Tribological Performance of Electrochemically Textured EN-GJS 400-15 Spheroidal Cast Iron
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Preparation
2.2. Tribological Experiment
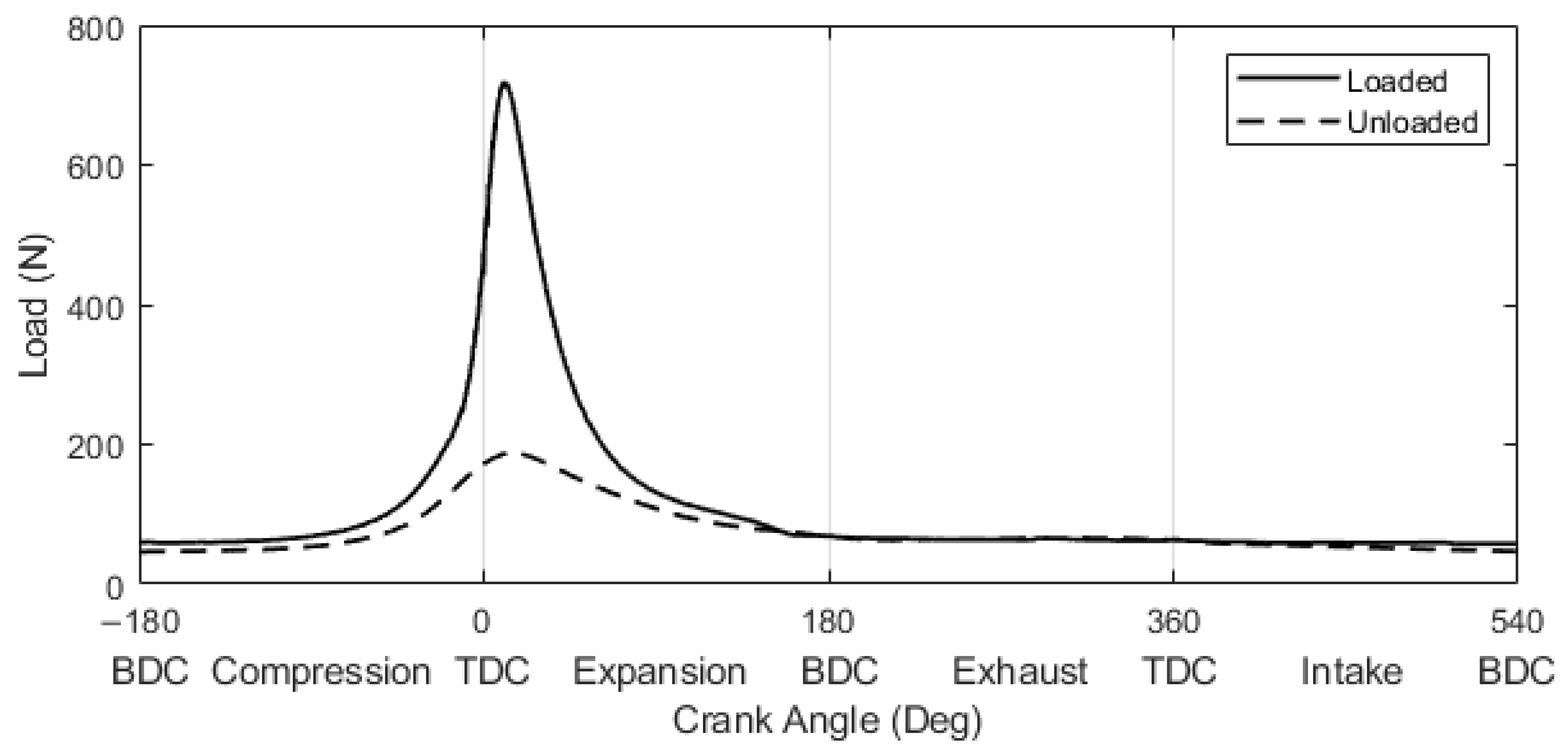
2.2.1. Testing Load
