Transcriptome Characterization and Identification of Chemosensory Genes in the Egg Parasitoid Anastatus orientalis, Along with Molecular Cloning, Sequence Analysis, and Prokaryotic Expression of the Odorant Binding Protein 8 (AoOBP8) from A. orientalis
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Insect Collection
2.2. RNA Extraction and cDNA Library Construction and Transcriptome Sequencing
2.3. Transcriptome Assembly, Gene Annotation, Identification and Sequence Analysis
2.4. Molecular Cloning and Prokaryotic Expression of the Odorant Binding Protein 8 of A. orientalis (AoOBP8)
2.4.1. RNA Isolation and AoOBP8 cDNA Synthesis
2.4.2. Molecular Cloning
2.4.3. Bioinformatic and Phylogenetic Analyses
2.4.4. Expression of AoOBP8 Gene
2.4.5. Prokaryotic Expression and Identification of His-AoOBP8
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Transcriptome Sequencing and Assembly of A. orientalis
3.2. Functional Annotation of the Unigenes in A. orientalis
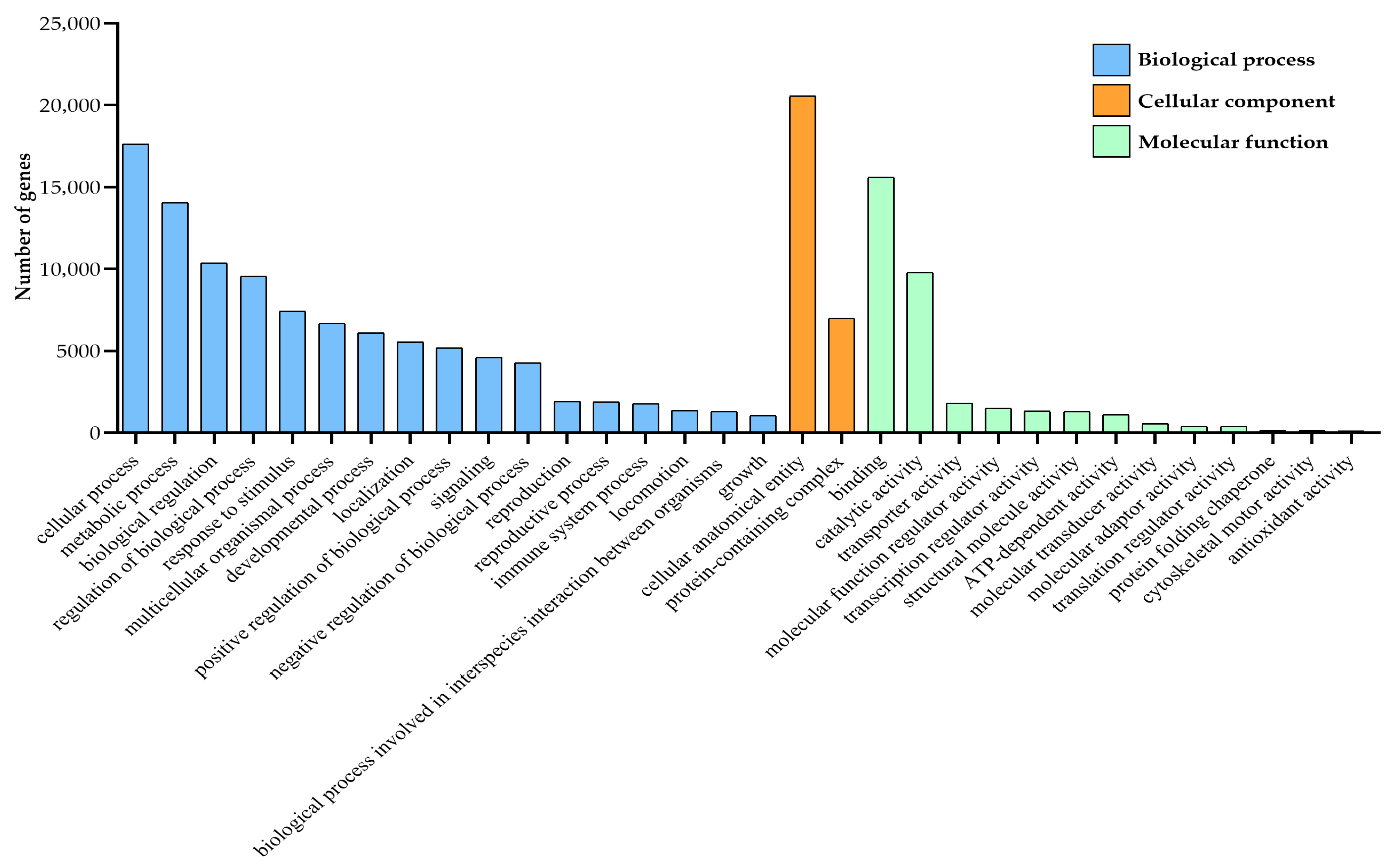
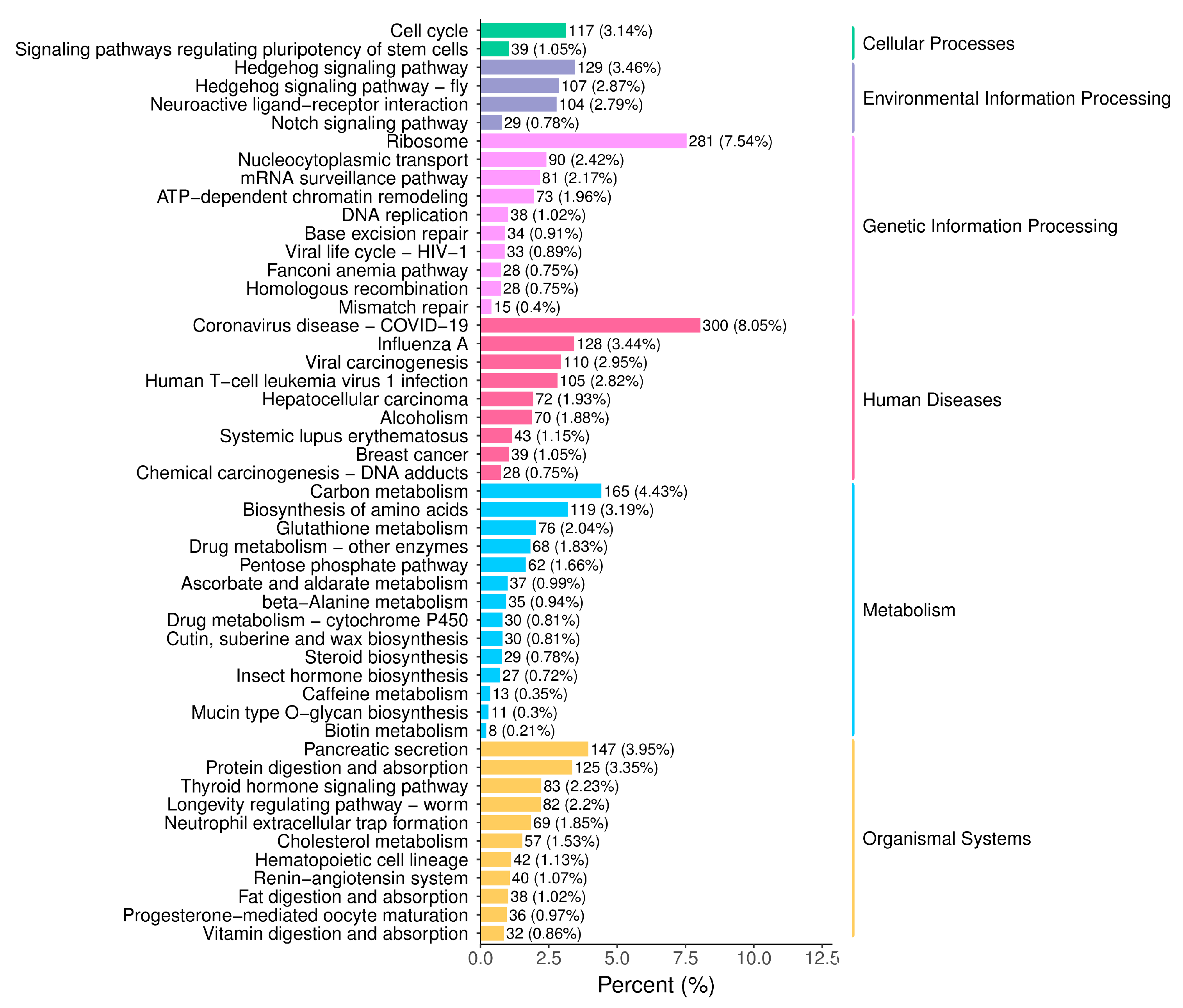
3.3. Functional Classification of Unigenes in A. orientalis
3.3.1. GO Enrichment Analysis
3.3.2. KEGG Enrichment Analysis
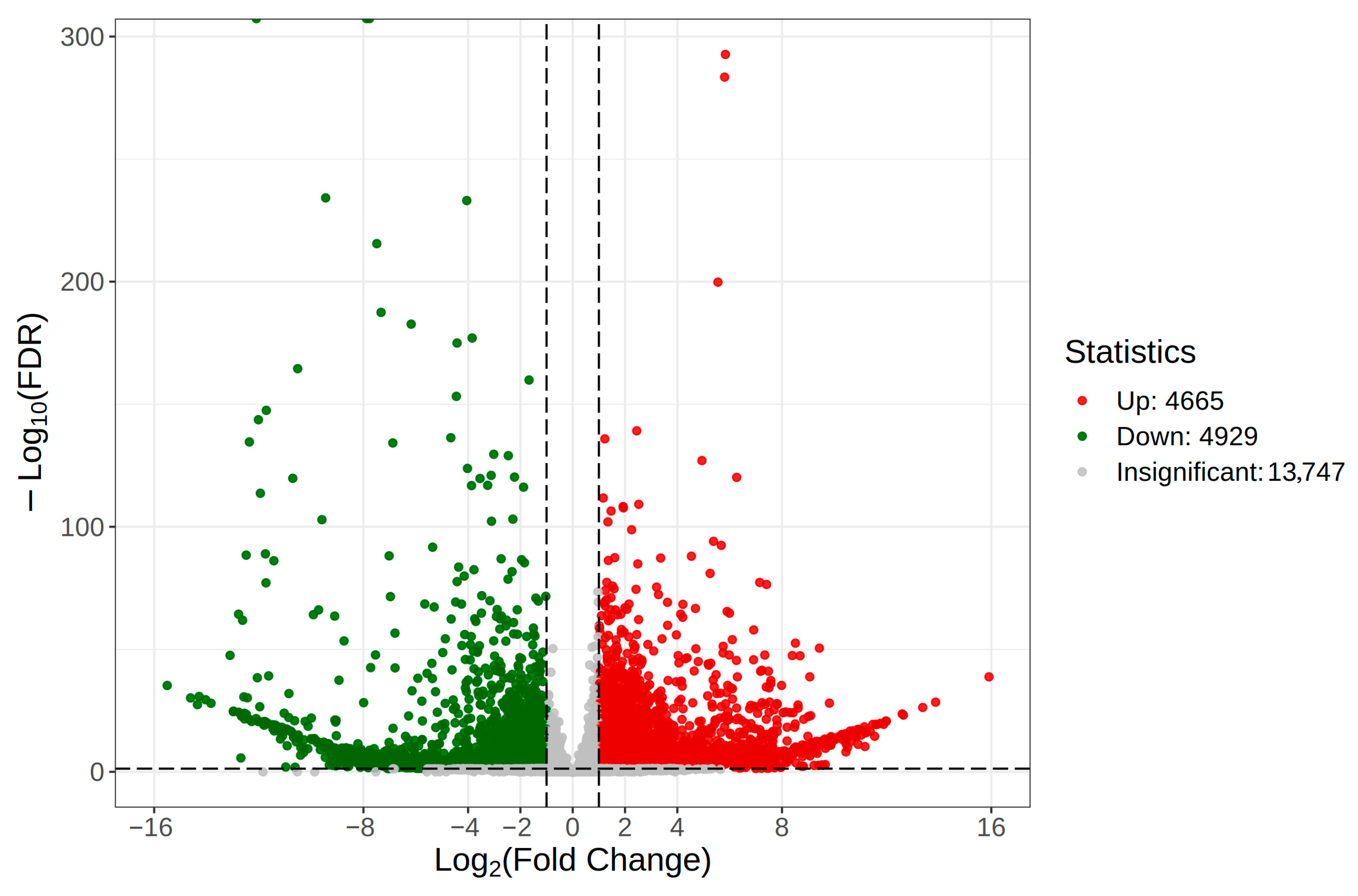
3.4. Analysis of Differentially Expressed Genes and Identification and Analysis of Candidate Chemosensory Protein Genes
3.5. Molecular Cloning and Prokaryotic Expression of AoOBP8
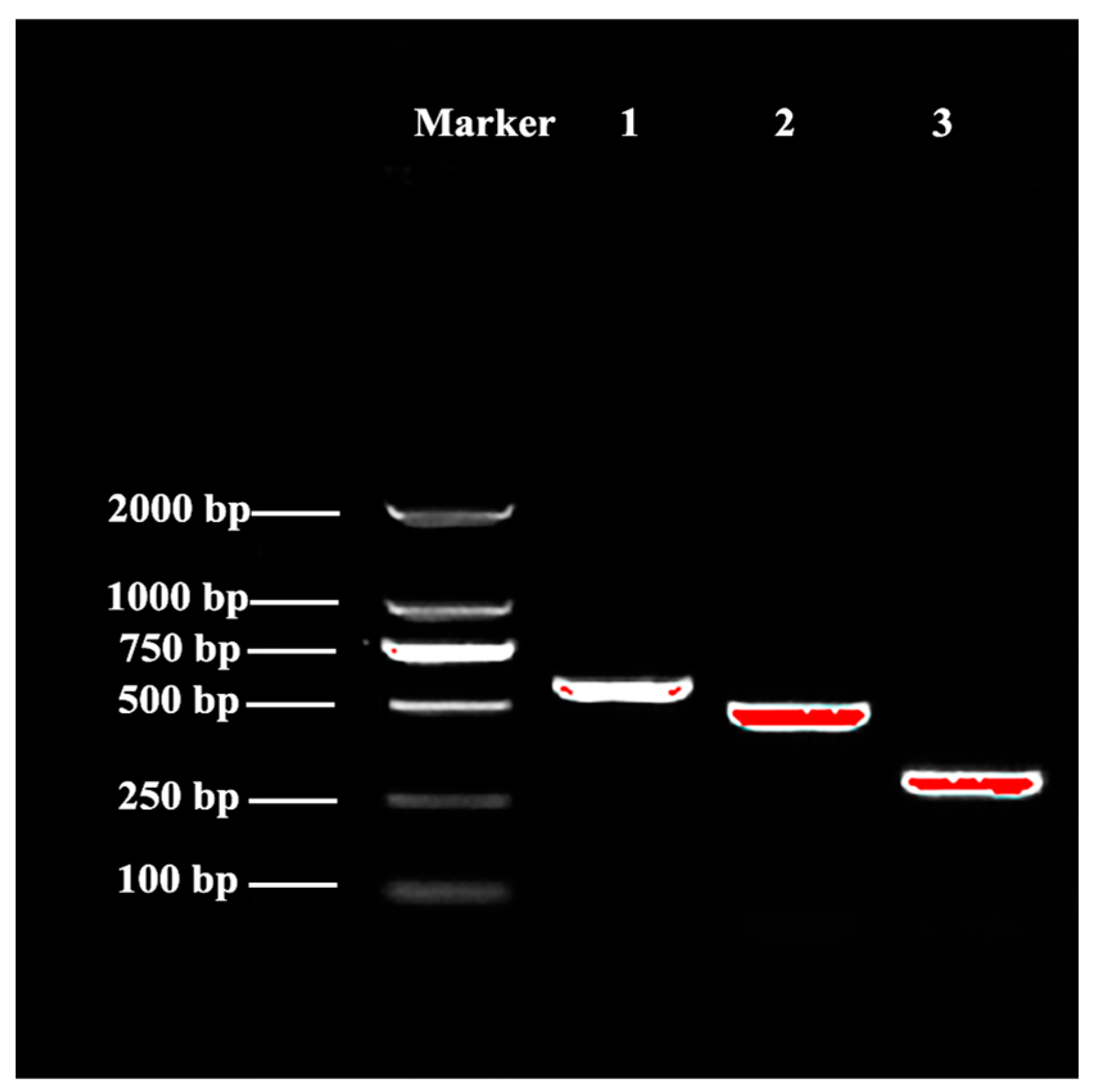
3.5.1. Cloning and Sequence Analysis of AoOBP8
3.5.2. Sequence Alignment and Phylogenetic Analysis of AoOBP8
3.5.3. Expression of AoOBP8 in Male and Female Adults and in Various Tissues
3.5.4. Prokaryotic Expression of AoOBP8
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lee, D.H.; Park, Y.L.; Leskey, T.C. A review of biology and management of Lycorma delicatula (Hemiptera: Fulgoridae), an emerging global invasive species. J. Asia-Pac. Entomol. 2019, 22, 589–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barringer, L.; Ciafré, C.M. Worldwide feeding host plants of spotted lanternfly, with significant additions from north America. Environ. Entomol. 2020, 49, 999–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leach, H.; Biddinger, D.J.; Krawczyk, G.; Smyers, E.; Urban, J.M. Evaluation of insecticides for control of the spotted lanternfly, Lycorma delicatula, (Hemiptera: Fulgoridae), a new pest of fruit in the Northeastern US. Crop Prot. 2019, 124, 104833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francese, J.A.; Cooperband, M.F.; Murman, K.M.; Cannon, S.L.; Booth, E.G.; Devine, S.M.; Wallace, M.S. Developing traps for the spotted lanternfly, Lycorma delicatula (Hemiptera: Fulgoridae). Environ. Entomol. 