An Experimental Study on Starved Grease Lubricated Contacts
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods and Materials
2.1. Tested Greases
2.2. Measurement Procedure
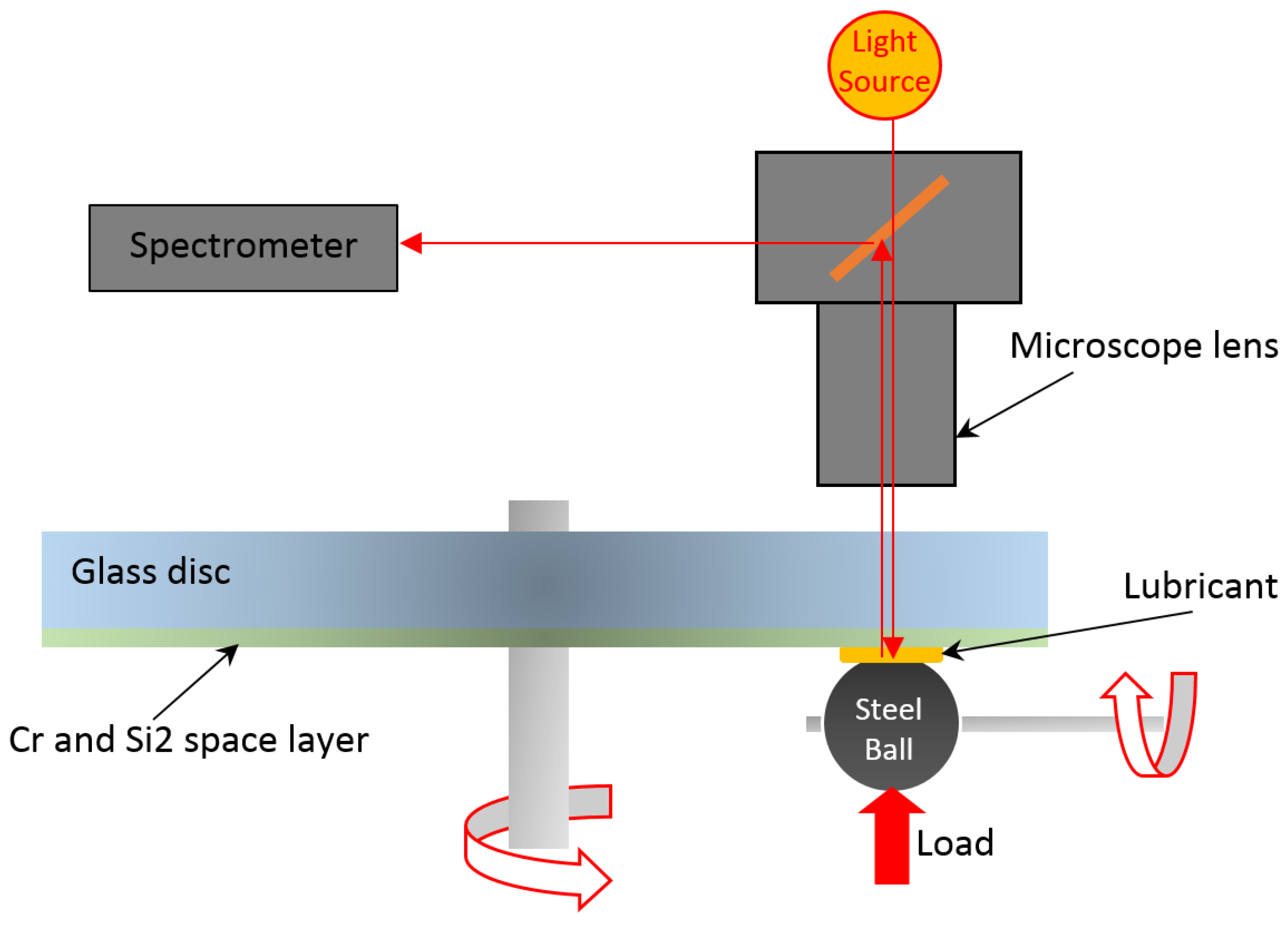
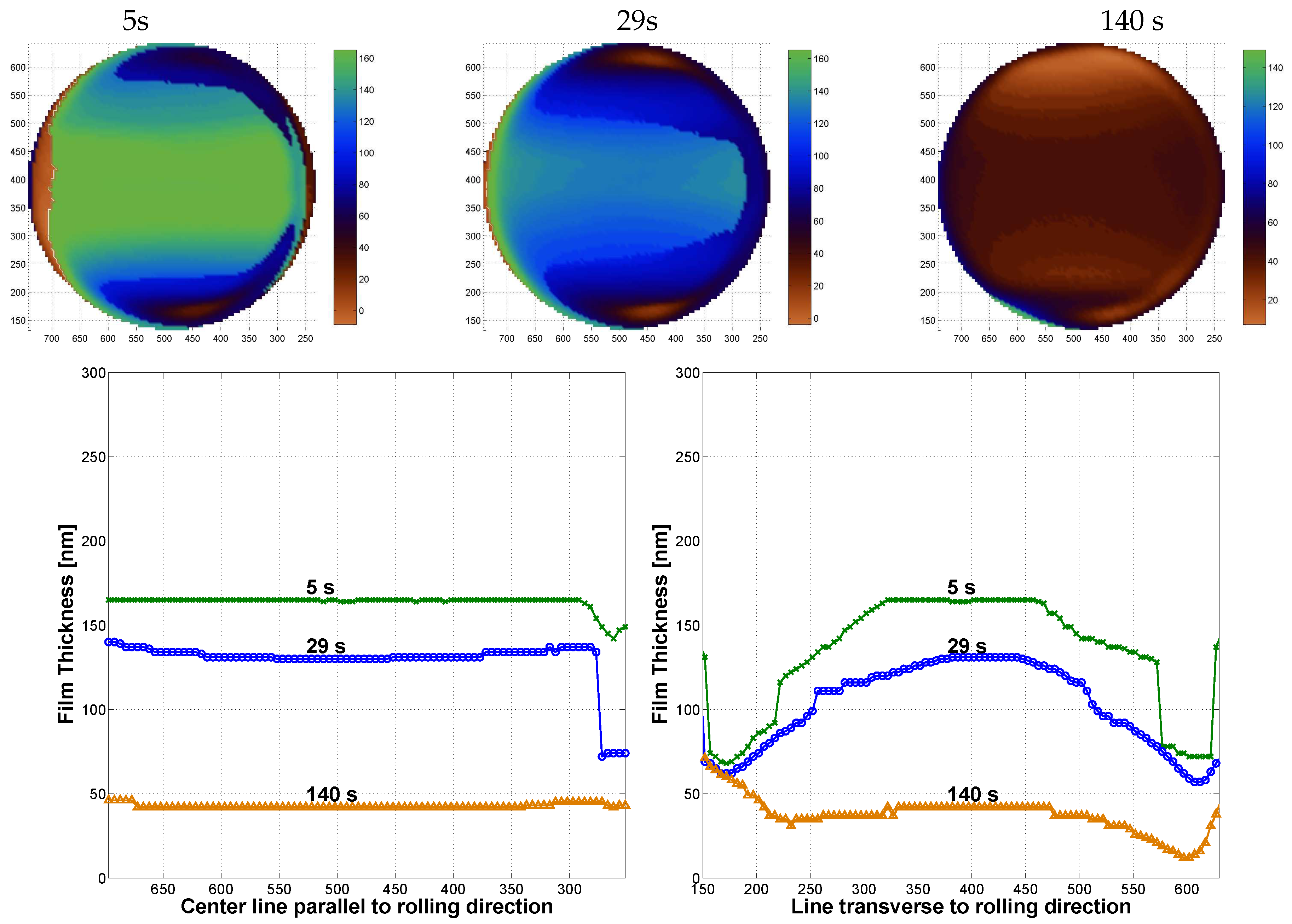
2.2.1. Film Thickness
- (1)
- Central film thickness, varying the entrainment speed;
- (2)
- Central film thickness, measured over time;
- (3)
- Film thickness profile pictures across the contact area, measured over time.
