The Sensory Equipment of Diving Lice, a Host Ecology-Based Comparative Study
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Insects
2.2. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.3. Sensilla Classification and Terminology
3. Results
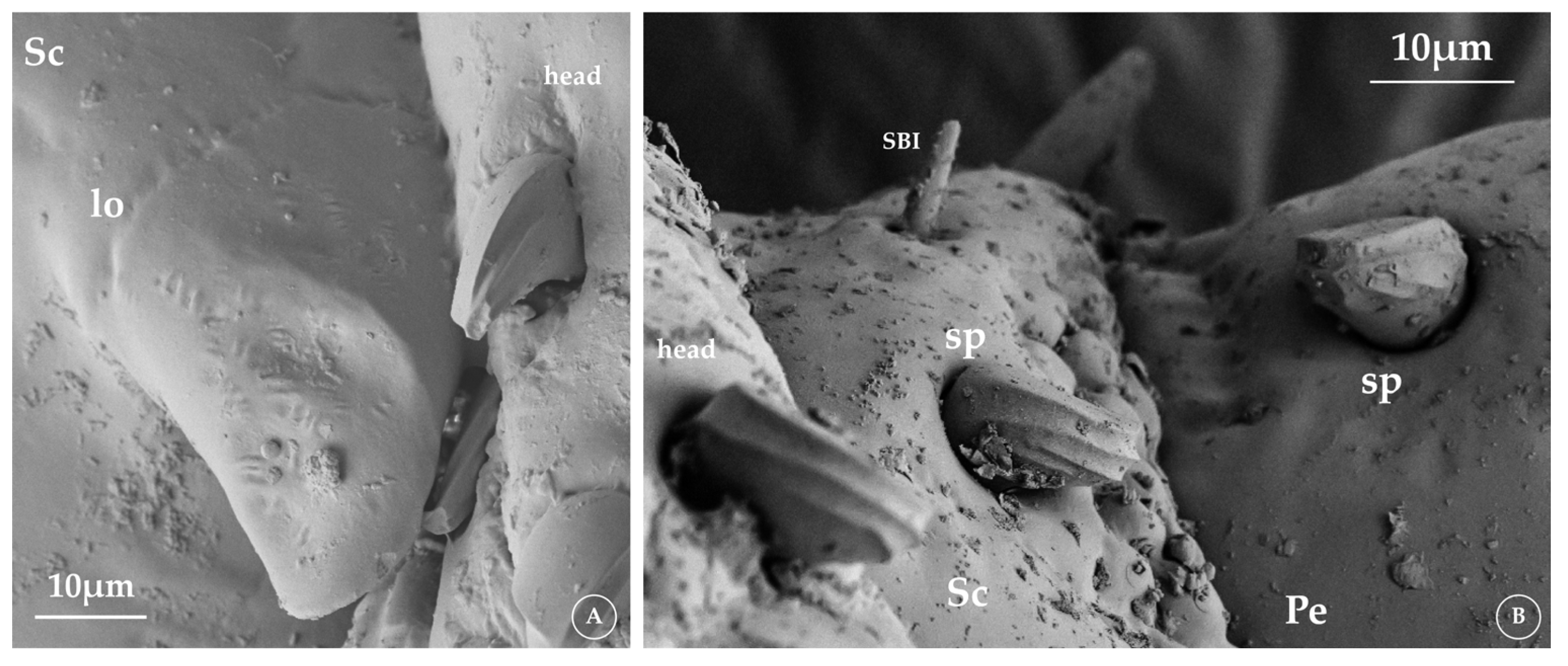
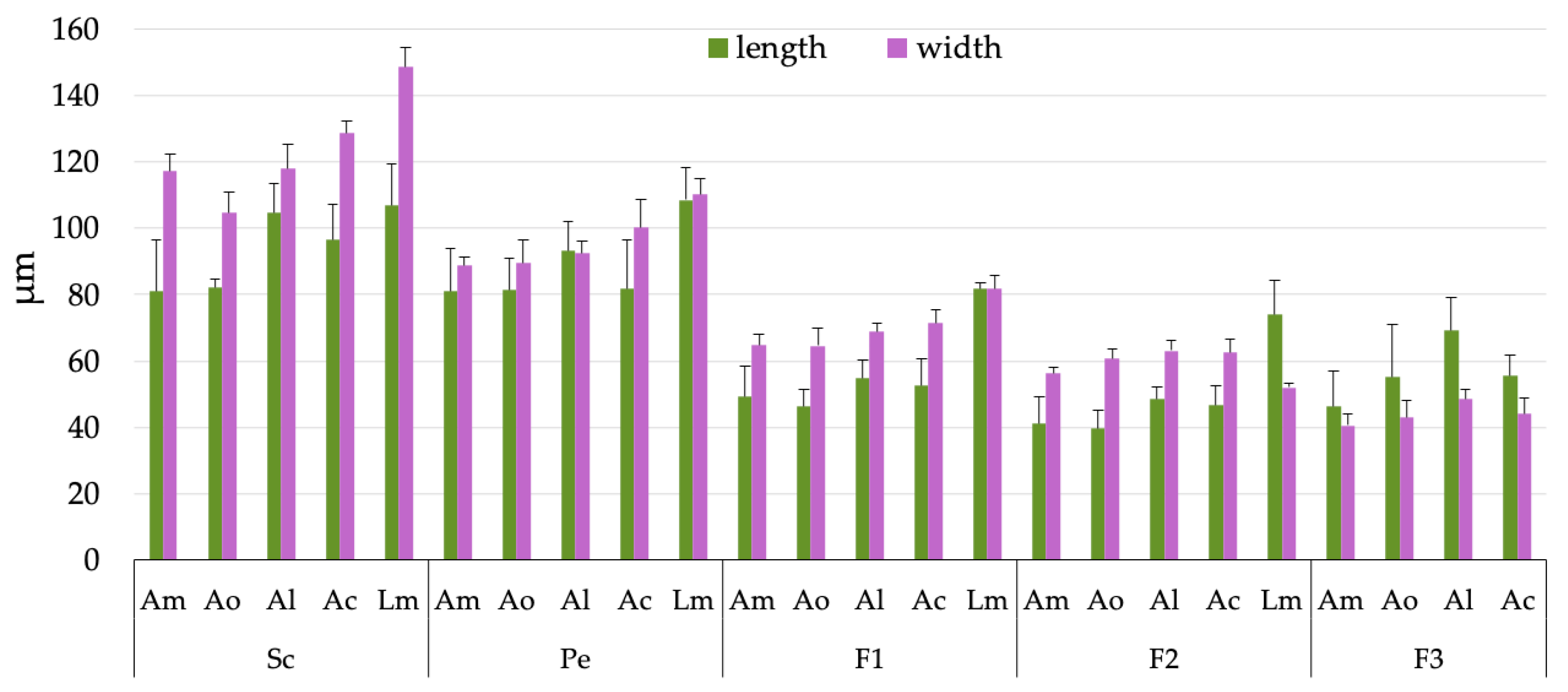
3.1. Antennae Description
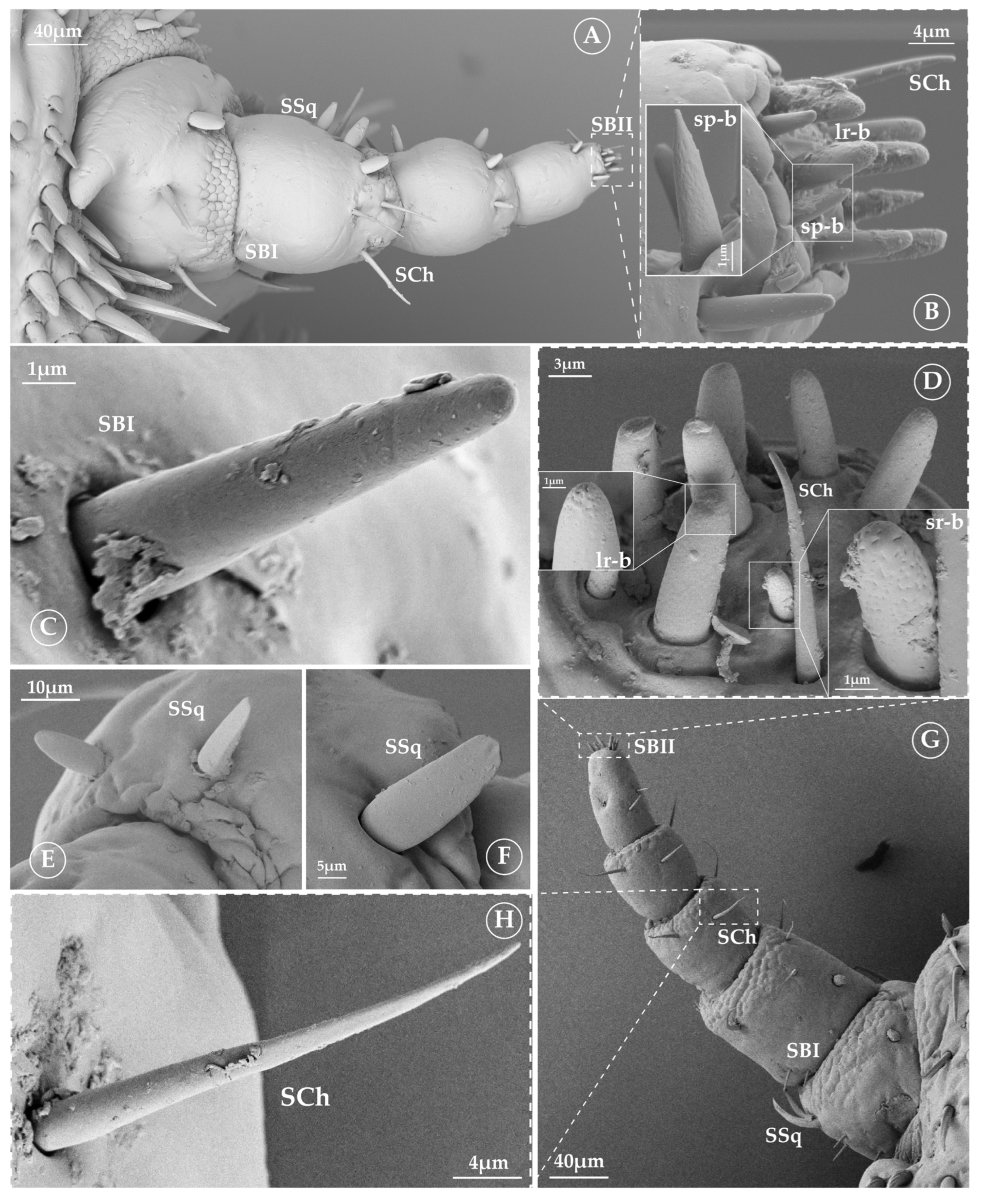
3.2. Sensilla Type and Its Morphology
3.2.1. Sensilla Squamiformia (SSq)
3.2.2. Sensilla Chaetica (SCh)
3.2.3. Sensilla Basiconica (SB)
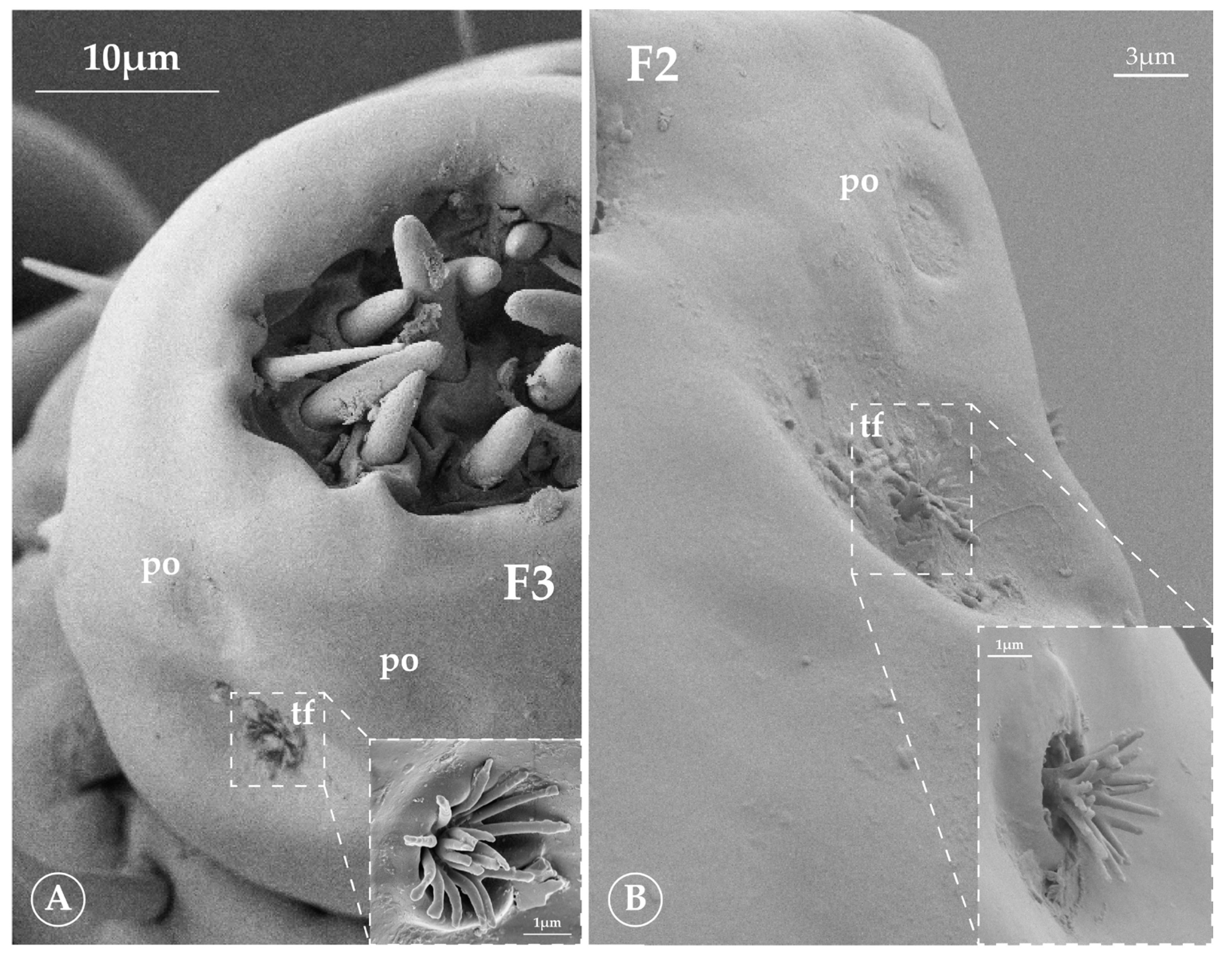
3.2.4. Tuft Organ (tf)
3.2.5. Pore Organ (po)
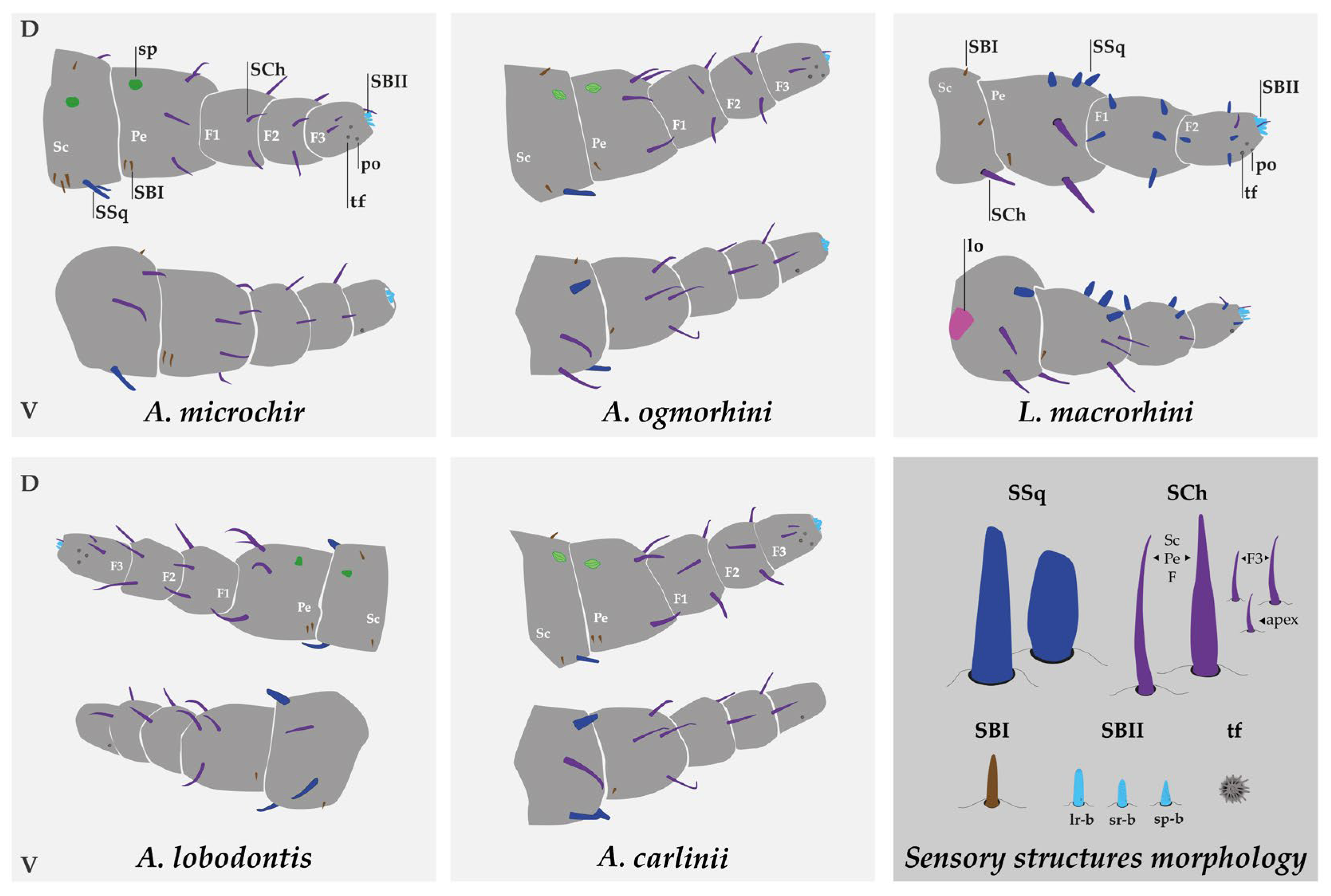
3.3. Sensory Structure Description and Distribution for Species
3.3.1. Description of Antarctophthirus microchir
3.3.2. Description of A. ogmorhini
3.3.3. Description of A. lobodontis
3.3.4. Description of A. carlinii
3.3.5. Description of Lepidophthirus macrorhini
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SCh | Sensilla chaetica |
| SSq | Sensilla squamiformia |
| SB | Sensilla basiconica |
| sp-b | Short pointed basiconica |
| lr-b | Large rounded basiconica |
| sr-b | Short rounded basiconica |
| Am | Antarctophthirus microchir |
| Ac | Antarctophthirus carlinii |
| Al | Antarctophthirus lobodontis |
| Ao | Antarctophthirus ogmorhini |
| Lm | Lepidophthirus macrorhini |
| Sc | Scape |
| Pe | Pedicel |
| F | Flagellomere |
