Non-Target Effects of Beta-Cypermethrin on Baryscapus dioryctriae and Ecological Risk Assessment
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Insect Rearing
2.2. Insecticide Preparation and Residue Film Method
2.3. Acute Toxicity Assay
2.4. Reproductive Performance, Life History Parameters and Developmental Durations
2.5. Enzyme Activity Assays
2.6. LC-MS/MS Analysis of Residues and Metabolites
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Acute Toxicity of Beta-Cypermethrin to B. Dioryctriae
3.2. Reproductive Performance
3.3. Developmental Durations
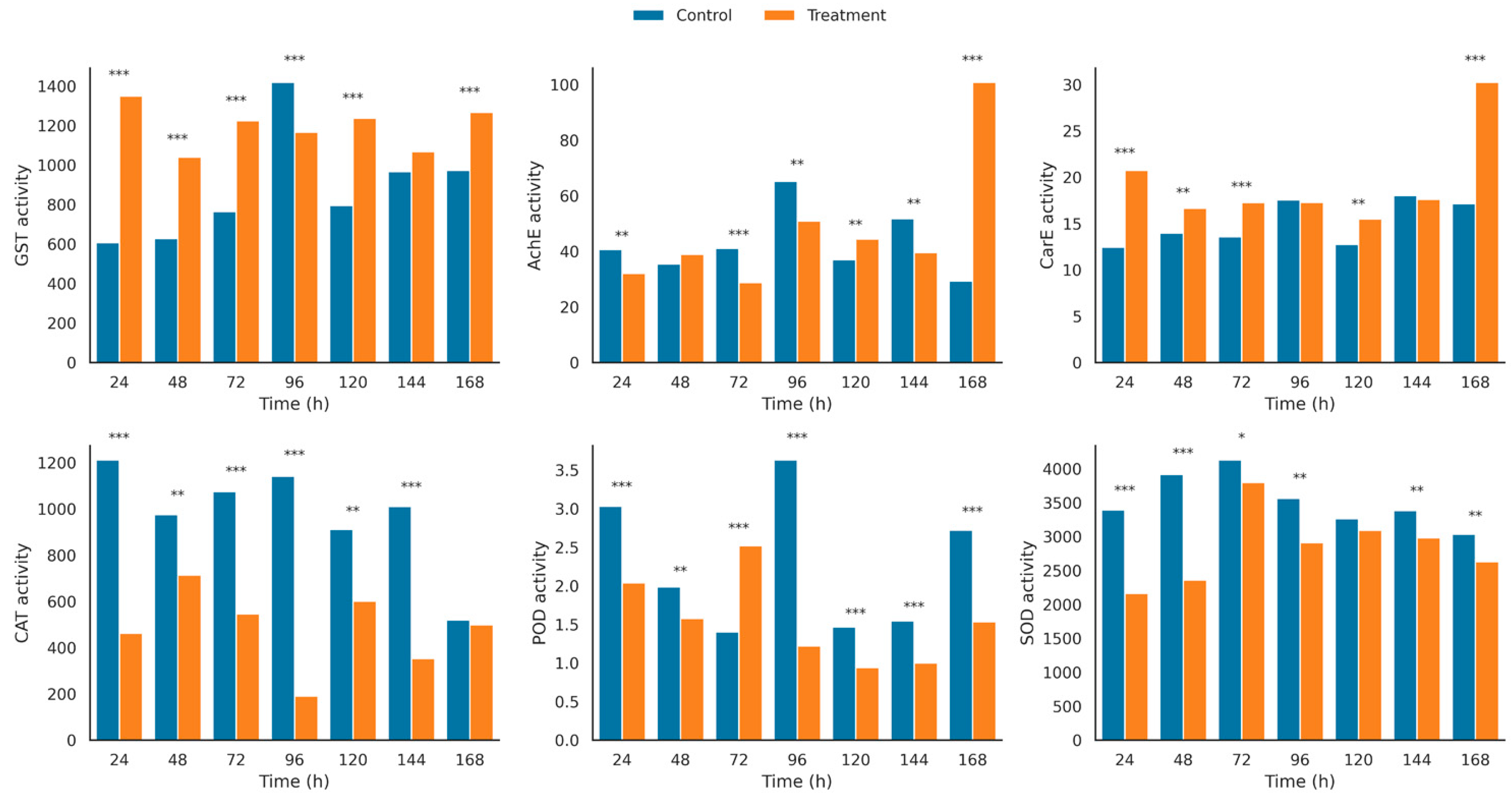
3.4. Enzyme Activity
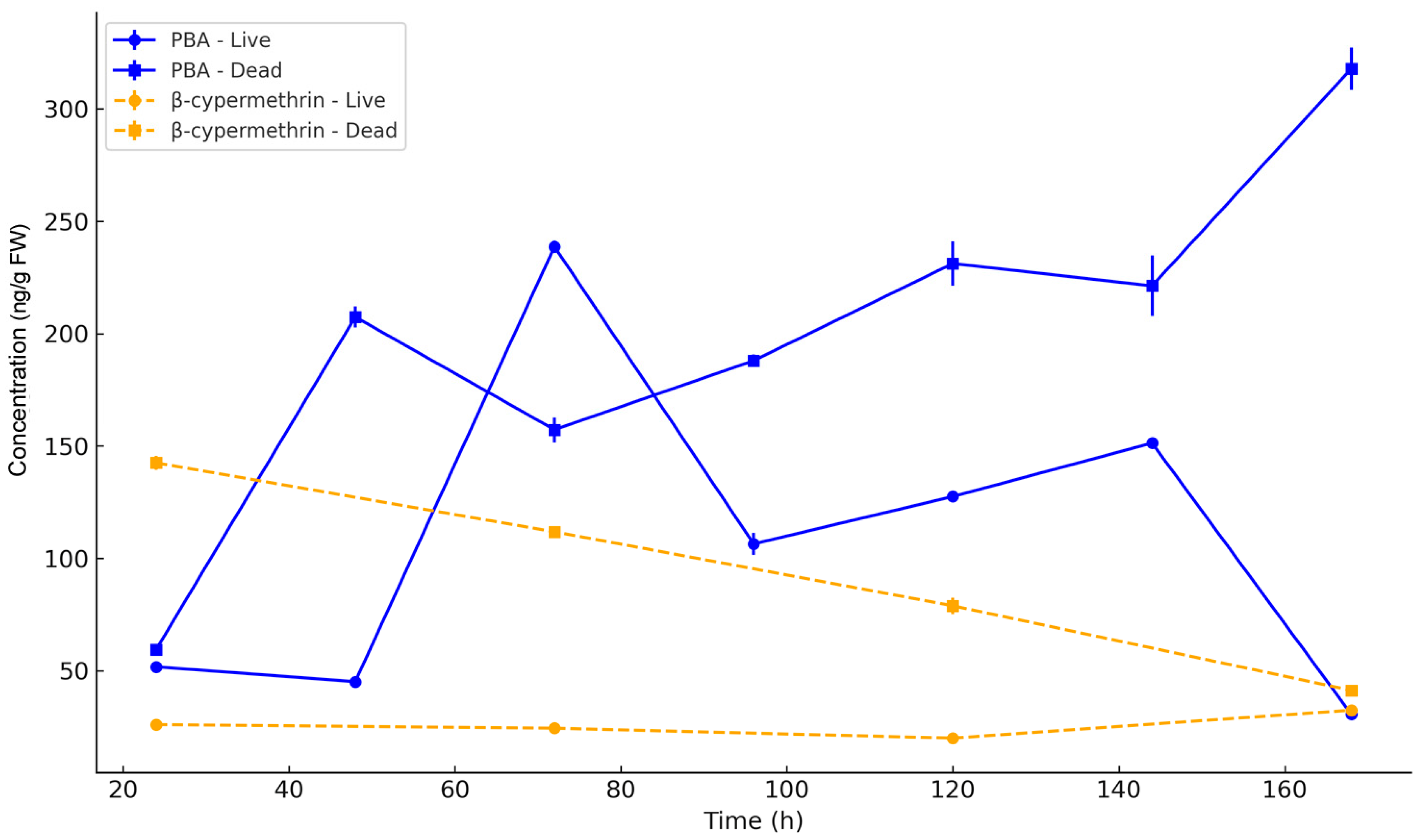
3.5. Residue Dynamics
4. Discussion
4.1. Reproductive Suppression and Developmental Disruption
4.2. Transgenerational Effects
4.3. Enzyme Dynamics and Mechanistic Interpretation
4.4. Residue Accumulation and Metabolite Risks
4.5. Ecological and IPM Implications
4.6. Future Directions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Van Lenteren, J.C. The state of commercial augmentative biological control: Plenty of natural enemies, but a frustrating lack of uptake. BioControl 2012, 57, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.-W.; Cao, L.-M.; Li, X.-P.; Yang, Z.-Q.; Chen, Y.-Q. A new species of Macrocentrus (Hymenoptera: Braconidae) parasitizing larva of Dioryctria pryeri (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae). Zootaxa 2017, 4303, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Yu, Q.; Gan, X.; Song, L.; Zhang, K.; Zuo, T.; Zhang, J.; Hu, Y.; Chen, Q.; Ren, B. Transcriptome Analysis and Identification of Chemosensory Genes in Baryscapus dioryctriae (Hymenoptera: Eulophidae). Insects 2022, 13, 1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barzman, M.; Bàrberi, P.; Birch, A.N.E.; Boonekamp, P.; Dachbrodt-Saaydeh, S.; Graf, B.; Hommel, B.; Jensen, J.E.; Kiss, J.; Kudsk, P. Eight principles of integrated pest management. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2015, 35, 1199–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heimpel, G.; Mills, N. Ecological Risk Analysis in Biological Control. In BioControl: Ecology and Applications; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2017; pp. 114–146. [Google Scholar]
- Samanta, S.; Maji, A.; Sutradhar, B.; Banerjee, S.; Shelar, V.B.; Khaire, P.B.; Yadav, S.V.; Bansode, G.D. Impact of pesticides on beneficial insects in various agroecosystem: A review. Int. J. Environ. Clim. Change 2023, 13, 1928–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdollahi, M.; Ranjbar, A.; Shadnia, S.; Nikfar, S.; Rezaie, A. Pesticides and oxidative stress: A review. Med. Sci. Monit. 2004, 10, 141–147. [Google Scholar]
