Exploring the Impact of Dietary EPA/DHA Supplementation on Lipid Metabolism of Tenebrio molitor Larvae
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Rearing and Treatment
2.2. Gas Chromatography (GC)
2.2.1. Lipid Extraction
2.2.2. Detection by GC
2.3. Non-Targeted Metabolomics
2.3.1. Lipid Metabolite Extraction
2.3.2. Liquid Phase Parameter Description
2.3.3. Description of Mass Spectrum Parameters
2.4. Statistics and Analysis
2.4.1. Basic Data
2.4.2. Comparison and Analysis of Non-Targeted Metabolomics
3. Results
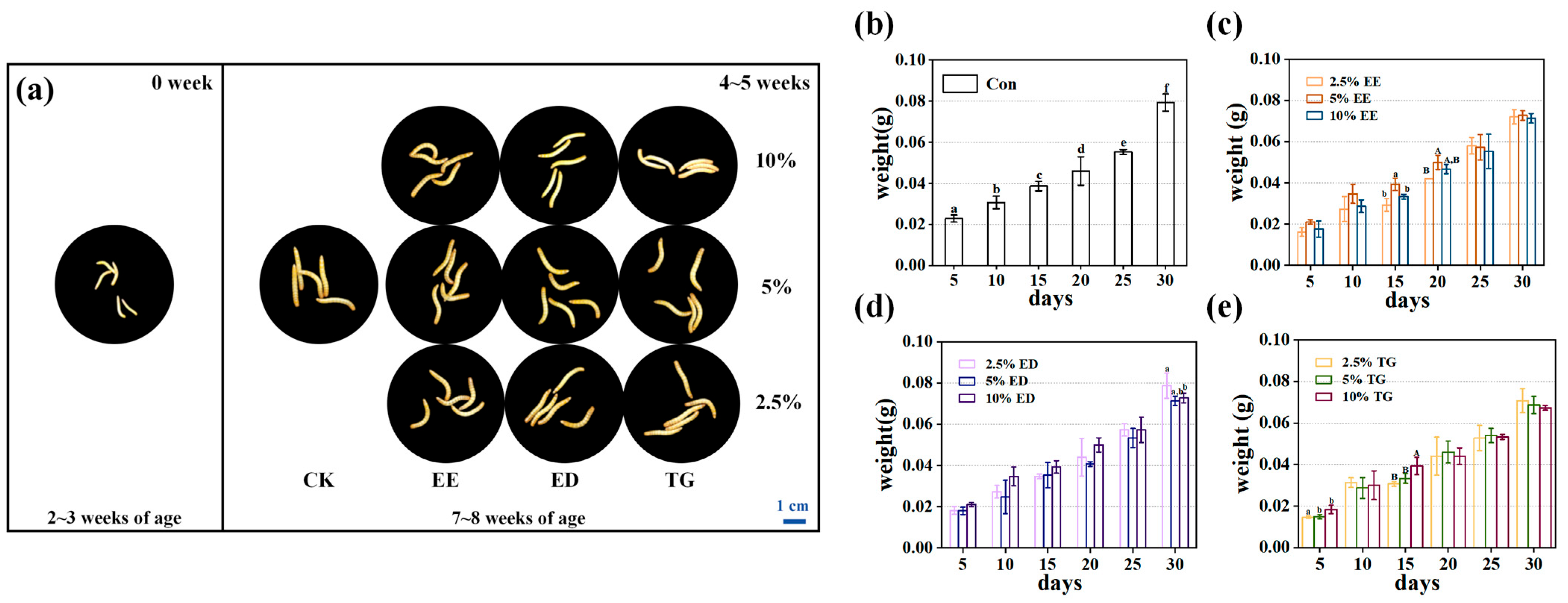
3.1. TM Growth
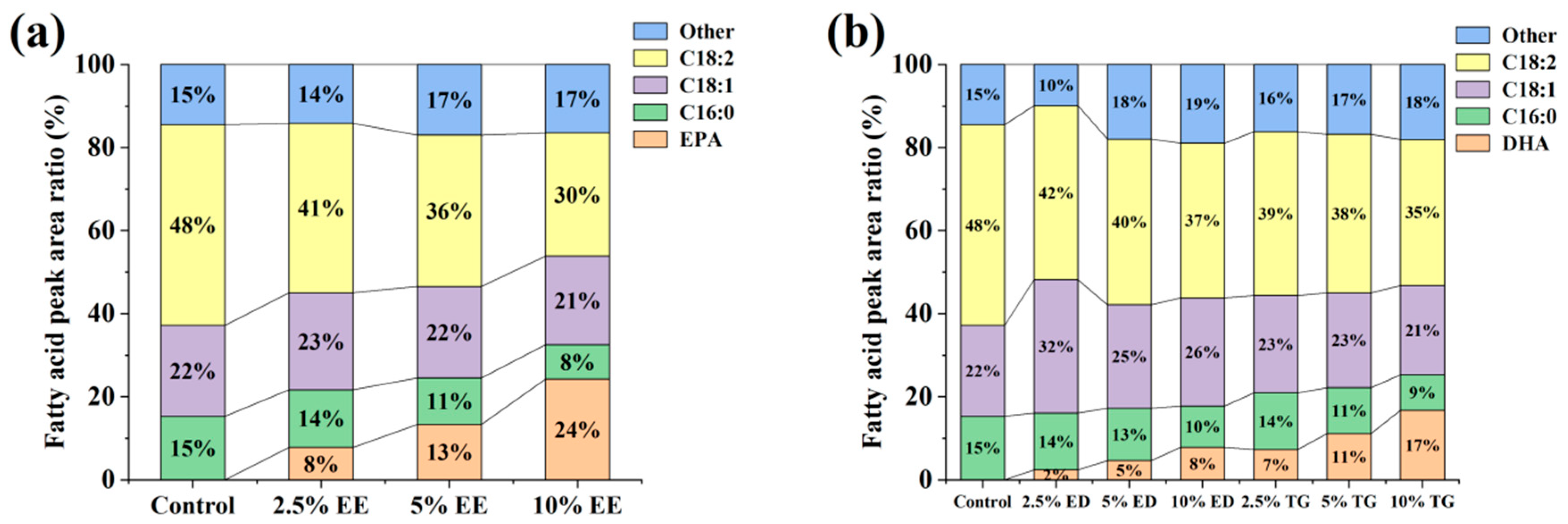
3.2. The Lipid Metabolites of TM Were Preliminarily Detected by GC
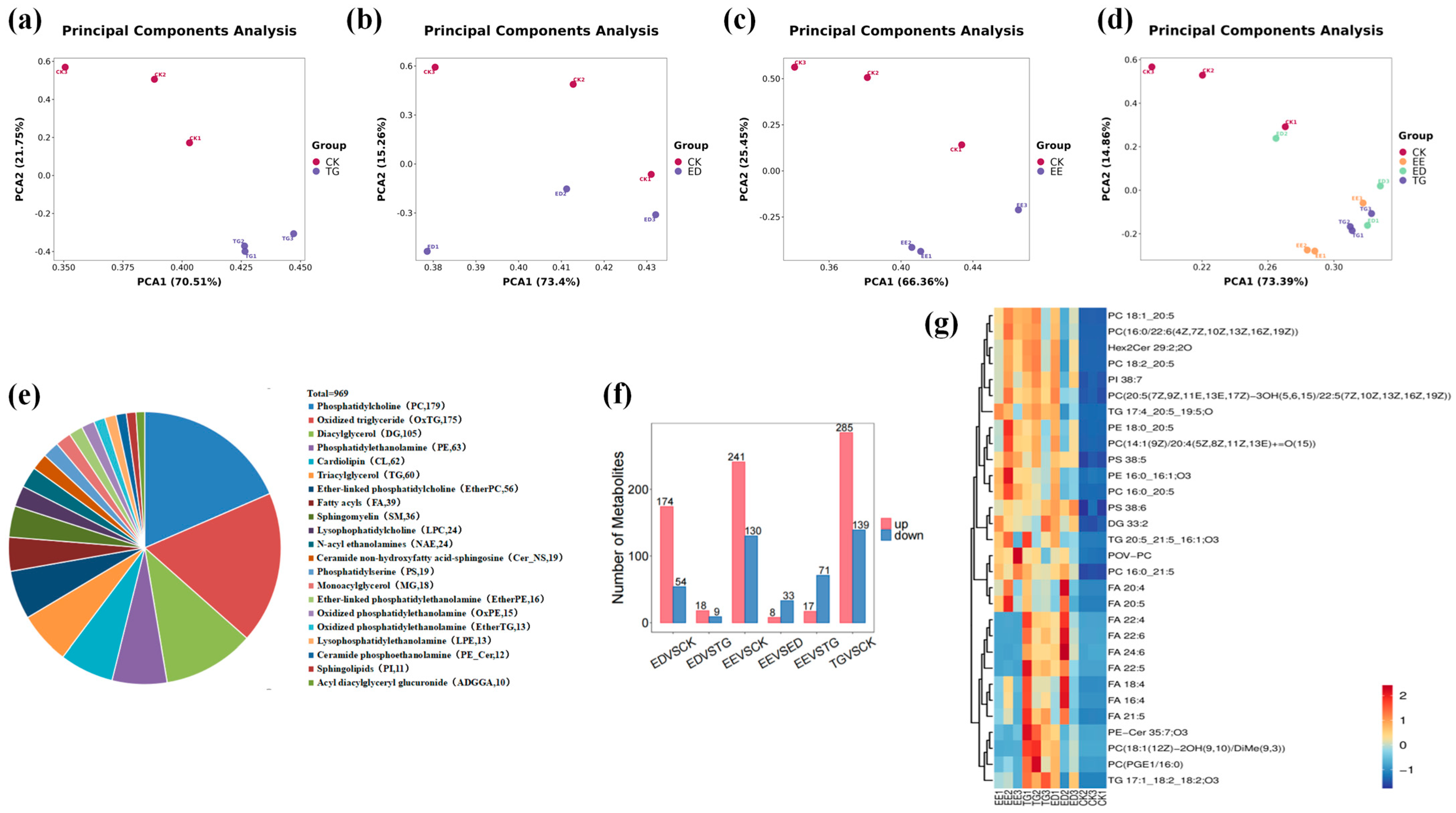
3.3. Non-Targeted Metabolomics
3.3.1. TG-DHA, ED-DHA and EE-EPA Affected the Lipid Metabolism of TM
3.3.2. Analysis of the Changes of 9 Major Lipid Metabolites in Each Group
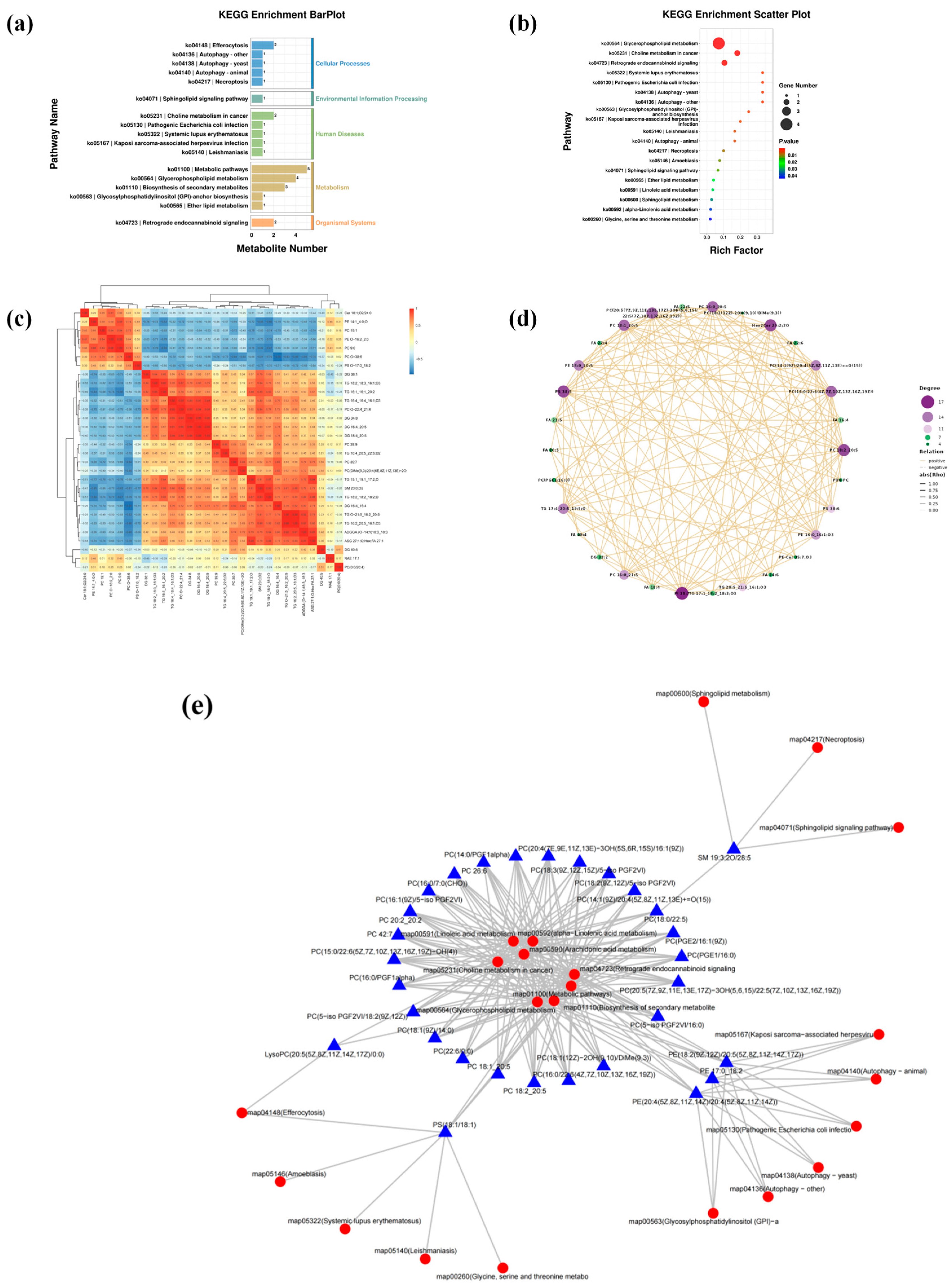
3.3.3. Regulatory Analysis of EPA/DHA Intervention on the TM Lipid Metabolism Pathway
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Abbreviations | Full name |
| CDP | Cytidine diphosphate glycerol |
| CK | Control group |
| CTP | Cytosine nucleoside triphosphate |
| DHA | Docosahexaenoic acid |
| ED-DHA | Ethyl ester docosahexaenoic acid |
| EE-EPA | Ethyl ester eicosapentaenoic acid |
| EPA | Eicosapentaenoic acid |
| FA | Fatty acyl groups |
| FAO | Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations |
| GC | Gas chromatography |
| GDP | Cytidine diphosphate glycerol |
| GTP | Cytosine nucleoside triphosphate |
| HCA | Hierarchical cluster analysis |
| HMDB | Human metabolome databases |
| HPLC-MS | High performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry |
| HPLC-MS/MS | High Performance Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry |
| IDA | Information-dependent acquisition |
| KEGG | Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes |
| LC-MS | Liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry |
| LIPID MAPS | Lipid metabolites and pathways strategy |
| OxTG | Oxidized triglycerides |
| PC | Phosphatidylcholines |
| PCA | Principal component analysis |
| PE | Phosphatidylethanolamines |
| POV-PC | Peroxide value-phosphatidylcholine |
| PUFAs | Polyunsaturated fatty acids |
| QC | Quality control |
| SFAs | Saturated fatty acids |
| TDC | Time-to-digital converter |
| TG | Triacylglycerols |
| TG-DHA | Triglyceride docosahexaenoic acid |
| TM | Tenebrio molitor |
References
- Kotsou, K.; Chatzimitakos, T.; Athanasiadis, V.; Bozinou, E.; Athanassiou, C.G.; Lalas, S.I. Innovative Applications of Tenebrio molitor Larvae in Food Product Development: A Comprehensive Review. Foods 2023, 12, 4223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Pineda, M.; Juan, T.; Antoniewska-Krzeska, A.; Vercet, A.; Abenoza, M.; Yagüe-Ruiz, C.; Rutkowska, J. Exploring the Potential of Yellow Mealworm (Tenebrio molitor) Oil as a Nutraceutical Ingredient. Foods 2024, 13, 3867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotsou, K.; Chatzimitakos, T.; Athanasiadis, V.; Bozinou, E.; Lalas, S.I. Exploiting Agri-Food Waste as Feed for Tenebrio molitor Larvae Rearing: A Review. Foods 2024, 13, 1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musembi, J.P.; Owino, E.A.; Oyieke, F.A.; Tanga, C.M.; Beesigamukama, D.; Subramanian, S.; Cheseto, X.; Egonyu, J.P. Efficient Agri-Food Waste Valorization Using Mealworm (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae) into Nutrient-Rich Biomass for Food and Feed. J. Econ. Entomol. 2024, 117, 1242–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pivato, A.F.; Miranda, G.M.; Prichula, J.; Lima, J.E.A.; Ligabue, R.A.; Seixas, A.; Trentin, D.S. Hydrocarbon-Based Plastics: Progress and Perspectives on Consumption and Biodegradation by Insect Larvae. Chemosphere 2022, 293, 133600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.; Han, T.; Kim, Y.Y. Mealworm (Tenebrio molitor Larvae) as an Alternative Protein Source for Monogastric Animal: A Review. Animals 2020, 10, 2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafique, L.; Abdel-Latif, H.M.R.; Hassan, F.