Friction Energy-Based Wear Simulation for Radial Shaft Sealing Ring
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. RSSR Tribological System and Half-Space Theory
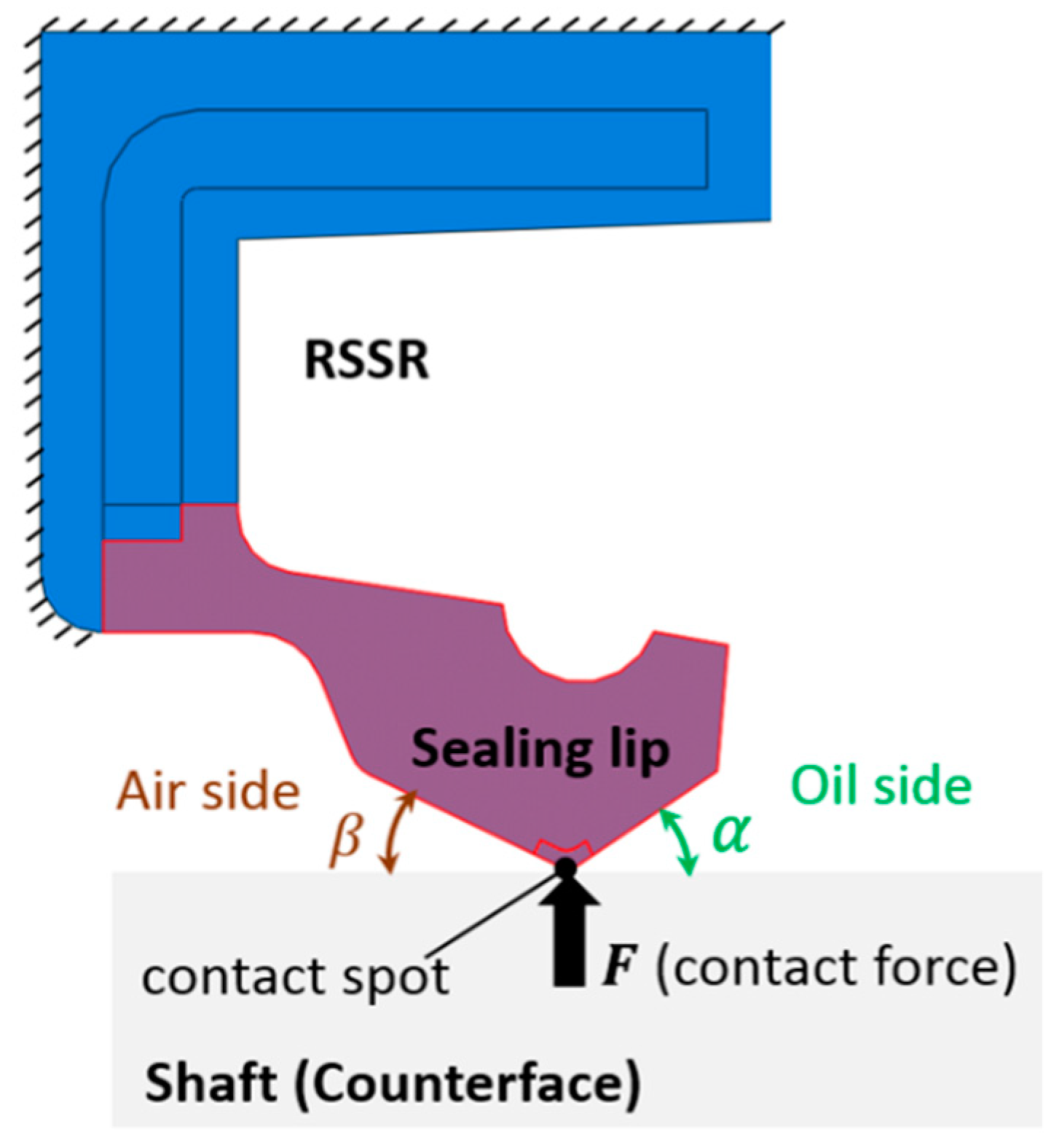
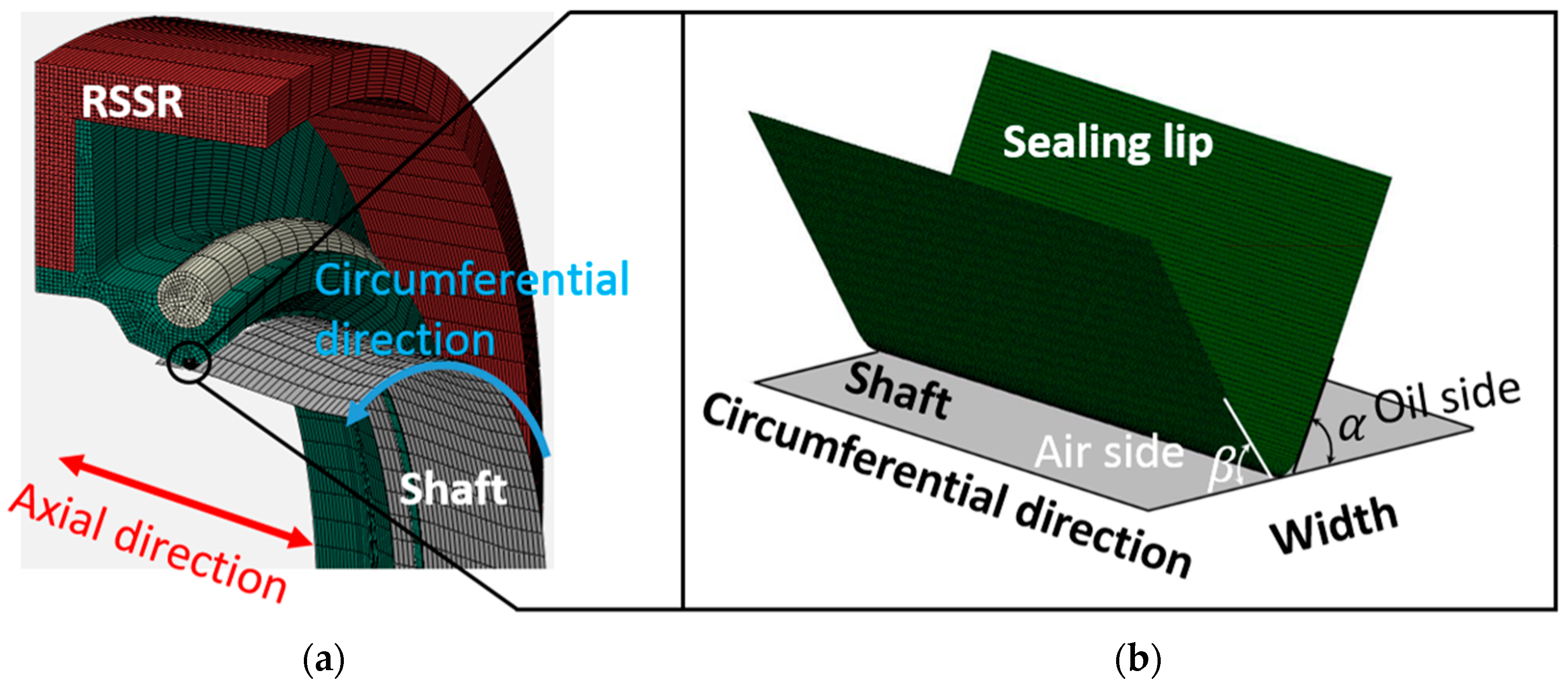
2.1. RSSR Tribological System
2.2. Half-Space Theory and Its Applicabiliy to RSSR Contact Problem
- Extremely small contact dimensions compared to body dimensions,
- A linear elastic behavior of the contact bodies, and
- No structural deformation influence on the contact problem.
