Occurrence and Genetic Variation of Monolepta hieroglyphica (Motschulsky, 1858) (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae), a Newly Emerging Pest, Among Hosts in Northeast China
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Population Dynamics Analyses
2.2. Molecular Analyses
2.3. Data Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Population Dynamics
3.2. Base Composition
3.3. Haplotypes
3.4. Genetic Diversity and AMOVA
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sun, W.; Hu, G.; Su, Q.; Wang, Y.; Yang, W.; Zhou, J.; Gao, Y. Population source of third-generation oriental armyworm in Jilin, China, determined by entomology radar, trajectory analysis, and mitochondrial COI sequences. Environ. Entomol. 2022, 51, 621–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, W.; Su, Q.; Yang, W.; Zhou, J.; Gao, Y. Genetic diversity and gene flow observed in two cereal aphid (Hemiptera: Aphididae) species and populations in the Chinese corn belt region. J. Entomol. Sci. 2022, 57, 363–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Song, X.; Ma, H.; Yin, Y. The complete mitochondrial genome of Monolepta hieroglyphica (Motschulsky) (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae). Mitochondrial DNA Part B 2021, 6, 2363–2365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, F.; Jiang, H.; Jia, J.; Wang, R.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, H. Effect of dimethoate in controlling Monolepta hieroglyphica (Motschulsky) and its distribution in maize by drip irrigation. Pest. Manag. Sci. 2019, 76, 1523–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinese academy of sciences, Institute of zoology. Research brief on Monolepta hieroglyphica (Motschulsky). Acta Entomol. Sin. 1979, 22, 115–117, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Chen, G.; Yin, W.; Li, Q.; Hu, H. Research progress on Monolepta hieroglyphica (Motschulsky). China. Plant. Prot. 2016, 36, 19–26, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.; Zheng, X.; Guo, J.; Liu, Y.; Luo, B.; Wang, L.; Wang, L.; Liu, Y.; Li, Q.; Wang, Z. Occurrence of Monolepta hieroglyphica adults in corn fields in Qiqihar. Chin. J. Appl. Entomol. 2021, 58, 979–984, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Gao, S.; Meng, W.; Zhang, L.; Yue, Q.; Zheng, X.; Xu, J. Parametarhizium (Clavicipitaceae) gen. nov. with two new species as a potential biocontrol agent isolated from forest litters in Northeast China. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 627744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Tan, Y.; Lv, F.