Abstract
Glioblastoma is the most common form of glioma, as well as the most aggressive. Patients suffering from this disease have a very poor prognosis. Surgery, radiotherapy, and temozolomide are the only approved treatments nowadays. Panobinostat is a pan-inhibitor of histone deacetylases (HDACs) that has been shown to break some pathways which play an important role in cancer development. A global intention of using panobinostat as a therapeutic agent against glioblastoma is beginning to be a reality. We have treated the LN405 glioblastoma cell line with temozolomide, panobinostat, and combined treatment, in order to test apoptosis, colony formation, and a possible molecular reversion of the mesenchymal phenotype of the cells to an epithelial one. Our results show that panobinostat decreased N-cadherin levels in the LN405 glioblastoma cell line while it increased the expression of E-cadherin, which might be associated with a mesenchymal–epithelial transition in glioblastoma cells. Colony formation was reduced, and apoptosis was increased with treatments. Our research highlights the importance of panobinostat as a potential adjuvant therapy to be used with temozolomide to treat glioblastoma and the advantages of the combined treatment versus temozolomide alone, which is currently the first-line treatment used to treat this tumor.
1. Introduction
Glioblastoma multiforme—or grade IV astrocytoma—is the most common form of glioma as well as the most aggressive [1,2], corresponding to 52% of all primary brain tumors and to a fifth of all kinds of intracranial malignancies. In Europe, the incidence of glioblastoma is two-to-three cases per 100,000 people. Current glioblastoma treatment strategies make use of surgery followed by a treatment with temozolomide, with or without radiotherapy. In spite of this therapeutic effort, glioblastoma patients have a poor prognosis, and their median survival is only 14.6 months after diagnosis [3].
The development of an efficient therapy against glioblastoma involves many problems, such as high inter- and intra-tumoral heterogeneity [4,5], poor blood–brain barrier penetration by almost all drugs [6], and the heterogeneity in the sensitivity of tumors to temozolomide, added to the possible resistance that some glioblastomas develop against temozolomide treatments. The mentioned challenges highlight the increasing need for research efforts to develop efficient therapies against glioblastoma.
Brain tumors are not only developed by silencing, over-expression, or genomic alteration of several genes. Epigenetic changes also occur in tumors, and might be related to their initiation and/or progression. Epigenetics refers to changes in gene expression without prior changes in the DNA nucleotide sequence, due to DNA methylation, post-translational covalent histone modification (methylation, acetylation, phosphorylation), and/or RNA interference [7]. In addition, these changes are heritable. Unlike genetic alterations, epigenetic alterations are reversible. Therefore, epigenetic changes are attractive targets for cancer therapy.
Histone deacetylases (HDACs) are becoming new targets against cancer, due to their relevant function in gene expression [8]. Subsequently, HDAC inhibitors could act as anticancer drugs [9,10]. Panobinostat -LBH589-, is a pan-inhibitor of HDAC that has been proven to disrupt some important pathways in cancer development [11]. Several works on the use of panobinostat as a therapeutic agent against glioblastoma are being published elsewhere [12,13,14,15,16,17].
Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) consists of a change in the cellular phenotype by which an epithelial cell can switch to a mesenchymal cell, increasing its migratory potential, its resistance to apoptosis, and its capacity of invasion [18]. This process can be demonstrated to be occurring by the loss of expression of epithelial markers like E-cadherin and the gain of expression of mesenchymal markers like N-cadherin and vimentin, together with other genetic and phenotypic cellular changes [19]. It is known that panobinostat modulates E-cadherin expression and suppresses migration and invasion in thyroid cancer cells [20]. Most glioblastomas do not express E-cadherin [21], which might be in favor of an epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition phenotype occurring in these aggressive tumors.