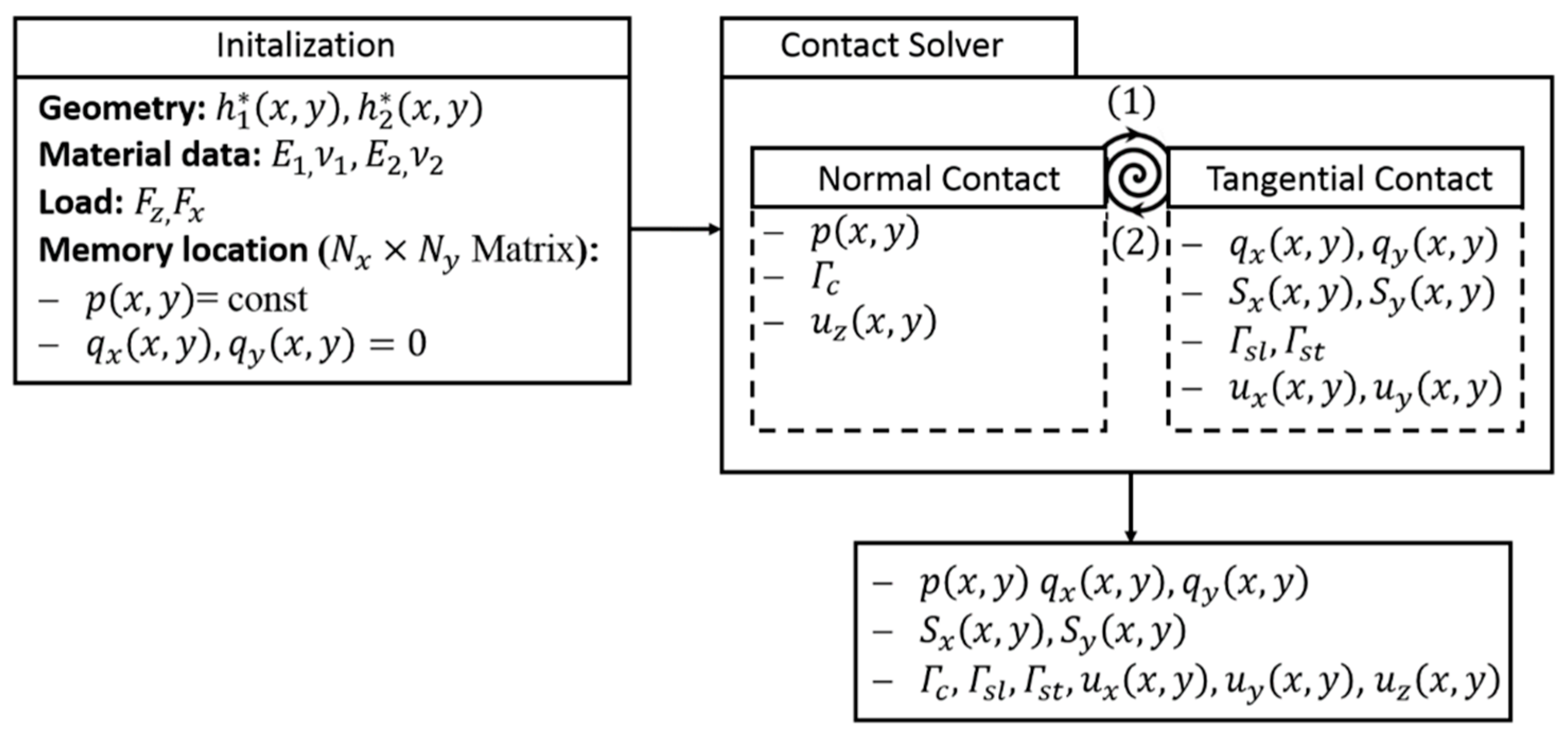
3. Semi-Analytical Frictional Contact Modelling of RSSR
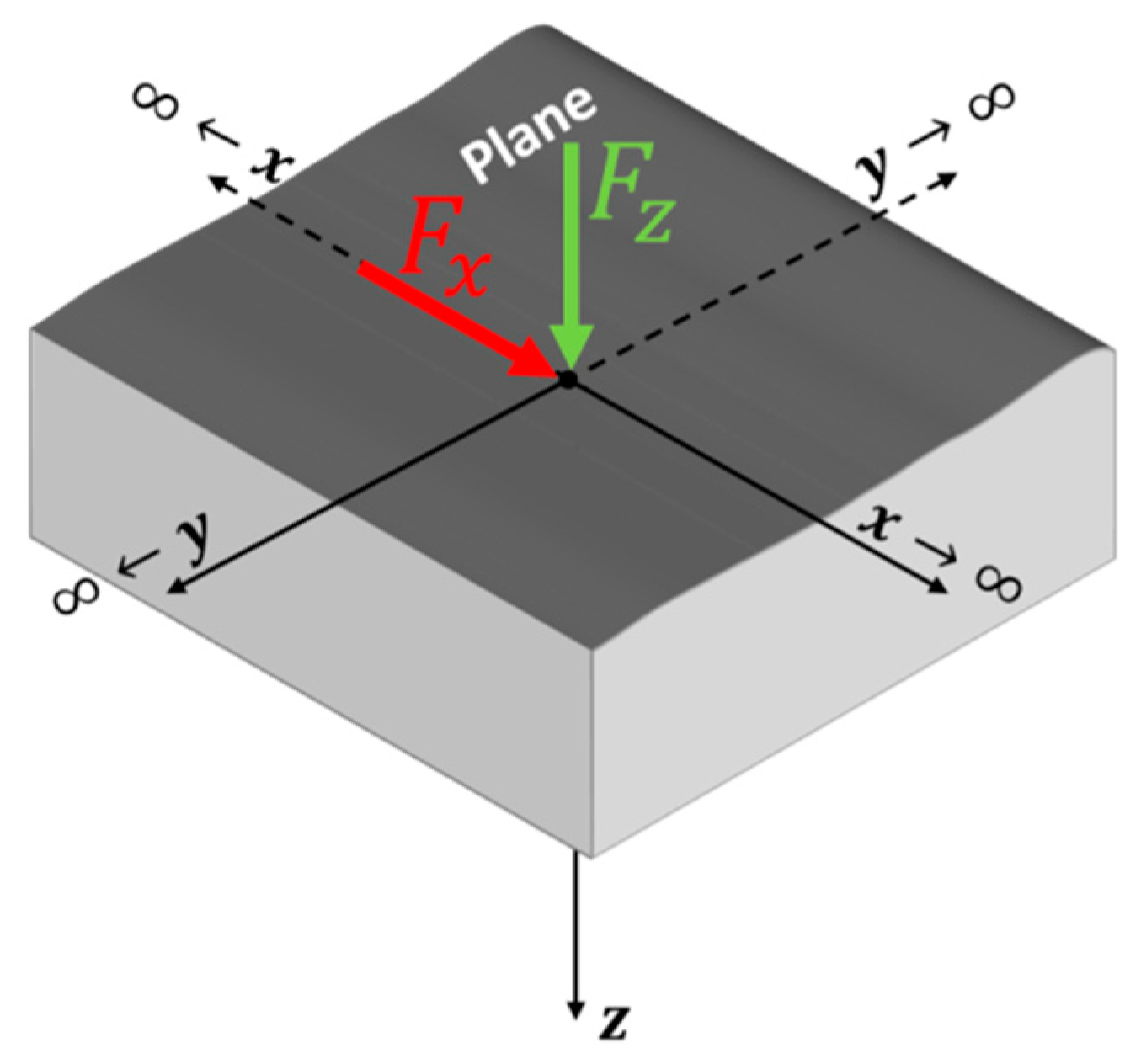
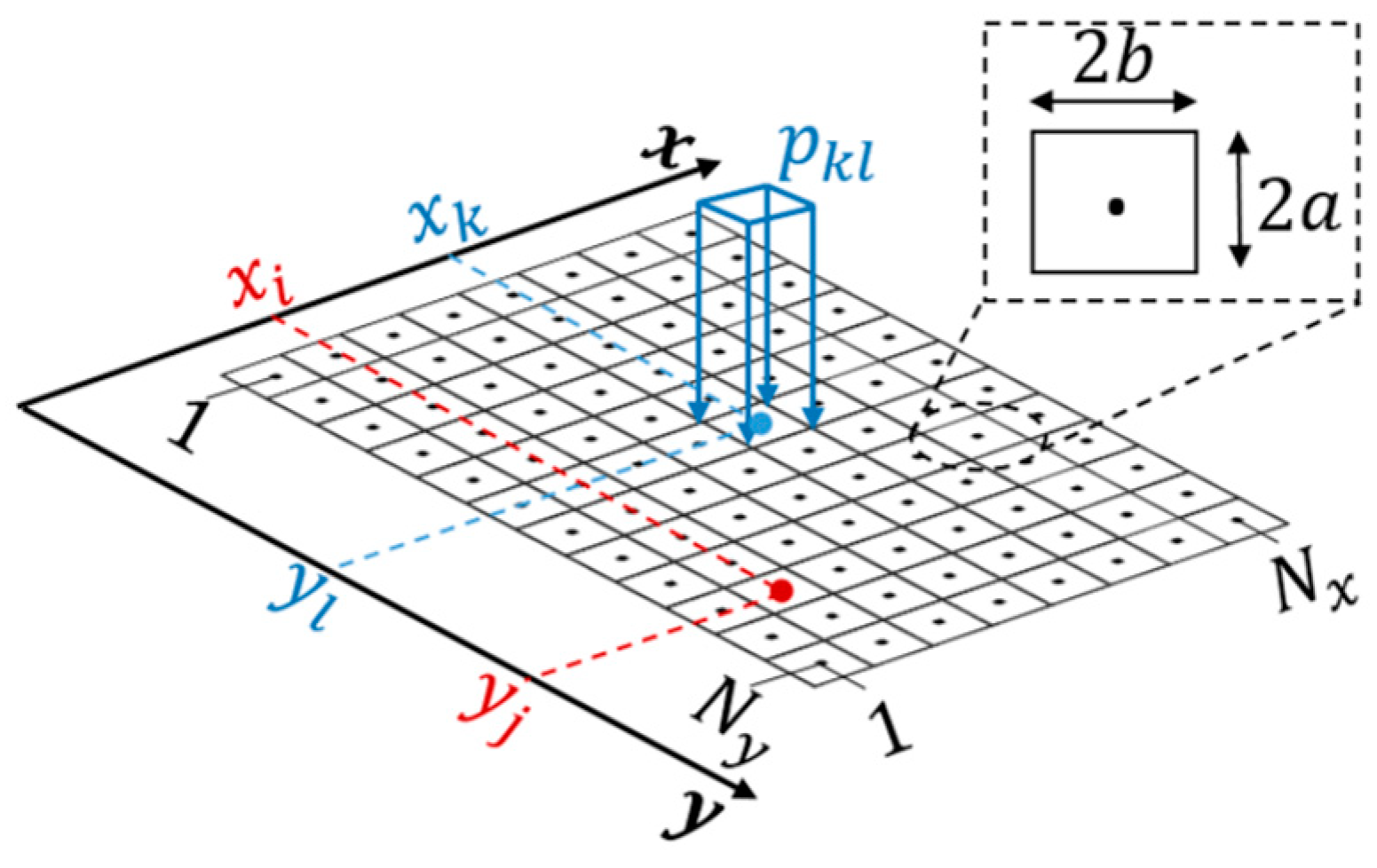
3.1. Fundamental Solution on the Half Space for RSSR Contact Problem
3.2. Material Parameters and Contact Surface Geometry for the Simulation
3.3. Contact Conditions and Itterative Solution Scheme
- : Normal force (radial force on sealing lip)
- : Surface profile heights of bodies 1 and 2
- : Body displacement of bodies 1 and 2 in normal direction, and
- : Centers of gravity of bodies 1 and 2,
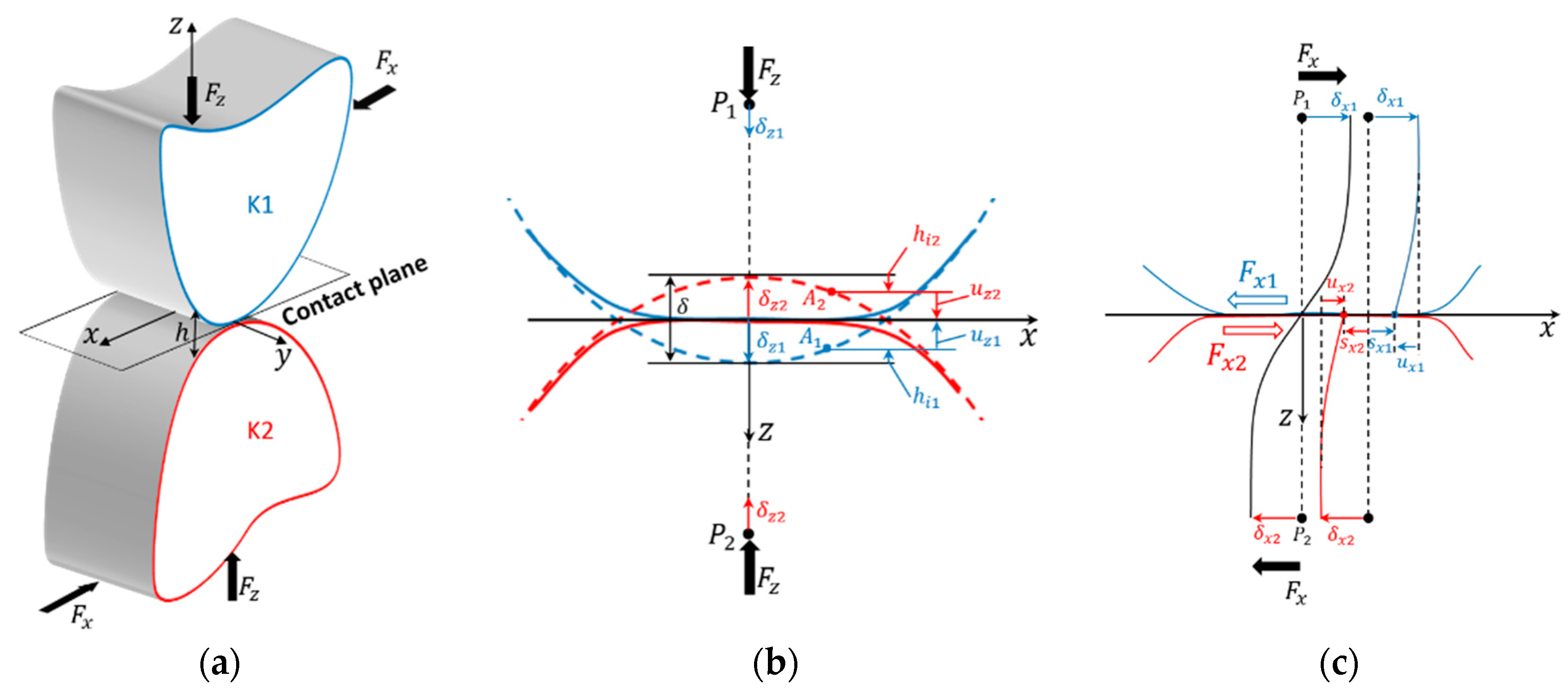
- The equilibrium. It forms an equivalent relationship between the externally applied normal force and the normal pressures to be determined in the contact region :
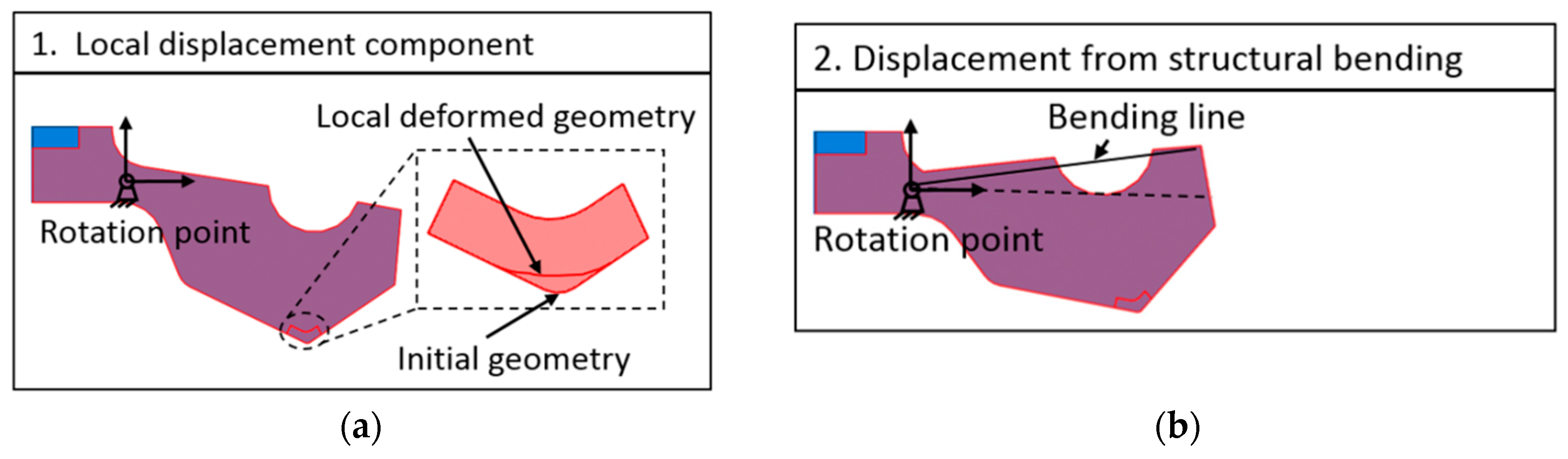
- The gap equation. This equation describes the change of the contact gap (distance between the contact bodies). Two cases are shown in Figure 9b to explain the gap equation. In the first case, the two contact bodies, K1 and K2, were considered as rigid bodies. Thus, their surface profiles remained undeformed (see dotted lines). Here, the centers of gravity under the contact force made the body displacements . As help geometry, tangent lines were formed as reference lines in the deepest profile points. In the second case, the two bodies were represented in a deformed state (see strong lines). At the origin (), the vertical distances from the contact point to the reference lines described the body displacements