Functional and Numerical Responses of Tytthus chinensis (Hemiptera: Miridae) to Sogatella furcifera (Hemiptera: Delphacidae)
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Insects and Plants
2.2. Predation Daily Average Predation and Functional Response
2.3. Numerical Response
2.3.1. Preparation of Sogatella furcifera Eggs
2.3.2. Preparation of Tytthus chinensis Nymphs
2.3.3. Observation of the Next Generation
2.3.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Daily Average Predation
3.2. Functional Response
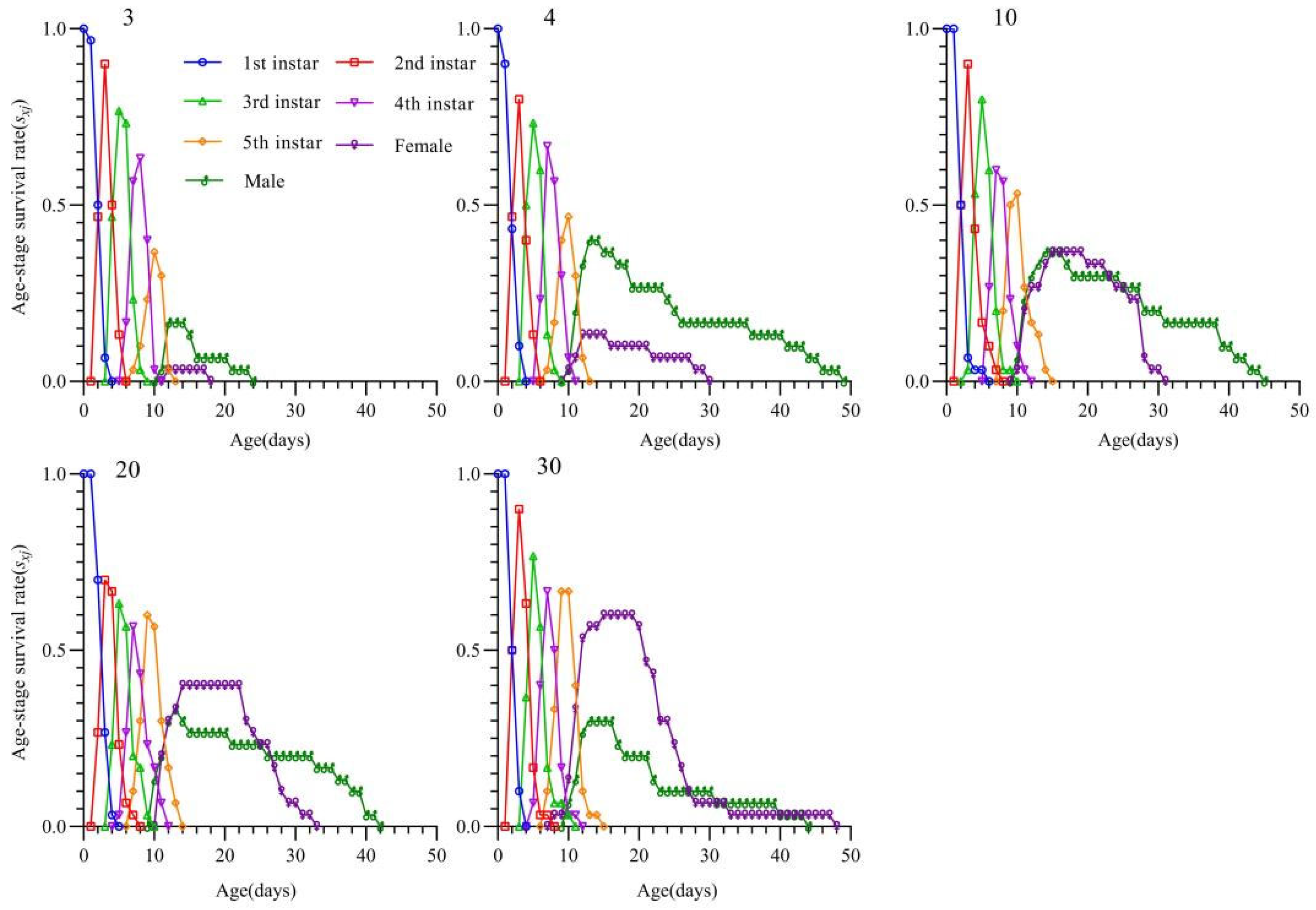
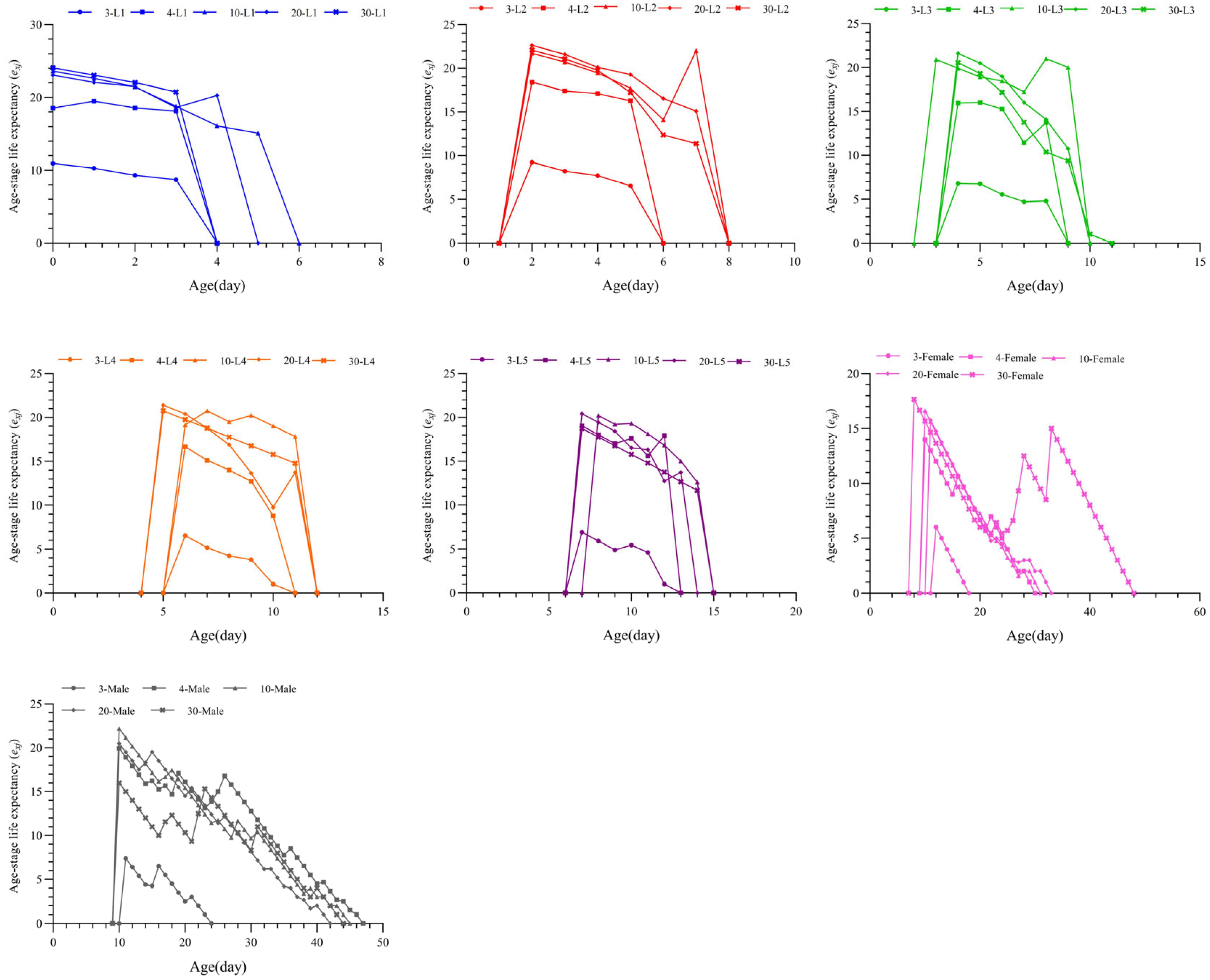
3.3. Effects of Different Prey Densities on the Survival Rate and Age-Stage-Specific Survival Rate of T. chinensis
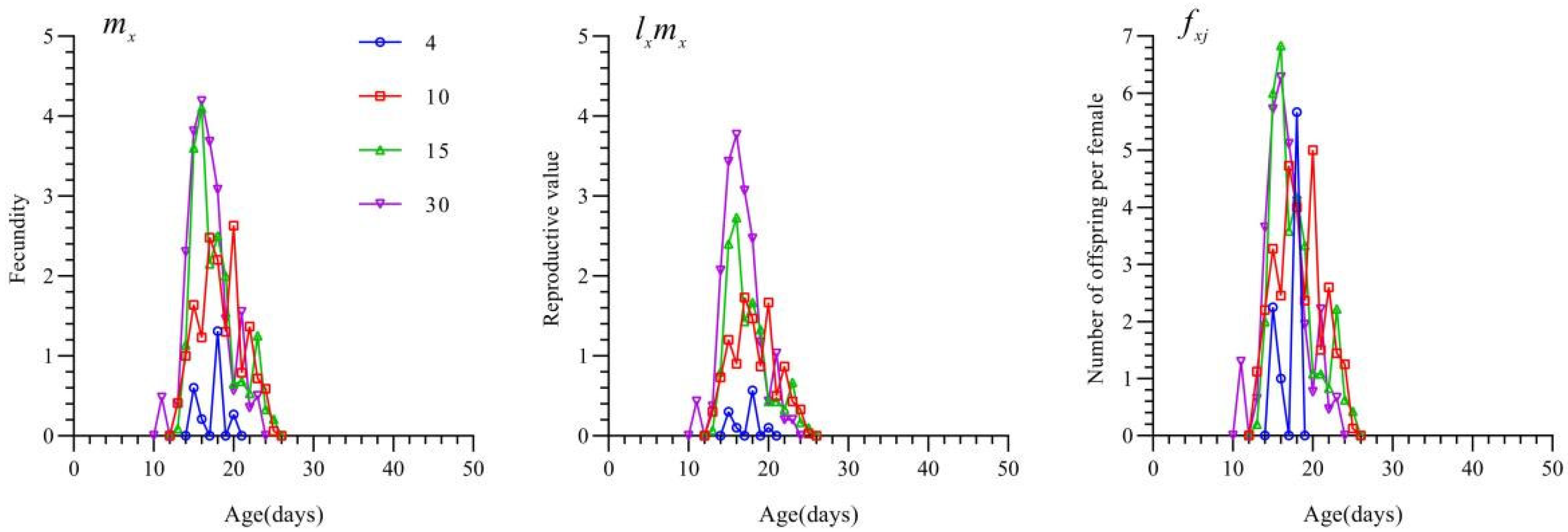
3.4. Reproductive Parameters of T. chinensis Under Different Prey Densities
3.5. Effects of S. furcifera Egg Density on the Growth and Development of T. chinensis
3.6. Effects of S. furcifera Egg Density on the Population Dynamics of T. chinensis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Asif, S.; Jang, Y.-H.; Kim, E.-G.; Jan, R.; Asaf, S.; Aaqil Khan, M.; Farooq, M.; Lubna; Kim, N.; Lee, I.-J.; et al. The role of exogenous gibberellic acid and methyl jasmonate against white-backed planthopper (Sogatella furcifera) stress in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 14737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, G.H.; Xu, D.L.; Xu, D.G.; Zhang, M.X. Southern rice black-streaked dwarf virus: A white-backed planthopper-transmitted fijivirus threatening rice production in asia. Front. Microbiol. 2013, 4, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, X.C.; Zhang, W.; Wang, L.X.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, K.; Gao, C.F.; Wu, S.F. Resistance monitoring and cross-resistance patterns of three rice planthoppers, Nilaparvata lugens, Sogatella furcifera and Laodelphax striatellus to dinotefuran in China. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2016, 134, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, Y.W.; Wang, X.G.; Xiang, X.; Xu, X.; Guo, Y.Q.; Liu, Y.H.; Yin, Y.; Wu, Y.Q.; Cheng, Q.H.; Gong, C.W.; et al. Status of insecticide resistance and biochemical characterization of chlorpyrifos resistance in Sogatella furcifera (Hemiptera: Delphacidae) in Sichuan Province, China. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2021, 171, 104723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.T.; Song, X.Y.; Zeng, B.; Zhang, W.J.; Chen, X.Y.; Feng, Z.R.; Yu, H.Y.; Gao, C.F.; Wu, S.F. The evolution of insecticide resistance in the white backed planthopper Sogatella furcifera (Horvath) of China in the period 2014–2022. Crop Prot. 2023, 172, 106312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, R.S.; Muthukrishnan, N.; Kuma, R.B.V.; Sathiah, N.; Prabakar, K. Toxicity of thiamethoxam 25wg and sulfoxaflor 21.8sc to rice white backed planthopper Sogatella furcifera (Horvath). Indian J. Entomol. 2023, 85, 1050–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleschner, C.A. Biological control of insect pests: Insect pests are economically controlled through the utilization of their natural enemies. Science 1959, 129, 537–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjørnson, S. Natural enemies of mass-reared predatory mites (family Phytoseiidae) used for biological pest control. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2008, 46, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, Y.G.; Cheng, J.A. Host-recognition kairomone from Sogatella furcifera for the parasitoid Anagrus nilaparvatae. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 2001, 101, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.Y.; Peng, Z.P.; He, Y. Effects of temperature on functional response of Anagrus nilaparvatae Pang et Wang (Hymenoptera: Mymaridae) on the eggs of whitebacked planthopper, Sogatella furcifera Horváth and Brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens Stål. J. Integr. Agric. 2012, 11, 1313–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, Y.G.; Zhang, G.R.; Zhang, W.Q.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, J. Biological control of rice insect pests in China. Biol. Control 2013, 67, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.Y.; Liu, F.; Li, J.S.; Cheng, Z.X.; Chen, H.F.; Wang, X.M.; Xiao, N.W.; Liu, Y.B. Coexistence of Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt)-transgenic and conventional rice affects insect abundance and plant fitness in fields. Pest Manag. Sci. 2018, 74, 1646–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pimsamarn, S.; Somboon, S. Functional response of mirid egg predators, Cyrtorhinus lividipennis Reuter and Tytthus chinensis Stal (Hemiptera: Miridae), to brown planthopper (Nilaparvata lugens Stal, Homoptera: Delphacidae). Thai J. Agric. Sci. 2002, 35, 17–23. [Google Scholar]
