Rapid Assessment of Cerambycid Beetle Biodiversity in a Tropical Rainforest in Yunnan Province, China, Using a Multicomponent Pheromone Lure
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sources of Chemicals
2.2. Field Trials
2.3. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Field Trials
3.1.1. Generic Lures
3.1.2. Racemic Anti-2,3-octanediol versus Its (2R,3S)- and (2S,3R)-Enantiomers
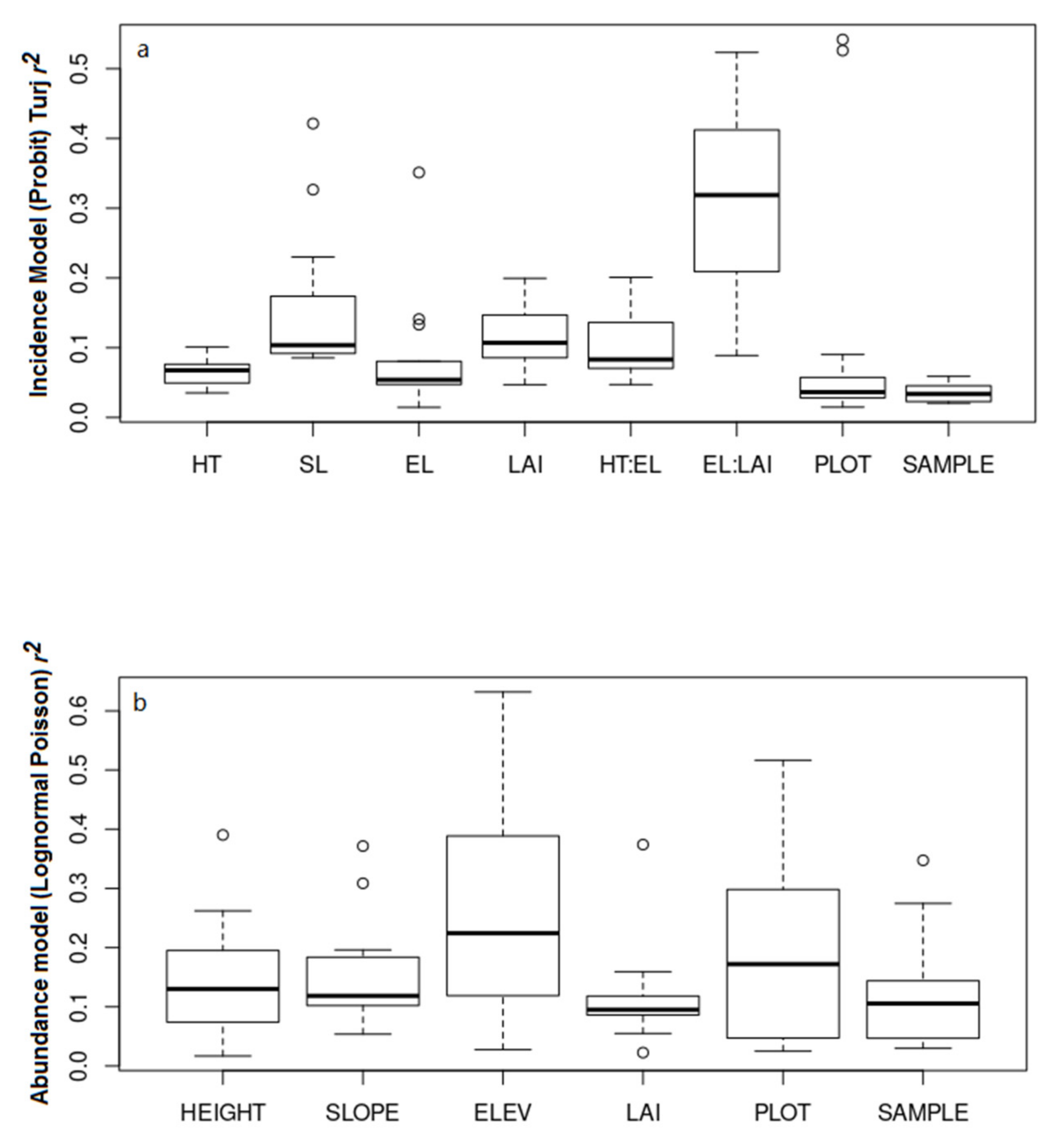
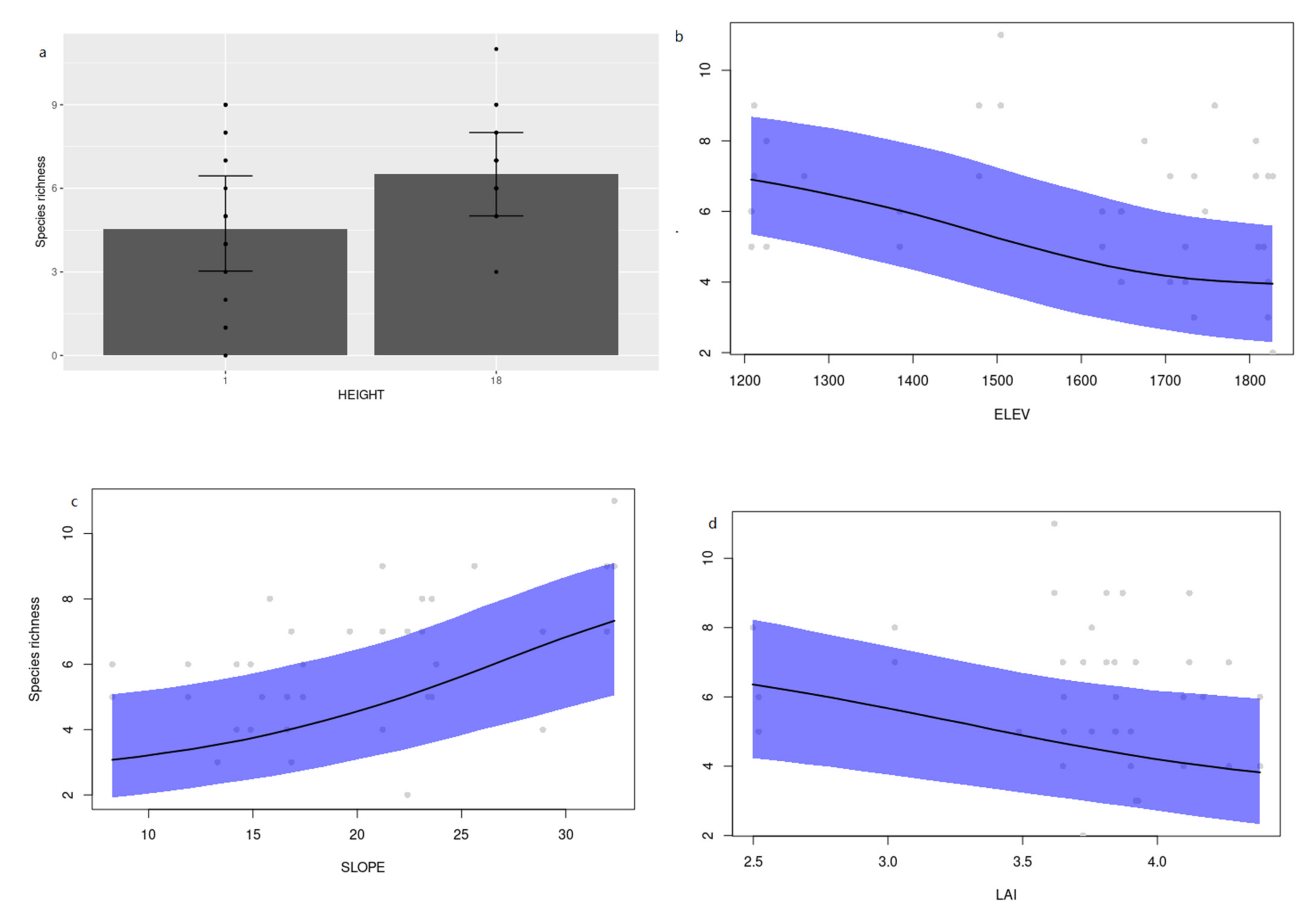
3.2. Environmental Determinants of Cerambycid Beetle Trap Captures
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Švácha, P.; Lawrence, J.F. Chapter 2.4 Cerambycidae Latreille, 1802. In Handbook of Zoology: Arthropoda: Insecta: Coleoptera, Beetles. Vol. 3: Morphology and Systematics (Phytophaga); Leschen, R.A.B., Beutel, R.G., Eds.; Walter de Gruyter: Berlin, Germany; Boston, MA, USA, 2014; pp. 77–177. [Google Scholar]
- Haack, R.A. Feeding Biology of Cerambycids. In Cerambycidae of the World: Biology and Pest Management; Wang, Q., Ed.; CRC Press/Taylor and Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017; pp. 105–124. [Google Scholar]
- Haack, R.A.; Hérard, F.; Sun, J.; Turgeon, J.J. Managing invasive populations of Asian longhorned beetle and citrus longhorned beetle: A worldwide perspective. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2010, 55, 521–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeto, K.; Sato, S.; Miyata, H. Species diversity of longicorn beetles in humid warm-temperate forests: The impact of forest management practices on old-growth forest species in southwestern Japan. Biodiv. Conserv. 2002, 11, 1919–1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brockerhoff, E.G.; Jones, D.C.; Kimberley, M.O.; Suckling, D.M.; Donaldson, T. Nationwide survey for invasive wood-boring and bark beetles (Coleoptera) using traps baited with pheromones and kairomones. For. Ecol. Manag. 2006, 228, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allison, J.D.; Borden, J.H.; Seybold, S.J. A review of the chemical ecology of the Cerambycidae (Coleoptera). Chemoecology 2004, 14, 123–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanks, L.M.; Millar, J.G. Sex and aggregation-sex pheromones of cerambycid beetles: Basic science and practical applications. J. Chem. Ecol. 2016, 42, 631–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millar, J.G.; Hanks, L.M. Chemical Ecology of Cerambycids. In Cerambycidae of the World: Biology and Pest Management; Wang, Q., Ed.; CRC Press/Taylor and Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017; pp. 161–208. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, J.T.; Denux, O.; Courtin, C.; Bernard, A.; Javal, M.; Millar, J.G.; Hanks, L.M.; Roques, A. Multi-component blends for trapping native and exotic longhorn beetles at potential points-of-entry and in forests. J. Pest Sci. 2019, 92, 281–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rassati, D.; Marini, L.; Marchioro, M.; Rapuzzi, P.; Magnani, G.; Poloni, F.; di Giovanni, F.; Mayo, P.; Sweeney, J. Developing trapping protocols for wood-boring beetles associated with broadleaf trees. J. Pest Sci. 2019, 92, 