-U.; Alagawany, M.; Naiel, M.A.E.; Dawood, M.A.O.; Yilmaz, S.; Liu, Q. The Feasibility of Using Yellow Mealworms (Tenebrio molitor): Towards a Sustainable Aquafeed Industry. Animals 2021, 11, 811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elahi, U.; Wang, J.; Ma, Y.-B.; Wu, S.-G.; Wu, J.; Qi, G.-H.; Zhang, H.-J. Evaluation of Yellow Mealworm Meal as a Protein Feedstuff in the Diet of Broiler Chicks. Animals 2020, 10, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Xue, R.; Sun, J.; Ji, H. Improving Flesh Quality of Grass Carp (Ctenopharyngodon idellus) by Completely Replacing Dietary Soybean Meal with Yellow Mealworm (Tenebrio molitor). Anim. Nutr. 2023, 12, 375–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thrastardottir, R.; Olafsdottir, H.T.; Thorarinsdottir, R.I. Yellow Mealworm and Black Soldier Fly Larvae for Feed and Food Production in Europe, with Emphasis on Iceland. Foods 2021, 10, 2744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Dijk, M.; Morley, T.; Rau, M.L.; Saghai, Y. A Meta-Analysis of Projected Global Food Demand and Population at Risk of Hunger for the Period 2010–2050. Nat. Food 2021, 2, 494–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salter, A.M. Improving the Sustainability of Global Meat and Milk Production. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2017, 76, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertoni, G. Human, Animal and Planet Health for Complete Sustainability. Animals 2021, 11, 1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moruzzo, R.; Riccioli, F.; Espinosa Diaz, S.; Secci, C.; Poli, G.; Mancini, S. Mealworm (Tenebrio molitor): Potential and Challenges to Promote