Comparative Mitogenomics of Pedetontus and Pedetontinus (Insecta: Archaeognatha) Unveils Phylogeny, Divergence History, and Adaptive Evolution
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Specimen Acquisition and Genomic DNA Extraction
2.2. Sequencing and Assembly of the Mitochondrial Genome
2.3. Sequence Annotation and Analyses
2.4. Phylogenetic Analyses
2.5. Estimation of Divergence Times
2.6. Selection Pressure Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Composition of Mitogenomes
3.2. Genetic and Intergroup Genetic Distance Analyses
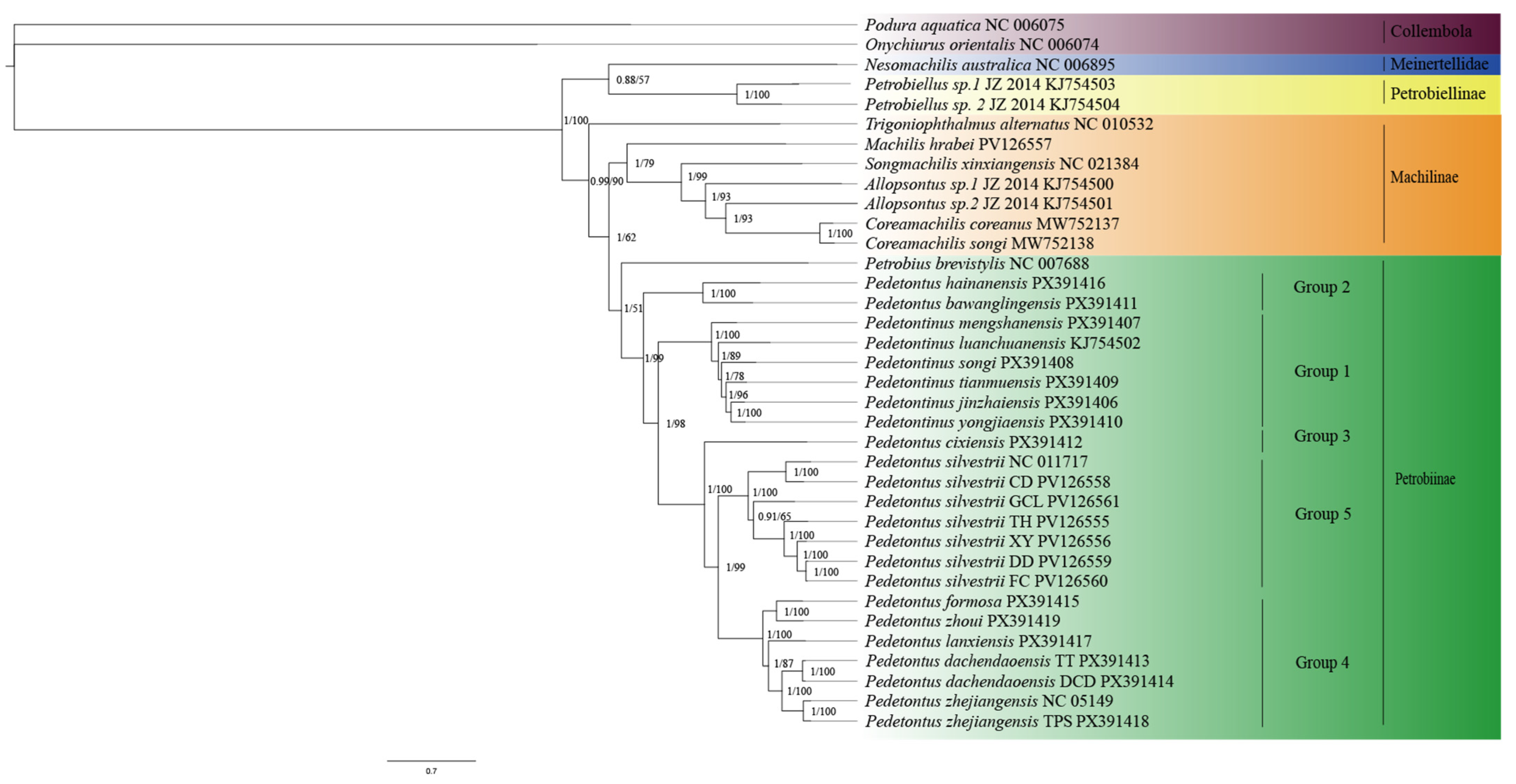
3.3. Phylogenetic Analyses of Archaeognatha
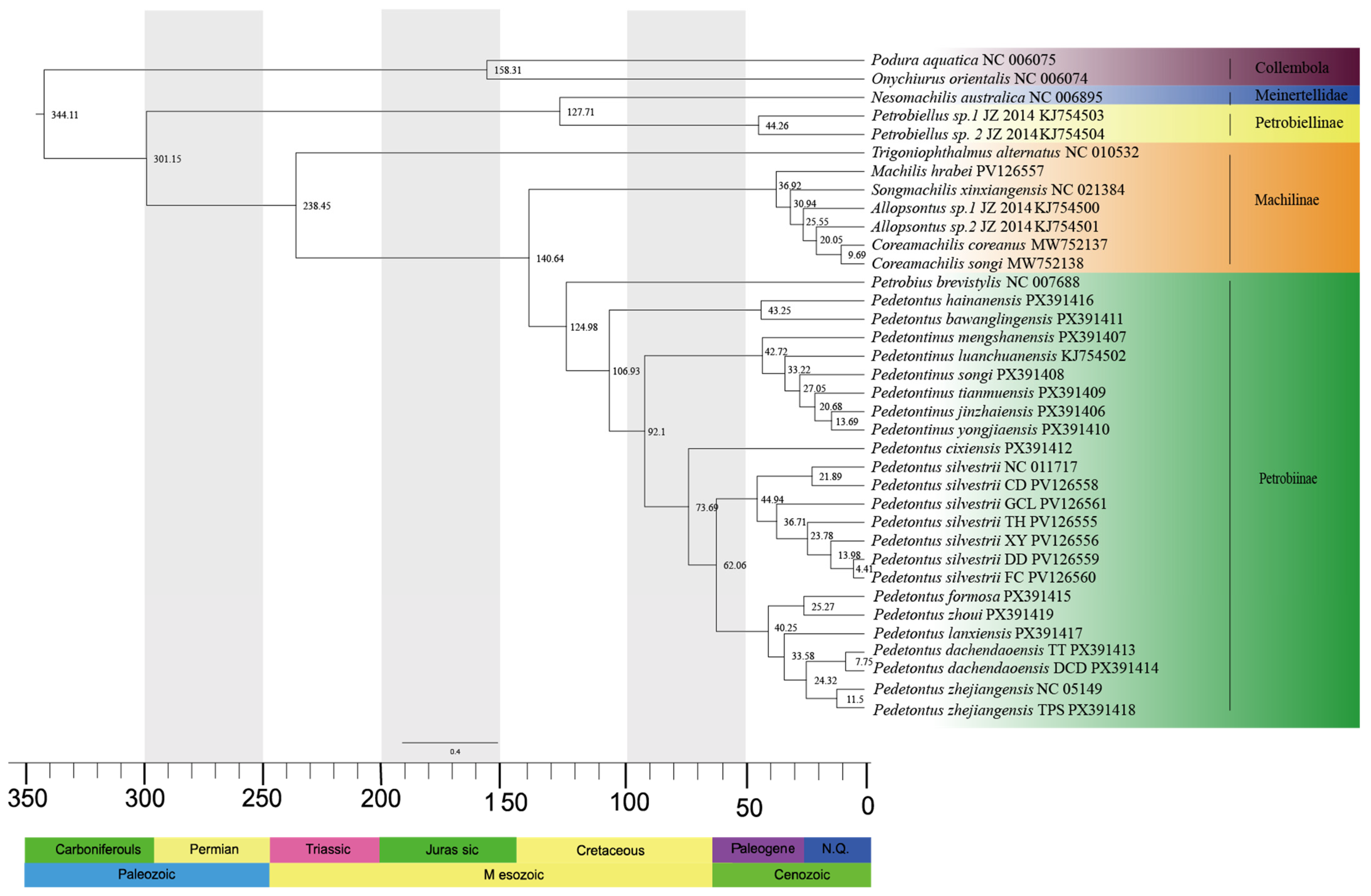
3.4. Divergence Time Calculation
3.5. Positive Selection Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Special Structure of Mitogenomes from Pedetontus and Pedetontinus
4.2. Analysis of Phylogenetic Tree Topology
4.3. Divergence Time Estimation and Evolutionary Node Calibration
4.4. Genetic-Morphological Discrepancy in Pedetontus Taxonomy
4.5. Positive Selection Pressure Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Palacios–Martinez, I.; Jiménez-Ruiz, Y.; Otero-Ferre, P.; García-París, M. Systematics of the genus Dilta Strand, 1911 (Machilidae) in the Canary Islands (NW Africa, Spain) with comments on the phylogeny of Microcoryphia (Insecta). Zool. Anz. 2025, 317, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Li, H.; Shih, C.; Zhang, A.; Ren, D. Phylogenetic analyses with four new Cretaceous bristletails reveal inter-relationships of Archaeognatha and Gondwana origin of Meinertellidae. Cladistics 2018, 34, 384–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; He, K.; Yu, P.P.; Yu, D.N.; Cheng, X.F.; Zhang, J.Y. The complete mitochondrial genomes of three bristletails (Insecta: Archaeognatha): The paraphyly of Machilidae and insights into Archaeognathan phylogeny. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0117669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sturm, H.; Bach, d.R.C. On the systematics of the Archaeognatha (Insecta). Entomol. Gen. 1993, 18, 55–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, M. Character evolution in the Archaeognatha: Consensus and conflict. Entomol. Abh. 2003, 61, 120–122. [Google Scholar]
- Mendes, L.F.; Foottit, R.; Adler, P. Biodiversity of the thysanurans (Microcoryphia and Zygentoma). Insect Biodivers. Sci. Soc. 2018, 2, 155–198. [Google Scholar]
- Matushkina, N.A.; Klass, K.-D. Male genitalia of Charimachilis (Insecta: Archaeognatha) and the status of archaeognathan “paleoforms”. Org. Divers. Evol. 2020, 20, 253–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klass, K.; Matushkina, N. The exoskeleton of the male genitalic region in Archaeognatha, with hypotheses on the early evolution and the morphological interpretation of genitalia in insects. Arthropod Syst. Phylogeny 2018, 76, 235–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.Y.; Song, D.X.; Zhou, K.Y. A new species of the genus Pedetontinus (Microcoryphia, Machilidae) from China. Acta Zootaxonomica Sin. 2005, 30, 549–554. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, D.N.; Zhang, W.W.; Zhang, J.Y. Two new species of the genus Pedetontus (Microcoryphia, Machilidae) from China. Acta Zootaxonomica Sin. 2010, 35, 444–450. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, L.; Yin, W. Two new species of Machilidae from the Tianmu Mountain, China (Microcoryphia). Contrib. Shanghai Inst. Entomol. 1991, 10, 77–86. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J. A new record genus and species of Machilinae from China (Microcoryphia: Machilidae). Jiangxi Plant Prot. 2010, 33, 57–59. [Google Scholar]
- Uchida, H. Pedetontus from Formosa: Thysanura: Machilidae. Spec. Bull. Lepidopterol. Soc. Jpn. 1965, 1, 249–252. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.Y.; Li, T. A new bristletail species of the genus Pedetontinus (Microcoryphia, Machilidae) from China. Acta Zootaxonomica Sin. 2009, 34, 203–206. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Zhou, K. Descriptions of one new genus and six new species of Machilidae (Insecta: Archaeognatha) from China: Morphological and molecular data. J. Nat. Hist. 2011, 45, 1131–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.S. Machilontus (s. str.) medogensis Song & Huang, sp. nov. from Tibet, the northernmost record of the genus Machilontus Silvestri, 1912 and the first record of the family Meinertellidae (Insecta: Microcoryphia: Machiloidea) in China. Zootaxa 2011, 2822, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvestri, F. Note sui Machilidae. III. Descrizione di un nuovo genere e di sei nuove specie. Redia 1906, 3, 325–335. [Google Scholar]