References
- Durden, L.A.; Musser, G.G. The sucking lice (Insecta, Anoplura) of the world: A taxonomic checklist with records of mammalian hosts and geographical distributions. Bull. Am. Mus. Nat. Hist. 1994, 218, 1–90. [Google Scholar]
- Leonardi, M.S.; Palma, R.L. Review of the systematics, biology and ecology of lice from pinnipeds and river otters (Insecta: Phthiraptera: Anoplura: Echinophthiriidae). Zootaxa 2013, 3630, 445–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leonardi, M.S.; Poljak, S.; Carlini, P.; Galliari, J.; Bobinac, M.; Santos, M.; Márquez, M.E.; Negrete, J. Antarctophthirus carlinii (Anoplura: Echinophthiriidae), a new species from the Weddell seal Leptonychotes weddellii. Parasitol. Res. 2014, 113, 3947–3951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, B. Diving behaviour. In Encyclopedia of Marine Mammals; Perrin, W.F., Würsig, B., Thewissen, J.G.M., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2009; pp. 321–329. [Google Scholar]
- Costa, D.P.; Huckstadt, L.A.; Crocker, D.E.; McDonald, B.I.; Goebel, M.E.; Fedak, M.A. Approaches to studying climatic change and its role on the habitat selection of Antarctic pinnipeds. Integr. Comp. Biol. 2010, 50, 1018–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McIntyre, T.; De Bruyn, N.; Ansorge, I.; Bester, M.; Bornemann, H.; Plötz, J.; Tosh, C. A lifetime at depth: Vertical distribution of