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Chi, D. Effect of jasmonate treatments on leaves of Rosa rugosa ‘Plena’ and detoxification enzymes and feeding of adult Monolepta hieroglyphica. J. For. Res. 2021, 32, 1253–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, R.; Li, L.; Yang, Y.; Ding, Y.; Guan, H.; Wang, X.; Zhang, A.; Wen, H. Negligible transcriptome and metabolome alterations in RNAi insecticidal maize against Monolepta hieroglyphica. Plant. Cell. Rep. 2020, 39, 1539–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Y.; Shi, C.; Bai, M.; Cao, Z.; Cao, L.; Wang, Z.; Dong, J.; Wang, Y. Molecular data confirm Monolepta hieroglyphica (Motschulsky, 1858) and M. quadriguttata (Motschulsky, 1860) being synonyms of M. signata (Oliver, 1808). Insect. Syst. Evol. 2023, 54, 402–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Shen, S.; Chen, H. Mitochondrial genome of Monolepta hieroglyphica (Coleoptera: Chrysomeloidea: Chrysomelidae) and phylogenetic analysis. Mitochondrial DNA Part B 2021, 6, 1541–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, R. Genetic differentiation of Monolepta hieroglyphica (Motschulsky) (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae) from North China Based on mtDNA COII and Cytb and Wolbachia Infection Detection. Master’s Thesis, Shenyang Agricultural University, Shenyang, China, 2011. (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Zhang, X.; Xu, L.; Shen, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, Z. Genetic structure and Wolbachia infection in geographical populations of Monolepta hieroglyphica (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae) in South China. Acta Entomol. Sin. 2021, 64, 730–742, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.; Cui, J.; Xu, W.; Qin, H.; Liu, D.; Wang, X.; Shi, S. Influences of several major crop hosts on adult oviposition of Monolepta hieroglyphica (Motschulsky). Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull. 2015, 31, 81–84, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- O’Neill, K.; Larson, D.; Kemp, W. Sweep sampling technique affects estimates of the relative abundance and community composition of grasshoppers (Orthoptera: Acrididae). J. Agr. Urban Entomol. 2003, 19, 125–131. [Google Scholar]
- Whipple, S.; Brust, M.; Hoback, W.; Farnsworth-Hoback, K. Sweep sampling capture rates for rangeland grasshoppers (Orthoptera: Acrididae) vary during morning hours. J. Orthoptera Res. 2010, 19, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avise, J. Ten unorthodox perspectives on evolution prompted by comparative population genetic findings on mitochondrial DNA. Annu. Rev. Genet. 