The Key Glutathione S-Transferase Family Genes Involved in the Detoxification of Rice Gramine in Brown Planthopper Nilaparvata lugens
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plants and Insects
2.2. Bioassay on Gramine Toxicity to BPH
2.3. GST Activity Assay
2.4. qRT-PCR
2.5. Double-Stranded RNA (dsRNA) Synthesis and Feeding Assays
2.6. Cotreatment of dsRNA and Gramine
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
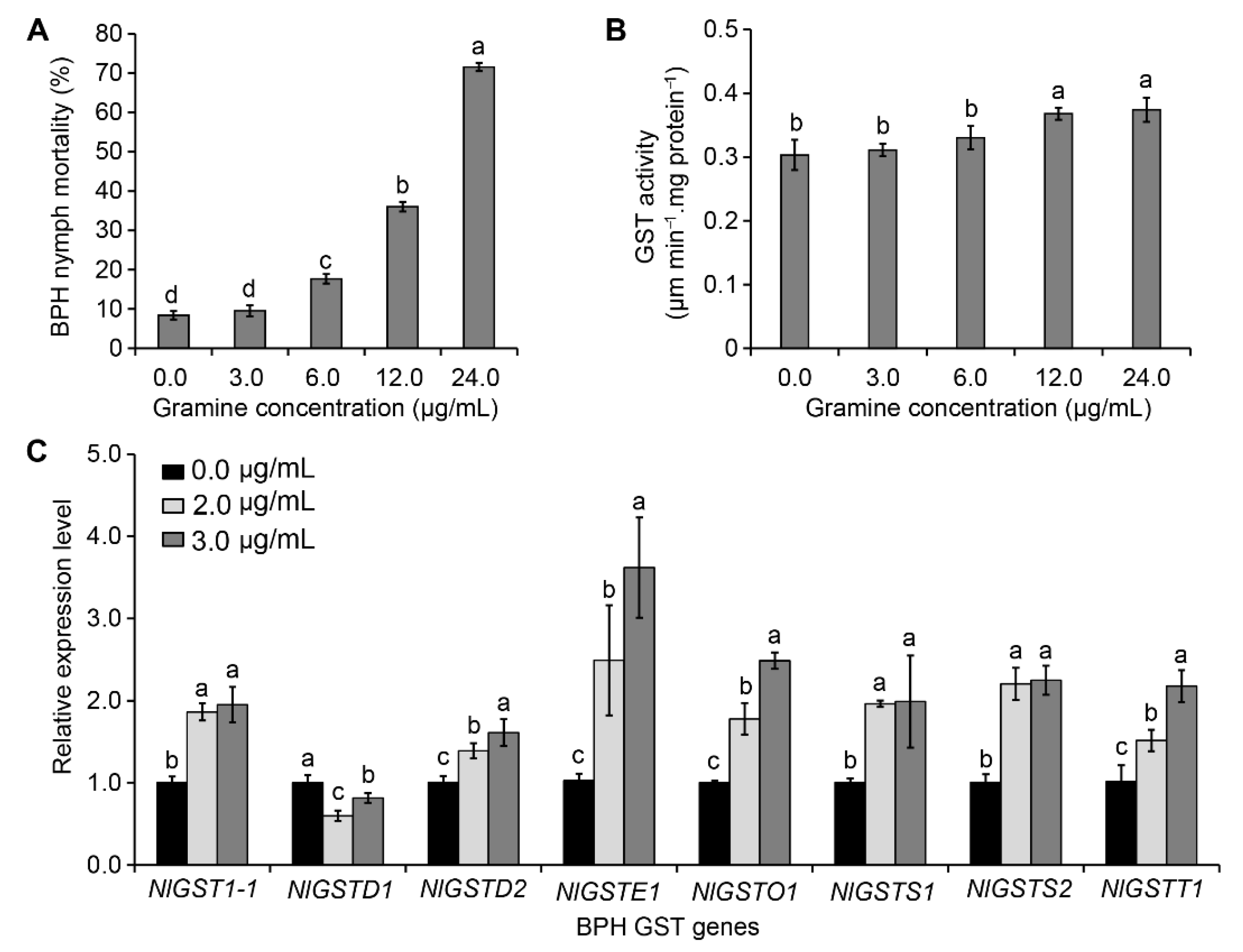
3.1. LC25 and LC50 of Gramine Toxicity to BPH
3.2. Effect of Gramine on NlGST Expression in BPH
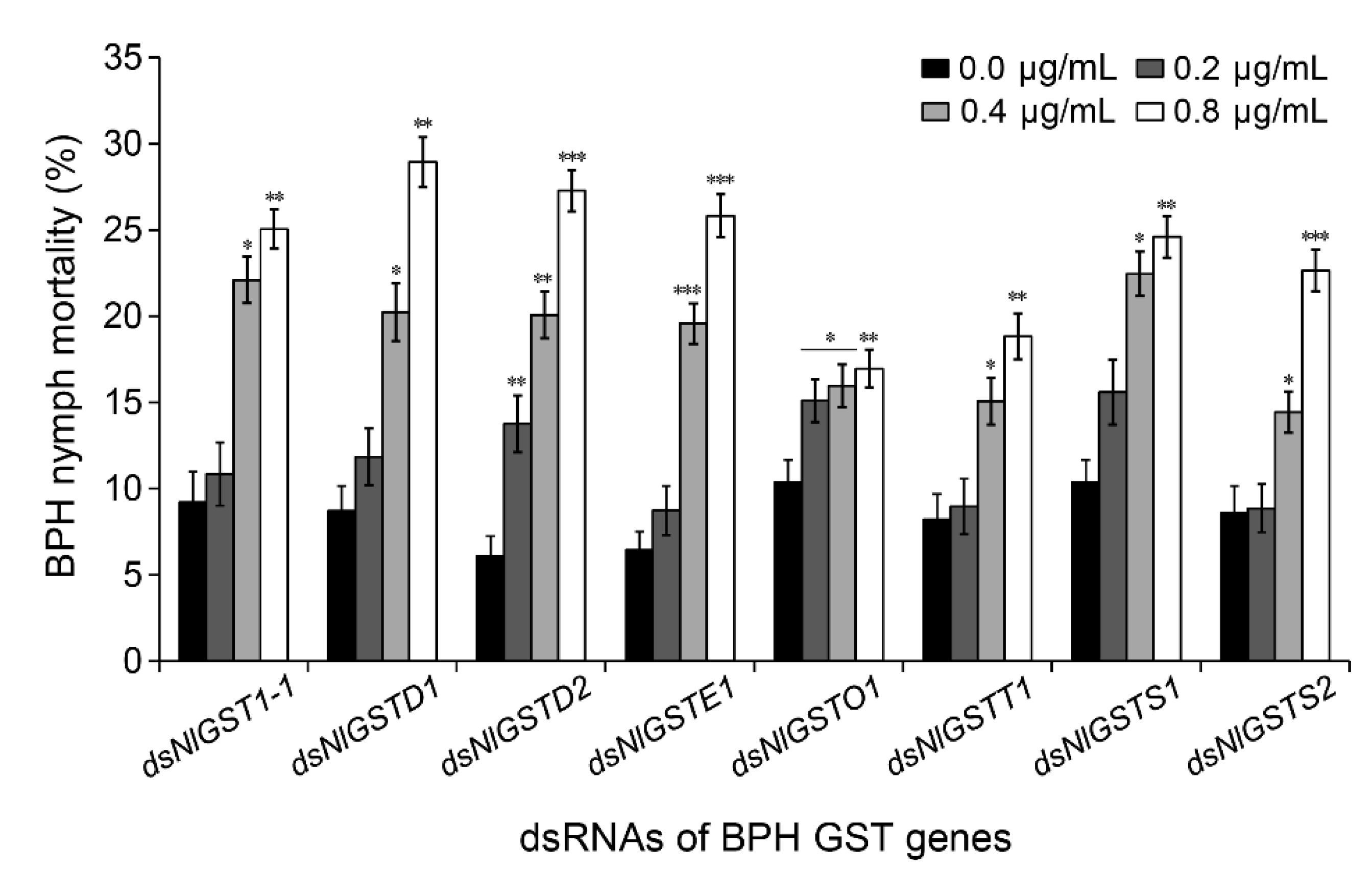
3.3. Correlation between Each GST Interference and GST Activity
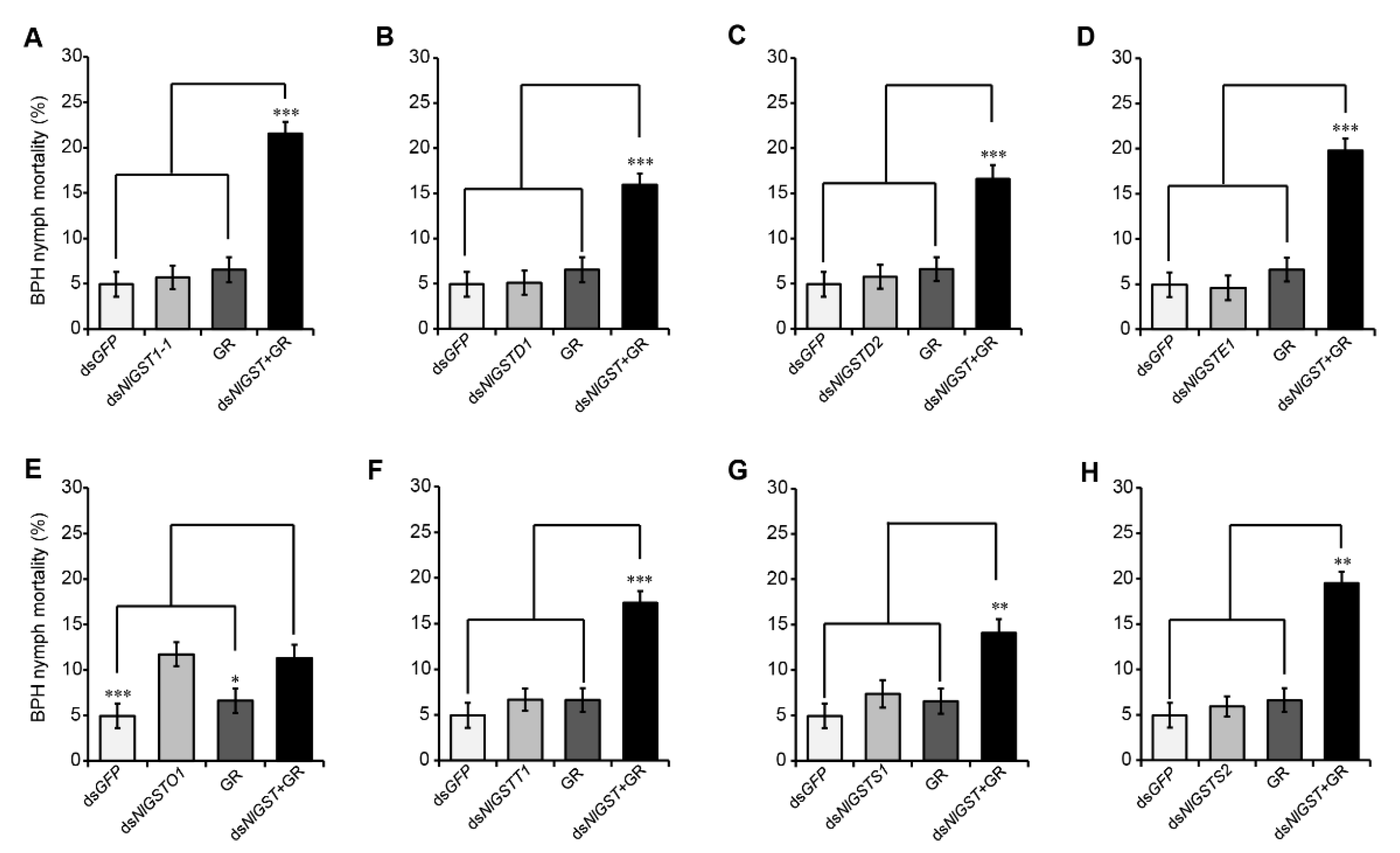
3.4. Suppression of GST Expression Increases BPH Susceptibility to Gramine
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chrzanowski, G.; Leszczyński, B.; Czerniewicz, P.; Sytykiewicz, H.; Matok, H.; Krzyżanowski, R.; Sempruch, C. Effect of phenolic acids from black currant, sour cherry and walnut on grain aphid (Sitobion avenae F.) development. Crop Prot. 2012, 35, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corcuera, L.J. Effects of indole alkaloids from gramineae on aphids. Phytochemistry 1984, 23, 539–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zúñiga, G.E.; Salgado, M.S.; Corcuera, L.J. Role of an indole alkaloid in the resistance of barley seedlings to aphids. Phytochemistry 1985, 24, 945–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, M.A. Plant Secondary Metabolism. In Plant Biotechnology for Health: From Secondary Metabolites to Molecular Farming; Alvarez, M.A., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2014; pp. 15–31. [Google Scholar]
- Jang, J.Y.; Le Dang, Q.; Choi, G.J.; Park, H.W.; Kim, J.C. Control of root-knot nematodes using Waltheria indica producing 4-quinolone alkaloids. Pest Manag. Sci. 2019, 75, 2264–2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Q.N.; Zhang, Q.W.; Zhou, M.Z. Correlation between indole alkaloid content in flag leaves and ears of wheat and its resistance to Sitobion avenae (F.). Plant Prot. 2002, 28, 11–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corcuera, L.J. Biochemical basis for the resistance of barley to aphids. Phytochemistry 1993, 33, 741–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanson, A.D.; Traynor, P.L.; Ditz, K.M.; Reicosky, D.A. Gramine in barley forage—Effects of genotype and environment. Crop Sci. 1981, 21, 726–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.-Q.; Zhang, M.-X.; Yu, J.-Y.; Jin, Y.; Ling, B.; Du, J.-P.; Li, G.-H.; Qin, Q.-M.; Cai, Q.