Use of Advanced Piston Ring Coatings on Agricultural Engines
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
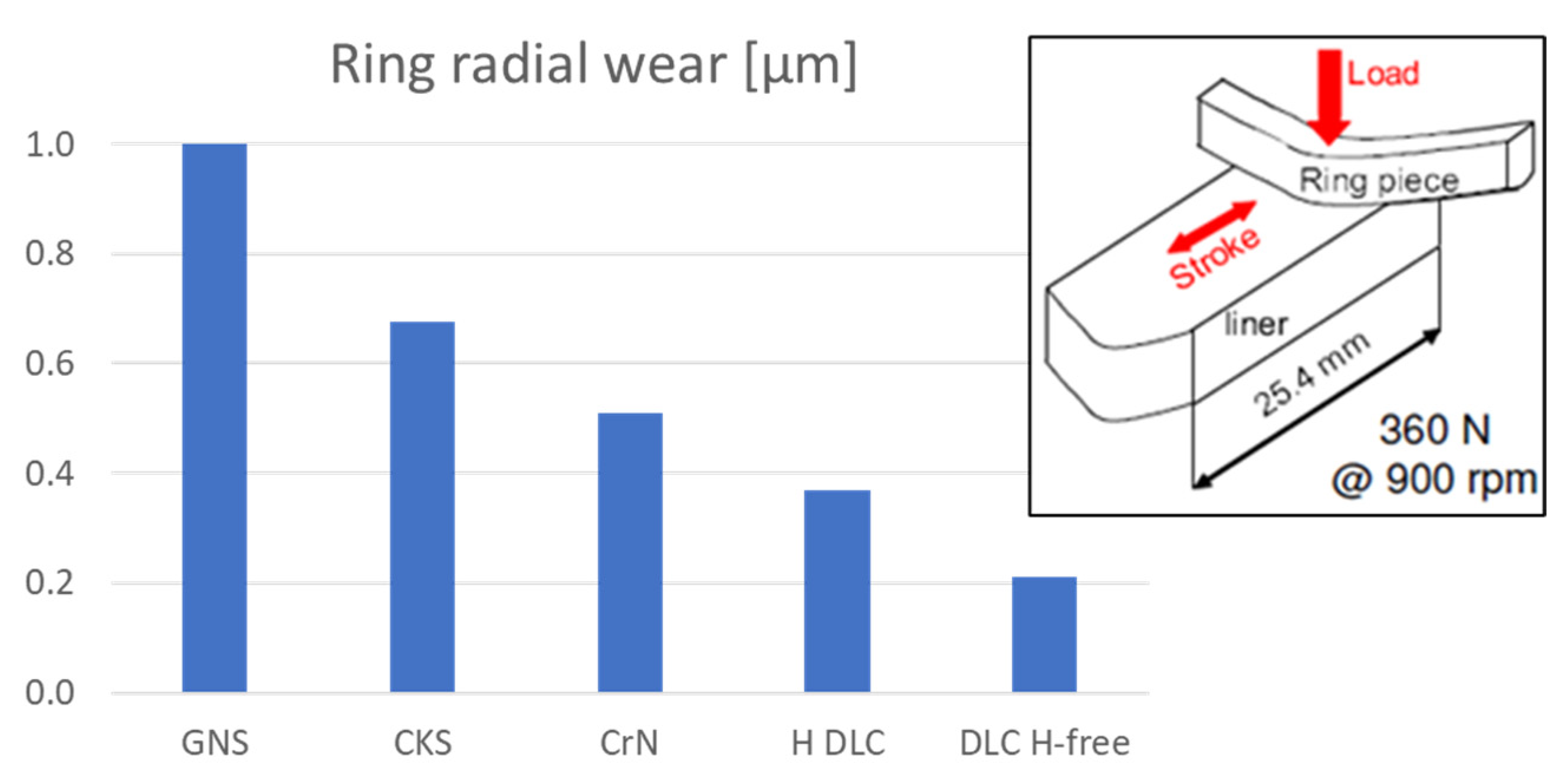
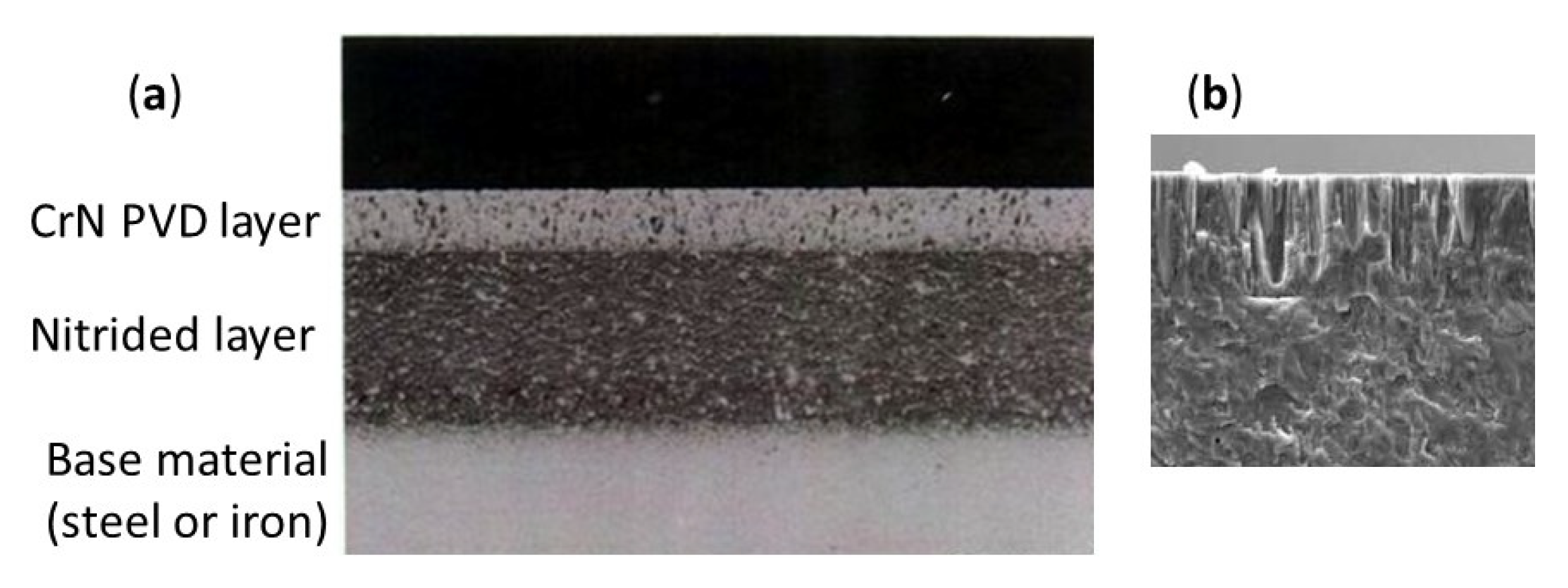
2.1. Rig Tribological Tests
2.2. Engine Tests
- (a)
- 0 to 300 h: full power.
- (b)
- 300 to 800 h: full power.
- (c)
- 800 to 1100 h: thermal shock, alternating every 6 min at full power with 95 °C cooling water and 4 min at idle with 30 °C cooling water.
3. Results
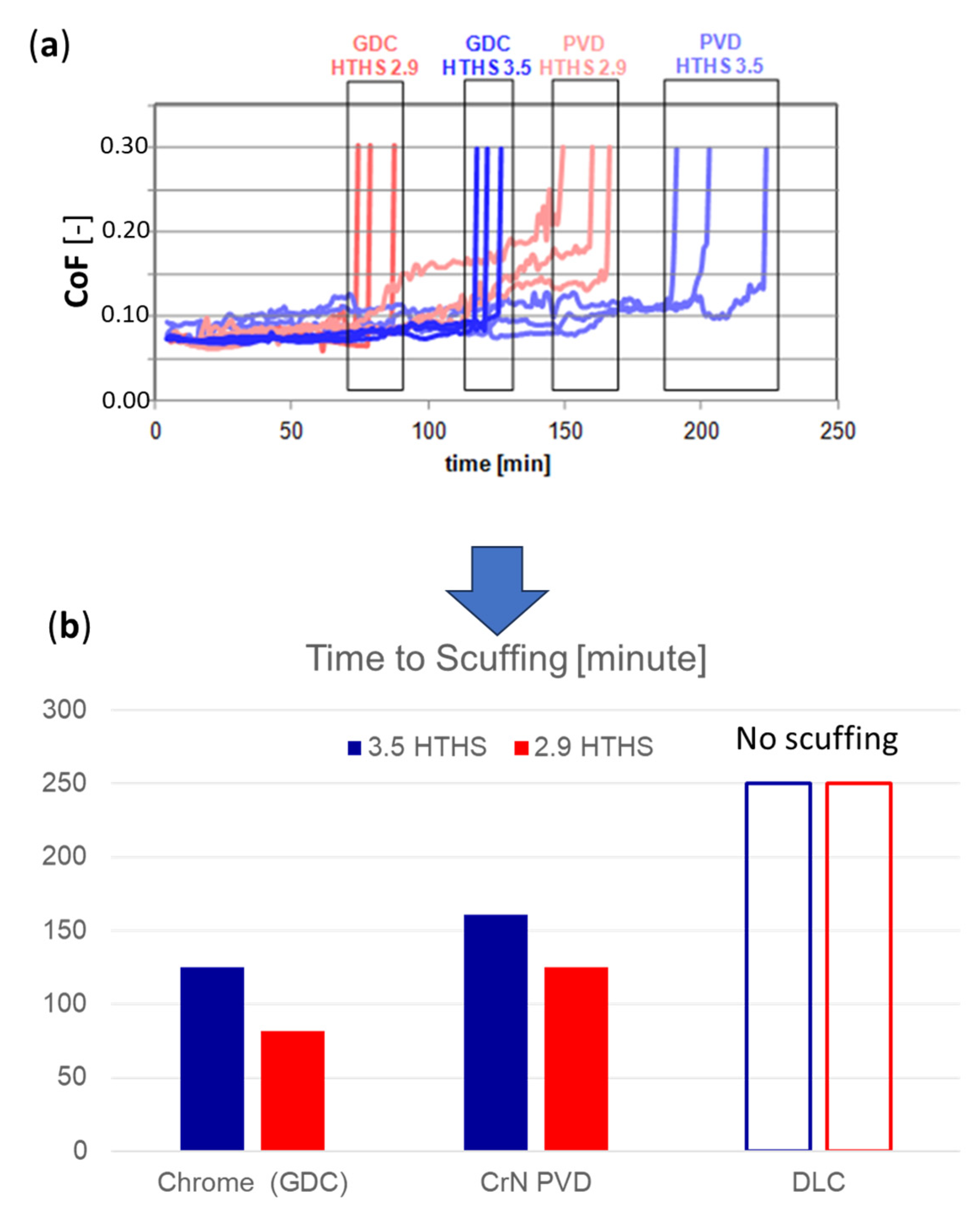
3.1. Rig Tribological Tests
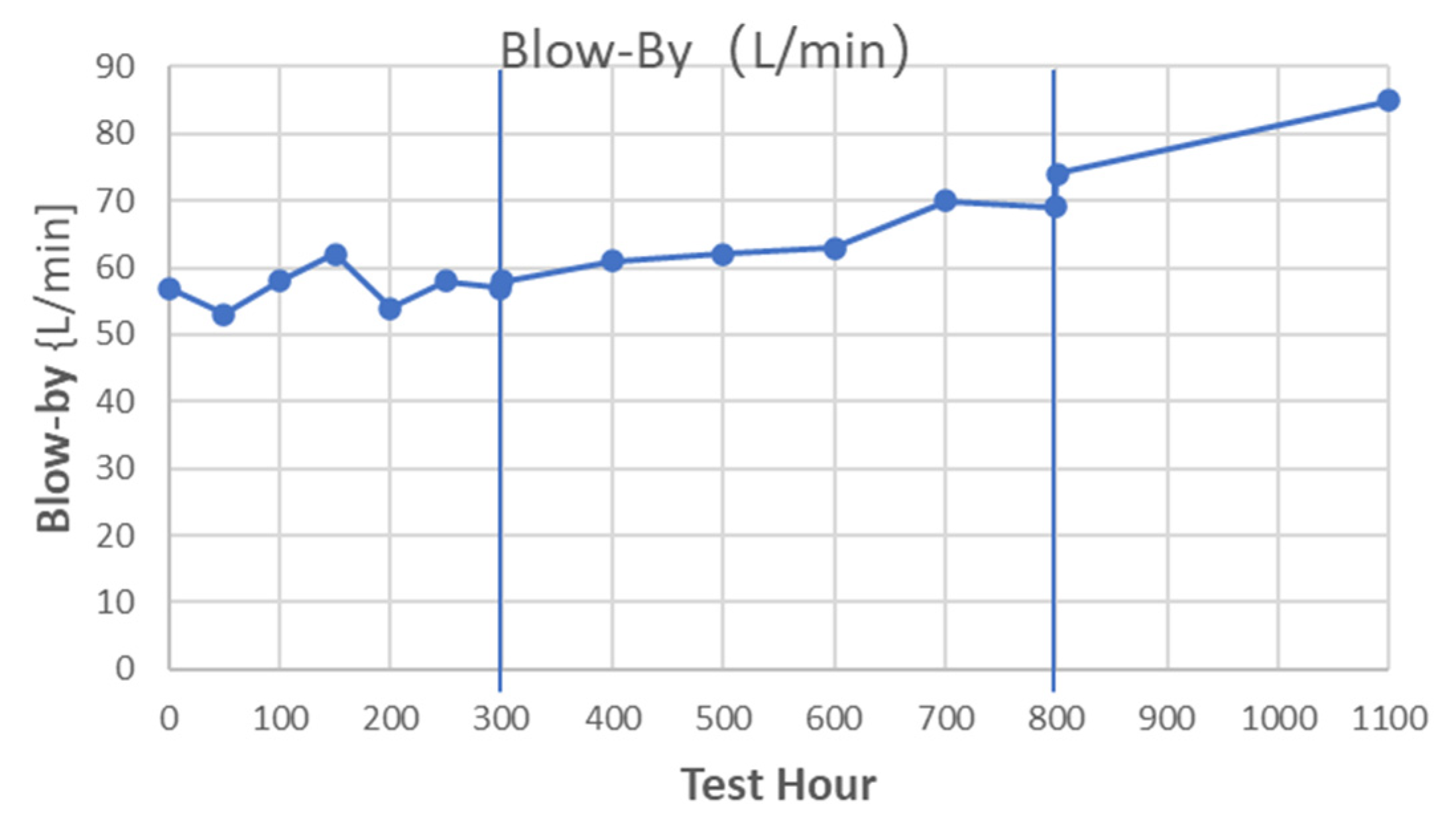
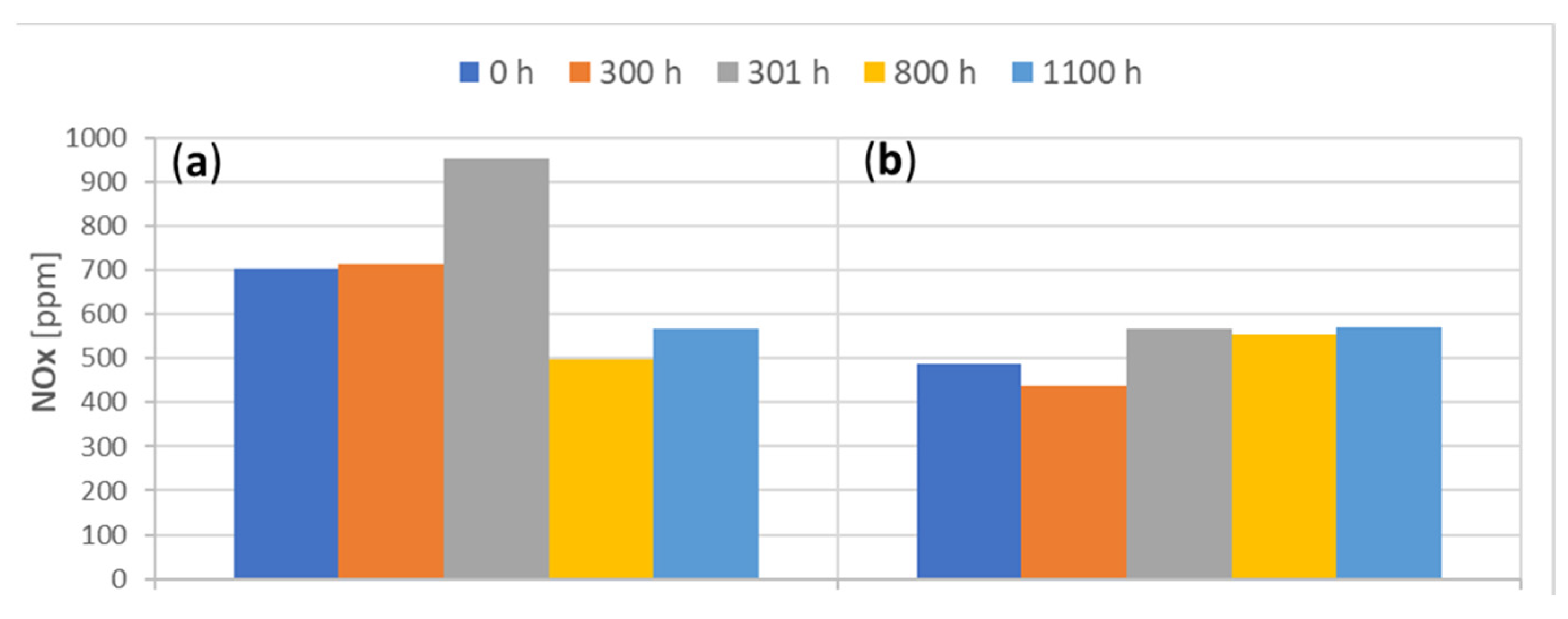
3.2. Engine Performance
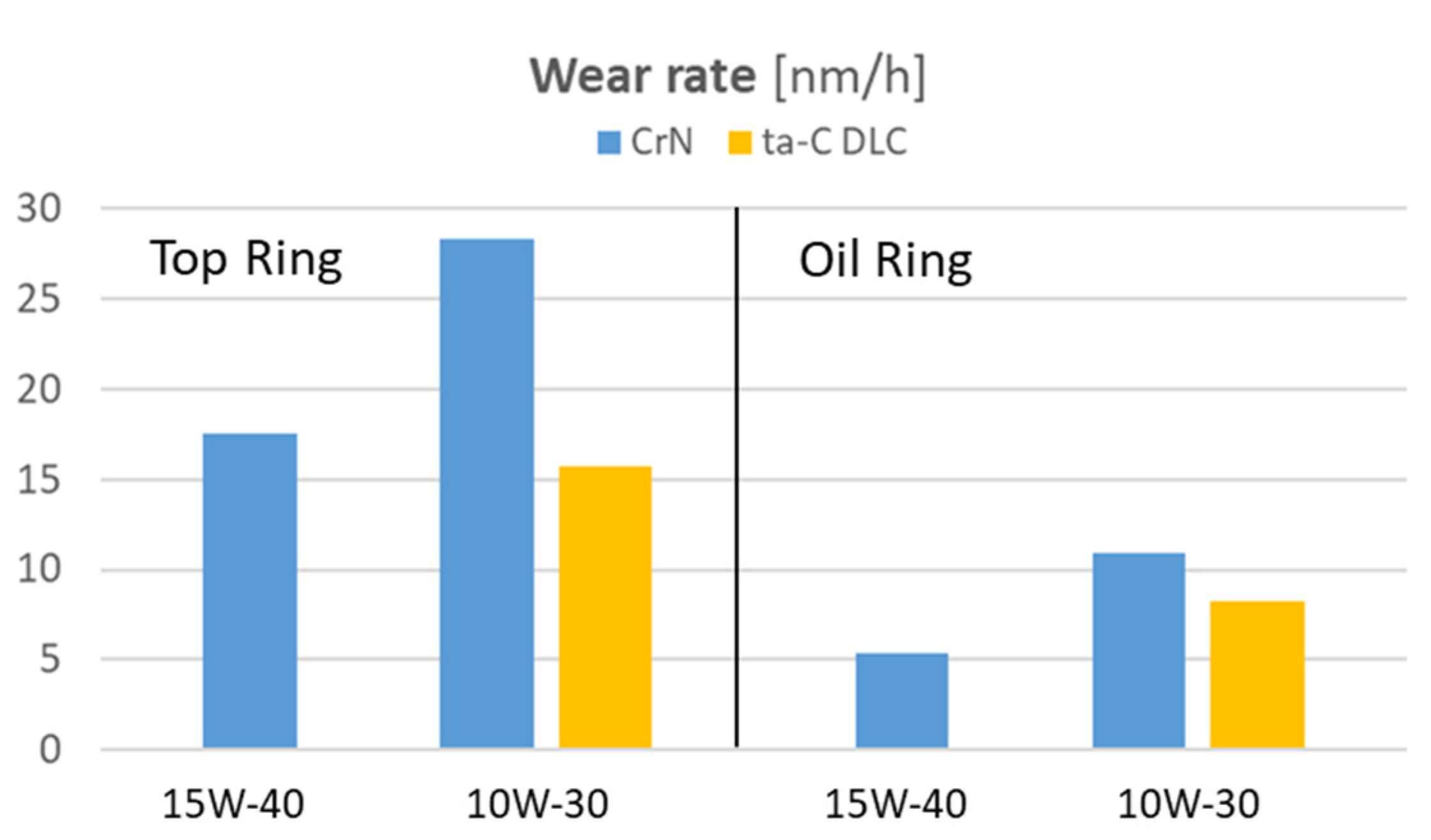
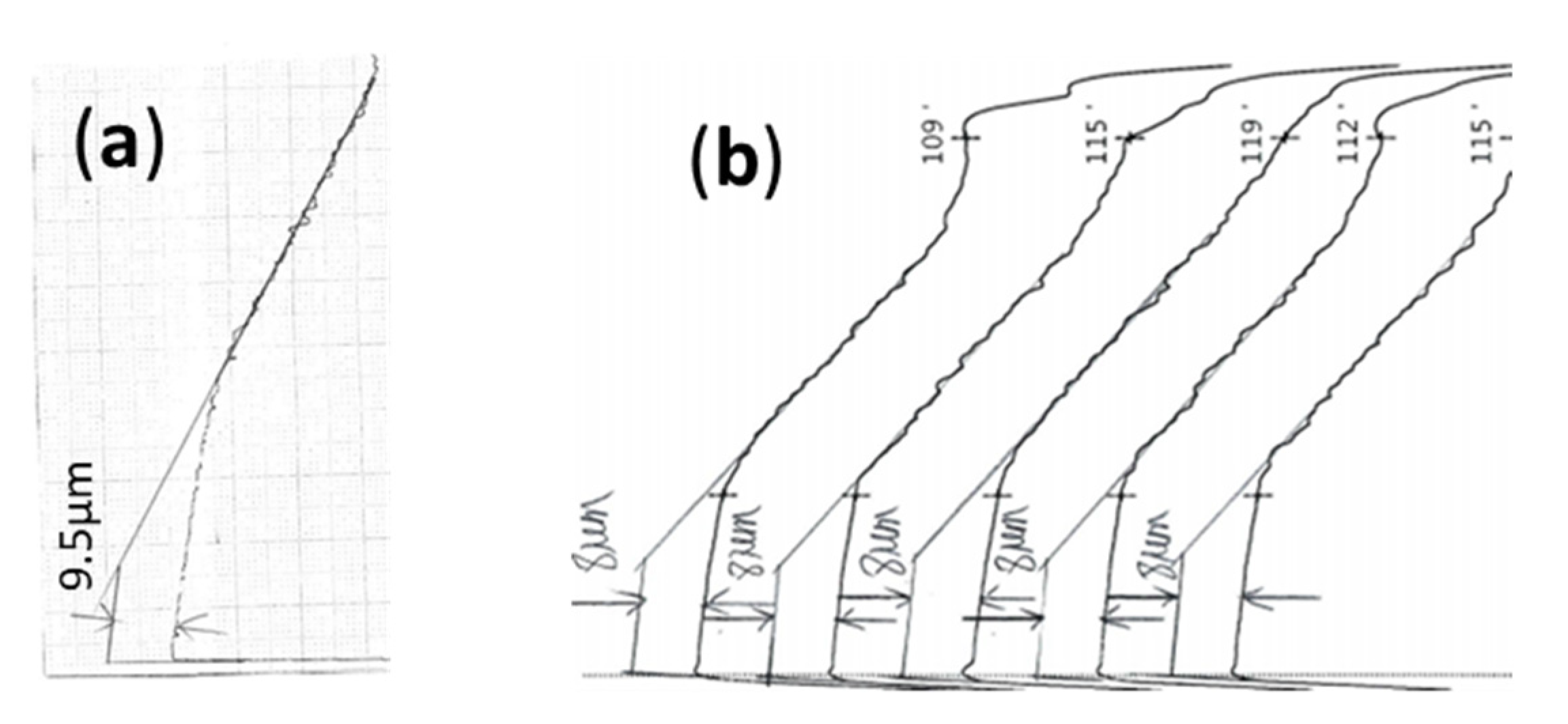
3.3. Ring Wear
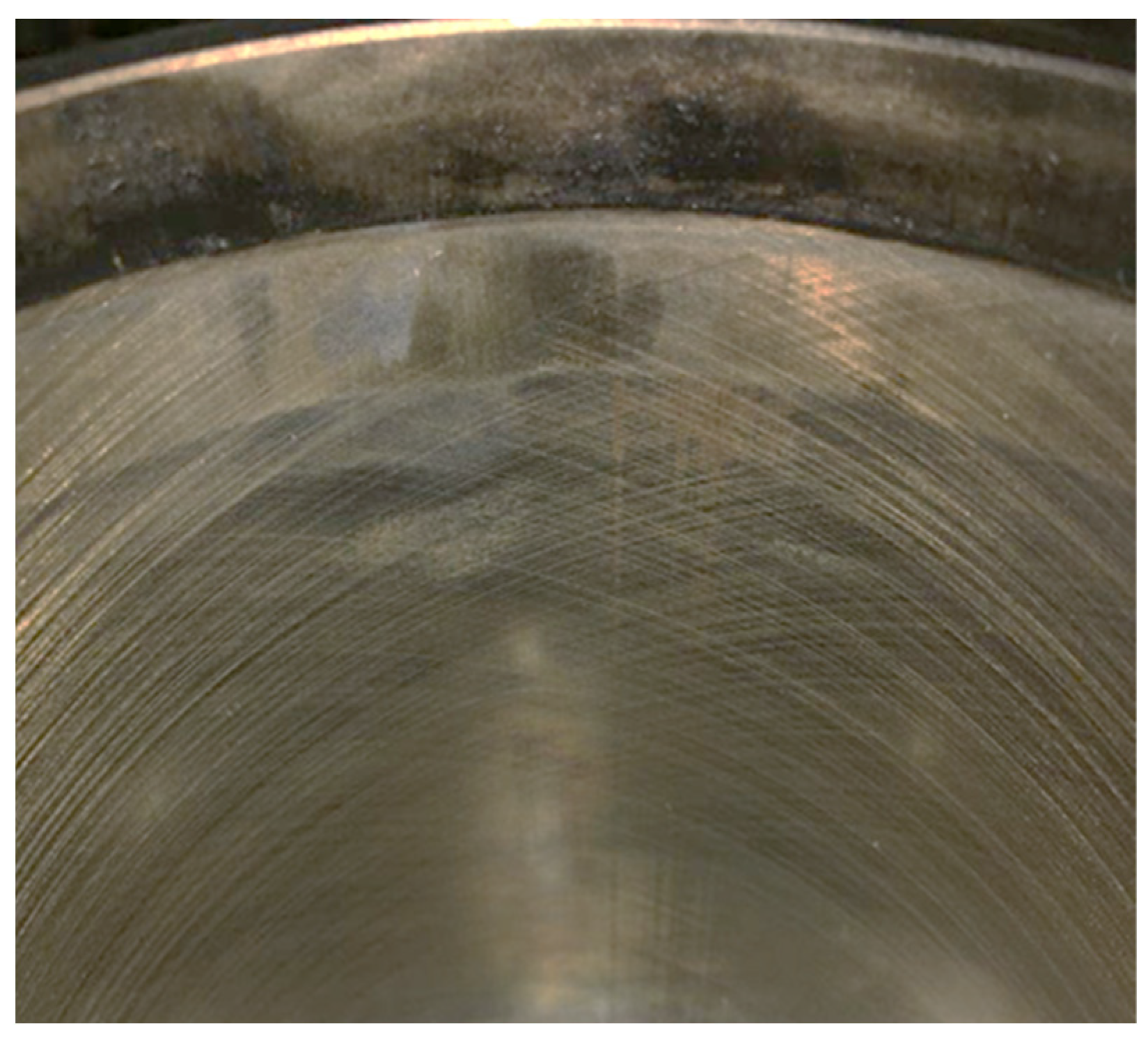
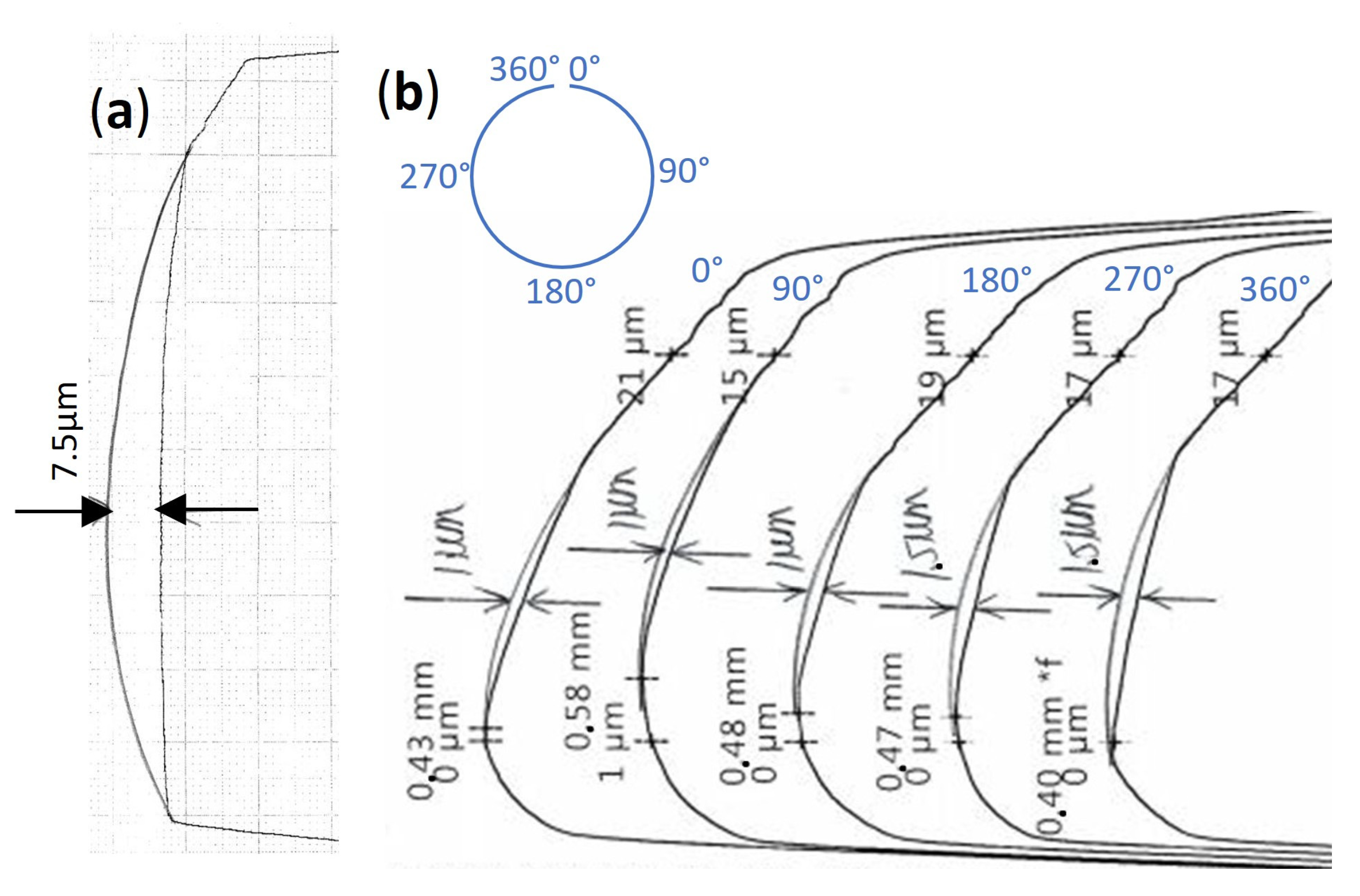
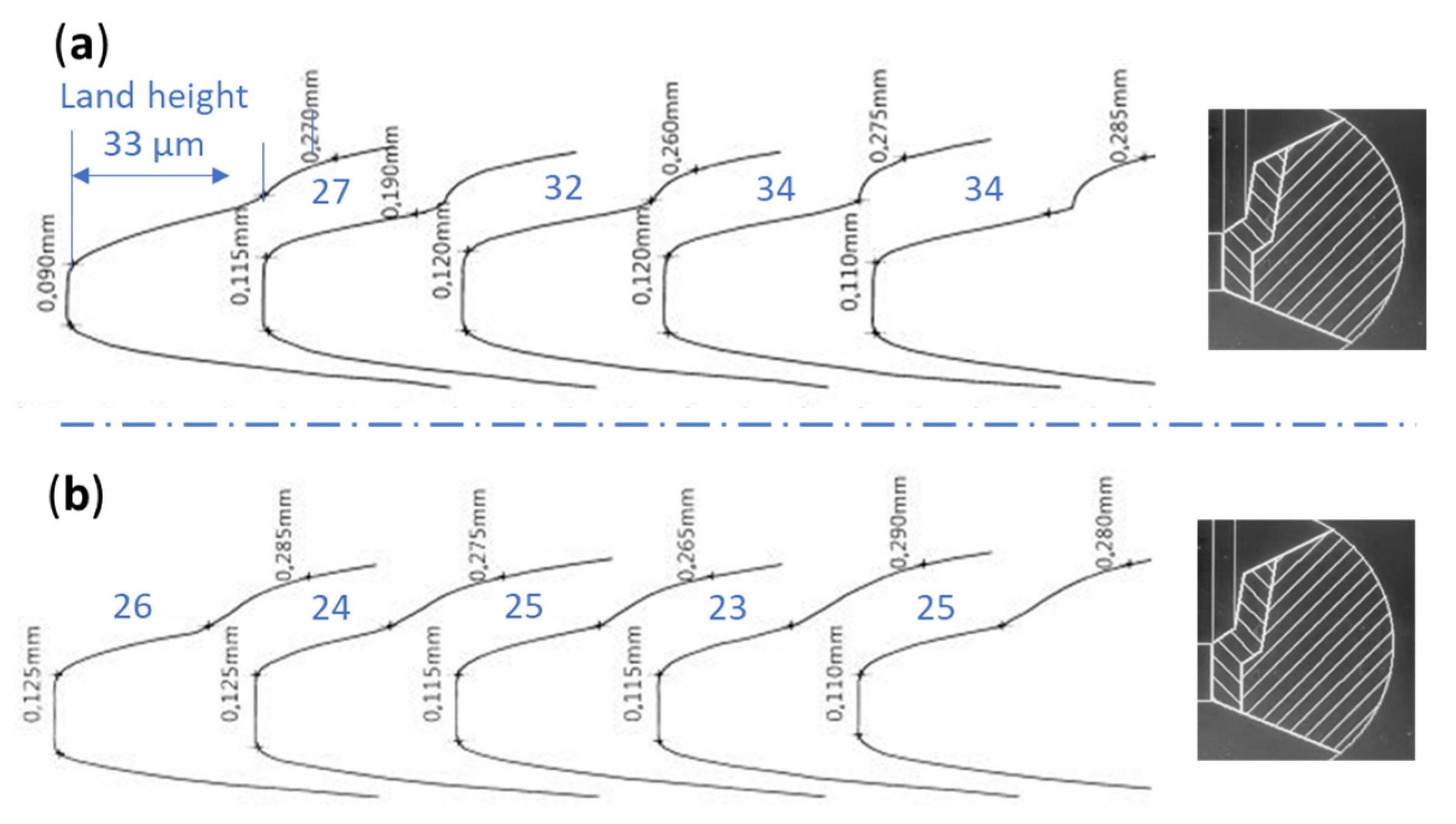
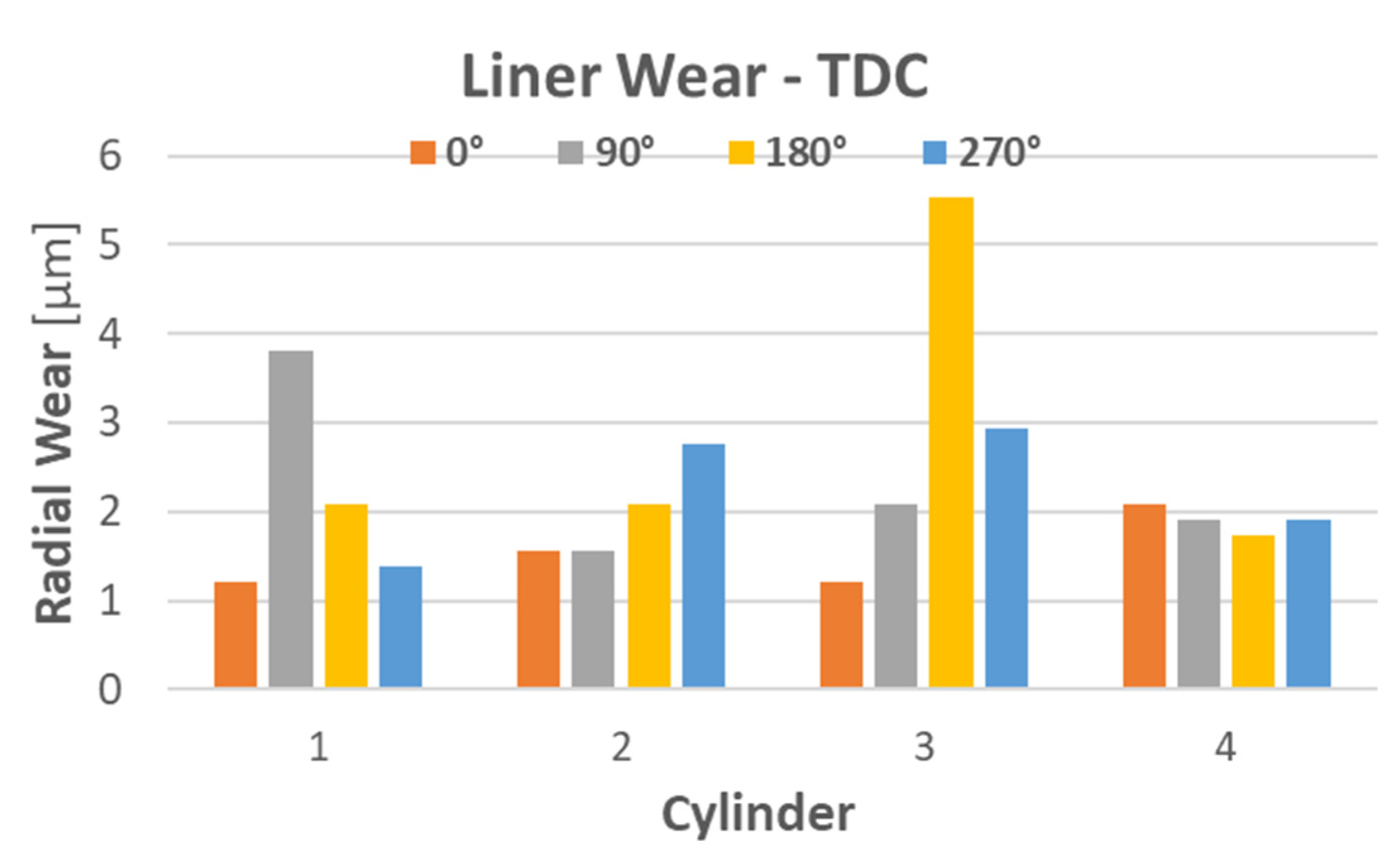
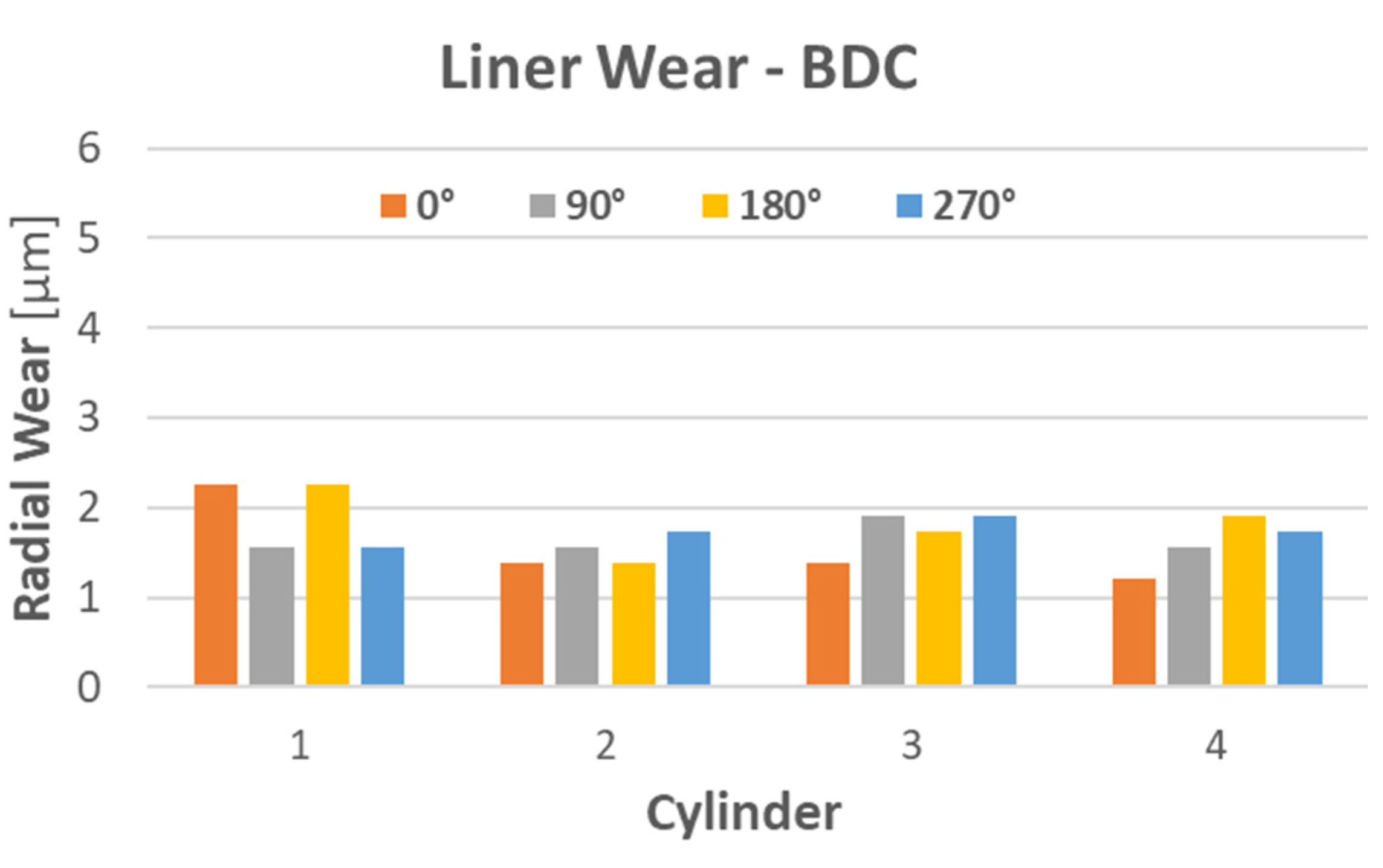
3.4. Cylinder Liner Wear
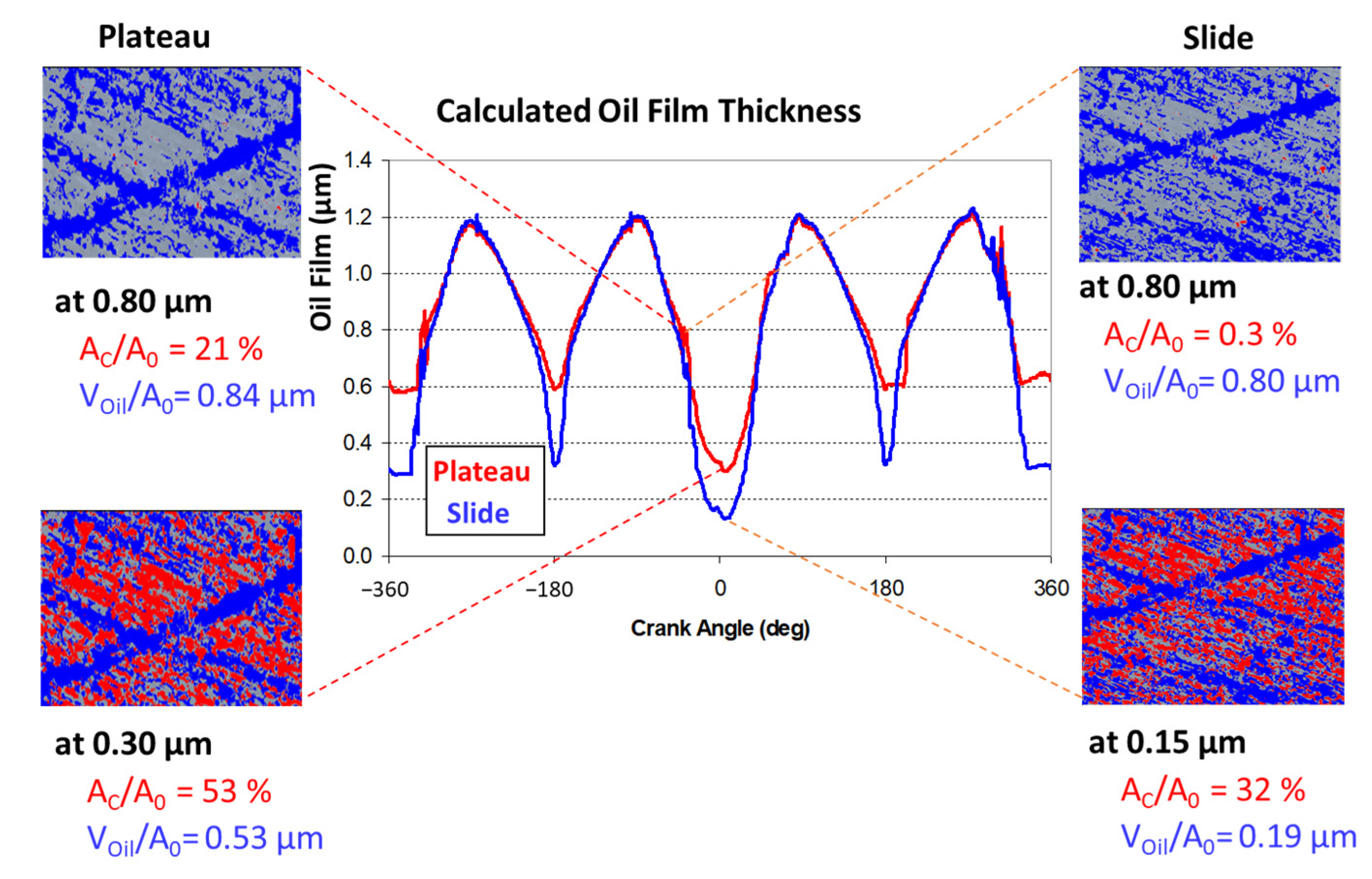
4. Discussion
- The use of lower-viscosity oils: lower oil film thickness and higher boundary contact would be acceptable.
- Smoother cylinder liners: honing grooves were preserved at the end of the test.
- Reduced tangential load on oil control ring tangential: contact pressure was not reduced along the engine life due to ring face wear.
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Venkatachalam, V. Oil and Gas in the Agriculture Sector. Research Canadian Energy Centre. 2024. Available online: https://www.canadianenergycentre.ca/energy-perspectives-oil-and-gas-in-the-agriculture-sector (accessed on 11 April 2025).
- Ali, M. Impact assessment of energy utilization in agriculture for India and Pakistan. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 648, 1520–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Lin, B. Factors affecting CO2 emissions in China’s agriculture sector: Evidence from geographically weighted regression model. Energy Policy 2017, 104, 404–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.; Xu, B. Factors affecting CO2 emissions in China’s agriculture sector: A quantile regression. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 94, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MEE. China Mobile Source Environmental Management Annual Report 2021; MEE: Beijing, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, X.; Zhang, X.; Huang, S.; Xu, P.; Shen, J. Measurement of engine performance and maps-based emission prediction of agricultural tractors under actual operating conditions. Measurement 2023, 222, 113637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janulevičius, A.; Juostas, A.; Pupinis, G. Engine performance during tractor operational period. Energy Convers. Manag. 2013, 68, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Special Agriculture 4.0. Centro de Ciências Agrárias—Universidade Federal do Ceará, Fortaleza, CE. Available online: www.ccarevista.ufc.br (accessed on 1 April 2025). [CrossRef]
- Raza, M.Y.; Zhongpan, Q.; Pengju, W. Agriculture-related energy consumption, food policy, and CO2 emission reduction: New insights from Pakistan. Front. Environ. Sci. 2023, 10, 1099813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubon, M.; Cupiał, M.; Szeląg-Sikora, A.; Kobuszewski, M. The Impact of Purchasing New Agricultural Machinery on Fuel Consumption on Farms. Sustainability 2024, 16, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Baležentis, T.; Makutėnienė, D.; Streimikiene, D.; Kriščiukaitienė, I. Energy-related CO2 emission in European Union agriculture: Driving forces and possibilities for reduction. Appl. Energy 2016, 180, 682–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Q.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, W.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, X.; Liu, J. Effects of ammonia energy fraction on combustion stability, carbon-based emissions and greenhouse effect of an agricultural ammonia-diesel dual-fuel engine. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2025, 198, 107107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmberg, K.; Andersson, P.; Erdemir, A. Global Energy Consumption Due to Friction in Passenger Cars. Tribol. Int. 2012, 47, 221–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmberg, K.; Andersson, P.; Nylund, N.-O.; Mäkelä, K.; Erdemir, A. Global energy consumption due to friction in trucks and buses. Tribol. Int. 2014, 78, 94–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tung, S.C.; McMillan, M.L. Automotive tribology overview of current advances and challenges for the future. Tribol. Int. 2004, 37, 517–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schommers, J.; Scheib, H.; Hartweg, M.; Bosler, A. Minimising Friction in Combustion Engines. MTZ Worldw. 