- Henry, T.J. Revision of the plant bug genus Tytthus (Hemiptera, Heteroptera, Miridae, Phylinae). ZooKeys 2012, 220, 1–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Anbaki, H.A.M.; Al-Hayali, T.S.A.; Alhadidi, S.N.; Shiblawi, L.M.A. New record species of Tytthus chinensis (Stål, 1859) (Hemiptera: Heteroptera: Miridae) from Iraq. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2023, 1262, 032034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, F.; Zhu, Q.Z.; Wang, X.Q.; Wang, G.H.; Gurr, G.M.; Zhu, Z.R.; Heong, K.L.; Cheng, J.A. Reciprocal intraguild predation between two mirid predators, Cyrtorhinus lividipennis and Tytthus chinensis (Hemiptera: Miridae). Biocontrol Sci. Technol. 2016, 26, 1267–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Quais, M.K.; Zhou, W.; Zhu, Z.R. Consequences of elevated temperature on the biology, predation, and competitiveness of two mirid predators in the rice ecosystem. J. Pest Sci. 2021, 95, 901–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajjad, D.; Hamidreza, H.; Yaghoub, F.; Mostafa, K. Age-dependent functional and numerical responses of Neoseiulus cucumeris (Acari: Phytoseiidae) on two-spotted spider mite (Acari: Tetranychidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 2021, 114, 50–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holling, C.S. The components of predation as revealed by a study of small mammal predation of the European pine sawfly. Can. Entomol. 1959, 91, 293–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehsan, G.; Yaghoub, F.; Abdoolnabi, B.; Ali, A.T.; Gadi, V.P.R. Changes in functional and numerical responses of the parasitoid wasp Trichogramma brassicae (Hymenoptera: Trichogrammatidae) over 45 generations of rearing on Ephestia kuehniella. Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 2022, 115, 326–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.; Li, S.; Jaleel, W.; Muhammad, M.K.; Wang, J.; Zhou, X. Using a two-sex life table tool to calculate the fitness of Orius strigicollis as a predator of Pectinophora gossypiella. Insects 2020, 11, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safeer, H.M.; Ishfaq, A.; Mukhtar, A.; Batool, M.; Zaka, S.M.; Tajdar, A.; Saood, A.; Shah, Z.A.; Shah Zaib, M.; Abbas, K.; et al. Chemotaxis response and age-stage, two-sex life table of the Cheilomenes sexmaculata (Fabricius) (Coccinellidae: Coleoptera) against different aphid species. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0289682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, H.; Liu, H. Two new methods for the study of insect population ecology. Bull. Inst. Zool. Acad. Sin. 1985, 24, 225–240. [Google Scholar]