-N. Glutathione S-transferase of brown planthoppers (Nilaparvata lugens) is essential for their adaptation to gramine-containing host plants. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e64026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cai, Q.N.; Zhang, Q.W.; Cheo, M. Contribution of indole alkaloids to Sitobion avenae (F.) resistance in wheat. J. Appl. Entomol. 2004, 128, 517–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Q.-N.; Han, Y.; Cao, Y.-Z.; Hu, Y.; Zhao, X.; Bi, J.-L. Detoxification of gramine by the cereal aphid Sitobion avenae. J. Chem. Ecol. 2009, 35, 320–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Cai, Q.-N.; Zhang, Q.-W.; Han, Y. Effect of the secondary substances from wheat on the growth and digestive physiology of cotton bollworm Helicoverpa armigera (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Eur. J. Entomol. 2006, 103, 255–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, M.; Fang, T.; Pu, G.; Sun, X.; Zhou, X.; Cai, Q. Xenobiotic metabolism of plant secondary compounds in the English grain aphid, Sitobion avenae (F.) (Hemiptera: Aphididae). Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2013, 107, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Han, Z.; Zhang, X.; Pang, C. Influence of rice varieties on the metabolizing enzymes of Nilaparvata lugens Stål. J. Nanjing Agric. Univ. 2003, 26, 24–28. [Google Scholar]
- Heidel-Fischer, H.M.; Vogel, H. Molecular mechanisms of insect adaptation to plant secondary compounds. Curr. Opin. Insect Sci. 2015, 8, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu-Salzman, K.; Bi, J.L.; Liu, T.X. Molecular strategies of plant defense and insect counter-defense. Insect Sci. 2005, 12, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damásio, J.; Guilhermino, L.; Soares, A.M.; Riva, M.C.; Barata, C. Biochemical mechanisms of resistance in Daphnia magna exposed to the insecticide fenitrothion. Chemosphere 2007, 70, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vontas, J.G.; Small, G.J.; Hemingway, J. Glutathione S-transferases as antioxidant defence agents confer pyrethroid resistance in Nilaparvata lugens. Biochem. J. 2001, 357, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Sun, X.-Q.; Yan, S.-Y.; Pan, W.-J.; Zhang, M.-X.; Cai, Q.-N. Interaction of ferulic acid with glutathione S-transferase and carboxylesterase genes in the brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens. J. Chem. Ecol. 2017, 43, 693–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Yan, H.; Lu, W.; Li, Y.; Guo, X.; Xu, B. A novel Omega-class glutathione S-transferase gene in Apis cerana cerana: Molecular characterisation of GSTO2 and its protective effects in oxidative stress. Cell Stress Chaperon. 