267–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanks, L.M.; Millar, J.G.; Mongold-Diers, J.A.; Wong, J.C.H.; Meier, L.R.; Reagel, P.F.; Mitchell, R.F. Using blends of cerambycid beetle pheromones and host plant volatiles to simultaneously attract a diversity of cerambycid species. Can. J. For. Res. 2012, 42, 1050–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweeney, J.D.; Silk, P.J.; Grebennikov, V. Efficacy of semiochemical–baited traps for detection of longhorn beetles (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae) in the Russian Far East. Eur. J. Entomol. 2014, 111, 397–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickham, J.D.; Harrison, R.D.; Lu, W.; Millar, J.G.; Hanks, L.M.; Chen, Y. Generic pheromone lures attract cerambycids in a tropical montane rain forest in southern China. J. Econ. Entomol. 2014, 107, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, D.R.; Crowe, C.M.; Mayo, P.D.; Silk, P.J.; Sweeney, J.D. Responses of Cerambycidae and other insects to traps baited with ethanol, 2,3-hexanediol, and 3,2-hydroxyketone lures in north-central Georgia. J. Econ. Entomol. 2015, 108, 2354–2365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allison, J.D.; McKenney, J.L.; Millar, J.G.; McElfresh, J.S.; Mitchell, R.F.; Hanks, L.M. Response of the woodborers Monochamus carolinensis and Monochamus titillator (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae) to known cerambycid pheromones in the presence and absence of the host plant volatile α-pinene. Environ. Entomol. 2012, 41, 1587–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fierke, M.K.; Skabeikis, D.D.; Millar, J.G.; Teale, S.A.; McElfresh, J.S.; Hanks, L.M. Identification of a male-produced aggregation pheromone for Monochamus scutellatus scutellatus and an attractant for the congener Monochamus notatus (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 2012, 105, 2029–2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macias-Samano, J.E.; Wakarchuk, D.; Millar, J.G.; Hanks, L.M. 2-Undecyloxy-1-ethanol in combination with other semiochemicals attracts three Monochamus species (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae) in British Columbia, Canada. Can. Entomol. 2012, 144, 821–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teale, S.A.; Wickham, J.D.; Zhang, F.; Chen, Y.; Xiao, W.; Hanks, L.M.; Millar, J.G. A male-produced aggregation pheromone of Monochamus alternatus (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae), a major vector of pine wood nematode. J. Econ. Entomol. 2011, 104, 1592–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wickham, J.D.; Millar, J.G.; Hanks, L.M.; Zou, Y.; Wong, J.C.; Harrison, R.D.; Chen, Y. (2R,3S)-2,3-Octanediol, a female-produced sex pheromone of Megopis costipennis (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae: Prioninae). Environ. Entomol. 