2013, 74, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhmud, B.; Tomanik, E.; Jiménez, A.J.; Profito, F.; Tormos, B. Powertrain Friction Reduction by Synergistic Optimization of Cylinder Bore Surface and Lubricant—Part 2: Engine Tribology Simulations and Tests; SAE Technical Paper; SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, R.; Morgan, N.; Mainwaring, R.; Davenport, T. How much mixed/boundary friction is there in an engine—And where is it? Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part J J. Eng. Tribol. 2020, 234, 1563–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomanik, E.; Profito, F.J.; Tormos, B.; Jiménez, A.J.; Zhmud, B. Powertrain Friction Reduction by Synergistic Optimization of the Cylinder Bore Surface and Lubricant Part 1: Basic Modelling; SAE Technical Paper; SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, V.W.; Tung, S.C. Overview of automotive engine friction and reduction trends–Effects of surface, material, and lubricant-additive technologies. Friction 2016, 4, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suthisripok, T.; Semsamran, P. The impact of biodiesel B100 on a small agricultural diesel engine. Tribol. Int. 2018, 128, 397–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araujo, J.A.; Banfield, R.R. DLC as a Low-Friction Coating for Engine Components; SAE Technical Paper; SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higuchi, T.; Mabuchi, Y.; Ichihara, H.; Murata, T.; Moronuki, M. Development of Hydrogen-Free Diamond-Like Carbon Coating for Piston Rings. Tribol. Online Jpn. Soc. Tribol. 2017, 12, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruno, R.; Rabello, R.; Silva, D.; Araujo, J. DLC Coated Ring Pack for Heavy Duty Diesel Engines; SIMEA 2017 Proceedings Ed.; Blucher: Vildbjerg, Denmark, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Björling, M.; Isaksson, P.; Marklund, P.; Larsson, R. The Influence of DLC Coating on EHL Friction Coefficient. Tribol. Lett. 2012, 47, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rübig, B.; Heim, D.; Forsich, C.; Dipolt, C.; Mueller, T.; Gebeshuber, A.; Kullmer, R.; Holecek, R.; Lugmair, C.; Krawinkler, M.; et al. Tribological behavior of thick DLC coatings under lubricated conditions. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2017, 314, 13–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tas, M.; Banerji, M.; Lukitsch, M.; Alpas, A. Roles of mirror-like surface finish and DLC coated piston rings on increasing scuffing resistance of cast iron cylinder liners. Wear 2017, 376–377, 1558–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mobarak, H.; Masjuki, H.; Mohamad, E.N.; Rahman, S.A.; Al Mahmud, K.; Habibullah, M.; Salauddin, S. Effect of DLC coating on tribological behavior of cylinder liner piston ring material combination when lubricated with Jatropha oil. Procedia Eng. 2014, 90, 733–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazuco, F.; Rezende, L.; Araujo, J.; Pereira, J.; Souza, R. Parameters study of carbon bombardment step for enhanced adhesion of thick DLC coating deposited by cathodic arc evaporation. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2023, 457, 129310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazuco, F.; Araujo, J.; Souza, R. Effect of long carbon bombardment step on the adhesion of thick amorphous carbon coating deposited by cathodic arc evaporation. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2021, 116, 108434. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0925963521001977 (accessed on 25 February 2025). [CrossRef]
- Banerji, A.; Lukitsch, M.; Alpas, A. Friction reduction mechanisms in cast iron sliding against DLC: Effect of biofuel (E85) diluted engine oil. Wear 2016, 368–369, 196–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrarese, A.; Banfield, R.; Tomanik, E. High Value PVD Top Ring for High Speed Diesel Engines; SAE Technical Paper; SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Zavos, A. Effect of Coating and Low Viscosity Oils on Piston Ring Friction under Mixed Regime of Lubrication through Analytical Modelling. Lubricants 2021, 9, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zavos, A.; Katsaros, K.P.; Nikolakopoulos, P.G. Optimum Selection of Coated Piston Rings and Thrust Bearings in Mixed Lubrication for Different Lubricants Using Machine Learning. Coatings 2022, 12, 704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rejowski, E.; Tomanik, E.; Souza, J. Low viscosity oils impact on heavy duty diesel engine components. In Anais do XXIV Simpósio Internacional de Engenharia Automotica—SIMEA 2016 [Blucher Engineering Proceedings]; Blucher: São Paulo, Brazil, 2016; pp. 118–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomanik, E.; Profito, F.; Sheets, B.; Souza, R. Combined lubricant–surface system approach for