Characteristics of the Insulin-like Peptide Genes and Their Roles in the Ovarian Development of Zeugodacus cucurbitae (Coquillett)
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Insects
2.2. RNA Isolation and cDNA Synthesis
2.3. Cloning and Molecular Sequence Analysis of Target Genes
2.4. Spatio-Temporal Expression Patterns Analysis
2.5. Gene Expression Analysis Induced by Starvation
2.6. RNA Interference (RNAi) and Functional Analysis
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
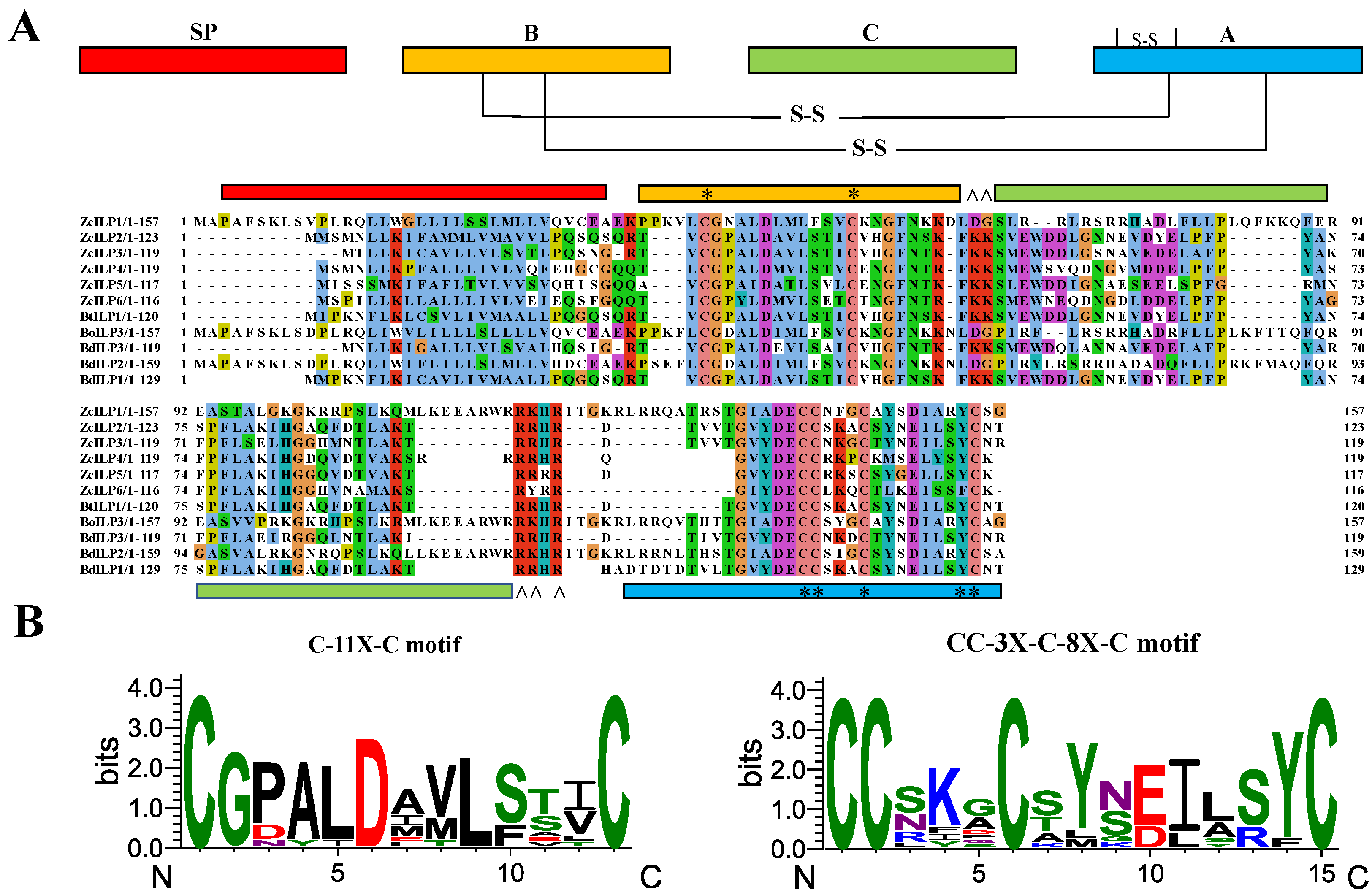
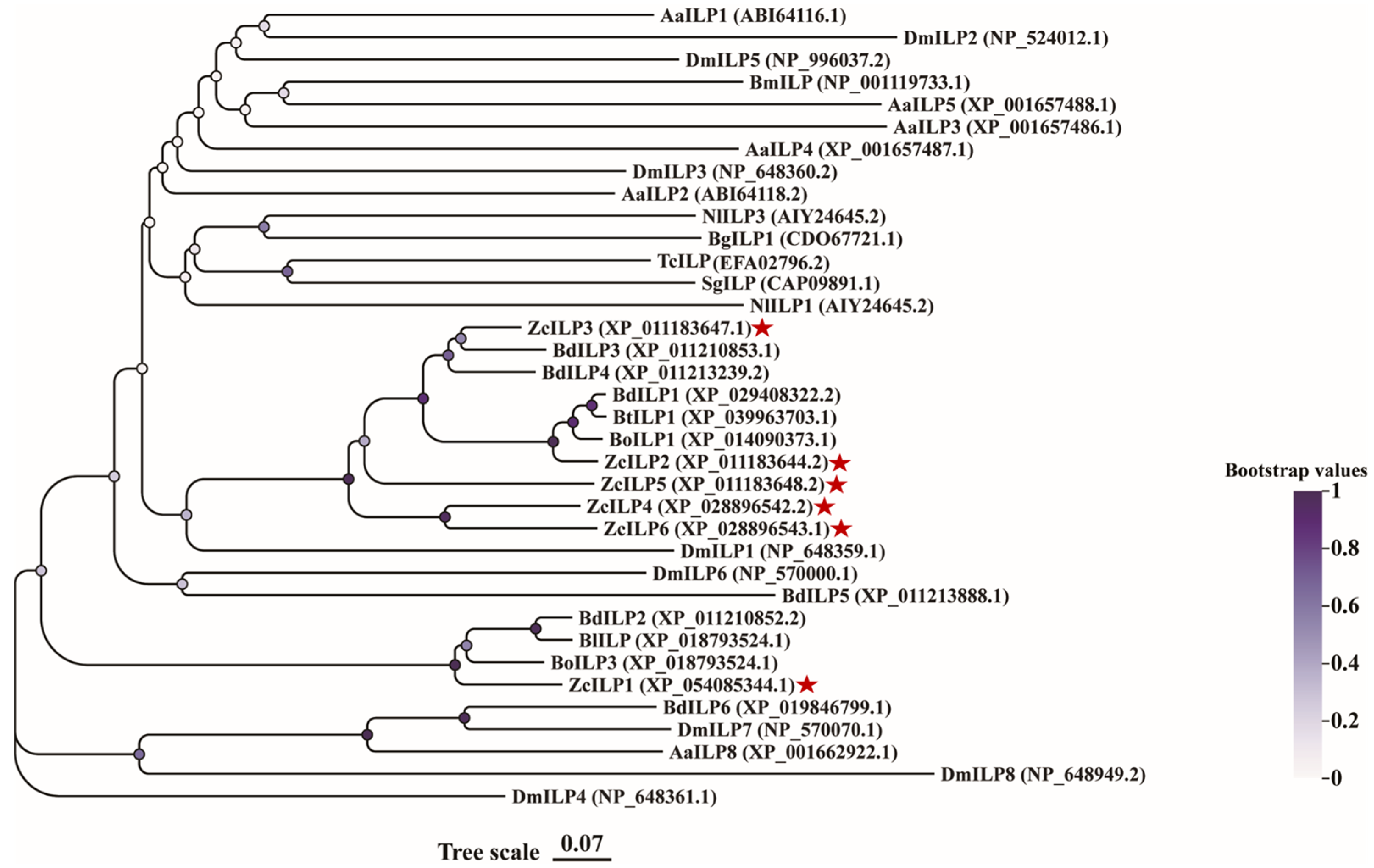
3.1. Sequence Analysis and Phylogenetic Comparison
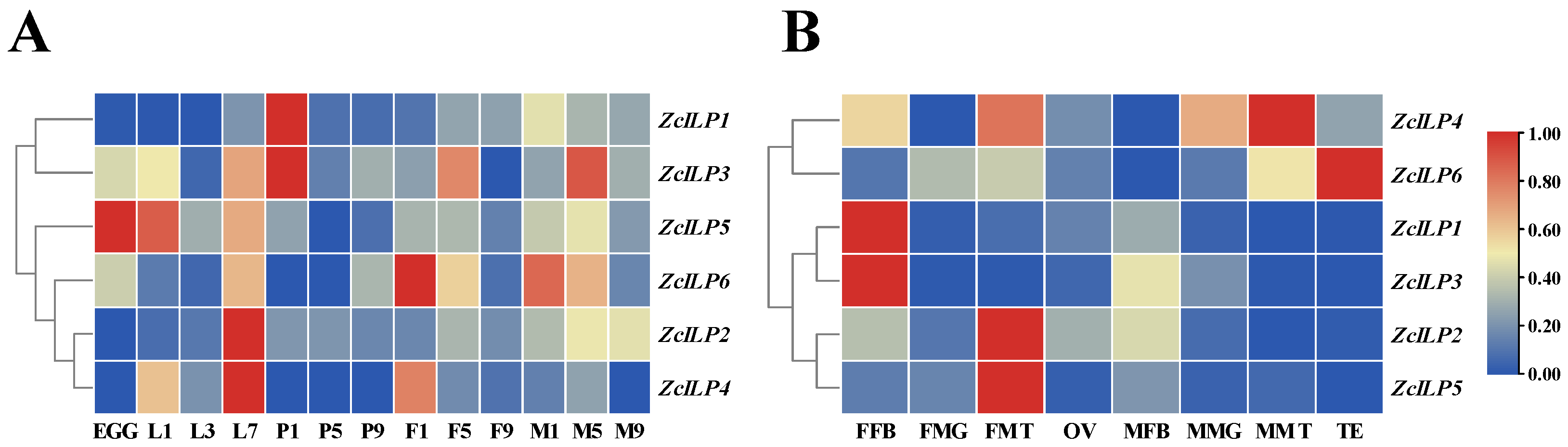
3.2. Spatio-Temporal Expression of the Insulin-like Peptide Genes
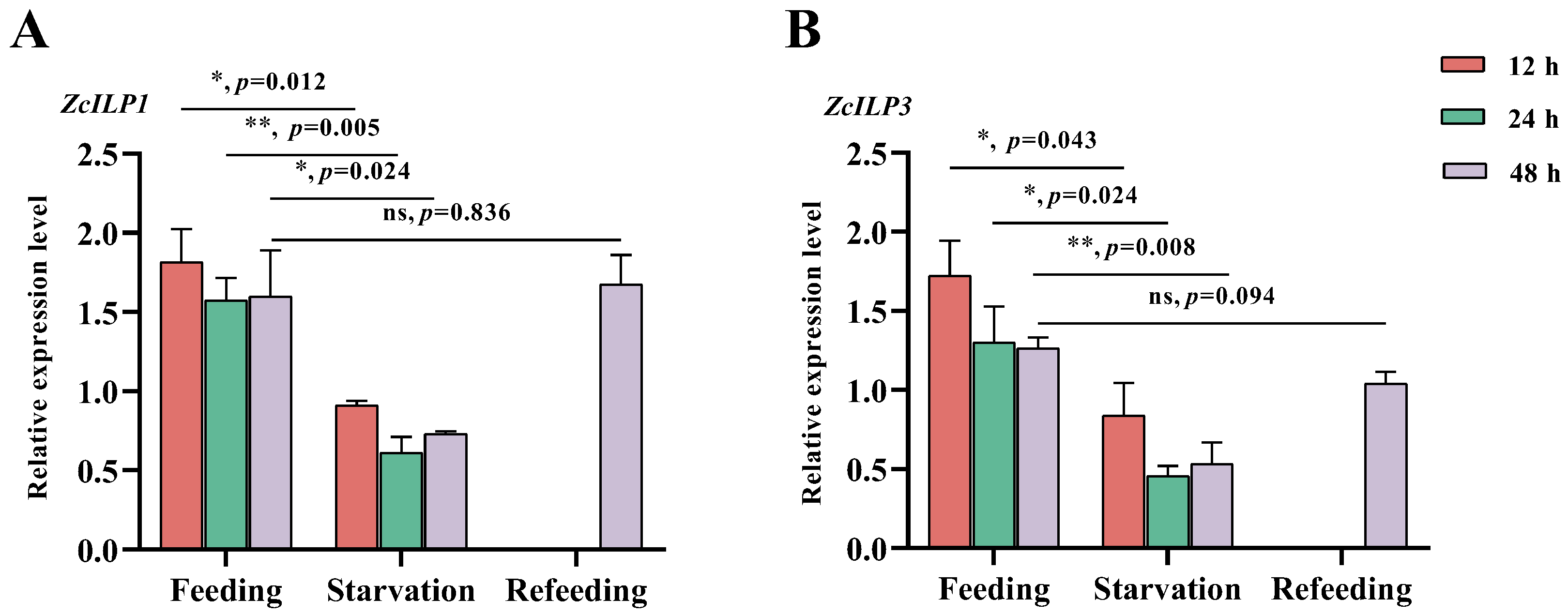
3.3. Expression of ZcILPs Induced by Starvation
3.4. Effect of RNAi on Adult Reproduction of Z. cucurbitae
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Diksha; Mahajan, E.; Singh, S.; Sohal, S.K. Potential biological control agents of Zeugodacus cucurbitae (Coquillett): A review. J. Appl. Entomol. 2022, 146, 917–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivaramu, S.; Parepally, S.K.; Chakravarthy, A.K.; Pagadala Damodaram, K.J.; Kempraj, V. Ridge gourd volatiles are attractive to gravid female melon fly, Zeugodacus cucurbitae (Coquillett) (Diptera: Tephritidae). J. Appl. Entomol. 2022, 146, 539–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subedi, K.; Regmi, R.; Thapa, R.B.; Tiwari, S. Evaluation of net house and mulching effect on Cucurbit fruit fly (Bactrocera cucurbitae Coquillett) on cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.). J. Agric. Food Res. 2021, 3, 100103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, T.; Lin, Y.Y.; Jin, Q.A.; Wen, H.B.; Peng, Z.Q. Population susceptibility to insecticides and the development of resistance in Bactrocera cucurbitae (Diptera: Tephritidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 2016, 109, 837–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, J.C.; Chou, M.Y.; Mau, R.F.; Maeda, C.; Shikano, I.; Manoukis, N.C.; Vargas, R.I. Spinosad resistance in field populations of melon fly, Zeugodacus cucurbitae (Coquillett), in Hawaii. Pest Manag. Sci. 2021, 77, 5439–5444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling, L.; Raikhel, A.S. Cross-talk of insulin-like peptides, juvenile hormone, and 20-hydroxyecdysone in regulation of metabolism in the mosquito Aedes aegypti. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2023470118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riehle, M.A.; Fan, Y.; Cao, C.; Brown, M.R. Molecular characterization of insulin-like peptides in the yellow fever mosquito, Aedes aegypti: Expression, cellular localization, and phylogeny. Peptides 2006, 27, 2547–2560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grönke, S.; Clarke, D.-F.; Broughton, S.; Andrews, T.D.; Partridge, L. Molecular evolution and functional characterization of Drosophila insulin-like peptides. PLoS Genet. 2010, 6, e1000857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garelli, A.; Gontijo, A.M.; Miguela, V.; Caparros, E.; Dominguez, M. Imaginal discs secrete insulin-like peptide 8 to mediate plasticity of growth and maturation. Science 2012, 336, 579–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veenstra, J.A.; Leyria, J.; Orchard, I.; Lange, A.B. Identification of Gonadulin and Insulin-Like Growth Factor From Migratory Locusts and Their Importance in Reproduction in Locusta migratoria. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 693068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowański, S.; Walkowiak Nowicka, K.; Winkiel, M.; Marciniak, P.; Urbański, A.; Pacholska-Bogalska, J. Insulin-like peptides and cross-talk with other factors in the regulation of insect metabolism. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 701203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, L.; Du, H.; Li, Y.; Li, X.; Sun, L.; Cao, C. Identification and characterization of key genes in insulin signaling pathway as molecular targets for controlling the fall webworm, Hyphantria cunea. Pest Manag. Sci. 2022, 79, 899–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, W.H.; Liu, Y.L.; Jiang, Y.Q.; He, S.F.; Wang, Q.Q.; Yang, Z.N.; Xu, H.J. Molecular characterization of insulin-like peptides in the brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens (Hemiptera: Delphacidae). Insect Mol. Biol. 2020, 29, 309–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biglou, S.G.; Bendena, W.G.; Chin Sang, I. An overview of the insulin signaling pathway in model organisms Drosophila