southern elephant seals in the water column. Polar Biol. 2010, 33, 1037–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teilmann, J.; Born, E.W.; Acquarone, M. Behaviour of ringed seals tagged with satellite transmitters in the North Water Polynya during fast-ice formation. Can. J. Zool. 1999, 77, 1934–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Light, J.E.; Smith, V.S.; Allen, J.M.; Durden, L.A.; Reed, D.L. Evolutionary history of mammalian sucking lice (Phthiraptera: Anoplura). BMC Evol. Biol. 2010, 10, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonardi, M.S.; Virrueta Herrera, S.; Sweet, A.; Negrete, J.; Johnson, K.P. Phylogenomic analysis of seal lice reveals codivergence with their hosts. Syst. Entomol. 2019, 44, 699–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonardi, M.S.; Crespo, J.E.; Soto, F.; Lazzari, C.R. How did seal lice turn into the only truly marine insects? Insects 2022, 13, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.C. Ecology and morphological adaptation of the sucking lice (Anoplura, Echinophthiriidae) on the northern fur seal. Rapp. P.-v. Reun. Cons. Int. Explor. Mer 1975, 169, 540–551. [Google Scholar]
- Aznar Avendaño, F.J.; Leonardi, M.S.; Berón Vera, B.; Vales, D.G.; Ameghino, S.P.; Raga, J.A.; Crespo, E.A. Population dynamics of Antarctophthirus microchir (Anoplura: Echinophthiriidae) in pups from South American sea