We have treated the LN405 glioblastoma cell line with temozolomide, panobinostat, and both in order to test apoptosis, colony formation, and a possible molecular reversion of the mesenchymal phenotype of the cells to an epithelial one. Our results show that panobinostat decreased N-cadherin levels in the LN405 glioblastoma cell line while it increased the expression of E-cadherin, which might be associated with a mesenchymal–epithelial transition in glioblastoma cells. Colony formation was reduced, and apoptosis was increased with treatments.
2. Results
2.1. Temozolomide Inhibits the Clonogenic Capacity of LN405 Glioblastoma Cell Line
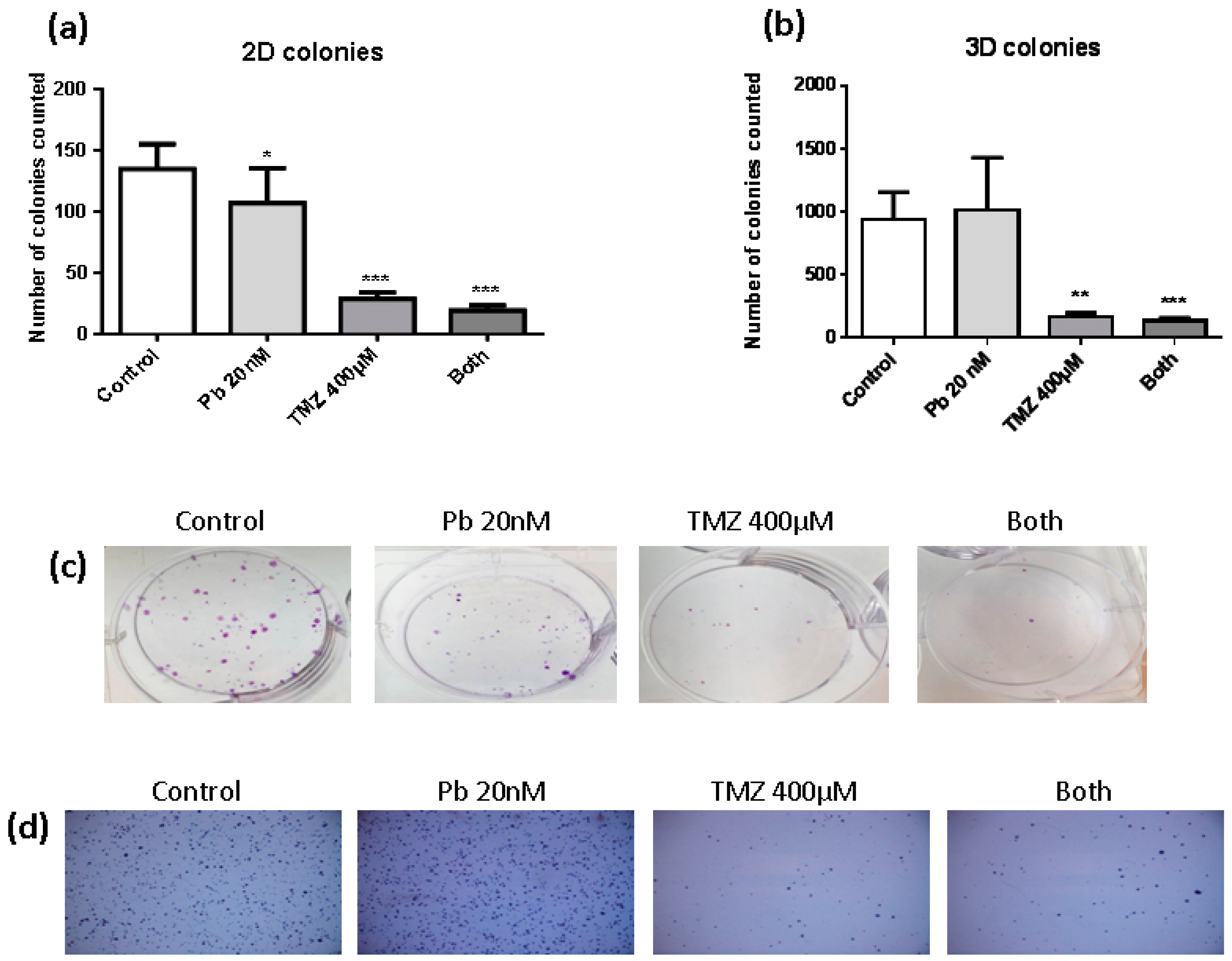
To evaluate the clonogenic capacity of LN405 glioblastoma cells after treatment with panobinostat, temozolomide, combined treatment, or DMSO as vehicle control for 72 h, studies of colony formation in attachment-dependent (2D colonies) and attachment-independent conditions (3D colonies) were performed. The number of colonies counted in the single panobinostat treatment reached a significant decrease in the quantity of colonies in attachment-dependent conditions (Figure 1a,c), but had no effect when it was evaluated in the experiment of colony formation in attachment-independent conditions (Figure 1b,d). On the other hand, temozolomide single treatment and its combination with panobinostat efficiently inhibited the colony formation in both kinds of experiment (Figure 1a,b). Panobinostat alone did not show any effect on inhibiting the formation of colonies in soft agar. Although no significant differences were detected between the treatment with temozolomide alone and the double treatment, a smaller number of colonies were seen after the double treatment compared with temozolomide alone. The same observation occurred in the colony formation in attachment-dependent conditions assay.
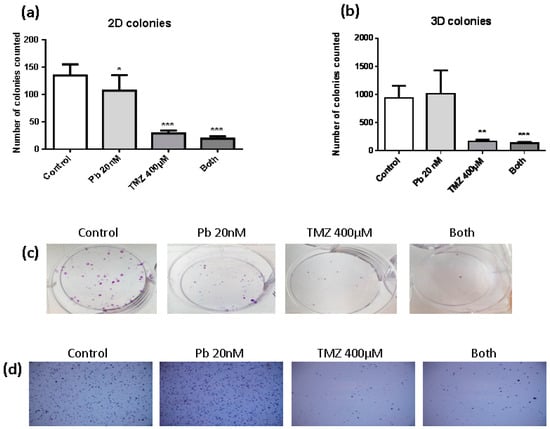
Figure 1.
Effect of different treatments on the clonogenic capacity of LN405 glioblastoma cell line: control, panobinostat 20 nM, temozolomide 400 µM or combined treatment (panobinostat 20 nM + temozolomide 400 µM). (a) 2D colonies count. (b) 3D colonies count. Data is represented as Mean + standard deviation (SD). * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001, one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with Tukey’s multiple comparison test. (*) vs. control. (c) Images for the colony formation assay. (d) Images for the soft agar assay.
2.2. Panobinostat Accelerates the Effect of Temozolomide to Induce Apoptosis in LN405 Glioblastoma Cells
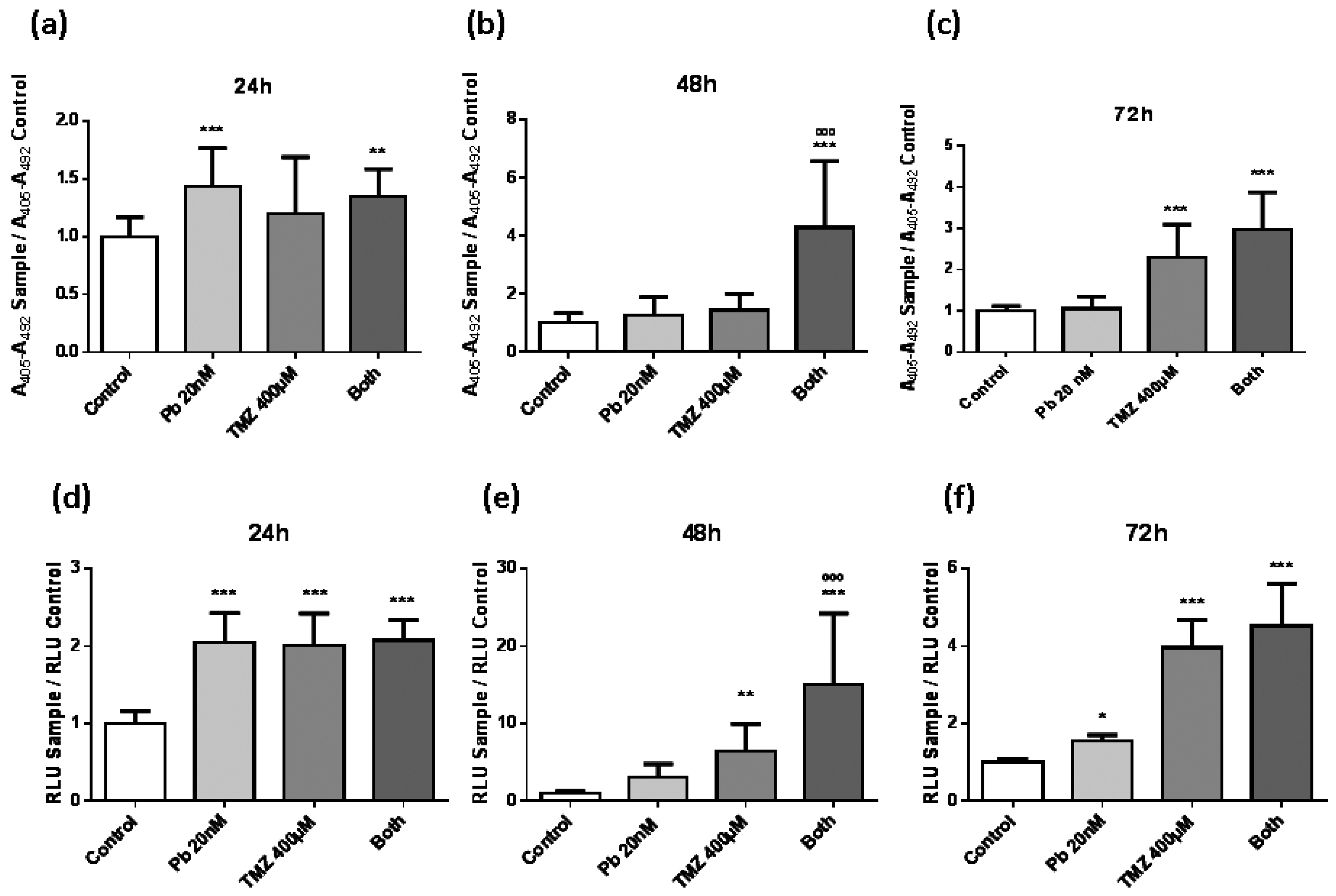
In order to study the effect of panobinostat and temozolomide on cell death, two different experiments to study apoptosis were performed: (i) Cell death detection enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA)PLUS (Roche Diagnostics GmbH, Mannheim, Germany) (Figure 2a–c) and (ii) Caspase-Glo 3/7 assay (Promega, Madison, WI, USA) (Figure 2d–f). Panobinostat presented a decreasing effect over time on inducing cell death. On the contrary, temozolomide had a slower activity in producing apoptosis, from two-fold with respect to control condition at 24 h (Figure 2d) to four-fold with respect to control condition at 72 h (Figure 2f). Both experiments showed similar results, strengthening the validation of these assays. The most interesting result obtained from these experiments was the highlighted apoptosis induction produced by the combination treatment, which was much higher than that induced by individual temozolomide treatment (Figure 2b,e). At 72 h of treatment, the effect of the double treatment was equally attained by the single temozolomide treatment (Figure 2d), suggesting that the addition of panobinostat to the temozolomide treatment could accelerate the effect of temozolomide in inducing apoptosis.