1991, 25, 45–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrison, H. Animal mtDNA as a genetic marker in population and evolutionary biology. Trends. Ecol. Evol. 1989, 4, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moritz, C.; Dowling, T.; Brown, W. Evolution of animal mitochondrial DNA: Relevance for population biology and systematics. Ann. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 1987, 18, 269–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, B.; Costa, G.; Godoy, R.; Júnior, A.; Cella, W.; Ferreira, G.; Medeiros, G.; Shimabukuro, P. Molecular and morphometric study of Brazilian populations of Psychodopygus davisi. Med. Vet. Entomol. 2023, 38, 83–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandra, D.; Luis, M.; Marcelo, B.; Octavio, M.; Juan, M.; Santiago, N.; Matias, S.; Evelina, T.; José, M.; José, D.; et al. Low genetic diversity of the only clade of the tick Rhipicephalus microplus in the Neotropics. Pathogens 2023, 12, 1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherzada, S.; Hussain, N.; Hussain, A.; Mohame, A.; Khan, S. Diversity and genetic structure of freshwater shark Wallago attu: An emerging species of commercial interest. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 15571–15579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Wang, Z. The Atlas of Maize Diseases, Insects, and Grass Pests in China; Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2018; pp. 176–178. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Tamura, K.; Dudley, J.; Nei, M.; Kumar, S. MEGA4: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2007, 24, 1596–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Librado, P.; Rozas, J. DnaSP V5: A software for comprehensive analysis of DNA polymorphism data. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1451–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bandelt, H.; Forster, P.; Rohl, A. Median-joining networks for inferring intraspecific phylogenies. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1999, 16, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Excoffier, L.; Laval, S.; Schneider, S. Arlequin (version 3.0): An integrated software package for population genetics data analysis. Evol. Bioinform. Online 2007, 23, 47–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gedifew, S.; Demelasa, H.; Abate, A.; Abebe, T. Association of quantitative traits and genetic diversity in Ethiopian sesame (Sesamum indicum L.) genotypes. Heliyon 2024, 10, e26676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramiro, M.; Asier, G.; Farnando, A.; Todd, J.; Lynda, A.; Kruger, T.; Mike, J.; Alex, G.; Chris, S.; James, R. Population genetic structure and predominance of cyclical parthenogenesis in the bird cherry-oat aphid Rhopalosiphum padi in England. Evol. Appl. 2020, 13, 1009–1025. [Google Scholar]