mentioned in the first case. The gap at any contact point pair was described by the initial profile height (point distances to the respective reference lines in the nondeformed state) and the displacements (distance changes from the nondeformed to the deformed state) as follows:
- The complementarity condition. This condition arises due to the impenetrability of the contact bodies. It links the contact gap Equation (21) and the contact pressure Equation (20) as follows:
- : Tangential force (friction force on sealing lip),
- : Action-reaction forces on bodies 1 and 2,
- : Surface displacement of bodies 1 and 2,
- : Body displacement of bodies 1 and 2, and
- : Centers of gravity of bodies 1 and 2.
- The contact region: ,
- The sliding and adhesion zone: , with ,
- Normal pressure: ,
- Shear stresses: ,
- Surface displacements: ,
- Body displacements: , and
- Sliding paths: , .
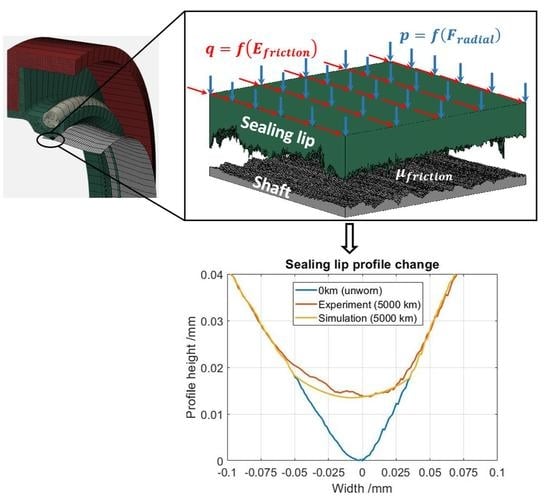
4. Wear Calculation
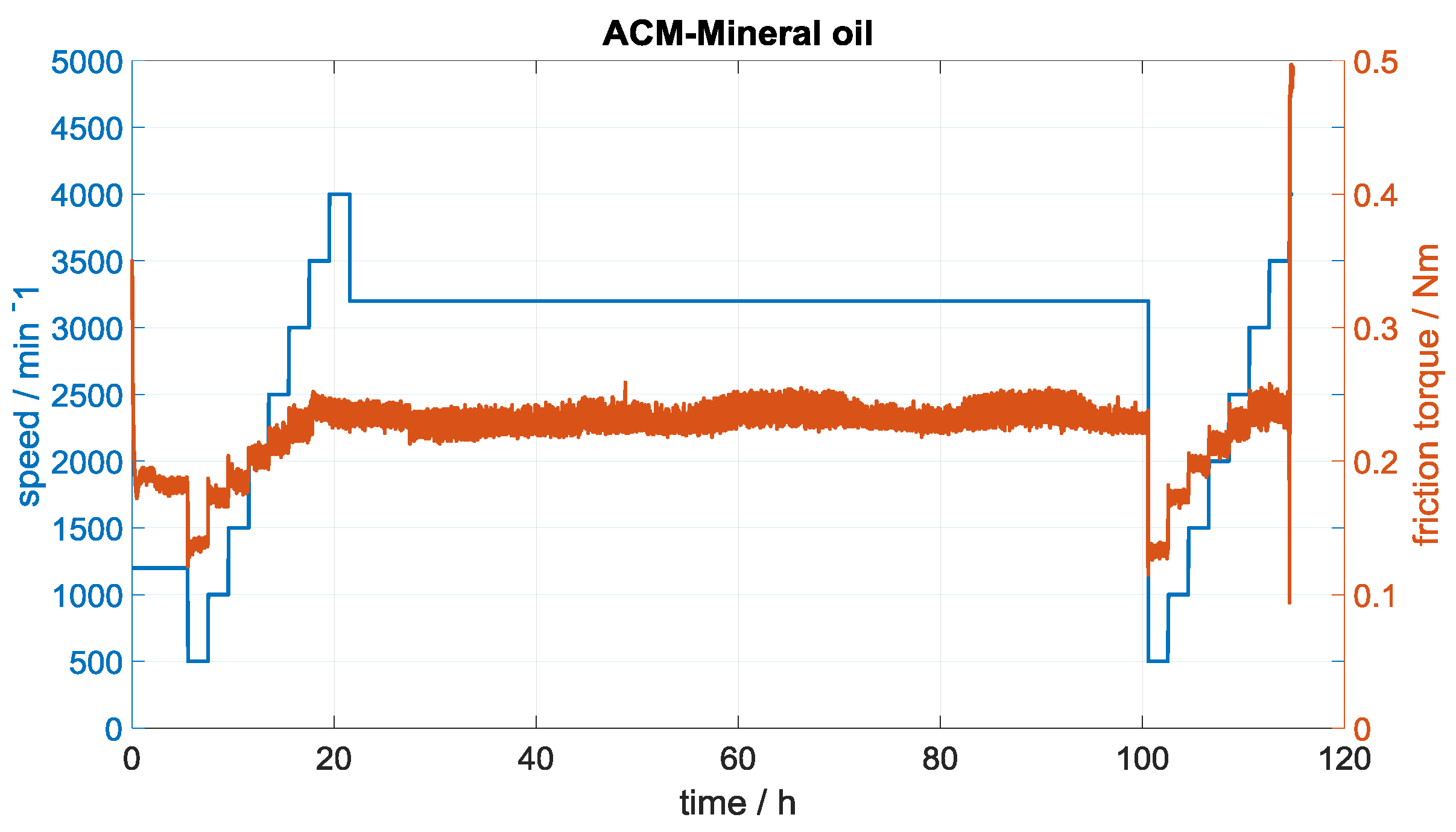
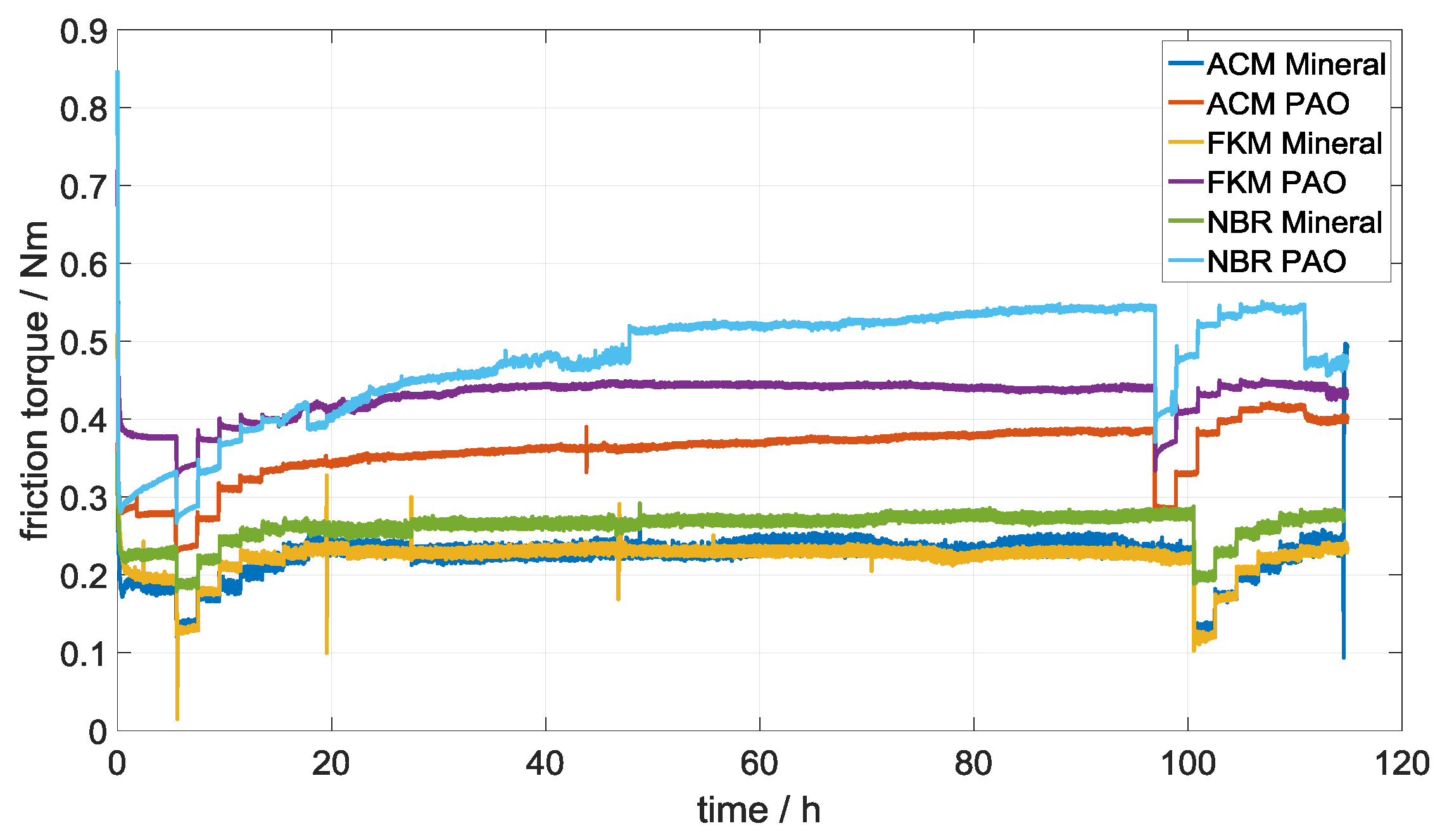
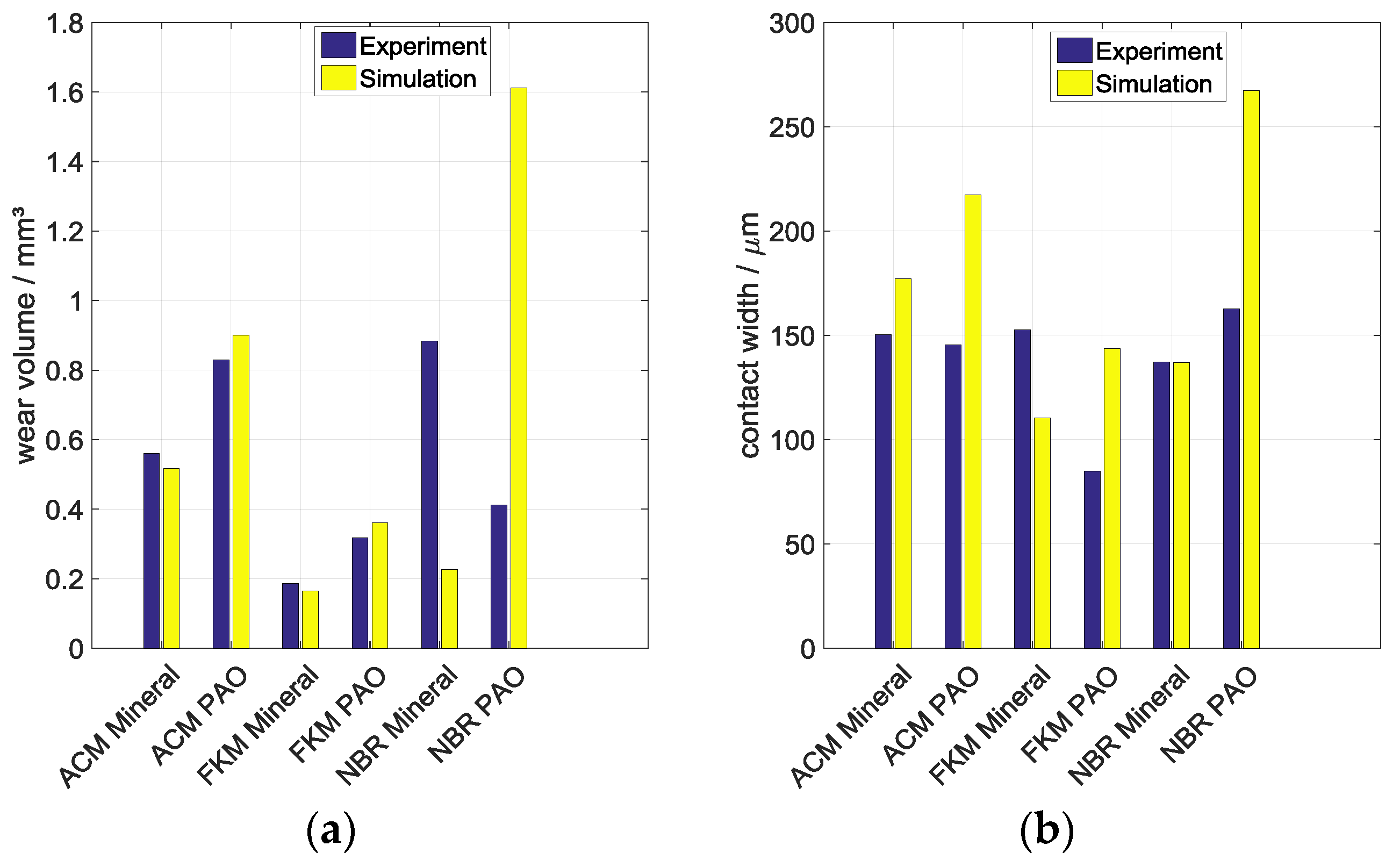
5. Experimental Determination of the Friction Work
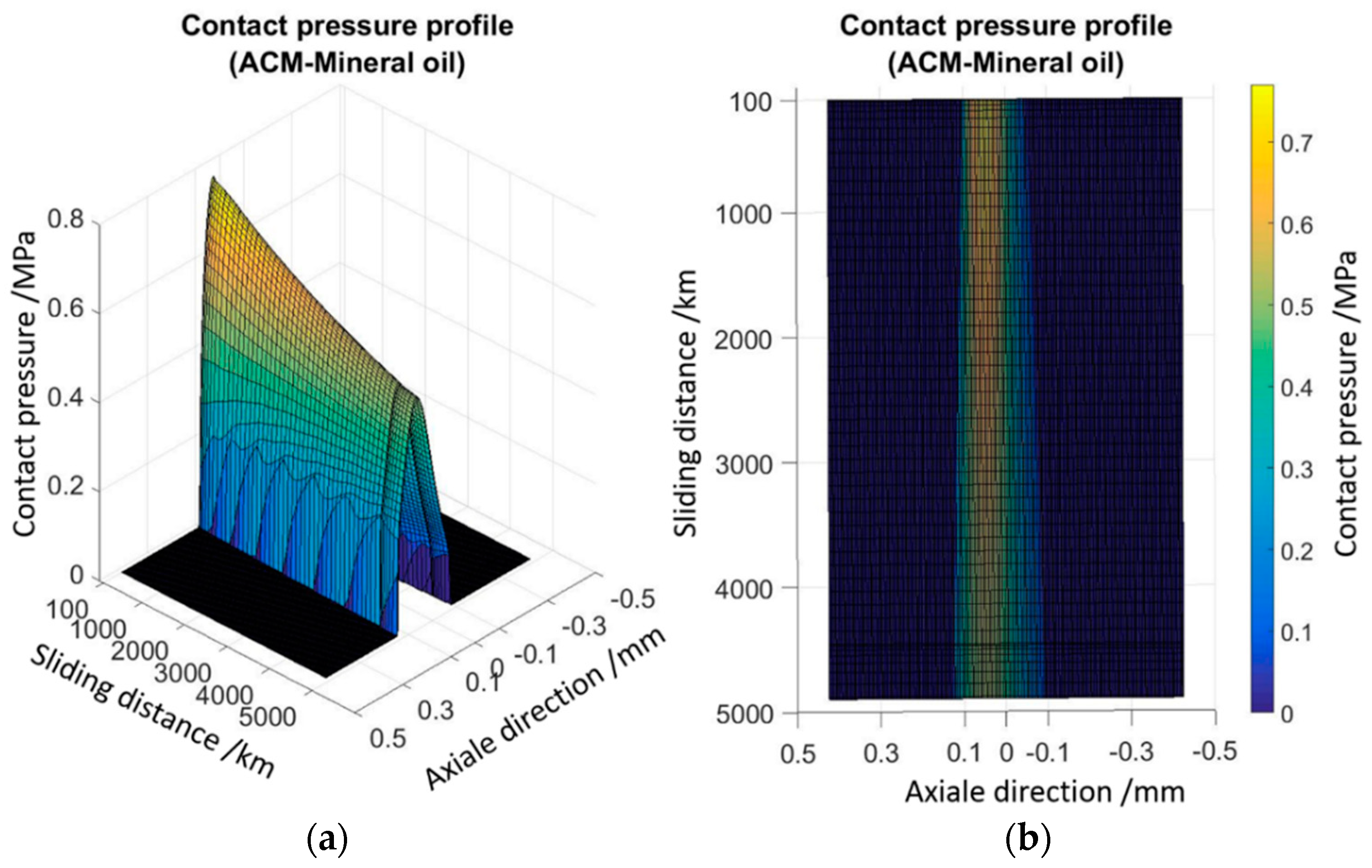
6. Simulation Results
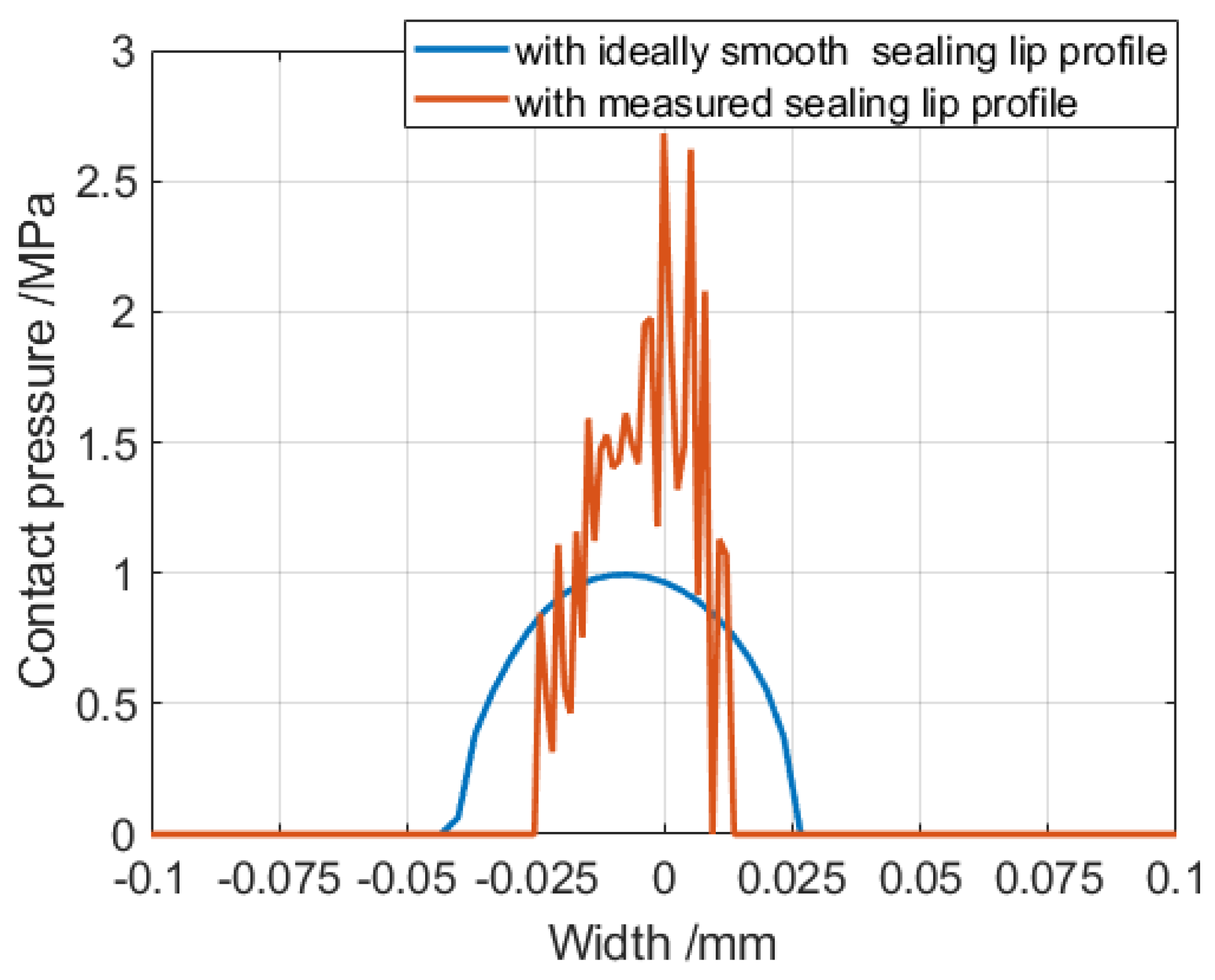
6.1. Simulation Results with Ideally Smooth Sealing Lip Profile
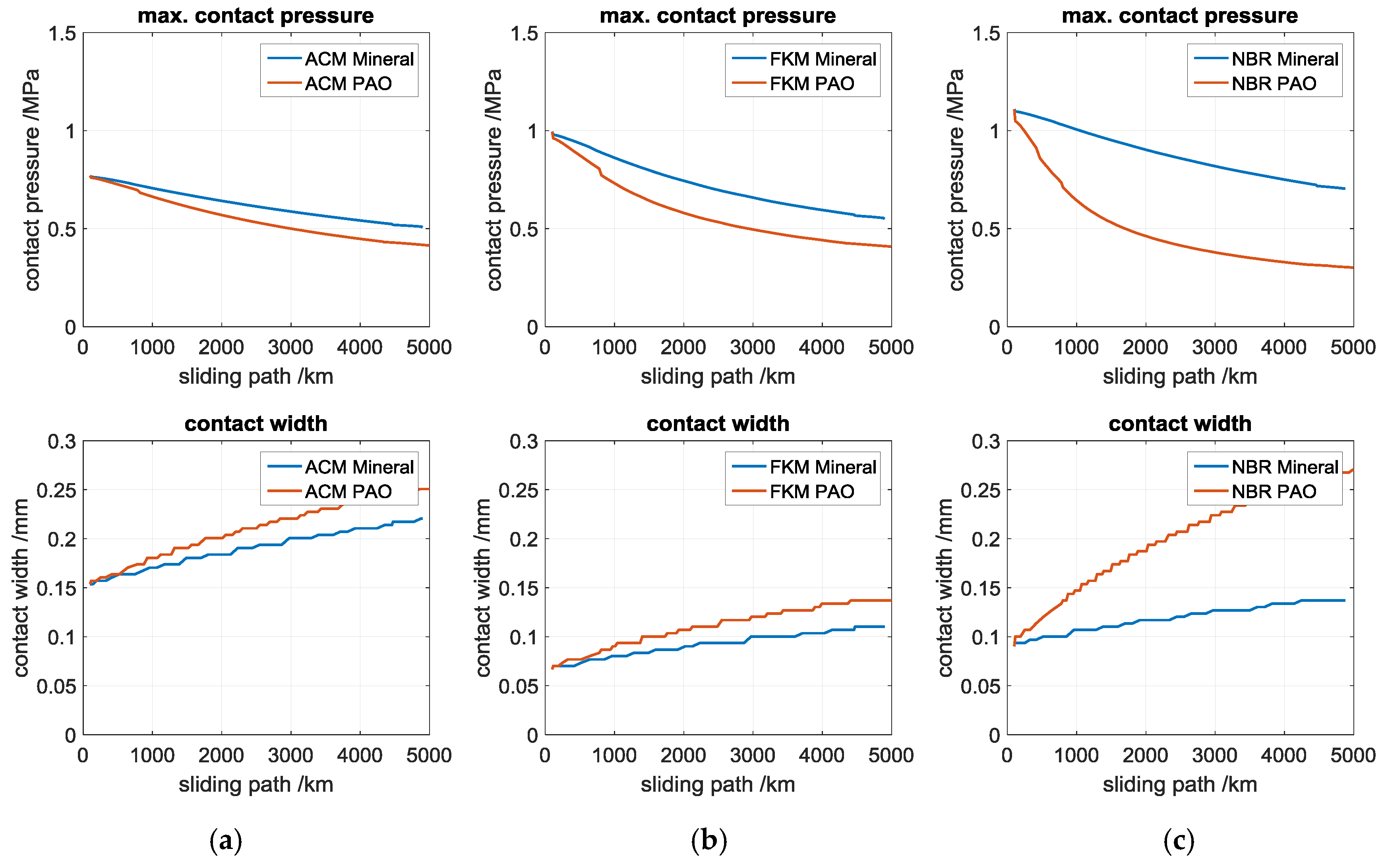
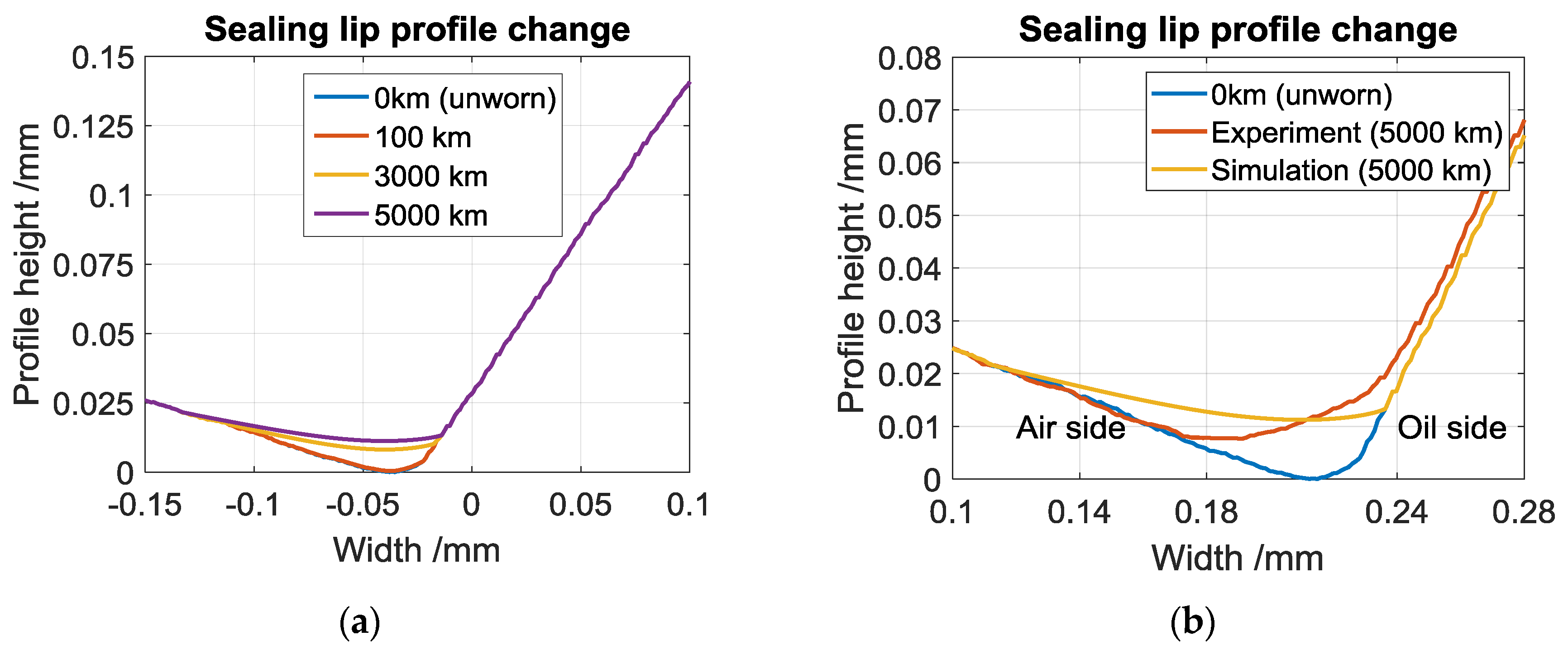
6.2. Simulation Results with Mesured Sealing Lip Profile for FKM-Mineral Oil Combination
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| Discretization and indices | |