- Silvestri, F. Schwedisch-chinesiche wissenschaftliche Expedition nach den nordwestlichen Provinzen Chinas (38. Thysanura, Machilidae). Ark. Zool. 1934, 27, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Silvestri, F. Descripzione di alcuni Machilidae (Thysanura) della China. Notes Entomol. Chin. Du Mus. Heude Shanghai 1936, 3, 103–115. [Google Scholar]
- Silvestri, F. Contributto alla conoscenza dei Machilidae (Insecta, Thysanura) del Giappone. Bollettino del Laboratorio di Zoologia, generale e agraria della R. Sc. Super. D’agricoltura Portici 1943, 32, 283–306. [Google Scholar]
- Mendes, L.F.; Gaju-Ricart, M.; de Roca, C.B.; Molero-Baltanás, R. On some Silvestri species of Machilidae (Microcoryphia, Insecta) which types are in the Muséum National d’Histoire Naturelle, Paris. Pedobiologia 2000, 44, 268–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Yu, D.N.; Zhang, J.Y. One new species of the genus Pedetontinus (Microcoryphia, Machilidae) from China with morphological and molecular data. Acta Zootaxon Sin. 2012, 37, 740–746. [Google Scholar]
- Kaplin, V. Description of a new species of the bristletail genus Pedetontinus Silv. (Thysanura, Machilidae) from China with a review of species of this genus. Entomol. Rev. 2015, 95, 73–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplin, V. A new species of the genus Allopsontus Silv. (Microcoryphia, Machilidae) from northwestern china. Entomol. Rev. 2016, 96, 126–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplin, V. A new species of bristletails of the genus Silvestrichilis Wygodzinsky, 1950 (Archaeognatha: Machilidae) from South China. Far East. Entomol. 2019, 376, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.S.; Song, Z.S.; Liang, A.P. A new bristletail species of the genus Allopsontus Silvestri (Microcoryphia: Machilidae) from Shaanxi, China. Orient. Insects 2006, 40, 267–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, K.Z.; Zhang, J.Y.; Yu, D.N. A new species of the genus Haslundichilis (Microcoryphia, Machilidae) from China and redescription of Haslundichilis hedini (Silvestri). Acta Zootaxonomica Sin. 2011, 36, 882–887. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, C.Y.; Wang, L.Y.; Wu, H.Y.; Zhang, J.Y. A new species of Silvestrichilis Wygodzinsky, 1950 (Insecta: Microcoryphia) from Wudang Mountain, Hubei, China, with the description of both sexes. Zootaxa 2025, 5621, 437–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.Y.; Yu, D.N.; Zhang, J.Y. One new species of the genus Pedetontinus (Microcoryphia, Machilidae) from China. Acta Zootaxonomica Sin. 2011, 36, 36–39. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, C.Y.; Yang, T.; Ji, J.H.; Zhang, J.Y. Six New Species of Genus Pedetontus Silvestri, 1911 (Microcoryphia: Machilidae), from Southern China. Insects 2025, 16, 916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaplin, V. On the classification and phylogeny of the Machilidae (Thysanura, Microcoryphia). Entomol. Rev. 1985, 64, 117–131. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, J.H.; Wu, H.Y.; Gao, Y.X.; Shen, C.Y.; Yang, Z.W.; Storey, K.B.; Yu, D.N.; Zhang, J.Y. Unusual genetic diversity within Thereuopoda clunifera (Wood, 1862) (Chilopoda: Scutigeromorpha) revealed by phylogeny and divergence times using mitochondrial genomes. Insects 2025, 16, 486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Y.; Wu, L.; Ayivi, S.P.G.; Storey, K.B.; Ma, Y.; Yu, D.N.; Zhang, J.Y. Cryptic species exist in Vietnamella sinensis Hsu, 1936 (Insecta: Ephemeroptera) from studies of complete mitochondrial genomes. Insects 2022, 13, 412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.Q.; Shen, C.Y.; Cheng, H.Y.; Chen, Y.X.; Wu, H.Y.; Storey, K.B.; Yu, D.N.; Zhang, J.Y. Mitogenome-Based phylogeny with divergence time estimates revealed the presence of cryptic species within Heptageniidae (Insecta, Ephemeroptera). Insects 2024, 15, 745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, F.; Lan, X.E.; Zhu, W.B.; You, P. Mitochondrial genomes of praying mantises (Dictyoptera, Mantodea): Rearrangement, duplication, and reassignment of tRNA genes. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 25634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, J.Y.; Shen, S.Q.