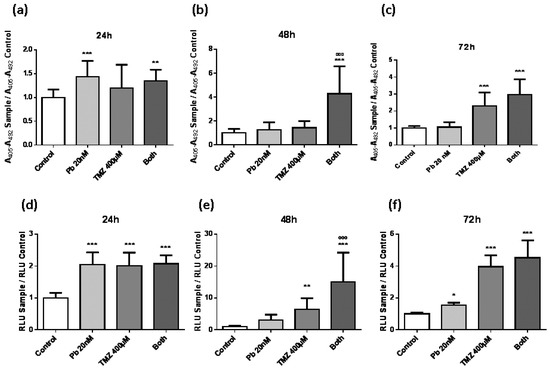
Figure 2.
Evolution of apoptosis assays in LN405 cell line in a period of 24, 48, and 72 h. LN405 cell line was cultured in a 96-well plate at a confluence of 5000 cells per plate. One day later, cells were treated with panobinostat, temozolomide, both, or dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) as vehicle control. Apoptosis was measured with cell death detection enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA)PLUS (a–c) and with Caspase-Glo 3/7 assay (d–f): (a,d) 24 h, (b,e) 48 h, and (c,f) 72 h after treatment. Data are represented as mean + standard deviation (SD). * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001, ººº p < 0.001, one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparison test. (*) vs. control, (º) vs. TMZ 400 µM. A405: Absorbance at 405 nm, A492: Absorbance at 492 nm, RLU: Relative light unit.
2.3. Panobinostat Treatment and Its Combination with Temozolomide Increase the Expression of Epithelial Markers and Decrease the Expression of Mesenchymal Markers Related with Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition
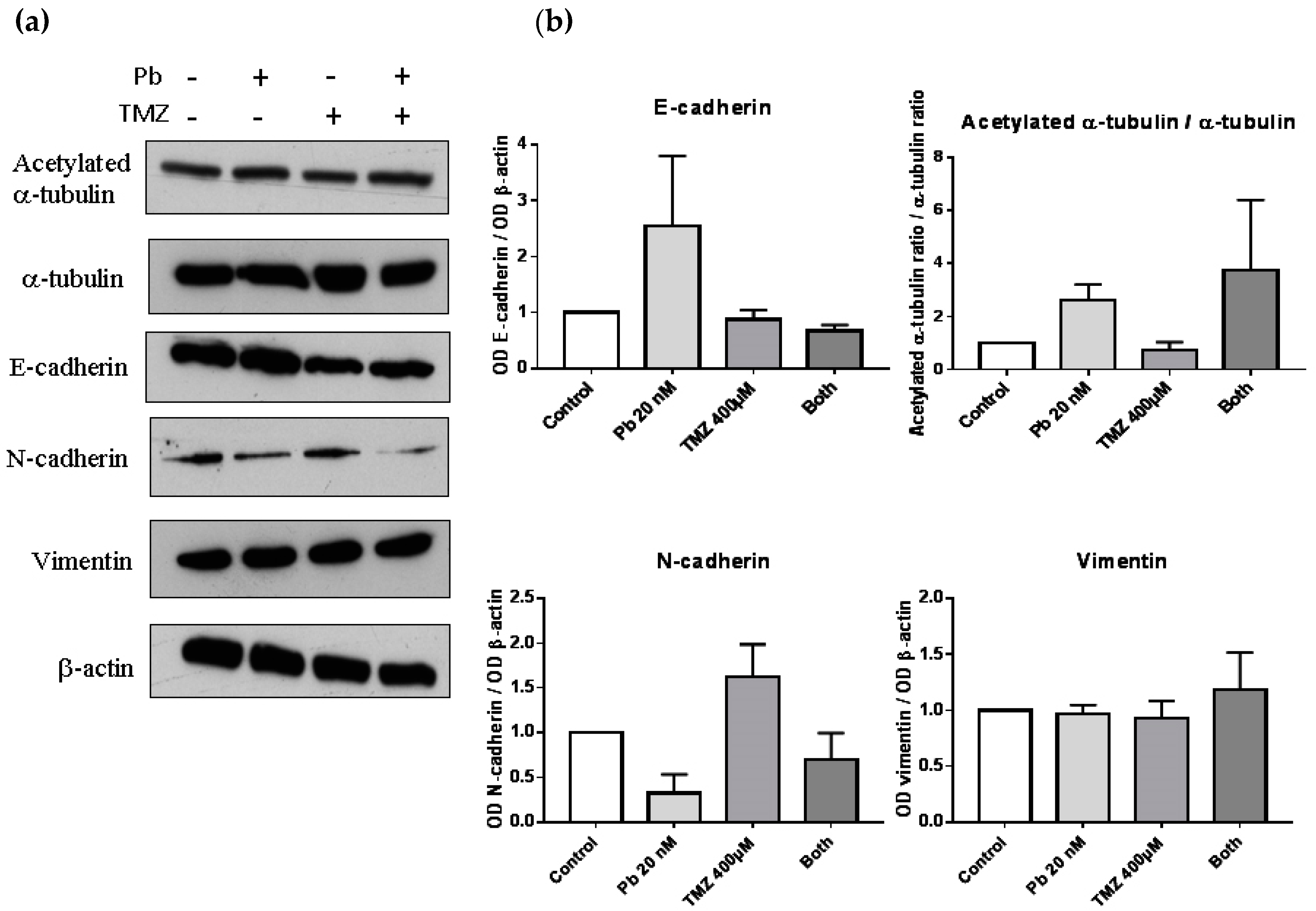
To study the change in protein expression of the markers related to EMT, we performed a Western blot of epithelial markers such as E-cadherin, and mesenchymal markers such as N-cadherin or vimentin. Besides, a Western blot of α-tubulin and acetylated α-tubulin was done to verify the effect of panobinostat as an inhibitor of HDAC, due to its capability of inhibiting HDAC6, the protein which deacetylates α-tubulin (Figure 3a). The expression of the epithelial marker E-cadherin was increased compared to control when we analyzed the sample treated with panobinostat, although no significant differences were observed. In that case, the combination treatment did not affect the expression of E-cadherin (Figure 3b). Panobinostat also decreased the protein levels of the mesenchymal marker N-cadherin, and as in the case of E-cadherin, no significant differences were observed. Combined treatment did not alter N-cadherin expression. In the case of the mesenchymal marker vimentin, no differences were observed after treatment. To study the effect of panobinostat as an inhibitor of HDAC, we observed that the ratio between the acetylated α-tubulin and total α-tubulin was increased in those samples treated with panobinostat, confirming the suggested mechanism of action of this drug.