potential passenger car CO2 reduction on piston-ring-cylinder bore assembly. Tribol. Int. 2020, 149, 105514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tormos, B.; Jiménez, A.J.; Fang, T.; Mainwaring, R.; Lizarraga-Garcia, E. Numerical assessment of tribological performance of different low viscosity engine oils in a 4-stroke CI light-duty ICE. SAE Int. J. Adv. Cur. Pract. Mob. 2022, 4, 1524–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rovai, F.F.; Sartori, E.; Crepaldi, J.; Rajala, S. Engine Lubricant Impact in Light-Vehicle Fuel Economy: A Combined Numerical Simulation and Experimental Validation. Lubricants 2025, 13, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robota, A.; Zwein, F. Influence of cylinder bore topography on the oil consumption and particulate emissions of a DI TCI diesel engine. MTZ 1999, 60, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Soderfjall, M.; Herbst, H.; Larsson, R.; Almqvist, A. Influence on friction from piston ring design, cylinder liner roughness and lubricant Properties. Tribol. Int. 2017, 116, 272–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obert, P.; Müller, T.; Füßer, H.; Bartel, D. The influence of oil supply and cylinder liner temperature on friction, wear and scuffing behavior of piston ring cylinder liner contacts—A new model test. In Tribology International—Amsterdam; Elsevier Science: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; Volume 94, pp. 306–314. [Google Scholar]
- Dimkovski, Z.; Cabanettes, F.; Löfgren, H.; Anderberg, C.; Ohlsson, R.; Rosén, B.G. Optimization of cylinder liner surface finish by slide honing. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part B 2012, 226, 575–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chen, H.; Tian, T. A Deterministic Model for Lubricant Transport Within Complex Geometry Under Sliding Contact and Its Application in the Interaction Between the Oil Control Ring and Rough Liner in Internal Combustion Engines; SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Li, Y.; Tian, T. A Novel Approach to Model the Lubrication and Friction Between the Twin-Land Oil Control Ring and Liner with Consideration of Micro Structure of the Liner Surface Finish in Internal Combustion Engines; SAE Technical Paper; SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Tomanik, E. Friction and wear bench tests of different engine liner surface finishes. Tribol. Int. 2008, 41, 1032–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spencer, A.; Avan, E.Y.; Almqvist, A.; Dwyer-Joyce, R.S.; Larsson, R. An experimental and numerical investigation of frictional losses and film thickness for four cylinder liner variants for a heavy duty diesel engine. Proc. Inst. Mec. Eng. Part J J. Eng. Tribol. 