| Spatial directions; position of a discretization point on the surface | |
| , : | Number of discretization points in X- and Y- spatial direction |
| contact calculation | |
| , ,; | Contact forces in normal direction (Z) and tangential directions (x,y) |
| ,…,; ,…, | displacement influence coefficients of the local and structural deformations |
| ,,; ,, | Normal and tangential contact pressure; surface displacements |
| ,,;,;, | contact area, sliding zone, adhesion zone; sliding paths in x- and y- direction; body displacement in x-, y- and z- direction |
| wear parameters | |
| , ;, | Wear coefficient according to Archard, Fleischer; wear volume, wear increment height; friction energy density; friction work in x- and y- direction |
References
- Foko, F.F.; Heimes, J.; Magyar, B.; Sauer, B. Reibenergiebasierte Verschleißsimulation für Radialwellendichtringe; Conference Paper; GfT-Tagung: Göttingen, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Polonsky, I.A.; Keer, L.M. A numerical method for solving rough contact problems based on the multi-level multi-summation and conjugate gradient techniques. Wear 1999, 231, 206–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magyar, B.; Sauer, B. Methods for the simulation of the pressure, stress, and temperature distribution in the contact of fractal generated rough surfaces. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part J J. Eng. Tribol. 2017, 231, 489–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallego, L.; Nelias, D.; Deyber, S. A fast and efficient contact algorithm for fretting problems applied to fretting modes I, II and III. Wear 2010, 268, 208–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willner, K. Fully Coupled Frictional Contact Using Elastic Halfspace Theory. J. Tribol. 2008, 130, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacq, C.; Nelias, D.; Lormand, G.; Girodin, D. Development of a Three-Dimensional Semi-Analytical Elastic-Plastic Contact Code. J. Tribol. 2002, 124, 653–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Q.J. Analytical frequency response functions for contact of multilayered materials. Mech. Mater. 2014, 76, 102–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Jin, X.; Zhou, Q.; Ai, X.; Keer, L.M.; Wang, Q. An Efficient Numerical Method with a Parallel Computational Strategy for Solving Arbitrarily Shaped Inclusions in Elastoplastic Contact Problems. J. Tribol. 2013, 135, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.J.; Wang, W.Z. Partial Slip Contact Analysis on Three-Dimensional Elastic Layered Half Space. J. Tribol. 2010, 132, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.-J.; Wang, W.-Z.; Meng, F.-M.; Wang, J.-X. Fretting Contact Analysis on Three-Dimensional Elastic Layered Half Space. J. Tribol. 2010, 133, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, K.L. Contact Mechanics; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Gallego, L. Fretting et Usure des Contacts Mécaniques: Modélisation Numérique. Ph.D. Thesis, L’Institut National des Sciences