2016, 45, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, A.M.; Barbour, J.D.; McElfresh, J.S.; Moreira, J.A.; Swift, I.; Wright, I.M.; Zunic, A.; Mitchell, R.F.; Graham, E.E.; Alten, R.L.; et al. 2,3-Hexanediols as sex attractants and a female-produced sex pheromone for cerambycid beetles in the prionine genus Tragosoma. J. Chem. Ecol. 2012, 38, 1151–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanks, L.M.; Millar, J.G. Field bioassays of cerambycid pheromones reveal widespread parsimony of pheromone structures, enhancement by host plant volatiles, and antagonism by components from heterospecifics. Chemoecology 2013, 23, 21–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millar, J.G.; Mitchell, R.F.; Mongold-Diers, J.A.; Zou, Y.; Bográn, C.E.; Fierke, M.K.; Ginzel, M.D.; Johnson, C.W.; Meeker, J.R.; Poland, T.M.; et al. Identifying possible pheromones of cerambycid beetles by field testing known pheromone components in four widely separated regions of the United States. J. Econ. Entomol. 2018, 111, 252–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanks, L.M.; Mongold-Diers, J.A.; Atkinson, T.H.; Fierke, M.K.; Ginzel, M.D.; Graham, E.E.; Poland, T.M.; Richards, A.B.; Richardson, M.L.; Millar, J.G. Blends of pheromones, with and without host plant volatiles, can attract multiple species of cerambycid beetles simultaneously. J. Econ. Entomol. 2018, 111, 716–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paudel, E.; Dossa, G.G.O.; Xu, J.; Harrison, R.D. Litter fall and nutrient return along a disturbance gradient in a tropical montane forest. For. Ecol. Manag. 2015, 353, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodds, K. Effects of trap height on captures of arboreal insects in pine stands of northeastern United States of America. Can. Entomol. 2014, 146, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardiani, M.; Tini, M.; Carpaneto, G.M.; Audisio, P.; Bussola, E.; Campanaro, A.; Cini, A.; Maurizi, E.; Mason, F.; Peverieri, G.S.; et al. Effects of trap baits and height on stag beetle and flower chafer monitoring: Ecological and conservation implications. J. Insect Conserv. 2017, 21, 157–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmeelk, T.C.; Millar, J.G.; Hanks, L.M. Influence of trap height and bait type on abundance and species diversity of cerambycid beetles captured in forests of east-central Illinois. J. Econ. Entomol. 2016, 109, 1750–1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flaherty, L.; Gutowski, J.M.; Mayo, P.; Mokrzycki, T.; Pohl, G.; Silk, P.; Webster, R.; Hughes, C.; Van Rooyen, K.; Sweeney, J. Pheromone-enhanced lure blends and multiple trap heights improve detection of bark and wood-boring beetles potentially moved in solid wood packaging. J. Pest Sci. 2019, 92, 309–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, D.R.; Crowe, C.M.; Sweeney, J.D. Trap height affects catches of bark and wood-boring beetles (Coleoptera, Curculionidae, Cerambycidae) in baited multiple-funnel traps in southeastern United States. J. Econ. Entomol. 2020, 113, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sweeney, J.; Hughes, C.; Webster, V.; Kostanoicz, C.; Webster, R.; Mayo, P.; Allison, J.D. Impact of horizontal edge–interior and vertical canopy–understory gradients on the abundance and diversity of bark and woodboring beetles in survey traps. Insects 2020, 11, 573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacey, E.S.; Ginzel, M.D.; Millar, J.G.; Hanks, L.M. Male-produced aggregation pheromone of the cerambycid beetle Neoclytus acuminatus acuminatus. J. Chem. Ecol. 2004, 30, 1493–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Geekiyanage, N.; Xu, J.; Khin, M.M.; Nurdiana, D.R.; Paudel, E.; Harrison, R.D. Structure of the epiphyte community in a tropical montane forest in SW China. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0122210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, E.; Poland, T. Efficacy of fluon conditioning for capturing cerambycid beetles in different trap designs and persistence on panel traps over time. J. Econ. Entomol. 2012, 105, 395–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gressitt, J.L. Longicorn beetles of China. Longicornia 1951, 2, 1–667. [Google Scholar]
- Gressitt, J.L.; Rondon, J.A.; von Bruening, S. Cerambycid beetles of Laos. Pac. Insects Monogr. 1920, 24, 1–651. [Google Scholar]
- Hua, L.Z.; Hajime, N.; Samuelson, G.A.; Lingafelter, S.W. Iconography of Chinese Longicorn Beetles; Sun Yat-sen University Press: Guangzhou, China, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Nga, C.T.; Long, K.D. A preliminary list of the subfamily Cerambycinae (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae) of Vietnam. Tap Chi Sinh Hoc. 2014, 36, 12–38. (In Vietnamese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nga, C.T.Q.; Long, K.D.; Thinh, T.H. Additions to the genus Demonax Thomson, 1860 (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae: Cerambycinae) from Vietnam. Tap Chi Sinh Hoc. 2016, 38, 19–32. (In Vietnamese) [Google Scholar]
- Ovaskainen, O.; Tikhonov, G.; Norberg, A.; Blanchet, F.G.; Duan, L.; Dunson, D.; Roslin, T.; Abrego, N. How to make more out of community data? A conceptual framework and its implementation as models and software. Ecol. Lett. 2017, 20, 561–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tikhonov, G.; Opedal, Ø.H.; Abrego, N.; Lehikoinen, A.; de Jonge, M.M.J.; Oksanen, J.; Ovaskainen, O. Joint species distribution modelling with the r-package Hmsc. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2020, 11, 442–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basset, Y.; Cizek, L.; Cuenoud, P.; Didham, R.K.; Guilhaumon, F.; Missa, O.; Novotny, V.; Odegaard, F.; Roslin, T.; Schmidl, J.; et al. Arthropod diversity in a tropical forest. Science 2012, 338, 1481–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Lin, S.; Ji, Y.; Yang, C.; Wang, X.; Yang, C.; Wang, H.; Jiang, H.; Harrison, R.D.; Yu, D. Plant diversity accurately predicts insect diversity in two tropical landscapes. Mol. Ecol. 2016, 25, 4407–4419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norberg, A.; Tikhonov, G.; Blanchet, F.G.; Abrego, N.; Ovaskainen, O. User Manual for the Software Packages HMSC-MATLAB 2.0 and HMSC-R 2.0. 2019. Available online: https://www2.helsinki.fi/sites/default/files/atoms/files/hmsc_manual_0.pdf (accessed on 7 February 2021).
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2020; Available online: https://www.R-project.org (accessed on 7 February 2021).