2.2.2. Coefficient of Friction
3. Results and Discussion
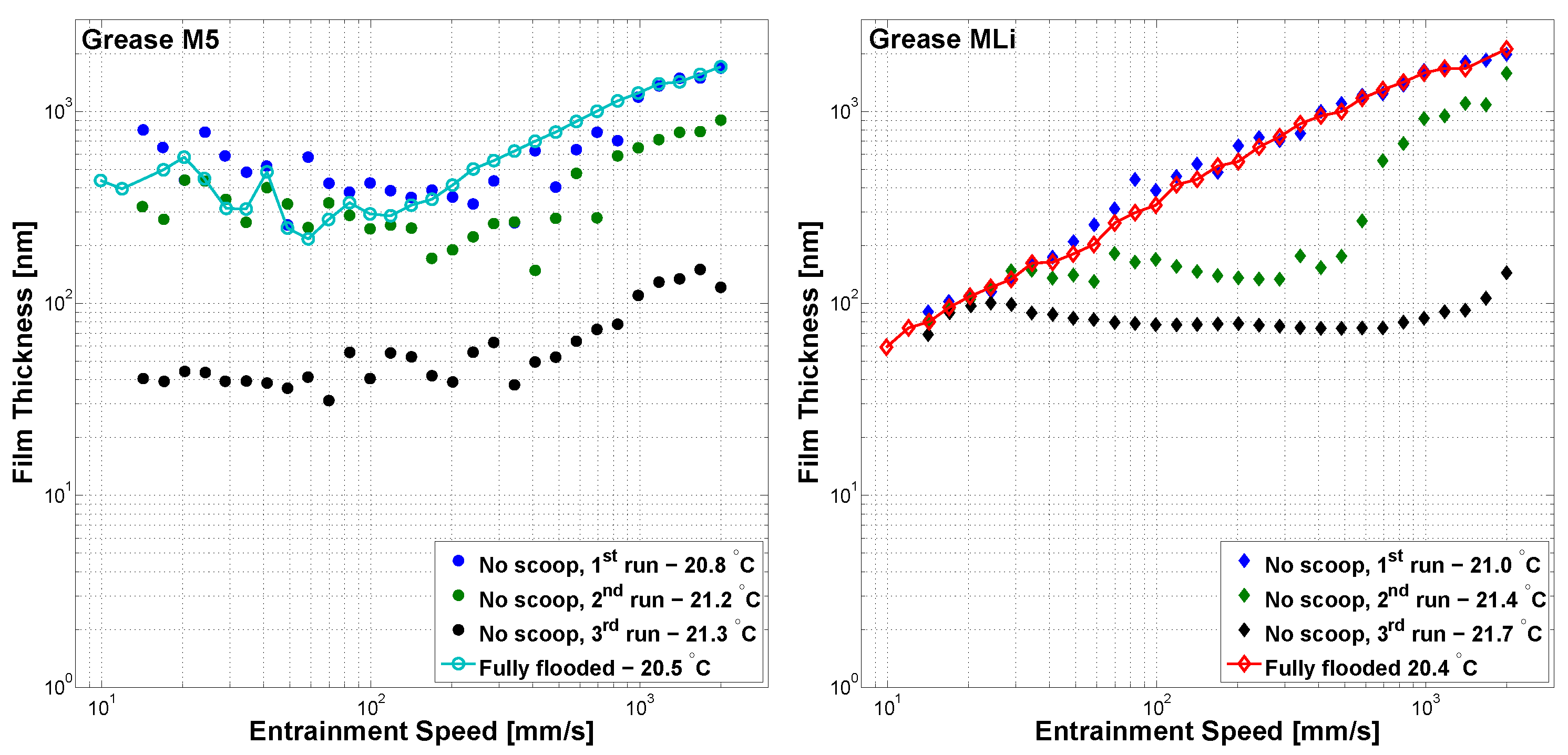
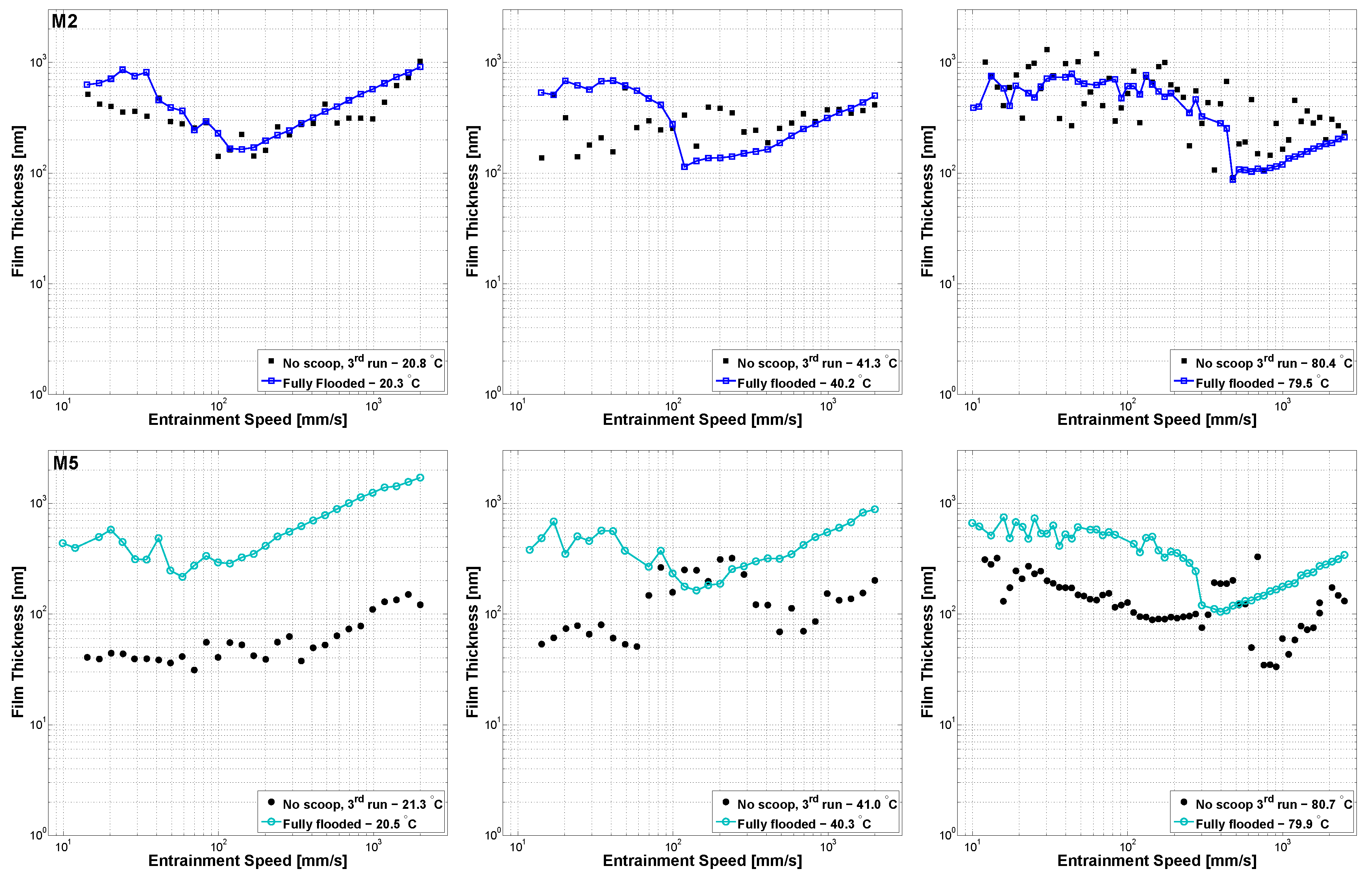
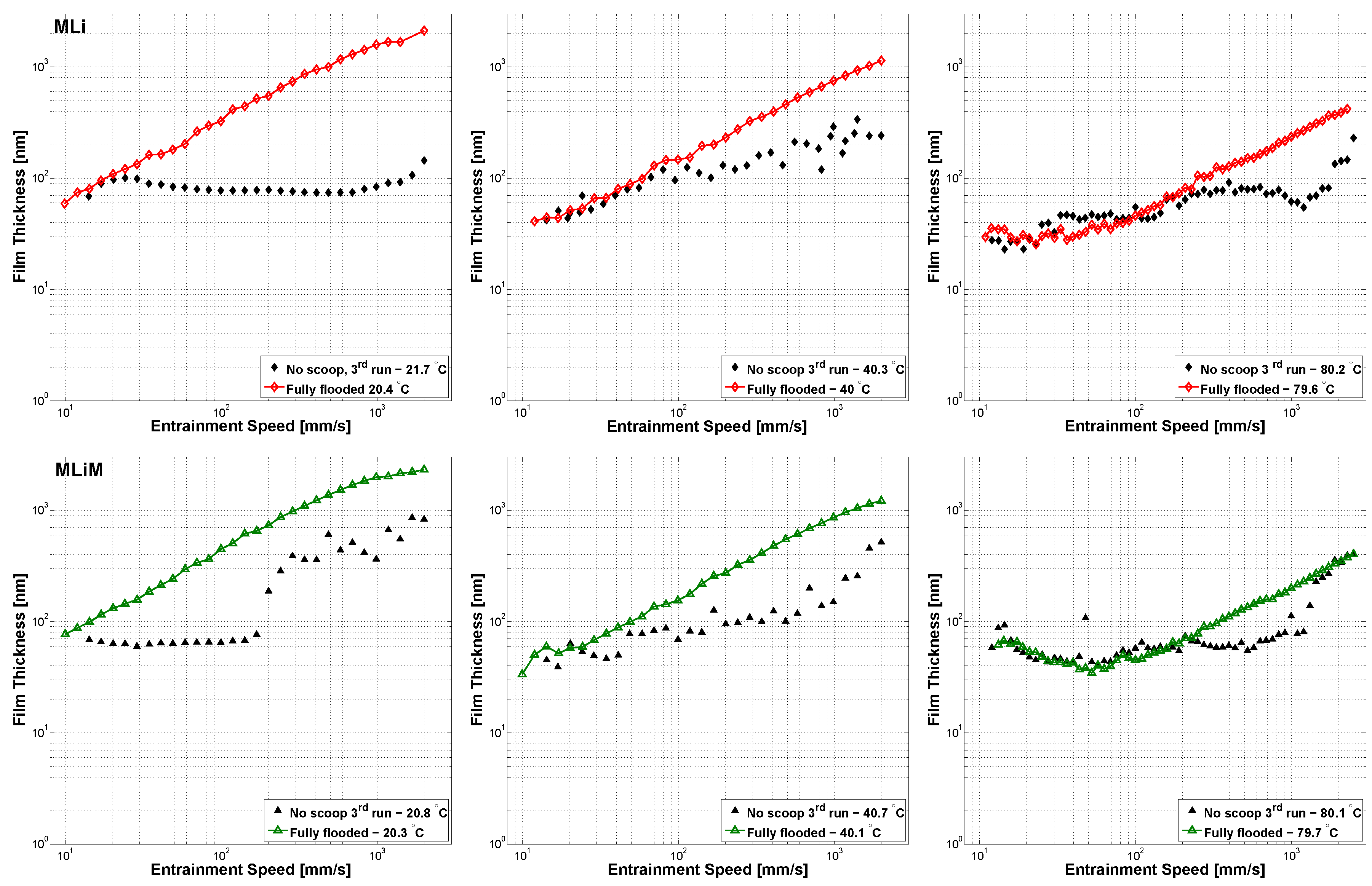
3.1. Central Film Thickness Measured With Varying Entrainment Speed
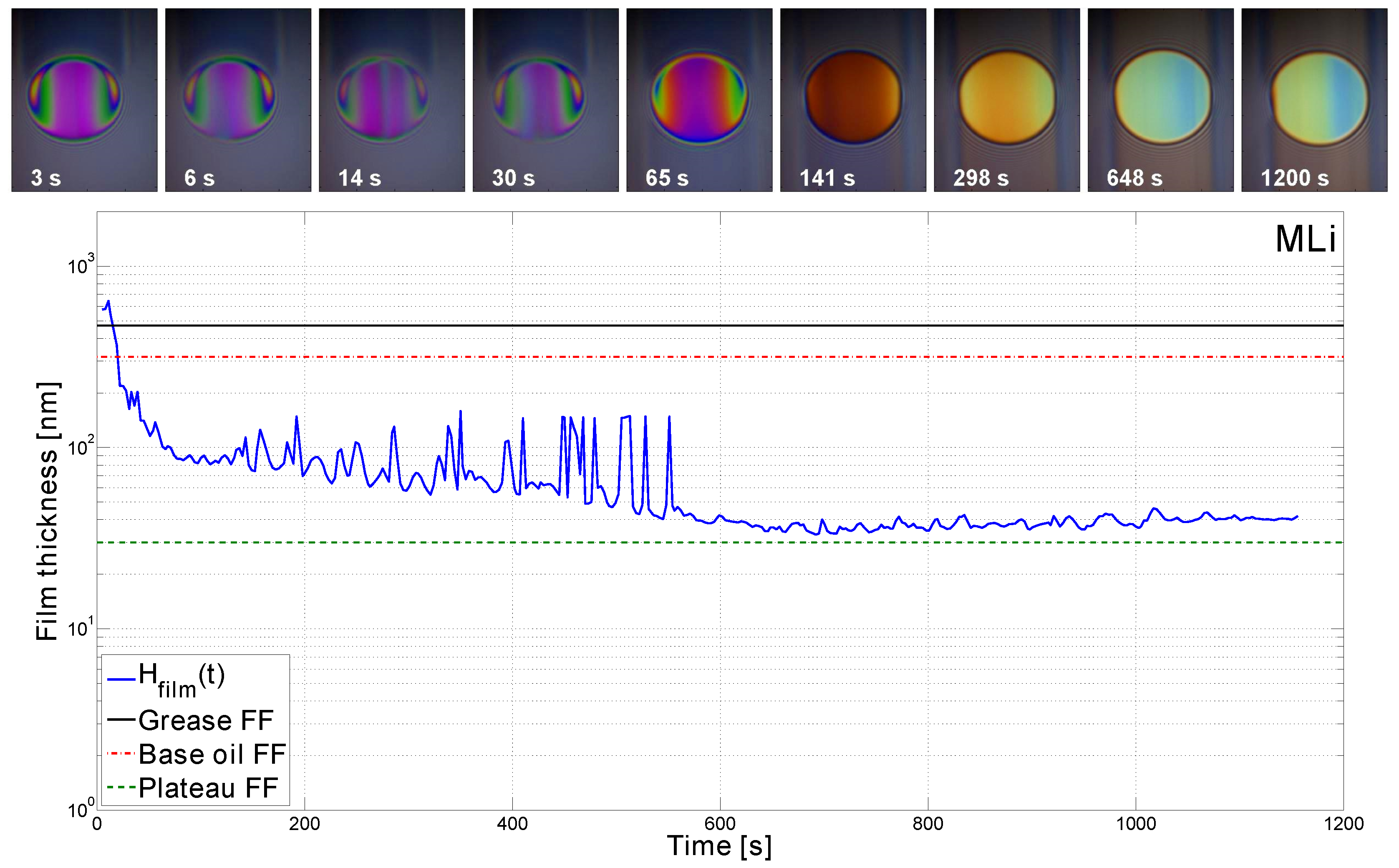
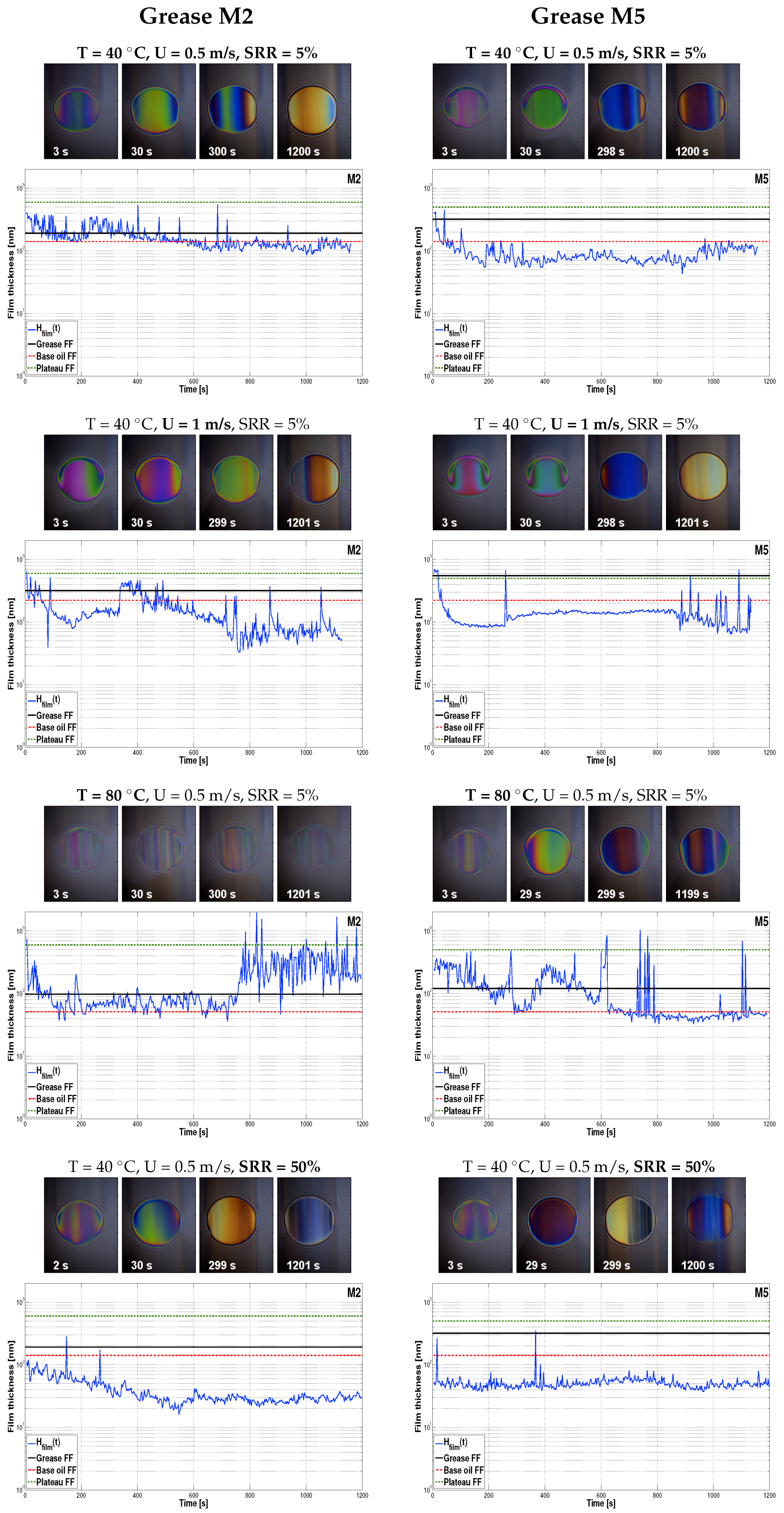
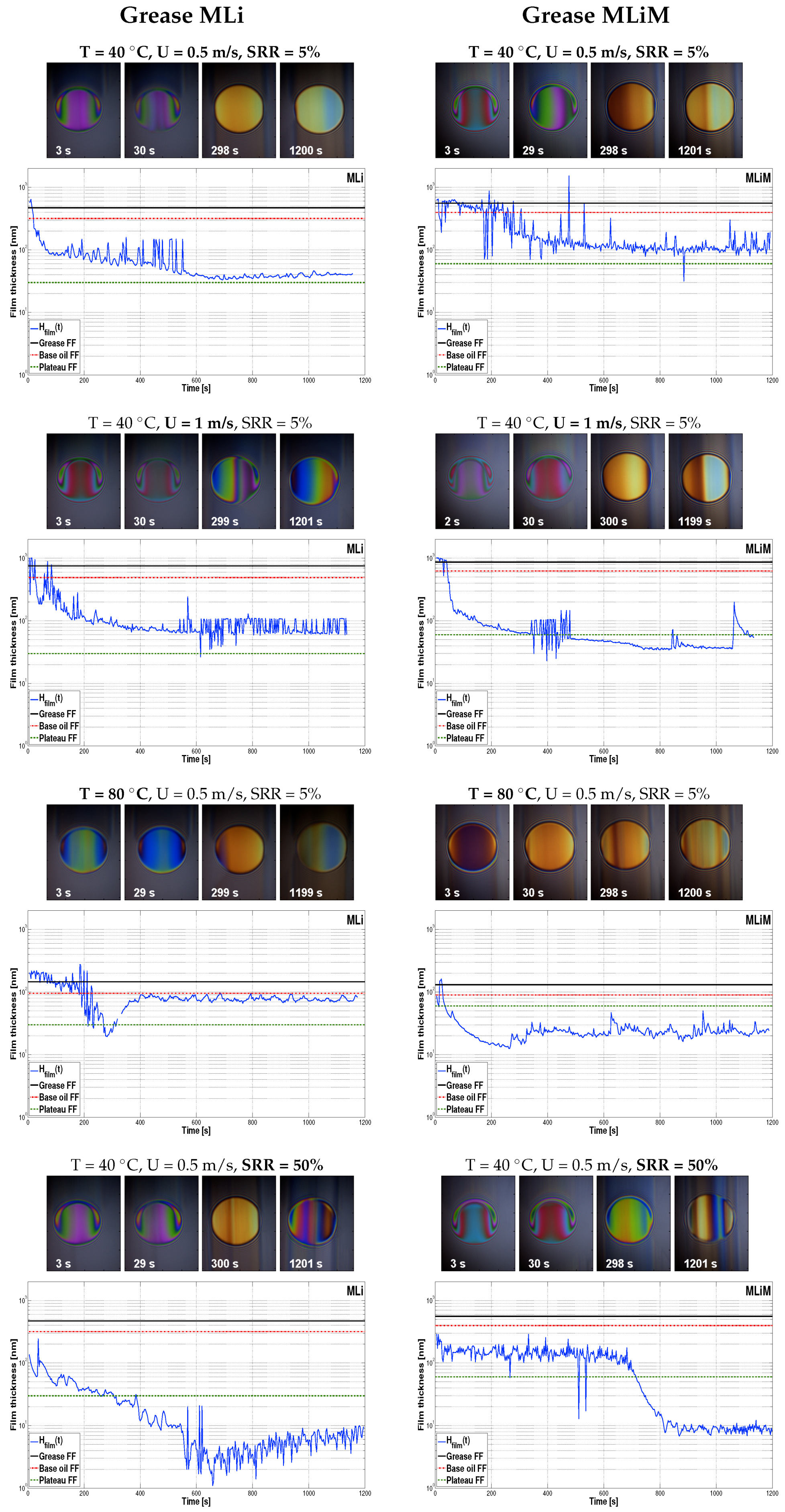
3.2. Central Film Thickness Measured over Time
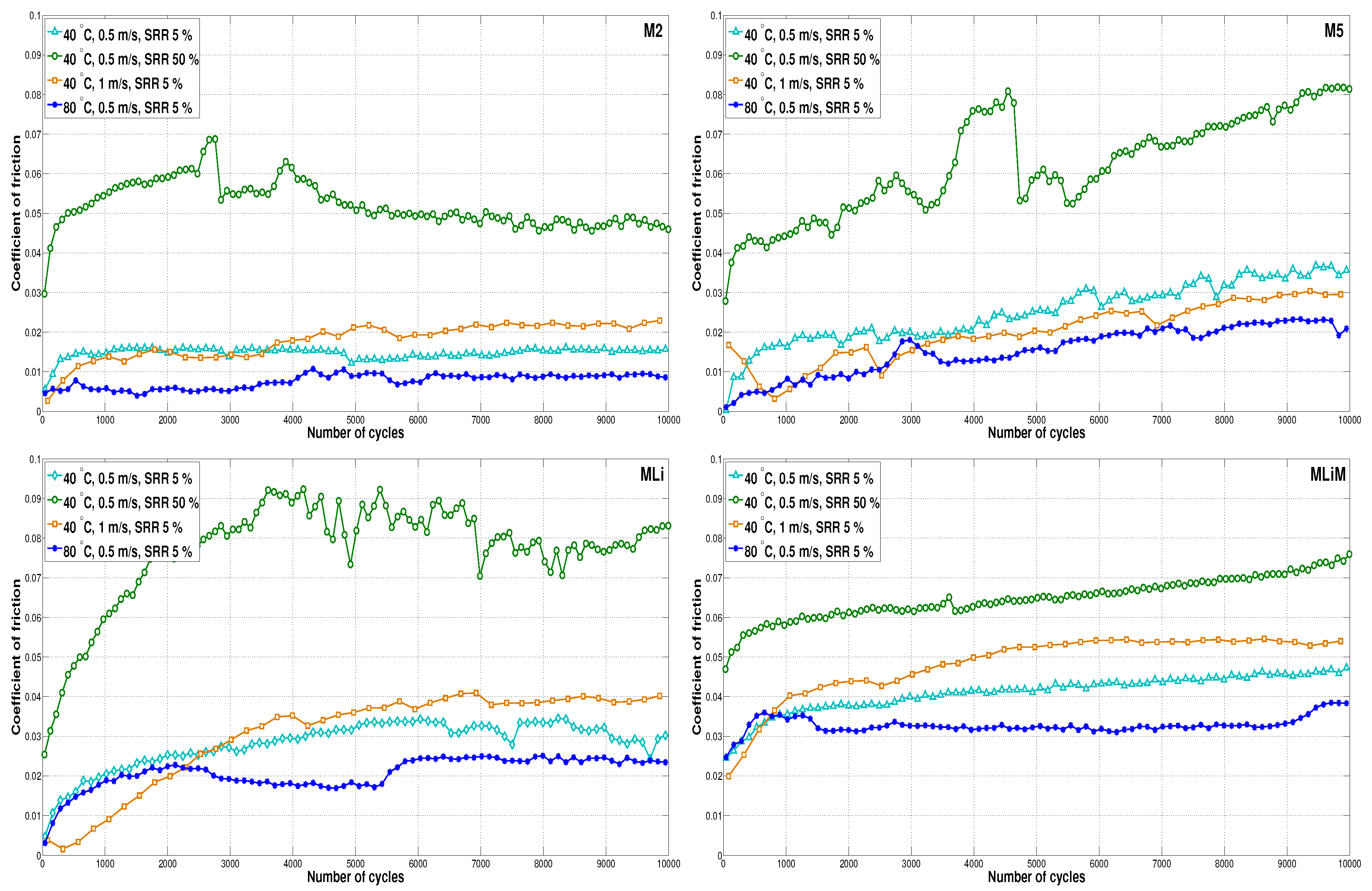
3.3. Coefficient of Friction Results
4. Conclusions
- Increasing the entrainment speed led to faster starvation due to the grease being pushed away from the contact and therefore, there was less time for the film to recover. As a consequence, the COF was higher;
- An increasing temperature led to later starvation (both in speed and time) and better replenishment due to decreased consistency, reduced bled oil viscosity, and improved oil-bleeding [12]. As a consequence, the COF reduced;
- AN increasing SRR led to faster starvation and reduced film thickness due to grease shearing and less time for the film to recover. Again, this led to an increased COF.
Author Contributions
Funding