Circular Economy. Animals 2021, 11, 2568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heileson, J.L.; Machek, S.B.; Harris, D.R.; Tomek, S.; de Souza, L.C.; Kieffer, A.J.; Barringer, N.D.; Gallucci, A.; Forsse, J.S.; Funderburk, L.K. The Effect of Fish Oil Supplementation on Resistance Training-Induced Adaptations. J. Int. Soc. Sports. Nutr. 2023, 20, 2174704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Innes, J.K.; Calder, P.C. Marine Omega-3 (N-3) Fatty Acids for Cardiovascular Health: An Update for 2020. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kousparou, C.; Fyrilla, M.; Stephanou, A.; Patrikios, I. DHA/EPA (Omega-3) and LA/GLA (Omega-6) as Bioactive Molecules in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 10717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherratt, S.C.R.; Mason, R.P.; Libby, P.; Steg, P.G.; Bhatt, D.L. Do Patients Benefit from Omega-3 Fatty Acids? Cardiovasc. Res. 2024, 119, 2884–2901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosti, R.I.; Kasdagli, M.I.; Kyrozis, A.; Orsini, N.; Lagiou, P.; Taiganidou, F.; Naska, A. Fish Intake, n-3 Fatty Acid Body Status, and Risk of Cognitive Decline: A Systematic Review and a Dose-Response Meta-Analysis of Observational and Experimental Studies. Nutr. Rev. 2022, 80, 1445–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favé, G.; Coste, T.C.; Armand, M. Physicochemical Properties of Lipids: New Strategies to Manage Fatty Acid Bioavailability. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2004, 50, 815–831. [Google Scholar]
- Alijani, S.; Hahn, A.; Harris, W.S.; Schuchardt, J.P. Bioavailability of EPA and DHA in Humans−A Comprehensive Review. Prog. Lipid Res. 2025, 97, 101318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Zhang, T.-T.; Cong, P.-X.; Xu, J.; Xue, C.-H.; Jiang, X.-M.; Wang, Y.