- Hughes, A.; Inouye, B.; Johnson, M.; Underwood, N.; Vellend, M. Ecological consequences of genetic diversity. Ecol. Lett. 2008, 11, 609–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khabiya, R.; Choudhary, G.; Sairkar, P.; Silawat, N.; Jnanesha, A.; Kumar, A.; Lal, R. Unraveling genetic diversity analysis of Indian ginseng (Withania somnifera (Linn.) Dunal) insight from RAPD and ISSR markers and implications for crop improvement vital for pharmacological and industrial potential. Ind. Crops Prod. 2024, 210, 118124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kononov, A.; Ustyantsev, K.; Wang, B.; Mastro, V.; Fet, V.; Blinov, A.; Yuri, B. Genetic diversity among eight Dendrolimus species in Eurasia (Lepidoptera: Lasiocampidae) inferred from mitochondrial COI and COII, and nuclear ITS2 markers. BMC Genom. Data 2016, 17, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misra, V.; Pandey, H.; Srivastava, S.; Sharma, A.; Kumar, R.; Pandey, A.; Singh, S.; Singh, V. Computational analysis of haplotype diversity, phylogenetic variation, and population structure of Candidatus Phytoplasma aurantifolia using tuf gene sequences. Ecol. Genet. Genom. 2024, 31, 100229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mooney, K. Genetically based population variation in aphid association with ants and predators. Arthropod-Plant. Inte. 2011, 5, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrada-Souza, V.; Silva, J.; Hamada, N. Phylogeography and population diversity of Simulium hirtipupa Lutz (Diptera: Simuliidae) based on mitochondrial COI sequences. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0190091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenzel, M.; Webster, L.; Blanco, G.; Burgess, M.; Kerbiriou, C.; Segelbacher, G.; Piertney, S.; Reid, J. Pronouced genetic structure and low genetic diversity in European red billed chough (Pyrrhocorax pyrrhocorax) populations. Conserv. Genet. 2012, 13, 1213–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wongsa, K.; Duangphakdee, O.; Rattanawannee, A. Genetic structure of the Aphis craccivora (Hemiptera: Aphididae) from Thailand inferred from mitochondrial COI gene sequence. J. Insect. Sci. 2017, 17, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tir, M.; Tombari, W.; Khawla, T.; Tarek, H.; Abdeljelil, G.; Mhamed, E. Genetic diversity and population structure of Sepia officinalis from the Tunisian cost revealed by mitochondrial COI sequences. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2015, 42, 77–86. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Yang, X.; Lu, B.; Zhou, L.; Wu, K. Genetic variation and phylogeographic structure of the cotton aphid, Aphis gossypii, based on mitochondrial DNA and microsatellite markers. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laopichienpong, N.; Muangmai, N.; Supikamolseni, A.; Twilprawat, P.; Chanhome, L.; Suntrarachun, S.; Peyachoknagul, S.; Srikulnath, K. Assessment of snake DNA barcodes based on mitochondrial COI and Cytb genes revealed multiple putative cryptic species in Thailand. Gene 2016, 594, 238–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakauskas, R.; Havelka, J.; Bernotiene, R. Mitochondrial (COI) and nuclear (EF-1α) DNA vatiability of Rhopalosiphum padi and Rhopalosiphum nymphaeae (Hemiptera: Aphididae) in Lithuania. Biologia 2014, 69, 1730–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thirumaraiselvi, R.; Thangaraj, M. Genetic diversity analysis of Indian salmon, Eleutheronema tetradactylum from South Asian countries based on mitochondrial COI gene sequences. Not. Sci. Biol. 2015, 7, 417–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Millar, C.; Libby, W. Genetics and Conservation of Rare Plants; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1991; pp. 149–170. [Google Scholar]
- Whitlock, M.; Mccauley, D. Indirect measures of gene flow and migration: Fst ≠ 1/(4Nm + 1). Heredity 1999, 82, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Criniti, A.; Mazzoni, E.; Pecchioni, N.; Rau, D.; Cassanelli, S.; Bizzaro, D.; Manicardi, G. Genetic variability among different Italian populations of the aphid Myzus persicae. Caryologia 2006, 59, 326–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mitić, Z.; Nikolić, J.; Jušković, M.; Ranđelović, V.; Nikolić, B.; Zlatković, B. Geographic differentiation of Abies alba, A. x borisii-regis, and A. cephalonica populations at the Balkan Peninsula based on needle morpho-anatomy. Trees-Struct. Funct. 2023, 37, 1465–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortego, J.; Bonal, R.; Cordero, P.; Aparicio, J. Phylogeography of the Iberian populations of Mioscirtus wagneri (Orthoptera: Acrididae), a specialized grasshopper inhabiting highly fragmented hypersaline environments. Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 2009, 97, 623–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palombo, N.; Carrizo, G. Geographical patterns of genetic variation in Locoto Chile (Capsicum pubescens) in the Americas inferred by genome-wide data analysis. Plants 2022, 11, 2911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anstead, J.; Burd, J.; Shufran, K. Mitochondrial DNA sequence divergence among Schizaphis graminum (Hemiptera: Aphididae) clones from cultivated and non-cultivated hosts: Haplotype and host