- FCT under the individual PHD grant SFRH/BD/111868/2015;
- NORTE-01-0145-FEDER-000022–SciTech–Science and Technology for Competitive and Sustainable Industries, cofinanced by Programa Operacional Regional do Norte (NORTE2020), through Fundo Europeu de Desenvolvimento Regional (FEDER);
- LAETA under the project UIDS/EMS/50022/2013.
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wedeven, L.D.; Evans, D.; Cameron, A. Optical Analysis of Ball Bearing Starvation. J. Lubr. Technol. 1971, 93, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, Y.P. An Analysis and Prediction of Lubricant Film Starvation in Rolling Contact Systems. ASLE Trans. 2008, 17, 22–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pemberton, J.; Cameron, A. A mechanism of fluid replenishment in elastohydrodynamic contacts. Wear 1976, 37, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lugt, P.M. Grease Lubrication in Rolling Bearings; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Cousseau, T.; Björling, M.; Graça, B.; Campos, A.; Seabra, J.; Larsson, R. Influence of grease bleed oil on ball-on-disc lubrication. In Proceedings of the 5th World Tribology Congress, Torino, Italy, 8–13 September 2013; Volume 2, pp. 1109–1112. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Tanaka, H.; Sugimura, J. Experimental Study of Starvation and Flow Behavior in Grease-Lubricated EHD Contact. Tribol. Online 2015, 10, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cann, P.M.E. Thin-film grease lubrication. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part J J. Eng. Tribol. 1999, 213, 405–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aihara, S.; Dowson, D. A study of film thickness in grease lubricated elastohydrodynamic contacts. In Proceedings of the 5th Leeds-Lyon Symposium on Tribology, Leeds, UK, September 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Kauzlarich, J.J.; Greenwood, J.A. Elastohydrodynamic Lubrication With Herschel-Bulkley Model Greases. ASLE Trans. 1972, 15, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Åström, H.; Östensen, J.O.; Höglund, E. Lubricating Grease Replenishment in an Elastohydrodynamic Point Contact. J. Tribol. 