melanogaster and Caenorhabditis elegans. Peptides 2021, 145, 170640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudson, A.M.; Cooley, L. Methods for studying oogenesis. Methods 2014, 68, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leyria, J.; Orchard, I.; Lange, A.B. Transcriptomic analysis of regulatory pathways involved in female reproductive physiology of Rhodnius prolixus under different nutritional states. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 11431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semaniuk, U.; Piskovatska, V.; Strilbytska, O.; Strutynska, T.; Burdyliuk, N.; Vaiserman, A.; Bubalo, V.; Storey, K.B.; Lushchak, O. Drosophila insulin-like peptides: From expression to functions—A review. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 2020, 169, 195–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, S.; Wang, R.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, S.; Su, L.; Dai, X.; Chen, H.; Yin, Z.; Zheng, L.; Liu, Q.; et al. Insulin Signaling Pathway Mediates FoxO–Pepck Axis Regulation of Glucose Homeostasis in Drosophila suzukii. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 10441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Britton, J.S.; Lockwood, W.K.; Li, L.; Cohen, S.M.; Edgar, B.A. Drosophila’s insulin/PI3-kinase pathway coordinates cellular metabolism with nutritional conditions. Dev. Cell 2002, 2, 239–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broughton, S.J.; Piper, M.D.W.; Ikeya, T.; Bass, T.M.; Jacobson, J.; Driege, Y.; Martinez, P.; Hafen, E.; Withers, D.J.; Leevers, S.J.; et al. Longer lifespan, altered metabolism, and stress resistance in Drosophila from ablation of cells making insulin-like ligands. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 3105–3110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, W.N.; Wang, B.Y.; Fu, K.Y.; Guo, W.C.; Jin, L.; Li, G.Q. The Leptinotarsa forkhead transcription factor O exerts a key function during larval-pupal-adult transition. J. Insect Physiol. 