Integrative Morphological and Molecular Diagnostics for Euseius nicholsi and Euseius oolong (Acari: Phytoseiidae)
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Species Considered
2.2. Morphological Analysis
2.3. Molecular Experiments and Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Morphological Analysis
3.2. Material Measured
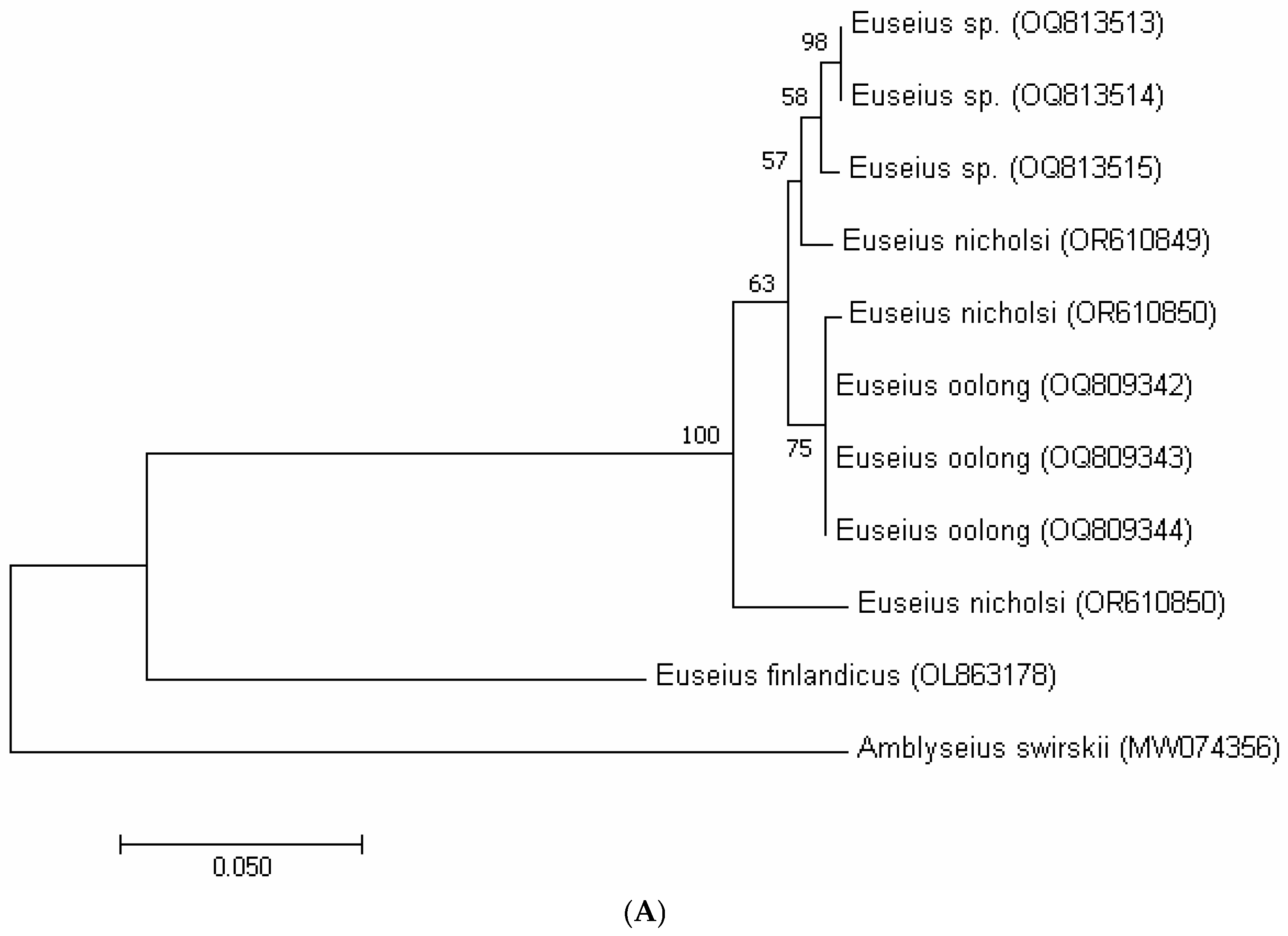
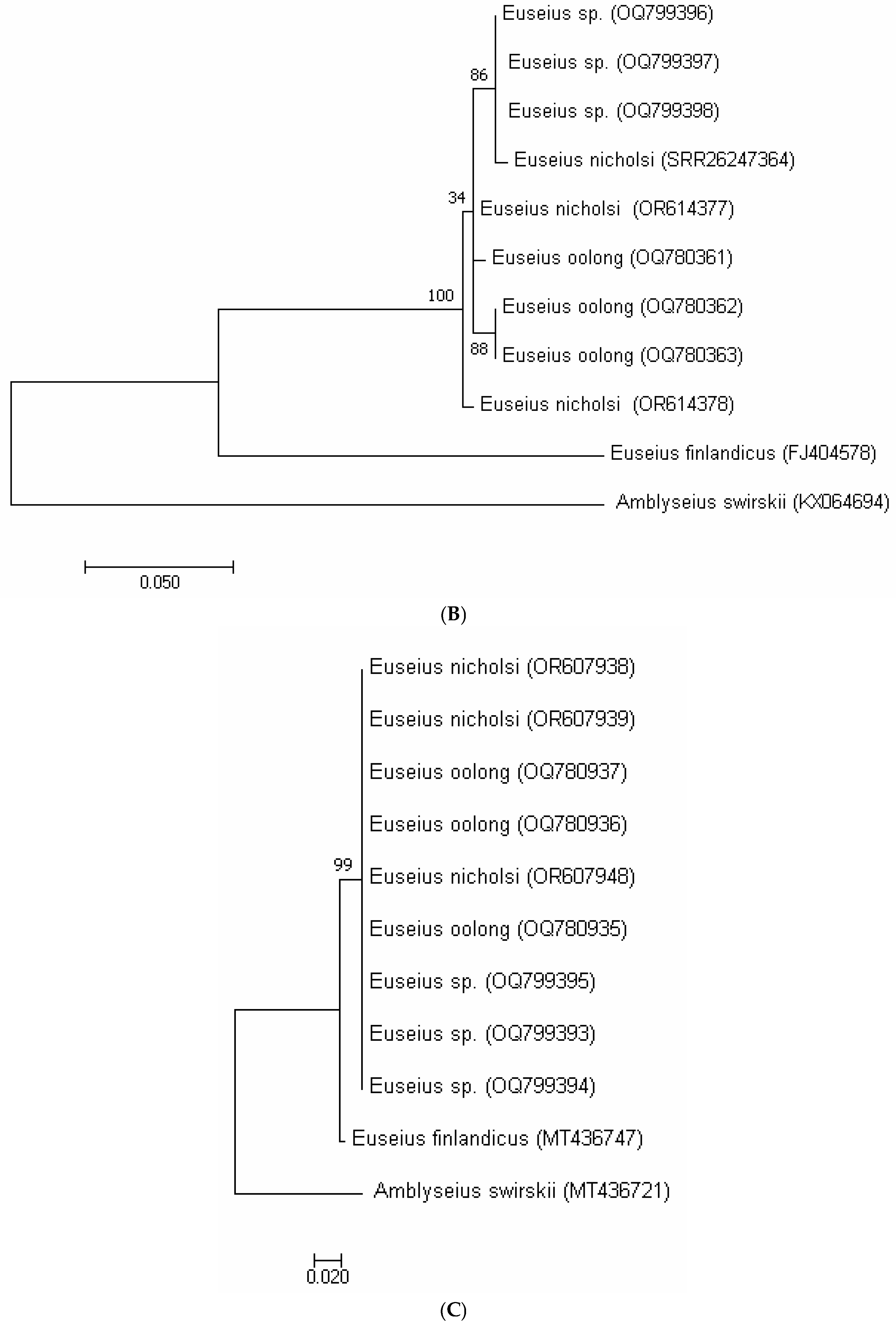
3.3. Molecular Analysis
3.4. Comparative Synthesis of Morphological and Molecular Results
| Putative Euseius sp. (OQ813513) | Putative Euseius sp. (OQ813514) | Putative Euseius sp. (OQ813515) | E. oolong (OQ809342) | E. oolong (OQ809343) | E. oolong (OQ809344) | E. nicholsi (OR610851) | E. nicholsi (OR610849) | E. nicholsi (OR610850) | E. finlandicus (OL863178) | Amblyseius swirskii (MW074356) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Putative Euseius sp. (OQ813513) | |||||||||||
| Putative Euseius sp. (OQ813514) | 0.00 | ||||||||||
| Putative Euseius sp. (OQ813515) | 0.01 | 0.01 | |||||||||
| E. oolong (OQ809342) | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | ||||||||
| E. oolong (OQ809343) | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.00 | |||||||
| E. oolong (OQ809344) | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.00 | 0.00 | ||||||
| E. nicholsi (OR610851) | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |||||
| E. nicholsi (OR610849) | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | ||||
| E. nicholsi (OR610850) | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.04 | |||
| E. finlandicus (OL863178) | 0.23 | 0.23 | 0.23 | 0.23 | 0.23 | 0.23 | 0.23 | 0.24 | 0.24 | ||
| Amblyseius swirskii (MW074356) | 0.31 | 0.31 | 0.31 | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.31 | 0.33 | 0.30 |