2.2.2. Tribological Testing
2.2.3. Surface Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
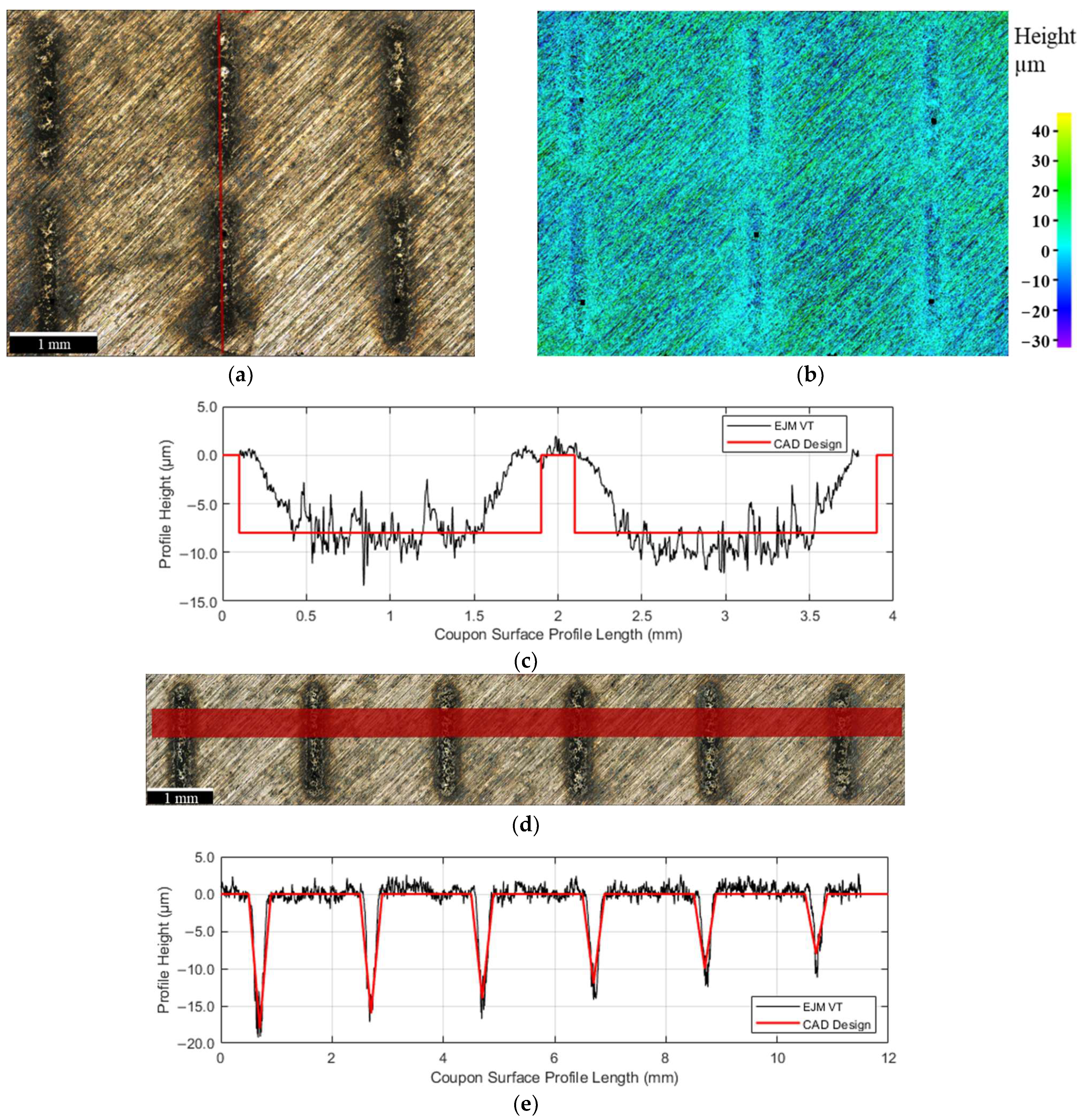