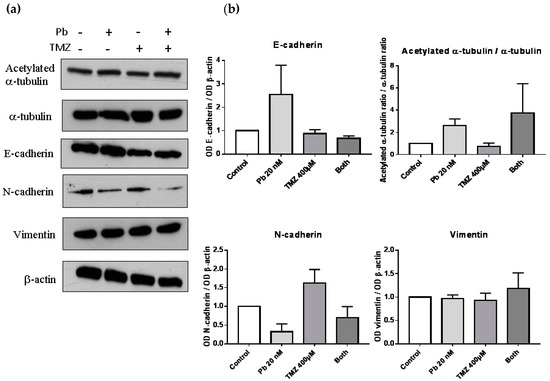
Figure 3.
Panobinostat increased levels of epithelial markers and decreased levels of N-cadherin. (a) Western blot images of acetylated α-tubulin, α-tubulin, E-cadherin, N-cadherin, vimentin, and β-actin of proteins extracted from cells treated with panobinostat 20 nM, temozolomide 400 µM, both, or DMSO as control vehicle for three days. (b) Graphs representing the optical density of proteins compared to β–actin, and the ratio of acetylated α-tubulin and total α-tubulin. Data is represented as mean + standard error of the mean (SEM). OD: optical density.
2.4. The Combination of Panobinostat and Temozolomide Reduces Cell Migration with Respect to Temozolomide Alone
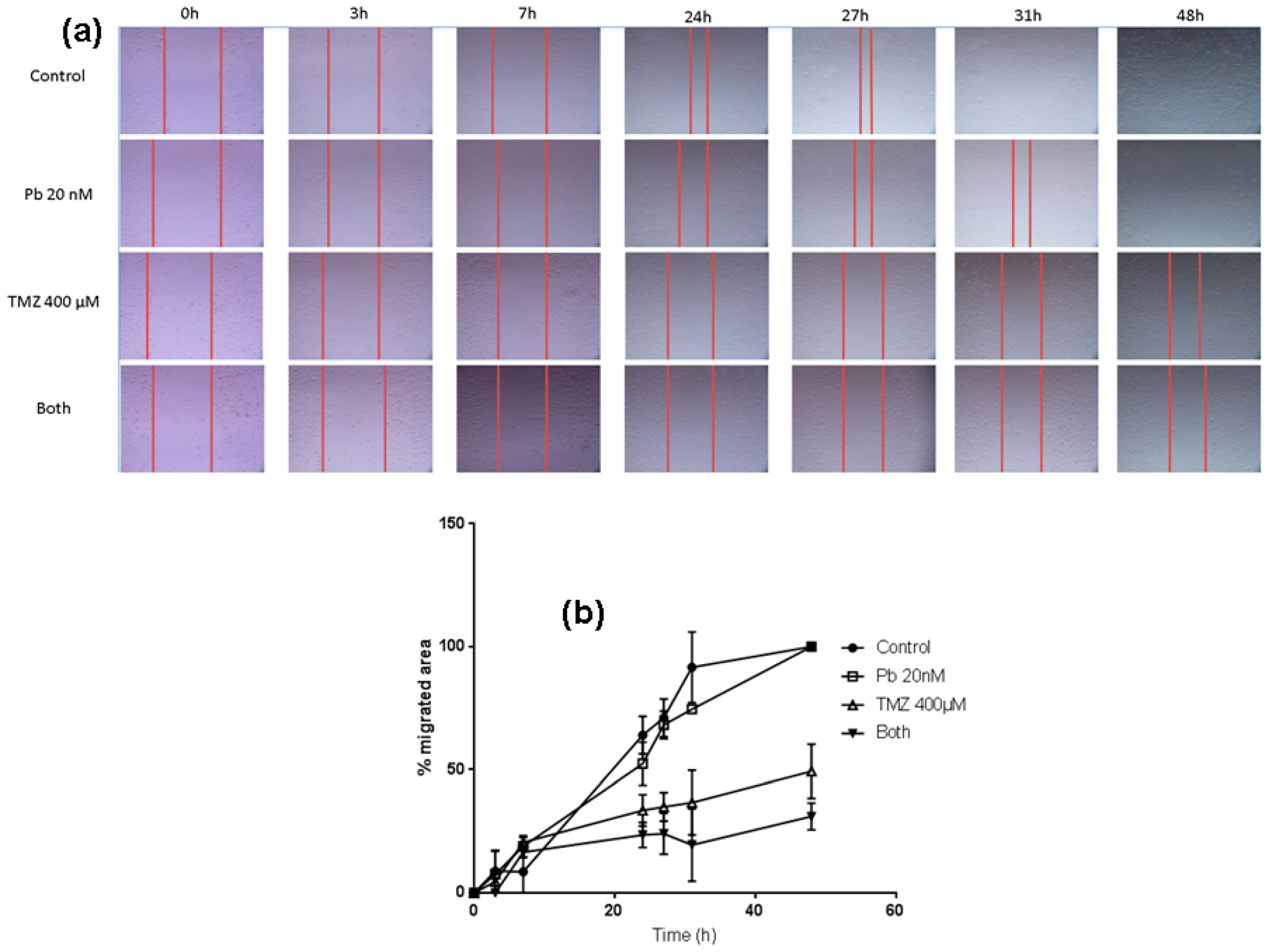
In order to analyze the effect of the two drugs on the migration capacity of LN405 glioblastoma cells, a wound healing assay was performed. The control condition presented a greater migration capacity than the treated conditions at 24 h, but differences were evident among different treatments. Panobinostat alone induced a smaller migration rate than control, nevertheless greater inhibition was observed in comparison to temozolomide individual treatment. Temozolomide alone reduced migration with respect to control; more inhibition was observed when temozolomide and panobinostat were added together.