- Desneux, N.; Decourtye, A.; Delpuech, J.M. The sublethal effects of pesticides on beneficial arthropods. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2007, 52, 81–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon-Delso, N.; Amaral-Rogers, V.; Belzunces, L.P.; Bonmatin, J.M.; Chagnon, M.; Downs, C.; Furlan, L.; Gibbons, D.W.; Giorio, C.; Girolami, V.; et al. Systemic insecticides (neonicotinoids and fipronil): Trends, uses, mode of action and metabolites. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2015, 22, 5–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sparks, T.C.; Crossthwaite, A.J.; Nauen, R.; Banba, S.; Cordova, D.; Earley, F.; Ebbinghaus-Kintscher, U.; Fujioka, S.; Hirao, A.; Karmon, D.; et al. Insecticides, biologics and nematicides: Updates to IRAC’s mode of action classification—A tool for resistance management. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2020, 167, 104587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maslakova, K.; Silivanova, E. The Effects of Neurotoxic Insecticides on Insect Antioxidant System Parameters: A Mini-Review. Adv. Life Sci. 2025, 12, 49–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Martínez, M.A.; Dai, M.; Chen, D.; Ares, I.; Romero, A.; Castellano, V.; Martínez, M.; Rodríguez, J.L.; Martínez-Larrañaga, M.R.; et al. Permethrin-induced oxidative stress and toxicity and metabolism. A review. Environ. Res. 2016, 149, 86–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biondi, A.; Mommaerts, V.; Smagghe, G.; Viñuela, E.; Zappalà, L.; Desneux, N. The non-target impact of spinosyns on beneficial arthropods. Pest. Manag. Sci. 2012, 68, 1523–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, C. Impacts of sublethal insecticide exposure on insects—Facts and knowledge gaps. Basic Appl. Ecol. 2018, 30, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guedes, R.N.C.; Walse, S.S.; Throne, J.E. Sublethal exposure, insecticide resistance, and community stress. Curr. Opin. Insect Sci. 2017, 21, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, S.; HUANG, J.-h. Parasitoid wasps as effective biological control agents. J. Integr. Agric. 2019, 18, 705–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfaro-Tapia, A.; Alvarez-Baca, J.K.; Fuentes-Contreras, E.; Figueroa, C.C. Biological control may fail on pests applied with high doses of insecticides: Effects of sub-lethal concentrations of a pyrethroid on the host-searching behavior of the aphid parasitoid Aphidius colemani (Hymenoptera, Braconidae) on aphid pests. Agriculture 2021, 11, 539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afza, R.; Afzal, A.; Riaz, M.A.; Majeed, M.Z.; Idrees, A.; Qadir, Z.A.; Afzal, M.; Hassan, B.; Li, J. Sublethal and transgenerational effects of synthetic insecticides on the biological parameters and functional response of Coccinella septempunctata (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) under laboratory conditions. Front. Physiol. 