| Putative Euseius sp. (OQ799396) | Putative Euseius sp. (OQ799397) | Putative Euseius sp. (OQ799398) | E. oolong (OQ780361) | E. oolong (OQ780362) | E. oolong (OQ780363) | E. nicholsi (PRJNA1022847) | E. nicholsi (OR614377) | E. nicholsi (OR614378) | E. finlandicus (FJ404578) | Amblyseius swirskii (KX064694) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Putative Euseius sp. (OQ799396) | |||||||||||
| Putative Euseius sp. (OQ799397) | 0.00 | ||||||||||
| Putative Euseius sp. (OQ799398) | 0.01 | 0.01 | |||||||||
| E. oolong (OQ780361) | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.01 | ||||||||
| E. oolong (OQ780362) | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.02 | |||||||
| E. oolong (OQ780363) | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.00 | ||||||
| E. nicholsi (PRJNA1022847) | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |||||
| E. nicholsi (OR614377) | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | ||||
| E. nicholsi (OR614378) | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.01 | |||
| E. finlandicus (FJ404578) | 0.21 | 0.21 | 0.21 | 0.21 | 0.22 | 0.22 | 0.22 | 0.21 | 0.22 | ||
| Amblyseius swirskii (KX064694) | 0.34 | 0.34 | 0.34 | 0.34 | 0.35 | 0.35 | 0.36 | 0.34 | 0.35 | 0.39 |
| Putative Euseius sp. (OQ799393) | Putative Euseius sp. (OQ799394) | Putative Euseius sp. (OQ799395) | E. oolong (OQ780935) | E. oolong (OQ780936) | E. oolong (OQ780937) | E. nicholsi (OR607938) | E. nicholsi (OR607939) | E. nicholsi (OR607948) | E. finlandicus (MT436747) | Amblyseius swirskii (MT436721) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Putative Euseius sp. (OQ799393) | |||||||||||
| Putative Euseius sp. (OQ799394) | 0.00 | ||||||||||
| Putative Euseius sp. (OQ799395) | 0.00 | 0.00 | |||||||||
| E. oolong (OQ780935) | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | ||||||||
