Effect of Hydrogen Peroxide on Oviposition Site Preference and Egg Hatching of the Aedes aegypti (Linnaeus) Mosquito
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Mosquitoes for Laboratory Assays
2.2. Hydrogen Peroxide Concentrations
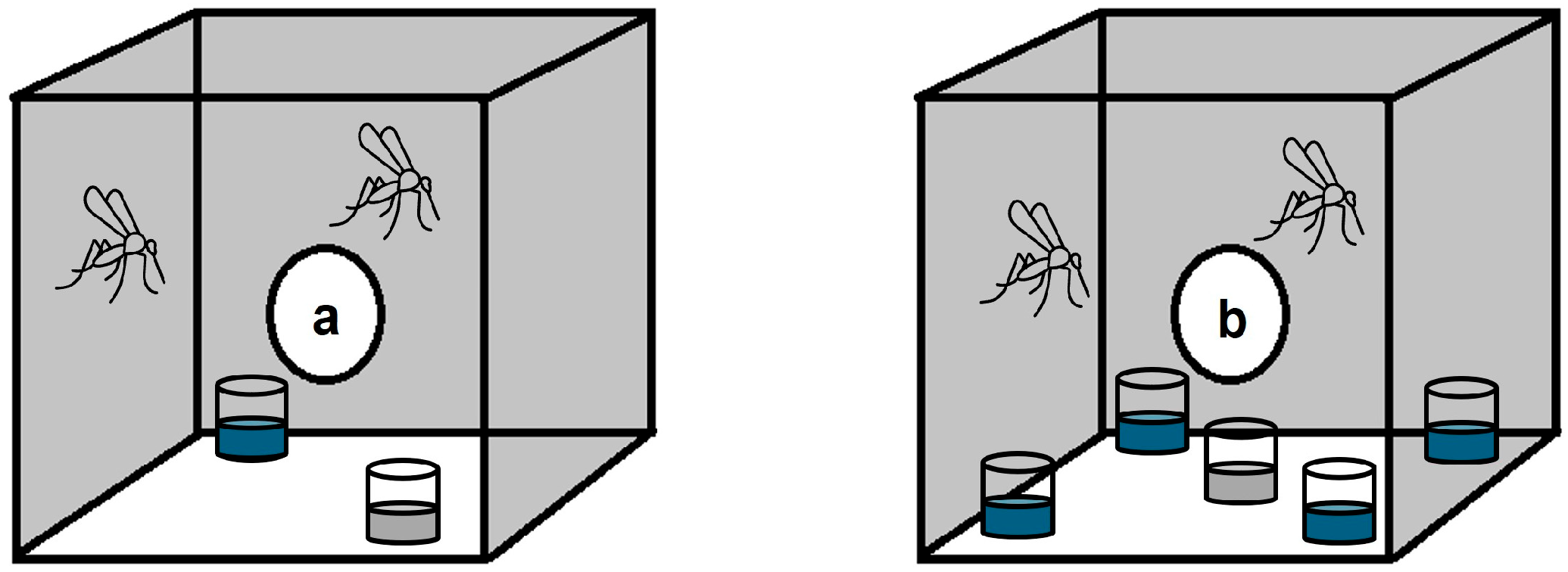
2.3. Oviposition Assay Experiments
2.4. Egg Hatching Experiments
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effect of Hydrogen Peroxide on Ae. aegypti Oviposition Site Preference
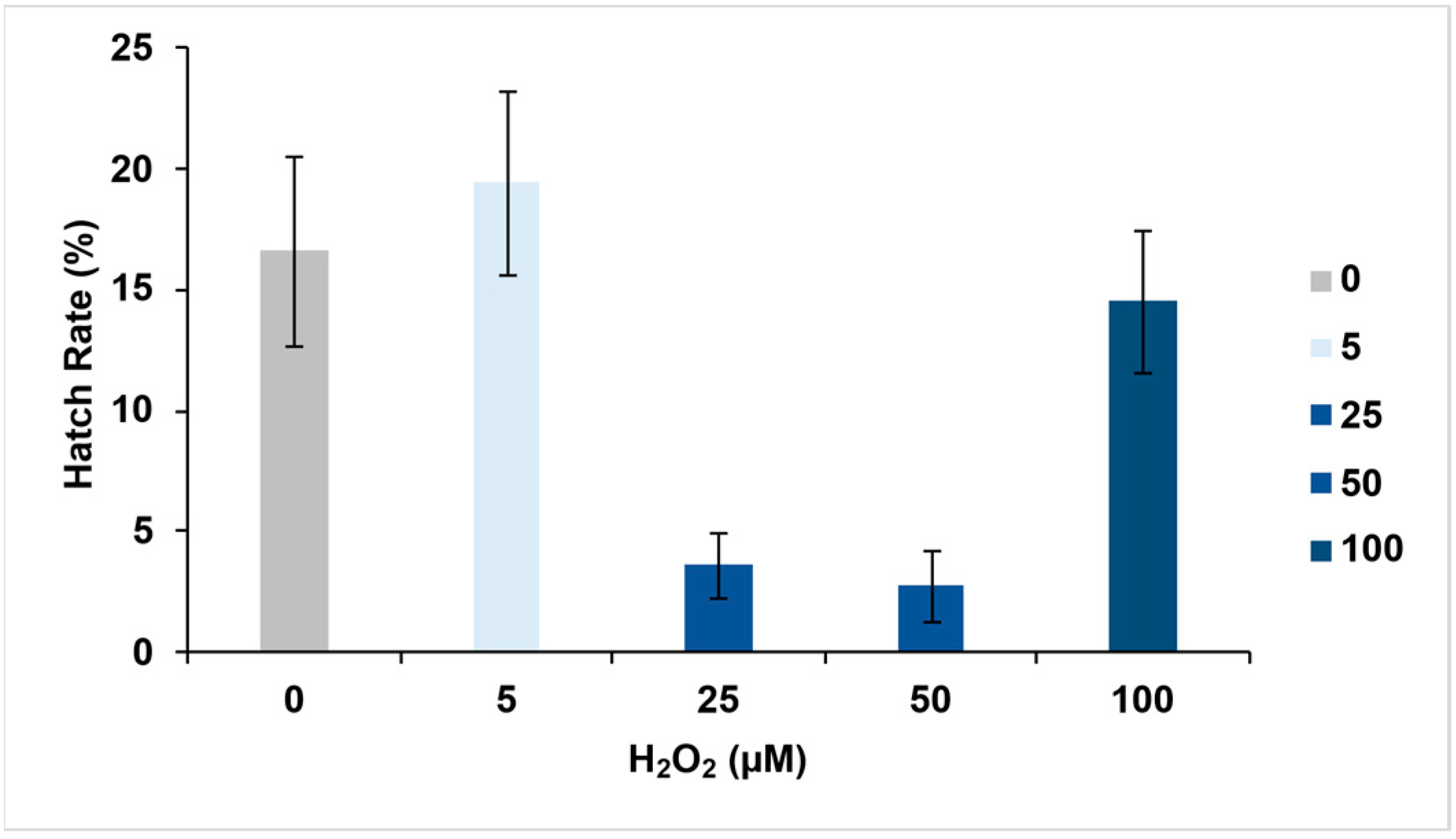
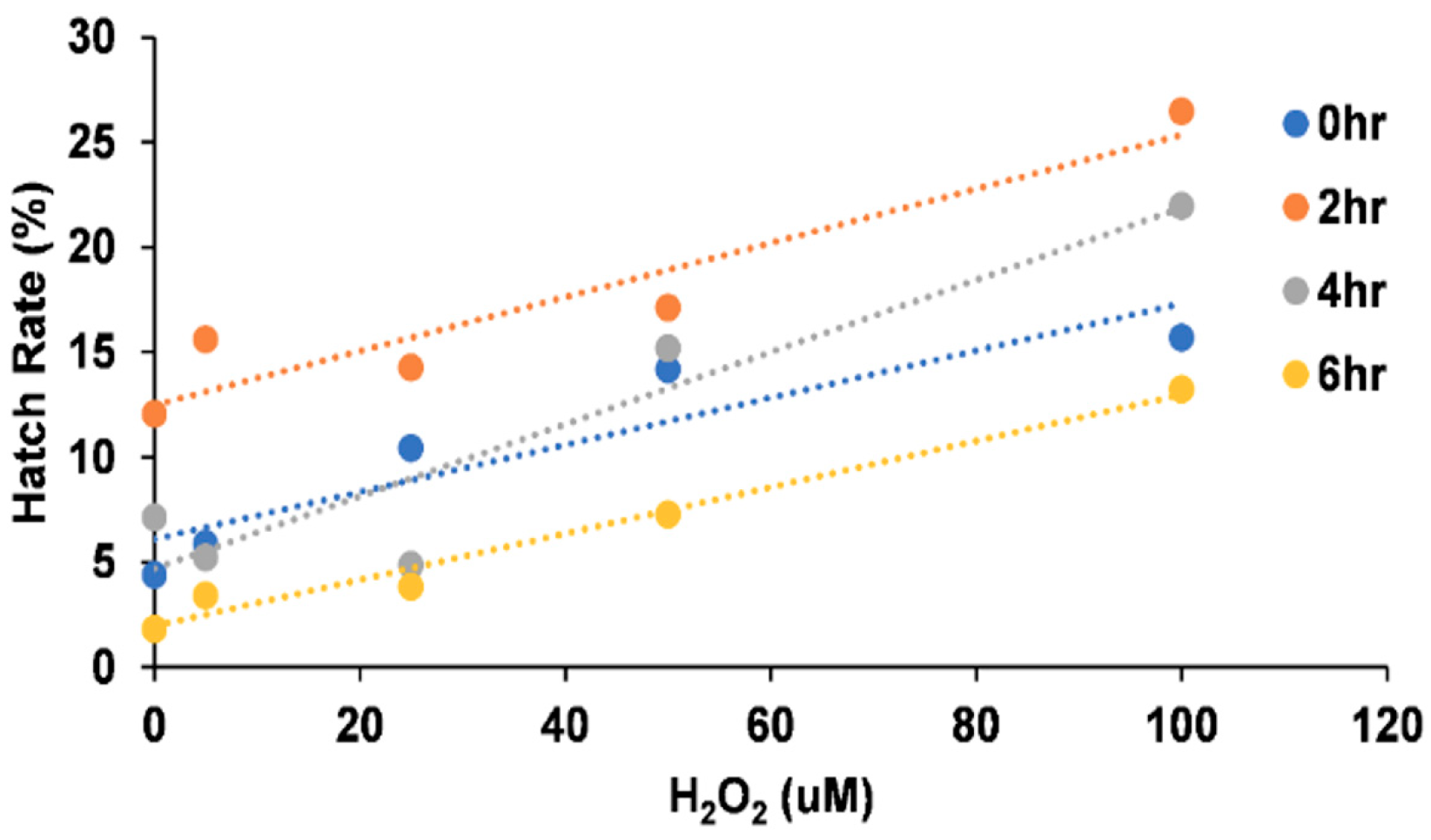
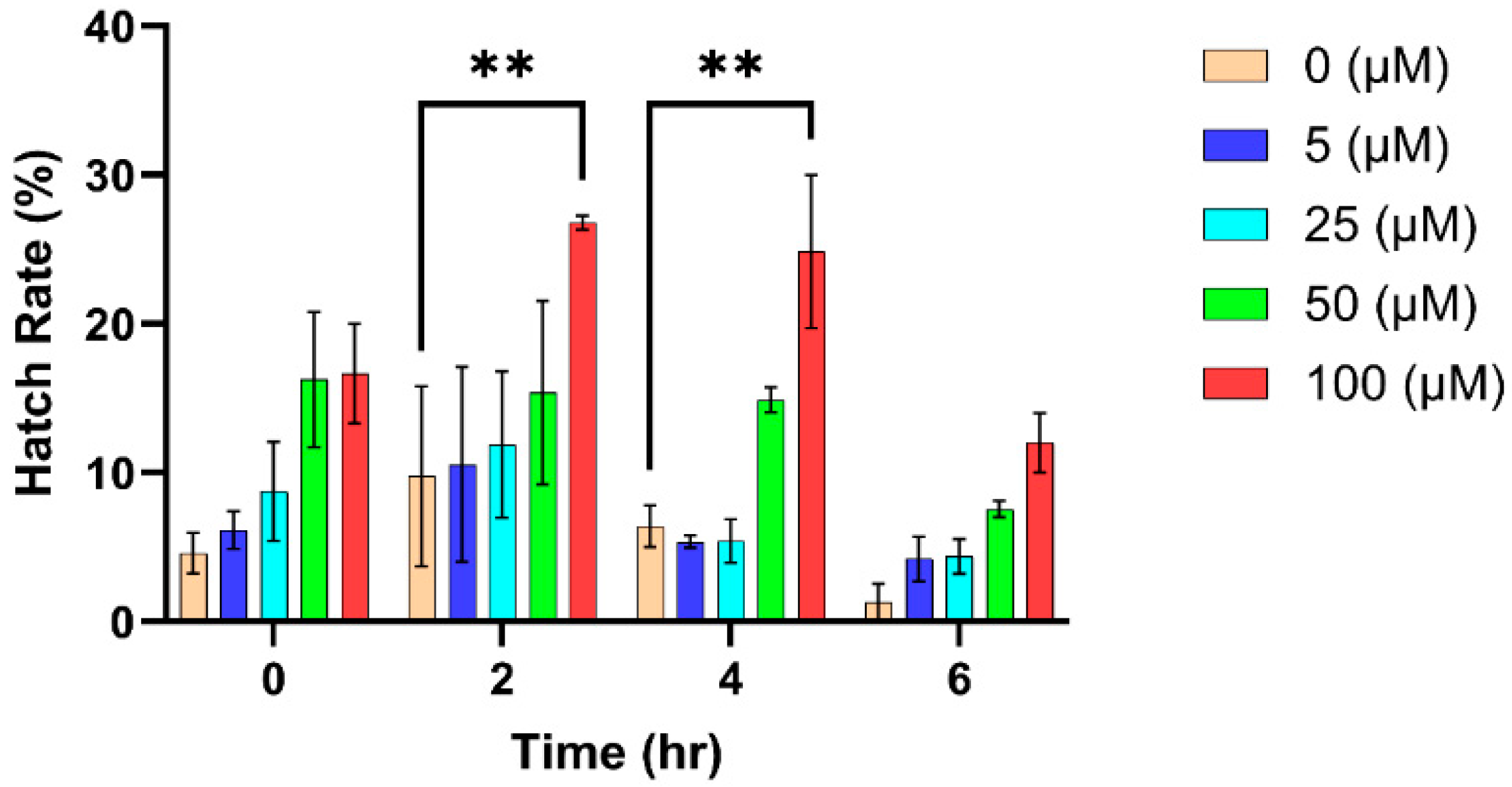
3.2. Effect of Hydrogen Peroxide on Egg Hatching
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- David, M.R.; Dantas, E.S.; Maciel-de-Freitas, R.; Codeço, C.T.; Prast, A.E.; Lourenço-de-Oliveira, R. Influence of larval habitat environmental characteristics on Culicidae immature abundance and body size of adult Aedes aegypti. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2021, 9, 626757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, R.; Gupta, P.T.; Srivastava, A. Urbanization, urban heat island effects and dengue outbreak in Delhi. In Climate Change and Human Health Scenario in South and Southeast Asia; Akhtar, R., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 99–111. [Google Scholar]
- Kolimenakis, A.; Heinz, S.; Wilson, M.L.; Winkler, V.; Yakob, L.; Michaelakis, A.; Papachristos, D.; Horstick, O. The role of urbanisation in the spread of Aedes mosquitoes and the diseases they transmit—A systematic review. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2021, 15, e0009631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, S.J.; Carlson, C.J.; Mordecai, E.A.; Johnson, L.R. Global expansion and redistribution of Aedes-borne virus transmission risk with climate change. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2019, 13, e0007213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burkot, T.; Handzel, T.; Schmaedick, M.; Tufa, J.; Roberts, J.; Graves, P. Productivity of natural and artificial containers for Aedes polynesiensis and Aedes aegypti in four american samoan villages. Med. Vet. Entomol. 