2023, 14, 1088712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt-Jeffris, R.A. Nontarget pesticide impacts on pest natural enemies: Progress and gaps in current knowledge. Curr. Opin. Insect Sci. 2023, 58, 101056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franeta, F.; Mirčić, D.; Todorović, D.; Milovac, Ž.; Granica, N.; Obradović, S.; Perić-Mataruga, V. Effects of different insecticides on the antioxidative defense system of the European Corn Borer (Ostrinia nubilalis Hübner) (Lepidoptera: Crambidae) larvae. Arch. Biol. Sci. 2018, 70, 765–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Zhao, L.; Zhu, X.; Wang, L.; Zhang, K.; Li, D.; Ji, J.; Niu, L.; Luo, J.; Cui, J. Exposure to flupyradifurone affect health of biocontrol parasitoid Binodoxys communis (Hymenoptera: Braconidae) via disrupting detoxification metabolism and lipid synthesis. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 255, 114785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ighodaro, O.; Akinloye, O. First line defence antioxidants-superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT) and glutathione peroxidase (GPX): Their fundamental role in the entire antioxidant defence grid. Alex. J. Med. 2018, 54, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sule, R.O.; Condon, L.; Gomes, A.V. A Common Feature of Pesticides: Oxidative Stress-The Role of Oxidative Stress in Pesticide-Induced Toxicity. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2022, 2022, 5563759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felton, G.W.; Summers, C.B. Antioxidant systems in insects. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 1995, 29, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolawole, A.O.; Olajuyigbe, F.M.; Ajele, J.O.; Adedire, C.O. Activity of the Antioxidant Defense System in a Typical Bioinsecticide-and Synthetic Insecticide-treated Cowpea Storage Beetle Callosobrochus maculatus F. (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae). Int. J. Insect Sci. 2014, 6, S19434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Branicky, R.; Noë, A.; Hekimi, S. Superoxide dismutases: Dual roles in controlling ROS damage and regulating ROS signaling. J. Cell Biol. 2018, 217, 1915–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ammar, H.A.; Soliman, Z.E.; Abouelghar, G.E. Abouelghar, Sublethal effects of selected insecticides on oxidative status and antioxidants in cowpea weevil, Callo-sobruchus maculatus (F.) [Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae]. Menoufia J. Plant Prot. 2024, 9, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velki, M.; Kodrík, D.; Večeřa, J.; Hackenberger, B.K.; Socha, R. Oxidative stress elicited by insecticides: A role for the adipokinetic hormone. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2011, 172, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbar, S.; Sharma, H.; Jayalakshmi, S.; Sreeramulu, K. Effect of pyrethroids, permethrin and fenvalarate, on the oxidative stress of Helicoverpa armigera. World J. Sci. Technol. 2012, 2, 01–05. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, F.; Yu, T.; Hu, J.; Yin, S.; Li, Y.; Kou, L.; Chi, X.; Wu, J.; Sun, Y.; Zhou, Q.; et al. The pyrethroids metabolite 3-phenoxybenzoic acid induces dopaminergic degeneration. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 838, 156027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Bayo, F.; Goka, K. Pesticide residues and bees—A risk assessment. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e94482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xavier, V.M.; Message, D.; Picanço, M.C.; Chediak, M.; Júnior, P.A.S.; Ramos, R.S.; Martins, J.C. Acute toxicity and sublethal effects of botanical insecticides to honey bees. J. Insect Sci. 2015, 15, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Li, G.; Cui, X.; Wang, H.; Liu, Z.; Yang, Y.; Xu, B. Review on effects of some insecticides on honey bee health. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2022, 188, 105219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.-W.; Cao, L.-M.; Li, X.-P.; Yang, Z.-Q.; Chen, Y.-Q. A new species of Baryscapus (Hymenoptera: Eulophidae) parasitizing pupae and larvae of two Dioryctria species (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae). Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 2017, 110, 286–293. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Zhang, K.; Zuo, T.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, X.; Song, L. Nontarget effects of insecticides on biological control agents: Insights from red pine forests and global challenges in forest pest management. J. Integr. Pest Manag. 2025, 16, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desneux, N.; Wajnberg, E.; Fauvergue, X.; Privet, S.; Kaiser, L. Oviposition behaviour and patch-time allocation in two aphid parasitoids exposed to deltamethrin residues. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 2004, 112, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desneux, N.; Denoyelle, R.; Kaiser, L.A. Multi-step bioassay to assess the effect of deltamethrin on the parasitic wasp Aphidius ervi (Hymenoptera: Braconidae). Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2006, 25, 2679–2686. [Google Scholar]
