Evaluation of Bacterial Strains as a Sustainable Approach for Control of Myzus cerasi (F.) (Hemiptera: Aphididae) Under Laboratory and Field Conditions
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strains Used in This Study
2.2. Laboratory Experiment
2.3. Field Experiment
2.4. Statistical Analysis
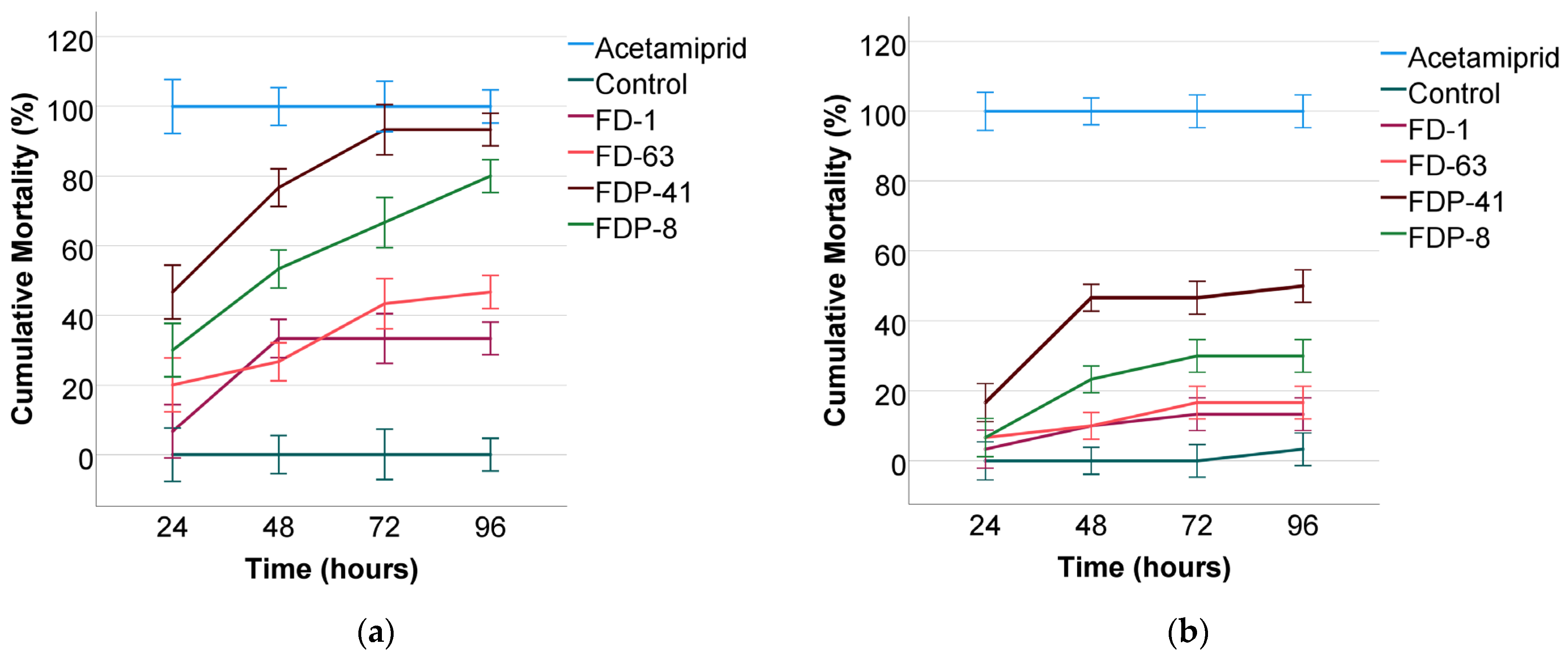
3. Results
3.1. Effectiveness of FDP-41
3.2. Effectiveness of FDP-8
3.3. Effectiveness of FD-63
3.4. Effectiveness of FD-1
4. Discussion
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Holman, J. Host Plant Catalog of Aphids, Palearctic Region; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; p. 1216. [Google Scholar]
- McLaren, G.F.; Fraser, J.A. Autumn and Spring Control of Black Cherry Aphid on Sweet Cherry in Central Otago. N. Z. Plant Prot. 2002, 55, 347–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kök, Ş.; Kasap, İ. Seasonal population fluctuation and life history in different temperatures of Myzus cerasi (Hemiptera: Aphididae) on cherry trees: A field and laboratory study. J. Econ. Entomol. 2024, 117, 865–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bokx, J.A.; Piron, P.G.M. Relative efficiency of a number of aphid species in the transmission of potato virus YN in the Netherlands. Neth. J. Plant Pathol. 1990, 96, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackman, R.L.; Eastop, V.F. Aphids on the World’s Crops: An Identification and Information Guide, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Basky, Z.; Almási, A. Differences in aphid transmissibility and translocation between PVYN and PVYO isolates. J. Pest Sci. 2005, 78, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanayakkara, U.N.; Nie, X.; Giguère, M.; Zhang, J.; Boquel, S.; Pelletier, Y. Aphid feeding behavior in relation to potato virus Y (PVY) acquisition. J. Econ. Entomol. 2012, 105, 1903–1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bielicki, P.; Badowska-Czubik, T.; Rozpara, E. Pests occurring in plum organic nursery. J. Res. Appl. Agric. Eng. 2011, 56, 23–26. [Google Scholar]
- Wojciechowicz-Żytko, E.; Dobińska-Graczyk, M. Urban green space as a reservoir of predatory syrphids (Diptera, Syrphidae) for aphid control in cities. Agronomy 2025, 15, 953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alford, D.V. Pests of Ornamental Trees, Shrubs and Flowers. A Colour Handbook, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: London, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Alford, D.V. Pests of Fruit Crops. A Colour Handbook, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: London, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Kindlmann, P.; Jarošík, V.; Dixon, A.F.G. Population dynamics. In Aphids as Crop Pests; van Emden, H.F., Harrington, R., Eds.; CABI International: Wallingford, UK, 2007; pp. 311–329. [Google Scholar]