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Xu, X.D.; Storey, K.B.; Yu, D.N.; Zhang, J.Y. Comparative mitogenomes of two Coreamachilis species (Microcoryphia: Machilidae) along with phylogenetic analyses of Microcoryphia. Insects 2021, 12, 795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, M.Y.; Lee, E.M.; Jo, Y.H.; Park, H.C.; Kim, S.R.; Hwang, J.S.; Jin, B.R.; Kang, P.D.; Kim, K.-G.; Han, Y.S. Complete nucleotide sequence and organization of the mitogenome of the silk moth Caligula boisduvalii (Lepidoptera: Saturniidae) and comparison with other lepidopteran insects. Gene 2008, 413, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fenn, J.; Cameron, S.; Whiting, M. The complete mitochondrial genome sequence of the Mormon cricket (Anabrus simplex: Tettigoniidae: Orthoptera) and an analysis of control region variability. Insect Mol. Biol. 2007, 16, 239–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clary, D.O.; Wolstenholme, D.R. The mitochondrial DNA molecule of Drosophila yakuba: Nucleotide sequence, gene organization, and genetic code. J. Mol. Evol. 1985, 22, 252–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regier, J.C.; Shultz, J.W.; Ganley, A.R.; Hussey, A.; Shi, D.; Ball, B.; Zwick, A.; Stajich, J.E.; Cummings, M.P.; Martin, J.W.; et al. Resolving arthropod phylogeny: Exploring phylogenetic signal within 41 kb of protein-coding nuclear gene sequence. Syst. Biol. 2008, 57, 920–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regier, J.C.; Shultz, J.W.; Zwick, A.; Hussey, A.; Ball, B.; Wetzer, R.; Martin, J.W.; Cunningham, C.W. Arthropod relationships revealed by phylogenomic analysis of nuclear protein-coding sequences. Nature 2010, 463, 1079–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meusemann, K.; von Reumont, B.M.; Simon, S.; Roeding, F.; Strauss, S.; Kück, P.; Ebersberger, I.; Walzl, M.; Pass, G.; Breuers, S.; et al. A phylogenomic approach to resolve the arthropod tree of life. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2010, 27, 2451–2464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Von Reumont, B.M.; Meusemann, K.; Szucsich, N.U.; Dell’Ampio, E.; Gowri-Shankar, V.; Bartel, D.; Simon, S.; Letsch, H.O.; Stocsits, R.R.; Luan, Y.X.; et al. Can comprehensive background knowledge be incorporated into substitution models to improve phylogenetic analyses? A case study on major arthropod relationships. BMC Evol. Biol. 2009, 9, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Von Reumont, B.M.; Jenner, R.A.; Wills, M.A.; Dell’Ampio, E.; Pass, G.; Ebersberger, I.; Meyer, B.; Koenemann, S.; Iliffe, T.M.; Stamatakis, A.; et al. Pancrustacean phylogeny in the light of new phylogenomic data: Support for Remipedia as the possible sister group of Hexapoda. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2012, 29, 1031–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montagna, M. Comment on phylogenetic analyses with four new Cretaceous bristletails reveal inter-relationships of Archaeognatha and Gondwana origin of Meinertellidae. Cladistics 2020, 36, 227–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cen, W.; Li, J.W.; He, J.T.; Chen, X.Y.; Li, L.Y.; Storey, K.B.; Yu, D.N.; Zhang, J.Y. Morpho-Molecular discordance and cryptic diversity in jumping Bristletails: A mitogenomic analysis of Pedetontus silvestrii (Insecta: Archaeognatha: Machilidae). Insects 2025, 16, 452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, D.C.; Hill, K.B.; Moulds, M.; Vanderpool, D.; Cooley, J.R.; Mohagan, A.B.; Simon, C. Inflation of molecular clock rates and dates: Molecular phylogenetics, biogeography, and diversification of a global cicada radiation from Australasia (Hemiptera: Cicadidae: Cicadettini). Syst. Biol. 2016, 65, 16–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shear, W.A.; Bonamo, P.M.; Grierson, J.D.; Rolfe, W.I.; Smith, E.L.; Norton, R.A. Early land animals in North America: Evidence from Devonian age arthropods from Gilboa, New York. Science 1984, 224, 492–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labandeira, C.C.; Beall, B.S.; Hueber, F.M. Early insect diversification: Evidence from a Lower Devonian bristletail from Québec. Science 1988, 242, 913–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasnitsyn, A.P.; Aristov, D.S.; Gorochov, A.V.; Rowland, J.M.; Sinitshenkova, N.D. Important new insect fossils from Carrizo Arroyo and the Permo-Carboniferous faunal boundary. N. M. Mus. Nat. Hist. Sci. Bull. 2004, 25, 215–246. [Google Scholar]
