Comparative Transcriptome Analysis Reveals the Effects of a High-Protein Diet on Silkworm Midgut
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Insect
2.2. Protein Treatment and RNA Preparation
2.3. Library Construction and Illumina Hiseq Xten Sequencing
2.4. Read Mapping
2.5. Differential Expression Analysis
2.6. Functional Annotation and Enrichment of DEGs
2.7. Gene Set Enrichment Analysis (GSEA)
2.8. Expression Validation of DEGs from RNA-Seq by qRT-PCR
2.9. Assessment of Total Nitrogen (TN) in Silkworm Feces and Enzyme Activity Assay
2.10. Data Processing
3. Results
3.1. Determination of HPD
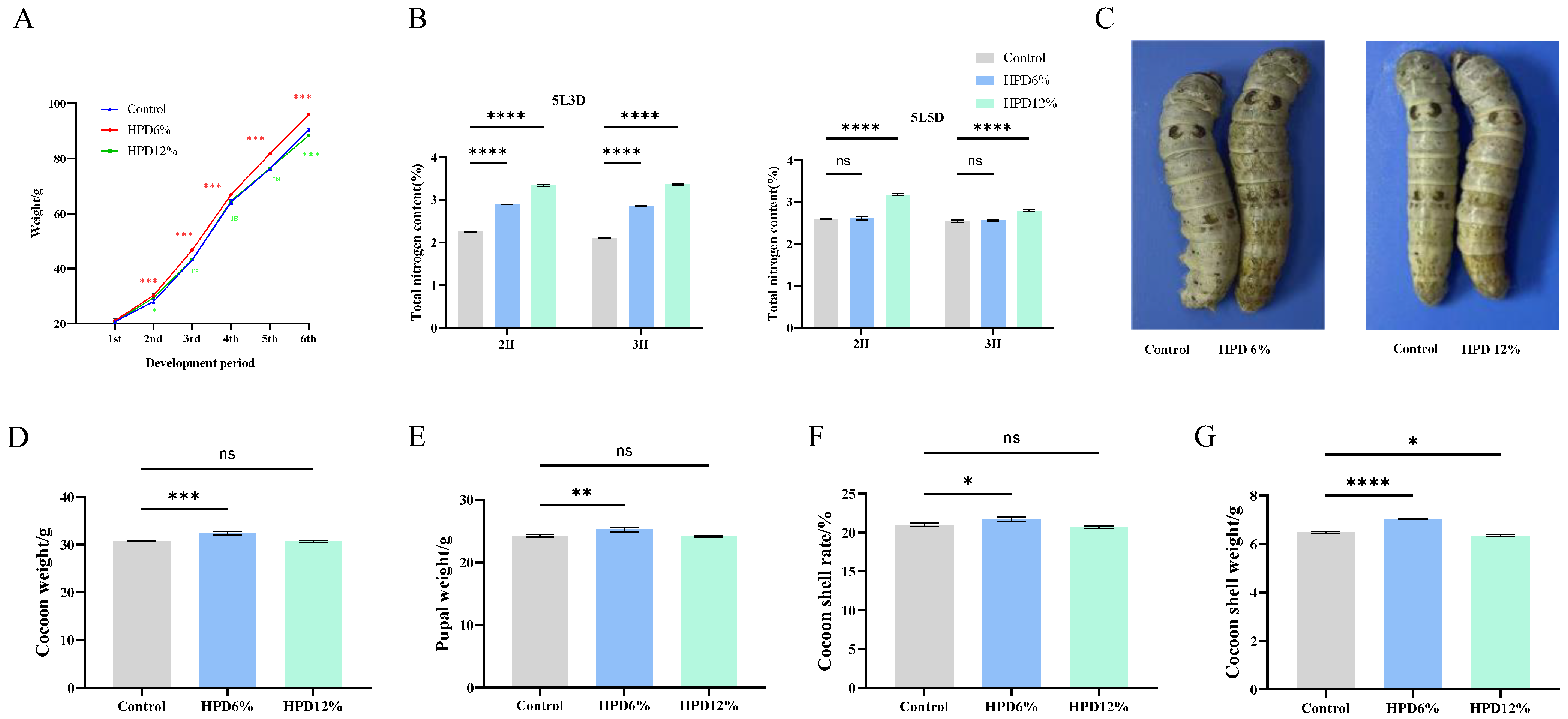
3.2. Effects of HPD on Larval Weight and Economic Character of Cocoon
3.3. Transcriptome Profiling of DEGs
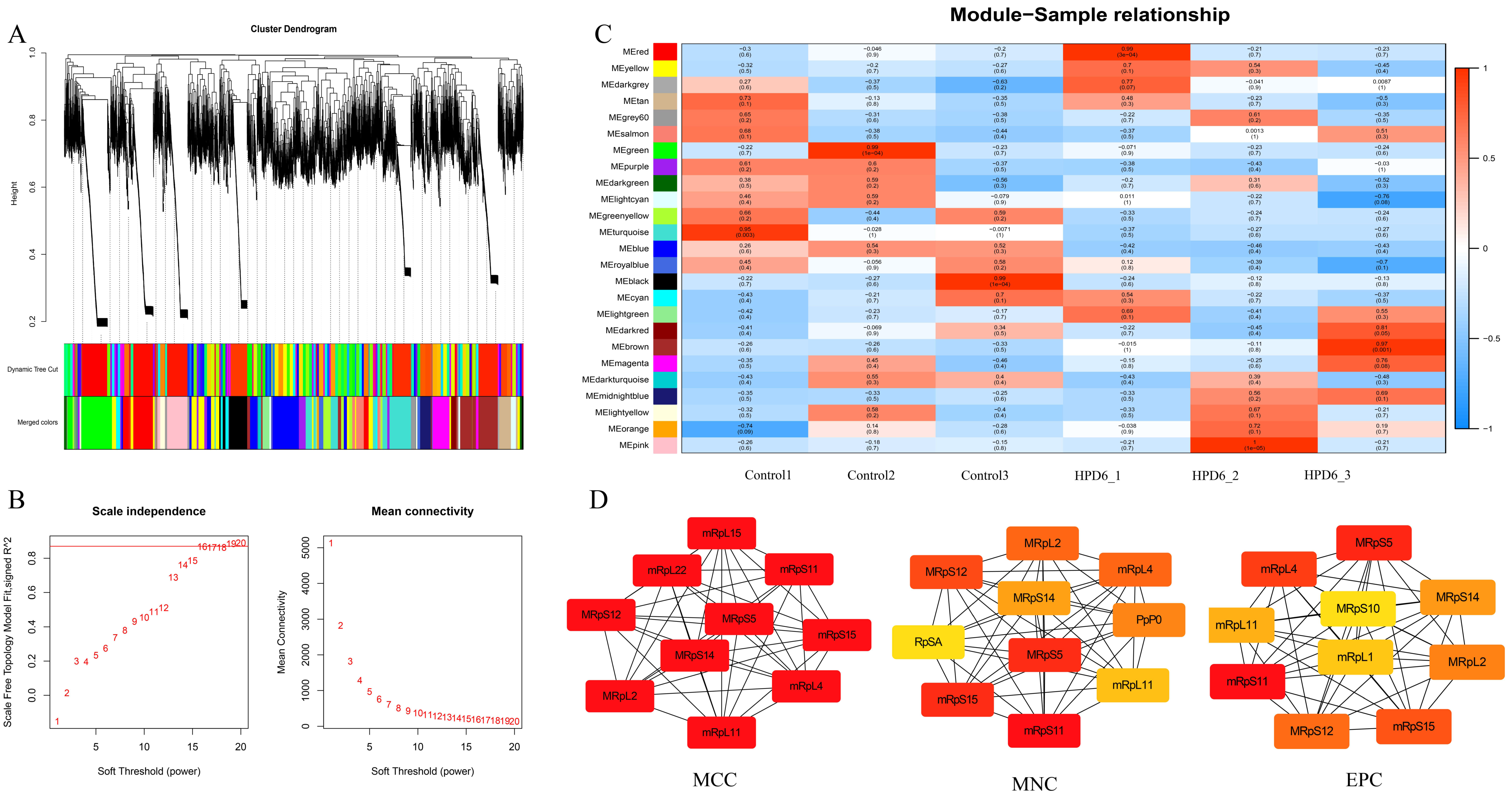
3.4. Weighted Correlation Network Analysis (WGCNA)
3.5. Functional Annotation and Enrichment Analysis of DEGs
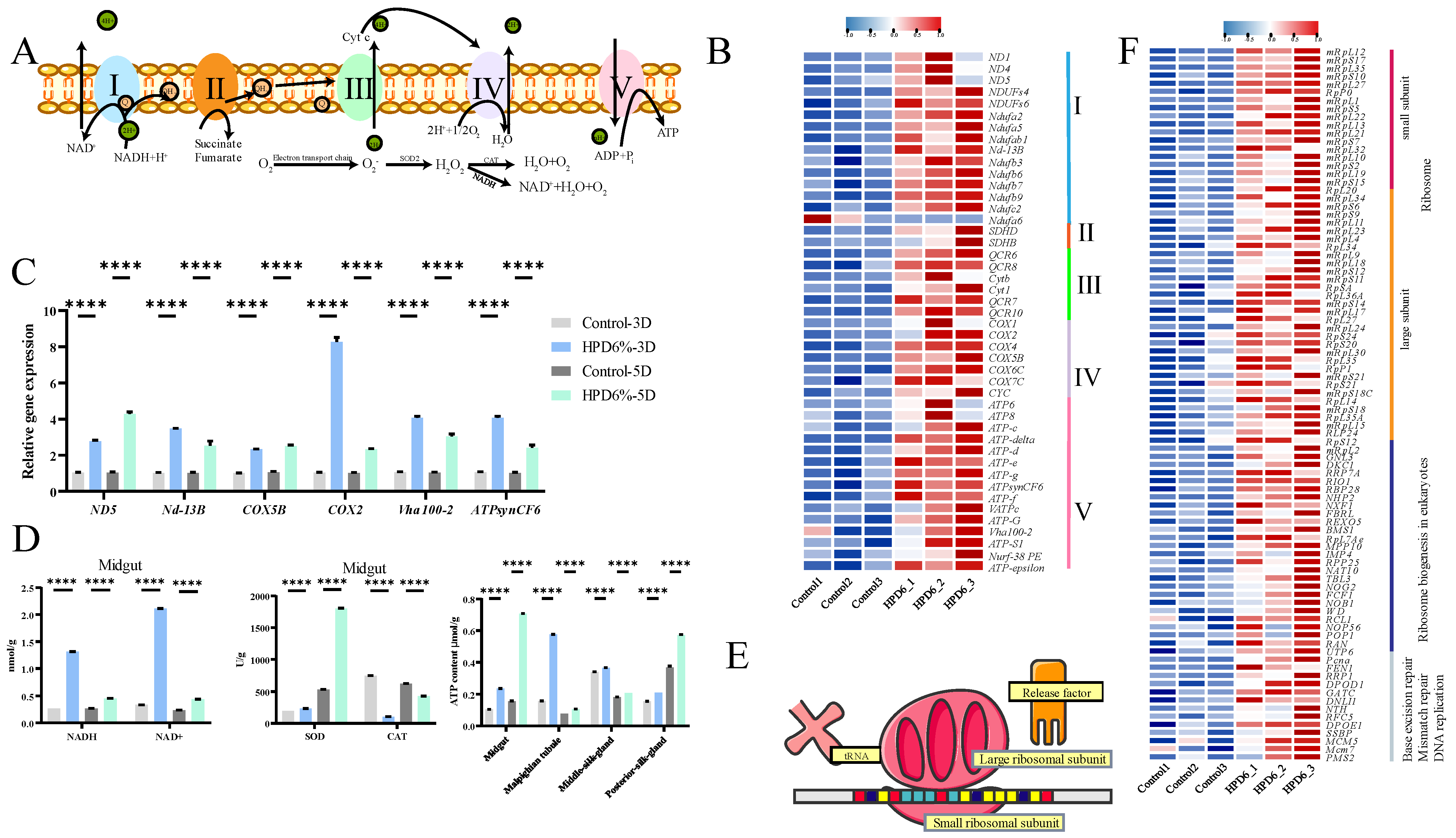
3.6. HPD 6% Activation Oxidative Phosphorylation and Nuclear Transcription
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xia, Q.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Li, D.; Xuan, Z.; Li, Z.; Dai, F.; Li, Y.; Cheng, D.; Li, R.; et al. Complete Resequencing of 40 Genomes Reveals Domestication Events and Genes in Silkworm (Bombyx). Science 2009, 326, 433–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurahashi, H.; Atiwetin, P.; Nagaoka, S.; Miyata, S.; Kitajima, S.; Sugimura, Y. Absorption of Mulberry Root Urease to the Hemolymph of the Silkworm, Bombyx mori. J. Insect Physiol. 2005, 51, 1055–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, P.; Zhang, M.; Qian, P.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Wu, Y. iTRAQ-Based Quantitative Proteomic Analysis of Digestive Juice across the First 48 Hours of the Fifth Instar in Silkworm Larvae. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 6113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borah, S.D.; Boro, P. A Review of Nutrition and Its Impact on Silkworm. J. Entomol. Zool. Stud. 2020, 8, 1921–1925. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, S.; Zhang, X.; He, Y.; Shuai, J.; Chen, X.; Ling, E. Expression of Antimicrobial Peptide Genes in Bombyx Mori Gut Modulated by Oral Bacterial Infection and Development. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2010, 34, 1191–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallet-Gely, I.; Lemaitre, B.; Boccard, F. Bacterial Strategies to Overcome Insect Defences. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2008, 6, 302–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Xie, Y.; Li, F.; Ma, L.; Sun, S.; Wu, Y.; Wang, B.; Wang, J.; Hong, F.; et al. The Adverse Effects of Phoxim Exposure in the Midgut of Silkworm, Bombyx mori. Chemosphere 2014, 96, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rinderer, K.T.; Dell Elliott, K. Worker Honey Beel Response to Infection with Nosema apis: Influence of Diet. J. Econ. Entomol. 1977, 70, 431–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dussutour, A.; Simpson, S.J. Ant Workers Die Young and Colonies Collapse When Fed a High-Protein Diet. Proc. R. Soc. B 2012, 279, 2402–2408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lihoreau, M.; Poissonnier, L.-A.; Isabel, G.; Dussutour, A. Drosophila Females Trade off Good Nutrition with High Quality Oviposition Sites When Choosing Foods. J. Exp. Biol. 2016, 219, 2514–2524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felton, G.W.; Donato, K.K.; Broadway, R.M.; Duffey, S.S. Impact of Oxidized Plant Phenolics on the Nutritional Quality of Dietar Protein to a Noctuid Herbivore, Spodoptera exigua. J. Insect Physiol. 1992, 38, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosakamoto, H.; Okamoto, N.; Aikawa, H.; Sugiura, Y.; Suematsu, M.; Niwa, R.; Miura, M.; Obata, F. Sensing of the Non-Essential Amino Acid Tyrosine Governs the Response to Protein Restriction in Drosophila. Nat. Metab. 2022, 4, 944–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fellous, S.; Lazzaro, B.P. Larval Food Quality Affects Adult (but Not Larval) Immune Gene Expression Independent of Effects on General Condition. Mol. Ecol. 2010, 19, 1462–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotter, S.C.; Reavey, C.E.; Tummala, Y.; Randall, J.L.; Holdbrook, R.; Ponton, F.; Simpson, S.J.; Smith, J.A.; Wilson, K. Diet Modulates the Relationship between Immune Gene Expression and Functional Immune Responses. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2019, 109, 128–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Xu, B.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Z.; Yang, W. Protein Content in Larval Diet Affects Adult Longevity and Antioxidant Gene Expression in Honey Bee Workers. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 2014, 151, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newsholme, P.; Bender, K.; Kiely, A.; Brennan, L. Amino Acid Metabolism, Insulin Secretion and Diabetes. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2007, 35, 1180–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campos-Nonato, I.; Hernandez, L.; Barquera, S. Effect of a High-Protein Diet versus Standard-Protein Diet on Weight Loss and Biomarkers of Metabolic Syndrome: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Obes. Facts 2017, 10, 238–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshino, K.; Sakai, K.; Okada, H.; Sakai, T.; Yamamoto, S. IgE Responses in Mice Fed Moderate Protein Deficient and High Protein Diets. J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. 2003, 49, 172–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Markova, M. Isocaloric Diets High in Animal or Plant Protein Reduce Liver Fat and Inflammation in Individuals with Type 2 Diabetes. Gastroenterology 2017, 152, 571–585.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konala, N.; Abburi, P.; Bovilla, V.R.; Mamillapalli, A. The Effect of Bovine Milk on the Growth of Bombyx mori. J. Insect Sci. 2013, 13, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoppe, C.; Andersen, G.S.; Jacobsen, S.; Mølgaard, C.; Friis, H.; Sangild, P.T.; Michaelsen, K.F. The Use of Whey or Skimmed Milk Powder in Fortified Blended Foods for Vulnerable Groups. J. Nutr. 2008, 138, 145S–161S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eller, L.K.; Reimer, R.A. A High Calcium, Skim Milk Powder Diet Results in a Lower Fat Mass in Male, Energy-Restricted, Obese Rats More Than a Low Calcium, Casein, or Soy Protein Diet. J. Nutr. 2010, 140, 1234–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parkhomchuk, D.; Borodina, T.; Amstislavskiy, V.; Banaru, M.; Hallen, L.; Krobitsch, S.; Lehrach, H.; Soldatov, A. Transcriptome Analysis by Strand-Specific Sequencing of Complementary DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, e123. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pertea, M.; Kim, D.; Pertea, G.M.; Leek, J.T.; Salzberg, S.L. Transcript-Level Expression Analysis of RNA-Seq Experiments with HISAT, StringTie and Ballgown. Nat. Protoc. 