2020, 49, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooperband, M.F.; Mack, R.; Spichiger, S.E. Chipping to destroy egg masses of the spotted lanternfly, Lycorma delicatula (Hemiptera: Fulgoridae). J. Insect Sci. 2018, 18, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urban, J.M.; Leach, H. Biology and management of the spotted lanternfly, Lycorma delicatula (Hemiptera: Fulgoridae), in the United States. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2023, 68, 151–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godfray, H.C.J. Parasitoids: Behavioral and Evolutionary Ecology; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 1994; p. 194. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.Q.; Choi, W.Y.; Cao, L.M.; Wang, X.Y.; Hou, Z.R. A new species of Anastatus (Hymenoptera: Eulpelmidae) from China, parasitizing eggs of Lycorma delicatula (Homoptera: Fulgoridae). Zool. Syst. 2015, 40, 290–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, K.X.; Dang, Y.Q.; Zhuang, Y.T.; Fan, M.X.; Wang, X.Y. Evaluation of parasitic capacity of Anastatus orientalis (Hymenoptera: Eupelmidae) on eggs of Antherea pernyi (Lepidoptera: Saturniidae) based on functional response Model. Chin. J. Biol. Control 2025, 41, 260–268. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, Z.R. Study on the Lycorma delicatula and Egg Parasitoids. Master’s Thesis, Chinese Academy of Forestry, Beijing, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, K.X. Studies on the Field Lethal Factor of Spotted Lanternfly and Biology of Its Natural Enemy at Egg Stage—Anastatus orientalis. Master’s Thesis, Agricultural University of Hebei, Baoding, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.B.; Wu, H.; Yi, J.Q.; Song, Z.W.; Li, D.S.; Zhang, G.R. Transcriptome characterization and gene expression analysis related to chemoreception in Trichogramma chilonis, an egg parasitoid. Gene 2018, 678, 288–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Zhou, X.; Xu, Z.Y.; Zhang, X.F.; Yuan, H.C.; Guo, J.X. Transcriptome analysis and identification of chemosensory membrane proteins in the head of Euplatypus parallelus. Insects 2025, 16, 504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.N.; Wang, F.Z.; Zhang, X.Y.; Zhang, S.H.; Guo, S.L.; Zhu, G.P.; Liu, Q.; Li, M. Transcriptome and expression patterns of chemosensory genes in antennae of the parasitoid wasp Chouioia cunea. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0148159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.J.C.; Chen, H.C.; Hong, T.L.; Yan, M.W.; Wang, J.; Shao, Z.M.; Wu, F.A.; Sheng, S.; Wang, J. Identification of chemosensory genes by antennal transcriptome analysis and expression profiles of odorant-binding proteins in parasitoid wasp Aulacocentrum confusum. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part D Genom. Proteom. 