| E. oolong (OQ780936) | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |||||||
| E. oolong (OQ780937) | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | ||||||
| E. nicholsi (OR607938) | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |||||
| E. nicholsi (OR607939) | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | ||||
| E. nicholsi (OR607948) | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |||
| E. finlandicus (MT436747) | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | ||
| Amblyseius swirskii ( MT436721) | 0.18 | 0.18 | 0.18 | 0.18 | 0.18 | 0.18 | 0.18 | 0.18 | 0.18 | 0.18 |
| Character | Putative Euseius sp. | E. nicholsi | E. oolong |
|---|---|---|---|
| Female dorsal shield length (µm) | 299–335 | 352–381 | 323–361 |
| Dorsal solenostomes | 7 | 7 | 5 (sometimes 7, weak gd1) |
| Spermathecal calyx | Tubular, weakly sclerotized | Funnel-shaped, flaring | Cup-shaped |
| Metapodal platelets | 1–2 pairs, hooked/unhooked | 1 pair, mostly hooked | 2 pairs, unhooked |
| Fixed digit teeth | 4 | 3–4 | 5 |
| j3 seta (µm) | 22–31 | 27–33 | 20–25 |
| St IV (µm) | 43–62 | 56–73 | 47–61 |
| Molecular divergence | COI 0–4%; 12S 0–2%; ITS 0% | Same | Same |
| Phylogenetic placement | Same clade | Same clade | Same clade |
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- The specimens of Euseius sp. from Bajiaozhai National Forest Park were morphologically characterized as E. nicholsi, due to their high similarity. Based on molecular analyses, the specimens identified as E. nicholsi exhibited minimal genetic divergence from Euseius sp., indicating they likely represented the same species. Therefore, the morphological differences between Euseius sp. and E. nicholsi were best interpreted as intraspecific variation.