- SAS Institute Inc. SAS/STAT 9.3 User’s Guide; SAS Institute Inc.: Cary, NC, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Hanks, L.M.; Mongold-Diers, J.A.; Mitchell, R.F.; Zou, Y.; Wong, J.C.; Meier, L.R.; Johnson, T.D.; Millar, J.G. The role of minor pheromone components in segregating 14 species of longhorned beetles (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae) of the subfamily Cerambycinae. J. Econ. Entomol. 2019, 112, 2236–2252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, R.F.; Reagel, P.F.; Wong, J.C.H.; Meier, L.R.; Silva, W.D.; Mongold-Diers, J.; Millar, J.G.; Lawrence, M. Hanks. Cerambycid beetle species with similar pheromones are segregated by phenology and minor pheromone components. J. Chem. Ecol. 2015, 41, 431–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, W.D.; Millar, J.G.; Hanks, L.M.; Costa, C.M.; Leite, M.O.G.; Tonelli, M.; Bento, J.M.S. Interspecific cross-attraction between the South American cerambycid beetle Cotyclytus curvatus and Megacyllene acuita is averted by minor pheromone components. J. Chem. Ecol. 2018, 44, 268–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rassati, D.; Marchioro, M.; Flaherty, L.; Poloni, R.; Edwards, S.; Faccoli, M.; Sweeney, J. Response of native and exotic longhorn beetles to common pheromone components provides partial support for the pheromone-free space hypothesis. Insect Sci. 2020, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wickham, J.D.; Lu, W.; Zhang, L.W.; Chen, Z.Y.; Hanks, L.M.; Millar, J.G. Likely aggregation-sex pheromones of the invasive beetle Callidiellum villosulum, and the related Asian species Allotraeus asiaticus, Semanotus bifasciatus, and Xylotrechus buqueti (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 2016, 109, 2243–2246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, Y.; Rutledge, C.E.; Nakamuta, K.; Maier, C.T.; Hanks, L.M.; Richards, A.B.; Lacey, E.L.; Millar, J.G. Identification of a pheromone component and a critical synergist for the invasive beetle Callidiellum rufipenne (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae). Environ. Entomol. 2016, 45, 216–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molander, M.A.; Larsson, M.C. Identification of the aggregation-sex pheromone of the cerambycid beetle Phymatodes pusillus ssp. pusillus and evidence of a synergistic effect from a heterospecific pheromone component. J. Chem. Ecol. 2018, 44, 987–998. [Google Scholar]
- Molander, M.A.; Winde, I.B.; Burman, J.; Nyabuga, F.N.; Lindblom, T.U.T.; Hanks, L.M.; Millar, J.G.; Larsson, M.C. Common cerambycid pheromone components as attractants for longhorn beetles (Cerambycidae) breeding in ephemeral oak substrates in Northern Europe. J. Chem. Ecol. 2019, 45, 537–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanks, L.M.; Reagel, P.F.; Mitchell, R.F.; Wong, J.C.H.; Meier, L.R.; Silliman, C.A.; Graham, E.E.; Striman, B.L.; Robinson, K.P.; Mongold-Diers, J.A.; et al. Seasonal phenology of the cerambycid beetles of east-central Illinois. Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 2014, 107, 211–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavaletto, G.; Faccoli, M.; Marini, L.; Spaethe, J.; Giannone, F.; Moino, S.; Rassati, D. Exploiting trap color to improve surveys of longhorn beetles. J. Pest. Sci. 2020, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allemand, R.; Aberlenc, H.P. Une méthode efficace d’échantillonnage de l’entomofaune des frondaisons: Le piège attractif aérien. Bull. Société Entomol. Suisse 1991, 64, 293–305. (In Swiss) [Google Scholar]
