Cloning, Expression Analysis, 20-Hydroxyecdysone Induction, and RNA Interference Study of Autophagy-Related Gene 8 from Heortia vitessoides Moore
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Insects
2.2. Sample Preparation
2.3. Sequence Verification and Phylogenetic Analysis
2.4. RNA Extraction and cDNA Synthesis
2.5. Primer Design and Quantitative Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-qPCR)
2.6. dsRNA Preparation and Injection
2.7. Phenotype Observation and Analysis
2.8. 20E Preparation
2.9. Starvation Treatment
2.10. Extreme Temperature Treatment
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
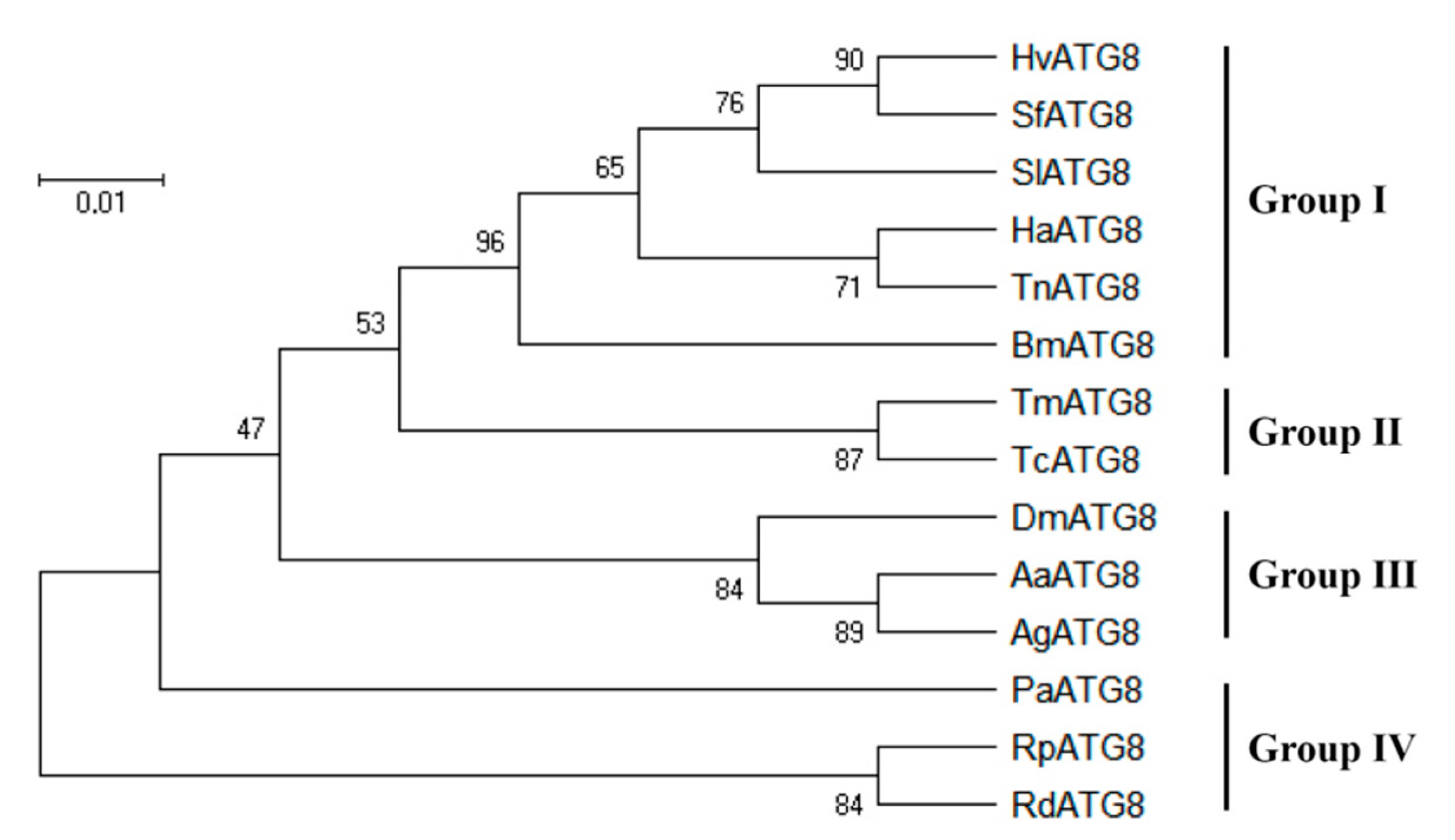
3.1. Sequence Analysis of Hvatg8 and Phylogenetic Analysis
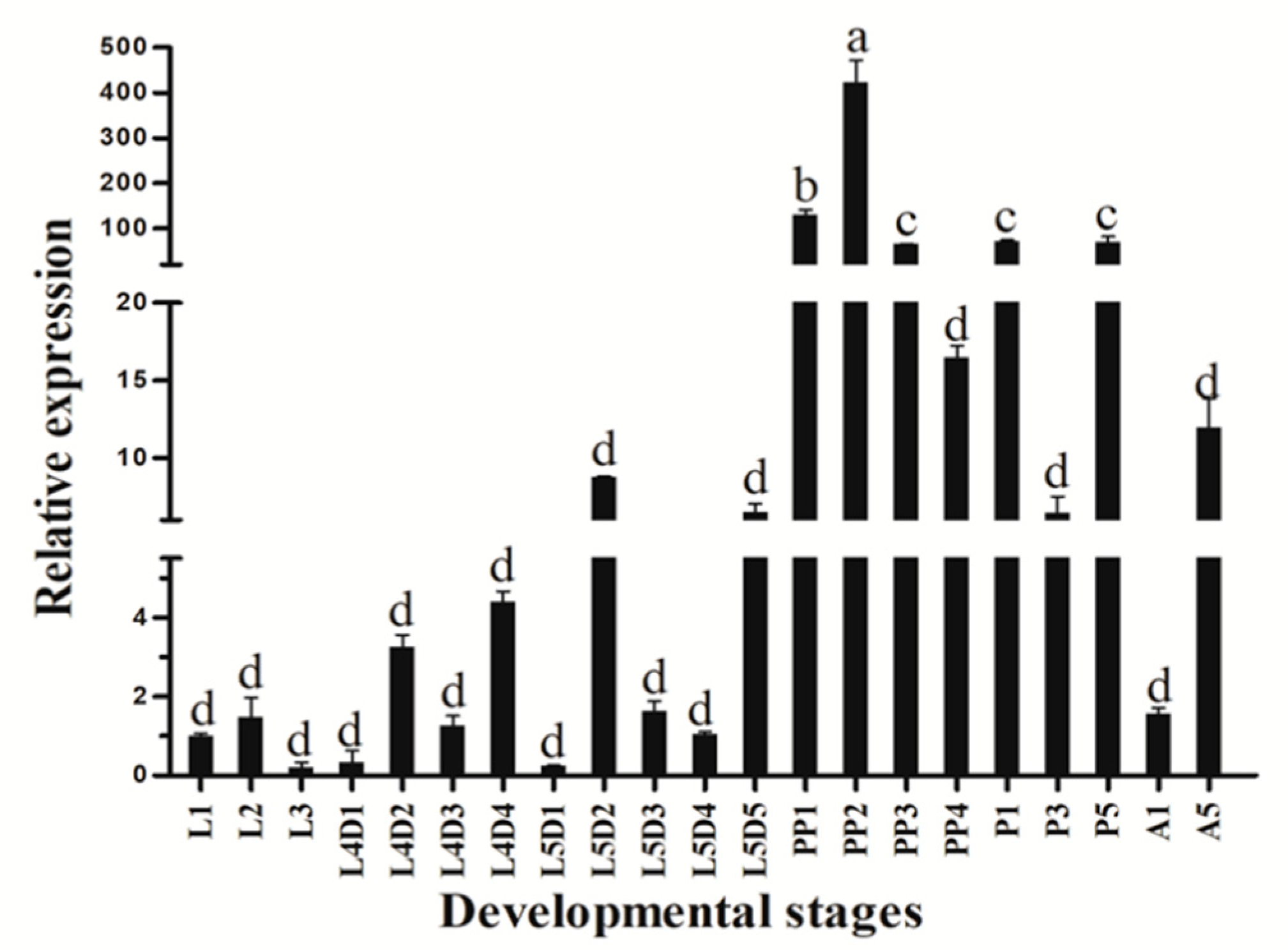
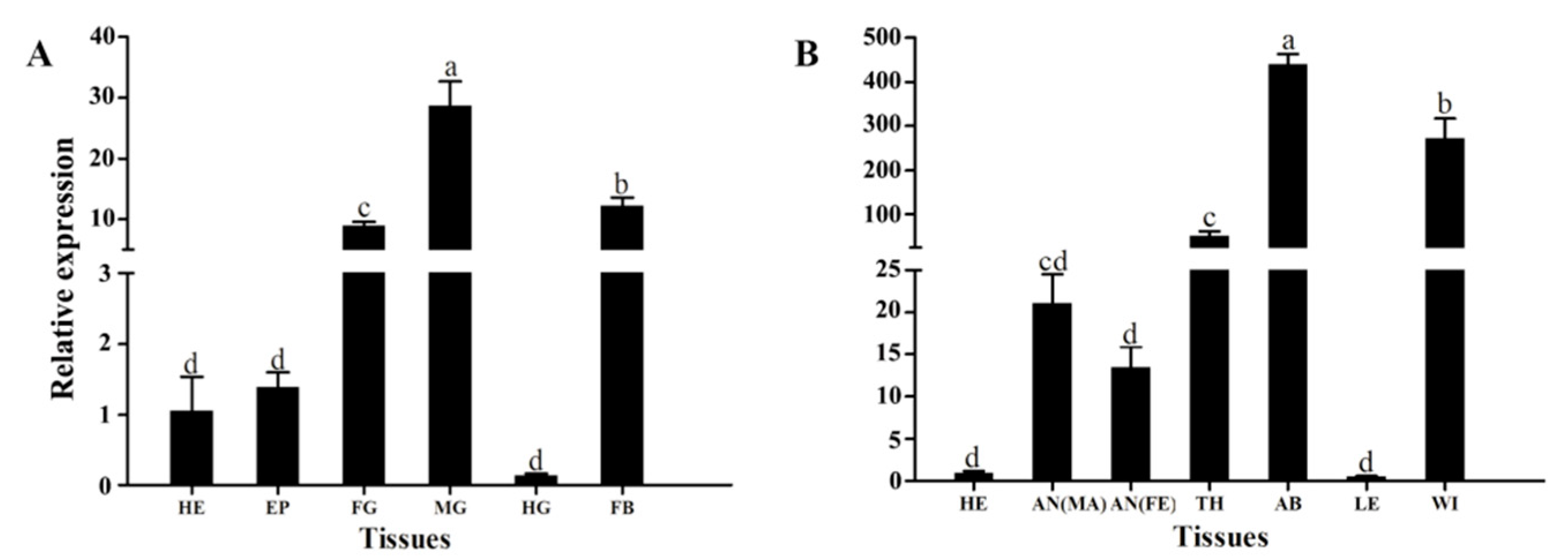
3.2. Stage-Specific and Tissue-Specific Expression Patterns of HvATG8
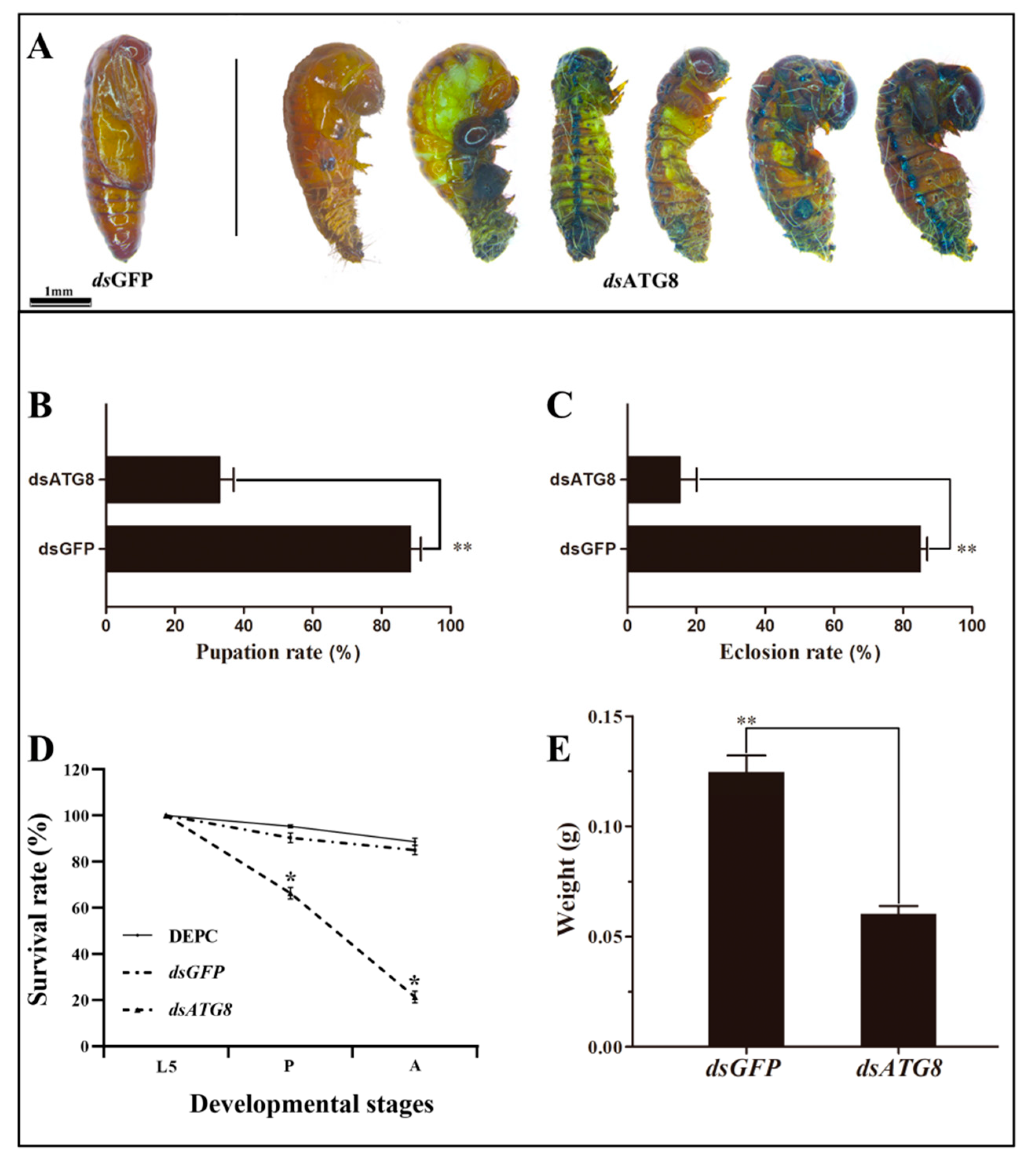
3.3. Silencing of HvATG8 by RNAi
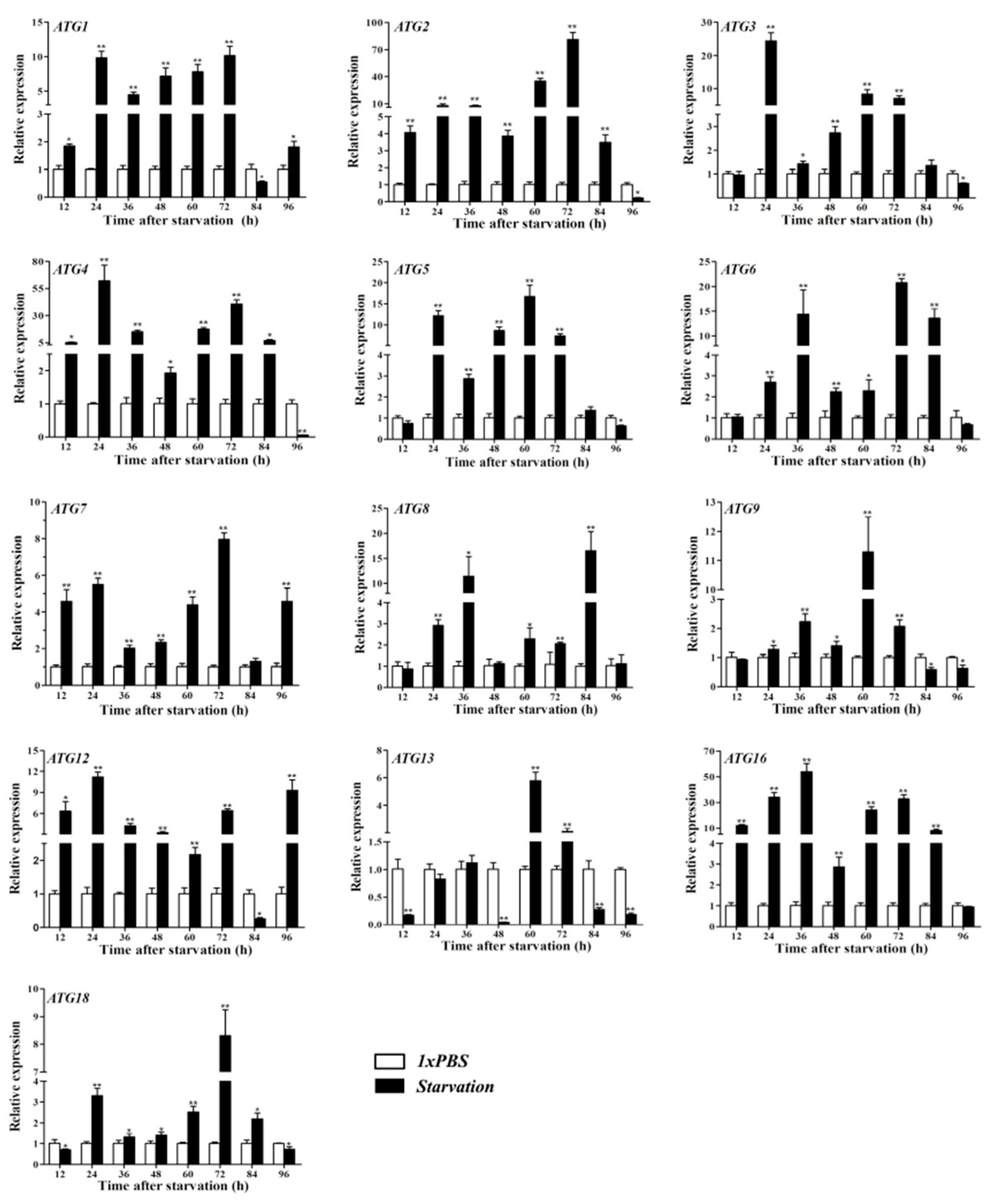
3.4. Gene Expression of ATGs after ATG8 Silencing
3.5. Phenotype Analysis and Survival Assay after RNAi
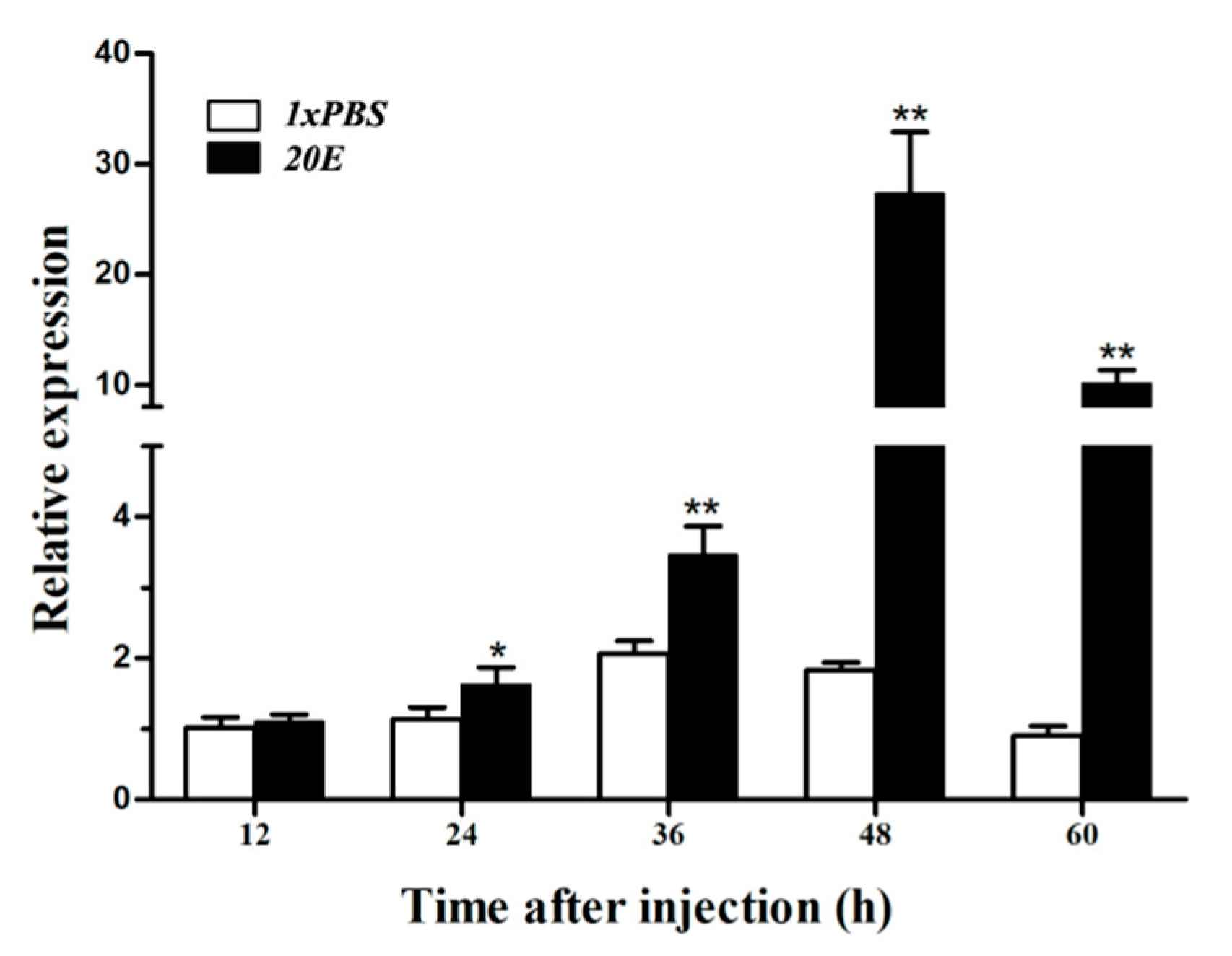
3.6. Expression of HvATG8 after 20E Injection
3.7. Starvation Treatment
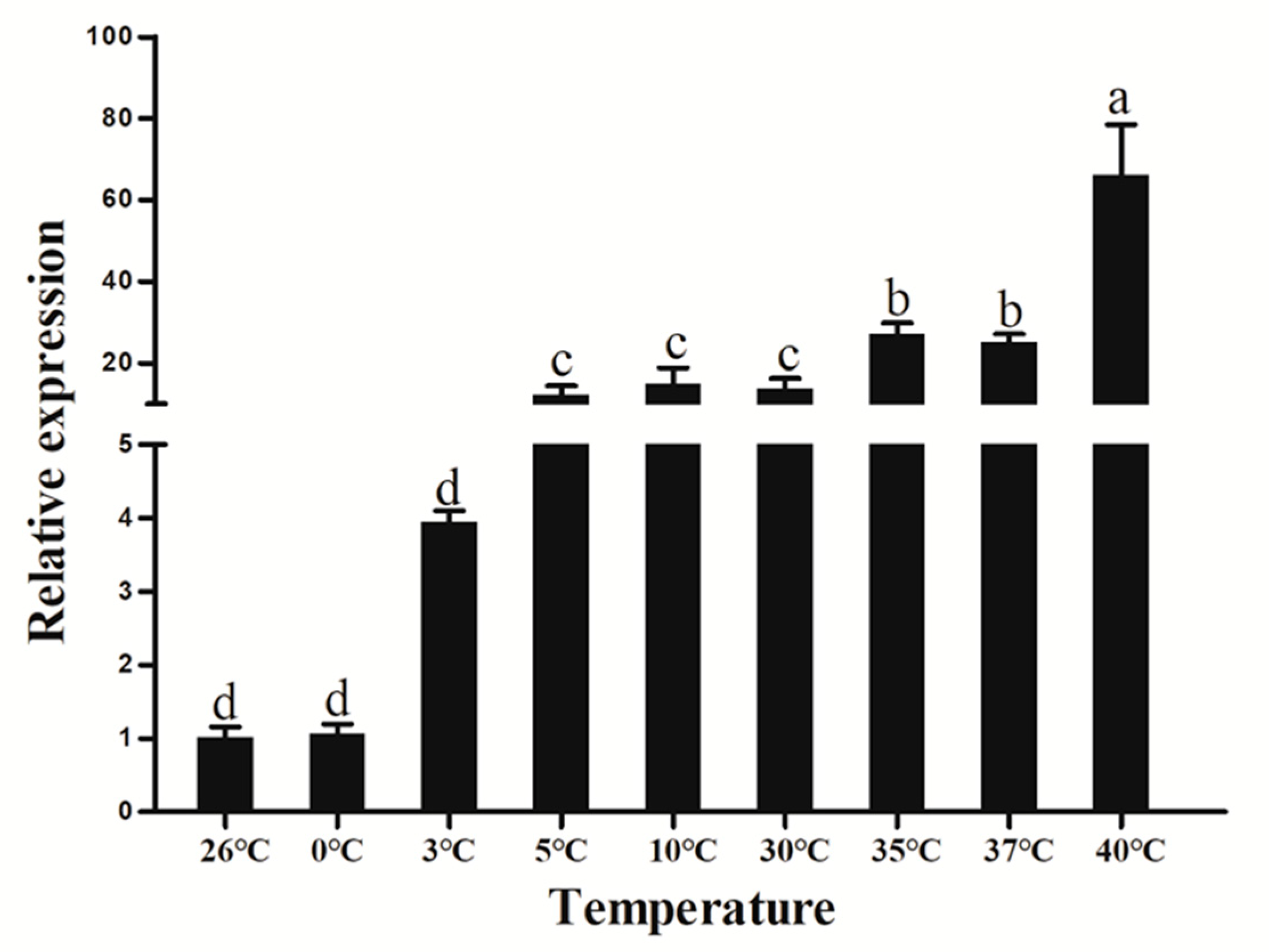
3.8. Extreme Temperature Treatment
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liang, S.; Cai, J.; Chen, X.; Jin, Z.; Zhang, J.; Huang, Z.; Tang, L.; Sun, Z.; Wen, X.; Wang, C. Larval aggregation of Heortia vitessoides Moore (Lepidoptera: Crambidae) and evidence of horizontal transfer of avermectin. Forests 2019, 10, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, Z.; Li, Z.; Cheng, J.; Wang, C.; Chen, J.; Lin, T. Suppression of gene juvenile hormone diol kinase delays pupation in Heortia vitessoides Moore. Insects 2019, 10, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, J.; Wang, C.Y.; Lyu, Z.H.; Chen, J.X.; Lin, T. Identification and characterization of the catalase gene involved in resistance to thermal stress in Heortia vitessoides using RNA interference. J. Therm. Biol. 2018, 78, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, J.; Chen, J.; Lin, T. De novo assembly and analysis of the Heortia vitessoides transcriptome via high-throughput Illumina sequencing. J. Asia-Pac. Entomol. 