Effects of Sitobion avenae Treated with Sublethal Concentrations of Dinotefuran on the Predation Function and Enzyme Activity of Harmonia axyridis
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Samples
2.2. Assessment of Indoor Toxicity of Dinotefuran Towards S. avenae
2.3. Assessment of Indoor Toxicity of Dinotefuran Towards H. axyridis
2.4. Effects of S. avenae Treated with Sublethal Concentrations of Dinotefuran on the Predation Function of H. axyridis
2.5. Assessment of Acetylcholinesterase and Detoxification Enzyme Activity in H. axyridis
2.5.1. Collection of Insect Samples
2.5.2. Assay of Carboxylesterase Activity
2.5.3. Glutathione-S-Transferase Activity Assay
2.5.4. Multifunctional Oxidase Activity Assay
2.6. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Indoor Toxicity Assessment of Dinotefuran on S. avenae
3.2. Indoor Toxicity Assessment of Dinotefuran on H. axyridis
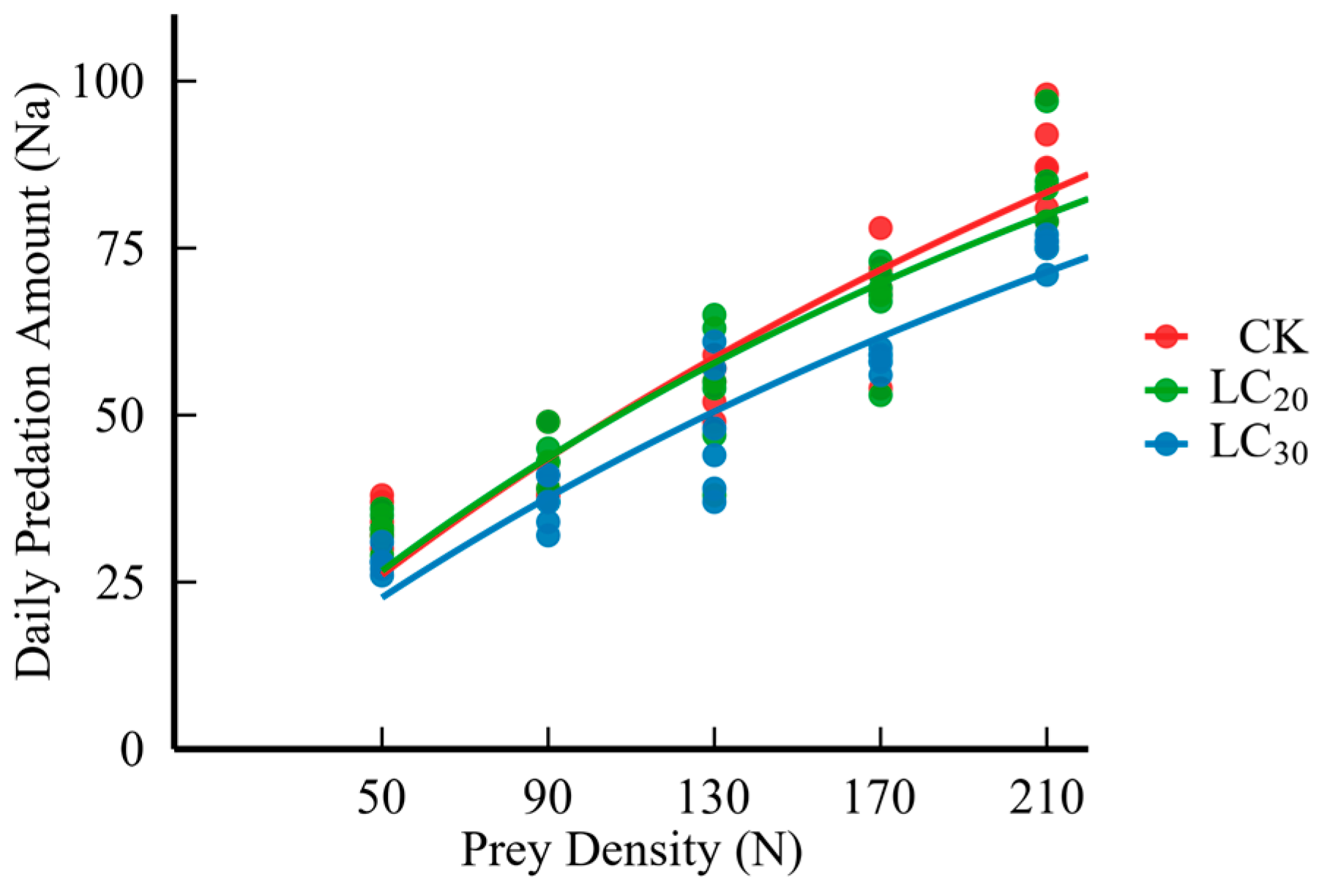
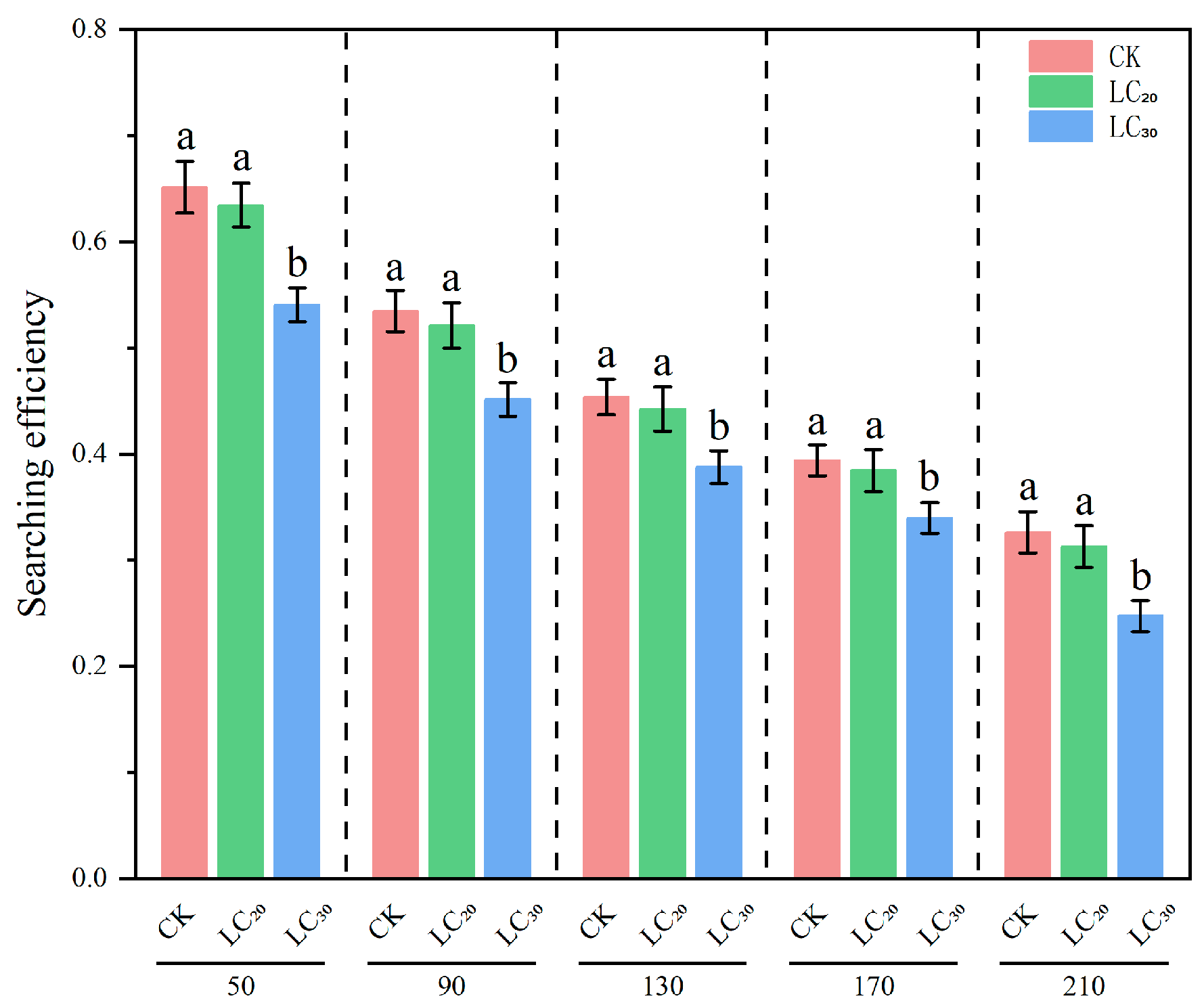
3.3. Results of Predation Function
3.4. Enzyme Activity Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, L.; Liu, B.; Zhang, Q.; Zeng, Y.; Pan, Y.; Li, M.; Lu, Y. Landscape structure alters the abundance and species composition of early-season aphid populations in wheat fields. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2019, 269, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.; Wei, C.; Li, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhong, Q.; Li, Y.; Bai, B.; Wu, Y. Barley yellow dwarf virus-GAV-derived vsiRNAs are involved in the production of wheat leaf yellowing symptoms by targeting chlorophyll synthase. Virol. J. 2020, 17, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Innes, P.J.; Tan, D.K.Y.; Van Ogtrop, F.; Amthor, J.S. Effects of high-temperature episodes on wheat yields in New South Wales, Australia. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2015, 208, 95–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dedryver, C.A.; Le Ralec, A.; Fabre, F. The conflicting relationships between aphids and men: A review of aphid damage and control strategies. C. R. Biol. 2010, 333, 539–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, H.E.; Brown, P.M.J. Ten years of invasion: Harmonia axyridis (Pallas) (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) in Britain. Ecol. Entomol. 2015, 40, 336–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koch, R.L. The multicolored Asian lady beetle, Harmonia axyridis: A review of its biology, uses in biological control, and non-target impacts. J. Insect Sci. 2003, 3, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; Bahlai, C.A.; Frewin, A.; Sears, M.K.; Schaafsma, A.W.; Hallett, R.H. Predation by Coccinella septempunctata and Harmonia axyridis (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) on Aphis glycines (Homoptera: Aphididae). Environ. Entomol. 2009, 38, 708–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L.; Gao, X.; Zhao, L.; Zhu, X.; Wang, L.; Zhang, K.; Li, D.; Ji, J.; Luo, J.; Cui, J. Assessment of the risk of imidaclothiz to the dominant aphid parasitoid Binodoxys communis (Hymenoptera: Braconidae). Environ. Res. 2023, 238, 117165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Guo, Y.; Yan, Z.; Bao, L.; Wang, Q. Safety Evaluation and Efficacy of Neonicotinoids Dinotefuran Against Nilaparvata lugens. Pestic. Sci. Adm. 2016, 37, 44–49. [Google Scholar]
- Cloyd, R.A.; Bethke, J.A. Impact of neonicotinoid insecticides on natural enemies in greenhouse and interiorscape environments. Pest Manag. Sci. 2011, 67, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, C.; Ricupero, M.; Wang, Z.; Desneux, N.; Biondi, A.; Lu, Y. Transgenerational Effects of a Neonicotinoid and a Novel Sulfoximine Insecticide on the Harlequin Ladybird. Insects 2021, 12, 681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Z.; Qin, Q.; Wang, D.; Han, S.; Zhang, S.; He, Y. Sublethal and transgenerational effects of exposures to the thiamethoxam on the seven-spotted lady beetle, Coccinella septempunctata L. (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 243, 114002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simelane, D.O.; Steinkraus, D.C.; Kring, T.J. Predation