Epigenomic Interactions Between Chronic Pain and Recurrent Pressure Injuries After Spinal Cord Injury
Abstract
1. Introduction
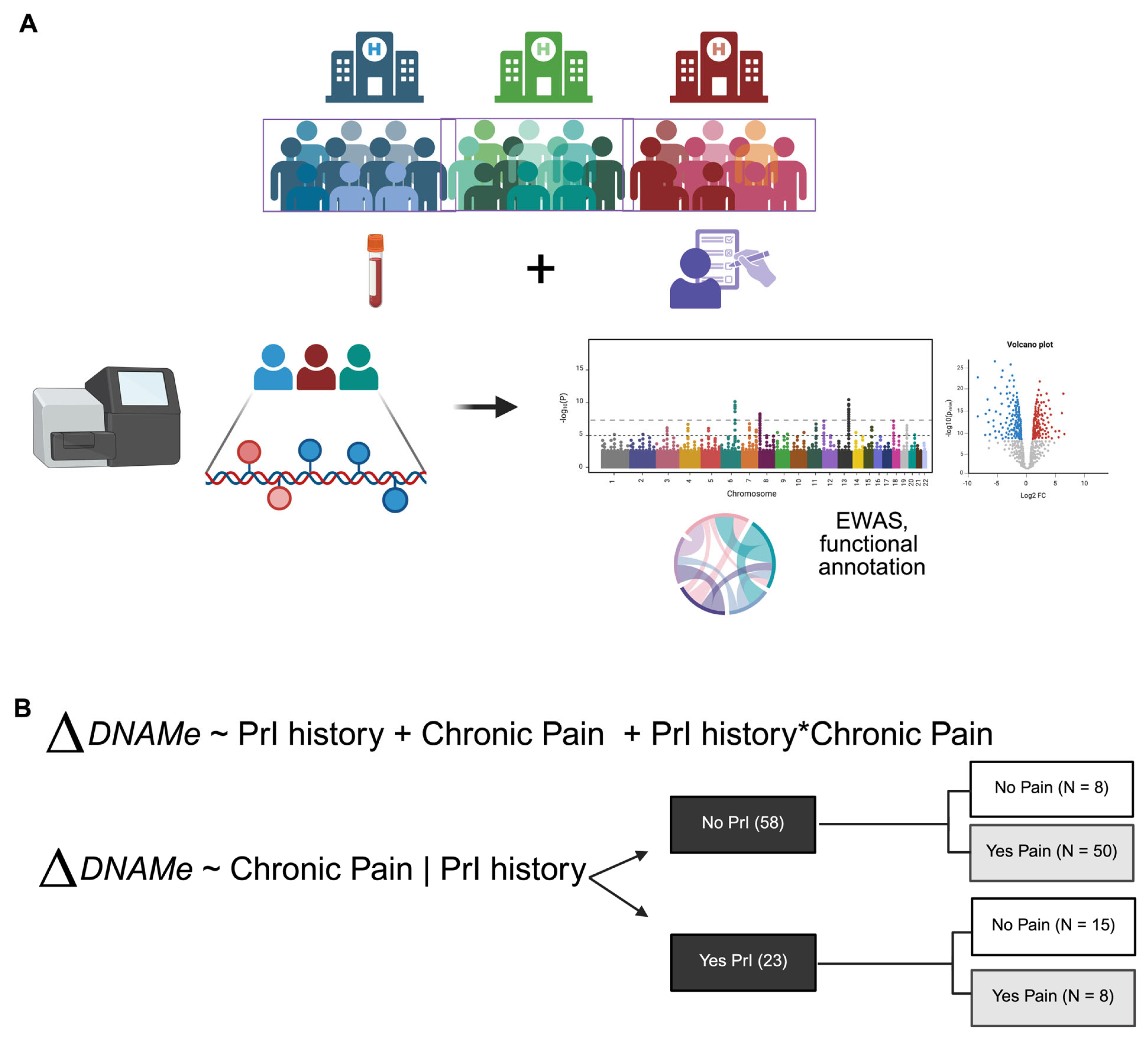
- (1)
- ΔDNAme~PrI + Pain + PrI*Pain
- (2)
- ΔDNAme~Pain|PrI
2. Results
2.1. Study Overview and Characteristics
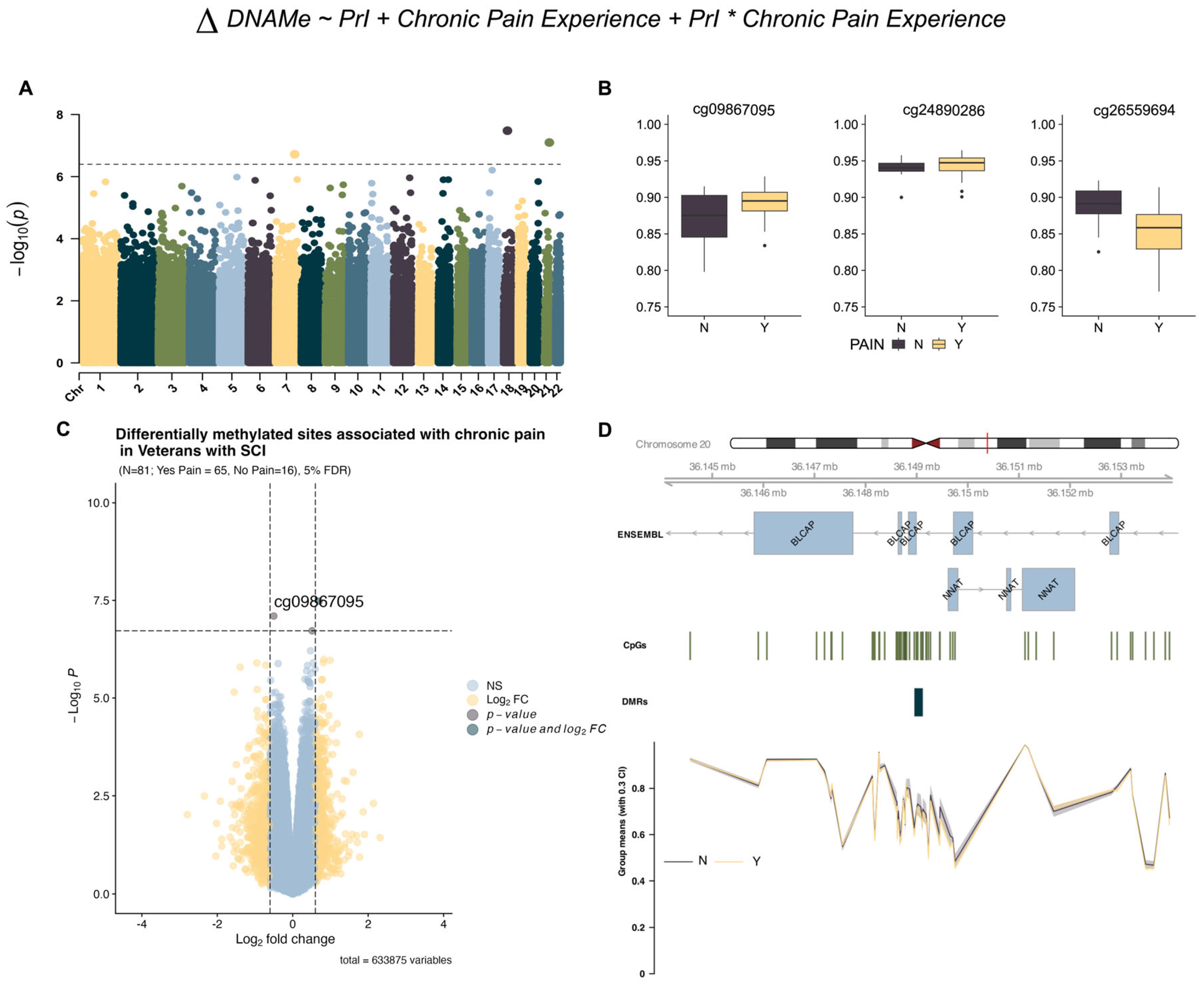
2.2. EWAS Identifies Differentially Methylated Sites Associated with Chronic Pain in Persons with SCI (Model 1)
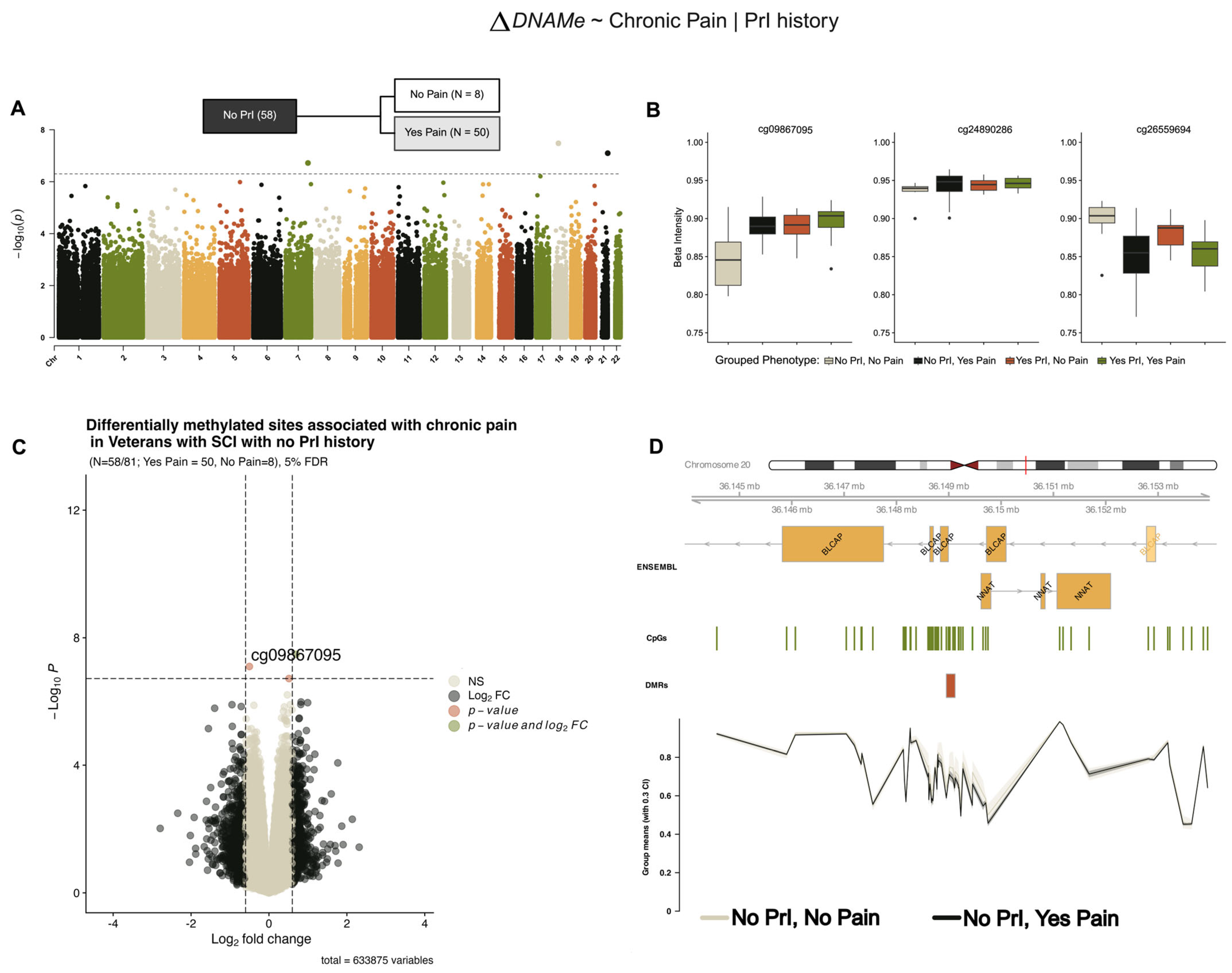
2.3. EWAS Identifies Differentially Methylated Sites Associated with and Chronic Pain Given Pressure Injury History (Model 2)
2.4. EWAS Identifies Differentially Methylated Sites Associated with Chronic Pain in Persons with SCI and Recurrent PrI (Model 2)
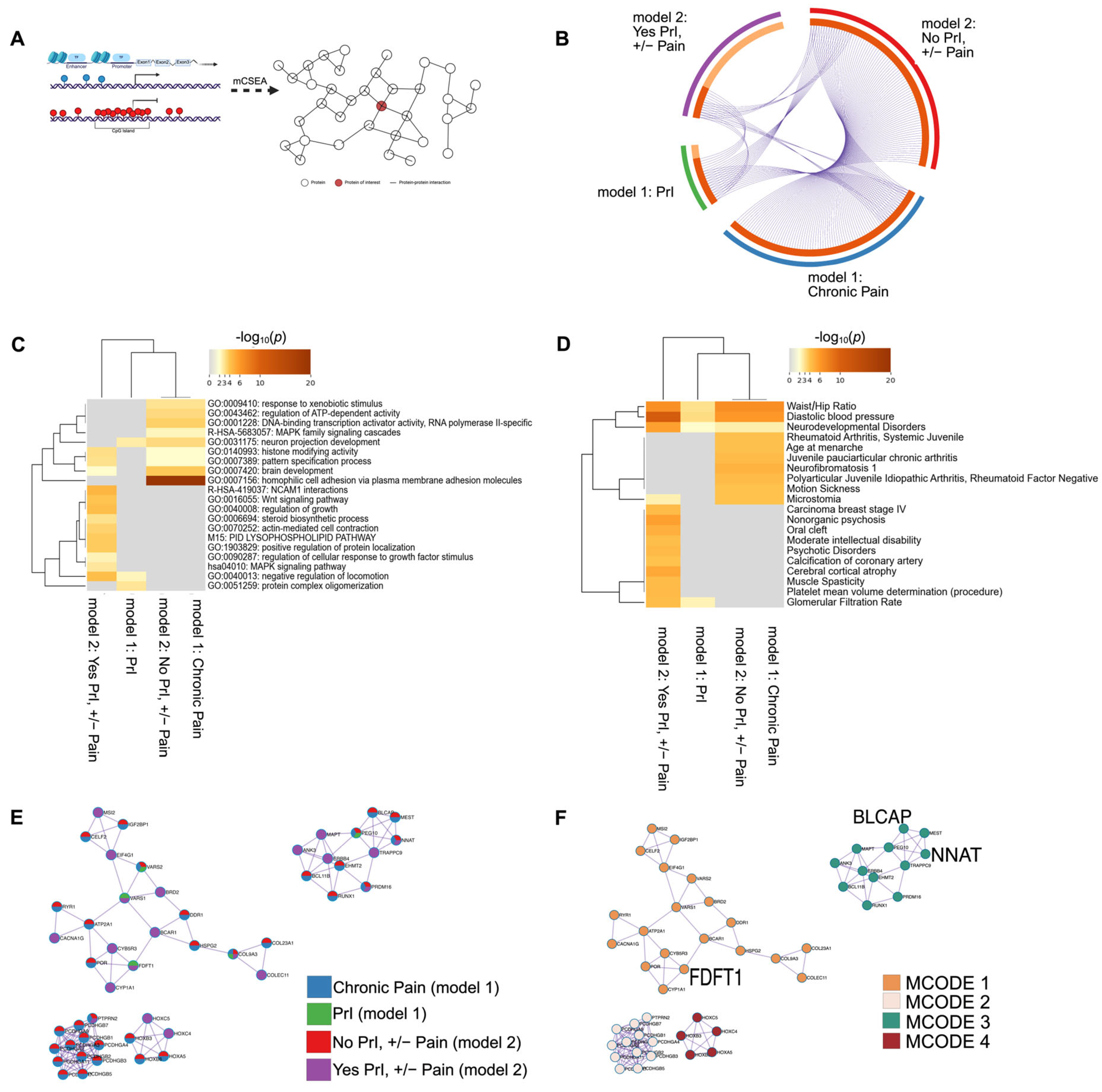
2.5. DMR Analysis in Features Known to Regulate Gene Expression Identifies Several Shared Genes, Promoters and CpG Islands Associated with Recurrent PrI History, Chronic Pain, and Chronic Pain Given Recurrent PrI History
| MCODE | GO # | Description | Log10 (p-Value) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Final MCODE | GO:0007156 | Homophilic cell adhesion via plasma membrane adhesion molecules | −14.6 |
| GO:0005509 | Calcium ion binding| | −14 | |
| GO:0098742 | Cell–cell adhesion via plasma-membrane adhesion molecules| | −12.4 | |
| Final: MCODE 1 | GO:0046209 | Nitric oxide metabolic process | −6 |
| GO:2001057 | Reactive nitrogen species metabolic process | −5.9 | |
| WP43 | Oxidation by cytochrome P450 | −5 | |
| Final: MCODE 2 | GO:0007156 | Homophilic cell adhesion via plasma membrane adhesion molecules | −23.9 |
| GO:0098742 | Cell–cell adhesion via plasma-membrane adhesion molecules | −21.7 | |
| GO:0098609 | Cell–cell adhesion | −18.1 | |
| Final: MCODE 3 | GO:1903829 | Positive regulation of protein localization| | −4.5 |