2021, 40, 100881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinson, S.B. The general host selection behavior of parasitoid Hymenoptera and a comparison of initial strategies utilized by larvaphagous and oophagous species. Biol. Control 1998, 11, 79–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vet, L.E.M.; Dicke, M. Ecology of Infochemical Use by Natural Enemies in a Tritrophic Context. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 1992, 37, 141–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turlings, T.C.; Tumlinson, J.H.; Lewis, W.J. Exploitation of herbivore-induced plant odors by host-seeking parasitic wasps. Science 1990, 250, 1251–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Moraes, C.M.; Lewis, W.J.; Pare, P.W.; Alborn, H.T.; Tumlinson, J.H. Herbivore-infested plants selectively attract parasitoids. Nature 1998, 393, 570–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.N.; Peng, Y.; Lu, Z.Y.; Dhiloo, K.H.; Gu, S.H.; Li, R.J.; Zhou, J.J.; Zhang, Y.J.; Guo, Y.Y. Identification and expression analysis of putative chemosensory receptor genes in Microplitis mediator by antennal transcriptome screening. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2015, 11, 737–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishimura, O.; Brillada, C.; Yazawa, S.; Maffei, M.E.; Arimura, G. Transcriptome pyrosequencing of the parasitoid wasp Cotesia vestalis: Genes involved in the antennal odorant-sensory system. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e50664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, H.X.; Li, L.; Li, F.Q.; Zang, L.S. Identification and comparative expression profiles of candidate olfactory receptors in the transcriptomes of the important egg parasitoid wasp Anastatus japonicus Ashmead (Hymenoptera: Eupelmidae). Plants 2023, 12, 915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.X.; Min, S.F.; Tang, Y.L.; Wang, M.Q. Analysis of antennal transcriptome and odorant binding protein expression profiles of the recently identified parasitoid wasp, Sclerodermus sp. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. D Genom. Proteom. 2015, 16, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Xu, Z.; Yang, W.J.; Mao, Y.; Sheng, L.Y.; Du, J.L.; Wu, D.G.; Wang, Z.X.; Huang, B.H. Analysis of the transcriptome and chemosensory-related genes of Telenomus remus Nixon. Plant Prot. 2022, 48, 264–277. [Google Scholar]
