The Mitochondrial Genomes of 18 New Pleurosticti (Coleoptera: Scarabaeidae) Exhibit a Novel trnQ-NCR-trnI-trnM Gene Rearrangement and Clarify Phylogenetic Relationships of Subfamilies within Scarabaeidae
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Taxon Sampling and Mitogenome DNA Sequencing
2.2. Gene Annotation and Sequence Analyses
2.3. Phylogenetic Analyses
3. Results
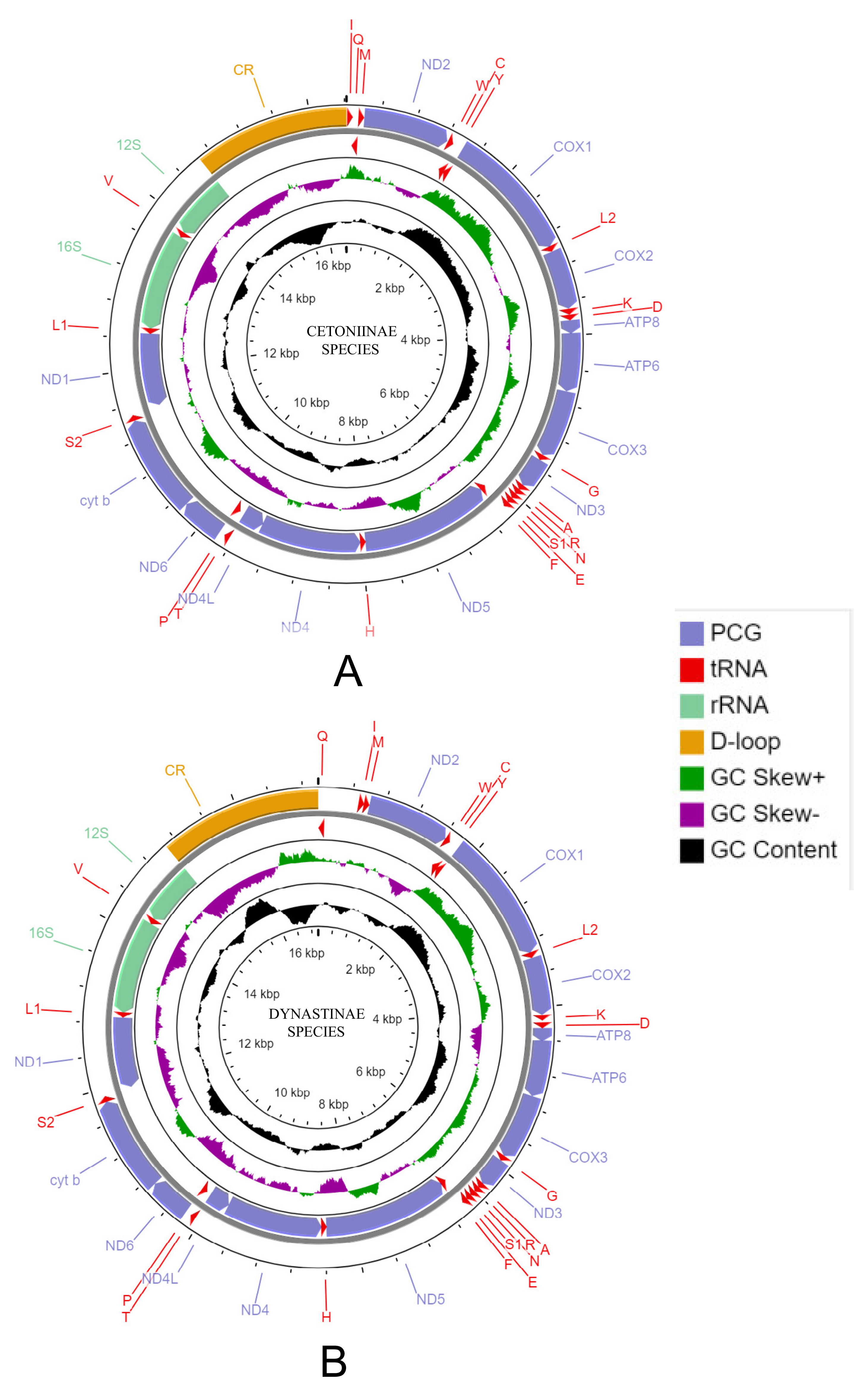
3.1. General Features of mt Genomes
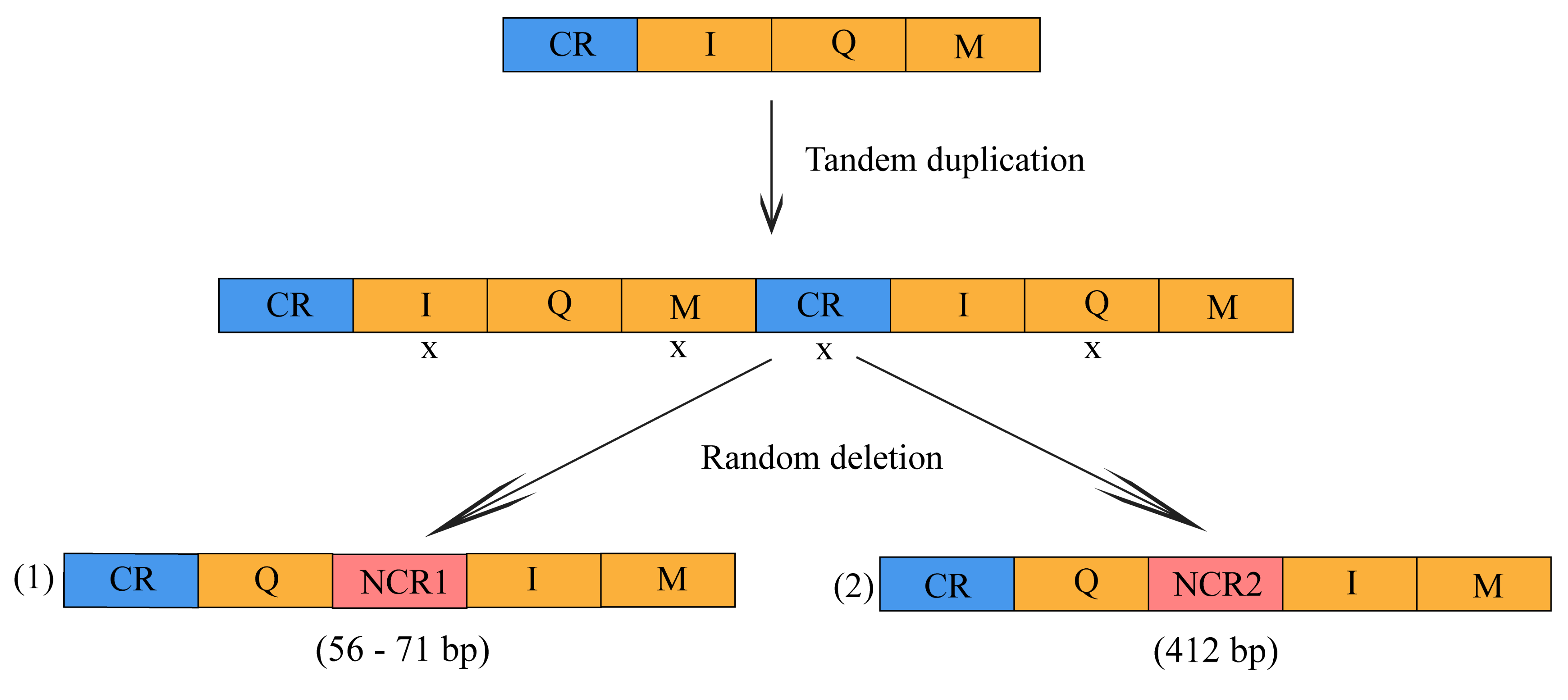
3.2. Gene Arrangement and Non-Coding Region
3.3. Protein-Coding Genes and Codon Usage
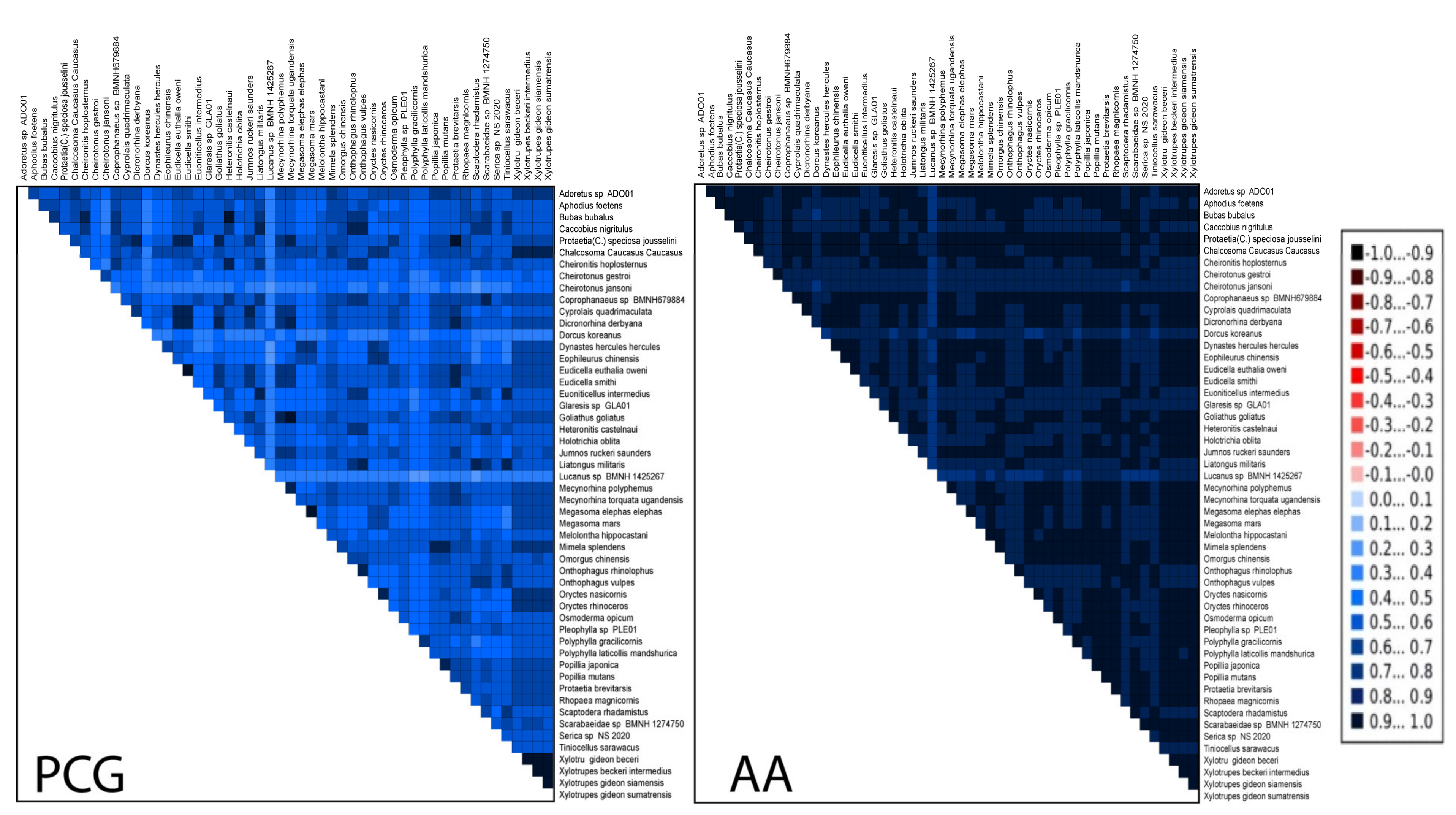