2007, 21, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murrell, E.G.; Damal, K.; Lounibos, L.; Juliano, S.A. Distributions of competing container mosquitoes depend on detritus types, nutrient ratios, and food availability. Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 2011, 104, 688–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Sánchez, D.C.; Pinilla, G.A.; Quintero, J. Ecological characterization of Aedes aegypti larval habitats (Diptera: Culicidae) in artificial water containers in Girardot, Colombia. J. Vect. Ecol. 2017, 42, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunday, M.O.; Jadoon, W.A.; Ayeni, T.T.; Iwamoto, Y.; Takeda, K.; Imaizumi, Y.; Arakaki, T.; Sakugawa, H. Heterogeneity and potential aquatic toxicity of hydrogen peroxide concentrations in selected rivers across Japan. Sci Total Environ. 2020, 733, 139349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ndungu, L.K.; Steele, J.H.; Hancock, T.L.; Bartleson, R.D.; Milbrandt, E.C.; Parsons, M.L.; Urakawa, H. Hydrogen peroxide measurements in subtropical aquatic systems and their implications for cyanobacterial blooms. Ecol. Eng. 2019, 138, 444–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hancock, T.L.; Dahedl, E.K.; Kratz, M.A.; Urakawa, H. Synechococcus dominance induced after hydrogen peroxide treatment of microcystis bloom in the caloosahatchee river, florida. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 345, 123508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urakawa, H.; Ndungu, L.K.; Hancock, T.L.; Steele, J.H.; Bartleson, R.D. Subtropical freshwater cyanobacterial blooms as hydrogen peroxide hot spots. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2021, 8, 911–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cory, R.M.; Davis, T.W.; Dick, G.J.; Johengen, T.; Denef, V.J.; Berry, M.A.; Page, S.E.; Watson, S.B.; Yuhas, K.; Kling, G.W. Seasonal dynamics in dissolved organic matter, hydrogen peroxide, and cyanobacterial blooms in lake erie. Front. Mar. Sci. 2016, 3, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, W.J.; Zika, R.G. Photochemical formation of hydrogen peroxide in surface and ground waters exposed to sunlight. Science 1983, 220, 