- Molecular evidence indicated that E. nicholsi and E. oolong are conspecific, with E. oolong treated as a synonym of E. nicholsi. Variations in body size, metapodal platelets, digit dentition, and setal lengths reflect intraspecific diversity.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, W.N.; Ou, J.F.; Huang, J.L. Fauna Sinica, Invertebrata Vol. 47, Arachnida, Acari, Phytoseiidae; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2009; 511p. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wu, W.N.; Fang, X.D. Phytoseiidae Systematics and Management of Pests; Guangdong Science and Technology Press: Guangzhou, China, 2021; 428p. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- McMurtry, J.A.; de Moraes, G.J.; Sourassou, N.F. Revision of the lifestyles of phytoseiid mites (Acari: Phytoseiidae) and implications for biological control strategies. Syst. Appl. Acarol. 2013, 18, 297–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demite, P.R.; De Moraes, G.J.; McMurtry, J.A.; Denmark, H.A.; Castilho, R.C. Phytoseiidae Database. Zootaxa 2014, 3795, 571–577. Available online: www.lea.esalq.usp.br/phytoseiidae/ (accessed on 1 December 2024). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tixier, M.S.; Okassa, M.; Kreiter, S. An integrative morphological and molecular diagnostics for Typhlodromus pyri (Acari: Phytoseiidae). Norw. Acad. Sci. Lett. 2012, 41, 68–78. [Google Scholar]
- Tixier, M.S. Statistical approaches for morphological continuous characters: A conceptual model applied to Phytoseiidae (Acari: Mesostigmata). Zool. Scr. 2013, 42, 327–334. [Google Scholar]
- Dos Santos, V.V.; Tixier, M.S. Molecular markers for analysing phylogenetic relationships within the mite family Phytoseiidae (Acari: Mesostigmata). Cladistics 2017, 28, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Döker, I.; Karut, K.; Karaca, M.M.; Cargnus, E.; Kazak, C. Internal Transcribed Spacer (ITS) sequences of some Kampimodromus (Acari: Phytoseiidae) species: Is Kampimodromus ragusai a valid species or a synonym of Kampimodromus aberrans? Syst. Appl. Acarol. 2018, 23, 2237–2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehara, S.; Lee, L.H.Y. Mites associated with plants in Hong Kong. J. Fac. Educ. Tottori Univ. Nat. Sci. 1971, 22, 61–78. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, J.H.; Ho, C.C.; Fang, X.D.; Ko, C.C. Contribution to the knowledge of the genera Euseius wainstein and Gynaseius wainstein (Acari: Mesostigmata: Amblyseiinae) from Taiwan. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2018, 23, 2192–2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, J.R.; Ho, C.C.; Lee, H.C.; Ko, C.C. Phytoseiidae of Taiwan (Acari: Mesostigmata). National Taiwan University Press: Taipei, Taiwan, 2020; 538p. [Google Scholar]