Appliquées de Lyon, Villeurbanne, France, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Schallamach, A. Friction and Abrasion of Rubber. Wear 1958, 1, 384–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debler, C. Bestimmung und Vorhersage des Verschleißes für die Auslegung von Dichtungen. Ph.D. Thesis, Universität Hannover, Hannover, Germany, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Hegadekatte, V.; Kurzenhäuser, S.; Huber, N.; Kraft, O. A predictive modelling scheme for wear in tribometers. Tribol. Int. 2008, 41, 1020–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Békési, N.; Váradi, K. Wear simulation of a reciprocating seal by global remeshing. Period. Polytech. Mech. Eng. 2010, 54, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frölich, D. Strategien und Modelle zur Simulation des Betriebsverhaltens von Radialwellendichtringen. Ph.D. Thesis, Universität Kaiserslautern, Kaiserslautern, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Jennewein, B. Integrierter Berechnungsansatz zur Prognose des Dynamischen Betriebsverhaltens von Radialwellendichtringen. Ph.D. Thesis, Universität Kaiserslautern, Kaiserslautern, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Engelke, T. Einfluss der Elastomer-Schmierstoff-Kombination auf das Betriebsverhalten von Radialwellendichtringen. Ph.D. Thesis, Leibniz Universität Hannover, Hannover, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Thielen, S. Entwicklung eines TEHD-Tribosimulationsmodells für Radialwellendichtringe. Ph.D. Thesis, Universität