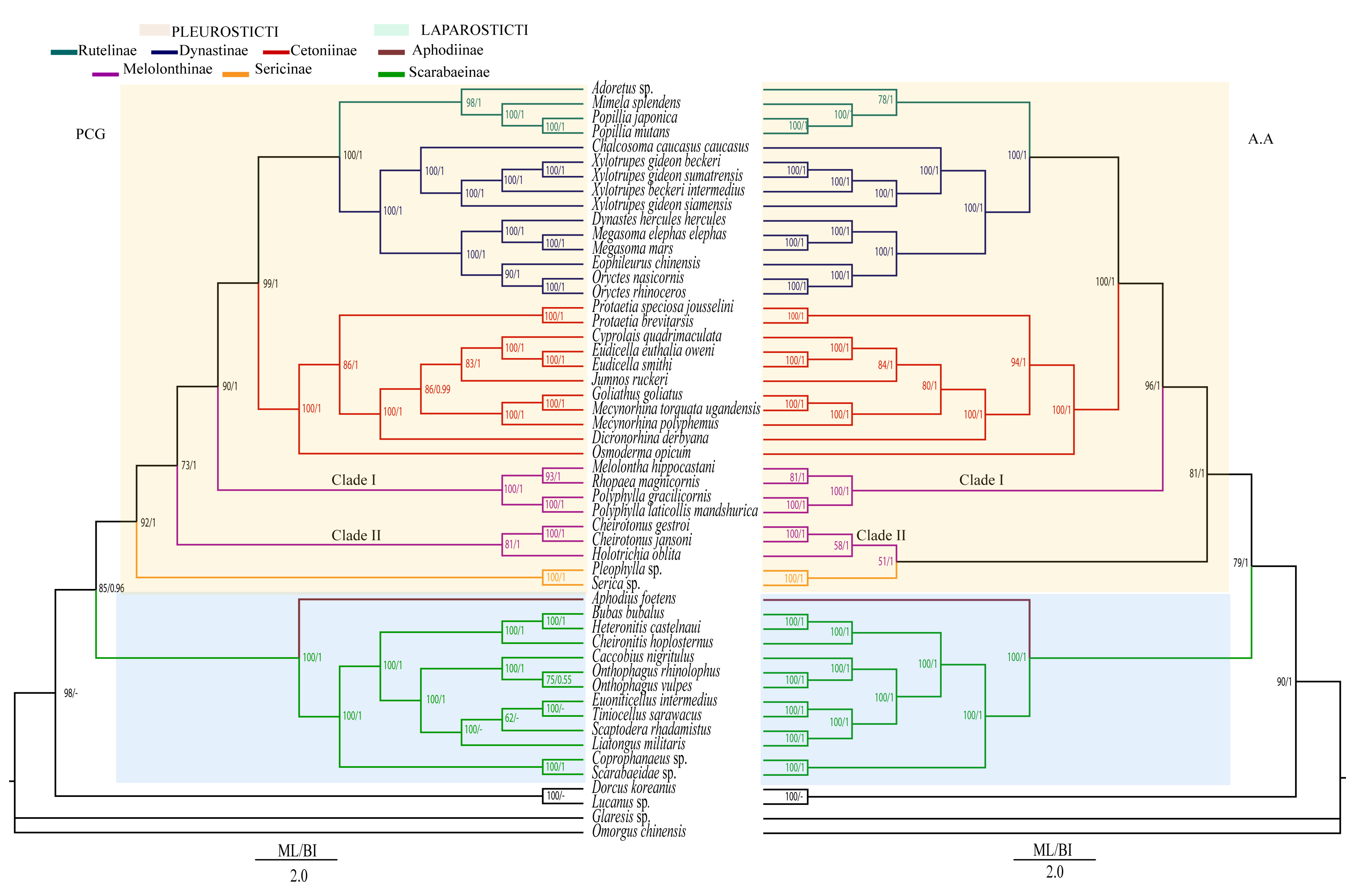
3.4. Heterogeneous Sequences Divergence and Phylogenetic Analyses
4. Discussion
4.1. General Features of mt Genomes in Cetoniinae and Dynastinae
4.2. Gene Rearrangement
4.3. Start Codons
4.4. Phylogenetic Relationship within Scarabaeidae
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, S.-Q.; Che, L.-H.; Li, Y.; Dan, L.; Pang, H.; Ślipiński, A.; Zhang, P. Evolutionary history of Coleoptera revealed by extensive sampling of genes and species. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McKenna, D.D.; Shin, S.; Ahrens, D.; Balke, M.; Beza-Beza, C.; Clarke, D.J.; Donath, A.; Escalona, H.E.; Friedrich, F.; Letsch, H.; et al. The evolution and genomic basis of beetle diversity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 24729–24737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rossa, R.; Goczał, J. Global diversity and distribution of longhorn beetles (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae). Eur. Zool. J. 2021, 88, 289–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choate, P.; Choate, P.M. Dichotomus keys to some Families of Florida Coleoptera. Introd. Identif. Beetles (Coleopt.) 1999, 23–33. Available online: https://entnemdept.ufl.edu/choate/beetles1a.pdf (accessed on 5 September 2021).