- Dos Santos, V.V.; Tixier, M.S. Integrative taxonomy approach for analysing evolutionary history of the tribe Euseiini Chant & McMurtry (Acari: Phytoseiidae). Syst. Biodivers. 2018, 16, 302–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Döker, I.; Çelik, S.O.; Karaca, M.M. Review of Euseius wainstein (Parasitiformes: Phytoseiidae) in Türkiye: An integrative taxonomic approach using morphological and molecular data with a new combination Euseius degenerans (Berlese). Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2025, 30, 560–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Döker, I.; Khaustov, V.A.; Ben-ami, R.; Tabic, A.; Joharchi, O. Integrative taxonomy reveals a new species of predatory mite in the subgenus Anthoseius De Leon (Acari: Phytoseiidae). Syst. Appl. Acarol. 2025, 30, 286–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanouh, M.; Tixier, M.S.; Guichou, S.; Cheval, B.; Kreiter, S. Two synonymy cases within the genus Neoseiulella (Acari: Phytoseiidae): Is the molecular evidence so evident? Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 2010, 101, 323–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tixier, M.S.; Kreiter, S.; Ferragut, F.; Cheval, B. The suspected synonymy of Kampimodromus hmiminal and Kampimodromus adrianae (Acari: Phytoseiidae): Morphological and molecular investigations. Can. J. Zool. 2006, 84, 1216–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tixier, M.S.; Kreiter, S.; Barbar, Z.; Ragusa, S.; Cheval, B. Status of two cryptic species, Typhlodromus exhilaratus Ragusa and Typhlodromus phialatus Athias-Henriot (Acari: Phytoseiidae): Consequences for taxonomy. Zool. Scr. 2006, 35, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tixier, M.S.; Guichou, S.; Kreiter, S. Assessment of the usefulness of eight DNA fragments for phylogenetic studies within the family Phytoseiidae. In Trends in Acarology; Sabelis, M.W., Bruin, J., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2010; pp. 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tixier, M.S.; Ferrero, M.; Okassa, M.; Guichou, S.; Kreiter, S. On the specific identity of specimens of Phytoseiulus longipes Evans (Mesostigmata: Phytoseiidae) showing different feeding behaviours: Morphological and molecular analysis. Bull. Entomol. Res. 2010, 100, 569–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tixier, M.S.; Otto, J.; Kreiter, S.; dos Santos, V.; Beard, J. Is Neoseiulus wearnei the Neoseiulus californicus of Australia? Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2014, 62, 267–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tixier, M.S.; dos Santos, V.; Douin, M.; Duso, C.; Kreiter, S. Great molecular variation within the species Phytoseius finitimus (Acari: Phytoseiidae): Implications for diagnosis decision within the mite family Phytoseiidae. Acarologia 2017, 57, 493–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tixier, M.S.; Dennj, P.; Douin, M.; Kreiter, S.; Haralabos, T. Mites of the genus Typhlodromus (Acari: Phytoseiidae) from Southern France: Combined morphological and molecular approaches for species identification. Zootaxa 2019, 4604, 242–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tixier M., S.; Auger, P.; Migeon, A.; Douina, M.; Fossoudc, A.; Navajas, M.; Arabuli, T. Integrated taxonomy supports the identification of some species of Phytoseiidae (Acari: Mesostigmata) from Georgia. Acarologia 2021, 61, 824–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okassa, M.; Tixier, M.S.; Cheval, B.; Kreiter, S. Molecular and morphological evidence for a new species status within the genus Euseius (Acari: Phytoseiidae). Can. J. Zool. 2009, 87, 689–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okassa, M.; Tixier, M.S.; Kreiter, S. Morphological and molecular diagnostics of Phytoseiulus persimilis and Phytoseiulus macropilis (Acari: Phytoseiidae). Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2010, 52, 291–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okassa, M.; Kreiter, S.; Tixier, M.S. Obtaining molecular data for all life stages of Typhlodromus (Typhlodromus) Exhilaratus (Mesostigmata: Phytoseiidae): Consequences for species identification. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2012, 57, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindquist, E.E.; Evans, G.O. Taxonomic concepts in the Ascidae with a modified setal nomenclature for the idiosoma of the Gamasina (Acarina: Mesostigmata). Mem. Entomol. Soc. Can. 1965, 47, 5–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowell, H.J.; Chant, D.A.; Hansell, R.I.C. The determination of setal homologies and setal patterns on the dorsal shield in the family Phytoseiidae (Acarina: Mesostigmata). Can. Entomol. 1978, 110, 859–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chant, D.A.; Yoshida-Shaul, E. Adult idiosomal setal patterns in the family Phytoseiidae (Acari: Gamasina). Intern. J. Acarol. 1992, 18, 177–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athias-Henriot, C. Nouvelles notes sur les Amblyseiini. II. Le relevé organotaxique de la face dorsale adulte (Gamasides protoadéniques, Phytoseiidae). Acarologia 1975, 17, 20–29. [Google Scholar]