-M. Comparative Study on the Digestion and Absorption Characteristics of N-3 LCPUFA-Enriched Phospholipids in the Form of Liposomes and Emulsions. Food Res. Int. 2020, 137, 109428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fetene, T.; Atlabachew, M.; Sheferaw, H.; Reta, C.; Hilawea, K.T. Fatty Acids and Chlorogenic Acid Content in Plectranthus Edulis Root Tubers. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0305910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salman, H.B.; Salman, M.A.; Yildiz Akal, E. The Effect of Omega-3 Fatty Acid Supplementation on Weight Loss and Cognitive Function in Overweight or Obese Individuals on Weight-Loss Diet. Nutr. Hosp. 2022, 39, 803–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordiean, A.; Krzyżaniak, M.; Aljewicz, M.; Stolarski, M.J. Influence of Different Diets on Growth and Nutritional Composition of Yellow Mealworm. Foods 2022, 11, 3075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senyilmaz, D.; Virtue, S.; Xu, X.; Tan, C.Y.; Griffin, J.L.; Miller, A.K.; Vidal-Puig, A.; Teleman, A.A. Regulation of Mitochondrial Morphology and Function by Stearoylation of TFR1. Nature 2015, 525, 124–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmmed, M.K.; Hachem, M.; Ahmmed, F.; Rashidinejad, A.; Oz, F.; Bekhit, A.A.; Carne, A.; Bekhit, A.E.-D.A. Marine Fish-Derived Lysophosphatidylcholine: Properties, Extraction, Quantification, and Brain Health Application. Molecules 2023, 28, 3088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibellini, F.; Smith, T.K. The Kennedy Pathway--De Novo Synthesis of Phosphatidylethanolamine and Phosphatidylcholine. IUBMB Life 2010, 62, 414–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patton-Vogt, J.; de Kroon, A.I.P.M. Phospholipid Turnover and Acyl Chain Remodeling in the Yeast ER. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)—Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2020, 1865, 158462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Vance, D.E. Phosphatidylcholine and Choline Homeostasis. J. Lipid Res. 2008, 49, 1187–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, N.; Van Dael, P. Arachidonic Acid in Human Milk. Nutrients 2020, 12, 626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luisoni, S.; Suomalainen, M.; Boucke, K.; Tanner, L.B.; Wenk, M.R.; Guan, X.L.; Grzybek, M.; Coskun, Ü.; Greber, U.F. Co-Option of Membrane Wounding Enables Virus Penetration into Cells. Cell Host Microbe 2015, 18, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, S.; Gessner, D.K.; Braune, M.S.; Friedhoff, T.; Most, E.; Höring, M.; Liebisch, G.; Zorn, H.; Eder, K.; Ringseis, R. Comprehensive Evaluation of the Metabolic Effects of Insect Meal from Tenebrio molitor L. in Growing Pigs by Transcriptomics, Metabolomics and Lipidomics. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2020, 11, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welty, F.K. Omega-3 Fatty Acids and Cognitive Function. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 2023, 34, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elagizi, A.; Lavie, C.J.; O’Keefe, E.; Marshall, K.; O’Keefe, J.H.; Milani, R.V. An Update on Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids and Cardiovascular Health. Nutrients 2021, 13, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.-M.; Jang, G.-H.; Seok, C.-H.; Kim, B.H.; Bae, J.-W.; Kim, B.-H.; Yoon, M.S. A Self-Emulsifying Omega-3 Fatty Acids Delivery System for Enhanced Gastro-Intestinal Absorption in Rats. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2022, 31, 1631–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couëdelo, L.; Joseph, C.; Abrous, H.; Chamekh-Coelho, I.; Vaysse, C.; Baury, A.; Guillemet, D. Effect of Gum Acacia on the Intestinal Bioavailability of N-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids in Rats. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morioka, S.; Perry, J.S.A.; Raymond, M.H.; Medina, C.B.; Zhu, Y.; Zhao, L.; Serbulea, V.; Onengut-Gumuscu, S.; Leitinger, N.; Kucenas, S.; et al. Efferocytosis Induces a Novel SLC Program to Promote Glucose Uptake and Lactate Release. Nature 2018, 563, 714–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vance, J.E.; Tasseva, G. Formation and Function of Phosphatidylserine and Phosphatidylethanolamine in Mammalian Cells. Acta (BBA)—Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2013, 1831, 543–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podrez, E.A.; Poliakov, E.; Shen, Z.; Zhang, R.; Deng, Y.; Sun, M.; Finton, P.J.; Shan, L.; Gugiu, B.; Fox, P.L.; et al. Identification of a Novel Family of Oxidized Phospholipids That Serve as Ligands for the Macrophage Scavenger Receptor CD36. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 38503–38516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Mei, J.; Ling, D.; Zhang, Z.; Li, S.; Gong, Z.; Liu, X.; Xu, M.; Lin, Y.; Yu, R. Improving stability and UV protection properties of phycocyanin nanoparticle-based Pickering emulgels via amorphous cationic starch complexation. Carbohydr. Polym. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, C.; Cheong, L.Z.; Zhang, X.; Ali, A.H.; Jin, Q.; Wei, W.; Wang, X. Dietary Sphingomyelin Metabolism and Roles in Gut Health and Cognitive Development. Adv. Nutr. 2022, 474–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.T.; Xu, J.; Wang, Y.M.; Xue, C.H. Health benefits of dietary marine DHA/EPA-enriched glycerophospholipids. Prog. Lipid Res. 2019, 75, 100997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
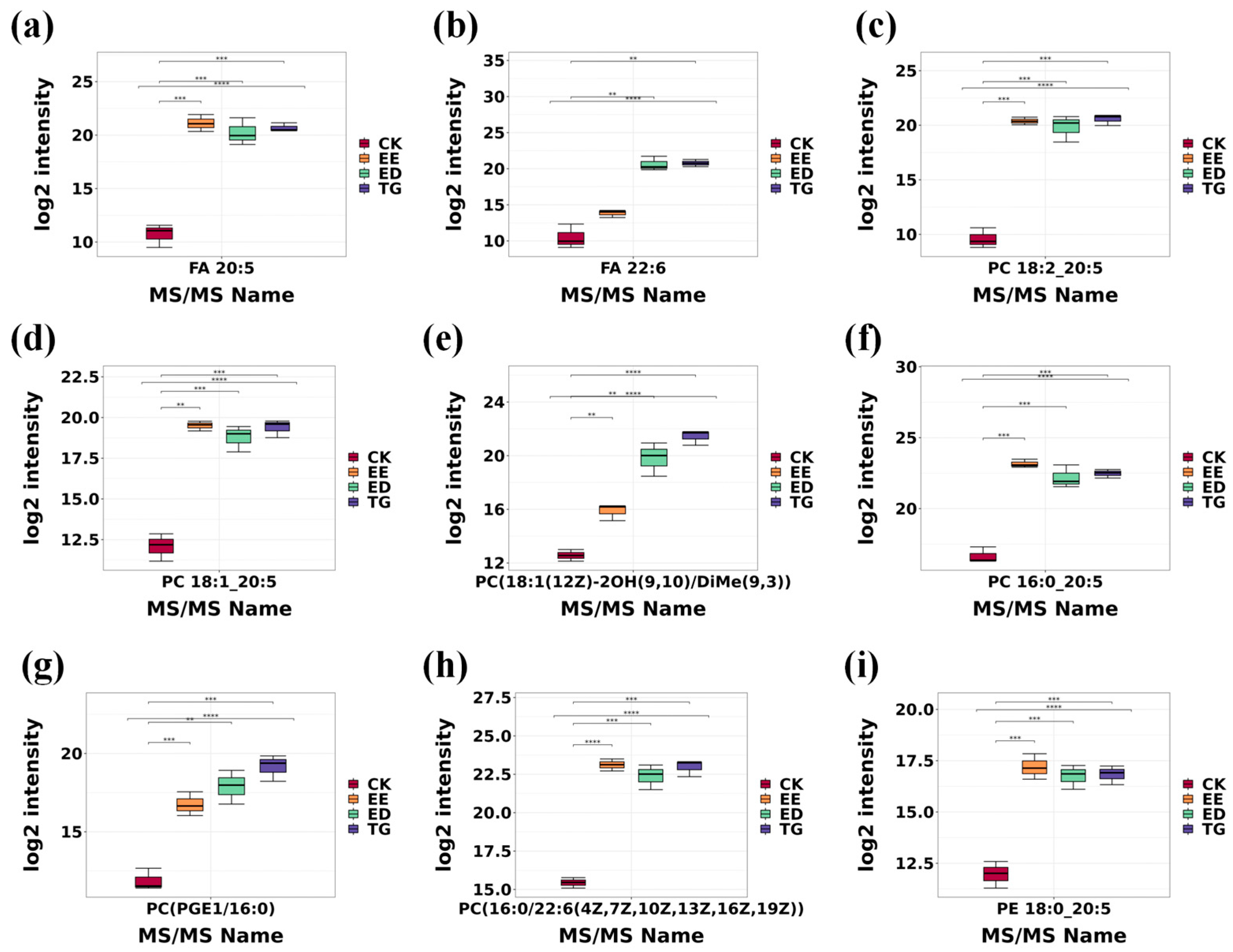
| s | m/z | MS/MS Name | Formula | Class | p Value | q Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 301.22 | FA 20:5 | C20H30O2 | FA | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| 2 | 327.23 | FA 22:6 | C22H32O2 | FA | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| 3 | 848.54 | PC 18:2_20:5 | C46H78NO8P | PC | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| 4 | 850.55 | PC 18:1_20:5 | C46H80NO8P | PC | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| 5 | 830.55 | PC (18:1(12Z)-2OH(9,10)/DiMe(9,3)) | C44H80NO11P | PC | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| 6 | 780.53 | PC 16:0_20:5 | C44H78NO8P | PC | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| 7 | 832.565 | PC(PGE1/16:0) | C44H82NO11P | PC | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| 8 | 806.55 | PC (16:0/22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) | C46H80NO8P | PC | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| 9 | 764.51 | PE 18:0_20:5 | C43H76NO8P | PE | 0.00 | 0.00 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Q.; Ni, X.; Chen, C.; Xu, J.; Pei, E.; Yang, A.; Xu, M.; Wang, X.; Fu, S.; Yu, R. Exploring the Impact of Dietary EPA/DHA Supplementation on Lipid Metabolism of Tenebrio molitor Larvae. Insects 2025, 16, 1007. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16101007
Liu Q, Ni X, Chen C, Xu J, Pei E, Yang A, Xu M, Wang X, Fu S, Yu R. Exploring the Impact of Dietary EPA/DHA Supplementation on Lipid Metabolism of Tenebrio molitor Larvae. Insects. 2025; 16(10):1007. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16101007
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Qiwei, Xiangxiang Ni, Chengcheng Chen, Jingjing Xu, Enqi Pei, Aifen Yang, Mingfeng Xu, Xiu Wang, Sida Fu, and Rongrong Yu. 2025. "Exploring the Impact of Dietary EPA/DHA Supplementation on Lipid Metabolism of Tenebrio molitor Larvae" Insects 16, no. 10: 1007. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16101007
APA StyleLiu, Q., Ni, X., Chen, C., Xu, J., Pei, E., Yang, A., Xu, M., Wang, X., Fu, S., & Yu, R. (2025). Exploring the Impact of Dietary EPA/DHA Supplementation on Lipid Metabolism of Tenebrio molitor Larvae. Insects, 16(10), 1007. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16101007