- Torres-Quintero, M.C.; Peña-Chora, G.; Hernández-Velázquez, V.M.; Arenas-Sosa, I. Signs of Bacillus thuringiensis (Bacillales: Bacillaceae) infection in Myzus persicae (Hemiptera: Aphididae): Koch’s postulates. Fla. Entomol. 2015, 98, 799–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Kamle, M.; Borah, R.; Mahato, D.K.; Sharma, B. Bacillus thuringiensis as microbial biopesticide: Uses and application for sustainable agriculture. Egypt. J. Biol. Pest Control. 2021, 31, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomis-Cebolla, J.; Berry, C. Bacillus thuringiensis as a biofertilizer in crops and their implications in the control of phytopathogens and insect pests. Pest Manag. Sci. 2023, 79, 2992–3001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadaşoğlu, F.; Karagöz, K.; Kotan, R.; Sarıhan, F.; Yıldırım, E.; Saraç, S.; Harmantepe, F. Biolarvicidal effects of nine Bacillus strains against larvae of Culex pipiens Linnaeus, 1758 (Diptera: Culicidae) and nontarget organisms. Egypt. J. Biol. Pest Control. 2013, 23, 35–42. [Google Scholar]
- Dadaşoğlu, F.; Tozlu, G.; Kotan, R.; Göktürk, T.; Karagöz, K. Biological control of pine sawfly (Diprion pini L.) and molecular characterization of effective strains. Rom. Biotechnol. Lett. 2016, 21, 11271–11280. [Google Scholar]
- Mampallil, L.J.; Faizal, M.H.; Anith, K.N. Bacterial bioagents for insect pest management. J. Entomol. Zool. Stud. 2017, 5, 2237–2244. [Google Scholar]
- Höfte, H.; Whiteley, H.R. Insecticidal crystal proteins of Bacillus thuringiensis. Microbiol. Rev. 1989, 53, 242–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knowles, B.H.; Dow, J.A.T. The crystal delta-endotoxins of Bacillus thuringiensis—Models for their mechanism of action on the insect gut. BioEssays 1993, 15, 469–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raymond, B.; Johnston, P.R.; Nielsen-LeRoux, C.; Lereclus, D.; Crickmore, N. Bacillus thuringiensis: An impotent pathogen? Trends Microbiol. 2010, 18, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roh, J.Y.; Choi, J.Y.; Li, M.S.; Jin, B.R.; Je, Y.H. Bacillus thuringiensis as a specific, safe, and effective tool for insect pest control. J. Mol. Biol. 2007, 17, 547–559. [Google Scholar]
- Palma, L.; Muñoz, D.; Berry, C.; Murillo, J.; Caballero, P. Bacillus thuringiensis toxins: An overview of their biocidal activity. Toxins 2014, 6, 3296–3325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toledo-Hernández, E.; Torres-Quíntero, M.C.; Mancilla-Dorantes, I.; Sotelo-Leyva, C.; Delgado-Núñez, E.J.; Hernández-Velázquez, V.M.; Dunstand-Guzmán, E.; Salinas-Sánchez, D.O.; Peña-Chora, G. Entomopathogenic bacteria species and toxins targeting aphids (Hemiptera: Aphididae): A review. Plants 2025, 14, 943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 25. Konecka, E.; Kaznowski, A.; Grzesiek, W.; Nowicki, P.; Czarniewska, E.; Baranek, J. Synergistic interaction between carvacrol and Bacillus thuringiensis crystalline proteins against Cydia pomonella and Spodoptera exigua. BioControl 2020, 65, 447–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 26. Baranek, J.; Pluskota, M.; Rusin, M.; Konecka, E.; Kaznowski, A.; Wiland-Szymańska, J. Insecticidal activity of Bacillus thuringiensis strains isolated from tropical greenhouses towards Cydia pomonella and Spodoptera exigua larvae. BioControl 2023, 68, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alper, M.; Güneş, H.; Civelek, H.; Dursun, O.; Eskin, A. Toxic effects of some native Bacillus thuringiensis Berliner (Bacillales: Bacillaceae) isolates against Tetranychus urticae Koch (Acarina: Tetranychidae), Ceroplastes rusci L. (Homoptera: Coccidae) and Ceratitis capitata (Wiedemann) (Diptera: Tephritidae). Bull. Entomol. Soc. Turk. 2014, 3, 75–88. [Google Scholar]