- Folmer, O.; Black, M.; Hoeh, W.; Lutz, R.; Vrijenhoek, R. DNA primers for amplification of mitochondrial cytochrome oxidase subunit I from diverse metazoan invertebrates. Mol. Mar. Biol. Biotechnol. 1994, 3, 294–299. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.B.; Li, Y.X.; Sun, J.T.; Xue, X.F.; Xu, X.N.; Hong, X.Y. COI barcoding as a molecular assay for the identification of phytoseiid mites. Syst. Appl. Acarol. 2012, 17, 397–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeyaprakash, A.; Hoy, M. Mitochondrial 12S rRNA sequences used to design a molecular ladder assay to identify six commercially available phytoseiids (Acari: Phytoseiidae). Biol. Control 2002, 25, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navajas, M.; Lagnel, J.; Fauvel, G.; de Moraes, G. Sequence variation of ribosomal Internal Transcribed Spacers (ITS) in commercially important Phytoseiidae mites. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 1999, 23, 851–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseininia, A.; Khanjani1, M.; Asadi, M.; Soltani1, J. Genetic diversity of predatory mite Typhlodromus bagdasarjani (Acari: Phytoseiidae) populations based on molecular markers. Syst. Appl. Acarol. 2023, 28, 2164–2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

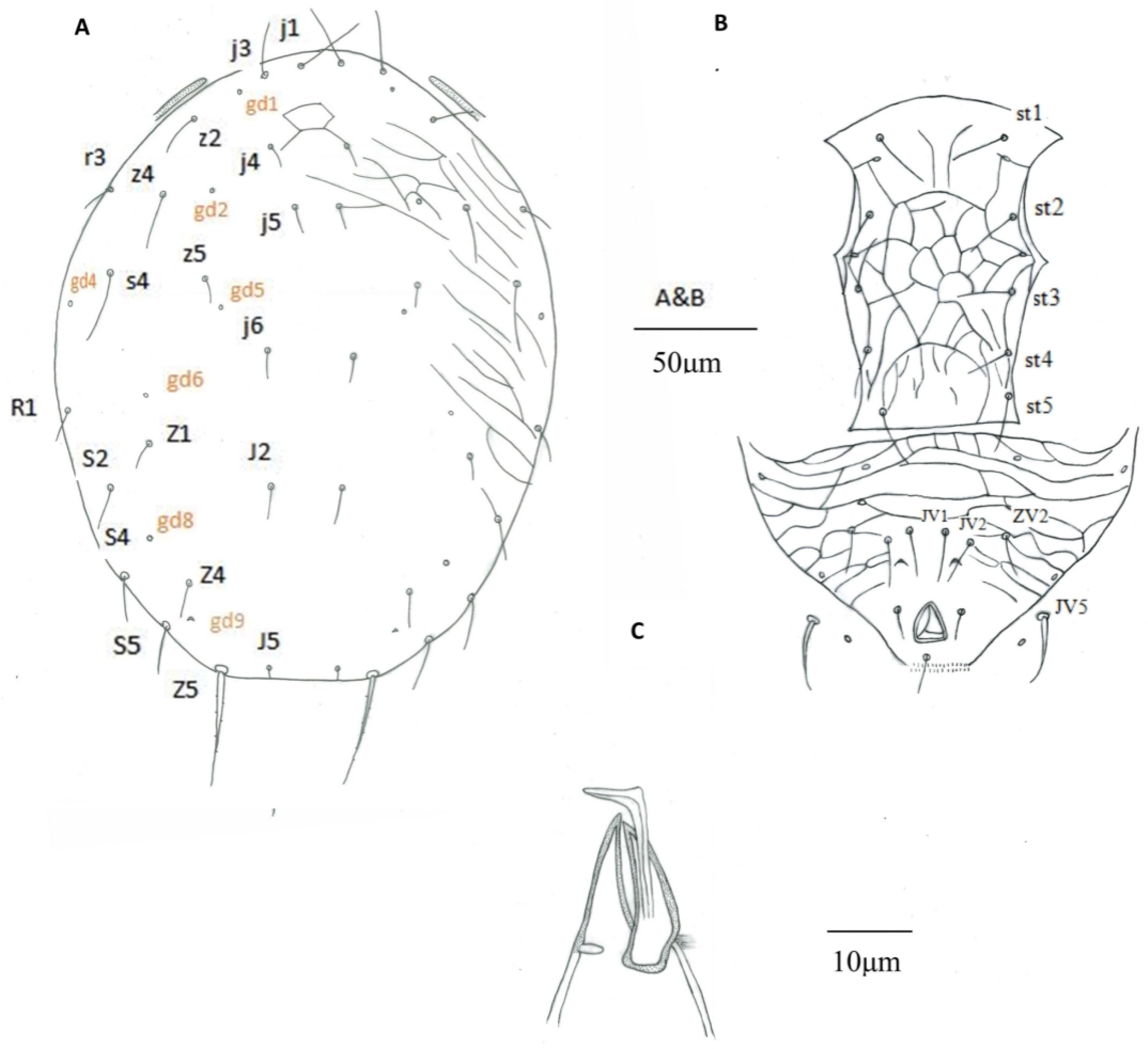
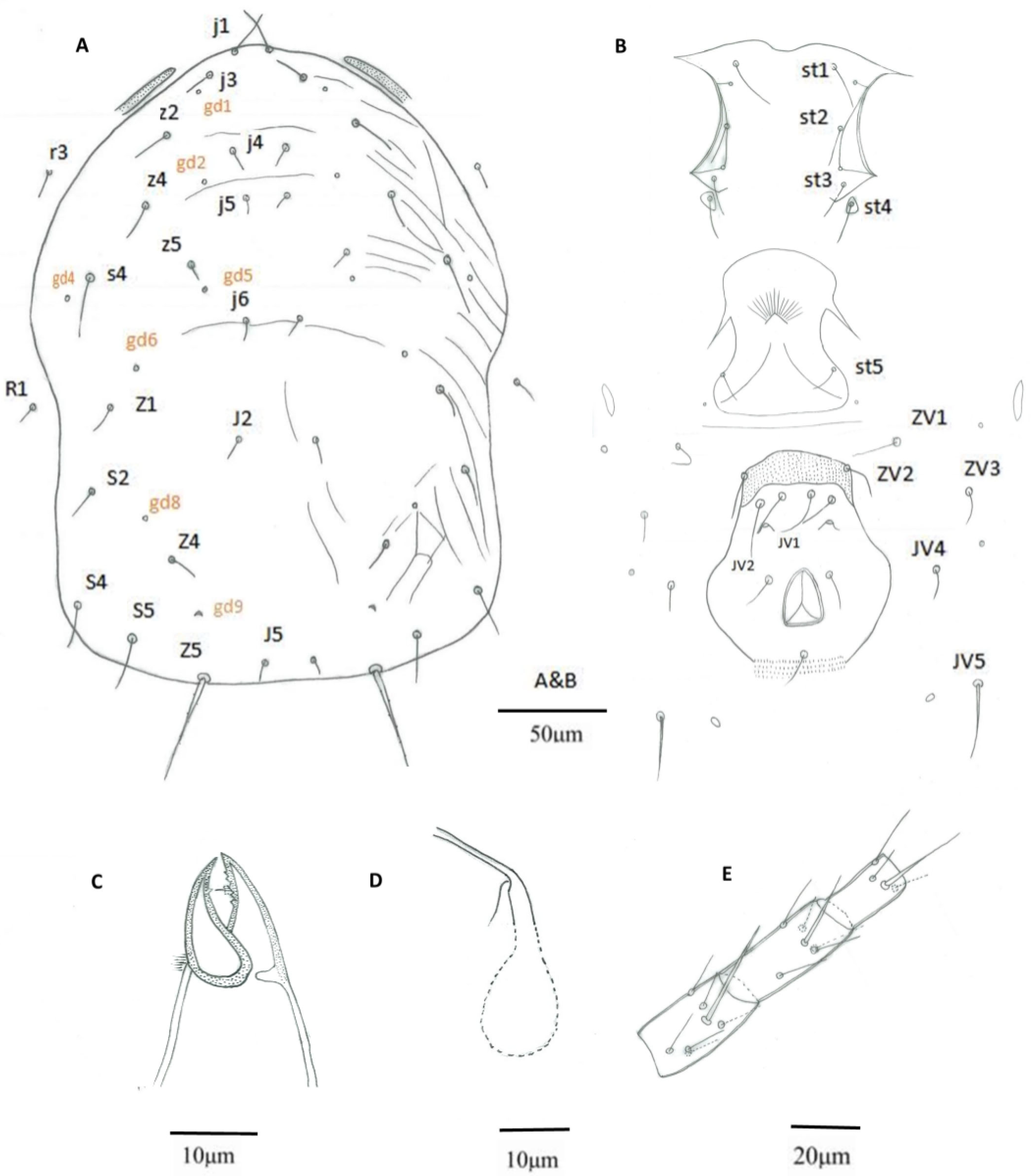
| Putative Euseius sp. a | E. nicholsi b | E. nicholsi c | E. nicholsi d | E. oolong e | E. oolong f | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dorsal shield length (µm) | 316 (299–335) | 360 | 365–381 | 352 (348–357) | 341 (324–361) | 323 (319–328) |
| Dorsal shield width (µm) (s4 level) | 239 (223–254) | 260 | 265–282 | 251 (246–257) | 246 (236–266) | 238 (233–243) |
| Dorsal shield | anterior reticulation and lateral striation | most surface reticulated | most surface reticulated | most surface reticulated | laterally reticulated | laterally reticulated |
| Solenostome on dorsal shield | gd1, gd2, gd4, gd5, gd6, gd8, gd9 | gd1, gd2, gd4, gd5, gd6, gd8, gd9 | gd1, gd2, gd4, gd5, gd6, gd8, gd9 | gd2, gd5, gd6, gd8, gd9 | gd1, gd2, gd4, gd5, gd6, gd8, gd9 | |
| Calyx of spermatheca | tubular, with distal half only lightly sclerotized; atrium c-shaped incorporated within the calyx | tubular, with basal half swollen | funnel-shaped, distal flaring; atrium knobbed, connected directly with calyx | funnel-shaped, distal flaring; atrium knobbed, connected directly with calyx | cup-shaped with distal half only lightly sclerotized; atrium c-shaped incorporated within the calyx | cup-shaped with distal half only lightly sclerotized; atrium c-shaped incorporated within the calyx |