- Stark, J.D.; Banks, J.E. Population-level effects of pesticides and other toxicants on arthropods. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2003, 48, 505–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, Y.; Li, T.; Hussain, A.; Xia, X.; Shang, Q.; Ali, A. Editorial: The side effects of insecticides on insects and the adaptation mechanisms of insects to insecticides. Front. Physiol. 2023, 14, 1287219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jomova, K.; Alomar, S.Y.; Alwasel, S.H.; Nepovimova, E.; Kuca, K.; Valko, M. Several lines of antioxidant defense against oxidative stress: Antioxidant enzymes, nanomaterials with multiple enzyme-mimicking activities, and low-molecular-weight antioxidants. Arch. Toxicol. 2024, 98, 1323–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Group | Parasitism Rate (%) | Emergence Rate (%) | Female Ratio (%) | Offspring per Female |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| F0 CK | 47.85 ± 0.93 a | 82.48 ± 1.74 a | 62.03 ± 3.28 a | 15.92 ± 1.13 a |
| F0 LC30 | 32.37 ± 5.62 b | 66.94 ± 2.09 b | 63.83 ± 2.75 a | 15.75 ± 0.46 a |
| F0 LC50 | 23.84 ± 3.78 c | 50.50 ± 6.52 c | 68.41 ± 6.43 a | 6.12 ± 1.05 b |
| F1 CK | 22.26 ± 4.09 d | 68.98 ± 1.19 a | 72.66 ± 0.30 b | 14.67 ± 1.85 c |
| F1 LC30 | 19.21 ± 3.39 d | 66.06 ± 3.53 a | 56.95 ± 1.73 c | 13.85 ± 0.42 c |
| F1 LC50 | 26.80 ± 8.25 d | 59.85 ± 6.62 b | 58.73 ± 2.36 c | 7.35 ± 1.16 d |
| Generation | Treatment | Egg–Larva Duration (d) | Pupa–Adult Duration (d) | Adult Longevity (d) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| F0 | CK | 13.67 ± 0.33 a | 4.00 ± 0.00 a | 10.25 ± 0.40 |
| LC30 | 12.33 ± 0.33 a | 4.33 ± 0.33 a | 11.12 ± 0.73 | |
| LC50 | 14.00 ± 0.00 a | 5.67 ± 0.33 b | 10.60 ± 0.40 | |
| F1 | CK | 14.33 ± 0.67 b | 3.67 ± 0.33 a | 11.01 ± 0.65 |
| LC30 | 14.33 ± 0.33 b | 4.00 ± 0.00 a | 11.52 ± 0.63 | |
| LC50 | 11.67 ± 0.67 a | 5.67 ± 0.33 b | 13.65 ± 0.95 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, J.; Zuo, T.; Fei, S.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Q.; Song, L.; Zhang, K. Non-Target Effects of Beta-Cypermethrin on Baryscapus dioryctriae and Ecological Risk Assessment. Insects 2025, 16, 948. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16090948
Li J, Zuo T, Fei S, Chen Y, Zhang X, Chen Q, Song L, Zhang K. Non-Target Effects of Beta-Cypermethrin on Baryscapus dioryctriae and Ecological Risk Assessment. Insects. 2025; 16(9):948. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16090948
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Jing, Tongtong Zuo, Sicheng Fei, Yuequ Chen, Xiangyu Zhang, Qi Chen, Liwen Song, and Kaipeng Zhang. 2025. "Non-Target Effects of Beta-Cypermethrin on Baryscapus dioryctriae and Ecological Risk Assessment" Insects 16, no. 9: 948. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16090948
APA StyleLi, J., Zuo, T., Fei, S., Chen, Y., Zhang, X., Chen, Q., Song, L., & Zhang, K. (2025). Non-Target Effects of Beta-Cypermethrin on Baryscapus dioryctriae and Ecological Risk Assessment. Insects, 16(9), 948. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16090948