2013, 18, 503–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gloss, A.D.; Vassão, D.G.; Hailey, A.L.; Dittrich, A.C.N.; Schramm, K.; Reichelt, M.; Rast, T.J.; Weichsel, A.; Cravens, M.G.; Gershenzon, J.; et al. Evolution in an ancient detoxification pathway is coupled with a transition to herbivory in the Drosophilidae. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2014, 31, 2441–2456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, S.P.; Coronella, J.A.; Benes, H.; Cochrane, B.J.; Zimniak, P. Catalytic function of Drosophila melanogaster glutathione S-transferase DmGSTS1-1 (GST-2) in conjugation of lipid peroxidation end products. Eur. J. Biochem. 2001, 268, 2912–2923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vontas, J.G.; Small, G.J.; Nikou, D.C.; Ranson, H.; Hemingway, J. Purification, molecular cloning and heterologous expression of a glutathione S-transferase involved in insecticide resistance from the rice brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens. Biochem. J. 2002, 362, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, W.-W.; Li, X.-W.; Quan, Y.-H.; Cheng, J.; Zhang, C.-X.; Gurr, G.; Zhu, Z.-R. Identification and expression profiles of nine glutathione S-transferase genes from the important rice phloem sap-sucker and virus vector Laodelphax striatellus (Fallen) (Hemiptera: Delphacidae). Pest Manag. Sci. 2012, 68, 1296–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.H.; Lee, C.M.; Huang, J.H.; Lee, H.J. Circadian regulation of permethrin susceptibility by glutathione S-transferase (BgGSTD1) in the German cockroach (Blattella germanica). J. Insect Physiol. 2014, 65, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazari, A.M.; Dahlberg, O.; Mannervik, B.; Mannervik, M. Overexpression of glutathione transferase E7 in Drosophila differentially impacts toxicity of organic isothiocyanates in males and females. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e110103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.-W.; Liang, Q.-M.; Xu, Y.; Gurr, G.M.; Bao, Y.-Y.; Zhou, X.-P.; Zhang, C.-X.; Cheng, J.; Zhu, Z.-R. Genomic insights into the glutathione S-transferase gene family of two rice planthoppers, Nilaparvata lugens (Stål) and Sogatella furcifera (Horváth) (Hemiptera: Delphacidae). PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e56604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ghaffar, M.B.A.; Pritchard, J.; Ford-Lloyd, B. Brown planthopper (Nilaparvata lugens Stal) feeding behavior on rice germplasm as an indicator of resistance. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e22137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.; Jaswal, A.; Sarkar, S. Incidence of brown planthopper in the rice field with the use of different doses of fertilizers. Agric. Sci. Digest. 2019, 39, 108–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Du, B.; Zhang, W.; Liu, B.; Hu, J.; Wei, Z.; Shi, Z.; He, R.; Zhu, L.; Chen, R.; Han, B.; et al. Identification and characterization of Bph14, a gene conferring resistance to brown planthopper in rice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2009, 106, 22163–22168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jairin, J.; Phengrat, K.; Teangdeerith, S.; Vanavichit, A.; Toojinda, T. Mapping of a broad-spectrum brown planthopper resistance gene, Bph3, on rice chromosome 6. Mol. Breed. 2007, 19, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jena, K.K.; Kim, S.M. Current status of brown planthopper (BPH) resistance and genetics. Rice 2010, 3, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bao, Y.-Y.; Wang, Y.; Wu, W.-J.; Zhao, D.; Xue, J.; Zhang, B.-Q.; Shen, Z.-C.; Zhang, C.-X. De novo intestine-specific transcriptome of the brown planthopper Nilaparvata lugens revealed potential functions in digestion, detoxification and immune response. Genomics 2012, 99, 256–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, B.; Lin, X.; Yu, N.; Gao, H.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, W.; Liu, Z. Contribution of glutathione S-transferases to imidacloprid resistance in Nilaparvata lugens. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 15403–15408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powell, K.S.; Gatehouse, A.M.R.; Hilder, V.A.; Gatehouse, J.A. Antimetabolic effects of plant lectins and plant and fungal enzymes on the nymphal stages of two important rice pests, Nilaparvata lugens and Nephotettix cinciteps. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 1993, 66, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Sun, X.-Q.; Zhu-Salzman, K.; Qin, Q.-M.; Feng, H.-Q.; Kong, X.-D.; Zhou, X.-G.; Cai, Q.-N. Host-induced gene silencing of brown planthopper glutathione S-transferase gene enhances rice resistance to sap-sucking insect pests. J. Pest Sci. 2021, 94, 769–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franciosa, H.; Berge, J.B. Glutathione S-transferases in housefly (Musca domestica): Location of GST-1 and GST-2 families. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1995, 25, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, H.; Chino, M. Chemical composition of phloem sap from the uppermost internode of the rice plant. Plant Cell Physiol. 