- Ruchin, A.B.; Egorov, L.V.; Khapugin, A.A.; Vikhrev, N.E.; Esin, M.N. The use of simple crown traps for the insects collection. Nat. Conserv. Res. 2020, 5, 87–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touroult, J.; Witté, I. Beer, wine, or fruit juice: Which is best? A case study of bait efficiency to sample saproxylic beetles (Coleoptera) in an oak woodland. Coleop. Bull. 2020, 74, 763–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwabuchi, K.; Takahashi, J.; Sakai, T. Occurrence of 2, 3-octanediol and 2-hydroxy-3-octanone, possible male sex pheromone in Xylotrechus chinensis Chevrolat (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae). Appl. Entomol. Zool. 1987, 22, 110–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuwahara, Y.; Matsuyamna, S.; Suzuki, T. Identification of 2, 3-octanediol, 2-hydroxy-3-octanone and 3-hydroxy-2-octanone from male Xylotrechus chinensis Chevrolat as possible sex pheromones (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae). Appl. Entomol. Zool. 1987, 22, 25–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cocquempot, C.; Lindelöw, Å. Longhorn beetles (Coleoptera, Cerambycidae). In A. Roques et al. Ed.; Alien terrestrial arthropods of Europe. Biorisk 2010, 4, 193–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarto i Monteys, V.; Torras i Tutusaus, G. A new alien invasive longhorn beetle, Xylotrechus chinensis (Cerambycidae), is infesting mulberries in Catalonia (Spain). Insects 2018, 9, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collignon, R.M.; Siderhurst, M.S.; Millar, J.G.; Cha, D. Response of invasive longhorn beetles (Coleoptera: Lamiinae) to known cerambycid aggregation-sex pheromones in the Puna District of Hawaii Island. Proc. Hawaii. Entomol. Soc. 2019, 51, 15–23. [Google Scholar]
- Meier, L.R.; Zou, Y.; Millar, J.G.; Mongold-Diers, J.A.; Hanks, L.M. Synergism between enantiomers creates species-specific pheromone blends and minimizes cross-attraction for two species of cerambycid beetles. J. Chem. Ecol. 2016, 42, 1181–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meier, L.; Zou, Y.; Mongold-Dyers, J.; Millar, J.G.; Hanks, L.M. Pheromone composition and chemical ecology of six species of cerambycid beetles in the subfamily Lamiinae. J. Chem. Ecol. 2020, 46, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foit, J.; Čermák, V.; Gaar, V.; Hradil, K.; Nový, V.; Rolincová, P. New insights into the life history of Monochamus galloprovincialis can enhance surveillance strategies for the pinewood nematode. J. Pest Sci. 2019, 92, 1203–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Species | Total # | Code |
|---|---|---|
| Cerambycinae | ||
| Artimpaza lineata (Pic) | 168 | Arti lin |
| Ceresium nilgiriense Gahan | 1 | Cere nil |
| Ceresium sinicum White | 1 | Cere sin |
| Chlorophorus arciferus (Chevrolat) | 3 | Chlo arc |
| Chlorophorus reductus Pic | 7 | Chlo red |
| Chlorophorus rubricollis (Castelnau and Gory) | 2 | Chlo rub |
| Demonax alcanor Gressitt and Rondon | 1 | Demo alc |
| Demonax gracilestriatus Gressitt and Rondon | 230 | Demo gra |
| Demonax occultus Gressitt and Rondon | 24 | Demo occ |
| Demonax pseudonotabilis Gressitt | 262 | Demo pse |
| Demonax theresae Pic | 43 | Demo the |