Kaiserslautern, Kaiserslautern, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Gross, D.; Becker, W. Mechanik Elastischer Körper und Strukturen; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Hauer, F. Die Elasto-Plastische Einglättung Rauer Oberflächen und ihr Einfluss auf die Reibung in der Umformtechnik. Ph.D. Thesis, Technischen Fakultät der Universität Erlangen-Nürnberg, Erlangen, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Teixeira Alves, J.; Guingand, M.D.E.; Vaujany, J.P. Set of functions for the calculation of bending displacements for spiral bevel gear teeth. Mech. Mach. Theory 2010, 45, 349–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira Alves, J. Définition Analytique des Surfaces de Denture et Comportement Sous Charge des Engrenages Spiro-Coniques. Ph.D. Thesis, L’Institut National des Sciences Appliquées de Lyon, Villeurbanne, France, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Archard, J.F. Wear theory and mechanisms. In Wear Control Handbook; Peterson, M.B., Winer, W.O., Eds.; ASME: New York, NY, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Fleischer, G. Energetische Methode zur Bestimmung des Verschleißes. Schmierungstechnik 1973, 4, 269–274. [Google Scholar]
- Kaiser, C. Entwicklung Einer Prüfmethodik für Modelluntersuchungen an Schmutzbeaufschlagten Radial-Wellendichtringen. Ph.D. Thesis, Universität Kaiserslautern, Kaiserslautern, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar]




| Contact Partner No. | Radius (mm) | Modulus of Elasticity (MPa) | Poisson’s Ratio (-) |