| Metapodal platelet | one or two pairs, hooked or not | one pair, hooked | one pair, hooked or not | one pair, hooked or not | two pairs, un-hooked | one pair, hooked |
| Number of teeth on the fixed digit of the chelicerae | 4 | 3–4 | 4 | 5 | 5 | |
| Seate j3 | 25 (22–31) | 27 (26–28) | 30 | 31 (30–33) | 22 (20–25) | 22 (20–25) |
| Macroseta Sge IV | 41 (33–48) | 50 (48–53) | 52 | 48 (45–51) | 44 (37–50) | 50 (47–54) |
| Macroseta Sti IV | 32 (27–37) | 38 (38–39) | 41 | 34 (33–35) | 34 (27–37) | 33 (32–34) |
| Macroseta St IV | 51 (43–62) | 68 (60–73) | 66 | 56 (55–57) | 58 (50–61) | 50 (47–51) |
| Species | Country | Locality | Plant Supports | GenBank Accession Number of COI Sequences | GenBank Accession Number of 12S rRNA Sequences | GenBank Accession Number of ITS Sequences |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Putative Euseius sp. | China | Guilin | Cyclobalanopsis glauca | OQ813513 OQ813514 OQ813515 | OQ799396 OQ799397 OQ799398 | OQ799393 OQ799394 OQ799395 |
| E. oolong | China | Guangzhou | Bauhinia purpurea | OQ809342 OQ809343 OQ809344 | OQ780361 OQ780362 OQ780363 | OQ780935 OQ780936 OQ780937 |
| E. nicholsi | China | Guangzhou Shaoguan Shaoguan | Bauhinia purpurea Eurya macartneyi Ficus hispida | OR610851 OR610849 OR610850 | SRR26247364 OR614377 OR614378 | OR607938 OR607939 OR607948 |
| E. finlandicus | Russia France Turkey | Sochi Unknown Unknown | Ulmus sp. Prunus cerasus Unknown | OL863178 | FJ404578 | MT436747 |
| Amblyseius swirskii | France The Netherlands Turkey | Unknown Unknown Unknown | Unknown Rearing population Unknown | MW074356 | KX064694 | MT436721 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fang, X.; Li, J.; Mahmood, S.U.; Fidelis, N.C.; Meng, J. Integrative Morphological and Molecular Diagnostics for Euseius nicholsi and Euseius oolong (Acari: Phytoseiidae). Insects 2025, 16, 950. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16090950
Fang X, Li J, Mahmood SU, Fidelis NC, Meng J. Integrative Morphological and Molecular Diagnostics for Euseius nicholsi and Euseius oolong (Acari: Phytoseiidae). Insects. 2025; 16(9):950. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16090950
Chicago/Turabian StyleFang, Xiaoduan, Jun Li, Syed Usman Mahmood, Nwanade Chuks Fidelis, and Jianglei Meng. 2025. "Integrative Morphological and Molecular Diagnostics for Euseius nicholsi and Euseius oolong (Acari: Phytoseiidae)" Insects 16, no. 9: 950. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16090950
APA StyleFang, X., Li, J., Mahmood, S. U., Fidelis, N. C., & Meng, J. (2025). Integrative Morphological and Molecular Diagnostics for Euseius nicholsi and Euseius oolong (Acari: Phytoseiidae). Insects, 16(9), 950. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16090950