| Euryphagus lundii F. | 1 | Eury lun |
| Gnatholea eburifera Thomson | 2 | Gnat ebu |
| Gnatholea subnuda Lacordaire | 4 | Gnat sub |
| Perissus atronotatus Pic | 10 | Peri atr |
| Perissus dilatus Gressitt and Rondon | 6 | Peri dil |
| Perissus griseus Gressitt | 47 | Peri gri |
| Perissus mimicus Gressitt and Rondon | 333 | Peri mim |
| Perissus mutabilis obscuricolor Pic | 14 | Peri mut |
| Rhaphuma anongi Gressitt and Rondon | 113 | Rhap ano |
| Rhaphuma circumscripta (Schwarzer) | 2 | Rhap cir |
| Rhaphuma horsfieldi (White) | 468 | Rhap hor |
| Rhaphuma laosica Gressitt and Rondon | 201 | Rhap lao |
| Rhaphuma patkaina Gahan | 1 | Rhap pat |
| Xoanodera maculata Schwarzer | 10 | Xoan mac |
| Xylotrechus buqueti (Castelnau and Gory) | 23 | Xylo buq |
| Xylotrechus chinensis (Chevrolat) | 11 | Xylo chi |
| Xylotrechus diversignatus magdelainei Pic | 3 | Xylo div |
| Xylotrechus incurvatus (Chevrolat) | 66 | Xylo inc |
| Xylotrechus lateralis Gahan | 3 | Xylo latf |
| Xylotrechus lateralis fracturis Guo and Chen | 75 | Xylo lat |
| Xylotrechus unicarinatus Pic | 2 | Xylo uni |
| Xylotrechus wauthieri Gressitt and Rondon | 3 | Xylo wau |
| Lamiinae | ||
| Acalolepta basiplagiata (Breuning) | 2 | Acal bas |
| Acalolepta formosana (Breuning) | 28 | Acal for |
| Alidus biplagiatus Gahan | 1 | Agel ton |
| Agelasta tonkinea Pic | 1 | Alid bip |
| Arctolamia fasciata Gestro | 1 | Arct fas |
| Blepephaeus fulvus (Pic) | 1 | Blep ful |
| Blepephaeus stigmosus Gahan | 1 | Blep sti |
| Blepephaeus succinctor (Chevrolat) | 1 | Blep suc |
| Cacia yunnana Breuning | 5 | Caci yun |
| Coptops annulipes Gahan | 1 | Copt ann |
| Coptops leucostictica rustica Gressitt | 3 | Copt leu |
| Diastocera wallichi (Hope) | 12 | Dias wal |
| Euseboides matsudai Gressitt | 1 | Euse mat |
| Glenea diverselineata intermedia Breuning | 12 | Glen div |
| Glenea relicta formosensis Breuning | 1 | Glen rel |
| Imantocera penicillata (Hope) | 2 | Iman pen |
| Mesocacia multimaculata (Pic) | 1 | Meso mul |
| Mesosa rupta (Pascoe) | 5 | Meso rup |
| Mispila khamvengae Breuning | 1 | Misp kha |
| Mispila sonthianae Breuning | 2 | Misp son |
| Monochamus bimaculatus Gahan | 78 | Mono bim |
| Monochamus dubius Gahan | 14 | Mono dub |
| Olenecamptus siamensis Breuning | 1 | Olen sia |
| Paraleprodera carolina Fairmaire | 1 | Para car |
| Paraleprodera diophthalma (Pascoe) | 1 | Para dio |
| Paraleprodera stephanus fasciata Breuning | 1 | Para ste |
| Pharsalia subgemmata (Thomson) | 1601 | Phar sub |
| Pseudocalamobius discolineatus Pic | 2 | Pseu dis |
| Pseudomacrochenus antennatus (Gahan) | 78 | Pseu ant |
| Pseudonemorphas versteegi (Ritsema) | 1 | Pseu ver |
| Pterolophia lateralis Gahan | 1 | Pter lat |
| Pterolophia serricornis Gressitt | 4 | Pter ser |
| Pterolophia subtubericollis Breuning | 3 | Pter sub |
| Sthenias gracilicornis Gressitt | 9 | Sthe gra |
| Uraecha punctata Gahan | 3 | Urae pun |
| Xenohammus bimaculatus Schwarzer | 32 | Xeno bim |
| Prioninae | ||
| Dorysthenes huegelii Redtenbacher | 2 | Dory hue |
| Megopis costipennis White | 487 | Mego cos |
| Total | 4541 |
| Treatment | Friedman’s Q (df) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Species | RS-diol | SR-diol | Racemate | Control | p | |
| Cerambycinae | ||||||