- Rasnitsyn, A.P. Taxonomy and morphology of Dasyleptus Brongniart, 1885, with description of a new species (Insecta: Machilida: Dasyleptidae). Russ. Entomol. J. 1999, 8, 145–154. [Google Scholar]
- Misof, B.; Liu, S.; Meusemann, K.; Peters, R.S.; Donath, A.; Mayer, C.; Frandsen, P.B.; Ware, J.; Flouri, T.; Beutel, R.G.; et al. Phylogenomics resolves the timing and pattern of insect evolution. Science 2014, 346, 763–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballard, J.W.O.; Kreitman, M. Is mitochondrial DNA a strictly neutral marker? Trends. Ecol. Evol. 1995, 10, 485–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Y.T.; Li, Q.; Zhang, J.Y.; Storey, K.B.; Yu, D.N. Characterization of the mitochondrial genomes of two toads, Anaxyrus americanus (Anura: Bufonidae) and Bufotes pewzowi (Anura: Bufonidae), with phylogenetic and selection pressure analyses. PeerJ 2020, 8, e8901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.D.; Jiang, G.F.; Yan, L.Y.; Li, R.; Mu, Y.; Deng, W.A. Positive selection drove the adaptation of mitochondrial genes to the demands of flight and high-altitude environments in grasshoppers. Front. Genet. 2018, 9, 605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.D.; Guan, J.Y.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Cao, Y.R.; Cai, Y.Y.; Storey, K.B.; Yu, D.N.; Zhang, J.Y. Insight into the phylogenetic relationships among three subfamilies within Heptageniidae (Insecta: Ephemeroptera) along with low-temperature selection pressure analyses using mitogenomes. Insects 2021, 12, 656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Y.F.; Cen, W.; Storey, K.B.; Liu, L.J.; Yu, D.N.; Zhang, J.Y. Comparative mitogenomic analysis of three Chionea species (Tipulomorpha: Limoniidae): Insights into phylogenetic relationships and selection pressure. Insects 2025, 16, 720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faddeeva, A.; Studer, R.; Kraaijeveld, K.; Sie, D.; Ylstra, B.; Mariën, J.; op den Camp, H.; Datema, E.; Den Dunnen, J.T.; Van Straalen, N.; et al. Collembolan transcriptomes highlight molecular evolution of hexapods and provide clues on the adaptation to terrestrial life. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0130600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folmer, O.; Black, M.; Hoeh, W.; Lutz, R.; Vrijenhoek, R. DNA primers for amplification of mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase subunit I from diverse metazoan invertebrates. Mol. Mar. Biol. Biotechnol. 1994, 3, 294–299. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.Y.; Zhou, C.F.; Gai, Y.H.; Song, D.X.; Zhou, K.Y. The complete mitochondrial genome of Parafronurus youi (Insecta: Ephemeroptera) and phylogenetic position of the Ephemeroptera. Gene 2008, 424, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burland, T.G. DNASTAR’s Lasergene sequence analysis software. Bioinform. Methods Protoc. 2000, 132, 71–91. [Google Scholar]
- Bernt, M.; Donath, A.; Jühling, F.; Externbrink, F.; Florentz, C.; Fritzsch, G.; Pütz, J.; Middendorf, M.; Stadler, P.F. MITOS: Improved de novo metazoan mitochondrial genome annotation. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2013, 69, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, J.D.; Higgins, D.G.; Gibson, T.J. CLUSTAL W: Improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994, 22, 4673–4680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donath, A.; Jühling, F.; Al-Arab, M.; Bernhart, S.H.; Reinhardt, F.; Stadler, P.F.; Middendorf, M.; Bernt, M. Improved annotation of protein-coding genes boundaries in metazoan mitochondrial genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, 10543–10552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Kumar, S. MEGA11: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 11. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 3022–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Gao, F.L.; Jakovlić, I.; Zou, H.; Zhang, J.; Li, W.X.; Wang, G.T. PhyloSuite: An integrated and scalable desktop platform for streamlined molecular sequence data management and evolutionary phylogenetics studies. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2020, 20, 348–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, J.R.; Stothard, P. The CGView Server: A comparative genomics tool for circular genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, W181–W184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Illustrator, A. Adobe Illustrator. 2021. Available online: https://www.adobe.com/products/illustrator.html#modal-hash (accessed on 2 July 2025).