2013, 227, 1319–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, R.; Almeida, R.; Carvalho, O.; Sobral, L.; Carvalho, S.; Silva, F. Influence of a DLC coating topography in the piston ring/cylinder liner tribological performance. J. Manuf. Process. 2021, 66, 483–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Liao, B. A review on preparation process and tribological performance of coatings for internal combustion engine piston ring. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2023, 15, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomanik, E.; Nigro, F. Piston Ring Pack and Cylinder Wear Modelling; SAE TRANS PAPER 2001; SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Corral, I.; Calvet, J.; Salcedo, M. Use of roughness probability parameters to quantify the material removed in plateau-honing. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2010, 50, 621–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, C.; Wang, R.; Tian, T. Modeling the Fatigue Wear of the Cylinder Liner in Internal Combustion Engines during the Break-In Period and Its Impact on Piston Ring Lubrication. Lubricants 2019, 7, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Henein, N.A.; Bryzik, W. A model for wear and friction in cylinder liners and piston rings. Tribol. Trans. 2006, 49, 315–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giorgio, M.; Guida, M.; Pulcini, G. A state-dependent wear model with an application to marine engine cylinder liners. Technometrics 2010, 52, 172–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezghani, S.; Demirci, I.; Yousfi, M.; El Mansori, M. Running-in wear modeling of honed surface for combustion engine cylinder liners. Wear 2013, 302, 1360–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koszalka, G.; Niewczas, A.; Guzik, M. Predicted and Actual Effect of Cylinder Liner Wear on the Blowby in a Truck Diesel Engine; SAE Technical Paper; SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Lubrecht, T.; Biboulet, N.; Dufils, J.; Lubrecht, A.A. Piston Ring Mixed Lubrication