| Tribe Clytini | ||||||
| Perissus mimicus | 0 b | 0 b | 2.8 ± 0.85 a | 0 b | 14.6 (3,16) | 0.0022 |
| Rhaphuma horsfieldi | 1.6 ± 0.1 ab | 2.5 ± 0.76 a | 1.8 ± 0.5 ab | 0 b | 12.9 (3,32) | 0.0048 |
| Species | Incidence Model (Probit) Turj r2 | Abundance Model (Lognormal Poisson) r2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Statistical | Predictive | Statistical | Predictive | |
| Pharsalia subgemmata | NA | NA | 0.672 | 0.297 |
| Megopis costipennis | 0.364 | 0.224 | 0.932 | 0.281 |
| Rhaphuma horsfieldi | 0.114 | 0.024 | 0.801 | 0.365 |
| Perissus mimicus | 0.461 | 0.163 | 0.823 | 0.612 |
| Demonax pseudonotabilis | 0.387 | 0.132 | 0.226 | −0.048 |
| Demonax gracilestriatus | 0.365 | 0.044 | 0.775 | 0.303 |
| Rhaphuma laosica | 0.375 | 0.278 | 0.518 | 0.142 |
| Artimpaza lineata | 0.381 | 0.271 | 0.529 | 0.097 |
| Rhaphuma anongi | 0.532 | 0.411 | 0.672 | 0.429 |
| Pseudomacrochenus antennatus | 0.218 | 0.061 | 0.604 | 0.253 |
| Monochamus bimaculatus | 0.228 | 0.026 | 0.364 | 0.019 |
| Xylotrechus lateralis fracturis | 0.439 | 0.142 | 0.593 | −0.011 |
| Xylotrechus incurvatus | 0.313 | 0.253 | 0.635 | 0.367 |
| Perissus griseus | 0.243 | 0.063 | 0.213 | −0.018 |
| Demonax theresae | 0.246 | 0.146 | 0.474 | 0.097 |
| Xenohammus bimaculatus | 0.298 | 0.175 | 0.528 | 0.169 |
| Acalolepta formosana | 0.145 | 0.005 | 0.051 | −0.095 |
| Xylotrechus buqueti | 0.504 | 0.399 | 0.100 | 0.000 |
| Demonax occultus | 0.178 | 0.039 | 0.243 | 0.000 |
| Monochamus dubius | 0.237 | 0.104 | 0.032 | −0.357 |
| Perissus mutabilis obscuricolor | 0.127 | 0.022 | 0.459 | −0.029 |
| Xoanodera maculata | 0.223 | −0.115 | 0.893 | 0.321 |
| Diastocera wallichi | 0.191 | 0.065 | 0.643 | −0.002 |
| Glenea diverselineata intermedia | 0.118 | -0.063 | 0.432 | −0.229 |
| Xylotrechus chinensis | 0.215 | 0.037 | 0.381 | −0.115 |
| Perissus atronotatus | 0.463 | 0.300 | 0.571 | −0.063 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wickham, J.D.; Harrison, R.D.; Lu, W.; Chen, Y.; Hanks, L.M.; Millar, J.G. Rapid Assessment of Cerambycid Beetle Biodiversity in a Tropical Rainforest in Yunnan Province, China, Using a Multicomponent Pheromone Lure. Insects 2021, 12, 277. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects12040277
Wickham JD, Harrison RD, Lu W, Chen Y, Hanks LM, Millar JG. Rapid Assessment of Cerambycid Beetle Biodiversity in a Tropical Rainforest in Yunnan Province, China, Using a Multicomponent Pheromone Lure. Insects. 2021; 12(4):277. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects12040277
Chicago/Turabian StyleWickham, Jacob D., Rhett D. Harrison, Wen Lu, Yi Chen, Lawrence M. Hanks, and Jocelyn G. Millar. 2021. "Rapid Assessment of Cerambycid Beetle Biodiversity in a Tropical Rainforest in Yunnan Province, China, Using a Multicomponent Pheromone Lure" Insects 12, no. 4: 277. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects12040277
APA StyleWickham, J. D., Harrison, R. D., Lu, W., Chen, Y., Hanks, L. M., & Millar, J. G. (2021). Rapid Assessment of Cerambycid Beetle Biodiversity in a Tropical Rainforest in Yunnan Province, China, Using a Multicomponent Pheromone Lure. Insects, 12(4), 277. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects12040277