- Güneş, H.; Alper, M.; Çöl, B.; Tunca, H. Bioactivities of cry gene positive Bacillus thuringiensis (Berliner) (Bacillales: Bacillaceae) strains on Ephestia kuehniella Zeller, 1879 and Plodia interpunctella (Hübner, 1813) (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae). Turk. J. Entomol. 2016, 40, 365–375. [Google Scholar]
- Şahin, B.; Gomis-Cebolla, J.; Güneş, H.; Ferré, J. Characterization of Bacillus thuringiensis isolates by their insecticidal activity and their production of Cry and Vip3 proteins. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0206813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crespo, A.L.; Spencer, T.A.; Nekl, E.; Pusztai-Carey, M.; Moar, W.J.; Siegfried, B.D. Comparison and validation of methods to quantify Cry1Ab toxin from Bacillus thuringiensis for standardization of insect bioassays. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 74, 130–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palma, L.; Muñoz, D.; Berry, C.; Murillo, J.; De Escudero, I.R.; Caballero, P. Molecular and insecticidal characterization of a novel Cry-related protein from Bacillus thuringiensis toxic against Myzus persicae. Toxins 2014, 6, 3144–3156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sattar, S.; Maiti, M.K. Molecular characterization of a novel vegetative insecticidal protein from Bacillus thuringiensis effective against sap-sucking insect pest. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2011, 21, 937–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bel, Y.; Ferré, J.; Hernández-Martínez, P. Bacillus thuringiensis toxins: Functional characterization and mechanism of action. Toxins 2020, 12, 785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, M.; Kumar, H.; Kaur, S. Vegetative insecticidal protein (Vip): A potential contender from Bacillus thuringiensis for efficient management of various detrimental agricultural pests. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 659736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnepf, E.; Crickmore, N.; Van Rie, J.; Lereclus, D.; Baum, J.; Feitelson, J.; Zeigler, D.R.; Dean, D. Bacillus thuringiensis and its pesticidal crystal proteins. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 1998, 62, 775–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rooney, A.P.; Price, N.P.; Ehrhardt, C.; Swezey, J.L.; Bannan, J.D. Phylogeny and molecular taxonomy of the Bacillus subtilis species complex and description of Bacillus subtilis subsp. inaquosorum subsp. nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2009, 59, 2429–2436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vovo, A.; Martínez de Castro, D.; Sánchez, J.; Cantón, P.E.; Mendoza, G.; Gómez, I.; Onofre, J.; Ocelotl, J.; Soberón, M. Mechanism of action of Bacillus thuringiensis insecticidal toxins and their use in the control of insect pests. In The Comprehensive Sourcebook of Bacterial Protein Toxins; Alouf, J., Ladant, D., Popoff, M., Eds.; Academic Press: London, UK, 2015; pp. 858–873. [Google Scholar]
