscle Cell Proliferation During Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 773235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunn, D.; Turkowski, K.; Günther, S.; Weigert, A.; Muley, T.; Kriegsmann, M.; Winter, H.; Dammann, R.H.; Stathopoulos, G.T.; Thomas, M.; et al. Interferon Regulatory Factor 9 Promotes Lung Cancer Progression via Regulation of Versican. Cancers 2021, 13, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muniz, J.J.; Joyce, M.M.; Taylor, J.D.; Burghardt, J.R.; Burghardt, R.C.; Johnson, G.A. Glycosylation Dependent Cell Adhesion Molecule 1-like Protein and L-Selectin Expression in Sheep Interplacentomal and Placentomal Endometrium. Reproduction 2006, 131, 751–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Deng, Y.; Lu, L.; Zhang, H.; Fu, Y.; Liu, T.; Chen, Y. The Role and Regulation of Maf Proteins in Cancer. Biomark. Res. 2023, 11, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Han, M.; Zhang, H.; Liu, F.; Pan, Y.; Zhu, J.; Liao, Z.; Chen, X.; Zhang, B. Structures and Biological Functions of Zinc Finger Proteins and Their Roles in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Biomark. Res. 2022, 10, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, X. Comprehensive Analysis of the Role of Forkhead Box J3 (FOXJ3) in Human Cancers. Wuhan. Univ. J. Nat. Sci. 2024, 29, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Zhang, Z. OVOL2: An Epithelial Lineage Determiner with Emerging Roles in Energy Homeostasis. Trends Cell Biol. 2023, 33, 824–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herwartz, C.; Castillo-Juárez, P.; Schröder, L.; Barron, B.L.; Steger, G. The Transcription Factor ZNF395 Is Required for the Maximal Hypoxic Induction of Proinflammatory Cytokines in U87-MG Cells. Mediat. Inflamm. 2015, 2015, 804264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, D.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Li, S.; Zhang, J.; Wu, Z.; Sun, M.; Jiang, J.; Liu, D.; Ji, X.; et al. Transcription Factor ELF4 in Physiology and Diseases: Molecular Roles and Clinical Implications. Genes. Dis. 2024, 12, 101394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Shi, H.; Wang, X.; Wang, T.; Wang, Y.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, W.; Chen, H.; Zhong, M.; Mao, X.; et al. Hepatocyte Nuclear Factor 4 Gamma (HNF4G) Is Correlated with Poor Prognosis and Promotes Tumor Cell Growth by Inhibiting Caspase-Dependent Intrinsic Apoptosis in Colorectal Cancer. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2022, 916, 174727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, F.; Mo, H.; Zhang, H.; Dai, Z.; Wang, Z.; Qu, C.; Liu, F.; Zhang, L.; Luo, P.; Zhang, J.; et al. HOXA5: A Crucial Transcriptional Factor in Cancer and a Potential Therapeutic Target. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 155, 113800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.; Huang, Y.; Lin, J.; Sun, S.; Che, K.; Shen, J.; Liao, J.; Chen, Y.; Chen, K.; Lin, Z.; et al. Mxi1 Participates in the Progression of Lung Cancer via the MicroRNA-300/KLF9/GADD34 Axis. Cell Death Dis. 2022, 13, 425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.; Hou, Y.; Hu, M.; Hu, J.; Liu, X. Clinical Significance and Oncogenic Function of NR1H4 in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma. BMC Cancer 2022, 22, 995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Nagy, L.E.; Liangpunsakul, S.; Wang, L. Non-Coding RNA Crosstalk with Nuclear Receptors in Liver Disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2021, 1867, 166083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, C.; Qiu, M.; Lin, M. Zinc Finger Proteins in Colorectal Cancer: Insights into Molecular Mechanisms and Therapeutic Implications. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2025, 24, 15330338251334447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebastian-Delacruz, M.; Gonzalez-Moro, I.; Olazagoitia-Garmendia, A.; Castellanos-Rubio, A.; Santin, I. The Role of LncRNAs in Gene Expression Regulation through MRNA Stabilization. Non-Coding RNA 2021, 7, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattick, J.S.; Amaral, P.P.; Carninci, P.; Carpenter, S.; Chang, H.Y.; Chen, L.L.; Chen, R.; Dean, C.; Dinger, M.E.; Fitzgerald, K.A.; et al. Long Non-Coding RNAs: Definitions, Functions, Challenges and Recommendations. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2023, 24, 430–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segal, D.; Dostie, J. The Talented LncRNAs: Meshing into Transcriptional Regulatory Networks in Cancer. Cancers 2023, 15, 3433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattioli, K.; Volders, P.J.; Gerhardinger, C.; Lee, J.C.; Maass, P.G.; Melé, M.; Rinn, J.L. High-Throughput Functional Analysis of LncRNA Core Promoters Elucidates Rules Governing Tissue Specificity. Genome Res. 2019, 29, 344–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, M.; Chen, J.; Li, Y.; Kuang, Z.; Dende, C.; Raj, P.; Quinn, G.; Hu, Z.; Srinivasan, T.; et al. The Gut Microbiota Reprograms Intestinal Lipid Metabolism through Long Noncoding RNA Snhg9. Science 2023, 381, 851–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, S.; Xing, J.; Jiang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Wang, D.; Tang, D. Effects of Long Non-Coding RNAs Induced by the Gut Microbiome on Regulating the Development of Colorectal Cancer. Cancers 2022, 14, 5813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, P.; Bensaoud, C.; Mekki, I.; Rehman, M.U.; Kotsyfakis, M. Long Non-Coding RNAs and Their Potential Roles in the Vector–Host–Pathogen Triad. Life 2021, 11, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liaci, A.M.; Förster, F. Take Me Home, Protein Roads: Structural Insights into Signal Peptide Interactions during Er Translocation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iijima, J.; Konno, K.; Itano, N. Inflammatory Alterations of the Extracellular Matrix in the Tumor Microenvironment. Cancers 2011, 3, 3189–3205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popova, N.V.; Jücker, M. The Functional Role of Extracellular Matrix Proteins in Cancer. Cancers 2022, 14, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumari, N.; Reabroi, S.; North, B.J. Unraveling the Molecular Nexus between GPCRs, ERS, and EMT. Mediat. Inflamm. 2021, 2021, 6655417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Hayre, M.; Degese, M.S.; Gutkind, J.S. Novel Insights into G Protein and G Protein-Coupled Receptor Signaling in Cancer. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2014, 27, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, X.; Zhu, W.; Zhou, J.; Li, H.; Xu, X.; Zhang, B.; Gao, X. Repetitive DNA Sequence Detection and Its Role in the Human Genome. Commun. Biol. 2023, 6, 954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhang, S.; Wang, X.; Dou, H.; Yu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, S.; Xiao, M. Extracellular Matrix Remodeling in Tumor Progression and Immune Escape: From Mechanisms to Treatments. Mol. Cancer 2023, 22, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, N.; Shen, G.; Gao, W.; Huang, Z.; Huang, C.; Fu, L. Neoantigens: Promising Targets for Cancer Therapy. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, E. Tumor Glycosylation: A Main Player in the Modulation of Immune Responses. Eur. J. Immunol. 2025, 55, e202451318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cassandri, M.; Smirnov, A.; Novelli, F.; Pitolli, C.; Agostini, M.; Malewicz, M.; Melino, G.; Raschellà, G. Zinc-Finger Proteins in Health and Disease. Cell Death Discov. 