associations. Bull. Entomol. Res. 2002, 92, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charaabi, K.; Carletto, J.; Chavigny, P.; Marrakchi, M.; Makni, M.; Vanlerberghe-Masutt, F. Clonal diversity of the melon aphid Aphis gossypii (Glover) in Tunisia is structured by host plants. Bull. Entomol. Res. 2008, 98, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corre, V.; Reibel, C.; Kati, V.; Gibot-Leclerc, S. Host-associated genetic differentiation and origin of a recent host shift in the generalist parasitic weed Phelipanche ramosa. Ecol. Evol. 2023, 13, e10529. [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald, Z.; Snape, K.; Roe, A.; Sperling, F. Host association, environment, and geography underlie genomic differentiation in a major forest pest. Evol. Appl. 2022, 15, 1749–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
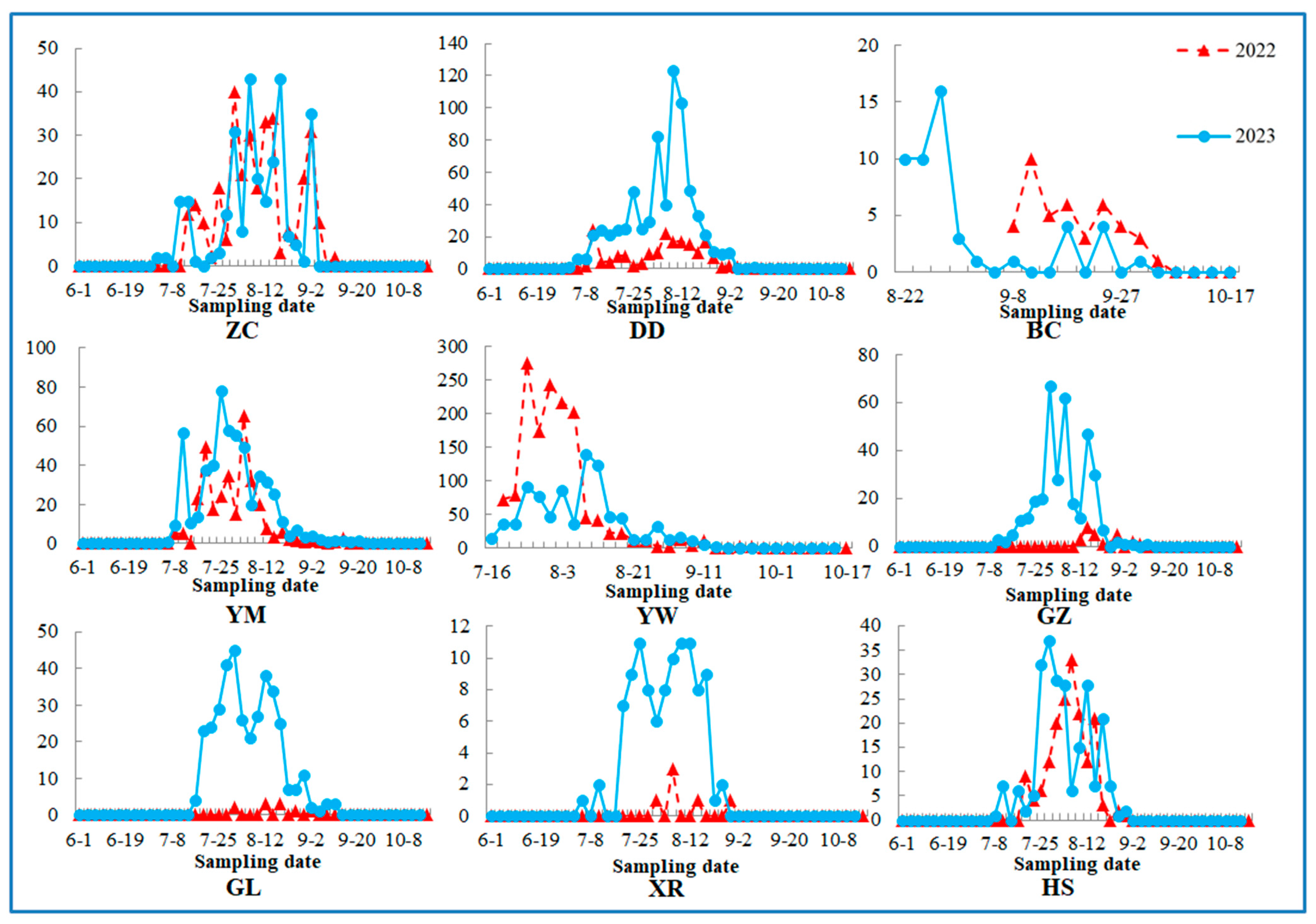
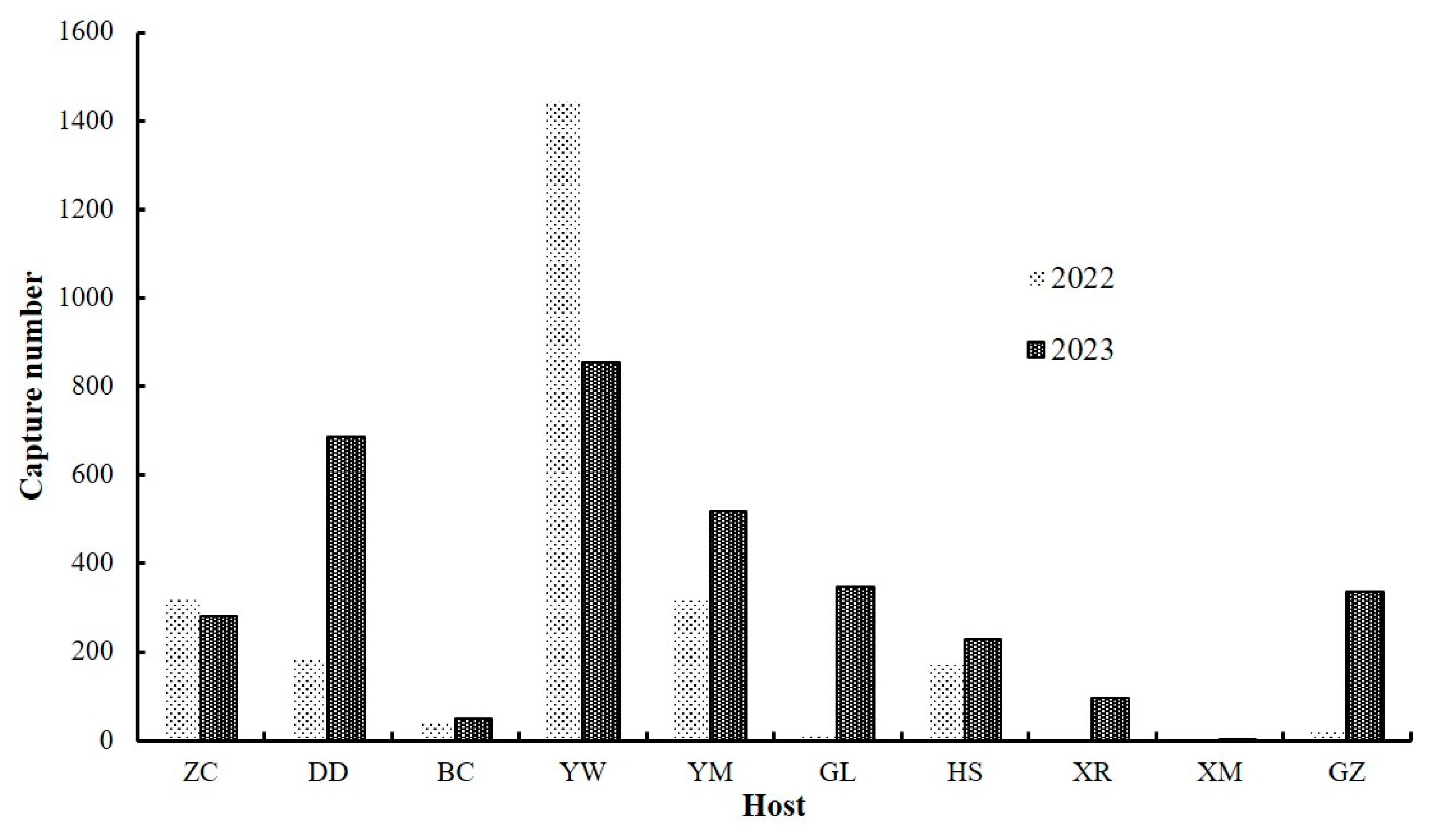
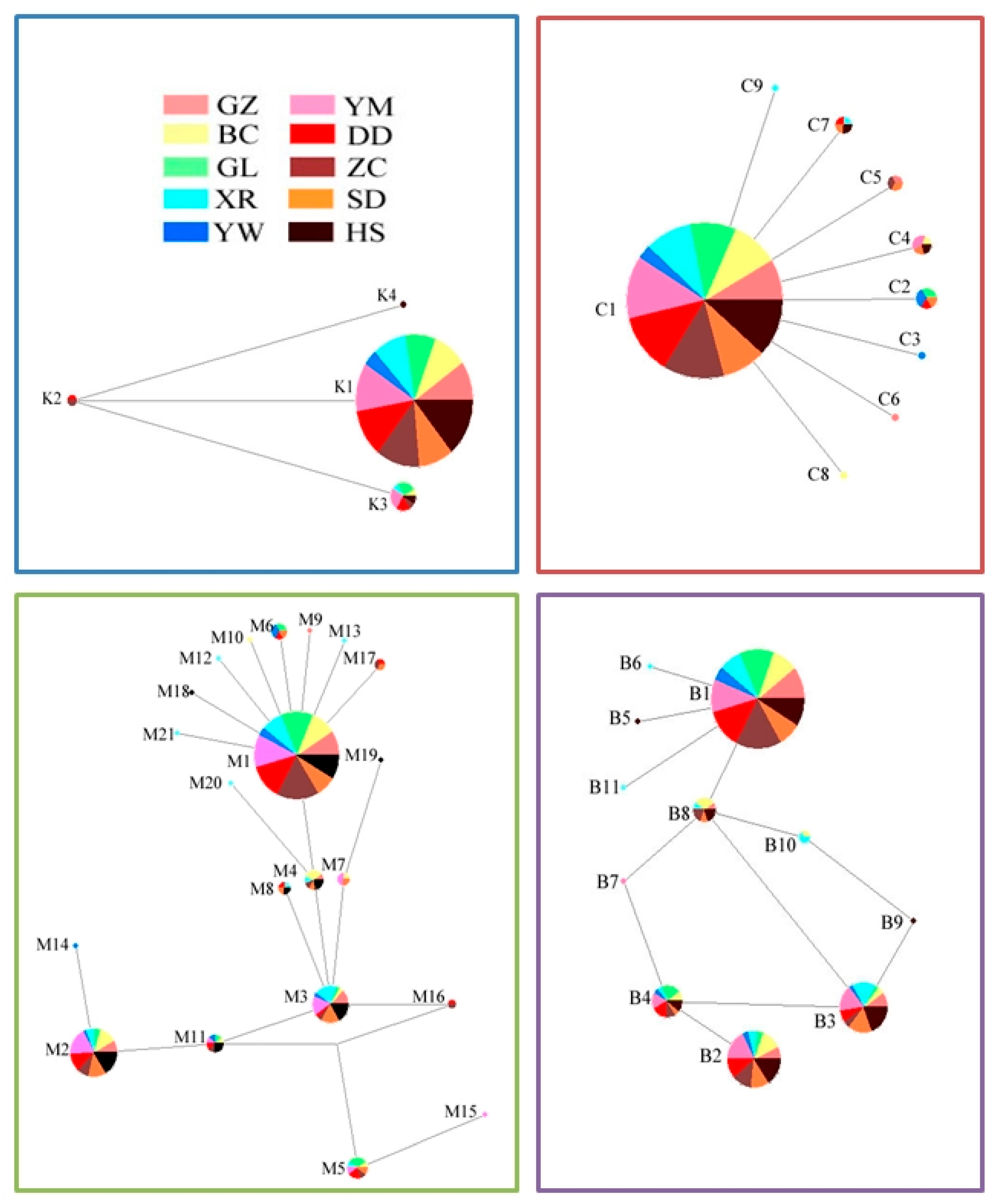
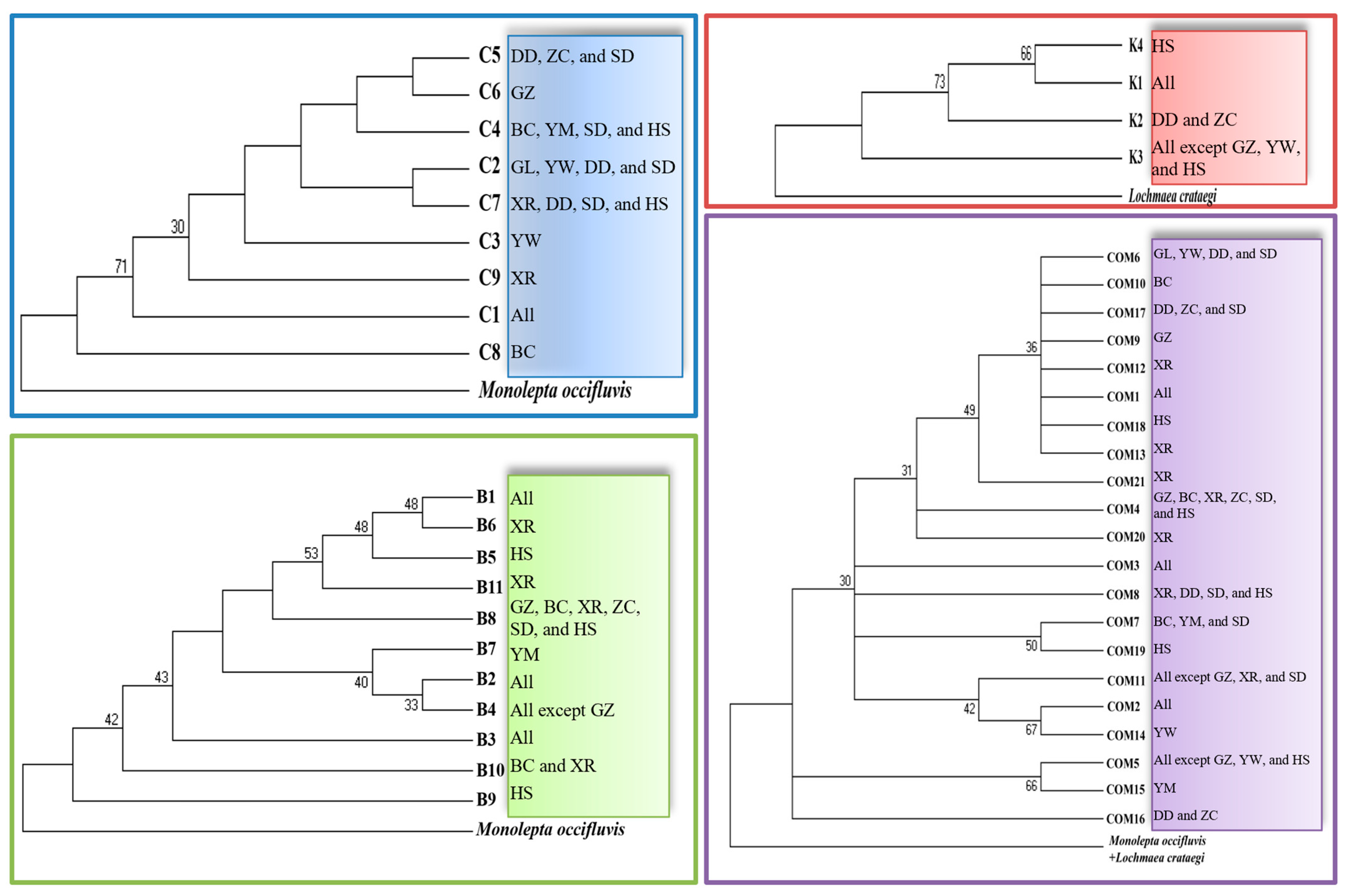
| Population Code | Host | Sampling Methods | Molecular Samples | PCR-Positive Samples | Sampling Date | Harvest Date | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Y | S | O | COI | COII | Cytb | COM | 2022 | 2023 | 2022 | 2023 | |||
| ZC | weed | - | ✓ | - | 40 | 36 | 40 | 40 | 36 | 06-01~10-17 | 06-01~10-16 | - | - |
| DD | soybean | ✓ | ✓ | - | 40 | 38 | 39 | 35 | 35 | 06-01~10-17 | 06-01~10-16 | 09-25 | 09-22~09-30 |
| BC | cabbage | ✓ | - | ✓ | 30 | 29 | 30 | 30 | 29 | 09-08~10-17 | 08-22~10-16 | 10-10 | 10-01 |
| YM | maize | ✓ | - | ✓ | 40 | 38 | 40 | 39 | 38 | 06-01~10-17 | 06-01~10-16 | 10-12 | 10-07 |
| YW | maize (L) | ✓ | - | ✓ | 12 | 11 | 12 | 12 | 11 | 07-16~10-17 | 07-13~10-16 | 10-12 | 10-07 |
| GZ | millet | ✓ | - | ✓ | 30 | 25 | 30 | 28 | 25 | 06-01~10-17 | 06-01~10-16 | 10-04 | 10-11 |
| GL | sorghum | ✓ | - | ✓ | 30 | 29 | 29 | 29 | 29 | 06-01~10-17 | 06-01~10-16 | 10-04 | 10-06 |
| XR | sunflower | ✓ | - | ✓ | 30 | 29 | 30 | 30 | 29 | 06-01~10-17 | 06-01~10-16 | 08-15~09-30 | 08~18-09~25 |
| HS | peanut | ✓ | - | ✓ | 55 | 35 | 44 | 38 | 34 | 06-01~10-17 | 06-01~10-16 | 09-06~10-07 | 09~04-09~28 |
| XM | wheat | ✓ | - | ✓ | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 06-01~07-17 | 06-01~07-16 | 07-20 | 07-19 |
| SD | rice | ✓ | - | ✓ | 30 | 29 | 30 | 29 | 29 | 06-01~10-17 | 06-01~10-16 | 10-02 | 10-03 |
| Gene | Primer Sequences | Primer Source |
|---|---|---|
| COI-F | AAAAATAGATTTTATCTAAGCCTTA | Designed from: NCBI MT178239 |
| COI-R | TATGCTCGAGTATCTACATCTATAC | |
| COII-F | GAGCATCTCCTTTAATAGAACA | [13] |
| COII-R | GTATAAATGAGTGATTGGCTCC | |
| Cytb-F | AATTATGGWTGAYTAATTCGAAC | [13] |
| Cytb-R | AAATATCATTCAGGTTGAATATG |