2016, 11, 1650–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beekman, R.; Chapaprieta, V.; Russiñol, N.; Vilarrasa-Blasi, R.; Verdaguer-Dot, N.; Martens, J.H.A.; Duran-Ferrer, M.; Kulis, M.; Serra, F.; Javierre, B.M.; et al. The Reference Epigenome and Regulatory Chromatin Landscape of Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 868–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klopfenstein, D.V. GOATOOLS: A Python Library for Gene Ontology Analyses. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 10872. [Google Scholar]
- Luzio, J.P.; Pryor, P.R.; Bright, N.A. Lysosomes: Fusion and Function. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2007, 8, 622–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lü, P.; Xia, H.; Gao, L.; Pan, Y.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, X.; Lü, H.; Lin, F.; Chen, L.; Yao, Q.; et al. V-ATPase Is Involved in Silkworm Defense Response against Bombyx mori Nucleopolyhedrovirus. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e64962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Zhang, F.; Ma, H.; Chen, X.; Yang, J.; Yang, Y.; Yang, X.; Tian, X.; Yu, Q.; Ma, Z.; et al. Effects of Different Types and Doses of Whey Protein on the Physiological and Intestinal Flora in D-Galactose Induced Aging Mice. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0248329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shertzer, H.G.; Woods, S.E.; Krishan, M.; Genter, M.B.; Pearson, K.J. Dietary Whey Protein Lowers the Risk for Metabolic Disease in Mice Fed a High-Fat Diet. J. Nutr. 2011, 141, 582–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shertzer, H.G. Dietary Whey Protein Stimulates Mitochondrial Activity and Decreases Oxidative Stress in Mouse Female Brain. Neurosci. Lett. 2013, 548, 159–164. [Google Scholar]
- Signes, A.; Fernandez-Vizarra, E. Assembly of Mammalian Oxidative Phosphorylation Complexes I–V and Supercomplexes. Essays Biochem. 2018, 62, 255–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinogradov, A.D. NADH/NAD+ Interaction with NADH: Ubiquinone Oxidoreductase (Complex I). Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Bioenerg. 2008, 1777, 729–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaila, V.R.I. Resolving Chemical Dynamics in Biological Energy Conversion: Long-Range Proton-Coupled Electron Transfer in Respiratory Complex I. Acc. Chem. Res. 2021, 54, 4462–4473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cormier, R.P.J.; Champigny, C.M.; Simard, C.J.; St-Coeur, P.