rate and development of Coccinella septempunctata L. influenced by Neozygites fresenii-infected cotton aphid prey. Biol. Control 2008, 44, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, D.; Tan, X.; Wang, W.; Zhang, F.; Desneux, N.; Wang, S. Modification of Flight and Locomotion Performances, Respiratory Metabolism, and Transcriptome Expression in the Lady Beetle Harmonia axyridis through Sublethal Pesticide Exposure. Front. Physiol. 2017, 8, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, M.; Gupta, G.P.; Rajam, M.V. Silencing of acetylcholinesterase gene of Helicoverpa armigera by siRNA affects larval growth and its life cycle. J. Insect Physiol. 2009, 55, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, J.; Lin, W.; Lu, Y.; Gao, Y. Acute and sublethal effects of neonicotinoids and pymetrozine on an important egg parasitoid, Trichogramma ostriniae (Hymenoptera: Trichogrammatidae). Biocontrol Sci. Technol. 2014, 25, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klinnert, A.; Barbosa, A.L.; Catarino, R.; Fellmann, T.; Baldoni, E.; Beber, C.; Hristov, J.; Paracchini, M.L.; Rega, C.; Weiss, F.; et al. Landscape features support natural pest control and farm income when pesticide application is reduced. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 5384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, R.; Choudhary, D.; Bali, S.; Bandral, S.S.; Singh, V.; Ahmad, M.A.; Rani, N.; Singh, T.G.; Chandrasekaran, B. Pesticides: An alarming detrimental to health and environment. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 915, 170113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, J.B.; de F. Bueno, A. Conservation biological control using selective insecticides—A valuable tool for IPM. Biol. Control 2018, 126, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NY/T1154.6-2006; Pesticides Guidelines for Laboratory Bioactivity Tests Part 6: The Immersion Test for Insecticide Activity. The Ministry of Agriculture of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2006.
- Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, K.; Wang, Q.; Liu, X. Safety evaluation of botanical insecticides on Macrocentrus cingulum. China Plant Prot. 2025, 45, 101–103. [Google Scholar]
- Juliano, A.S. Nonlinear Curve Fitting Predation and Functional Response Curves. In Design and Analysis of Ecological Experiments, 2nd ed.; Scheiner, M.S., Juliano, A.S., Eds.; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2001; Volume 10, pp. 178–196. [Google Scholar]
- Wumuerhan, P.; Jiang, Y.; Ma, D. Effects of exposure to imidacloprid direct and poisoned cotton aphids Aphis gossypii on ladybird Hippodamia variegata feeding behavior. J. Pestic. Sci. 2020, 45, 24–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, Y.; Shah, F.M.; Guncan, A.; DeLong, J.P.; Zhou, X. Functional Response of Harmonia axyridis to the Larvae of Spodoptera litura: The Combined Effect of Temperatures and Prey Instars. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 849574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kansman, J.T.; Nersten, C.E.; Hermann, S.L. Smelling danger: Lady beetle odors affect aphid population abundance and feeding, but not movement between plants. Basic Appl. Ecol. 2023, 71, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganjisaffar, F.; Perring, T.M. Prey stage preference and functional response of the predatory mite Galendromus flumenis to Oligonychus pratensis. Biol. Control 2015, 82, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youn, Y.N.; Seo, M.J.; Shin, J.G.; Jang, C.; Yu, Y.M. Toxicity of greenhouse pesticides to multicolored Asian lady beetles, Harmonia axyridis (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae). Biol. Control 2003, 28, 164–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Yu, J.; Mao, R.; Kang, K.; Xu, L.; Wu, M. Functional and Numerical Responses of Harmonia axyridis (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) to Rhopalosiphum nymphaeae (Hemiptera: Aphididae) and Their Potential for Biological Control. Insects 2024, 15, 633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirvonen, H.; Ranta, E. Prey to predator size ratio influences foraging efficiency of larval Aeshna juncea dragonflies. Oecologia 1996, 106, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, F.; Ul Haq, I.; Li, C.; Gou, Y.; Zhang, K.; Liu, H.; Liu, C. Comparative toxicity and enzymatic detoxification responses in Spodoptera frugiperda (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) to two insecticides. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 284, 116917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Yuan, Y.; Teng, H.; Wang, D.; Gu, H. Exposure to Cyantraniliprole Adversely Impacts Fitness of Harmonia axyridis: Acute Toxicity and Sublethal Effects on Development, Fecundity and Antioxidant Responses. Insects 2024, 15, 773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlidi, N.; Vontas, J.; Van Leeuwen, T. The role of glutathione S-transferases (GSTs) in insecticide resistance in crop pests and disease vectors. Curr. Opin. Insect Sci. 2018, 27, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Wang, M.; Xue, C.; Mao, J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, L. Acute Toxicity of Dinotefuran to Picromerus lewisi Scott (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae) and Its Impact on Offspring Growth and Predation Ability in Integrated Pest Management. Insects 2025, 16, 404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Cai, X.; Qi, Y.; Lu, Y.; Li, X. Lethal, Sublethal, and Offspring Effects of Fluralaner and Dinotefuran on Three Species of Bactrocera Fruit Flies. Insects 2024, 15, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Toxic Regression Equation | Slope | SE | Chi-Square Value χ2 | Correlation Coefficient R2 | DF | p-Value | LC20 (mg/mL) (95% Fiducial Limits) | LC30 (mg/mL) (95% Fiducial Limits) | LC50 (mg/mL) (95% Fiducial Limits) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| y = 3.2604x + 8.4963 | 3.2604 | 0.707 | 0.7742 | 0.9932 | 3 | 0.8556 | 0.0467 (0.0314~0.0565) | 0.0585 (0.0450~0.0682) | 0.0847 (0.0792~0.1040) |