- Seo, M.; Kim, J.H.; Seo, B.Y.; Park, C.; Choi, B.R.; Kim, K.H.; Ji, C.W.; Cho, J.R. Mass-rearing techniques of Anastatus orientalis (Hymenoptera: Eupelmidae), as the egg-parasitoid of Lycorma delicatula (Hemiptera: Fulgoridae): An using method of Antheraea pernyi (Lepidoptera: Saturniidae) and L. delicatula eggs in laboratory. Kor. J. Appl. Entomol. 2018, 57, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchfink, B.; Xie, C.; Huson, D.H. Fast and sensitive protein alignment using DIAMOND. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 59–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanehisa, M.; Goto, S.; Kawashima, S.; Okuno, Y.; Hattori, M. The KEGG resource for deciphering the genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, 277–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, C.; Mao, X.; Huang, J.; Ding, Y.; Wu, J.; Dong, S.; Kong, S.; Gao, G.; Li, C.Y.; Wei, L.P. KOBAS 2.0: A web server for annotation and identification of enriched pathways and diseases. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, 316–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, P.; Binns, D.; Chang, H.Y.; Fraser, M.; Li, W.; McAnulla, C.; McWilliam, H.; Maslen, J.; Mitchell, A.; Nuka, G.; et al. InterProScan 5: Genome-scale protein function classification. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 1236–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashburner, M.; Ball, C.A.; Blake, J.A.; Botstein, D.; Butler, H.; Cherry, J.M.; Davis, A.P.; Dolinski, K.; Dwight, S.S.; Eppig, J.T.; et al. Gene ontology: Tool for the unification of biology. Nat. Genet. 2000, 25, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eddy, S.R. Profile hidden Markov models. Bioinformatics 1998, 14, 755–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finn, R.D.; Bateman, A.; Clements, J.; Coggill, P.; Eberhardt, R.Y.; Eddy, S.R.; Heger, A.; Hetherington, K.; Holm, L.; Mistry, J.; et al. Pfam: The protein families database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, 222–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortazavi, A.; Williams, B.A.; McCue, K.; Schaeffer, L.; Wold, B. Mapping and quantifying mammalian transcriptomes by RNA-Seq. Nat Methods 2008, 5, 621–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.Q.; Yu, C.; Li, Y.R.; Lam, T.W.; Yiu, S.M.; Kristiansen, K.; Wang, J. SOAP2: An improved ultrafast tool for short read alignment. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1966–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods Enzymol. 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broadley, H.J.; Sipolski, S.J.; Pitt, D.B.; Hoelmer, K.A.; Wang, X.Y.; Cao, L.M.; Tewksbury, L.A.; Hagerty, T.J.; Bartlett, C.R.; Russell, A.D.; et al. Assessing the host range of Anastatus orientalis, an egg parasitoid of spotted lanternfly (Lycorma delicatula) using Eastern U.S. non-target species. Front. Insect Sci. 2023, 3, 1154697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, I.K.; Koh, S.H.; Lee, J.S.; Choi, W.I.; Shin, S.C. Discovery of an egg parasitoid of Lycorma delicatula (Hemiptera: Fulgoridae) an invasive species in South Korea. J. Asia-Pac. Entomol. 