- Williams, D.M. Book of Insect Records; University of Florida: Gainesville, FL, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Song, N.; Zhang, H. The mitochondrial genomes of phytophagous scarab beetles and systematic implications. J. Insect Sci. 2018, 18, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohacz, C.; du Harrison, J.G.; Ahrens, D. Comparative morphology of antennal surface structures in pleurostict scarab beetles (Coleoptera). Zoomorphology 2020, 139, 327–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, S.R.; de Barros, A.T.M.; Puker, A.; Taira, T.L. Diversity of coprophagous scarab beetles (Coleoptera, Scarabaeidae) collected with flight intercept trap in the Southern Pantanal, Brazil. Biota Neotrop. 2010, 10, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barbero, E.; Palestrini, C.; Rolando, A. Dung beetle conservation: Effects of habitat and resource selection (Coleoptera: Scarabaeoidea). J. Insect Conserv. 1999, 3, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, M.; Li, S.; Lu, Y.; Yang, H.; Tong, Y.; Yang, X. Mandible evolution in the Scarabaeinae (Coleoptera: Scarabaeidae) and adaptations to coprophagous habits. Front. Zool. 2015, 12, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Erichson, W.F. Naturgeschichte der Insecten Deutschlands: Erste Abtheilung. Coleoptera; Nabu Press: Charleston, SC, USA, 1847; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Gunter, N.L.; Weir, T.A.; Slipinksi, A.; Bocak, L.; Cameron, S.L. If dung beetles (Scarabaeidae: Scarabaeinae) arose in association with dinosaurs, did they also suffer a mass co-extinction at the K-Pg boundary? PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0153570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, K.; Gupta, D. An inventory of scarab beetles (Coleoptera: Scarabaeidae) of Achanakmar-Amarkantak biosphere reserve, Chhattisgarh, India. Int. J. Sci. Nat. 2012, 3, 886–891. [Google Scholar]
- Marczak, D.; Mroczynski, R. A contribution to the knowledge of the fauna of the Kampinos National Park: Scarabaeidae. Part 1. Subfamilies: Melolonthinae, Sericinae, Rutelinae, Dynastinae i Cetoninae. Entomol. News 2016, 35, 161–171. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, A.B. A review of the family-group names for the superfamily Scarabaeoidea (Coleoptera) with corrections to nomenclature and a current classification. Coleopt. Bull. 2006, 60, 144–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eberle, J.; Myburgh, R.; Ahrens, D. The evolution of morphospace in phytophagous scarab chafers: No competition—No divergence? PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e98536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahrens, D.; Schwarzer, J.; Vogler, A.P. The evolution of scarab beetles tracks the sequential rise of angiosperms and mammals. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2014, 281, 20141470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.T.; Jeng, M.L.; Tsai, J.F.; Li, C.L.; Wu, L.W. Two mitochondrial genomes of Taiwanese rhinoceros beetles, Oryctes rhinoceros and Eophileurus chinensis (Coleoptera: Scarabaeidae). Mitochondrial DNA Part B 2021, 6, 2260–2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filipovic, I.; Hereward, J.P.; Rasic, G.; Devine, G.J.; Furlong, M.J.; Etebari, K. The complete mitochondrial genome sequence of Oryctes rhinoceros (Coleoptera: Scarabaeidae) based on long-read nanopore sequencing. PeerJ 2021, 9, e10552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahrens, D. The phylogeny of Sericini and their position within the Scarabaeidae based on morphological characters (Coleoptera: Scarabaeidae). Syst. Entomol. 2006, 31, 113–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coca-Abia, M.M. Phylogenetic relationships of the subfamily Melolonthinae (Coleoptera, Scarabaeidae). Insect Syst. Evol. 2007, 38, 447–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Král, D.; Batelka, J. Order Coleoptera, superfamily Scarabaeoidea. Arthropod Fauna UAE 2017, 6, 78–168. [Google Scholar]
- Ratcliffe, B.C.; Jameson, M.L.; Smith, A.B. 34. Scarabaeidae Latreille 1802. Am. Beetles 2002, 2, 39–81. [Google Scholar]
- Leal, W.S. Chemical ecology of phytophagous scarab beetles. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 1998, 43, 39–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yusifov, E.F.; Ahmadov, B.A.; Narimanova, V.S. Diversity study of scarab beetles belonging to the subfamily cetoniinae spread in the natural region of the greater Caucasus of Azerbaijan. J. Entomol. Zool. Stud. 2016, 4, 1118–1122. [Google Scholar]