- Pomari, E.; Orza, P.; Bernardi, M.; Fracchetti, F.; Campedelli, I.; De Marta, P.; Recchia, A.; Paradies, P.; Buonfrate, D. A pilot study for the characterization of Bacillus spp. and analysis of possible B. thuringiensis-Strongyloides stercoralis correlation. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafsa, M.; Benfekih, L.A. New insights on entomopathogenic bacteria isolated from soil of citrus crops to combat the polyphagous aphid pest Hyalopterus pruni (Geoffroy 1762) (Hemiptera: Aphididae). Egypt. J. Biol. Pest Control. 2024, 34, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tozlu, E.; Tozlu, G.; Kotan, R.; Çalmaşur, Ö.; Dadaşoğlu, F. Investigation of some entomopathogens as biocontrol agents of Tinocallis (Sappocallis) saltans (Nevsky, 1929) (Hemiptera: Aphididae). Turk. J. Agric. For. 2021, 45, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tozlu, E.; Dadaşoğlu, F.; Kotan, R.; Tozlu, G. Insecticidal effect of some bacteria on Bruchus dentipes Baudi (Coleoptera: Bruchidae). Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2011, 20, 918–923. [Google Scholar]
- Göktürk, T.; Tozlu, E.; Kotan, R. Prospects of entomopathogenic bacteria and fungi for biological control of Ricania simulans (Walker, 1851) (Hemiptera: Ricaniidae). Pakistan J. Zool. 2018, 50, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tozlu, E.; Tozlu, G.; Kotan, R.; Tekiner, N.; Dadaşoğlu, F.; Göktürk, T. Eco-friendly control method against invasive pest box tree moth (Cydalima perspectalis (Walker) (Lepidoptera: Crambidae)). Egypt. J. Biol. Pest Control. 2022, 32, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narmanlıoglu, H.K.; Dadaşoğlu, F. Investigation of the possibilities use of some bacterial biopesticides in the biological control against Aphis pomi (De Geer, 1773). Fresenius Enviromental Bull. 2021, 30, 7433–7435. [Google Scholar]
- Bravo, A.; Soberón, M. How to cope with insect resistance to Bt toxins? Trends Biotechnol. 2008, 26, 573–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alahyane, H.; Ouknin, M.; Alahyane, A.; Aboussaid, H.; Oufdou, K.; El Messoussi, S.; Majidi, L. Aphicidal activities of Moroccan Bacillus thuringiensis strains against cotton aphid (Aphis gossypii). Biointerface Res. Appl. Chem. 2021, 12, 3348–3356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajuna, H.B.; Kim, I.; Han, Y.S.; Maung, C.E.H.; Kim, K.Y. Aphicidal activity of Bacillus thuringiensis strain AH-2 against cotton aphid (Aphis gossypii). Entomol. Res. 2021, 51, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Guo, Y. Influences of Bacillus thuringiensis Berliner cotton planting on population dynamics of the cotton aphid, Aphis gossypii Glover, in northern China. Environ. Entomol. 2003, 32, 312–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, L.G.; Menn, J.J. Biopesticides: A review of their action, applications and efficacy. Pest Manag. Sci. 2000, 56, 651–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeschke, P.; Nauen, R.; Schindler, M.; Elbert, A. Overview of the status and global strategy for neonicotinoids. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 2897–2908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palma, L.; de Escudero, I.R.; Maneru-Oria, F.; Berry, C.; Caballero, P. UV protection and insecticidal activity of micro-encapsulated Vip3Ag4 protein in Bacillus megaterium. Toxicon 2024, 247, 107807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrington, R.; Clark, S. Trends in the timings of the start and end of annual flight periods. In Aphid Biodiversity under Environmental Change: Patterns and Processes; Kindlmann, P., Dixon, A.F.G., Michaud, J.P., Eds.; Springer Science & Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 2010; pp. 41–54. [Google Scholar]