1993, 115, 501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cann, P.M.; Lubrecht, A.A. Bearing performance limits with grease lubrication: the interaction of bearing design, operating conditions and grease properties. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2007, 40, 5446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cann, P.M. Starvation and reflow in a grease-lubricated elastohydrodynamic contact. Tribol. Trans. 1996, 39, 698–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneta, M.; Ogata, T.; Takubo, Y.; Naka, M. Effects of a thickener structure on grease elastohydrodynamic lubrication films. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part J J. Eng. Tribol. 2000, 214, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mérieux, J.S.; Hurley, S.; Lubrecht, A.A.; Cann, P.M. Shear-Degradation of Grease and Base Oil Availability in Starved EHL Lubrication; Elsevier: New York, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Cann, P. Grease Lubrication of Rolling Element Bearings—role of the grease thickener. Lubr. Sci. 2007, 19, 183–196. [Google Scholar]
- van Zoelen, M.T.; Venner, C.H.; Lugt, P.M. Prediction of film thickness decay in starved elasto-hydrodynamically lubricated contacts using a thin layer flow model. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part J J. Eng. Tribol. 2009, 223, 541–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Zoelen, M.T.; Venner, C.H.; Lugt, P.M. The prediction of contact pressure-induced film thickness decay in starved lubricated rolling bearings. Tribol. Trans. 2010, 53, 831–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, D.; Graça, B.; Campos, A.V.; Seabra, J.; Leckner, J.; Westbroek, R. On the film thickness behaviour of polymer greases at low and high speeds. Tribol. Int. 2015, 90, 435–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meijer, D.; Lankamp, H. Polymer Thickened Lubricating Grease. U.S. Patent 5846918A, 12 March 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Meijer, D.; Lankamp, H. Polymer Thickened Lubricating Grease. U.S. Patent 5874391A, 23 February 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Dodson, S.; Newman, R. Grease Composition. U.S. Patent 3850828A, 26 November 1974. [Google Scholar]
- Mitacek, B. Grease; Technical Report. Available online: https://patents.google.com/patent/US3392119 (accessed on 10 September 2018).