- Cameron, S.L. Insect mitochondrial genomics: Implications for evolution and phylogeny. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2014, 59, 95–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boore, J.L. Animal mitochondrial genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1999, 27, 1767–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, D.-X.; Hewitt, G.M. Insect mitochondrial control region: A review of its structure, evolution and usefulness in evolutionary studies. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 1997, 25, 99–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Feng, S.; Liu, L.; Li, Z. The first complete mitochondrial genome of the Japanese beetle Popillia japonica (Coleoptera: Scarabaeidae) and its phylogenetic implications for the superfamily Scarabaeoidea. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 118, 1406–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; You, C.J.; Tsui, C.K.M.; Tembrock, L.R.; Wu, Z.Q.; Yang, P. Phylogeny and biogeography of the Japanese rhinoceros beetle, Trypoxylus dichotomus (Coleoptera: Scarabaeidae) based on SNP markers. Ecol. Evol. 2021, 11, 153–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheffield, N.C.; Song, H.; Cameron, S.L.; Whiting, M.F. A comparative analysis of mitochondrial genomes in Coleoptera (Arthropoda: Insecta) and genome descriptions of six new beetles. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2008, 25, 2499–2509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brown, J.; Pirrung, M.; McCue, L.A. FQC Dashboard: Integrates FastQC results into a web-based, interactive, and extensible FASTQ quality control tool. Bioinformatics 2017, 33, 3137–3139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Sena Brandine, G.; Smith, A.D. Falco: High-speed FastQC emulation for quality control of sequencing data. F1000Research 2019, 8, 1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dierckxsens, N.; Mardulyn, P.; Smits, G. NOVOPlasty: De novo assembly of organelle genomes from whole genome data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, e18. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bernt, M.; Donath, A.; Jühling, F.; Externbrink, F.; Florentz, C.; Fritzsch, G.; Pütz, J.; Middendorf, M.; Stadler, P.F. MITOS: Improved de novo metazoan mitochondrial genome annotation. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2013, 69, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowe, T.M.; Chan, P.P. tRNAscan-SE On-line: Integrating search and context for analysis of transfer RNA genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, W54–W57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Benson, G. Tandem repeats finder: A program to analyze DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1999, 27, 573–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grant, J.R.; Stothard, P. The CGView Server: A comparative genomics tool for circular genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, W181–W184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Gao, F.; Jakovlić, I.; Zou, H.; Zhang, J.; Li, W.X.; Wang, G.T. PhyloSuite: An integrated and scalable desktop platform for streamlined molecular sequence data management and evolutionary phylogenetics studies. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2020, 20, 348–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickham, H. ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis (Use R); Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2009; Volume 10, p. 978. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, M.J.; Im, H.H.; Lee, K.Y.; Han, Y.S.; Kim, I. Complete mitochondrial genome of the whiter-spotted flower chafer, Protaetia brevitarsis (Coleoptera: Scarabaeidae). Mitochondrial DNA 2014, 25, 177–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.J.; Jeong, S.Y.; Jeong, J.C.; Kim, S.S.; Kim, I. Complete mitochondrial genome of the endangered flower chafer Osmoderma opicum (Coleoptera: Scarabaeidae). Mitochondrial DNA B Resour. 2016, 1, 148–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, C.; Zhu, E.-J.; He, Q.-J.; Yi, C.-H.; Hu, S.-J.; Wang, X.-B. Complete mitochondrial genome of the endangered long-armed scarab Cheirotonus gestroi (Coleoptera: Euchiridae). Mitochondrial DNA Part B Resour. 2020, 5, 869–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shao, L.L.; Huang, D.Y.; Sun, X.Y.; Hao, J.S.; Cheng, C.H.; Zhang, W.; Yang, Q. Complete mitochondrial genome sequence of Cheirotonus jansoni (Coleoptera: Scarabaeidae). Genet. Mol. Res. 2014, 13, 1047–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameron, S.L.; Sullivan, J.; Song, H.; Miller, K.B.; Whiting, M.F. A mitochondrial genome phylogeny of the Neuropterida (lace-wings, alderflies and snakeflies) and their relationship to the other holometabolous insect orders. Zool. Scr. 2009, 38, 575–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.J.; Kim, K.-G.; Kim, I. Description of nearly completed mitochondrial genome sequences of the garden chafer Polyphylla laticollis manchurica, endangered in Korea (Insecta: Coleoptera). Int. J. Ind. Entomol. 2013, 27, 185–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breeschoten, T.; Doorenweerd, C.; Tarasov, S.; Vogler, A.P. Phylogenetics and biogeography of the dung beetle genus Onthophagus inferred from mitochondrial genomes. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2016, 105, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.; Kim, P.; An, S.L. The complete mitochondrial genome of Korean indigenous stag beetle, Dorcus koreanus. Mitochondrial DNA Part B 2020, 5, 3741–3742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linard, B.; Arribas, P.; Andujar, C.; Crampton-Platt, A.; Vogler, A.P. Lessons from genome skimming of arthropod-preserving ethanol. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2016, 16, 1365–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maddison, W.P. Mesquite: A modular system for evolutionary analysis. Evolution 2008, 62, 1103–1118. [Google Scholar]
- Kück, P.; Meid, S.A.; Groß, C.; Wägele, J.W.; Misof, B. AliGROOVE–visualization of heterogeneous sequence divergence within multiple sequence alignments and detection of inflated branch support. BMC Bioinf. 2014, 15, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huelsenbeck, J.P.; Ronquist, F. MRBAYES: Bayesian inference of phylogenetic trees. Bioinformatics 2001, 17, 754–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nguyen, L.-T.; Schmidt, H.A.; Von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q. IQ-TREE: A fast and effective stochastic algorithm for estimating maximum-likelihood phylogenies. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2015, 32, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowton, M.; Cameron, S.L.; Dowavic, J.I.; Austin, A.D.; Whiting, M.F. Characterization of 67 Mitochondrial tRNA Gene rearrangements in the Hymenoptera suggests that mitochondrial tRNA gene position is selectively neutral. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2009, 26, 1607–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Silvestre, D.; Arias, M.C. Mitochondrial tRNA gene translocations in highly eusocial bees. Genet. Mol. Biol. 2006, 29, 572–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roberti, M.; Polosa, P.L.; Bruni, F.; Musicco, C.; Gadaleta, M.N.; Cantatore, P. DmTTF, a novel mitochondrial transcription termination factor that recognises two sequences of Drosophila melanogaster mitochondrial DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003, 31, 1597–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Taanman, J.-W. The mitochondrial genome: Structure, transcription, translation and replication. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Bioenerg. 1999, 1410, 103–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cameron, S. How to sequence and annotate insect mitochondrial genomes for systematic and comparative genomics research. Syst. Entomol. 2014, 39, 400–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramírez-Ríos, V.; Alvarez, J.C.; Villanueva-Mejia, D. Mitochondrial genomes of Lepidopteran insects considered crop pests. Lepidoptera 2017, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ojala, D.; Montoya, J.; Attardi, G. tRNA punctuation model of RNA processing in human mitochondria. Nature 1981, 290, 470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donath, A.; Jühling, F.; Al-Arab, M.; Bernhart, S.H.; Reinhardt, F.; Stadler, P.F.; Middendorf, M.; Bernt, M. Improved annotation of protein-coding genes boundaries in metazoan mitochondrial genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, 10543–10552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, J.S.; Kim, M.J.; Kim, I. The mitochondrial genome of the dung beetle, Copris tripartitus, with mitogenomic comparisons within Scarabaeidae (Coleoptera). Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 144, 874–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, E.H.; Mun, S.; Baek, S.Y.; Hwang, J.; Hwang, U.W. The complete mitochondrial genome of a whiter-spotted flower chafer, Protaetia brevitarsis (Coleoptera: Scarabaeidae). Mitochondrial DNA Part B 2020, 5, 3584–3586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.-Z.; Zhang, L.; Feng, R.-Q.; Zhang, L.-J.; Luo, F.-Z.; Yuan, M.-L. Mitochondrial genome of Amphimallon solstitiale (Coleoptera: Scarabaeidae: Melolonthinae) and phylogenetic analysis. Mitochondrial DNA Part B 2018, 4, 110–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, P.-C.; Shieh, H.K.; Shien, J.-H.; Kang, S.