lion, Otaria flavescens, in northern Patagonia. Parasitology 2009, 136, 527–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonardi, M.S.; Crespo, E.A.; Raga, J.A.; Aznar, F.J. Lousy mums: Patterns of vertical transmission of an amphibious louse. Parasitol. Res. 2013, 112, 3315–3323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leonardi, M.S.; Lazzari, C.R. Uncovering deep mysteries: The underwater life of an amphibious louse. J. Insect Physiol. 2014, 71, 164–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, C.-S.; Chang, Z.-M.; Zu, Z.-Y.; Han, L.; Chen, X.-S.; Long, J.-K. Comparison of morphological characteristics of antennae and antennal sensilla among four species of bumblebees (Hymenoptera: Apidae). Insects 2023, 14, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.C. Coevolution of Parasitic Arthropods and Mammals; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1985; ISBN 978-0-471-08546-1. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, F.H. Scanning electron microscopy of Echinophthirius horridus (von Olfers), Antarctophthirus callorhini (Osborn), and Proechinophthirius fluctus (Ferris) with emphasis on the antennal structures (Anoplura: Echinophthiriidae). J. Parasitol. 1971, 57, 668–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castro, D.D.C.; Romero, M.D.; Dreon, M. Ultrastructure of Proechinophthirus zumpti (Anoplura, Echinophthiriidae) by scanning electron microscopy. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 2002, 97, 813–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehlhorn, B.; Mehlhorn, H.; Plötz, J. Light and scanning electron microscopical study on Antarctophthirus ogmorhini lice from the Antarctic seal Leptonychotes weddellii. Parasitol. Res. 2002, 88, 651–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonardi, M.S.; Crespo, J.E.; Soto, F.A.; Vera, R.B.; Rua, J.C.; Lazzari, C.R. Under pressure: The extraordinary survival of seal lice in the depth of the sea. J. Exp. Biol. 2020, 223, jeb226811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, C.A.; Rasband, W.S.; Eliceiri, K.W. NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snodgrass, R.E. Principles of Insect Morphology; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1935. [Google Scholar]
- Ortega Insaurralde, I.; Minoli, S.; Toloza, A.C.; Picollo, M.I.; Barrozo, R.B. The sensory machinery of the head louse Pediculus humanus capitis: From the antennae to the brain. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega-Insaurralde, I.; Picollo, M.I.; Barrozo, R.B. Sensory features of the human louse antenna: New contributions and comparisons between ecotypes. Med. Vet. Entomol. 2021, 35, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adobe. Adobe Illustrator, Version 2021; Adobe Inc.: San Jose, CA, USA, 2021.
- Wigglesworth, V.B. The sensory physiology of the human louse Pediculus humanus corporis De Geer (Anoplura). Parasitology 1941, 33, 67–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemeth, D.C.; Ammagarahalli, B.; Layne, J.E.; Rollmann, S.M. Evolution of coeloconic sensilla in the peripheral olfactory system of Drosophila mojavensis. J. Insect Physiol. 2018, 110, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Correlative Nomenclature | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lm | Al | Ao | Ac | Am | Eh/Acal/Pf | Pz | |||
| putative function | structure | position (#) | position (#) | position (#) | position (#) | position (#) | Miller Jr., 1971 [17] | Castro et al., 2002 [18] | |
| mechanosensory | SSq | Sc(1), Pe(3), F1(6), F2(5) | Sc(3) | Sc(2) | Sc(3) | Sc(2) | undescribed | undescribed | |
| mechanosensory | SCh | Sc(3), Pe(5), F1(1), F2(2) | Sc(1), Pe(7), F1(4), F2(4), F3(3) | Sc(2), Pe(7), F1(4), F2(4), F3(3) | Sc(1), Pe(6), F1(4), F2(4), F3(3) | Sc(2), Pe(8), F1(4), F2(4), F3(3) | hair | caeloconic senosira tactile | |
| mechanosensory | SBI | Sc(2), Pe(2) | Sc(3), Pe(3) | Sc(2), Pe(2) | Sc(2), Pe(3) | Sc(4), Pe(4) | undescribed | undescribed | |
| chemosensory (olfactory) | SBII | lr-b | F2(6) | F3(6) | F3(6) | F3(6) | F3(6) | undescribed | apical chemoreceptors |
| chemosensory (olfactory) | sr-b/sp-b | F2(4) | F3(4) | F3(3) | F3(3) | F3(4) | undescribed | ||