- Gonçalves, D.; Graça, B.; Campos, A.; Seabra, J. Film thickness and friction behaviour of thermally aged lubricating greases. Tribol. Int. 2016, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cann, P.M.; Spikes, H.A.; Hutchinson, J. The Development of a Spacer Layer Imaging Method (SLIM) for Mapping Elastohydrodynamic Contacts. Tribol. Trans. 1996, 39, 915–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cen, H.; Lugt, P.M.; Morales-Espejel, G.E. Film Thickness of Mechanically Worked Lubricating Grease at Very Low Speeds. Tribol. Trans. 2014, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cen, H.; Lugt, P.M.; Morales-Espejel, G.E. On the film thickness of grease lubricated contacts at low speeds. Tribol. Trans. 2014, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, D.; Marques, R.; Graça, B.; Campos, A.V.; Seabra, J.H.; Leckner, J.; Westbroek, R. Formulation, rheology and thermal aging of polymer greases—Part II: Influence of the co-thickener content. Tribol. Int. 2015, 87, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, D.; Graça, B.; Campos, A.; Seabra, J. On the friction behaviour of polymer greases. Tribol. Int. 2015, 93, 399–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Laurentis, N.; Kadiric, A.; Lugt, P.M.; Cann, P.M. The Influence of Bearing Grease Composition on Friction in Rolling/Sliding Concentrated Contacts. Tribol. Int. 2015, 94, 624–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lugt, P.M.; Velickov, S.; Tripp, J.H. On the Chaotic Behavior of Grease Lubrication in Rolling Bearings. Tribol. Trans. 2009, 52, 581–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandão, J.A.; Meheux, M.; Ville, F.; Seabra, J.H.; Castro, J. Comparative overview of five gear oils in mixed and boundary film lubrication. Tribol. Int. 2012, 47, 50–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, D.; Graça, B.; Campos, A.V.; Seabra, J.; Leckner, J.; Westbroek, R. Formulation, rheology and thermal ageing of polymer greases—Part I: Influence of the thickener content. Tribol. Int. 2015, 87, 160–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, D.; Cousseau, T.; Gama, A.; Campos, A.; Seabra, J.H. Friction torque in thrust roller bearings lubricated with greases, their base oils and bleed-oils. Tribol. Int. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cousseau, T.; Björling, M.; Graça, B.; Campos, A.; Seabra, J.H.O.; Larsson, R. Film thickness in a ball-on-disc contact lubricated with greases, bleed oils and base oils. Tribol. Int. 2012, 53, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lugt, P.M. A Review on Grease Lubrication in Rolling Bearings. Tribol. Trans. 2009, 52, 470–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lugt, P.M. Modern Advancements in Lubricating Grease Technology. Tribol. Int. 2016, 97, 467–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
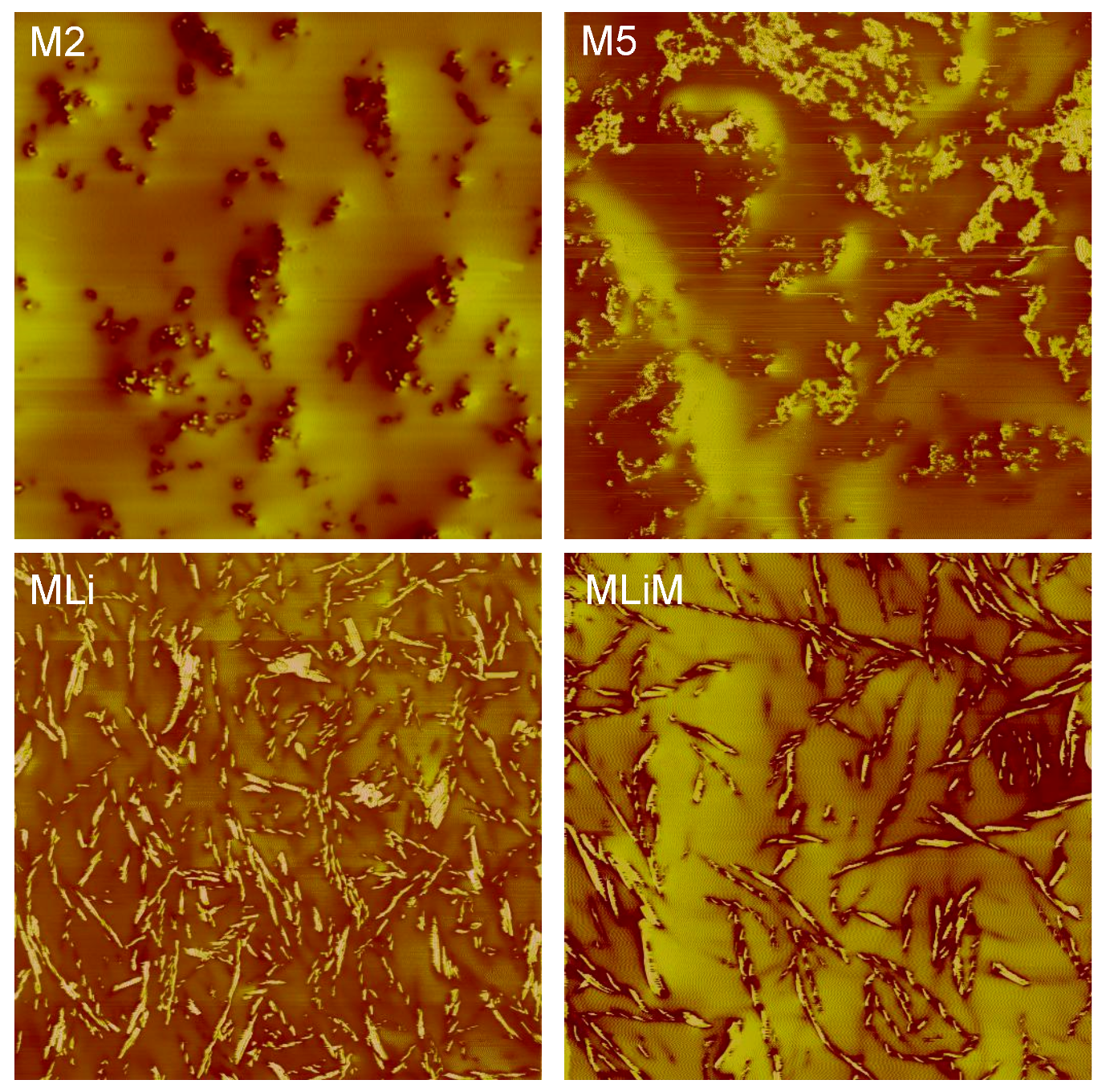
| Grease Reference | M2 | M5 | MLi | MLiM | Units | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thickener type | PP | PP | LiX | LiX | — | |