-W. A homopolymer stretch composed of variable numbers of cytidine residues in the terminal repeats of infectious laryngotracheitis virus. Avian Dis. 2000, 44, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stewart, J.E.; Fisher, C.L.; Aagaard, P.J.; Wilson, M.R.; Isenberg, A.R.; Polanskey, D.; Pokorak, E.; DiZinno, J.A.; Budowle, B. Length variation in HV2 of the human mitochondrial DNA control region. J. Forensic Sci. 2001, 46, 862–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, S.; Tamura, K.; Aotsuka, T. Replication origin of mitochondrial DNA in insects. Genetics 2005, 171, 1695–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dowton, M.; Castro, L.; Austin, A. Mitochondrial gene rearrangements as phylogenetic characters in the invertebrates: The examination of genome ‘morphology’. Invertebr. Syst. 2002, 16, 345–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, A.; Li, H.; Bai, X.; Dai, X.; Chang, J.; Guilbert, E.; Cai, W. The complete mitochondrial genome of the flat bug Aradacanthia heissi (Hemiptera: Aradidae). Zootaxa 2012, 3238, 23–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, P.; Li, H.; Song, F.; Cai, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, J.; Cai, W. Duplication and Remolding of tRNA Genes in the Mitochondrial Genome of Reduvius tenebrosus (Hemiptera: Reduviidae). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, F.; Li, H.; Shao, R.; Shi, A.; Bai, X.; Zheng, X.; Heiss, E.; Cai, W. Rearrangement of mitochondrial tRNA genes in flat bugs (Hemiptera: Aradidae). Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 25725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sayadi, A.; Immonen, E.; Tellgren-Roth, C.; Arnqvist, G. The evolution of dark matter in the mitogenome of seed beetles. Genome Biol. Evol. 2017, 9, 2697–2706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Clary, D.O.; Wolstenholme, D.R. The mitochondrial DNA molecular of Drosophila yakuba: Nucleotide sequence, gene organization, and genetic code. J. Mol. Evol. 1985, 22, 252–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Bruijn, M.H. Drosophila melanogaster mitochondrial DNA, a novel organization and genetic code. Nature 1983, 304, 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, L.R.; Ruberu, K.; Dowton, M. Mitochondrial genomes of Vanhornia eucnemidarum (Apocrita: Vanhorniidae) and Primeuchroeus spp. (Aculeata: Chrysididae): Evidence of rearranged mitochondrial genomes within the Apocrita (Insecta: Hymenoptera). Genome 2006, 49, 752–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameron, S.L.; Whiting, M.F. The complete mitochondrial genome of the tobacco hornworm, Manduca sexta, (Insecta: Lepidoptera: Sphingidae), and an examination of mitochondrial gene variability within butterflies and moths. Gene 2008, 408, 112–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oliveira, M.T.; de Azeredo-Espin, A.M.; Lessinger, A.C. Evolutionary and structural analysis of the cytochrome c oxidase subunit I (COI) gene from Haematobia irritans, Stomoxys calcitrans and Musca domestica (Diptera: Muscidae) mitochondrial DNA. DNA Seq. 2005, 16, 156–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenn, J.D.; Cameron, S.L.; Whiting, M.F. The complete mitochondrial genome sequence of the Mormon cricket (Anabrus simplex: Tettigoniidae: Orthoptera) and an analysis of control region variability. Insect Mol. Biol. 2007, 16, 239–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.S.; Shin, K.S.; Kim, M.S.; Park, H.; Cho, S.; Kim, C.B. The mitochondrial genome of the smaller tea tortrix Adoxophyes honmai (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae). Gene 2006, 373, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocak, L.; Barton, C.; Crampton-Platt, A.; Chesters, D.; Ahrens, D.; Vogler, A.P. Building the Coleoptera tree-of-life for >8000 species: Composition of public DNA data and fit with Linnaean classification. Syst. Entomol. 2014, 39, 97–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, T.; Bergsten, J.; Levkanicova, Z.; Papadopoulou, A.; John, O.S.; Wild, R.; Hammond, P.M.; Ahrens, D.; Balke, M.; Caterino, M.S. A comprehensive phylogeny of beetles reveals the evolutionary origins of a superradiation. Science 2007, 318, 1913–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Subfamily | Species | Accession No. | Size (bp) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ingroups | ||||
| Cetoniinae | Protaetia brevitarsis | KC775706 | 20,319 | [42] |
| Osmoderma opicum | KU500641 | 15,341 | [43] | |
| Dynastinae | Eophileurus chinensis | MW632132 | 16,624 | [18] |
| Oryctes rhinoceros | MT457815 | 20,898 | [19] | |
| Rutelinae | Popillia mutans | MF997049 | 16,192 | [6] |
| Popillia japonica | NC_038115 | 16,541 | [29] | |
| Adoretus sp. | JX412788 | 12,581 | Unpublished | |
| Mimela splendens | MZ064554 | 15,148 | Unpublished | |
| Melolonthinae | Polyphylla gracilicornis | NC_054285 | 16,793 | Unpublished |
| Cheirotonus gestroi | MN893347 | 16,899 | [44] | |
| Melolontha hippocastani | KX087316 | 15,485 | Unpublished | |
| Cheirotonus jansoni | NC_023246 | 17,249 | [45] | |
| Rhopaea magnicornis | NC_013252 | 17,522 | [46] | |
| Polyphylla laticollis mandshurica | KF544959 | 14,473 | [47] | |
| Holotrichia oblita | MF997046 | 15,968 | [6] | |
| Sericinae | Pleophylla sp. | JX412736 | 12,579 | Unpublished |
| Serica sp. | MF997050 | 13,815 | [6] | |
| Aphodiinae | Aphodius foetens | KX087240 | 15,907 | Unpublished |
| Scarabaeinae | Coprophanaeus sp. | KU739465 | 15,554 | [48] |