- Fernández-Grandon, G.M.; Harte, S.J.; Ewany, J.; Bray, D.; Stevenson, P.C. Additive effect of botanical insecticide and entomopathogenic fungi on pest mortality and the behavioral response of its natural enemy. Plants 2020, 9, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bravo, A.; Gill, S.S.; Soberón, M. Mode of action of Bacillus thuringiensis Cry and Cyt toxins and their potential for insect control. Toxicon 2007, 49, 423–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortiz, A.; Sansinenea, E. Genetically modified plants based on Bacillus genes and commercial Bacillus-based biopesticides for sustainable agriculture. Horticulturae 2023, 9, 963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Bacterial Strains No | Isolated from | MIS Identification Results | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| FDP-41 | Apion spp. | Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. kurstaki | [41] |
| FDP-8 | Hypera postica | Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. kenyae | [41] |
| FD-1 | Malacosoma neustria | Brevibacillus brevis | [42] |
| FD-63 | Yponomeuta evonymella | Bacillus cereus | [43] |
| Condition | Source of Variation | F | df | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Laboratory | Time | 49.207 | 3, 8 | <0.001 |
| Treatment | 600.937 | 5, 12 | <0.001 | |
| Time × Treatment | 8.738 | 15, 36 | <0.001 | |
| Field | Time | 152.594 | 3, 8 | <0.001 |
| Treatment | 21.419 | 5, 12 | <0.001 | |
| Time × Treatment | 203.804 | 15, 36 | <0.001 |
| Treatments | Laboratory | Field | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LT50 ± SE | MST ± SE | LT50 ± SE | MST ± SE | |
| FD-1 | 102.476 ± 0.438 | 130.5 ± 2.5 | 192.135 ± 0.576 | 210.4 ± 3.1 |
| FD-63 | 87.758 ± 0.397 | 115.3 ± 2.3 | 178.454 ± 0.523 | 195.6 ± 2.9 |
| FDP-8 | 46.969 ± 0.304 | 60.2 ± 1.8 | 138.384 ± 0.395 | 150.7 ± 2.4 |
| FDP-41 | 25.37 ± 0.267 | 32.8 ± 1.2 | 86.404 ± 0.326 | 95.1 ± 1.9 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bulak Korkmaz, Y. Evaluation of Bacterial Strains as a Sustainable Approach for Control of Myzus cerasi (F.) (Hemiptera: Aphididae) Under Laboratory and Field Conditions. Insects 2025, 16, 857. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16080857
Bulak Korkmaz Y. Evaluation of Bacterial Strains as a Sustainable Approach for Control of Myzus cerasi (F.) (Hemiptera: Aphididae) Under Laboratory and Field Conditions. Insects. 2025; 16(8):857. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16080857
Chicago/Turabian StyleBulak Korkmaz, Yeşim. 2025. "Evaluation of Bacterial Strains as a Sustainable Approach for Control of Myzus cerasi (F.) (Hemiptera: Aphididae) Under Laboratory and Field Conditions" Insects 16, no. 8: 857. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16080857
APA StyleBulak Korkmaz, Y. (2025). Evaluation of Bacterial Strains as a Sustainable Approach for Control of Myzus cerasi (F.) (Hemiptera: Aphididae) Under Laboratory and Field Conditions. Insects, 16(8), 857. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16080857