| GO:0021953 | Central nervous system neuron differentiation | −4.2 | |
| GO:0045165 | Cell fate commitment| | −3.9 | |
| Final: MCODE 4 | GO:0048706 | Embryonic skeletal system development | −11.8 |
| GO:0009952 | Anterior/posterior pattern specification | −10.8 | |
| GO:0003002 | Regionalization| | −9.30 |
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cohort Description
4.2. Blood Collection
4.3. DNA Isolation and Quality Control for Genome-Wide Analysis
5. Data Analysis
5.1. Covariate Analysis
5.2. Methylation Data Processing: Site and Sample QC
5.3. Epigenome-Wide Association Study (EWAS)
5.4. Annotation and Enrichment Analyses for Genes Identified by mCSEA
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hunter Revell, S.M. Symptom clusters in traumatic spinal cord injury: An exploratory literature review. J. Neurosci. Nurs. 2011, 43, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shields, R.K.; Dudley-Javoroski, S. Epigenetics and the International Classification of Functioning, Disability and Health Model: Bridging Nature, Nurture, and Patient-Centered Population Health. Phys. Ther. 2022, 102, pzab247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feinberg, A.P. The Key Role of Epigenetics in Human Disease Prevention and Mitigation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 1323–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finnerup, N.B.; Kuner, R.; Jensen, T.S. Neuropathic Pain: From Mechanisms to Treatment. Physiol. Rev. 2021, 101, 259–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simeoli, R.; Montague, K.; Jones, H.R.; Castaldi, L.; Chambers, D.; Kelleher, J.H.; Vacca, V.; Pitcher, T.; Grist, J.; Al-Ahdal, H.; et al. Exosomal cargo including microRNA regulates sensory neuron to macrophage communication after nerve trauma. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baskozos, G.; Dawes, J.M.; Austin, J.S.; Antunes-Martins, A.; McDermott, L.; Clark, A.J.; Trendafilova, T.; Lees, J.G.; McMahon, S.B.; Mogil, J.S.; et al. Comprehensive analysis of long noncoding RNA expression in dorsal root ganglion reveals cell-type specificity and dysregulation after nerve injury. Pain 2019, 160, 463–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graves, L.Y.; Keane, K.F.; Taylor, J.Y.; Wang, T.F.; Saligan, L.; Bogie, K.M. Subacute and chronic spinal cord injury: A scoping review of epigenetics and secondary health conditions. Epigenetics Insights 2023, 16, 25168657231205679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Xu, W.; Ren, Y.; Wang, Z.; He, X.; Huang, R.; Ma, B.; Zhao, J.; Zhu, R.; Cheng, L. Spinal cord injury: Molecular mechanisms and therapeutic interventions. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Jaiswal, A.; Norman, K.; DePaul, V. Heterogeneity and its impact on rehabilitation outcomes and interventions for community reintegration in people with spinal cord injuries: An integrative review. Top. Spinal Cord. Inj. Rehabil. 2019, 25, 164–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Jin, S. Epigenome-wide association studies, methods and protocols. Methods Mol. Biol. 2022, 2432, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martorell-Marugán, J.; González-Rumayor, V.; Carmona-Sáez, P. mCSEA: Detecting subtle differentially methylated regions. Bioinformatics 2019, 35, 3257–3262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toikumo, S.; Vickers-Smith, R.; Jinwala, Z.; Xu, H.; Saini, D.; Hartwell, E.E.; Pavicic, M.; Sullivan, K.A.; Xu, K.; Jacobson, D.A.; et al. A multi-ancestry genetic study of pain intensity in 598,339 