| Bubas bubalus | KU739469 | 16,035 | [48] | |
| Onthophagus rhinolophus | KU739498 | 15,237 | [48] | |
| Onthophagus vulpes | KU739474 | 15,884 | [48] | |
| Scaptodera rhadamistus | KU739460 | 15,119 | [48] | |
| Cheironitis hoplosternus | KU739450 | 14,924 | [48] | |
| Euoniticellus intermedius | KU739490 | 15,578 | [48] | |
| Liatongus militaris | KU739488 | 15,832 | [48] | |
| Tiniocellus sarawacus | KU739486 | 15,592 | [48] | |
| Caccobius nigritulus | KU739484 | 15,039 | [48] | |
| Heteronitis castelnaui | KU739468 | 13,441 | [48] | |
| Scarabaeidae sp. | KT696268 | 18,626 | Unpublished | |
| Trogidae | Omorgus chinensis | MK937809 | 18,858 | Unpublished |
| Glaresidae | Glaresis sp. | JX412819 | 12,663 | Unpublished |
| Lucanidae | Dorcus koreanus | NC_054278 | 17,787 | [49] |
| Lucanus sp. | KT876903 | 20,634 | [50] |
| Species | Protein Coding Genes (PCGs) START-STOP CODONS | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ND2 | COX1 | COX2 | COX3 | ATP8 | ATP6 | ND3 | ND5 | ND4 | ND4L | ND6 | CYTB | ND1 | |
| P.s.j | ATT/TAG | AAC/T | ATT/T | ATC/T | ATG/TAA | ATG/TAA | ATT/TAG | ATT/TAA | ATG/T | ATG/TAA | ATT/TAA | ATG/TAG | ATT/TAA |
| C.q | ATA/TAA | AAC/T | ATA/T | ATC/T | ATG/TAA | ATG/TAA | ATA/TAG | ATA/TAA | ATG/TAA | ATG/TAA | GTC/TAA | ATG/TAG | ATA/TAG |
| D.d | ATT/TAA | AAC/T | ATA/T | ATC/T | ATG/TAA | ATG/TAA | ATT/TAG | ATT/TAA | ATG/TAG | ATG/TAA | ATT/TAA | ATG/TAG | ATT/TAA |
| E.e.o | ATA/TAA | AAC/T | ATA/T | ATC/T | ATG/TAA | ATG/TAA | ATA/TAG | ATA/TAA | ATG/TAG | ATG/TAA | ATC/TAA | ATG/TAG | ATA/TAA |
| E.s | ATA/TAA | AAC/T | ATA/T | ATC/T | ATG/TAA | ATG/TAA | ATA/TAG | ATA/TAA | ATG/TAG | ATG/TAA | ATC/TAA | ATG/TAG | ATA/TAA |
| G.g | ATT/TAA | AAC/T | ATT/T | ATT/T | ATG/TAA | ATG/TAA | ATC/TAG | ATT/TAA | ATG/TAG | ATG/TAA | ATT/TAA | ATG/TAG | ATT/TAA |
| J.r | ATA/TAA | AAC/T | ATA/T | ATA/T | ATG/TAA | ATG/TAA | ATT/TAG | ATT/TAA | ATG/TAG | ATG/TAA | ATC/TAA | ATG/TAG | ATT/TAG |
| M.p | ATA/TAA | AAT/T | ATA/T | ATT/T | ATG/TAA | ATG/TAA | ATT/TAG | ATT/TAA | ATG/TAA | ATG/TAA | ATT/TAA | ATG/TAG | ATT/TAA |
| M.t.u | ATT/TAA | AAC/T | ATT/T | ATT/T | ATG/TAA | ATG/TAA | ATC/TAG | ATT/TAA | ATG/TAG | ATG/TAA | ATT/TAA | ATG/TAG | ATT/TAA |
| C.c.c | ATT/TAA | ATT/T | ATT/T | ATC/T | ATG/TAA | ATG/TAA | ATC/TAG | ATT/T | ATG/TAA | ATG/TAA | ATT/TAA | ATG/TAG | ATT/TAA |
| D.h.h | GTC/TAA | ATC/T | ATC/T | ATT/T | ATG/TAA | ATG/TAA | ATC/TAG | ATT/T | ATG/TAA | ATG/TAA | ATC/TAA | ATG/TAG | ATT/TAA |
| M.e.e | ATC/TAA | ATT/T | ATC/T | ATT/T | ATG/TAA | ATG/TAA | ATC/TAG | ATT/T | ATG/TAA | ATG/TAA | ATC/TAA | ATG/TAA | ATT/TAA |
| M.m | ATC/TAA | ATT/T | ATC/T | ATT/T | ATG/TAA | ATG/TAA | ATC/TAG | ATT/T | ATG/TAA | ATG/TAA | ATC/TAA | ATG/TAA | ATT/TAA |
| O.n | ATA/TAA | ATC/T | ATA/T | ATT/T | ATG/TAA | ATG/TAA | ATC/TAG | ATT/T | ATG/TAA | ATG/TAA | ATC/TAA | ATG/TAG | ATT/TAA |
| X.b.i | ATT/TAA | ATT/T | ATT/T | ATC/T | ATG/TAA | ATG/TAA | ATC/TAG | ATT/T | ATG/TAA | ATG/TAA | ATT/TAA | ATG/TAG | ATT/TAA |
| X.g.b | ATT/TAA | ATT/T | ATT/T | ATT/T | ATG/TAA | ATG/TAA | ATC/TAG | ATT/T | ATG/TAA | ATG/TAA | ATT/TAA | ATG/TAG | ATT/TAA |
| X.g.s | ATT/TAA | ATT/T | ATT/T | ATC/T | ATG/TAA | ATG/TAA | ATC/TAG | ATT/T | ATG/TAA | ATG/TAA | ATT/TAA | ATG/TAG | ATT/TAA |
| X.g.s | ATT/TAA | ATT/T | ATT/T | ATC/T | ATG/TAA | ATG/TAA | ATC/TAG | ATT/T | ATG/TAA | ATG/TAA | ATT/TAA | ATG/TAG | ATT/TAA |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ayivi, S.P.G.; Tong, Y.; Storey, K.B.; Yu, D.-N.; Zhang, J.-Y. The Mitochondrial Genomes of 18 New Pleurosticti (Coleoptera: Scarabaeidae) Exhibit a Novel trnQ-NCR-trnI-trnM Gene Rearrangement and Clarify Phylogenetic Relationships of Subfamilies within Scarabaeidae. Insects 2021, 12, 1025. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects12111025
Ayivi SPG, Tong Y, Storey KB, Yu D-N, Zhang J-Y. The Mitochondrial Genomes of 18 New Pleurosticti (Coleoptera: Scarabaeidae) Exhibit a Novel trnQ-NCR-trnI-trnM Gene Rearrangement and Clarify Phylogenetic Relationships of Subfamilies within Scarabaeidae. Insects. 2021; 12(11):1025. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects12111025
Chicago/Turabian StyleAyivi, Sam Pedro Galilee, Yao Tong, Kenneth B. Storey, Dan-Na Yu, and Jia-Yong Zhang. 2021. "The Mitochondrial Genomes of 18 New Pleurosticti (Coleoptera: Scarabaeidae) Exhibit a Novel trnQ-NCR-trnI-trnM Gene Rearrangement and Clarify Phylogenetic Relationships of Subfamilies within Scarabaeidae" Insects 12, no. 11: 1025. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects12111025
APA StyleAyivi, S. P. G., Tong, Y., Storey, K. B., Yu, D.-N., & Zhang, J.-Y. (2021). The Mitochondrial Genomes of 18 New Pleurosticti (Coleoptera: Scarabaeidae) Exhibit a Novel trnQ-NCR-trnI-trnM Gene Rearrangement and Clarify Phylogenetic Relationships of Subfamilies within Scarabaeidae. Insects, 12(11), 1025. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects12111025