2017, 20, 1241–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, H.; Lu, P.; Chen, J.; Ma, W.; Qin, R.; Li, X. Antennal and behavioural responses of Heortia vitessoides females to host plant volatiles of Aquilaria sinensis. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 2012, 143, 269–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.Y.; Cheng, J.; Lyu, Z.H.; Li, Z.X.; Chen, J.X.; Lin, T. Chitin deacetylase 1 and 2 are indispensable for larval–pupal and pupal–adult molts in Heortia vitessoides (Lepidoptera: Crambidae). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2019, 237, 110325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Yi, L.; Liling, L.; Meng, Z.; Xiujun, W.; Yizhen, L. An experiment on 7 kinds of insecticides against Heortia vitessoides Moore. J. Shandong For. Sci. Technol. 2014, 6, 37–39. [Google Scholar]
- Zhi-yun, C.; LI, D.; Wang, L.; LI, Y.; Huang, X.; Qin, C. Studies on biological characteristics of Heortia vitessoides Moore on Aquilaris sinensis. China Plant Prot. 2011, 31, 10–14. [Google Scholar]
- Lyu, Z.; Chen, J.; Li, Z.; Cheng, J.; Wang, C.; Lin, T. Knockdown ofβ-N-acetylglucosaminidase gene disrupts molting process inHeortia vitessoides Moore. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 2019, 101, e21561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.Y.; Wang, J.J.; Feng, M.G.; Ying, S.H. Autophagy-related gene ATG7 participates in the asexual development, stress response and virulence of filamentous insect pathogenic fungus Beauveria bassiana. Curr. Genet. 2019, 65, 1015–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizushima, N.; Ohsumi, Y.; Yoshimori, T. Autophagosome formation in mammalian cells. Cell Struct. Funct. 2002, 27, 421–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farré, J.C.; Subramani, S. Mechanistic insights into selective autophagy pathways: Lessons from yeast. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2016, 17, 537–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ying, S.H.; Feng, M.G. Insight into vital role of autophagy in sustaining biological control potential of fungal pathogens against pest insects and nematodes. Virulence 2019, 10, 429–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizushima, N.; Levine, B.; Cuervo, A.M.; Klionsky, D.J. Autophagy fights disease through cellular self-digestion. Nature 2008, 451, 1069–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizushima, N.; Yamamoto, A.; Matsui, M.; Yoshimori, T.; Ohsumi, Y. In vivo analysis of autophagy in response to nutrient starvation using transgenic mice expressing a fluorescent autophagosome marker. Mol. Biol. Cell 2004, 15, 1101–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, D.L.; Baehrecke, E.H. Growth arrest and autophagy are required for salivary gland cell degradation in Drosophila. Cell 2007, 131, 1137–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velentzas, A.D.; Nezis, I.P.; Stravopodis, D.J.; Papassideri, I.S.; Margaritis, L.H. Apoptosis and autophagy function cooperatively for the efficacious execution of programmed nurse cell death during Drosophila virilis oogenesis. Autophagy 2007, 3, 130–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denton, D.; Shravage, B.; Simin, R.; Mills, K.; Berry, D.L.; Baehrecke, E.H.; Kumar, S. Autophagy, not apoptosis, is essential for midgut cell death in Drosophila. Curr. Biol. 2009, 19, 1741–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsukada, M.; Ohsumi, Y. Isolation and characterization of autophagy-defective mutants of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. FEBS Lett. 1993, 333, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umemiya-Shirafuji, R.; Matsuo, T.; Liao, M.; Boldbaatar, D.; Battur, B.; Suzuki, H.I.; Fujisaki, K. Increased expression of ATG genes during nonfeeding periods in the tick Haemaphysalis longicornis. Autophagy 2010, 6, 473–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoa, D.B.; Takeda, M. Expression