Veterans. Nat. Med. 2024, 30, 1075–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Polli, A.; Godderis, L.; Ghosh, M.; Ickmans, K.; Nijs, J. Epigenetic and miRNA Expression Changes in People with Pain: A Systematic Review. J. Pain 2020, 21, 763–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livshits, G.; Malkin, I.; Freidin, M.B.; Xia, Y.; Gao, F.; Wang, J.; Spector, T.D.; MacGregor, A.; Bell, J.T.; Williams, F.M. Genome-wide methylation analysis of a large population sample shows neurological pathways involvement in chronic widespread musculoskeletal pain. Pain 2017, 158, 1053–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ferguson, A.R.; Stück, E.D.; Nielson, J.L. Syndromics: A bioinformatics approach for neurotrauma research. Transl. Stroke Res. 2011, 2, 438–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fallah, N.; Hong, H.A.; Wang, D.; Humphreys, S.; Parsons, J.; Walden, K.; Street, J.; Charest-Morin, R.; Cheng, C.L.; Cheung, C.J.; et al. Network analysis of multimorbidity and health outcomes among persons with spinal cord injury in Canada. Front. Neurol. 2024, 14, 1286143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Welsh, H.; Batalha, C.M.P.F.; Li, W.; Mpye, K.L.; Souza-Pinto, N.C.; Naslavsky, M.S.; Parra, E.J. A systematic evaluation of normalization methods and probe replicability using infinium EPIC methylation data. Clin. Epigenetics 2023, 15, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, W.; Kaur, D.; Horvath, S.; Zhou, W. Comparative epigenome analysis using Infinium DNA methylation BeadChips. Brief. Bioinform. 2023, 24, bbac617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Triche, T.J.; Laird, P.W.; Shen, H. SeSAMe: Reducing artifactual detection of DNA methylation by Infinium BeadChips in genomic deletions. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, e123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritchie, M.E.; Phipson, B.; Wu, D.; Hu, Y.; Law, C.W.; Shi, W.; Smyth, G.K. limma powers differential ex-pression analyses for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, e47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pidsley, R.; Wong, C.C.Y.; Volta, M.; Lunnon, K.; Mill, J.; Schalkwyk, L.C. A data-driven approach to pre-processing Illumina 450K methylation array data. BMC Genom. 2013, 14, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aryee, M.J.; Jaffe, A.E.; Corrada-Bravo, H.; Ladd-Acosta, C.; Feinberg, A.P.; Hansen, K.D.; Irizarry, R.A. Minfi: A flexible and comprehensive Bioconductor package for the analysis of Infinium DNA methylation microarrays. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 1363–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fortin, J.P.; Triche, T.J.; Hansen, K.D. Preprocessing, normalization and integration of the Illumina Hu-manMethylationEPIC array with minfi. Bioinformatics 2017, 33, 558–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, T.J.; Buckley, M.J.; Statham, A.L.; Pidsley, R.; Samaras, K.; Lord, R.V.; Clark, S.J.; Molloy, P.L. De novo identification of differentially methylated regions in the human genome. Epigenetics Chromatin 2015, 8, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, T.J.; Buckley, M.J.; Chen, Y.; Smyth, G.K.; Goodnow, C.C.; Clark, S.J. Calling differentially methylated regions from whole genome bisulphite sequencing with DMRcate. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, e109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triche, T.J.; Weisenberger, D.J.; Van Den Berg, D.; Laird, P.W.; Siegmund, K.D. Low-level processing of Illumina Infinium DNA Methylation BeadArrays. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, e90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leek, J.T.; Johnson, W.E.; Parker, H.S.; Fertig, E.J.; Jaffe, A.E.; Zhang, Y.; Storey, J.D.; Torres, L.C. sva: Surrogate Variable Analysis; R package version 3.56.0; Bioconductor: Gosford, NSW, Canada, 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhou, B.; Pache, L.; Chang, M.; Khodabakhshi, A.H.; Tanaseichuk, O.; Benner, C.; Chanda, S.K. Metascape provides a biologist-oriented resource for the analysis of systems-level datasets. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| No PrI History, No Chronic Pain (N = 8) | No PrI History, Yes Chronic Pain (N = 50) | Recurrent PrI History, No Chronic Pain (N = 8) | Recurrent PrI History, Yes Chronic Pain (N = 15) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Collection Site (VAMC) | Cleveland | 4 | 30 | 6 | 15 |
| Bronx | 2 | 10 | 2 | 1 | |
| Minneapolis | 2 | 10 | - | 1 | |
| Age | Median (years), (IQR) | 43.5 (23.875) | 48.50 (40.750) | 25.25 (40.375) | 29.50 (26.000) |
| Gender | M | 8 | 49 | 8 | 15 |
| F | - | 1 | - | 2 | |
| Ancestry (self-reported) | European | 7 | 35 | 6 | 14 |
| African American or LatinX | 1 | 15 | 2 | 3 | |
| IMAT | Median%, IQR | 26 (38) | 9.5 (16.5) | 15.5 (19.5) | 23 (30.5) |
| AIS | Incomplete | 6 | 43 | 4 | 7 |
| Complete | 1 | 7 | 4 | 10 | |
| NA | 1 | - | - | - | |
| Level of Injury | Above T6 | 6 | 39 | 5 | 13 |
| Below T6 | 2 | 11 | 3 | 4 | |
| Length of Injury | Median (years), IQR | 43.0 (32.875) | 44.5 (38.375) | 38.0 (43.250) | 41.00 (80.00) |
| Probe Name | cg09867095 | cg26559694 | cg24890286 |
| Chromosome | chr18 | chr7 | chr21 |
| Position | 28470269 | 139317303 | 47739342 |
| Strand | - | - | + |
| p Value | 3.32 × 10−8 | 7.98 × 10−8 | 1.91 × 10−7 |