711–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García, P.E.; Queimaliños, C.; Diéguez, M.C. Natural levels and photo-production rates of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) in andean patagonian aquatic systems: Influence of the dissolved organic matter pool. Chemosphere 2019, 217, 550–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richard, L.E.; Peake, B.M.; Rusak, S.A.; Cooper, W.J.; Burritt, D.J. Production and decomposition dynamics of hydrogen peroxide in freshwater. Environ. Chem. 2007, 4, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szymczak, R.; Waite, T.D. Generation and decay of hydrogen peroxide in estuarine waters. Mar. Freshw. Res. 1988, 39, 289–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Häkkinen, P.J.; Anesio, A.M.; Granéli, W. Hydrogen peroxide distribution, production, and decay in boreal lakes. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2004, 61, 1520–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakugawa, H.; Kaplan, I.R.; Tsai, W.; Cohen, Y. Atmospheric hydrogen peroxide. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1990, 24, 1452–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujiwara, K.; Ushiroda, T.; Takeda, K.; Kumamoto, Y.i.; Tsubota, H. Diurnal and seasonal distribution of hydrogen peroxide in seawater of the Seto Inland Sea. Geochem. J. 1993, 27, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinel’nikov, V. Hydrogen peroxide level in river water, and methods for detecting it. Gibrobiol. Zh. 1971, 7, 115–119. [Google Scholar]
- Barrington, D.J.; Ghadouani, A. Application of hydrogen peroxide for the removal of toxic cyanobacteria and other phytoplankton from wastewater. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 8916–8921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drábková, M.; Admiraal, W.; Maršálek, B. Combined exposure to hydrogen peroxide and light selective effects on cyanobacteria, green algae, and diatoms. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthijs, H.C.; Visser, P.M.; Reeze, B.; Meeuse, J.; Slot, P.C.; Wijn, G.; Talens, R.; Huisman, J. Selective suppression of harmful cyanobacteria in an entire lake with hydrogen peroxide. Water Res. 2012, 46, 1460–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wohl, M.P.; McMeniman, C.J. Batch rearing Aedes aegypti. Cold Spring Harb. Protoc. 