- Lorenz, R.; Bernhart, S.H.; Höner zu Siederdissen, C.; Tafer, H.; Flamm, C.; Stadler, P.F.; Hofacker, I.L. ViennaRNA package 2.0. algorithms. Mol. Biol. 2011, 6, 26. [Google Scholar]
- Perna, N.T.; Kocher, T.D. Patterns of nucleotide composition at fourfold degenerate sites of animal mitochondrial genomes. J. Mol. Evol. 1995, 41, 353–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Zhang, J.Y.; Deng, K.Z.; Chen, Z. The complete mitochondrial genome of the bristletail Songmachilis xinxiangensis (Archaeognatha: Machilidae). Mitochondr. DNA 2013, 24, 99–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameron, S.L.; Miller, K.B.; D’Haese, C.A.; Whiting, M.F.; Barker, S.C. Mitochondrial genome data alone are not enough to unambiguously resolve the relationships of Entognatha, Insecta and Crustacea sensu lato (Arthropoda). Cladistics 2004, 20, 534–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carapelli, A.; Liò, P.; Nardi, F.; Van der Wath, E.; Frati, F. Phylogenetic analysis of mitochondrial protein coding genes confirms the reciprocal paraphyly of Hexapoda and Crustacea. BMC Evol. Biol. 2007, 7 (Suppl. S2), S8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Podsiadlowski, L. The mitochondrial genome of the bristletail Petrobius brevistylis (Archaeognatha: Machilidae). Insect Mol. Biol. 2006, 15, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, S.Q.; Cai, Y.Y.; Xu, K.K.; Chen, Q.P.; Cao, S.S.; Yu, D.N.; Zhang, J.Y. The complete mitochondrial genome of Pedetontus zhejiangensis (Microcoryphia: Machilidae) and its phylogeny. Mitochondr. DNA B 2020, 5, 3143–3145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, C.E.; Yue, Q.; Akam, M. Mitochondrial genomes suggest that hexapods and crustaceans are mutually paraphyletic. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2005, 272, 1295–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoh, K.; Standley, D.M. MAFFT multiple sequence alignment software version 7: Improvements in performance and usability. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talavera, G.; Castresana, J. Improvement of phylogenies after removing divergent and ambiguously aligned blocks from protein sequence alignments. Syst. Biol. 2007, 56, 564–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castresana, J. Selection of conserved blocks from multiple alignments for their use in phylogenetic analysis. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2000, 17, 540–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.; Xie, Z. DAMBE: Software package for data analysis in molecular biology and evolution. J. Hered. 2001, 92, 371–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrago, C.G.; Aguiar, B.O.; Mello, B. Comparative evaluation of maximum parsimony and Bayesian phylogenetic reconstruction using empirical morphological data. J. Evol. Biol. 2018, 31, 1477–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes-Hernández, J.L.; Hansen, A.K.; Jenkins Shaw, J.; Solodovnikov, A. Phylogeny-based taxonomic revision and niche modelling of the rove beetle genus Loncovilius Germain, 1903 (Coleoptera: Staphylinidae: Staphylininae). Zool. J. Linn. Soc. 2024, 202, zlad143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanfear, R.; Calcott, B.; Ho, S.Y.; Guindon, S. PartitionFinder: Combined selection of partitioning schemes and substitution models for phylogenetic analyses. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2012, 29, 1695–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrieze, S.I. Model selection and psychological theory: A discussion of the differences between the Akaike information criterion (AIC) and the Bayesian information criterion (BIC). Psychol. Methods 2012, 17, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minh, B.Q.; Schmidt, H.A.; Chernomor, O.; Schrempf, D.; Woodhams, M.D.; Von Haeseler, A.; Lanfear, R. IQ-TREE 2: New models and efficient methods for phylogenetic inference in the genomic era. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2020, 37, 1530–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronquist, F.; Teslenko, M.; Van Der Mark, P.; Ayres, D.L.; Darling, A.; Höhna, S.; Larget, B.; Liu, L.; Suchard, M.A.; Huelsenbeck, J.P. MrBayes 3.2: Efficient Bayesian phylogenetic inference and model choice across a large model space. Syst. Biol. 2012, 61, 539–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rambaut, A. FigTree Version 1.4.4. Available online: http://tree.bio.ed.ac.uk/software/figtree/ (accessed on 1 July 2025).