2017, 3, 17071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Zazzo, E.; De Rosa, C.; Abbondanza, C.; Moncharmont, B. PRDM Proteins: Molecular Mechanisms in Signal Transduction and Transcriptional Regulation. Biology 2013, 2, 107–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Tullio, F.; Schwarz, M.; Zorgati, H.; Mzoughi, S.; Guccione, E. The Duality of PRDM Proteins: Epigenetic and Structural Perspectives. FEBS J. 2022, 289, 1256–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakhra, G.; Rakhra, G. Zinc Finger Proteins: Insights into the Transcriptional and Post Transcriptional Regulation of Immune Response. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2021, 48, 5735–5743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Wen, D.; Zhang, S.; Jiang, H.; Di, X. The Role of Zinc Finger Proteins in Malignant Tumors. FASEB J. 2023, 37, e23157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Liu, H.; Liu, Z.; Yi, X.; Bickeboller, H.; Hung, R.J.; Brennan, P.; Landi, M.T.; Caporaso, N.; Christiani, D.C.; et al. Genetic Variant in DNA Repair Gene GTF2H4 Is Associated with Lung Cancer Risk: A Large-Scale Analysis of Six Published GWAS Datasets in the TRICL Consortium. Carcinogenesis 2016, 37, 888–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Qi, H.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, W.; Li, Y.; Li, A.; Liu, Q.; Wang, Y. TAF1L Promotes Development of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma via Decreasing Autophagy-Dependent Apoptosis. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2020, 16, 1180–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, S.; Yan, H.; Chen, Z.; Li, Y.; Shen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, L.; Sheng, S.; Wang, Y. Overexpression of TAF1L Promotes Cell Proliferation, Migration and Invasion in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. J. Cancer 2019, 10, 979–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.Y.; Lin, K.C.; Lawal, B.; Wu, A.T.H.; Wu, C.Z. MXD3 as an Onco-Immunological Biomarker Encompassing the Tumor Microenvironment, Disease Staging, Prognoses, and Therapeutic Responses in Multiple Cancer Types. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2021, 19, 4970–4983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, J.Y.; Hsiao, Y.W.; Liu, H.L.; Fan, X.J.; Wan, X.B.; Liu, T.L.; Hung, S.J.; Chen, Y.T.; Liang, H.Y.; Wang, J.M. Fibroblast CEBPD/SDF4 Axis in Response to Chemotherapy-Induced Angiogenesis through CXCR4. Cell Death Discov. 2021, 7, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geeleher, P.; Nath, A.; Wang, F.; Zhang, Z.; Barbeira, A.N.; Fessler, J.; Grossman, R.L.; Seoighe, C.; Stephanie Huang, R. Cancer Expression Quantitative Trait Loci (EQTLs) Can Be Determined from Heterogeneous Tumor Gene Expression Data by Modeling Variation in Tumor Purity. Genome Biol. 2018, 19, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Xu, C.; Guo, J.; Liu, K.; Hu, Y.; Wu, D.; Fang, H.; Zou, Y.; Wei, Z.; Wang, Z.; et al. Cis- and Trans-Acting Expression Quantitative Trait Loci of Long Non-Coding RNA in 2,549 Cancers With Potential Clinical and Therapeutic Implications. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 602104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Gorospe, M.; Wang, J.-Y.; Gorospe, X.L.; Wang, M. THEME Physiological Roles of Non-Coding RNAs Long Noncoding RNAs in Intestinal Epithelium Homeostasis. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2019, 317, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Xue, Y.; Amin, M.T.; Yang, Y.; Yang, J.; Zhang, W.; Yang, W.; Niu, X.; Zhang, H.Y.; Gong, J. NcRNA-EQTL: A Database to Systematically Evaluate the Effects of SNPs on Non-Coding RNA Expression across Cancer Types. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, D956–D963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, N.; Li, Y.; Li, J.; Gao, Z.; Yang, Z.; Li, Y.; Liu, H.; Fan, T. Long Non-Coding RNAs: The Regulatory Mechanisms, Research Strategies, and Future Directions in Cancers. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 598817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Wan, L.; Wang, W.; Xi, W.J.; Yang, A.G.; Wang, T. Re-Recognition of Pseudogenes: From Molecular to Clinical Applications. Theranostics 2020, 10, 1479–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Xu, H.; Pi, S.; Tan, H.; Huang, B.; Chen, Y. The Prognostic and Immunological Role of FKBP1A in an Integrated Muti-Omics Cancers Analysis, Especially Lung Cancer. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 149, 16589–16608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pink, R.C.; Wicks, K.; Caley, D.P.; Punch, E.K.; Jacobs, L.; Carter, D.R.F. Pseudogenes: Pseudo-Functional or Key Regulators in Health and Diseasě. RNA 2011, 17, 792–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Y.; Furber, K.L.; Ji, S. Pseudogenes Regulate Parental Gene Expression via CeRNA Network. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2017, 21, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura-García, A.K.; Espinal-Enríquez, J. Pseudogenes in Cancer: State of the Art. Cancers 2023, 15, 4024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xu, G.; Li, L. LncRNA GATA3-AS1-MiR-30b-5p-Tex10 Axis Modulates Tumorigenesis in Pancreatic Cancer. Oncol. Rep. 2021, 45, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Zhou, N.; Wang, L.; Zeng, Q.; Tang, H. Long Noncoding RNA GATA3-AS1 Promotes Cell Proliferation and Metastasis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Suppression of PTEN, CDKN1A, and TP53. Can. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 2019, 1389653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbons, H.R.; Shaginurova, G.; Kim, L.C.; Chapman, N.; Spurlock, C.F.; Aune, T.M. Divergent LncRNA GATA3-AS1 Regulates GATA3 Transcription in T-Helper 2 Cells. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, N.; Cao, L.; Zhang, D.; Peng, H.; Xue, P. Long Non-Coding RNA HOXB-AS1 Is a Prognostic Marker and Promotes Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells’ Proliferation and Invasion. Open Life Sci. 2022, 17, 944–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Huo, X.; Yang, X.R.; He, J.; Cheng, L.; Wang, N.; Deng, X.; Jin, H.; Wang, N.; Wang, C.; et al. STAT3-Mediated Upregulation of LncRNA HOXD-AS1 as a CeRNA Facilitates Liver Cancer Metastasis by Regulating SOX4. Mol. Cancer 2017, 16, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Bai, H.; Jiang, M.; Zhou, C.; Gong, Z. Emerging Role of Long Non-Coding RNA JPX in Malignant Processes and Potential Applications in Cancers. Chin. Med. J. 2023, 136, 757–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bechtel, T.J.; Weerapana, E. From Structure to Redox: The Diverse Functional Roles of Disulfides and Implications in Disease. Proteomics 2017, 17, 1600391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Gao, J.; Liang, Z.; Yang, D. PDI-Regulated Disulfide Bond Formation in Protein Folding and Biomolecular Assembly. Molecules 2020, 26, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feige, M.J.; Hendershot, L.M. Disulfide Bonds in ER Protein Folding and Homeostasis. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2011, 23, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Zhou, J.; Jiang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Huang, J.; Li, W.; Huang, Z.; Chen, Z.; Tang, X.; Chen, H.; et al. The Novel Protein ADAMTS16 Promotes Gastric Carcinogenesis by Targeting IFI27 through the NF-Κb Signaling Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 11022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, Q.; Zhou, L.; Xie, N.; Nice, E.C.; Zhang, H.; Huang, C.; Lei, Y. Cancer Drug Resistance: Redox Resetting Renders a Way. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 42740–42761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Li, Q.; Chen, S.; Huang, Y.; Ma, L.; Wang, Y.; Chen, J.; Zhang, J.; Liu, A.; Yuan, X.; et al. ADAMTS16 Drives Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition and Metastasis through a Feedback Loop upon TGF-Β1 Activation in Lung Adenocarcinoma. Cell Death Dis. 2024, 15, 837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanahan, D. Hallmarks of Cancer: New Dimensions. Cancer Discov. 2022, 12, 31–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.; Lubman, D.M. The Role of N-Glycosylation in Cancer. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2024, 14, 1098–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinoshita, T.; Ariga, H.; Matsumoto, K.-I. Distinct Glycosylation in Interstitial and Serum Tenascin-X. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2007, 30, 354–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, R.; Wu, C.; Guo, L.; Liu, Y.; Mo, W.; Wang, H.; Ding, J.; Wong, E.T.; Yu, M. The Role of Brevican in Glioma: Promoting Tumor Cell Motility in Vitro and in Vivo. BMC Cancer 2012, 12, 607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coleman, J.L.J.; Ngo, T.; Smythe, R.E.; Cleave, A.J.; Jones, N.M.; Graham, R.M.; Smith, N.J. The N-Terminus of GPR37L1 Is Proteolytically Processed by Matrix Metalloproteases. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 19995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pindwarawala, M.; Abid, F.A.K.; Lee, J.; Miller, M.L.; Noppers, J.S.; Rideout, A.P.; Agosto, M.A. Defective Glycosylation and ELFN1 Binding of MGluR6 Congenital Stationary Night Blindness Mutants. Life Sci. Alliance 2025, 8, e202403118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Przygodzka, P.; Sochacka, E.; Soboska, K.; Pacholczyk, M.; Papiewska-Pająk, I.; Przygodzki, T.; Płociński, P.; Ballet, S.; De Prins, A.; Boncela, J. Neuromedin U Induces an Invasive Phenotype in CRC Cells Expressing the NMUR2 Receptor. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 40, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, H.; Wu, J.; Yuan, C.; Chen, S.; Liu, S.; Huo, M.; Zhang, C.; He, Y. GALNT1 Enhances Malignant Phenotype of Gastric Cancer via Modulating CD44 Glycosylation to Activate the Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2022, 18, 6068–6083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinho, S.S.; Macauley, M.S.; Läubli, H. Tumor Glyco-Immunology, Glycoimmune Checkpoints and Immunotherapy. J. Immunother. Cancer 2025, 13, e012391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maestri, C.A.; Nisihara, R.; Mendes, H.W.; Jensenius, J.; Thiel, S.; Messias-Reason, I.; De Carvalho, N.S. MASP-1 and MASP-2 Serum Levels Are Associated with Worse Prognostic in Cervical Cancer Progression. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolev, M.; Das, M.; Gerber, M.; Baver, S.; Deschatelets, P.; Markiewski, M.M. Inside-Out of Complement in Cancer. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 931273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandler, K.B.; Costello, C.E.; Rahimi, N. Glycosylation in the Tumor Microenvironment: Implications for Tumor Angiogenesis and Metastasis. Cells 2019, 8, 544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, Y.; Shi, Y.; Yang, Z.; Wu, W.; Ma, R.; Wang, B.; Sun, Y.; Yuan, P. The Oncogenic Role of TNFRSF12A in Colorectal Cancer and Pan-Cancer Bioinformatics Analysis. Cancer Res. Treat. 