2023, 2023, pdb.prot108017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudolf, V.H.W.; Rödel, M.O. Oviposition site selection in a complex and variable environment: The role of habitat quality and conspecific cues. Oecologia 2005, 142, 316–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Himeidan, Y.E.; Temu, E.A.; El Rayah, E.A.; Munga, S.; Kweka, E.J. Chemical cues for malaria vectors oviposition site selection: Challenges and opportunities. J. Insects 2013, 2013, 685182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, J.F. Mosquito oviposition behavior and vector control. Insects 2016, 7, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koenraadt, C.J.M.; Paaijmans, K.P.; Githeko, A.K.; Knols, B.G.J.; Takken, W. Egg hatching, larval movement and larval survival of the malaria vector Anopheles gambiae in desiccating habitats. Malar. J. 2003, 2, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dieng, H.; Boots, M.; Tamori, N.; Higashihara, J.; Okada, T.; Kato, K.; Eshita, Y. Some technical and ecological determinants of hatchability in Aedes albopictus, a potential candidate for transposon-mediated transgenesis. J. Am. Mosq. Control Assoc. 2006, 22, 382–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warkentin, K.M. Environmentally cued hatching across taxa: Embryos respond to risk and opportunity. Integr. Comp. Biol. 2011, 51, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, H.; Kim, H.C.; Kim, S. Long-term seasonal and temporal changes of hydrogen peroxide from cyanobacterial blooms in fresh waters. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 298, 113515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bentley, M.D.; Day, J.F. Chemical ecology and behavioral aspects of mosquito oviposition. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 1989, 34, 401–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulsson, O.; Widerlund, A. Diel variations in dissolved oxygen concentration and algal growth in the Laver pit lake, northern Sweden. Appl. Geochem. 