- Near, T.J.; Sanderson, M.J. Assessing the quality of molecular divergence time estimates by fossil calibrations and fossil–based model selection. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. London Ser. B Biol. Sci. 2004, 359, 1477–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Rannala, B. Bayesian estimation of species divergence times under a molecular clock using multiple fossil calibrations with soft bounds. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2006, 23, 212–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Püschel, H.P.; O’Reilly, J.E.; Pisani, D.; Donoghue, P.C. The impact of fossil stratigraphic ranges on tip-calibration, and the accuracy and precision of divergence time estimates. Palaeontology 2020, 63, 67–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keilbach, R. Bibliographie und Liste der Arten tierischer Einschlüsse in fossilen Harzen sowie ihrer Aufbewahrungsorte. Deut. Entomol. Z. 1982, 29, 129–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sturm, H.; Poinar Jr, G.O. Cretaceomachilis libanensis, the oldest known bristle-tail of the family Meinertellidae (Machiloidea, Archaeognatha, Insecta) from the Lebanese Amber. Deut. Entomol. Z. 1998, 45, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z. PAML 4: Phylogenetic analysis by maximum likelihood. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2007, 24, 1586–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rambaut, A.; Drummond, A.J.; Xie, D.; Baele, G.; Suchard, M.A. Posterior summarization in Bayesian phylogenetics using Tracer 1.7. Syst. Biol. 2018, 67, 901–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drummond, A.J.; Rambaut, A. BEAST: Bayesian evolutionary analysis by sampling trees. BMC Evol. Biol. 2007, 7, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, F.; Chen, C.; Arab, D.A.; Du, Z.; He, Y.; Ho, S.Y. EasyCodeML: A visual tool for analysis of selection using CodeML. Ecol. Evol. 2019, 9, 3891–3898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z. Likelihood ratio tests for detecting positive selection and application to primate lysozyme evolution. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1998, 15, 568–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Nielsen, R.; Yang, Z. Evaluation of an improved branch-site likelihood method for detecting positive selection at the molecular level. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2005, 22, 2472–2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bielawski, J.P.; Yang, Z. A maximum likelihood method for detecting functional divergence at individual codon sites, with application to gene family evolution. J. Mol. Evol. 2004, 59, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bielawski, J.P.; Yang, Z. Maximum likelihood methods for detecting adaptive evolution after gene duplication. J. Struct. Funct. Genom. 2003, 3, 201–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huelsenbeck, J.P.; Rannala, B. Phylogenetic methods come of age: Testing hypotheses in an evolutionary context. Science 1997, 276, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Wong, W.S.; Nielsen, R. Bayes empirical Bayes inference of amino acid sites under positive selection. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2005, 22, 1107–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplin, V. A new species of bristletails of the genus Petrobiellus (Microcoryphia: Machilidae) from Sakhalin. Zoosystematica Ross. 2020, 29, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mtow, S.; Machida, R. What are Halomachilis akkesiensis and Halomachilis kojimai described from Hokkaido, Japan? (Insecta: Archaeognatha: Machilidae). Zootaxa 2024, 5543, 445–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olfers, E.V. Die «Ur-Insekten» (Thysanura und Collembola im Bernstein). Schr. K. Phys.-ökon. Ges. Königsb. 1907, 48, 1–40. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.; Xu, C.; Jarzembowski, E.A. Ecological radiations of insects in the Mesozoic. Trends. Ecol. Evol. 2022, 37, 529–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Huang, C.; Sun, B.; Quan, C.; Wu, J.; Lin, Z. Paleo-CO2 variation trends and the Cretaceous greenhouse climate. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2014, 129, 136–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLoughlin, S. The breakup history of Gondwana and its impact on pre-Cenozoic floristic provincialism. Aust. J. Bot. 2001, 49, 271–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laenen, B.; Shaw, B.; Schneider, H.; Goffinet, B.; Paradis, E.; Désamoré, A.; Heinrichs, J.; Villarreal, J.; Gradstein, S.; McDaniel, S. Extant diversity of bryophytes emerged from successive post-Mesozoic diversification bursts. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benton, M.J. The origins of modern biodiversity on land. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B. Biol. Sci. 2010, 365, 3667–3679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.Y.; Yuan, P.B.; Tsao, S.-J. Temporal and spatial records of active arc-continent collision in Taiwan: A synthesis. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 2006, 118, 274–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.F.; Xu, X.; Lin, J.; Sun, Z.; Zhu, J.; Yao, Y.; Zhao, X.; Liu, Q.; Kulhanek, D.K.; Wang, J. Ages and magnetic structures of the South China Sea constrained by deep tow magnetic surveys and IODP Expedition 349. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2014, 15, 4958–4983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashman, L.G.; Shin, S.; Zwick, A.; Ślipiński, A.; McKenna, D.D. The first phylogeny of Australasian Lamiinae longhorn beetles (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae) reveals poor tribal classification and a complex biogeographic history. Syst. Entomol. 2022, 47, 213–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decru, E.; Moelants, T.; De Gelas, K.; Vreven, E.; Verheyen, E.; Snoeks, J. Taxonomic challenges in freshwater fishes: A mismatch between morphology and DNA barcoding in fish of the north-eastern part of the Congo basin. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2016, 16, 342–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirano, T.; Kameda, Y.; Kimura, K.; Chiba, S. Substantial incongruence among the morphology, taxonomy, and molecular phylogeny of the land snails Aegista, Landouria, Trishoplita, and Pseudobuliminus (Pulmonata: Bradybaenidae) occurring in East Asia. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2014, 70, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreu, A.L.; Hanna, M.G.; Reichmann, H.; Bruno, C.; Penn, A.S.; Tanji, K.; Pallotti, F.; Iwata, S.; Bonilla, E.; Lach, B. Exercise intolerance due to mutations in the cytochrome b gene of mitochondrial DNA. N. Engl. J. Med. 1999, 341, 1037–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chance, B.; Wilson, D.; Dutton, P.; Erecińska, M. Energy-coupling mechanisms in mitochondria: Kinetic, spectroscopic, and thermodynamic properties of an energy-transducing form of cytochrome b. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1970, 66, 1175–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, K.M.; Strauss, M.; Daum, B.; Kief, J.H.; Osiewacz, H.D.; Rycovska, A.; Zickermann, V.; Kühlbrandt, W. Macromolecular organization of ATP synthase and complex I in whole mitochondria. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 14121–14126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Dotto, V.; Musiani, F.; Baracca, A.; Solaini, G. Variants in human ATP synthase mitochondrial genes: Biochemical dysfunctions, associated diseases, and therapies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 2239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazarou, M.; Smith, S.M.; Thorburn, D.R.; Ryan, M.T.; McKenzie, M. Assembly of nuclear DNA-encoded subunits into mitochondrial complex IV, and their preferential integration into supercomplex forms in patient mitochondria. FEBS J. 2009, 276, 6701–6713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourens, M.; Barrientos, A. A CMC 1-knockout reveals translation-independent control of human mitochondrial complex IV biogenesis. EMBO Rep. 2017, 18, 477–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.H.; Huang, H.M.; Wu, L.; Storey, K.B.; Zhang, J.Y.; Zhang, Y.P.; Yu, D.N. Characterization of two mitogenomes of Hyla sanchiangensis (Anura: Hylidae), with phylogenetic relationships and selection pressure analyses of Hylidae. Animals 2023, 13, 1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngatia, J.N.; Lan, T.M.; Dinh, T.D.; Zhang, L.; Ahmed, A.K.; Xu, Y.C. Signals of positive selection in mitochondrial protein-coding genes of woolly mammoth: Adaptation to extreme environments? Ecol. Evol. 2019, 9, 6821–6832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Species | Sampling Localities | Geographic Coordinates | Accession No. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pedetontinus songi | Taimushan, Fujian | 27°07′27″ N, 120°11′05″ E | PX391408 |