| thermo-hygro sensory | tf | F2(2) | F3(2) | F3(2) | F3(2) | F3(2) | sensilla basiconica | placodeas olfactory chemoreceptor | |
| chemo-thermo sensory | po | F2(2) | F3(2) | F3(2) | F3(2) | F3(2) | pore organ | undescribed | |
| - | spine | - | Sc(1), Pe(1) | Sc(1), Pe(1) | Sc(1), Pe(1) | Sc(1), Pe(1) | campaniform organ | spines | |
| - | cuticular lobe | Sc(1) | - | - | - | - | lobe | undescribed | |
| Am | Ao | Al | Ac | Lm | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| length ± SD | length ± SD | length ± SD | length ± SD | length ± SD | |||
| Sc | Squamiformia | 33.28 ± 4.97 | 30.43 ± 6.54 | 31.65 ± 5.61 | 34.57 ± 5.24 | 23.4 ± 1.54 | |
| Chaetica | 26.39 ± 7.78 | 35.72 ± 8.65 | 37.96 ± 5.00 | 50.01 ± 7.35 | 36.77 ± 6.07 | ||
| Basiconica I | 11.31 ± 2.73 | 9.32 ± 0.96 | 12.73 ± 2.68 | 10.76 ± 1.90 | 11.41 ± 1.47 | ||
| Pe | Squamiformia | - | - | - | - | 21.4 ± 3.40 | |
| Chaetica | 27.61 ± 7.26 | 28.36 ± 7.71 | 29.73 ± 8.01 | 30.48 ± 7.21 | 44.01 ± 10.38 | ||
| Basiconica I | 11.06 ± 2.31 | 8.25 ± 1.22 | 14.59 ± 7.16 | 8.90 ± 2.32 | 10.11 ± 1.44 | ||
| F1 | Squamiformia | - | - | - | - | 18.99 ± 4.98 | |
| Chaetica | 26.94 ± 7.97 | 27.7 ± 7.33 | 27.28 ± 10.35 | 28.27 ± 7.83 | 19.29 ± 4.90 | ||
| F2 | Squamiformia | - | - | - | - | 11.34 ± 2.23 | |
| Chaetica | 24.8 ± 7.56 | 27.48 ± 6.15 | 29.29 ± 12.57 | 22.94 ± 5.59 | 15.05 ± 2.08 | ||