2023, 155, 105725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merritt, R.W.; Dadd, R.; Walker, E.D. Feeding behavior, natural food, and nutritional relationships of larval mosquitoes. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 1992, 37, 349–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Judson, C.L. The physiology of hatching of aedine mosquito eggs: Hatching stimulus. Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 1960, 53, 688–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, T.M.; Flis, B.J.; Remold, S.K. pH tolerances and regulatory abilities of freshwater and euryhaline Aedine mosquito larvae. J. Exp. Biol. 2004, 207, 2297–2304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, M.F.; Dos Santos, A.S.; Marotta, H.R.; Mansur, J.F.; Ramos, I.B.; Machado, E.A.; Souza, G.H.M.F.; Eberlin, M.N.; Kaiser, C.R.; Kramer, K.J. A chitin-like component in Aedes aegypti eggshells, eggs and ovaries. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2007, 37, 1249–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezende, G.L.; Martins, A.J.; Gentile, C.; Farnesi, L.C.; Pelajo-Machado, M.; Peixoto, A.A.; Valle, D. Embryonic desiccation resistance in Aedes aegypti: Presumptive role of the chitinized serosal cuticle. BMC Dev. Biol. 2008, 8, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, C.Q.; Du, Y.M.; Xiao, L. Effect of hydrogen peroxide treatment on the molecular weight and structure of chitosan. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2002, 76, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, F.; Liu, Y.; Hu, K.; Zhao, B. Study of the depolymerization behavior of chitosan by hydrogen peroxide. Carbohydr. Polym. 2004, 57, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheeseman, J.M. Hydrogen peroxide concentrations in leaves under natural conditions. J. Exp. Bot. 2006, 57, 2435–2444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, A.J.; Radomski, A.A.; Straus, D.L.; Carter, R. The effect of hydrogen peroxide on the hatch rate and Saprolegnia spp. infestation of channel catfish eggs. N. Am. J. Aquacult. 