1990, 31, 247–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Susumu, K.; Tomoyoshi, F.; Mitsuo, C. Collection of rice phloem sap from stylets of homopterous insects severed by YAG laser. Plant Cell Physiol. 1980, 21, 1319–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, F.; Vanhaelen, N.; Haubruge, E. Glutathione S-transferases in the adaptation to plant secondary metabolites in the Myzus persicae aphid. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 2005, 58, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bass, C.; Puinean, A.M.; Andrews, M.; Cutler, P.; Daniels, M.; Eliáš, J.; Paul, V.L.; Crossthwaite, A.J.; Denholm, I.; Field, L.M.; et al. Mutation of a nicotinic acetylcholine receptor beta subunit is associated with resistance to neonicotinoid insecticides in the aphid Myzus persicae. BMC Neurosci. 2011, 12, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ding, Z.; Wen, Y.; Yang, B.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, S.; Liu, Z.; Han, Z. Biochemical mechanisms of imidacloprid resistance in Nilaparvata lugens: Over-expression of cytochrome P450 CYP6AY1. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2013, 43, 1021–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.; Shi, X.; Desneux, N.; Gao, X. Effects of spirotetramat treatments on fecundity and carboxylesterase expression of Aphis gossypii Glover. Ecotoxicology 2016, 25, 655–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, R.; Li, Y.; Dong, Y.; Liang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, W. Identification of promoter polymorphisms in the cytochrome P450 CYP6AY1 linked with insecticide resistance in the brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens. Insect Mol. Biol. 2014, 23, 768–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, X. Two novel cytochrome P450 genes CYP6CS1 and CYP6CW1 from Nilaparvata lugens (Hemiptera: Delphacidae): cDNA cloning and induction by host resistant rice. Bull. Entomol. Res. 2011, 101, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Ge, P.; Li, D.; Guo, Y.; Zhu, K.Y.; Ma, E.; Zhang, J. Two homologous carboxylesterase genes from Locusta migratoria with different tissue expression patterns and roles in insecticide detoxification. J. Insect Physiol. 2015, 77, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.X.; Yu, N.; Zhang, J.H.; Zhang, Y.X.; Liu, Z.W. Induction of P450 genes in Nilaparvata lugens and Sogatella furcifera by two neonicotinoid insecticides. Insect Sci. 2018, 25, 401–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, R. Genomic organization of the glutathione S-transferase family in insects. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2011, 61, 924–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavlidi, N.; Khalighi, M.; Myridakis, A.; Dermauw, W.; Wybouw, N.; Tsakireli, D.; Stephanou, E.G.; Labrou, N.E.; Vontas, J.; Van Leeuwen, T. A glutathione-S-transferase (TuGSTd05) associated with acaricide resistance in Tetranychus urticae directly metabolizes the complex II inhibitor cyflumetofen. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2017, 80, 101–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.-W.; Zhong, Q.-S.; Ji, Y.-H.; Zhang, Y.-M.; Tang, J.; Feng, F.; Bi, J.-X.; Xie, J.; Li, B. Characterization of a sigma class GST (GSTS6) required for cellular detoxification and embryogenesis in Tribolium castaneum. Insect Sci. 2021, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, H.; Jia, H.; Gao, H.; Guo, X.; Xu, B. Identification, genomic organization, and oxidative stress response of a sigma class glutathione S-transferase gene (AccGSTS1) in the honey bee, Apis cerana cerana. Cell Stress Chaperon. 2013, 18, 415–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wongtrakul, J.; Pongjaroenkit, S.; Leelapat, P.; Nachaiwieng, W.; Prapanthadara, L.A.; Ketterman, A.J. Expression and characterization of three new glutathione transferases, an Epsilon (AcGSTE2-2), Omega (AcGSTO1-1), and Theta (AcGSTT1-1) from Anopheles cracens (Diptera: Culicidae), a major Thai Malaria vector. J. Med. Entomol. 2010, 47, 162–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saruta, F.; Yamada, N.; Yamamoto, K. An omega-class glutathione S-transferase in the brown planthopper Nilaparvata lugens exhibits glutathione transferase and dehydroascorbate reductase activities. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 2019, 102, e21599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preall, J.B.; He, Z.; Gorra, J.M.; Sontheimer, E.J. Short interfering RNA strand selection is independent of dsRNA processing polarity during RNAi in Drosophila. Cur. Biol. 2006, 16, 530–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zamore, P.D.; Tuschl, T.; Sharp, P.A.; Bartel, D.P. RNAi: Double-stranded RNA directs the ATP-dependent cleavage of mRNA at 21 to 23 nucleotide intervals. Cell 2000, 101, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pan, H.; Xu, L.; Noland, J.E.; Li, H.; Siegfried, B.D.; Zhou, X. Assessment of potential risks of dietary rnai to a soil micro-arthropod, Sinella curviseta Brook (Collembola: Entomobryidae). Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pan, H.; Yang, X.; Bidne, K.; Hellmich, R.L.; Siegfried, B.D.; Zhou, X. Dietary risk assessment of v-ATPase A dsRNAs on monarch butterfly larvae. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Casacuberta, J.M.; Devos, Y.; du Jardin, P.; Ramon, M.; Vaucheret, H.; Nogué, F. Biotechnological uses of RNAi in plants: Risk assessment considerations. Trends Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 145–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Devos, Y.; Álvarez-Alfageme, F.; Gennaro, A.; Mestdagh, S. Assessment of unanticipated unintended effects of genetically modified plants on non-target organisms: A controversy worthy of pursuit? J. Appl. Entomol. 2016, 140, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| n | LC25 (μg/mL) a | LC50 (μg/mL) a | Slope ± SE b | (χ2) c | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 186 | 7.11 (5.07–9.16) | 14.99 (11.57–21.88) | 2.084 ± 0.37 | 2.71 | 0.987 |
| GST Transcript-GST Activity | n | Equation | r | p | Significance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NlGST1-1-GSTs | 4 | y = 1.6649x − 0.7865 | 0.9719 | 0.0141 | * |
| NlGSTD1-GSTs | 4 | y = 0.3453x + 0.5347 | 0.7612 | 0.1194 | ns |
| NlGSTD2-GSTs | 4 | y = 1.1624x − 0.1754 | 0.9839 | 0.0080 | ** |
| NlGSTE1-GSTs | 4 | y = 0.6451x + 0.2213 | 0.9541 | 0.0230 | * |
| NlGSTO1-GSTs | 4 | y = 0.2159x + 0.9205 | 0.5605 | 0.2197 | ns |
| NlGSTS1-GSTs | 4 | y = 0.1235x + 0.9928 | 0.4532 | 0.2734 | ns |
| NlGSTS2-GSTs | 4 | y = 0.2489x + 0.8809 | 0.8772 | 0.0614 | ns |
| NlGSTT1-GSTs | 4 | y = 0.3803x + 0.7793 | 0.8408 | 0.0796 | ns |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, J.; Kong, X.-D.; Zhu-Salzman, K.; Qin, Q.-M.; Cai, Q.-N. The Key Glutathione S-Transferase Family Genes Involved in the Detoxification of Rice Gramine in Brown Planthopper Nilaparvata lugens. Insects 2021, 12, 1055. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects12121055
Yang J, Kong X-D, Zhu-Salzman K, Qin Q-M, Cai Q-N. The Key Glutathione S-Transferase Family Genes Involved in the Detoxification of Rice Gramine in Brown Planthopper Nilaparvata lugens. Insects. 2021; 12(12):1055. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects12121055
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Jun, Xiang-Dong Kong, Keyan Zhu-Salzman, Qing-Ming Qin, and Qing-Nian Cai. 2021. "The Key Glutathione S-Transferase Family Genes Involved in the Detoxification of Rice Gramine in Brown Planthopper Nilaparvata lugens" Insects 12, no. 12: 1055. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects12121055
APA StyleYang, J., Kong, X.-D., Zhu-Salzman, K., Qin, Q.-M., & Cai, Q.-N. (2021). The Key Glutathione S-Transferase Family Genes Involved in the Detoxification of Rice Gramine in Brown Planthopper Nilaparvata lugens. Insects, 12(12), 1055. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects12121055