| Population Code | Number of Haplotypes (H) | Haplotype Diversity (Hd) | Average Number of Nucleotide Differences (K) | Nucleotide Diversity (Pi) | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| COI | COII | Cytb | COM | COI | COII | Cytb | COM | COI | COII | Cytb | COM | COI | COII | Cytb | COM | |
| GZ | 2 | 1 | 4 | 5 | 0.0800 | 0.0000 | 0.5158 | 0.6100 | 0.0800 | 0.0000 | 1.3836 | 1.5733 | 0.0001 | 0.0000 | 0.0032 | 0.0010 |
| BC | 3 | 2 | 6 | 8 | 0.1354 | 0.0666 | 0.6781 | 0.6970 | 0.1379 | 0.1333 | 1.7770 | 2.0098 | 0.0002 | 0.0003 | 0.0041 | 0.0013 |
| GL | 2 | 2 | 4 | 6 | 0.1330 | 0.1921 | 0.4137 | 0.5197 | 0.1330 | 0.3842 | 1.2315 | 1.7487 | 0.0002 | 0.0008 | 0.0028 | 0.0011 |
| XR | 3 | 2 | 8 | 10 | 0.1354 | 0.0666 | 0.7333 | 0.7635 | 0.1379 | 0.1333 | 1.6689 | 1.9064 | 0.0002 | 0.0003 | 0.0038 | 0.0012 |
| YW | 3 | 1 | 4 | 6 | 0.4727 | 0.0000 | 0.5606 | 0.8000 | 0.5090 | 0.0000 | 1.6818 | 2.2909 | 0.0008 | 0.0000 | 0.0039 | 0.0015 |
| YM | 2 | 2 | 5 | 7 | 0.1024 | 0.1423 | 0.6882 | 0.6899 | 0.1024 | 0.2846 | 1.8461 | 2.1479 | 0.0001 | 0.0006 | 0.0042 | 0.0014 |
| DD | 4 | 3 | 4 | 9 | 0.1536 | 0.1484 | 0.5395 | 0.6201 | 0.1578 | 0.2456 | 1.6134 | 2.0571 | 0.0002 | 0.0005 | 0.0037 | 0.0013 |
| ZC | 2 | 3 | 5 | 8 | 0.0555 | 0.0987 | 0.4628 | 0.4746 | 0.0555 | 0.1474 | 1.2871 | 1.4492 | 0.0000 | 0.0003 | 0.0029 | 0.0009 |
| SD | 5 | 2 | 5 | 9 | 0.2610 | 0.0666 | 0.6871 | 0.7758 | 0.2758 | 0.1333 | 1.7536 | 2.1674 | 0.0004 | 0.0003 | 0.0040 | 0.0014 |
| HS | 3 | 2 | 7 | 8 | 0.1126 | 0.0454 | 0.7468 | 0.7664 | 0.1142 | 0.0909 | 1.8662 | 2.0570 | 0.0001 | 0.0002 | 0.0043 | 0.0013 |
| Total | 9 | 4 | 11 | 21 | 0.1412 | 0.0893 | 0.6144 | 0.6663 | 0.1456 | 0.1663 | 1.6229 | 1.9295 | 0.0002 | 0.0003 | 0.0037 | 0.0013 |
| Source of Variation | Variance Components | Percentage of Variation | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| COI | COII | Cytb | COM | COI | COII | Cytb | COM | |
| Among populations | 0.00085 | −0.00041 | 0.006 | 0.00377 | 1.17067 | −0.4957 | 0.73946 | 0.39074 |
| Within populations | 0.07205 | 0.08352 | 0.80607 | 0.96140 | 98.82933 | 100.4957 | 99.26054 | 99.60926 |
| GZ | BC | GL | XR | YW | YM | DD | ZC | SD | HS | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GZ | 0.00000 0.00000 | 0.07949 0.00000 | 0.00000 0.00000 | 0.00000 0.00000 | 0.03975 0.01019 | 0.03187 0.00000 | 0.00779 0.00000 | 0.00000 0.00000 | 0.00000 0.01960 | |
| BC | 0.00000 0.00000 | 0.00441 0.01550 | 0.00000 0.00000 | 0.00000 0.00000 | 0.00000 0.00000 | 0.00000 0.00000 | 0.00000 0.01543 | 0.00000 0.00000 | 0.00000 0.00000 | |
| GL | 0.02132 0.00000 | 0.01818 0.01981 | 0.00441 0.01496 | 0.01868 0.00000 | 0.00000 0.05745 | 0.00000 0.00000 | 0.00683 0.00000 | 0.00441 0.05175 | 0.05724 0.08945 | |