2009, 71, 276–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hacker, I.K.R.; Eichner, G.; Martin, J.; Liapi, E.; Rühl, J.; Rehling, T.; Schetelig, M.F. Evaluation of hydrogen peroxide fumigation and heat treatment for standard emergency arthropod inactivation in bsl-3 insectaries. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 602937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Bioassay | Parameter | Water | 5 µM | 25 µM | 50 µM | 100 µM | Overall | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Multi choice oviposition | No. eggs | 80.25 ± 14.26 | 130.75 ± 56.06 | 94.75 ± 30.62 | 75.25 ± 35.63 | 133.25 ± 46.83 | 108.5 ± 20.42 | 0.775 |
| OAI | na | −0.24 ± 0.25 | −0.09 ± 0.29 | 0.03 ± 0.32 | −0.25 ± 0.24 | −0.135 ± 0.06 | 0.138 | |
| Dual choice oviposition | No. eggs | 111.31 ± 14.11 | 76 ± 39.11 | 95.25 ± 46.74 | 63.75 ± 3.57 | 66 ± 38.53 | 75.25 ± 16.46 | 0.811 |
| OAI | na | 0.24 ± 0.29 | 0.17 ± 0.30 | 0.19 ± 0.06 | 0.22 ± 0.26 | 0.195 ± 0.01 | <0.001 * |
| H2O2 (μM) | Hatched | Total | Hatch Rate (%) | CI Lower | CI Upper |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 57 | 344 | 16.56 | 12.64 | 20.50 |
| 5 | 82 | 423 | 19.39 | 15.62 | 23.15 |
| 25 | 25 | 699 | 3.58 | 2.20 | 4.95 |
| 50 | 13 | 479 | 2.71 | 1.26 | 4.17 |
| 100 | 80 | 552 | 14.49 | 11.57 | 17.43 |
| Overall Mean | 257 | 2497 | 11.35 | 8.65 | 14.04 |
| Hatch Rate | Sum of Squares | df | Mean Square | F | Sig. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Between Groups | 558.8 | 4 | 139.7 | 1.171 | 0.363 |
| Within Groups | 1789 | 15 | 119.267 | ||
| Total | 2347.8 | 19 |
| Exposure Period | H2O2 (μM) | Hatched Eggs | Total Eggs | Hatch Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 h | 0 | 19 | 307 | 6.19 |
| 5 | 14 | 270 | 5.19 | |
| 25 | 23 | 278 | 8.27 | |
| 50 | 139 | 302 | 46.03 | |
| 100 | 156 | 351 | 44.44 | |
| 2 h | 0 | 145 | 307 | 47.23 |
| 5 | 134 | 258 | 51.94 | |
| 25 | 142 | 302 | 47.02 | |
| 50 | 151 | 313 | 48.24 | |
| 100 | 193 | 339 | 56.93 | |
| 4 h | 0 | 181 | 348 | 52.01 |
| 5 | 136 | 295 | 46.10 | |
| 25 | 123 | 308 | 39.94 | |
| 50 | 150 | 318 | 47.17 | |
| 100 | 178 | 336 | 52.98 | |
| 6 h | 0 | 28 | 320 | 8.8 |
| 5 | 15 | 242 | 6.2 | |
| 25 | 51 | 345 | 14.8 | |
| 50 | 56 | 277 | 20.2 | |
| 100 | 78 | 274 | 28.5 |