| F2/F3 | Squamiformia | - | - | - | - | - | |
| Chaetica | 12.09 ± 4.44 | 11.92 ± 6.8 | 14.88 ± 8.19 | 11.27 ± 3.4 | |||
| Basiconica II | lr-b | 9.16 ± 1.87 | 7.23 ± 1.30 | 8.68 ± 1.07 | unkown | 8.40 ± 1.26 | |
| sr-b | 6.01 ± 1.14 | 5.27 ± 1.11 | 5.58 ± 0.41 | unkown | - | ||
| sp-b | - | - | - | - | 6.58 ± 0.96 | ||
| Pore Organ | 4.76 ± 0.46 | unkown | unkown | 3.80 ± 0.27 | 4.35 ± 0.22 | ||
| Tuft Organ | 4.51 ± 0.67 | 3.76 ± 0.80 | 4.60 ± 0.41 | unkown | 3.53 ± 0.49 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Olivera, P.; Lazzari, C.R.; Leonardi, M.S. The Sensory Equipment of Diving Lice, a Host Ecology-Based Comparative Study. Insects 2025, 16, 574. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16060574
Olivera P, Lazzari CR, Leonardi MS. The Sensory Equipment of Diving Lice, a Host Ecology-Based Comparative Study. Insects. 2025; 16(6):574. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16060574
Chicago/Turabian StyleOlivera, Paula, Claudio R. Lazzari, and María Soledad Leonardi. 2025. "The Sensory Equipment of Diving Lice, a Host Ecology-Based Comparative Study" Insects 16, no. 6: 574. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16060574
APA StyleOlivera, P., Lazzari, C. R., & Leonardi, M. S. (2025). The Sensory Equipment of Diving Lice, a Host Ecology-Based Comparative Study. Insects, 16(6), 574. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16060574