LN405 cells treated with panobinostat closed the gap later than in the control condition, but the scratch was completely closed at 48 h. (Figure 4). Cells treated with temozolomide showed a slower migration rate than those treated with panobinostat. The scratch did not get closed after 48 h after treatment with temozolomide, which implies that temozolomide alone reduced cell migration more than the individual treatment with panobinostat. The combination of panobinostat and temozolomide also reduced the migration capacity of the LN405 glioblastoma cell line due to the inability of these cells to close the gap. Interestingly, although panobinostat alone did not present any differences with respect to the control condition, panobinostat seemed to enhance the effect of temozolomide in closing the gap.
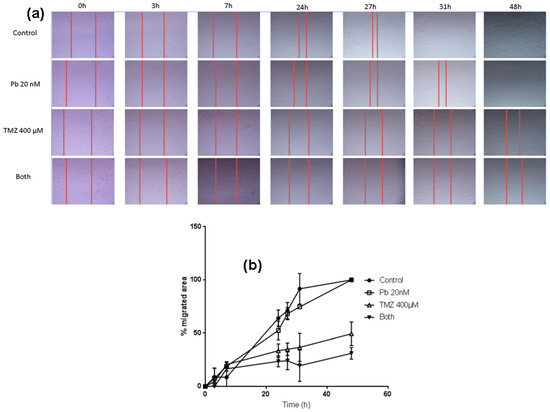
Figure 4.
The combination of panobinostat and temozolomide reduced cell migration with respect to temozolomide alone. (a) Pictures taken from the gap after 0, 3, 7, 24, 27, 31, and 48 h from scratching the cell monolayer in the well of a 24-well plate of every treatment condition. (b) Graph representing the percentage of the migrated area from every condition in a period of time between 0 h and 48 h from scratching.
3. Discussion
Glioblastoma is the most common and malignant form of brain tumor. Despite all different therapeutic approaches, the median survival is less than 15 months [3]. The aim of this study was to analyze if panobinostat could behave as an adjuvant antineoplastic agent of temozolomide in the treatment of glioblastoma, which is currently used in the clinic. Our results showed statistical differences encountered after treating the LN405 glioblastoma cell line with panobinostat, temozolomide, both combined, or DMSO as a vehicle control.
The findings demonstrated that panobinostat was not able to inhibit the clonogenic potential of the LN405 cell line on its own. Nevertheless, when panobinostat was supplied in combination with temozolomide, the number of colonies counted were lower than in the case of the single temozolomide treatment. Although these differences (temozolomide treatment vs. combination treatment) did not appear to be significant, we must consider that the panobinostat dose was between six-to-seven times lower than the inhibitory concentration (IC50) calculated.
In the apoptosis assays, panobinostat showed no significant differences versus temozolomide in inducing cell death in any of the three days of study. However, panobinostat induced apoptosis in 24 h (Figure 2), compared with control. On the contrary, temozolomide presented a slow effect in the time of producing apoptosis, since it did not reach a great peak in either the luminometric assay or in the ELISA assay until the third day (Figure 2c,f). However, the effect of temozolomide on inducing apoptosis appeared one day before (on the second day) when double treatments were applied (Figure 2b,e). This may be due to the fact that the inhibition of HDAC favours the sensitization of the cells to temozolomide, since tumors with over-expression of HDAC6 have a greater resistance to temozolomide [22]. This fact might be taken into account, as it might possibly represent an advancement toward the clinical treatment of glioblastoma.
The wound healing assay performed to test for the migration capacity of LN405 glioblastoma cells after treatment with temozolomide, panobinostat, or both, versus controls revealed that panobinostat alone did not reduce cell migration, while temozolomide alone did. The combination treatment of both drugs was the most effective treatment in reducing the migration of this cell line.
When studying EMT, the treatment with panobinostat decreased the levels of the mesenchymal marker N-cadherin, and in turn, elevated the levels of E-cadherin and the ratio of acetylated α-tubulin. Gu and Liu [23] have demonstrated that a loss of α-tubulin acetylation acts as a marker for EMT. Therefore, we can assume that panobinostat is inducing the molecular reversion of the EMT phenotype to a MET phenotype in LN405 glioblastoma cells. This might even be in agreement with Kahlert et al. [21], since they found that most glioblastomas did not express E-cadherin intrinsically.
Clinical trials of panobinostat have recently been performed. So far, two studies on multiple myeloma have reached phase 3 [24,25], suggesting that panobinostat could be a useful addition to the treatment with bortezomib and dexamethasone for patients with relapsed or relapsed and refractory multiple myeloma [24], despite the only modest overall survival benefit after the addition of panobinostat [25]. Six other studies have been done as phase 2 clinical trials in lymphoma [26,27] and solid tumors [28,29,30,31], and several more studies have been conducted as phase 1 clinical trials in solid tumors [32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45]. The three clinical trials made on glioblastoma are of special interest for our work [13,46,47]. One of them was a phase 2 clinical trial [13] in which—although reasonably well-tolerated—the addition of panobinostat to bevacizumab did not significantly improve progression-free survival rate compared with historical controls of bevacizumab monotherapy in either cohort. The other two [46,47] corresponded to phase I clinical trials.
Our research highlights the importance of panobinostat as a possible adjuvant therapy to be used with temozolomide to treat glioblastoma. The advantages of the combined treatment versus temozolomide alone—presently the only drug used against this kind of brain tumor—is also elaborated.
4. Material and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture
The LN405 glioblastoma cell line was used in this study. It was cultured in Gibco™ Roswell Park Memorial Institute (RPMI) 1640 GlutaMAX™ medium (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS) (Thermo Fisher Scientific), 4% non-essential amino acids (Lonza, Verviers, Belgium), and 1% penicillin/streptomycin (Thermo Fisher Scientific). LN405 was maintained in an incubator at 37 °C in an atmosphere with 5% CO2 to grow the cells.
4.2. Pharmacologic Treatment
The HDAC inhibitor panobinostat and the chemotherapeutic agent temozolomide were the drugs used in this study, at a final concentration of 20 nM and 400 µM, respectively. When confluence was around 80%, cells were harvested and subcultured. The same medium was used to add the drugs. Panobinostat and temozolomide were added to the glioblastoma cells both separately and in combination for 24 h, 48 h, and 72 h. DMSO was also used as a vehicle control for the same periods of time.