| XR | 0.00000 0.00000 | 0.00000 0.00000 | 0.01818 0.02218 | 0.00000 0.00000 | 0.00000 0.00000 | 0.00000 0.00000 | 0.00000 0.01217 | 0.00000 0.00000 | 0.00000 0.00186 | |
| YW | 0.14270 0.00000 | 0.12279 0.00000 | 0.02783 0.00000 | 0.12279 0.00000 | 0.00000 0.00000 | 0.00000 0.00000 | 0.00000 0.00000 | 0.00000 0.00000 | 0.00000 0.00000 | |
| YM | 0.01353 0.04262 | 0.00000 0.00000 | 0.03471 0.08112 | 0.01333 0.01104 | 0.17475 0.00000 | 0.00000 0.00000 | 0.00000 0.06583 | 0.00000 0.00000 | 0.02462 0.00000 | |
| DD | 0.00000 0.00000 | 0.00000 0.00000 | 0.00000 0.00000 | 0.00000 0.00000 | 0.08682 0.00000 | 0.01093 0.00690 | 0.00000 0.00000 | 0.00000 0.00000 | 0.01303 0.01555 | |
| ZC | 0.00232 0.00000 | 0.00304 0.01335 | 0.03031 0.00000 | 0.00304 0.01509 | 0.20990 0.00000 | 0.01743 0.07804 | 0.00000 0.00000 | 0.00000 0.05830 | 0.00000 0.09312 | |
| SD | 0.00000 0.02277 | 0.00000 0.00000 | 0.00000 0.06908 | 0.00000 0.00000 | 0.03676 0.00000 | 0.00000 0.00000 | 0.00000 0.00000 | 0.00000 0.06218 | 0.00000 0.00000 | |
| HS | 0.00000 0.04104 | 0.00000 0.00000 | 0.02053 0.08785 | 0.00000 0.00000 | 0.15081 0.00000 | 0.00000 0.00000 | 0.00000 0.01361 | 0.00028 0.08216 | 0.00000 0.00000 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, W.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, J.; Gao, Y. Occurrence and Genetic Variation of Monolepta hieroglyphica (Motschulsky, 1858) (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae), a Newly Emerging Pest, Among Hosts in Northeast China. Insects 2025, 16, 605. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16060605
Sun W, Zhang X, Zhou J, Gao Y. Occurrence and Genetic Variation of Monolepta hieroglyphica (Motschulsky, 1858) (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae), a Newly Emerging Pest, Among Hosts in Northeast China. Insects. 2025; 16(6):605. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16060605
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Wei, Xiuhua Zhang, Jiachun Zhou, and Yuebo Gao. 2025. "Occurrence and Genetic Variation of Monolepta hieroglyphica (Motschulsky, 1858) (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae), a Newly Emerging Pest, Among Hosts in Northeast China" Insects 16, no. 6: 605. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16060605
APA StyleSun, W., Zhang, X., Zhou, J., & Gao, Y. (2025). Occurrence and Genetic Variation of Monolepta hieroglyphica (Motschulsky, 1858) (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae), a Newly Emerging Pest, Among Hosts in Northeast China. Insects, 16(6), 605. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16060605