- Chi, H. Life-table analysis incorporating both sexes and variable development rate among individuals. Environ. Entomol. 1988, 17, 26–34. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.B.; Chi, H. Life tables of Bactrocera cucurbitae (Diptera: Tephrtidae) with an invalidation of the jackknife technique. J. Appled Entomol. 2012, 137, 327–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, H. Twosex-Mschart: A Computer Program for the Age-Stage, Two-Sex Life Table Analysis; Fujian Academy of Agricultural Sciences: Fuzhou, China, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.C.; Chen, D.F.; Yang, M.F.; Liu, J.F. The effect of temperatures and hosts on the life cycle of Spodoptera frugiperda (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Insects 2022, 13, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tangkawanit, U.; Hinmo, N.; Khlibsuwan, W. Numerical response of Cyrtorhinus lividipennis (Hemiptera: Miridae) to Nilaparvata lugens (Hemiptera: Delphacidae). J. Entomol. Sci. 2018, 53, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandana, P.S.; Sood, A.; Sharma, P.L. Functional response of green lacewing, Chrysoperla zastrowi silemmi (Esben-Petersen) to its prey, cabbage aphid, Brevicoryne brassicae L. J. Biol. Control 2023, 37, 177–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, G.d.S.; Truzi, C.C.; Cardoso, C.P.; Vieira, N.F.; Ramalho, D.G.; Souza, J.M.d.; De Bortoli, S.A. Temperature-dependent functional response of Euborellia annulipes (Dermaptera: Anisolabididae) preying on Plutella xylostella (Lepidoptera: Plutellidae) larvae. J. Therm. Biol. 2020, 93, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, A.; Hosseini, M.; Michaud, J.; Awal, M.M.; Ghadamyari, M. Life history responses of Hippodamia variegata (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) to changes in the nutritional content of its prey, Aphis gossypii (Hemiptera: Aphididae), mediated by nitrogen fertilization. Biol. Control 2019, 130, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, J.L.; Yang, K.; Wang, E.D.; Xu, X.N. Prey diet quality affects predation, oviposition and conversion rate of the predatory mite Neoseiulus barkeri (Acari: Phytoseiidae). Syst. Appl. Acarol. 2016, 21, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.D.; Li, Y.H.; Li, X.; Mo, W.F.; Cong, Z.; Jing, W.; Xin, T.R.; Zou, Z.W.; Xia, B. Predation of Cheyletus malaccensis (Acari: Cheyletidae) on Megoura japonica (Hemiptera: Aphididae) under five different temperatures. Int. J. Acarol. 2019, 45, 176–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashedi, A.; Rajabpour, A.; Sohani, N.Z.; Rasekh, A. Prey stage preference and functional response of Orius albidipennis (Hetetroptera, Anthocoridae) to Aphis fabae (Homomoptera, Aphididae). Int. J. Trop. Insect Sci. 2020, 40, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.L.; Tang, R.; Liu, T.X.; Qiu, B.L. Larval and/or adult exposure to intraguild predator Harmonia axyridis alters reproductive allocation decisions and offspring growth in Menochilus sexmaculatus. Insects 2023, 14, 496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Happe, A.