| Source | df | Sum of Squares | Mean Square | F-Value | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H2O2 (µM) | 4 | 1196 | 298.9 | 13.02 | <0.0001 * |
| Time (h) | 3 | 411.5 | 137.2 | 5.974 | 0.0044 * |
| H2O2 (µM) × Time (h) | 12 | 166.4 | 13.86 | 0.603 | 0.8143 |
| Multiple Comparison | Mean Difference | 95% CI | Sig. | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 h | ||||
| 0 (μM) vs. 5 (μM) | −0.7900 | −13.49 to 11.91 | ns | 0.9994 |
| 0 (μM) vs. 25 (μM) | −2.120 | −14.82 to 10.58 | ns | 0.9759 |
| 0 (μM) vs. 50 (μM) | −5.623 | −18.33 to 7.081 | ns | 0.5979 |
| 0 (μM) vs. 100 (μM) | −17.03 | −29.73 to −4.322 | ** | 0.0070 |
| 4 h | ||||
| 0 (μM) vs. 5 (μM) | 1.046 | −11.66 to 13.75 | ns | 0.9983 |
| 0 (μM) vs. 25 (μM) | 0.9895 | −11.71 to 13.69 | ns | 0.9986 |
| 0 (μM) vs. 50 (μM) | −8.485 | −21.19 to 4.218 | ns | 0.2592 |
| 0 (μM) vs. 100 (μM) | −18.45 | −31.16 to −5.749 | ** | 0.0036 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ndungu, L.; Roberts, D.; Long, L.; Goguet, E.; Stubner, A.; Beeman, S.; Lewandowski, S.; Okech, B. Effect of Hydrogen Peroxide on Oviposition Site Preference and Egg Hatching of the Aedes aegypti (Linnaeus) Mosquito. Insects 2025, 16, 928. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16090928
Ndungu L, Roberts D, Long L, Goguet E, Stubner A, Beeman S, Lewandowski S, Okech B. Effect of Hydrogen Peroxide on Oviposition Site Preference and Egg Hatching of the Aedes aegypti (Linnaeus) Mosquito. Insects. 2025; 16(9):928. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16090928
Chicago/Turabian StyleNdungu, Luka, Donald Roberts, Lewis Long, Emilie Goguet, Alex Stubner, Sean Beeman, Stephen Lewandowski, and Bernard Okech. 2025. "Effect of Hydrogen Peroxide on Oviposition Site Preference and Egg Hatching of the Aedes aegypti (Linnaeus) Mosquito" Insects 16, no. 9: 928. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16090928
APA StyleNdungu, L., Roberts, D., Long, L., Goguet, E., Stubner, A., Beeman, S., Lewandowski, S., & Okech, B. (2025). Effect of Hydrogen Peroxide on Oviposition Site Preference and Egg Hatching of the Aedes aegypti (Linnaeus) Mosquito. Insects, 16(9), 928. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16090928