2025, 57, 212–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, D.; Yuan, H.; Hu, Y.; Wang, C.; Ge, S.; Shao, K.; Wang, H.; Tian, X.; Hu, H. Loss of TNFRSF21 Induces Cisplatin Sensitivity in Lung Adenocarcinoma. Oncol. Res. 2025, 33, 653–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, C.; Gan, R. Signaling Pathways of EBV-Induced Oncogenesis. Cancer Cell Int. 2021, 21, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, A.K.F.; Dawson, C.W.; Lung, H.L.; Wong, K.L.; Young, L.S. The Role of EBV-Encoded LMP1 in the NPC Tumor Microenvironment: From Function to Therapy. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 640207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Li, X.; Liu, L.; Zhu, Z.; He, C. Exosomes in Lung Cancer Metastasis, Diagnosis, and Immunologically Relevant Advances. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1326667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Xie, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, S.; Zhan, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Li, J.; Li, P.; Wang, C. Characterization of a Novel LUCAT1/MiR-4316/VEGF-A Axis in Metastasis and Glycolysis of Lung Adenocarcinoma. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 833579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, K.; Li, S.; Ding, J.; Wang, Z.; Wang, D.; Cao, X.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, Z. Expression and Clinical Value of CircRNAs in Serum Extracellular Vesicles for Gastric Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 962831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, T.; Huang, X.; Woodcock, M.; Du, M.; Dittmar, R.; Wang, Y.; Tsai, S.; Kohli, M.; Boardman, L.; Patel, T.; et al. Plasma Extracellular RNA Profiles in Healthy and Cancer Patients. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, srep19413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.; Song, C.; Fan, S.; Yin, M.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, X.; Li, Y.; Shang, D.; Li, C.; et al. LncSEA 2.0:Ãn Updated Platform for Long Non-Coding RNA Related Setsãnd Enrichmentãnalysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024, 52, D919–D928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherman, B.T.; Hao, M.; Qiu, J.; Jiao, X.; Baseler, M.W.; Lane, H.C.; Imamichi, T.; Chang, W. DAVID: A Web Server for Functional Enrichment Analysis and Functional Annotation of Gene Lists (2021 Update). Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, W216–W221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huynh-Thu, V.A.; Irrthum, A.; Wehenkel, L.; Geurts, P. Inferring Regulatory Networks from Expression Data Using Tree-Based Methods. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e12776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almeida-Silva, F.; Venancio, T.M. BioNERO: An All-in-One R/Bioconductor Package for Comprehensive and Easy Biological Network Reconstruction. Funct. Integr. Genom. 2022, 22, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otasek, D.; Morris, J.H.; Bouças, J.; Pico, A.R.; Demchak, B. Cytoscape Automation: Empowering Workflow-Based Network Analysis. Genome Biol. 2019, 20, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keenan, A.B.; Torre, D.; Lachmann, A.; Leong, A.K.; Wojciechowicz, M.L.; Utti, V.; Jagodnik, K.M.; Kropiwnicki, E.; Wang, Z.; Ma’ayan, A. ChEA3: Transcription Factor Enrichment Analysis by Orthogonal Omics Integration. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W212–W224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



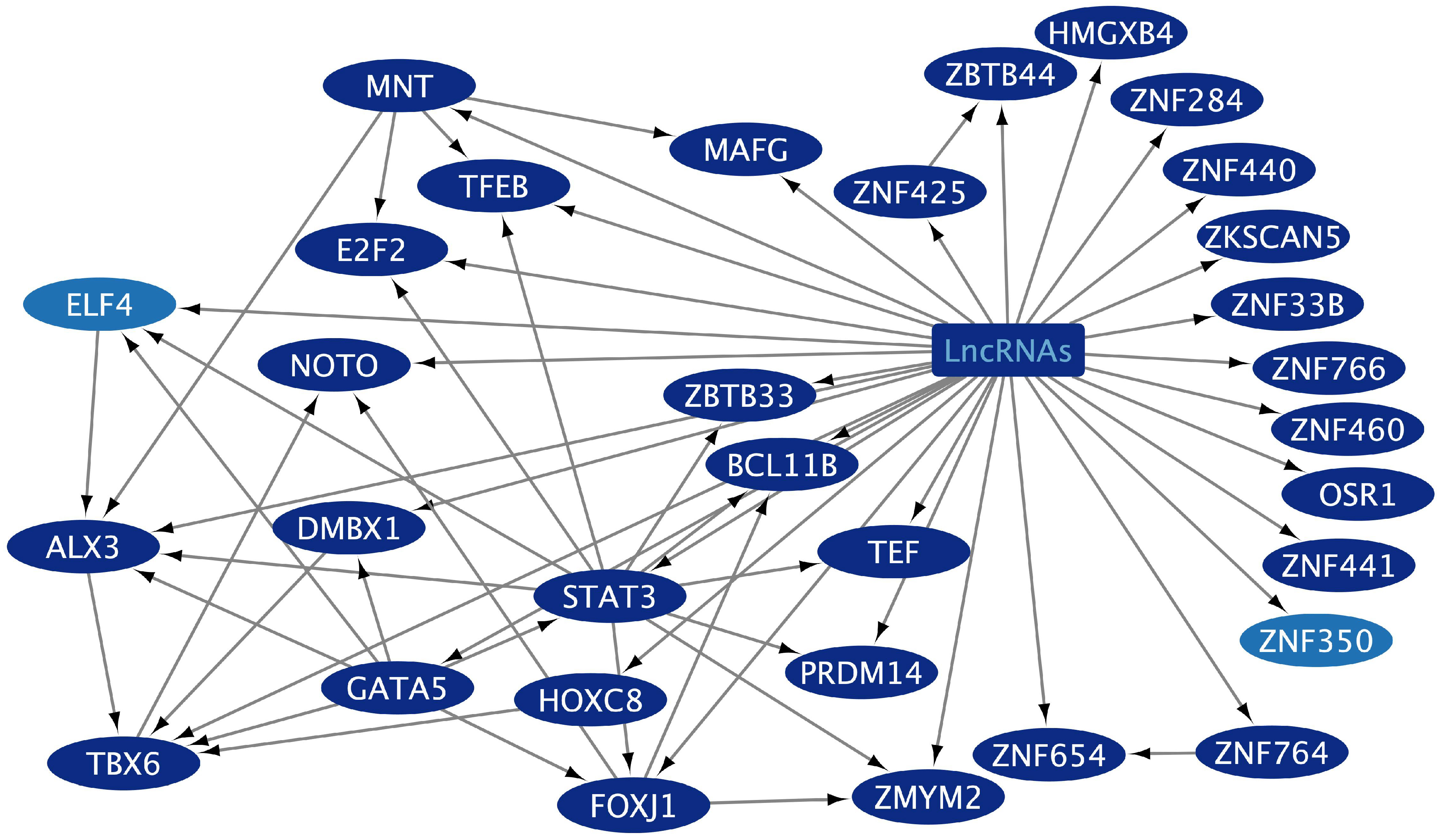
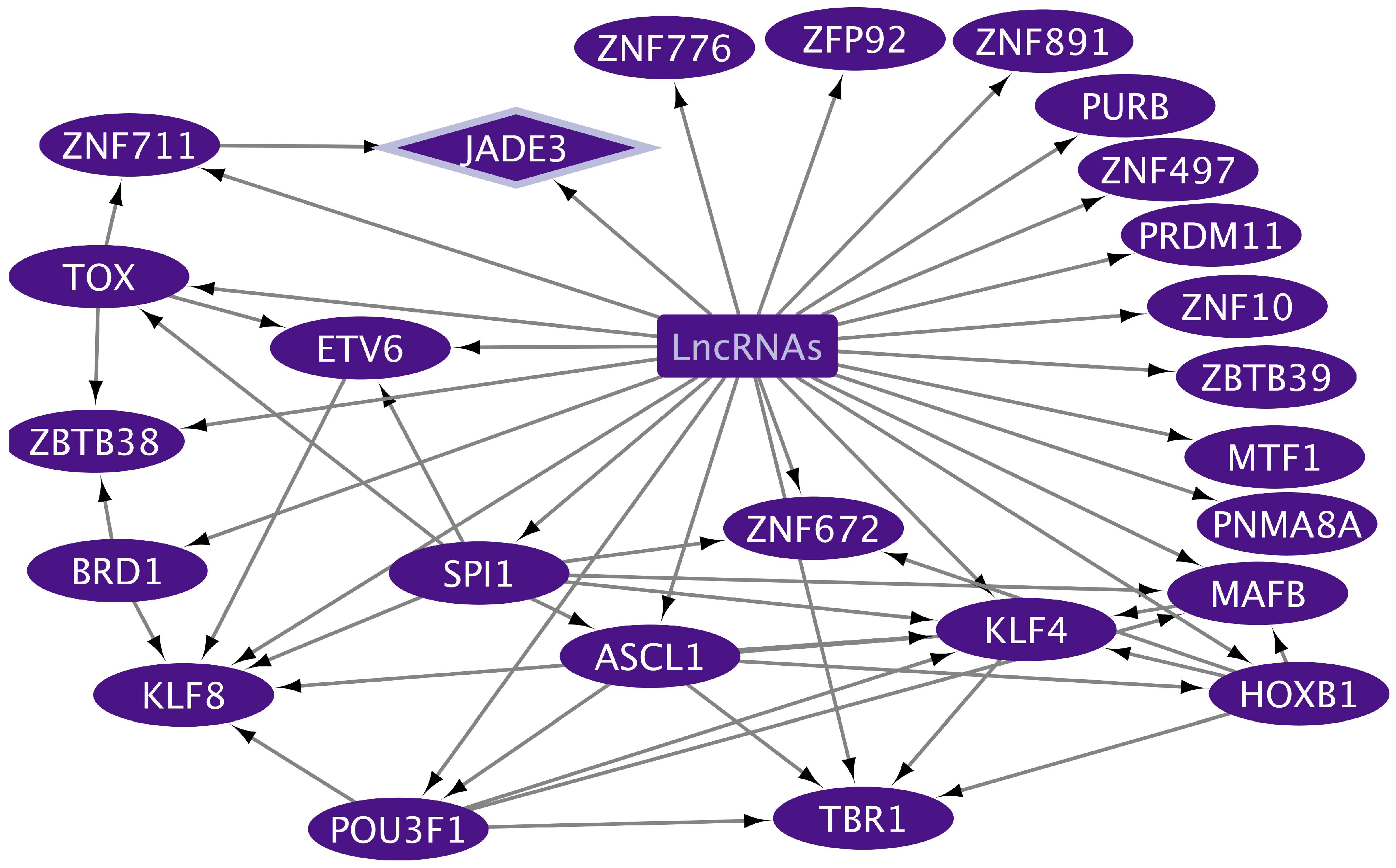

| Tissue | TF | Blood | Gene Targets Cellular Processes |
|---|---|---|---|