of autophagy 8 (Atg8) and its role in the midgut and other organs of the greater wax moth, Galleria mellonella, during metamorphic remodelling and under starvation. Insect Mol. Biol. 2012, 21, 473–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.; Ma, L.; Guo, E.; Deng, X.; Ma, S.; Xia, Q.; Cao, Y.; Li, S. 20-Hydroxyecdysone upregulates Atg genes to induce autophagy in the Bombyx fat body. Autophagy 2013, 9, 1172–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Bartolomeo, S.; Corazzari, M.; Nazio, F.; Oliverio, S.; Lisi, G.; Antonioli, M.; Pagliarini, V.; Matteoni, S.; Fuoco, C.; Giunta, L.; et al. The dynamic interaction of AMBRA1 with the dynein motor complex regulates mammalian autophagy. J. Cell Biol. 2010, 191, 155–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, H. Cloning, Expression and Functional Analysis of Spodoptera Litura SlAtg1; Central China Normal University: Wuhan, China, 2015; p. 77. [Google Scholar]
- Ichimura, Y.; Kirisako, T.; Takao, T.; Satomi, Y.; Shimonishi, Y.; Ishihara, N.; Mizushima, N.; Tanida, I.; Kominami, E.; Ohsumi, M.; et al. An ubiquitin-like system mediates protein lipidation. Nature 2000, 408, 488–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, S.; Mao, F.; Hu, D.; Yan, H.; Lei, J.; Obeng, E.; Zhou, Y.; Quan, Y.; Yu, W. Acetylation of BmAtg8 inhibits starvation-induced autophagy initiation. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2019, 457, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, C.; Zhang, X.; Teng, Y.; Hu, H.; Li, W. Structure of autophagy-related protein Atg8 from the silkworm Bombyx mori. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. F Struct. Biol. Cryst. Commun. 2010, 66, 787–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eng, M.W.; van Zuylen, M.N.; Severson, D.W. Apoptosis-related genes control autophagy and influence DENV-2 infection in the mosquito vector, Aedes aegypti. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2016, 76, 70–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Lu, H.; Ai, H.; Peng, R.; Yang, Y.; Li, A.; Hong, H.; Peng, J.; Liu, K. Distribution, cleavage and lipidation of Atg8 fusion proteins in Spodoptera litura sl-HP cells. PLOS ONE 2014, 9, e96059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Peterson, D.; Peterson, N.; Stecher, G.; Nei, M.; Kumar, S. MEGA5: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2011, 28, 2731–2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Wang, C.Y.; Lyu, Z.H.; Lin, T. Multiple glutathione S-transferase genes in Heortia vitessoides (Lepidoptera: Crambidae): Identification and expression patterns. J. Insect Sci. 2018, 18, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-ΔΔCT method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knorr, E.; Vilcinskas, A. Post-embryonic functions of HSP90 in Tribolium castaneum include the regulation of compound eye development. Dev. Genes Evol. 2011, 221, 357–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gai, Z.; Zhang, X.; Islam, M.; Wang, X.; Li, A.; Yang, Y.; Li, Y.; Peng, J.; Hong, H.; Liu, K. Characterization of Atg8 in lepidopteran insect cells. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 2013, 84, 57–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casati, B.; Terova, G.; Cattaneo, A.G.; Rimoldi, S.; Franzetti, E.; de Eguileor, M.; Tettamanti, G. Molecular cloning, characterization and expression analysis of ATG1 in the silkworm, Bombyx mori. Gene 2012, 511, 326–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malagoli, D.; Abdalla, F.C.; Cao, Y.; Feng, Q.; Fujisaki, K.; Gregorc, A.; Matsuo, T.; Nezis, I.P.; Papassideri, I.S.; Sass, M.; et al. Autophagy and its physiological relevance in arthropods: Current knowledge and perspectives. Autophagy 2010, 6, 575–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusten, T.E.; Lindmo, K.; Juhász, G.; Sass, M.; Seglen, P.O.; Brech, A.; Stenmark, H. Programmed autophagy in the Drosophila fat body is induced by ecdysone through regulation of the PI3K pathway. Dev. Cell 2004, 7, 179–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.S.; Takeda, M. Cloning of PaAtg8 and roles of autophagy in adaptation to starvation with respect to the fat body and midgut of the Americana cockroach, Periplaneta americana. Cell Tissue Res. 2014, 356, 405–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McPhee, C.K.; Baehrecke, E.H. Autophagy in Drosophila melanogaster. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2009, 1793, 1452–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryant, B.; Raikhel, A.S. Programmed autophagy in the fat body of Aedes aegypti is required to maintain egg maturation cycles. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e25502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, J.; Zhang, D.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, S.; Liu, Q. Identification of AaAtg8 as a marker of autophagy and a functional autophagy-related protein inAedes albopictus. Peer J. 2018, 6, e5988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tindwa, H.; Jo, Y.H.; Patnaik, B.B.; Noh, M.Y.; Kim, D.H.; Kim, I.; Han, Y.S.; Lee, Y.S.; Lee, B.L.; Kim, N.J. Depletion of autophagy-related genes ATG3 and ATG5 INTenebrio molitor leads to decreased survivability AGAINST an intracellular pathogen, Listeria monocytogenes. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 2015, 88, 85–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gottesman, M.M.; Ling, V. The molecular basis of multidrug resistance in cancer: the early years of P-glycoprotein research. FEBS Lett. 2006, 580, 998–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parthasarathy, R.; Palli, S.R. Developmental and hormonal regulation of midgut remodeling in a lepidopteran insect, Heliothis virescens. Mech. Dev. 2007, 124, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuervo, A.M. Autophagy: many paths to the same end. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2004, 263, 55–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tettamanti, G.; Grimaldi, A.; Pennacchio, F.; de Eguileor, M. Lepidopteran larval midgut during prepupal instar: Digestion or self-digestion? Autophagy 2007, 3, 630–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tindwa, H.; Jo, Y.H.; Patnaik, B.B.; Lee, Y.S.; Kang, S.S.; Han, Y.S. Molecular cloning and characterization of autophagy-related gene TmATG8 in Listeria-invaded hemocytes of Tenebrio molitor. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2015, 51, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogov, V.; Dötsch, V.; Johansen, T.; Kirkin, V. Interactions between autophagy receptors and ubiquitin-like proteins form the molecular basis for selective autophagy. Mol. Cell 2014, 53, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, B. The Role of ATG3 and ATG8 in Autophagy and Their Interaction in Bombyx mori; East China Normal University: Shanghai, China, 2016; p. 82. [Google Scholar]
- Li, K.; Guo, E.; Hossain, M.S.; Li, Q.; Cao, Y.; Tian, L.; Deng, X.; Li, S. Bombyx E75 isoforms display stage- and tissue-specific responses to 20-hydroxyecdysone. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 12114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thummel, C.S. Flies on steroids--Drosophila metamorphosis and the mechanisms of steroid hormone action. Trends Genet. 1996, 12, 306–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.Y.; Clough, E.A.; Yellon, P.; Teslovich, T.M.; Stephan, D.A.; Baehrecke, E.H. Genome-wide analyses of steroid- and radiation-triggered programmed cell death in Drosophila. Curr. Biol. 2003, 13, 350–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.; Liu, S.; Liu, H.; Li, S. 20-Hydroxyecdysone upregulates apoptotic genes and induces apoptosis in the Bombyx fat body. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 2012, 79, 207–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franzetti, E.; Huang, Z.J.; Shi, Y.X.; Xie, K.; Deng, X.J.; Li, J.P.; Li, Q.R.; Yang, W.Y.; Zeng, W.N.; Casartelli, M.; et al. Autophagy precedes apoptosis during the remodeling of silkworm larval midgut. Apoptosis 2012, 17, 305–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, K.; Tian, L.; Guo, X.; Li, K.; Li, J.; Deng, X.; Li, Q.; Xia, Q.; Zhong, Y.; Huang, Z.; et al. BmATG5 and BmATG6 mediate apoptosis following autophagy induced