-K.; Alins, G.; Blüthgen, N.; Boreux, V.; Bosch, J.; García, D.; Hambäck, P.A.; Klein, A.-M.; Martínez-Sastre, R.; Miñarro, M.; et al. Predatory arthropods in apple orchards across europe: Responses to agricultural management, adjacent habitat, landscape composition and country. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2019, 273, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamila, E.X.A.; Diego, M.M.; Rafael, d.A.M.; José, M.S.B. Weathering the hunt: The role of barometric pressure in predator insects’ foraging behaviour. Ecol. Evol. 2023, 13, e10416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.M.; Zhou, Y.T.; Xu, T.; Zong, S.X. Impact of climate change on the habitat suitability of Monochamus saltuarius Gebler (Coleoptera; Cerambycidae) and its natural enemies in China. Forests 2024, 15, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, K.Q.; Lan, R.M.; Yang, X.J.; Gong, B.; Zhang, J.J.; Zhou, X.; Jin, L.H. Two-sex life table analysis of the predator Arma chinensis (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae) and the prediction of its ability to suppress populations of Scopula subpunctaria (Lepidoptera: Geometridae). Agriculture 2023, 13, 1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwala, B.K.; Bardhanroy, P.; Yasuda, H.; Takizawa, T. Prey consumption and oviposition of the aphidophagous predator Menochilus sexmaculatus (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) in relation to prey density and adult size. Environ. Entomol. 2001, 30, 1182–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jervis, M.A.; Ellers, J.; Harvey, J.A. Resource acquisition, allocation, and utilization in parasitoid reproductive strategies. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2008, 53, 361–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batool, A.; Abdullah, K.; Mamoon-ur-Rashid, M.; Khattak, M.K.; Abbas, S.S. Effect of prey density on biology and functional response of Chrysoperla carnea (Stephens) (Neuroptera: Chrysopidae). Pak. J. Zool. 2014, 46, 129–137. [Google Scholar]
- Hemptinne, J.L.; Dixon, A.F.G.; Coffin, J. Attack strategy of ladybird beetles (coccinellidae): Factors shaping their numerical response. Oecologia 1992, 90, 238–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.P.; Fang, Y.L.; Zhang, Z.N. Effect of male and female multiple mating on the fecundity, fertility, and longevity of diamondback moth, Plutella xylostella (L.). J. Appl. Entomol. 2005, 129, 39–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madahi, K.; Sahragard, A.; Hossieni, R. Influence of aphis Gossypii glover (Hemiptera: Aphididae) density on life table parameters of Aphidoletes aphidimyza Rondani (Diptera: Cecidomyiidae) under laboratory conditions. J. Crop Prot. 2013, 2, 355–368. [Google Scholar]