| LC | FOXE1 | GC | Biological processes: chromosome segregation, DNA repair, CMG and MCM complex, DNA damage, extracellular exosome, cell proliferation, RNA binding, apoptosis, homologous recombination, cell junction, and RNA splicing. Signaling pathways: DNA replication; base excision repair; mismatch repair; p53, pyrimidine, purine, and glutathione metabolism; nucleotide excision repair; nucleotide metabolism; cellular senescence; small cell LC; HTLV-1, EBV, and HPV infection; viral carcinogenesis; microRNAs; and pathways in cancer. Epigenetic reprogramming: Phosphoprotein, acetylation, Ubl conjugation, histone kinase activity, histone binding, protein modification process, methylation, prenylation, and hydroxylation. |
| HDGF | LC | ||
| GC | BHLHE40 | LC | Biological process: Collagen-containing extracellular matrix, integrin binding, cell surface, cell adhesion, differentiation, migration, division, proliferation, migration, junction, and projection, extracellular exosome, angiogenesis, apoptosis, receptor ligand activity, DNA replication, membrane raft, and host cell receptor for virus entry Signaling pathways: ECM–receptor interaction, focal adhesion, protein digestion and absorption, cell cycle, amoebiasis, PI3K-Akt, HPV, cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction, malaria, phagosome, small cell LC, IL-17, response to type II interferon, NF-kappa B, and KSHV infection. Epigenetic reprogramming: Glycoprotein, hydroxylation, phosphorylation, protein homodimerization activity, histone acetyltransferase binding, and protein ubiquitination. |
| CEBPB | LC | ||
| YBX3 TEAD4 | LC | ||
| CC | CEBPB | LC | Biological process: Protein binding, cell division, collagen-containing extracellular matrix, RNA binding and splicing, nucleotide-binding, ATP binding, mRNA 5′-UTR binding, transcription coregulator binding, DNA replication, rRNA processing, cell surface, extracellular exosome, host–virus interaction, translation, apoptosis, cell migration and proliferation, EMT, DNA damage response, ribosome biogenesis, and stem cell factor receptor activity. Signaling pathways: Cell cycle, ECM–receptor interaction, nucleocytoplasmic transport, HPV infection, cellular senescence, focal adhesion, small cell LC, EBV infection, proteoglycans in cancer, pathways in cancer, malaria, hippo HPC, amoebiasis, influenza A, insulin receptor, lysosome, chemokine-mediated, WNT, and VEGF receptor-1. Epigenetic reprogramming: Acetylation, Ubl conjugation, phosphoprotein, histone binding, protein digestion and absorption, methylation, histone kinase activity, and histone phosphatase activity. |
| GTF3A | LC | ||
| JADE3 | CC | ||
| JUN | LC | ||
| MAZ | LC | ||
| MYC | LC | ||
| NFE2L3 | GC | ||
| SOX9 | LC | ||
| TGIF2 | LC | ||
| ZEB1 | LC | ||
| ZNF503 | GC |
| Tissue | TF | Blood | Gene Targets Cellular Processes |
|---|---|---|---|
| PAH | IRF9 | LC | Biological process: Extracellular exosome, transmembrane helix, cell junction, adhesion, migration and growth, cytoplasmic vesicle, Golgi apparatus, membrane raft, angiogenesis, nuclear inner membrane, mitochondrial ribosome binding, retromer complex binding, and innate immunity. Signaling pathways: HPV, hepatitis C, salmonella, vibrio cholerae and epithelial cell signaling in Helicobacter pylori infection, leukocyte transendothelial migration, endocrine resistance, efferocytosis, mTOR, phagosome, VEGF, NOTCH, autophagy, neurotrophin, sphingolipid, thyroid hormone, central carbon metabolism in cancer, inositol phosphate metabolism, lysosome, chemokine, FoxO, aldosterone-regulated sodium reabsorption, phosphatidylinositol signaling system, PD-L1 expression and PD-1 checkpoint pathway in cancer, EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor resistance, chemical carcinogenesis—reactive oxygen species, pathways and microRNAs in cancer, and cell surface receptor. Epigenetic reprogramming: Glycoprotein, phosphoprotein, prenylation, negative regulation of protein phosphorylation, protein dephosphorylation, and histone phosphatase activity. |