| Base oil nature | PAO | PAO | PAO + 5%E | MIN | — | |
| Thickener content | 13 | 13 | 17.5 | 10.6 | % | |
| Elastomer content | 0 | 2.6 | 0 | 1.7 | % | |
| Worked penetration (ISO 2137) | 269 | 249 | 276 | n.a. | mm | |
| NLGI | 2 | 3 | 2 | 2 | — | |
| Storage Modulus G | 80 C | 21,347 | 29,810 | 22,285 | 15,820 | Pa |
| Loss Modulus G | 4596 | 6029 | 7102 | 1861 | Pa | |
| Cross-over stress | 80 C | 187 | 92 | 64 | 163 | Pa |
| Yield stress | 112 | 31 | 33 | 37 | Pa | |
| Base oil viscosity (ASTM D445) | 40 C | 48.0 | 178.7 | 153.3 | mm/s | |
| 100 C | 8.0 | 21.4 | 15.7 | |||
| Bleed oil viscosity (ISO 12058) | 40 C | 49.3 | 779.1 | 135.2 | 159.9 | mm/s |
| 100 C | 8.3 | 93.3 | 18.9 | 16.6 | ||
| Surface Properties | Glass Disc | Steel Ball | Steel Disc |
|---|---|---|---|
| Radius, [mm] | ∞ | 9.525 | ∞ |
| Roughness, [m] | 5 | <20 | |
| Material | Glass | AISI 52100 | |
| Young’s Modulus | 64 | 207 | |
| Poisson coefficient | 0.29 | 0.2 | |
| Test Number | 1 (Ref.) | 2 | 3 | 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Entrainment speed—U [m/s] | 0.5 | 1 | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| Temperature—T [C] | 40 | 40 | 80 | 40 |
| Slide-to-roll ratio—SRR [%] | 5 | 5 | 5 | 50 |
| Load—F [N] | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 |
| Test Conditions | Test 1 40 C 0.5 m/s 5% | Test 2 40 C 1 m/s 5% | Test 3 80 C 0.5 m/s 5% | Test 4 40 C 0.5 m/s 50% | Trends in Starvation Tests | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M2 | 192 | 318 | 98 | 192 * | ||
| 123 | 80 | 321 | 30 | |||
| 17 | 56 | 85 | 10 | |||
| M5 | 320 | 551 | 121 | 320 * | ||
| 112 | 121 | 66 | 50 | |||
| 13 | 85 | 156 | 12 | |||
| MLi | 470 | 756 | 146 | 470 * | ||
| 41 | 79 | 76 | 7 | |||
| 5 | 27 | 8 | 29 | |||
| MLiM | 558 | 867 | 131 | 558 * | ||
| 123 | 59 | 24 | 9 | |||
| 34 | 54 | 13 | 11 | |||
| Test Conditions | Test 1 40 C 0.5 m/s 5% | Test 2 40 C 1 m/s 5% | Test 3 80 C 0.5 m/s 5% | Test 4 40 C 0.5 m/s 50% | Trends | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M2 | 0.016 | 0.022 | 0.009 | 0.047 | ||
| M5 | 0.035 | 0.027 | 0.022 | 0.079 | ||
| MLi | 0.031 | 0.039 | 0.024 | 0.079 | ||
| MLiM | 0.046 | 0.054 | 0.035 | 0.073 | ||
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gonçalves, D.E.P.; Campos, A.V.; Seabra, J.H.O. An Experimental Study on Starved Grease Lubricated Contacts. Lubricants 2018, 6, 82. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants6030082
Gonçalves DEP, Campos AV, Seabra JHO. An Experimental Study on Starved Grease Lubricated Contacts. Lubricants. 2018; 6(3):82. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants6030082
Chicago/Turabian StyleGonçalves, David E. P., Armando V. Campos, and Jorge H. O. Seabra. 2018. "An Experimental Study on Starved Grease Lubricated Contacts" Lubricants 6, no. 3: 82. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants6030082
APA StyleGonçalves, D. E. P., Campos, A. V., & Seabra, J. H. O. (2018). An Experimental Study on Starved Grease Lubricated Contacts. Lubricants, 6(3), 82. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants6030082