by 20-hydroxyecdysone or starvation. Autophagy 2016, 12, 381–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shelly, S.; Lukinova, N.; Bambina, S.; Berman, A.; Cherry, S. Autophagy is an essential component of Drosophila immunity against vesicular stomatitis virus. Immunity 2009, 30, 588–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicklin, P.; Bergman, P.; Zhang, B.; Triantafellow, E.; Wang, H.; Nyfeler, B.; Yang, H.; Hild, M.; Kung, C.; Wilson, C.; et al. Bidirectional transport of amino acids regulates mTOR and autophagy. Cell 2009, 136, 521–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarnowski, B.I.; Coons, L.B. Ultrastructure of the midgut and blood meal digestion in the adult tick Dermacentor variabilis. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 1989, 6, 263–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Z.; Lyu, Z.; Ye, Q.; Cheng, J.; Wang, C.; Lin, T. Cloning, Expression Analysis, 20-Hydroxyecdysone Induction, and RNA Interference Study of Autophagy-Related Gene 8 from Heortia vitessoides Moore. Insects 2020, 11, 245. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11040245
Li Z, Lyu Z, Ye Q, Cheng J, Wang C, Lin T. Cloning, Expression Analysis, 20-Hydroxyecdysone Induction, and RNA Interference Study of Autophagy-Related Gene 8 from Heortia vitessoides Moore. Insects. 2020; 11(4):245. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11040245
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Zhixing, Zihao Lyu, Qingya Ye, Jie Cheng, Chunyan Wang, and Tong Lin. 2020. "Cloning, Expression Analysis, 20-Hydroxyecdysone Induction, and RNA Interference Study of Autophagy-Related Gene 8 from Heortia vitessoides Moore" Insects 11, no. 4: 245. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11040245
APA StyleLi, Z., Lyu, Z., Ye, Q., Cheng, J., Wang, C., & Lin, T. (2020). Cloning, Expression Analysis, 20-Hydroxyecdysone Induction, and RNA Interference Study of Autophagy-Related Gene 8 from Heortia vitessoides Moore. Insects, 11(4), 245. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11040245