|---|---|---|---|
| No.1(Shaft) | 40 | 210 | 0.3 |
| No.2 (ACM-Elastomer) | 1.93 | 0.49 | |
| No.2 (FKM-Elastomer) | 4.42 | 0.49 | |
| No.2 (NBR-Elastomer) | 3.83 | 0.49 |
| Exp No | Elastomer-Lubricant-Combination | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ACM-Mineral Oil | 19.022 | 10.68 | 5.3445 × 1010 |
| 2 | ACM-PAO | 19.022 | 12.33 | 4.9256 × 1010 |
| 3 | FKM-Mineral Oil | 12.723 | 9.58 | 1.6791 × 1011 |
| 4 | FKM-PAO | 12.723 | 9.27 | 1.4806 × 1011 |
| 5 | NBR-Mineral Oil | 18.57 | 10.68 | 3.6394 × 1010 |
| 6 | NBR-PAO | 18.57 | 11.93 | 1.4230 × 1011 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Foko Foko, F.; Heimes, J.; Magyar, B.; Sauer, B. Friction Energy-Based Wear Simulation for Radial Shaft Sealing Ring. Lubricants 2020, 8, 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants8020015
Foko Foko F, Heimes J, Magyar B, Sauer B. Friction Energy-Based Wear Simulation for Radial Shaft Sealing Ring. Lubricants. 2020; 8(2):15. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants8020015
Chicago/Turabian StyleFoko Foko, Flavien, Julia Heimes, Balázs Magyar, and Bernd Sauer. 2020. "Friction Energy-Based Wear Simulation for Radial Shaft Sealing Ring" Lubricants 8, no. 2: 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants8020015
APA StyleFoko Foko, F., Heimes, J., Magyar, B., & Sauer, B. (2020). Friction Energy-Based Wear Simulation for Radial Shaft Sealing Ring. Lubricants, 8(2), 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants8020015