2011, 14, 213–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.Y.; Bai, Y.Y.; Zhao, Y.Y.; Qi, Y.; Jiang, N.; Liu, B.Z.; Lü, S.J.; Xie, S.A. Morphology and ultrastructure of the antennal sensilla of adult Anastatus orientalis (Hymenoptera: Eupelmidae), a parasitoid of Lycorma delicatula (Hemiptera: Fulgoridae). Acta Entomol. Sin. 2025, 68, 123–132. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; Wei, K.; Bao, K.X.; Xie, J.Y.; Wang, X.Y. Ultrastructure of antennal sensilla of Anastatus orientalis (Hymenoptera: Eupelmidae), an egg parasitoid of the invasive spotted lanternfly, Lycorma delicatula (Hemiptera: Fulgoridae). Ultramicroscopy 2025, 276, 114179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.P.; Du, L.X.; Zhu, Y.; Yang, S.Y.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, G.R.; Liu, Y. Identification and sex-biased profiles of candidate olfactory genes in the antennal transcriptome of the parasitoid wasp Cotesia vestalis. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. D Genom. Proteom. 2020, 34, 100657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.Y.; Wang, X.Y.; Lu, W.; Zheng, X.L. Sensory gene identification in the transcriptome of the ectoparasitoid Quadrastichus mendeli. Sci. Rep. 2021, 111, 9726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Guo, Z.X.; Wang, L.Y.; Wang, B.Y.; Huang, T.F.; Tang, B.J.; Zhang, G.R.; Zhou, Q. The genome of the rice planthopper egg parasitoid wasps Anagrus nilaparvatae casts light on the chemo- and mechanosensation in parasitism. BMC Genom. 2022, 23, 541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, X.P.; Li, Q.L.; Xu, C.; Li, D.Z.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, M.Q.; Zhou, A.M.; Li, S.Q. Antennal transcriptome and odorant binding protein expression profiles of an invasive mealybug and its parasitoid. J. Appl. Entomol. 2018, 142, 149–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Z.W.; Tian, H.G.; Liu, F.H.; Liu, X.; Jing, X.F.; Liu, T.X. Identification and expression analysis of chemosensory receptor genes in an aphid endoparasitoid Aphidius gifuensis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 3939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, T.; Zhang, T.T.; Wang, Z.Y.; He, K.L.; Bai, S.X. Gene set of chemosensory receptors in the polyembryonic endoparasitoid Macrocentrus cingulum. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelosi, P.; Maida, R. Odorant-binding proteins in insects. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1995, 111, 503–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.F.; Kong, X.B.; Wang, H.B.; Zhou, G.; Yu, J.X.; Liu, F.; Zhang, Z. Sensory and immune genes identification and analysis in a widely used parasitoid wasp Trichogramma dendrolimi (Hymenoptera: Trichogrammatidae). Insect Sci. 2016, 23, 417–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.D.; Shen, Z.C.; Hua, H.Q.; Zhang, F.; Li, Y.X. Identification and sex expression profiling of odorant-binding protein genes in Trichogramma japonicum, (Hymenoptera: Trichogrammatidae) using RNA-seq. Appl. Entomol. Zool. 2017, 52, 623–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonduriansky, R. The evolution of male mate choice in insects: A synthesis of ideas and evidence. Biol. Rev. 2001, 76, 305–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal, W.S. Odorant reception in insects: Roles of receptors, binding proteins, and degrading enzymes. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2013, 58, 373–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vosshall, L.B.; Amrein, H.; Morozov, P.S.; Rzhetsky, A.; Axel, R. A spatial map of olfactory receptor expression in the Drosophila antenna. Cell 1999, 96, 725–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, T.; Zhang, T.T.; Wang, Z.Y.; He, K.L.; Bai, S.X. Identification and expression pattern analysis of chemosensory receptor genes in the Macrocentrus cingulum (Hymenoptera: Braconidae) antennae. Eur. J. Entomol. 2016, 113, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poivet, E.; Gallot, A.; Montagné, N.; Glaser, N.; Legeai, F.; Jacquinjoly, E. A comparison of the olfactory gene repertoires of adults and larvae in the noctuid moth Spodoptera littoralis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e60263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheng, S.; Liao, C.W.; Zheng, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Xu, Y.; Song, W.M.; He, P.; Zhang, J.; Wu, F.A. Candidate chemosensory genes identified in the endoparasitoid Meteorus pulchricornis (Hymenoptera: Braconidae) by antennal transcriptome analysis. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. D Genom. Proteom. 2017, 22, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benton, R.; Vannice, K.S.; Gomez-Diaz, C.; Vosshall, L.B. Variant ionotropic glutamate receptors as chemosensory receptors in Drosophila. Cell 2009, 136, 149–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, M.; Min, S.; Grosjean, Y.; Leblanc, C.; Bell, R.; Benton, R.; Suh, G.B. Acid sensing by the Drosophila olfactory system. Nature 2010, 468, 691–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forstner, M.; Gohl, T.; Gondesen, I.; Raming, K.; Breer, H.; Krieger, J. Differential expression of snmp-1 and snmp-2 proteins in pheromone-sensitive hairs of moths. Chem. Senses 2008, 33, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, M.E.; Krieger, J.; Vogt, R.G. Antennal SNMPs (sensory neuron membrane proteins) of lepidoptera define a unique family of invertebrate CD36-like proteins. J. Neurobiol. 