- Hayali, E.M.A.A.; Jalal, H.M.M.A. Effect of the nutritional host on some biological manifestations of the tobacco leaf worm Spodoptera litura fab (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2022, 1060, 012124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Force, E.; Suray, C.; Dacher, M.; Debernard, S. Effect of adult male diet on fertilization and hatching in an insect. Micropubl. Biol. 2024, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Q.; Ang, Y.; Shikano, I. Effects of adult diet on the longevity, fecundity and ovarian development of the rice leaffolder, Cnaphalocrocis medinalis. Physiol. Entomol. 2024, 49, 422–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Treatment | Number of Sogatella furcifera Eggs (Eggs/Unit) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1st Instar | 2nd Instar | 3rd Instar | 4th Instar | 5th Instar | Female | Male | |
| 1 | 1 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| 2 | 3 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 |
| 3 | 5 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 20 | 20 |
| 4 | 8 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 30 | 30 |
| 5 | 10 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 60 | 60 |
| Developmental Stage | r2 | Attack Rate ± SE (a) | Handling Time ± SE (Th) | Theoretical Daily Maximum Prey Consumption | Predation Capacity (a/Th) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1st instar | 0.938 | 0.987 ± 0.0.264 | 0.138 ± 0.041 | 7.25 | 7.15 |
| 2nd instar | 0.972 | 0.653 ± 0.067 | 0.109 ± 0.008 | 9.17 | 5.99 |
| 3rd instar | 0.921 | 0.882 ± 0.203 | 0.043 ± 0.014 | 23.26 | 20.51 |
| 4th instar | 0.970 | 1.659 ± 0.348 | 0.032 ± 0.008 | 31.25 | 51.84 |
| 5th instar | 0.997 | 3.108 ± 0.309 | 0.029 ± 0.002 | 34.48 | 107.17 |
| Female | 0.989 | 2.242 ± 0.299 | 0.024 ± 0.002 | 41.67 | 93.42 |
| Male | 0.985 | 11.354 ± 1.211 | 0.053 ± 0.006 | 18.87 | 214.23 |
| Parameters | Prey Density (Eggs/Day) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4 | 10 | 20 | 30 | ||
| Nymphal duration (days) | 1st instar | 2.59 ± 0.13 b | 2.63 ± 0.16 ab | 3.00 ± 0.15 a | 2.60 ± 0.12 b |
| 2nd instar | 2.00 ± 0.68 a | 2.07 ± 0.11 a | 2.07 ± 0.09 a | 2.27 ± 0.64 a | |
| 3rd instar | 2.29 ± 0.62 a | 2.28 ± 0.14 a | 2.04 ± 0.15 a | 1.93 ± 0.13 b | |