2021, 132, 104266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Meng, Z.; Wen, M.; Kang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Zhao, P.; Xia, Q. Overexpression of BmFoxO inhibited larval growth and promoted glucose synthesis and lipolysis in silkworm. Mol. Genet. Genomics 2019, 294, 1375–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, D.; Xu, H.Q.; Chen, D.; Zhang, S.Y.; Li, W.J.; Smagghe, G.; Wang, J.J. Genome-wide gene expression profiling of the melon fly, Zeugodacus cucurbitae, during thirteen life stages. Sci. Data 2020, 7, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.; Han, H.L.; Li, W.J.; Wang, J.J.; Wei, D. Expression and role of vitellogenin genes in ovarian development of Zeugodacus cucurbitae. Insects 2022, 13, 452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.J.; Song, Y.J.; Xu, H.Q.; Wei, D.; Wang, J.J. Vitelline membrane protein gene ZcVMP26Ab and its role in preventing water loss in Zeugodacus cucurbitae (Coquillett) embryos. Entomol. Gen. 2021, 41, 279–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Wang, Z.; Gong, S.; Zhang, Y.; Xue, C. Sublethal concentration of λ-cyhalothrin inhibits insulin-like peptides and leads to reproductive toxicity in Chrysoperla sinica. Insect Sci. 2024, 31, 1744–7917.13463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Li, X.; Ding, J.; Liang, Z.; Guo, R.; Yi, T.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, S.; Liang, S.; Liu, W. Molecular and expression characterization of insulin-like signaling in development and metabolism of Aedes albopictus. Parasit. Vectors 2023, 16, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Post, S.; Tatar, M. Nutritional geometric profiles of insulin/IGF expression in Drosophila melanogaster. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0155628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.K.; Yang, W.J.; Tian, Y.; Wu, Y.B.; Wang, J.J. Insulin signaling pathway in the oriental fruit fly: The role of insulin receptor substrate in ovarian development. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2015, 216, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Azevedo, S.V.; Hartfelder, K.; Amdam, G.V. Insulin-like peptides (AmILP1 and AmILP2) differentially affect female caste development in the honey bee (Apis mellifera). J. Exp. Biol. 2013, 216, 4347–4357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Yang, L.; He, Q.; Zhou, S. Regulatory mechanisms of vitellogenesis in insects. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 8, 593613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, H.; Kang, P.; Tatar, M. Drosophila insulin-like peptide-6 (dilp6) expression from fat body extends lifespan and represses secretion of Drosophila insulin-like peptide-2 from the brain. Aging Cell 2012, 11, 978–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, K.; Dou, X.; Eum, J.H.; Harrison, R.E.; Brown, M.R.; Strand, M.R. Insulin-like peptides and ovary ecdysteroidogenic hormone differentially stimulate physiological processes regulating egg formation in the mosquito Aedes aegypti. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2023, 163, 104028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Luo, X.; Li, N.; Liu, T.; Zhang, J. Insulin-like peptide 8 (Ilp8) regulates female fecundity in flies. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2023, 11, 1103923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrese, E.L.; Soulages, J.L. Insect fat body: Energy, metabolism, and regulation. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2010, 55, 207–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skowronek, P.; Wójcik, Ł.; Strachecka, A. Fat body—Multifunctional insect tissue. Insects 2021, 12, 547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veenstra, J.A.; Agricola, H.-J.; Sellami, A. Regulatory peptides in fruit fly midgut. Cell Tissue Res. 2008, 334, 499–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonkowski, M.S.; Rocha, J.S.; Masternak, M.M.; Al Regaiey, K.A.; Bartke, A. Targeted disruption of growth hormone receptor interferes with the beneficial actions of calorie restriction. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 7901–7905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fridell, Y.W.C.; Sánchez Blanco, A.; Silvia, B.A.; Helfand, S.L. Targeted expression of the human uncoupling protein 2 (hUCP2) to adult neurons extends life span in the fly. Cell Metab. 2005, 1, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domínguez, C.V.; Pagone, V.; Maestro, J.L. Regulation of insulin-like peptide expression in adult Blattella germanica females. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2022, 141, 103706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Yang, Z.; Gong, C.; Wu, Q.; Wang, S.; Li, C.