2001, 49, 47–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, L.A.; Dahanukar, A.; Kwon, J.Y.; Banerjee, D.; Carlson, J.R. The molecular and cellular basis of bitter taste in Drosophila. Neuron 2011, 69, 258–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, K.; Brady, R.; Cravchik, A.; Morozov, P.; Rzhetsky, A.; Zuker, C.; Axel, R. A chemosensory gene family encoding candidate gustatory and olfactory receptors in Drosophila. Cell 2001, 104, 661–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.W.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.P.; Wu, J.X.; Xu, X.L. Cloning, expression, and functional analysis of three odorant-binding proteins of the oriental fruit moth, Grapholita molesta (busck) (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae). Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 2016, 91, 67–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.R.; Pei, Y.W.; Zhang, X.Q.; Lu, M.; Liu, X.L. Different binding properties of odorant-binding protein 8 to insecticides in Orius sauteri. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2024, 200, 105842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







| Primer Names | Primer Sequences | Length of Primer | Primer Usage |
|---|---|---|---|
| AoOBP8-F | GATATTCGTCCTCGTTGG | 18 bp | amplification of intermediate fragments |
| AoOBP8-R | ATCTTTCGGCGTAGCATT | 18 bp | |
| AoOBP8-R1 | GCAGCCGTAGCAATCATCTT | 20 bp | 5′RACE |
| AoOBP8-R2 | ATCAATGGCAGTCTCGTGTA | 20 bp | |
| AoOBP8-F1 | CTATTAGCGAGTGCAAGGC | 19 bp | 3′RACE |
| AoOBP8-F2 | ACAAATGCTACGCCGAAAG | 19 bp | |
| UPM long | CTAATACGACTCACTATAGGGCAAGCAGTGGTATCAACGCAGAGT | 45 bp | Universal Primer |
| UPM short | CTAATACGACTCACTATAGGGC | 22 bp | |
| NUP | AAGCAGTGGTAACAACGCAGAGT | 23 bp | |
| M13F | GTTGTAAAACGACGGCCAG | 19 bp | |
| M13R | CAGGAAACAGCTATGAC | 17 bp | |
| β-Actin-F | GTGCGACGTGGACGTGAGAA | 20 bp | RT-qPCR |
| β-Actin-R | AGACGGAGCAAGAGCGGTGA | 20 bp | |
| α-tubulin-F | TTTCGACGGAGCTTTGAATGTAG | 23 bp | |
| α-tubulin-R | TTGGTGATTTCAGCAACGGATAA | 23 bp | |
| Q-AoOBP8-F | CGGCATACCGTACTGAAGTT | 20 bp | |
| Q-AoOBP8-R | CTTTCGGCGTAGCATTTGTT | 20 bp |
| Sample | Raw Reads | Clean Reads | Clean Base (G) | Error Rate (%) | Q20 (%) | Q30 (%) | GC Content (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AoF1 | 54,635,230 | 51,945,542 | 7.79 | 0.01 | 99.02 | 97.03 | 38.015 |
| AoF2 | 45,726,002 | 42,760,376 | 6.41 | 0.01 | 98.78 | 96.14 | 37.905 |
| AoF3 | 54,278,948 | 51,546,124 | 7.73 | 0.01 | 98.94 | 96.74 | 37.775 |
| AoM1 | 67,109,646 | 64,403,836 | 9.66 | 0.01 | 98.95 | 96.93 | 37.175 |