4.3. 2D Colony Formation Assay
Cells treated for 3 days with panobinostat, temozolomide, both, and DMSO as a vehicle control were cultured in six-well plates for 10 days (three wells per condition). After this time, cells were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde for 40 min and stained with crystal violet (Sigma Aldrich, St Louis, MO, USA) for 15 min. Resulting colonies were counted using a Suntex 560 Colony Counter (Gemini, Apeldoorn, Netherlands). Three hundred cells per well were cultured from the LN405 cell line. This experiment was repeated three times.
4.4. 3D Colony Formation Assay in Soft Agar
Cells treated for three days with panobinostat, temozolomide, both, and DMSO as a vehicle control were cultured in agarose in a six-well plate (three wells per condition). Before that, 2 mL of agarose 0.5% (Cat No 8016, Pronadisa, Laboratorios Conda, Torrejón de Ardoz, Madrid, Spain) with DMEM (Sigma Aldrich) were added. Once this first layer gelified, 10,000 cells contained in 2 mL of agarose 0.2% and DMEM were added onto the first agar layer. When this top layer gelified, 2 mL of fresh medium were added and changed every 3 days. Four weeks later, the medium was discarded, and the colonies were stained with 250 µL of 1% crystal violet for 5 min. Samples were washed with H2O to improve visualization of the colonies. To count the colonies, a photo was taken from each well and it was counted with the colony-forming unit (CFU) free software OpenCFU [48] under the same conditions. Each experiment was repeated three times.
4.5. Wound Healing Assay
Cells treated for three days with panobinostat, temozolomide, both, and DMSO as a vehicle control were cultured in a 24-well plate; 250,000 cells were plated in each well, reaching confluence. Twenty-four hours later, a scratch was done, and medium was changed to a medium supplemented with 2.5% FBS in order to avoid proliferation and apoptosis. Photos were taken 0, 3, 7, 24, 27, 31, and 48 h after scratching.
4.6. Cell Detection Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent AssayPLUS
To study de effect of our drugs on apoptosis, the Cell detection ELISAPLUS (Roche Diagnostics GmbH) was used. Cells were plated in 96-well plates, at a confluence of 5000 cells per well and six wells per condition. The day after seeding, medium was changed by new fresh medium containing the drugs at the concentration described above, and apoptosis was measured at 24, 48, and 72 h following the manufacturer’s instructions. Each experiment was repeated three times.
4.7. Caspase-Glo 3/7 Assay
To study the effect of our drugs on the activation of caspases 3/7, we used the Caspase-Glo 3/7 assay (Promega). Cells were plated in 96-well plates, at a confluence of 5000 cells per well and six wells per condition. The day after seeding, medium was changed by new fresh medium containing the drugs at the concentration previously described, and caspase 3/7 activation was measured at 24, 48, and 72 h following the manufacturer’s instructions. Each experiment was repeated three times.
4.8. Protein Extraction
The LN405 cell line was treated with panobinostat, temozolomide, both in combination, or with DMSO as a vehicle control for 72 h. Then, total proteins were extracted from cells using the radio immunoprecipitation assay (RIPA) lysis buffer (50 mM tris-hidroximetil- aminometano (TRIS)-HCl, pH 8.0, 150 mM NaCl, 0.5% Triton® X-100, and 0.5% sodium deoxycholate).
4.9. Western Blot
Equal amounts of each protein sample were separated in a 12% sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) and then transferred to a nitrocellulose membrane. After blocking with Tris-buffered saline (TBS)-Tween 0.1%, 5% non-fat milk, membranes were incubated overnight with the primary antibody at 4 °C. The primary antibodies used in this study were the antibodies against: α-tubulin 1/4000 (#T6074, Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany), acetylated α-tubulin 1/10,000 (#T6793, Merck KGaA), E-cadherin 1/1000 (#3195 Cell Signaling Danvers, MA, USA), N-cadherin 1/1000 (#13116, Cell Signaling), vimentin 1/500 (#V2258, Merck KGaA), and β-actin 1/10,000 (#A5441, Merck KGaA). After three washes with TBS-Tween 0.1%, membranes were incubated with the corresponding secondary antibody at room temperature for 1 h. To reveal the experiment, we used the Lumi-LightPLUS Western blotting Substrate (Merck KGaA). Each experiment was repeated three times.
4.10. Analytical Statistics
GraphPad 7.0 Software [49] was used to analyze the statistics of the results obtained from the experiments. Values are expressed as mean + standard deviation (SD) or as mean + standard error of the mean (SEM). The statistical tests used were one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) and Tukey’s multiple comparisons test, and p < 0.05 was taken as significant.
Acknowledgments
Financial support for this work was provided by a grant from the Fundación Universidad de Navarra, Pamplona, Spain. A.U. received a predoctoral fellowship from the Asociación de Amigos de la Universidad de Navarra, Pamplona, Spain.