| Pedetontinus jinzhaiensis | Jinzhai, Anhui | 31°18′13″ N, 115°40′38″ E | PX391406 |
| Pedetontinus mengshanensis | Mengshan, Shandong | 35°31′07″ N, 117°49′17″ E | PX391407 |
| Pedetontinus tianmuensis | Chuzhou, Anhui | 32°20′42″ N, 118°25′30″ E | PX391409 |
| Pedetontinus yongjiaensis | Yongjia, Zhejiang | 28°09′14″ N, 120°41′29″ E | PX391410 |
| Pedetontus lanxiensis | Lanxi, Zhejiang | 29°12′33″ N, 119°27′38″ E | PX391417 |
| Pedetontus hainanensis | Wuzhishan, Hainan | 18°51′43″ N, 109°37′33″ E | PX391416 |
| Pedetontus formosa | Baxiandong, Taiwan | 23°23′28″ N, 121°29′04″ E | PX391415 |
| Pedetontus zhoui | Taimushan, Fujian | 27°07′27″ N, 120°11′05″ E | PX391419 |
| Pedetontus bawanglingensis | Bawangling, Hainan | 19°03′49″ N, 109°10′14″ E | PX391411 |
| Pedetontus dachendaoensis DCD | Dachendao, Zhejiang | 28°28′20″ N, 121°54′06″ E | PX391414 |
| Pedetontus cixiensis | Cixi, Zhejiang | 30°10′18″ N, 121°15′39″ E | PX391412 |
| Pedetontus dachendaoensis TT | Taizhou, Zhejiang | 28°50′49″ N, 121°06′50″ E | PX391413 |
| Pedetontus zhejiangensis TPS | Suzhou, Zhejiang | 31°01′59″ N, 120°51′14″ E | PX391418 |
| Subset | Best Model | Partition Names |
|---|---|---|
| Partition_1 | GTR + I + G | COII_codon1, COIII_codon1, ND3_codon1, Cytb_codon1, ATP6_codon1 |
| Partition_2 | GTR + I + G | COI_codon2, COIII_codon2, Cytb_codon2, ATP6_codon2, COII_codon2 |
| Partition_3 | GTR + G | ND3_codon3, COIII_codon3, Cytb_codon3, COI_codon3, COII_codon3 |
| Partition_4 | TIM + G | ND6_codon3, ND2_codon3, ATP8_codon3, ATP6_codon3 |
| Partition_5 | GTR + I + G | ND6_codon1, ATP8_codon2, ND2_codon1, ATP8_codon1 |
| Partition_6 | SYM + I + G | COI_codon1 |
| Partition_7 | GTR + I + G | ND5_codon1, ND4_codon1, ND1_codon1, ND4L_codon1 |
| Partition_8 | GTR + I + G | ND1_codon2, ND5_codon2, ND4_codon2, ND4L_codon2 |
| Partition_9 | TVM + G | ND5_codon3, ND4L_codon3, ND1_codon3, ND4_codon3 |
| Partition_10 | TVM + I + G | ND6_codon2, ND2_codon2, ND3_codon2 |
| Branch Site Model (BSM) | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | np | Ln L | Estimates of Parameters | Model Compared | LRT p-Value | Positive Sites | ||||
| Model A | 71 | −221,646.437857 | Site class | 0 | 1 | 2a | 2b | Model A vs. Model A null | 0.000884974 | 66 S 0.965 *, 1168 S 0.980 * |
| Proportion | 0.83698 | 0.15409 | 0.00754 | 0.00139 | ||||||
| Background ω | 0.05727 | 1.00000 | 0.05727 | 1.00000 | ||||||
| Foreground ω | 0.05727 | 1.00000 | 46.18276 | 46.18276 | ||||||
| Model A null | 70 | −221,651.964843 | ||||||||
| Branch Site Model (BSM) | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | np | Ln L | Estimates of Parameters | Model Compared | LRT p-Value | Positive Sites | ||||
| Model A | 71 | −221,635.143815 | Site class | 0 | 1 | 2a | 2b | Model A vs. Model A null | 0.000018027 | 622 F 0.953 *, 1633 Q 0.967 *, 2591 S 0.968 *, 2841 V 0.960 *, 3075 I 0.955 *, 3109 M 0.963 * |
| Proportion | 0.83368 | 0.15291 | 0.01133 | 0.00208 | ||||||
| Background ω | 0.05721 | 1.00000 | 0.05721 | 1.00000 | ||||||
| Foreground ω | 0.05721 | 1.00000 | 106.37636 | 106.37636 | ||||||
| Model A null | 70 | −221,644.337408 | ||||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cen, W.; Yang, T.; Li, J.-W.; Yu, D.-N.; Storey, K.B.; Zhang, J.-Y. Comparative Mitogenomics of Pedetontus and Pedetontinus (Insecta: Archaeognatha) Unveils Phylogeny, Divergence History, and Adaptive Evolution. Insects 2025, 16, 1194. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16121194
Cen W, Yang T, Li J-W, Yu D-N, Storey KB, Zhang J-Y. Comparative Mitogenomics of Pedetontus and Pedetontinus (Insecta: Archaeognatha) Unveils Phylogeny, Divergence History, and Adaptive Evolution. Insects. 2025; 16(12):1194. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16121194
Chicago/Turabian StyleCen, Wei, Ting Yang, Jia-Wen Li, Dan-Na Yu, Kenneth B. Storey, and Jia-Yong Zhang. 2025. "Comparative Mitogenomics of Pedetontus and Pedetontinus (Insecta: Archaeognatha) Unveils Phylogeny, Divergence History, and Adaptive Evolution" Insects 16, no. 12: 1194. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16121194
APA StyleCen, W., Yang, T., Li, J.-W., Yu, D.-N., Storey, K. B., & Zhang, J.-Y. (2025). Comparative Mitogenomics of Pedetontus and Pedetontinus (Insecta: Archaeognatha) Unveils Phylogeny, Divergence History, and Adaptive Evolution. Insects, 16(12), 1194. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16121194