| AoM2 | 50,562,262 | 47,874,422 | 7.18 | 0.01 | 98.87 | 96.62 | 36.035 |
| AoM3 | 54,119,120 | 51,134,978 | 7.67 | 0.01 | 98.89 | 96.66 | 36.675 |
| Length Range | Transcript | Unigene | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Transcript length interval | 200~500 bp | 27,120 | 5610 |
| 500~1000 bp | 14,422 | 12,008 | |
| 1000~2000 bp | 13,241 | 9938 | |
| ≥2000 bp | 16,728 | 12,626 | |
| Sequencing Statistics | Total Number | 71,513 | 40,182 |
| Mean Length | 1417 | 1833 | |
| N50 | 2692 | 2904 | |
| N90 | 563 | 774 | |
| Total Bases | 101,331,167 | 73,664,248 |
| Database | Number of Genes | Percentage (%) |
|---|---|---|
| KEGG | 22,709 | 56.52 |
| NR | 26,113 | 64.99 |
| SwissProt | 20,542 | 51.12 |
| TrEMBL | 26,326 | 65.52 |
| KOG | 19,036 | 47.37 |
| GO | 23,074 | 57.42 |
| Pfam | 23,512 | 58.51 |
| Annotated in at least one Database | 28,075 | 69.87 |
| Total Unigenes | 40,182 | 100 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, X.; Bai, Y.; Qi, Y.; Liu, B.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, Y.; Yang, J.; Wang, Y.; Xie, S. Transcriptome Characterization and Identification of Chemosensory Genes in the Egg Parasitoid Anastatus orientalis, Along with Molecular Cloning, Sequence Analysis, and Prokaryotic Expression of the Odorant Binding Protein 8 (AoOBP8) from A. orientalis. Insects 2025, 16, 1117. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16111117
Liu X, Bai Y, Qi Y, Liu B, Zhao Y, Wu Y, Yang J, Wang Y, Xie S. Transcriptome Characterization and Identification of Chemosensory Genes in the Egg Parasitoid Anastatus orientalis, Along with Molecular Cloning, Sequence Analysis, and Prokaryotic Expression of the Odorant Binding Protein 8 (AoOBP8) from A. orientalis. Insects. 2025; 16(11):1117. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16111117
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Xinyu, Yanyan Bai, Yu Qi, Baozhi Liu, Yingying Zhao, Yuting Wu, Jiating Yang, Yanan Wang, and Shouan Xie. 2025. "Transcriptome Characterization and Identification of Chemosensory Genes in the Egg Parasitoid Anastatus orientalis, Along with Molecular Cloning, Sequence Analysis, and Prokaryotic Expression of the Odorant Binding Protein 8 (AoOBP8) from A. orientalis" Insects 16, no. 11: 1117. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16111117
APA StyleLiu, X., Bai, Y., Qi, Y., Liu, B., Zhao, Y., Wu, Y., Yang, J., Wang, Y., & Xie, S. (2025). Transcriptome Characterization and Identification of Chemosensory Genes in the Egg Parasitoid Anastatus orientalis, Along with Molecular Cloning, Sequence Analysis, and Prokaryotic Expression of the Odorant Binding Protein 8 (AoOBP8) from A. orientalis. Insects, 16(11), 1117. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16111117