Author Contributions
A.U., B.M., J.A.R., M.A.I., and J.S.C. conceived and designed the experiments; A.U. performed the experiments; A.U. and J.S.C. analyzed the data and drafted the paper; all authors contributed to refine writing; M.A.I. and J.S.C. were granted research funds from the Fundación Universidad de Navarra.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Jovcevska, I.; Kocevar, N.; Komel, R. Glioma and glioblastoma—How much do we (not) know? Mol. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 1, 935–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamza, M.A.; Gilbert, M. Targeted therapy in gliomas. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2014, 16, 379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stupp, R.; Mason, W.P.; van den Bent, M.J.; Weller, M.; Fisher, B.; Taphoorn, M.J.; Belanger, K.; Brandes, A.A.; Marosi, C.; Bogdahn, U.; et al. Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 987–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, M.; Reimand, J.; Lan, X.; Head, R.; Zhu, X.; Kushida, M.; Bayani, J.; Pressey, J.C.; Lionel, A.C.; Clarke, I.D.; et al. Single cell-derived clonal analysis of human glioblastoma links functional and genomic heterogeneity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 851–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pardridge, W.M. The blood-brain barrier: Bottleneck in brain drug development. NeuroRx 2005, 2, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo, H.W. EGFR-targeted therapy in malignant glioma: Novel aspects and mechanisms of drug resistance. Curr. Mol. Pharmacol. 2010, 3, 37–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathews, L.A.; Crea, F.; Farrar, W.L. Epigenetic gene regulation in stem cells and correlation to cancer. Differentiation 2009, 78, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, W.; Herman, J.G.; Guo, M. Epigenome-based personalized medicine in human cancer. Epigenomics 2016, 8, 119–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drummond, D.C.; Noble, C.O.; Kirpotin, D.B.; Guo, Z.; Scott, G.K.; Benz, C.C. Clinical development of histone deacetylase inhibitors as anticancer agents. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2005, 45, 495–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Kuljaca, S.; Tee, A.; Marshall, G.M. Histone deacetylase inhibitors: Multifunctional anticancer agents. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2006, 32, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atadja, P. Development of the pan-DAC inhibitor panobinostat (LBH589): Successes and challenges. Cancer Lett. 2009, 280, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lotte, M.E.; Pont, B.; Kleijn, A.; Kloezeman, J.J.; van den Bossche, W.; Kaufmann, J.K.; de Vrij, J.; Leenstra, S.; Clemens, M.F.; Dirven, C.M.; et al. The HDAC inhibitors scriptaid and LBH589 combined with the oncolytic virus delta24-RGD exert enhanced anti-tumor efficacy in patient-derived glioblastoma cells. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0127058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.Q.; Reardon, D.A.; Schiff, D.; Drappatz, J.; Muzikansky, A.; Grimm, S.A.; Norden, A.D.; Nayak, L.; Beroukhim, R.; Rinne, M.L.; et al. Phase II study of panobinostat in combination with bevacizumab for recurrent glioblastoma and anaplastic glioma. Neuro Oncol. 2015, 17, 862–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lotte, M.E.; Pont, B.; Naipal, K.; Kloezeman, J.J.; Venkatesan, S.; van den Bent, M.; van Gent, D.C.; Dirven, C.M.; Kanaar, R.; Lamfers, M.L.; et al. DNA damage response and anti-apoptotic proteins predict radiosensitization efficacy of HDAC inhibitors SAHA and LBH589 in patient-derived glioblastoma cells. Cancer Lett. 2015, 356, 525–535. [Google Scholar]
- Singleton, W.G.; Collins, A.M.; Bienemann, A.S.; Killick-Cole, C.L.; Haynes, H.R.; Asby, D.J.; Butts, C.P.; Wyatt, M.J.; Barua, N.U.; Gill, S.S. Convection enhanced delivery of panobinostat (LBH589)-loaded pluronicnano-micelles prolongs survival in the F98 rat glioma model. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 1385–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, Z.G.; Li, W.H.; Hua, F.; Cheng, H.X.; Zhao, M.Q.; Sun, X.C.; Qin, Y.J.; Li, J.M. LBH589 inhibits glioblastoma growth and angiogenesis through suppression of HIF-1αexpression. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2017, 76, 1000–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, C.; Friday, B.B.; Yang, L.; Atadja, P.; Wigle, D.; Sarkaria, J.; Adjei, A.A. Mitochondrial Bax translocation partially mediates synergistic cytotoxicity between histone deacetylase inhibitors and proteasome inhibitors in glioma cells. Neuro Oncol. 2008, 10, 309–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalluri, R.; Weinberg, R.A. The basics of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J. Clin. Investig. 2009, 119, 1420–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kast, R.E.; Skuli, N.; Karpel-Massler, G.; Frosina, G.; Ryken, T.; Halatsch, M.E. Blocking epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in glioblastoma with a sextet of repurposed drugs: The EIS regimen. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 60727–60749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catalano, M.G.; Fortunati, N.; Pugliese, M.; Marano, F.; Ortoleva, L.; Poli, R.; Asioli, S.; Bandino, A.; Palestini, N.; Grange, C.; et al. Histone deacetylase inhibition modulates E-cadherin expression and suppresses migration and invasion of anaplastic thyroid cancer cells. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 97, E1150–E1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kahlert, U.D.; Maciaczyk, D.; Doostkam, S.; Orr, B.A.; Simons, B.; Bogiel, T.; Reithmeier, T.; Prinz, M.; Schubert, J.; Niedermann, G.; et al. Activation of canonical WNT/β-catenin signaling enhances in vitro motility of glioblastoma cells by activation of ZEB1 and other activators of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Cancer Lett. 2012, 325, 42–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.Y.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, L.; Chen, B.D.; Li, Q.Z.; Zhang, X.J.; Li, W.P. A novel HDAC6 inhibitor Tubastatin A: Controls HDAC6-p97/VCP-mediated ubiquitination-autophagy turnover and reverses Temozolomide-induced ER stress-tolerance in GBM cells. Cancer Lett. 2017, 391, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, S.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, B.; Ding, K.; Yao, T.P.; Chen, F.; Zhan, L.; Xu, P.; Ehrlich, M.; Liang, T.; et al. Loss of α-tubulin acetylation is associated with TGF-β -induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 5396–5405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- San-Miguel, J.F.; Hungria, V.T.; Yoon, S.S.; Beksac, M.; Dimopoulos, M.A.; Elghandour, A.; Jedrzejczak, W.W.; Gunther, A.; Nakorn, T.N.; Siritanaratkul, N.; et al. Panobinostat plus bortezomib and dexamethasone versus placebo plus bortezomib and dexamethasone in patients with relapsed or relapsed and refractory multiple myeloma: Amulticentre, randomised, double-blind phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2014, 15, 1195–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- San-Miguel, J.F.; Hungria, V.T.; Yoon, S.S.; Beksac, M.; Dimopoulos, M.A.; Elghandour, A.; Jedrzejczak, W.W.; Gunther, A.; Nakorn, T.N.; Siritanaratkul, N.; et al. Overall survival of patients with relapsed multiple myeloma treated with panobinostat or placebo plus bortezomib and dexamethasone (the PANORAMA 1 trial): A randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Haematol. 