-D.; Pichaud, N. Dynamic Mitochondrial Responses to a High-Fat Diet in Drosophila melanogaster. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 4531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Vranken, J.G.; Na, U.; Winge, D.R.; Rutter, J. Protein-Mediated Assembly of Succinate Dehydrogenase and Its Cofactors. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2015, 50, 168–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braymer, J.J.; Lill, R. Iron–Sulfur Cluster Biogenesis and Trafficking in Mitochondria. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 12754–12763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yankovskaya, V.; Horsefield, R.; Törnroth, S.; Luna-Chavez, C.; Miyoshi, H.; Léger, C.; Byrne, B.; Cecchini, G.; Iwata, S. Architecture of Succinate Dehydrogenase and Reactive Oxygen Species Generation. Science 2003, 299, 700–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, F.; Huo, X.; Zhai, Y.; Wang, A.; Xu, J.; Su, D.; Bartlam, M.; Rao, Z. Crystal Structure of Mitochondrial Respiratory Membrane Protein Complex II. Cell 2005, 121, 1043–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steitz, T.A. A Structural Understanding of the Dynamic Ribosome Machine. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2008, 9, 242–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazar, R. Ribosomal RNA Processing and Ribosome Biogenesis in Eukaryotes. IUBMB Life 2004, 56, 457–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goehring, L.; Huang, T.T.; Smith, D.J. Transcription–Replication Conflicts as a Source of Genome Instability. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2023, 57, 157–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, F.; Wang, D.; Li, H.; Xia, P.; Ran, Y.; You, J. Toxicogenomics Provides Insights to Toxicity Pathways of Neonicotinoids to Aquatic Insect, Chironomus dilutus. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 260, 114011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, D.N.; Nierhaus, K.H. Ribosomal Proteins in the Spotlight. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2005, 40, 243–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korobeinikova, A.V.; Garber, M.B.; Gongadze, G.M. Ribosomal Proteins: Structure, Function, and Evolution. Biochem. Mosc. 2012, 77, 562–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stouthamer, A.H. A Theoretical Study on the Amount of ATP Required for Synthesis of Microbial Cell Material. Antonie Leeuwenhoek 1973, 39, 545–565. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Liang, Y.; Yang, C.; Shi, R.; Lu, W.; Wang, X.; Wang, R.; Xia, Q.; Ma, S. A Deep Insight into the Transcriptome of Midgut and Fat Body Reveals the Toxic Mechanism of Fluoride Exposure in Silkworm. Chemosphere 2021, 262, 127891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.P.; Simpson, S.J.; Wilson, K. Dietary Protein-quality Influences Melanization and Immune Function in an Insect. Funct. Ecol. 2008, 22, 1052–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woods, H.A. Patterns and Mechanisms of Growth of Fifth-Instar Manduca sexta Caterpillars Following Exposure to Low- or High-Protein Food during Early Instars. Physiol. Biochem. Zool. 1999, 72, 445–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.-Z.; Fu, P.; Li, S.-S.; Zhang, C.-J.; Yu, Q.-Y.; Qiu, C.-Z.; Zhang, H.-B.; Zhang, Z. A Comparison of Co-Expression Networks in Silk Gland Reveals the Causes of Silk Yield Increase During Silkworm Domestication. Front. Genet. 2020, 11, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, X.; Li, J.; Shan, Y.; Wang, Q.; Xu, P.; Qian, H.; Wu, Y. Comparative Transcriptome Analysis Reveals the Effects of a High-Protein Diet on Silkworm Midgut. Insects 2025, 16, 337. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16040337
Chen X, Li J, Shan Y, Wang Q, Xu P, Qian H, Wu Y. Comparative Transcriptome Analysis Reveals the Effects of a High-Protein Diet on Silkworm Midgut. Insects. 2025; 16(4):337. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16040337
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Xinyi, Jiahao Li, Yuxi Shan, Qiaoling Wang, Pingzhen Xu, Heying Qian, and Yangchun Wu. 2025. "Comparative Transcriptome Analysis Reveals the Effects of a High-Protein Diet on Silkworm Midgut" Insects 16, no. 4: 337. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16040337
APA StyleChen, X., Li, J., Shan, Y., Wang, Q., Xu, P., Qian, H., & Wu, Y. (2025). Comparative Transcriptome Analysis Reveals the Effects of a High-Protein Diet on Silkworm Midgut. Insects, 16(4), 337. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16040337