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, Z. Molecular characterization of insulin-like peptide genes and their important roles in Bemisia tabaci reproduction. Entomol. Gen. 2022, 42, 977–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinson, E.O.; Chen, K.; Valzania, L.; Brown, M.R.; Strand, M.R. Insulin-like peptide 3 stimulates hemocytes to proliferate in anautogenous and facultatively autogenous mosquitoes. J. Exp. Biol. 2022, 225, jeb243460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenaerts, C.; Monjon, E.; Van Lommel, J.; Verbakel, L.; Vanden Broeck, J. Peptides in insect oogenesis. Curr. Opin. Insect Sci. 2019, 31, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Liu, X.; Zhang, L.; Wang, M.; Li, Y.; Mao, J. Four insulin-like peptides orchestrate reproductive signaling of the green lacewing, Chrysopa pallens (Rambur) (Neuroptera: Chrysopidae). Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 2022, 115, 352–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.-H.; Zhao, P.; Ning, X.-Y.; Xie, Y.-Q.; Li, Z.; Liu, X.-X. Nanomaterial-Encapsulated dsRNA-Targeting Chitin Pathway─A Potential Efficient and Eco-Friendly Strategy against Cotton Aphid, Aphis gossypii (Hemiptera: Aphididae). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2024, 72, 20905–20917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Liu, X.; Lu, W.; Yin, X.; An, S. Application progress of plant-mediated RNAi in pest control. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 963026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Khan, S.A.; Heckel, D.G.; Bock, R. Next-Generation Insect-Resistant Plants: RNAi-Mediated Crop Protection. Trends Biotechnol. 2017, 35, 871–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Q.; Brown, M.R. Signaling and function of insulin-like peptides in insects. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2006, 51, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Jiao, P.; Xu, X.; Ma, W.; Hull, J.J.; Hua, H.; Chen, L. Identification of a TOR signaling pathway gene as a candidate target for reproductive management of Adelphocoris suturalis. J. Integr. Agric. 2024, 23, S209531192400296X. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Tan, D.; Wang, F.; Guo, S.; Liu, J.; Cuthbertson, A.G.S.; Qiu, B.; Sang, W. Insulin peptides and their receptors regulate ovarian development and oviposition behavior in Diaphorina citri. Insect Sci. 2023, 30, 95–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.H.; Liu, Y.M.; Wang, Z.Y.; Wang, F.F.; Mao, Y.K.; Hu, Y.W.; Han, P.; Cuthbertson, A.G.S.; Qiu, B.L.; Sang, W. Transcriptome analysis reveals TOR signalling-mediated plant flush shoots governing kuwayama oviposition. Insect Mol. Biol. 2021, 30, 264–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maestro, J.L.; Cobo, J.; Bellés, X. Target of Rapamycin (TOR) mediates the transduction of nutritional signals into juvenile hormone production. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 5506–5513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zoncu, R.; Bar-Peled, L.; Efeyan, A.; Wang, S.; Sancak, Y.; Sabatini, D.M. mTORC1 Senses Lysosomal Amino Acids Through an Inside-Out Mechanism That Requires the Vacuolar H+-ATPase. Science 2011, 334, 678–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gui, T.; Burgering, B.M.T. FOXOs: Masters of the equilibrium. FEBS J. 2021, 289, 7918–7939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; He, Q.; Zeng, B.; Zhou, H.; Zhou, S. Juvenile hormone acts through FoxO to promote Cdc2 and Orc5 transcription for polyploidy-dependent vitellogenesis. Development 2020, 147, dev188813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yi, J.-C.; Liu, C.-L.; Chen, D.; Wei, D.; Zhang, Z.-T. Characteristics of the Insulin-like Peptide Genes and Their Roles in the Ovarian Development of Zeugodacus cucurbitae (Coquillett). Insects 2025, 16, 854. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16080854
Yi J-C, Liu C-L, Chen D, Wei D, Zhang Z-T. Characteristics of the Insulin-like Peptide Genes and Their Roles in the Ovarian Development of Zeugodacus cucurbitae (Coquillett). Insects. 2025; 16(8):854. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16080854
Chicago/Turabian StyleYi, Jun-Chen, Chuan-Lian Liu, Dong Chen, Dong Wei, and Zhu-Ting Zhang. 2025. "Characteristics of the Insulin-like Peptide Genes and Their Roles in the Ovarian Development of Zeugodacus cucurbitae (Coquillett)" Insects 16, no. 8: 854. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16080854
APA StyleYi, J.-C., Liu, C.-L., Chen, D., Wei, D., & Zhang, Z.-T. (2025). Characteristics of the Insulin-like Peptide Genes and Their Roles in the Ovarian Development of Zeugodacus cucurbitae (Coquillett). Insects, 16(8), 854. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16080854