| 4th instar | 2.33 ± 0.14 a | 2.17 ± 0.15 a | 2.00 ± 0.12 a | 2.10 ± 0.10 a | |
| 5th instar | 2.38 ± 0.15 a | 2.45 ± 0.19 a | 2.59 ± 0.20 a | 2.59 ± 0.12 a | |
| Pre-adult duration (days) | 11.50 ± 0.22 a | 11.72 ± 0.30 a | 11.55 ± 0.25 a | 11.37 ± 0.25 a | |
| Pre-oviposition period (APOP) (days) | 4.00 ± 0.28 a | 3.36 ± 0.02 a | 3.17 ± 0.07 a | 3.67 ± 0.01a | |
| Male longevity (days) | 18.33 ± 3.49 a | 20.73 ± 3.14 a | 19.40 ± 3.29 a | 14.56 ± 3.25 a | |
| Female longevity (days) | 12.75 ± 3.45 a | 14.64 ± 0.90 a | 14.83 ± 0.86 a | 14.33 ± 1.51 a | |
| Fecundity (eggs/female) | 8.00 ± 2.40 b | 30.10 ± 3.70 a | 31.42 ± 3.08 a | 31.06 ± 2.99 a | |
| Egg duration of the next generation | 8.10 ± 0.16 a | 8.10 ± 0.14 a | 8.06 ± 0.15 a | 8.00 ± 0.15 a | |
| Hatchingn rate of the next generation | 53.13 ± 5.98% b | 87.50 ± 5.10% a | 96.88 ± 3.13% a | 96.88 ± 3.13% a | |
| Prey Density (Eggs/Day) | Net Reproductive Rate (R0) | Mean GENERATION Time (T) | Intrinsic Rate of Increase (rm) | Finite Rate of Increase (λ) | Sex Ratio (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4 | 1.07 ± 0.56 b | 25.15 ± 2.56 a | 0.003 ± 0.02 c | 1.00 ± 0.032 c | 25% |
| 10 | 11.03 ± 2.96 a | 25.83 ± 0.43 a | 0.09 ± 0.01 b | 1.10 ± 0.01 b | 50% |
| 20 | 12.57 ± 3.05 a | 25.07 ± 0.51 ab | 0.10 ± 0.01 ab | 1.11 ± 0.01 ab | 66.67% |
| 30 | 18.63 ± 3.29 a | 24.25 ± 0.40 b | 0.12 ± 0.01 a | 1.13 ± 0.01 a | 66.67% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, Q.; Long, L.; Huang, S.; Wu, B.; Li, C.; Ling, Y. Functional and Numerical Responses of Tytthus chinensis (Hemiptera: Miridae) to Sogatella furcifera (Hemiptera: Delphacidae). Insects 2025, 16, 339. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16040339
Huang Q, Long L, Huang S, Wu B, Li C, Ling Y. Functional and Numerical Responses of Tytthus chinensis (Hemiptera: Miridae) to Sogatella furcifera (Hemiptera: Delphacidae). Insects. 2025; 16(4):339. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16040339
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Qian, Liping Long, Suosheng Huang, Biqiu Wu, Cheng Li, and Yan Ling. 2025. "Functional and Numerical Responses of Tytthus chinensis (Hemiptera: Miridae) to Sogatella furcifera (Hemiptera: Delphacidae)" Insects 16, no. 4: 339. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16040339
APA StyleHuang, Q., Long, L., Huang, S., Wu, B., Li, C., & Ling, Y. (2025). Functional and Numerical Responses of Tytthus chinensis (Hemiptera: Miridae) to Sogatella furcifera (Hemiptera: Delphacidae). Insects, 16(4), 339. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16040339