| Insect States of H. axyridis | Toxic Regression Equation | Slope | SE | Chi-Square Value χ2 | Correlation Coefficient R2 | DF | p-Value | LC50 (mg/mL) (95% Fiducial Limits) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2nd instar | Y = 1.7604X + 2.4665 | 1.7604 | 0.3411 | 3.6343 | 0.9584 | 3 | 0.3038 | 0.0275 (0.0196~0.0404) |
| 3rd instar | Y = 1.6272X + 1.9817 | 1.6272 | 0.3642 | 2.5113 | 0.9303 | 3 | 0.4733 | 0.0716 (0.0454~0.1902) |
| 4th instar | Y = 2.7274X − 1.5085 | 2.7274 | 0.4521 | 1.4219 | 0.9591 | 3 | 0.7004 | 0.2434 (0.1795~0.4111) |
| Adult | Y = 2.2620X + 0.1413 | 2.2620 | 0.3294 | 0.2374 | 0.9979 | 3 | 0.9713 | 0.1406 (0.1101~0.1921) |
| Dinotefuran Concentration | P1 (N) | P2 (N2) | P3 (N3) | Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 (CK) | −0.06245 | 0.000377 | −7.411 × 10−7 | Type II |
| LC20 | −0.04876 | 0.000271 | −4.941 × 10−7 | Type II |
| LC30 | −0.03355 | 0.000170 | −2.767 × 10−7 | Type II |
| Prey Density (ind./vessel) | Daily Predation Amount (ind.) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 (CK) | LC20 | LC30 | |
| 50 | 34.0 ± 1.24 a | 33.0 ± 1.00 a | 28.0 ± 1.67 b |
| 90 | 42.8 ± 1.80 a | 42.7 ± 1.74 a | 37.0 ± 1.48 a |
| 130 | 54.8 ± 1.51 a | 53.7 ± 4.11 a | 47.7 ± 3.95 a |
| 170 | 68.7 ± 3.26 a | 66.8 ± 2.90 a | 58.3 ± 1.38 a |
| 210 | 87.3 ± 2.86 a | 84.0 ± 3.03 ab | 75.0 ± 0.86 b |
| Dinotefuran Concentration | 0 (CK) | LC20 | LC30 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Holling-II equation | Na = 0.8961N0/(1 + 0.0075N0) | Na = 0.8739N0/(1 + 0.0078N0) | Na = 0.7187N0/(1 + 0.0069N0) |
| Correlation coefficient-r | 0.9154 | 0.9080 | 0.9239 |
| Instantaneous attack rate-a | 0.8961 ± 0.0365 | 0.8739 ± 0.0123 | 0.7187 ± 0.0159 |
| Handling time-Th(d) | 0.0084 ± 0.0004 | 0.0089 ± 0.0008 | 0.0093 ± 0.0007 |
| pest controlefficiency-a/Th | 107.96 ± 7.76 | 103.47 ± 9.31 | 79.80 ± 6.59 |
| Daily maximum predation amount-Na-max(ind.) | 119.89 ± 4.87 | 117.83 ± 9.15 | 110.66 ± 7.87 |
| Chi-square value-χ2 | 2.715 | 1.768 | 1.753 |
| Dinotefuran Concentration | Searching Efficiency Equation | Correlation Coefficient r |
|---|---|---|
| 0 (CK) | S = 0.8961/(1 + 0.0075N) | 0.9330 |
| LC20 | S = 0.8739/(1 + 0.0078N) | 0.9219 |
| LC30 | S = 0.7187/(1 + 0.0069N) | 0.9304 |
| Dinotefuran Concentration | CarE (U/g) | GSTs (U/g) | MFOs(U/g) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 (CK) | 112.26 ± 1.7984 a | 1.635 ± 0.0093 a | 29.227 ± 2.2538 a |
| LC20 | 108.57 ± 8.2661 a | 3.198 ± 0.0136 b | 57.867 ± 0.9460 b |
| LC30 | 105.21 ± 3.3494 a | 2.398 ± 0.0094 c | 88.837 ± 4.6882 c |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fei, S.; Sun, J.; Ren, X.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Y. Effects of Sitobion avenae Treated with Sublethal Concentrations of Dinotefuran on the Predation Function and Enzyme Activity of Harmonia axyridis. Insects 2025, 16, 671. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16070671
Fei S, Sun J, Ren X, Zhang H, Liu Y. Effects of Sitobion avenae Treated with Sublethal Concentrations of Dinotefuran on the Predation Function and Enzyme Activity of Harmonia axyridis. Insects. 2025; 16(7):671. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16070671
Chicago/Turabian StyleFei, Shaodan, Jiacong Sun, Xingping Ren, Haiying Zhang, and Yonggang Liu. 2025. "Effects of Sitobion avenae Treated with Sublethal Concentrations of Dinotefuran on the Predation Function and Enzyme Activity of Harmonia axyridis" Insects 16, no. 7: 671. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16070671
APA StyleFei, S., Sun, J., Ren, X., Zhang, H., & Liu, Y. (2025). Effects of Sitobion avenae Treated with Sublethal Concentrations of Dinotefuran on the Predation Function and Enzyme Activity of Harmonia axyridis. Insects, 16(7), 671. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16070671