Model Including Real Geometry Using Analytical Correction Coefficients: Theory and Experimental Validation. Tribol. Lett. 2023, 71, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheeja, D.; Tay, B.; Lau, S.; Shi, X.; Ding, X. Structural and tribological characterization of multilayer ta-C films prepared by filtered cathodic vacuum arc with substrate pulse biasing. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2000, 132, 228–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.-Y.; Jang, Y.-J.; Tokoroyama, T.; Murashima, M.; Umehara, N. Effect of defects on wear behavior in ta-C coating prepared by filtered cathodic vacuum arc deposition. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2020, 105, 107789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dellis, P. Comparative Research in the Field of the Parametric Effect of Lubricant Cavitation Initiation and Development on Friction and Wear in Piston Ring and Cylinder Liner Assemblies. Lubricants 2024, 12, 460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.-Y.; Li, M.; Tian, T. Modeling Inertia-Driven Oil Transport Inside the Three-Piece Oil Control Ring of Internal Combustion Engines. Lubricants 2024, 12, 394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Tian, T. Sources and Destinations of Oil Leakage through TPOCR Based on 2D-LIF Observation and Modeling Analysis. Lubricants 2023, 11, 522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rovai, F.F.; Tomanik, E. Lubricant Viscosity Impact in Fuel Economy: Experimental Uncertainties Compensation. Lubricants 2025, 13, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, H.; Hu, H.; Luo, Y.; Hua, L.; Pan, J.; Zhu, G.; Jiao, Y.; Yan, J.; Wei, G. Impact of Mid-to-Low-Ash, Low-Viscosity Lubricants on Aftertreatment Systems after 210,000-Kilometer Real-World Road Endurance Trials. Lubricants 2024, 12, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stelljes, F.; Pohlmann-Tasche, F.; Dinkelacker, F. Experimental Investigation of a Free-Form Honed Cylinder Liner for Heavy-Duty Engines. Lubricants 2024, 12, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



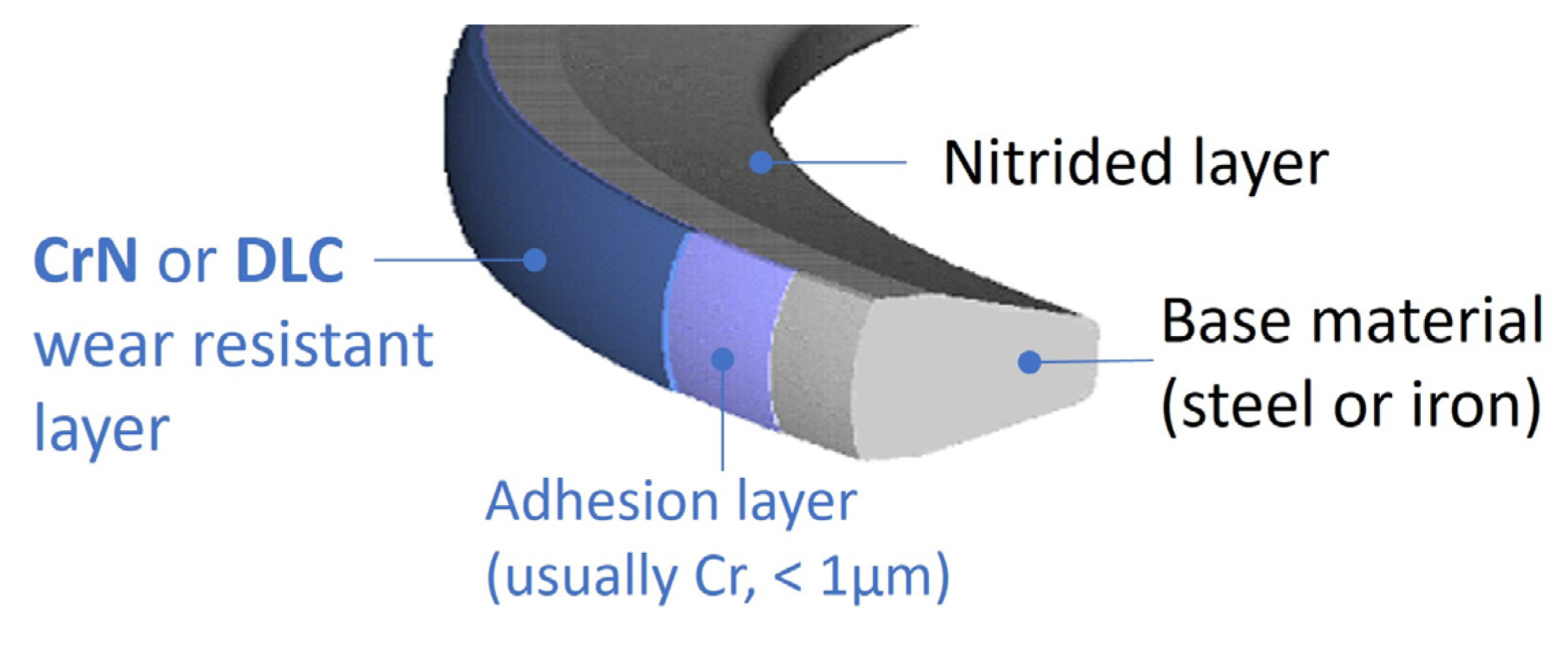

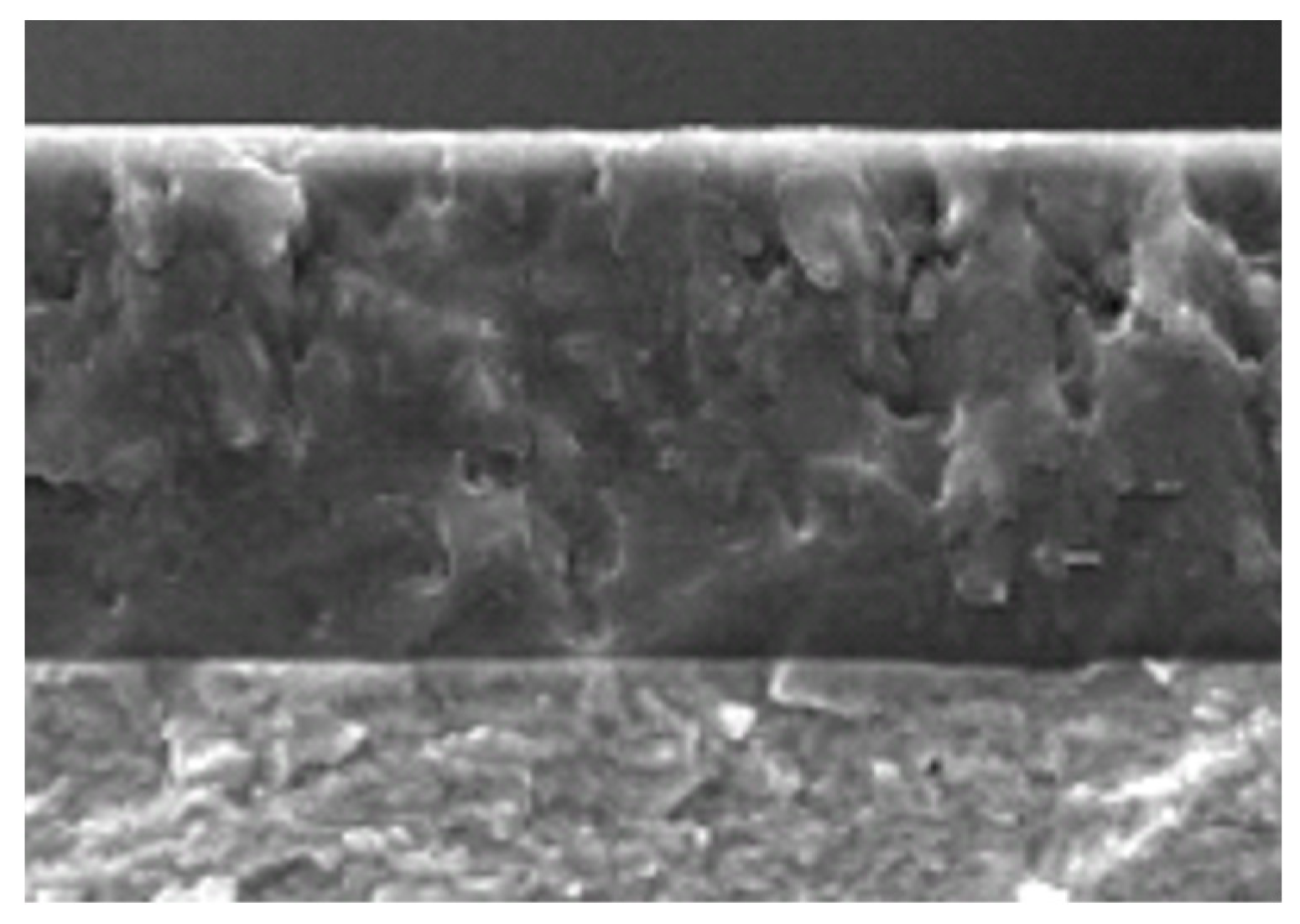
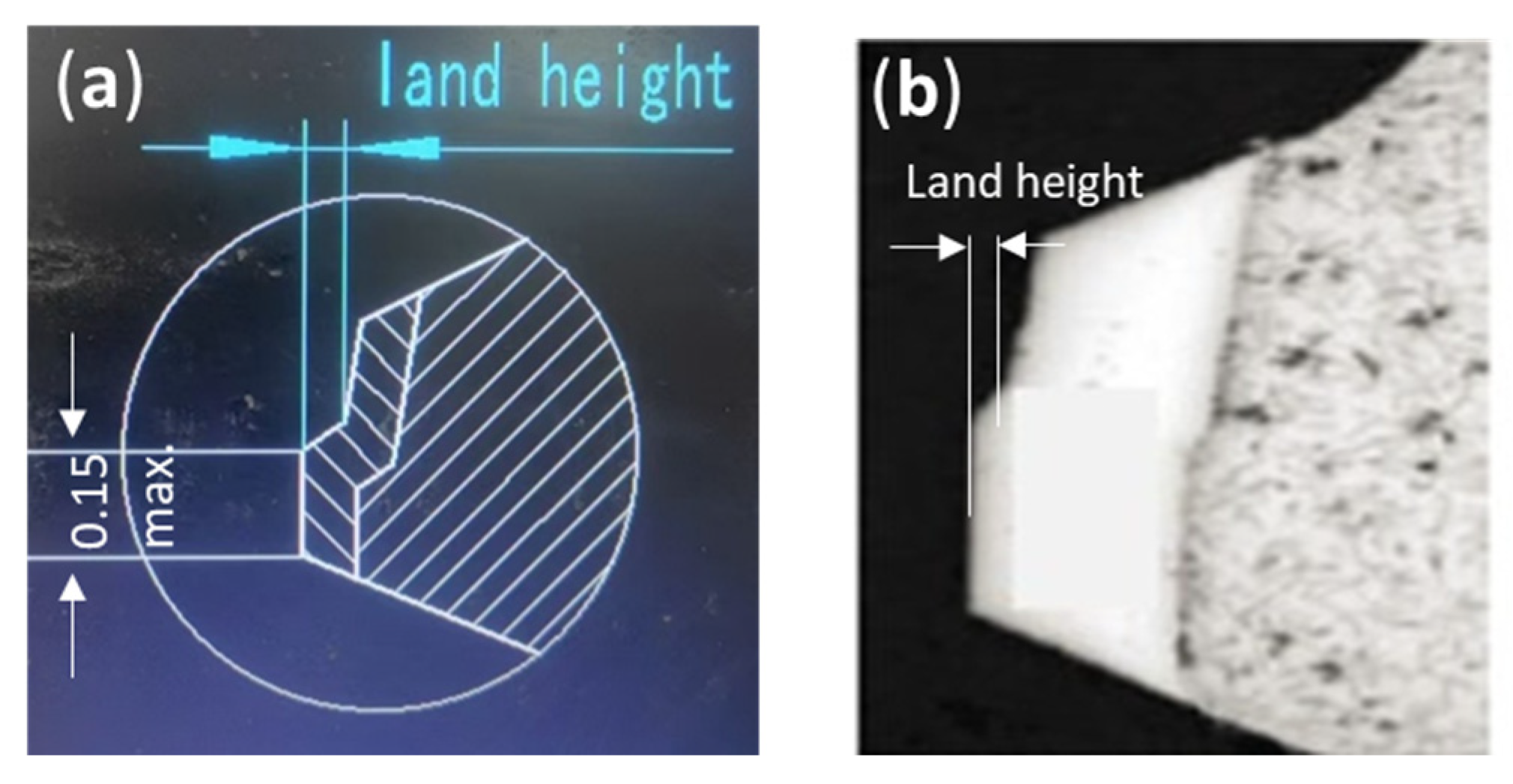
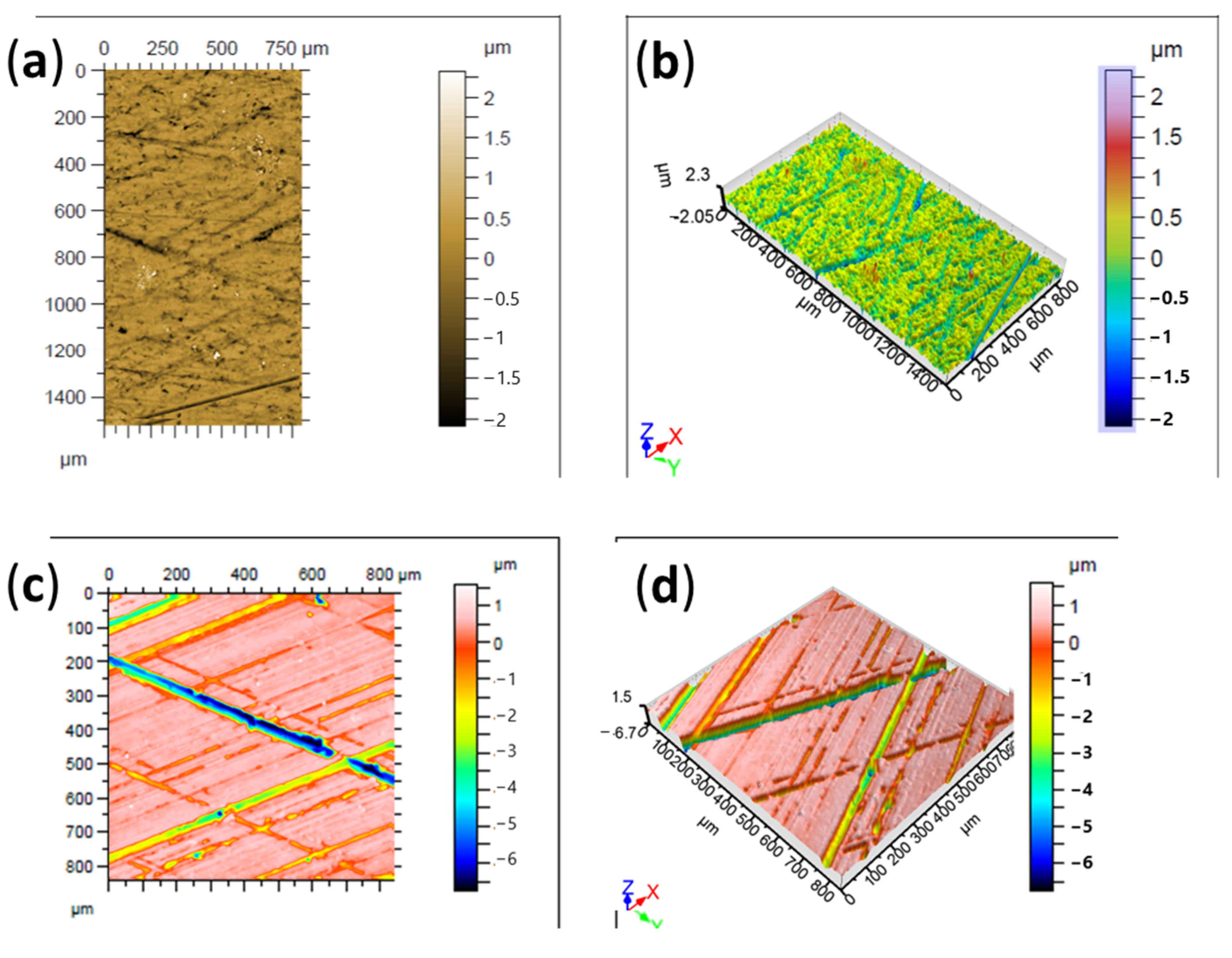







| Production | New | |
|---|---|---|
| Displacement volume [L] | 3.5 | 3.6 |
| Bore × stroke [mm] | 98 × 115 | 98 × 120 |