| Adjusted p value | 0.021 | 0.025 | 0.04 |
| Log2 Fold Change (95% CI) | 0.698 (0.4750, 0.9218) | −0.502 (−0.6670, −0.3360) | 0.513 (0.3370, 0.6902) |
| Island Name | chr21:47742779–47743269 | ||
| Relation to Island | Open Sea | Open Sea | N. Shelf |
| UCSC RefGene Name | HIPK2 | C21orf58 | |
| UCSC RefGene Group | Body | 5′UTR;TSS1500;Body |
| Chromosome | chr20 |
| Start (bp) | 36148954 |
| End (bp) | 36149121 |
| Width (bp) | 168 |
| Number of CpGs within DMR | 8 |
| Minimum FDR of the smoothed estimate. | 1.063 × 10−27 |
| Harmonic mean of the individual CpG p-values | 0.00243 |
| Maximum differential/coefficient within the DMR | −0.095 |
| Mean differential/coefficient within the DMR | −0.065 |
| Overlapping Genes | BLCAP |
| Probe Name | cg09867095 | cg24890286 | cg26559694 |
| Chromosome | chr18 | chr7 | chr21 |
| Position (bp) | 28470269 | 139317303 | 47739342 |
| Strand | - | - | + |
| p Value | 3.32 × 10−8 | 1.91 × 10−7 | 7.98 × 10−8 |
| Adjusted p Value | 0.021 | 0.04 | 0.025 |
| Log2 Fold Change (95% CI) | 0.698 (0.475, 0.921) | 0.513 (0.337, 0.69) | −0.502 (−0.668, −0.335) |
| Island Name | chr21:47742779–47743269 | ||
| Relation to Island | Open Sea | Open Sea | N. Shelf |
| UCSC RefGene: Name | HIPK2 | C21orf58 | |
| UCSC RefGene: Group | Body | 5′UTR;TSS1500;Body |
| Probe Name | cg21756558 | cg26217441 |
| Chromosome | chr4 | chr16 |
| Position (bp) | 101502764 | 89643414 |
| Strand | - | - |
| p Value | 4.41 × 10−8 | 5.43 × 10−9 |
| Adjusted p Value | 0.0140 | 0.00344 |
| Log2 Fold Change (95% CI) | −0.644 (−0.852, −0.436) | 0.901 (0.632, 1.170) |
| Island Name | na | |
| Relation to Island | Open Sea | Island |
| UCSC RefGene: Name | na | CPNE7 |
| UCSC RefGene: Group | na | Body |
| Gencode v12: Name | EMCN | na |
| Gencode v12: Group | 3′UTR | na |