2016, 3, e506–e515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assouline, S.E.; Nielsen, T.H.; Yu, S.; Alcaide, M.; Chong, L.; MacDonald, D.; Tosikyan, A.; Kukreti, V.; Kezouh, A.; Petrogiannis-Haliotis, T.; et al. Phase 2 study of panobinostat with or without rituximab in relapsed diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Blood 2016, 128, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, D.; Phipps, C.; Hwang, W.Y.; Tan, S.Y.; Yeap, C.H.; Chan, Y.H.; Tay, K.; Lim, S.T.; Lee, Y.S.; Kumar, S.G.; et al. Panobinostat in combination with bortezomib in patients with relapsed or refractory peripheral T-cell lymphoma: An open-label, multicentre phase 2 trial. Lancet Haematol. 2015, 2, e326–e333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Marinis, F.; Atmaca, A.; Tiseo, M.; Giuffreda, L.; Rossi, A.; Gebbia, V.; D’Antonio, C.; DalZotto, L.; Al-Batran, S.E.; Marsoni, S.; et al. A phase II study of the histone deacetylase inhibitor panobinostat (LBH589) in pretreated patients with small-cell lung cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2013, 8, 1091–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hainsworth, J.D.; Infante, J.R.; Spigel, D.R.; Arrowsmith, E.R.; Boccia, R.V.; Burris, H.A. A phase II trial of panobinostat, a histone deacetylase inhibitor, in the treatment of patients with refractory metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Investig. 2011, 29, 451–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, N.; Lubner, S.J.; Mulkerin, D.L.; Rajguru, S.; Carmichael, L.; Chen, H.; Holen, K.D.; LoConte, N.K. A phase II trial of a histone deacetylase inhibitor panobinostat in patients with low-grade neuroendocrine tumors. Oncologist 2016, 21, 785–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rathkopf, D.E.; Picus, J.; Hussain, A.; Ellard, S.; Chi, K.N.; Nydam, T.; Allen-Freda, E.; Mishra, K.K.; Porro, M.G.; Scher, H.I.; et al. A phase 2 study of intravenous panobinostat in patients with castration-resistant prostate cancer. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2013, 72, 537–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauer, S.; Hilger, R.A.; Muhlenberg, T.; Grabellus, F.; Nagarajah, J.; Hoiczyk, M.; Reichardt, A.; Ahrens, M.; Reichardt, P.; Grunewald, S.; et al. Phase I study of panobinostat and imatinib in patients with treatment-refractory metastatic gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Br. J. Cancer 2014, 110, 1155–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukutomi, A.; Hatake, K.; Matsui, K.; Sakajiri, S.; Hirashima, T.; Tanii, H.; Kobayashi, K.; Yamamoto, N. A phase I study of oral panobinostat (LBH589) in Japanese patients with advanced solid tumors. Investig. New Drugs 2012, 30, 1096–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gray, J.E.; Haura, E.; Chiappori, A.; Tanvetyanon, T.; Williams, C.C.; Pinder-Schenck, M.; Kish, J.A.; Kreahling, J.; Lush, R.; Neuger, A.; et al. A phase I, pharmacokinetic, and pharmacodynamic study of panobinostat, an HDAC inhibitor, combined with erlotinib in patients with advanced aerodigestive tract tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 1644–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, N.; Buchbinder, E.I.; Granter, S.R.; Rodig, S.J.; Giobbie-Hurder, A.; Becerra, C.; Tsiaras, A.; Gjini, E.; Fisher, D.E.; Hodi, F.S. A phase I trial of panobinostat (LBH589) in patients with metastatic melanoma. Cancer Med. 2016, 5, 3041–3050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, S.F.; Bendell, J.C.; Infante, J.R.; Spigel, D.R.; Thompson, D.S.; Yardley, D.A.; Greco, F.A.; Murphy, P.B.; Burris, H.A. 3rd. A phase I study of panobinostat in combination with gemcitabine in the treatment of solid tumors. Clin. Adv. Hematol. Oncol. 2011, 9, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jones, S.F.; Infante, J.R.; Thompson, D.S.; Mohyuddin, A.; Bendell, J.C.; Yardley, D.A.; Burris, H.A., 3rd. A phase I trial of oral administration of panobinostat in combination with paclitaxel and carboplatin in patients with solid tumors. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2012, 70, 471–475. [Google Scholar]
- Morita, S.; Oizumi, S.; Minami, H.; Kitagawa, K.; Komatsu, Y.; Fujiwara, Y.; Inada, M.; Yuki, S.; Kiyota, N.; Mitsuma, A.; et al. Phase I dose-escalating study of panobinostat (LBH589) administered intravenously to Japanese patients with advanced solid tumors. Investig. New Drugs 2012, 30, 1950–1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rathkopf, D.; Wong, B.Y.; Ross, R.W.; Anand, A.; Tanaka, E.; Woo, M.M.; Hu, J.; Dzik-Jurasz, A.; Yang, W.; Scher, H.I. A phase I study of oral panobinostat alone and in combination with docetaxel in patients with castration-resistant prostate cancer. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2010, 66, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, S.; Witteveen, P.O.; Lolkema, M.P.; Hess, D.; Gelderblom, H.; Hussain, S.A.; Porro, M.G.; Waldron, E.; Valera, S.Z.; Mu, S. A phase I, open-label, multicenter study to evaluate the pharmacokinetics and safety of oral panobinostat in patients with advanced solid tumors and varying degrees of renal function. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2015, 75, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strickler, J.H.; Starodub, A.N.; Jia, J.; Meadows, K.L.; Nixon, A.B.; Dellinger, A.; Morse, M.A.; Uronis, H.E.; Marcom, P.K.; Zafar, S.Y.; et al. Phase I study of bevacizumab, everolimus, and panobinostat (LBH-589) in advanced solid tumors. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2012, 70, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takhar, H.S.; Singhal, N.; Gowda, R.; Penniment, M.; Takhar, P.; Brown, M.P. Phase I study evaluating the safety and efficacy of oral panobinostat in combination with radiotherapy or chemoradiotherapy in patients with inoperable stage III non-small-cell lung cancer. Anticancer Drugs 2015, 26, 1069–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, W.W.; Allred, J.B.; Moreno-Aspitia, A.; Northfelt, D.W.; Ingle, J.N.; Goetz, M.P.; Perez, E.A. Phase I study of panobinostat(LBH589) and letrozole in postmenopausal metastatic breast cancer patients. Clin. Breast Cancer 2016, 16, 82–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarhini, A.A.; Zahoor, H.; McLaughlin, B.; Gooding, W.E.; Schmitz, J.C.; Siegfried, J.M.; Socinski, M.A.; Argiris, A. Phase I trial of carboplatin and etoposide in combination with panobinostat in patients with lung cancer. Anticancer Res. 2013, 33, 4475–4481. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Thomas, S.; Aggarwal, R.; Jahan, T.; Ryan, C.; Troung, T.; Cripps, A.M.; Raha, P.; Thurn, K.T.; Chen, S.; Grabowsky, J.A.; et al. A phase I trial of panobinostat and epirubicin in solid tumors with a dose expansion in patients with sarcoma. Ann. Oncol. 2016, 27, 947–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drappatz, J.; Lee, E.Q.; Hammond, S.; Grimm, S.A.; Norden, A.D.; Beroukhim, R.; Gerard, M.; Schiff, D.; Chi, A.S.; Batchelor, T.T.; et al. Phase I study of panobinostat in combination with bevacizumab for recurrent high-grade glioma. J. Neurooncol. 2012, 107, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, W.; Palmer, J.D.; Werner-Wasik, M.; Andrews, D.W.; Evans, J.J.; Glass, J.; Kim, L.; Bar-Ad, V.; Judy, K.; Farrell, C.; et al. Phase I trial of panobinostat and fractionated stereotactic re-irradiation therapy for recurrent high-grade gliomas. J. Neurooncol. 2016, 127, 535–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geissmann, Q. OpenCFU, a new free and open-source software to count cell colonies and other circular objects. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e54072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GraphPath software. Available online: https://www.graphpad.com/scientific-software/prism/ (accessed on 15 November 2017).
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).