| GLMP | GC | ||
| MAF | LC | ||
| ZNF346 | GC | ||
| ZNF503 | GC | ||
| CD | FOXJ3 | LC | Biological processes: Transit peptide, mitochondrion, transmembrane helix, protein transport, and extracellular exosome and endosome. Signaling pathways: Multiple metabolic pathways, fatty acid degradation, citrate cycle (TCA cycle), thermogenesis, peroxisome, Rap1, drug metabolism—cytochrome P450, phosphatidylinositol signaling system, PPAR, biosynthesis of cofactors, valine, leucine and isoleucine degradation, chemical carcinogenesis—receptor activation, inflammatory mediator regulation of TRP channels, proteoglycans in cancer, ErbB, phospholipase D, longevity regulating, calcium, PI3K-Akt, endocrine resistance, MAPK, ABC transporters, tight junction, oxidative phosphorylation, gastric acid secretion, and virion—hepatitis viruses. Epigenetic reprogramming: Acetylation, phosphoprotein, protein glycosylation, protein dephosphorylation, and histone phosphatase activity. |
| OVOL2 | GC | ||
| ZNF395 | LC | ||
| UC | ELF4 | LC GC | Biological process: Mitochondrion, transit peptide, extracellular exosome, nucleotide-binding, ATP-binding, cellular respiration, projection, differentiation and detoxification, endosome, transmembrane transporter activity, transmembrane helix, membrane raft, protein transport, and phosphatidic acid binding. Signaling pathways: Multiple metabolic pathways, valine, leucine, and isoleucine degradation; citrate cycle (TCA cycle); PPAR; peroxisomes; thermogenesis; biosynthesis of cofactors; phosphatidylinositol signaling system; calcium; cAMP; AMPK; aldosterone synthesis and secretion; Ras; Rap1; oxidative phosphorylation; and ErbB. Epigenetic reprogramming: Acetylation, phosphoprotein, protein phosphorylation, histone kinase activity, and protein dephosphorylation. |
| FOXJ3 | LC | ||
| HNF4G | LC | ||
| HOXA5 | CC | ||
| MXI1 | LC | ||
| NR1H4 | LC | ||
| NR1I2 | GC | ||
| OVOL2 | GC | ||
| ZNF350 | GC | ||
| ZNF395 | LC |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Otálora-Otálora, B.A.; Payán-Gómez, C.; López-Rivera, J.J.; Patiño-Unibio, L.F.; Arboleda-Mojica, S.L.; Aristizábal-Guzmán, C.; Isaza-Ruget, M.A.; Álvarez-Moreno, C.A. The Exosome-Mediated Epigenome: Non-Coding RNA and mRNA-Coding Networks in Microbiome–Cellular Communication, Inflammation, and Tumorigenesis Along the Oral–Gut–Lung Axis. Epigenomes 2025, 9, 52. https://doi.org/10.3390/epigenomes9040052
Otálora-Otálora BA, Payán-Gómez C, López-Rivera JJ, Patiño-Unibio LF, Arboleda-Mojica SL, Aristizábal-Guzmán C, Isaza-Ruget MA, Álvarez-Moreno CA. The Exosome-Mediated Epigenome: Non-Coding RNA and mRNA-Coding Networks in Microbiome–Cellular Communication, Inflammation, and Tumorigenesis Along the Oral–Gut–Lung Axis. Epigenomes. 2025; 9(4):52. https://doi.org/10.3390/epigenomes9040052
Chicago/Turabian StyleOtálora-Otálora, Beatriz Andrea, César Payán-Gómez, Juan Javier López-Rivera, Luisa Fernanda Patiño-Unibio, Sally Lorena Arboleda-Mojica, Claudia Aristizábal-Guzmán, Mario Arturo Isaza-Ruget, and Carlos Arturo Álvarez-Moreno. 2025. "The Exosome-Mediated Epigenome: Non-Coding RNA and mRNA-Coding Networks in Microbiome–Cellular Communication, Inflammation, and Tumorigenesis Along the Oral–Gut–Lung Axis" Epigenomes 9, no. 4: 52. https://doi.org/10.3390/epigenomes9040052
APA StyleOtálora-Otálora, B. A., Payán-Gómez, C., López-Rivera, J. J., Patiño-Unibio, L. F., Arboleda-Mojica, S. L., Aristizábal-Guzmán, C., Isaza-Ruget, M. A., & Álvarez-Moreno, C. A. (2025). The Exosome-Mediated Epigenome: Non-Coding RNA and mRNA-Coding Networks in Microbiome–Cellular Communication, Inflammation, and Tumorigenesis Along the Oral–Gut–Lung Axis. Epigenomes, 9(4), 52. https://doi.org/10.3390/epigenomes9040052