| Phenotype Group: | Yes PrI, +/−Pain | No PrI, +/−Pain |
| Chromosome | chr8 | chr20 |
| DMR: Start (bp) | 11666485 | 36148954 |
| DMR: End (bp) | 11666594 | 36149121 |
| Width (bp) | 110 | 168 |
| Number of CpGs within DMR | 5 | 8 |
| Minimum FDR of the smoothed estimate | 4.15 × 10−11 | 1.063 × 10−27 |
| Harmonic mean of the individual CpG p-values | 0.000240 | 0.0024 |
| Maximum differential/coefficient within the DMR | −0.13 | −0.095 |
| Mean differential/coefficient within the DMR | −0.093 | −0.066 |
| Overlapping Genes | FDFT1 | BLCAP |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Graves, L.Y.; Alcorn, M.R.; Chan, E.R.; Schwartz, K.; Henzel, M.K.; Galea, M.; Toth, A.M.; Olney, C.M.; Bogie, K.M. Epigenomic Interactions Between Chronic Pain and Recurrent Pressure Injuries After Spinal Cord Injury. Epigenomes 2025, 9, 26. https://doi.org/10.3390/epigenomes9030026
Graves LY, Alcorn MR, Chan ER, Schwartz K, Henzel MK, Galea M, Toth AM, Olney CM, Bogie KM. Epigenomic Interactions Between Chronic Pain and Recurrent Pressure Injuries After Spinal Cord Injury. Epigenomes. 2025; 9(3):26. https://doi.org/10.3390/epigenomes9030026
Chicago/Turabian StyleGraves, Letitia Y., Melissa R. Alcorn, E. Ricky Chan, Katelyn Schwartz, M. Kristi Henzel, Marinella Galea, Anna M. Toth, Christine M. Olney, and Kath M. Bogie. 2025. "Epigenomic Interactions Between Chronic Pain and Recurrent Pressure Injuries After Spinal Cord Injury" Epigenomes 9, no. 3: 26. https://doi.org/10.3390/epigenomes9030026
APA StyleGraves, L. Y., Alcorn, M. R., Chan, E. R., Schwartz, K., Henzel, M. K., Galea, M., Toth, A. M., Olney, C. M., & Bogie, K. M. (2025). Epigenomic Interactions Between Chronic Pain and Recurrent Pressure Injuries After Spinal Cord Injury. Epigenomes, 9(3), 26. https://doi.org/10.3390/epigenomes9030026