| Max. Power [kW] | 95 @ 2600 rpm | 118 @ 2400 rpm |
| Specific Power [kW/l] | 27.1 | 32.8 |
| Max. Torque [Nm] | 450 @ 2000 rpm | 550 @ 1700–1800 rpm |
| Cylinder | Chrome Coated | Cast Iron |
| Lubricant | 20W-50 | 20W-50 |
| Top | 2nd | OCR | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Coating | Nitrided | Phosphate | Nitrided |
| material | Steel | Cast Iron | Nodular Cast Iron |
| Axial width [mm] | 2.5 | 2.0 | 3.0 |
| Radial [mm] | 3.80 | 3.6 | 3.5 |
| type | Keystone | taper-faced | 2-piece |
| Tangential Force [N] | 19.6 | 14.5 | 30.0 |
| Top | 2nd | OCR | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Coating | CrN | Phosphate | ta-C, DLC |
| material | GNS | Cast iron | Nodular Cast Iron |
| Axial width [mm] | 2 | 2 | 3 |
| Radial [mm] | 3.55 | 4.0 | 2.54 |
| type | Keystone | taper-faced | 2-piece, “LKZ” profile |
| Tangential Force [N] | 15.1 | 15.9 | 41.8 |
| GNS | CrN | ta-C | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Deposition method | Gas Nitriding | PVD—Cathodic Arc | FCVA |
| Hardness [Hv] | 900 min. at 10 µm | 1100 min. | 1700–3500 |
| Thickness [µm], min. | 100 | 100 | 20 |
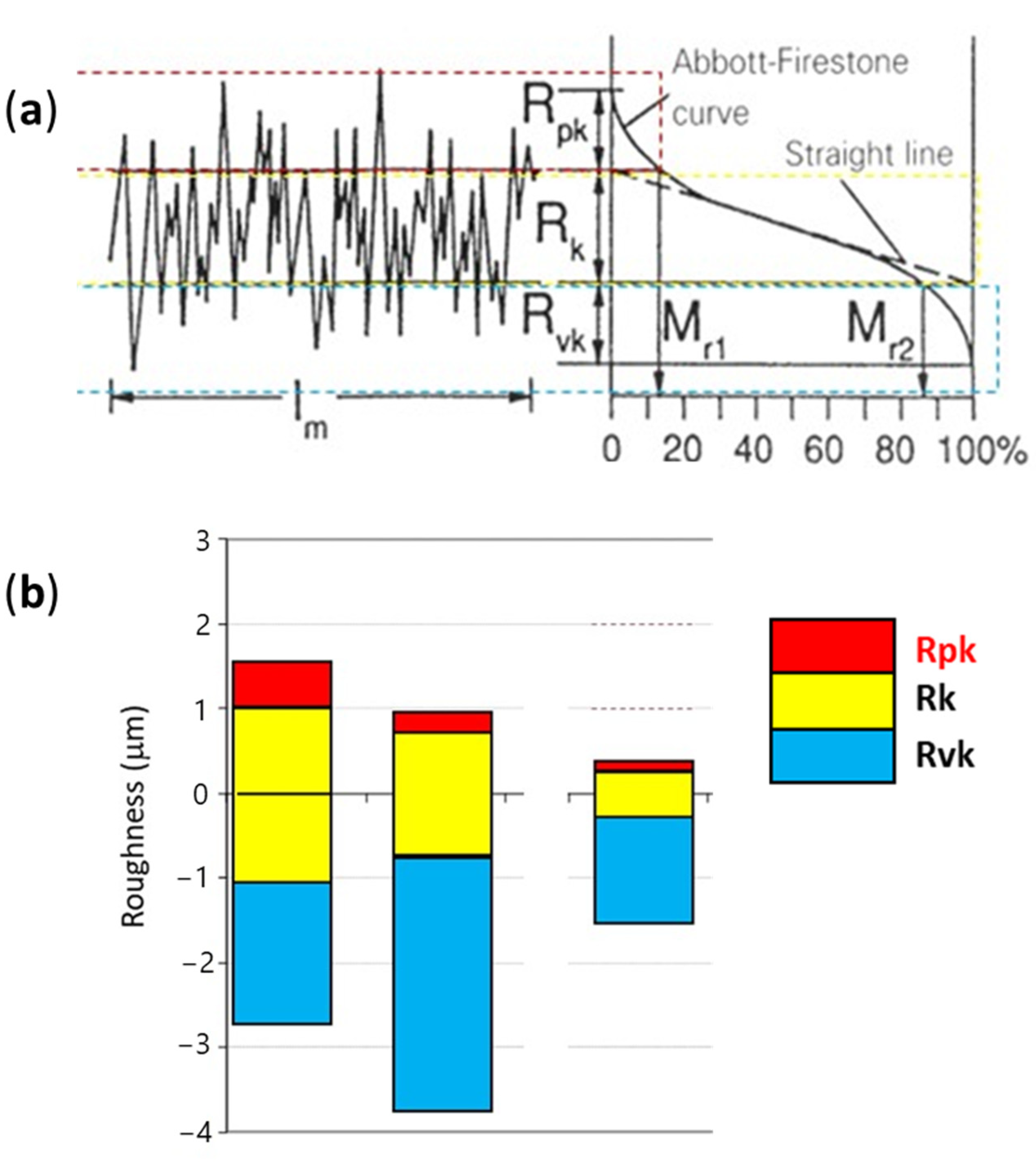
| Roughness [µm], max. | Rz 3.0 | Rz 1.6 | Rpk 0.2, Rk 0.6 |
| Chromed | Cast Iron | |
|---|---|---|
| Hardness, Hv | 800 min. | 400 |
| Sa [µm] | 0.28 | 0.62 |
| Spk [µm] | 0.21 | 0.19 |
| Sk [µm] | 0.66 | 0.28 |
| Svk [µm] | 0.77 | 2.62 |
| Mr1 [%] | 5.4 | 7.4 |
| Mr2 [%] | 81.3 | 72.6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
He, X.; Liu, B.; Tomanik, E.; Koszalka, G.; Orlova, A. Use of Advanced Piston Ring Coatings on Agricultural Engines. Lubricants 2025, 13, 239. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants13060239
He X, Liu B, Tomanik E, Koszalka G, Orlova A. Use of Advanced Piston Ring Coatings on Agricultural Engines. Lubricants. 2025; 13(6):239. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants13060239
Chicago/Turabian StyleHe, Xiaochao, Bang Liu, Eduardo Tomanik, Grzegorz Koszalka, and Anna Orlova. 2025. "Use of Advanced Piston Ring Coatings on Agricultural Engines" Lubricants 13, no. 6: 239. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants13060239
APA StyleHe, X., Liu, B., Tomanik, E., Koszalka, G., & Orlova, A. (2025). Use of Advanced Piston Ring Coatings on Agricultural Engines. Lubricants, 13(6), 239. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants13060239