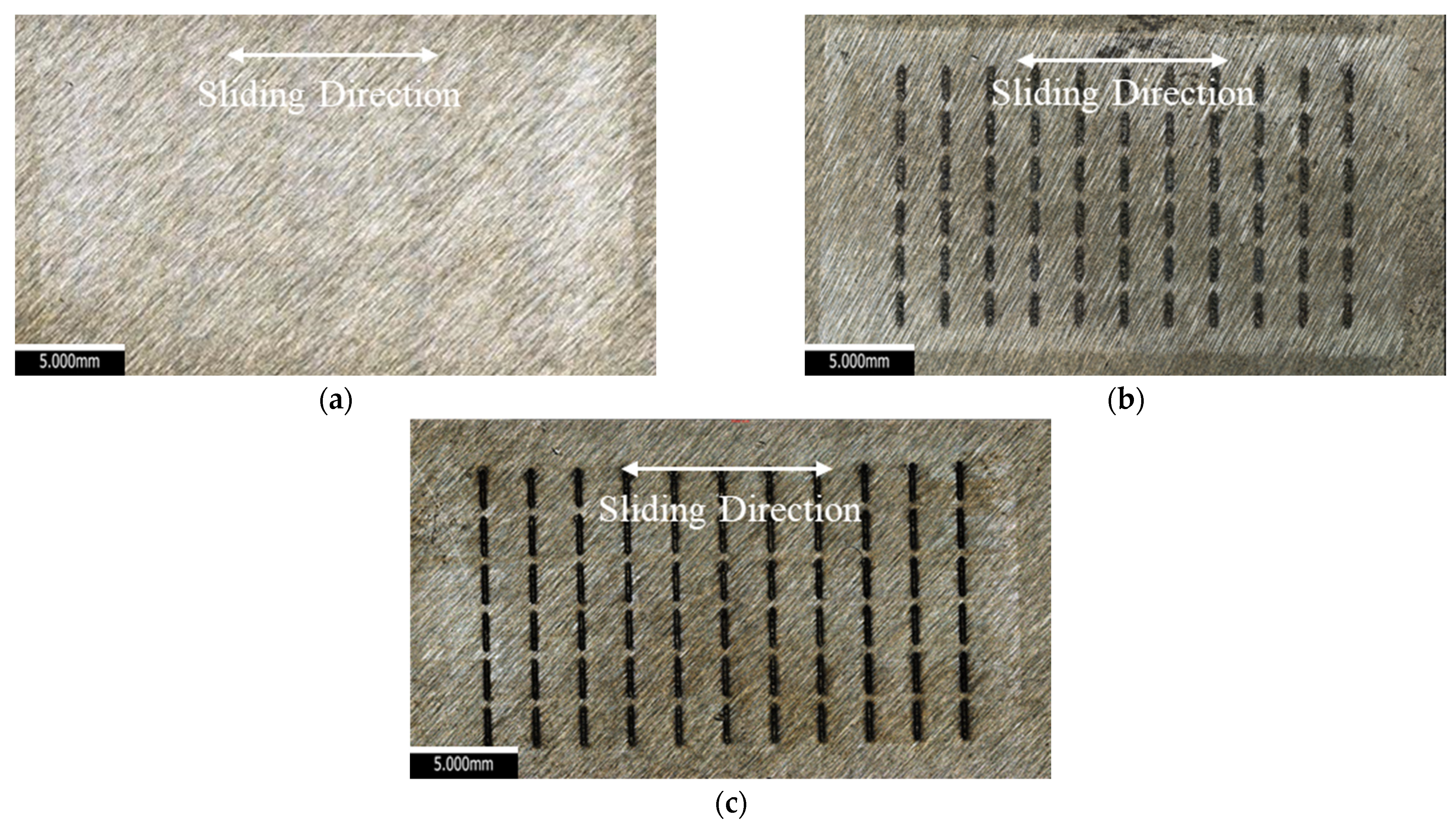
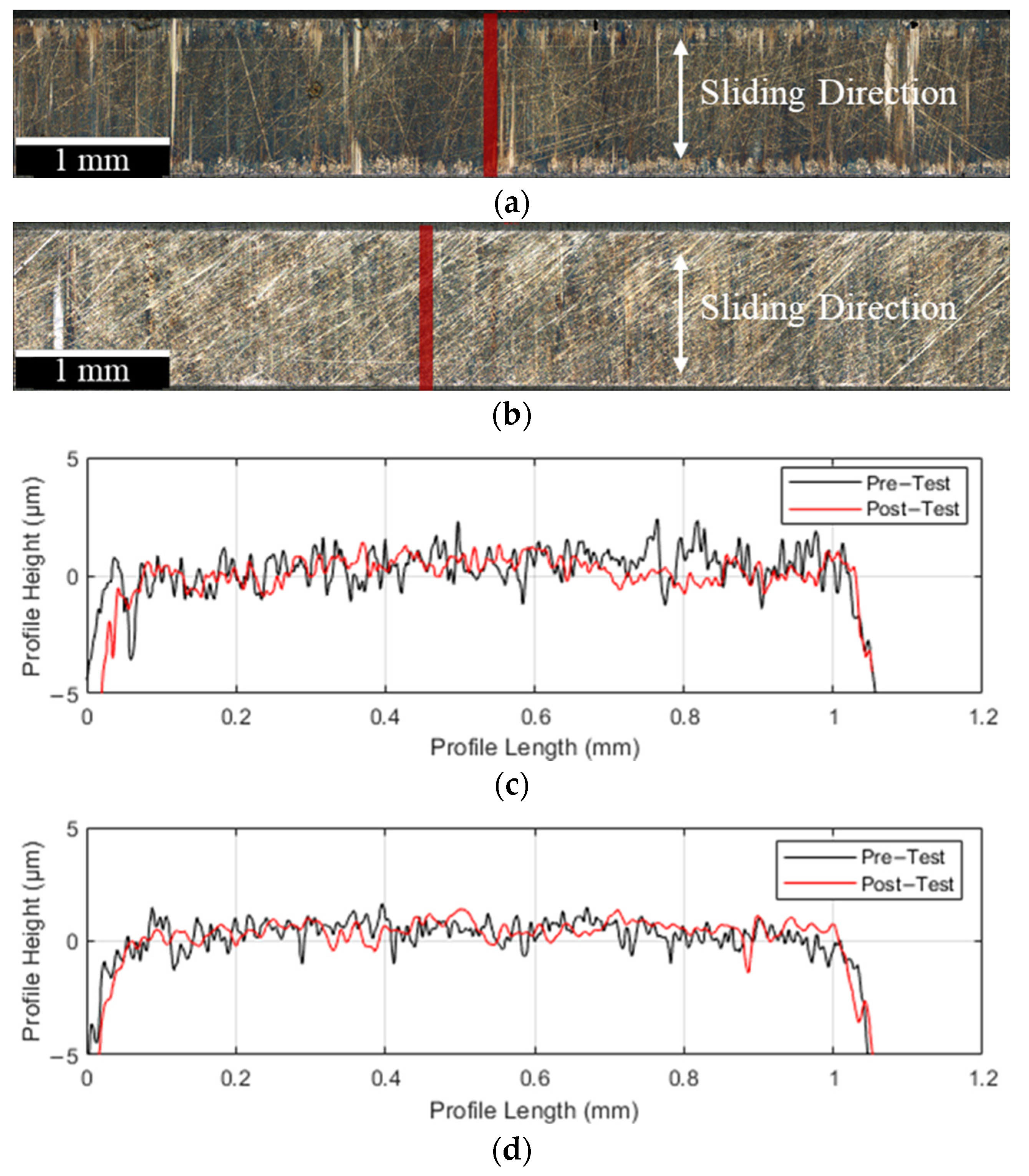
3.1. Surface Topography
3.1.1. Untextured Surface
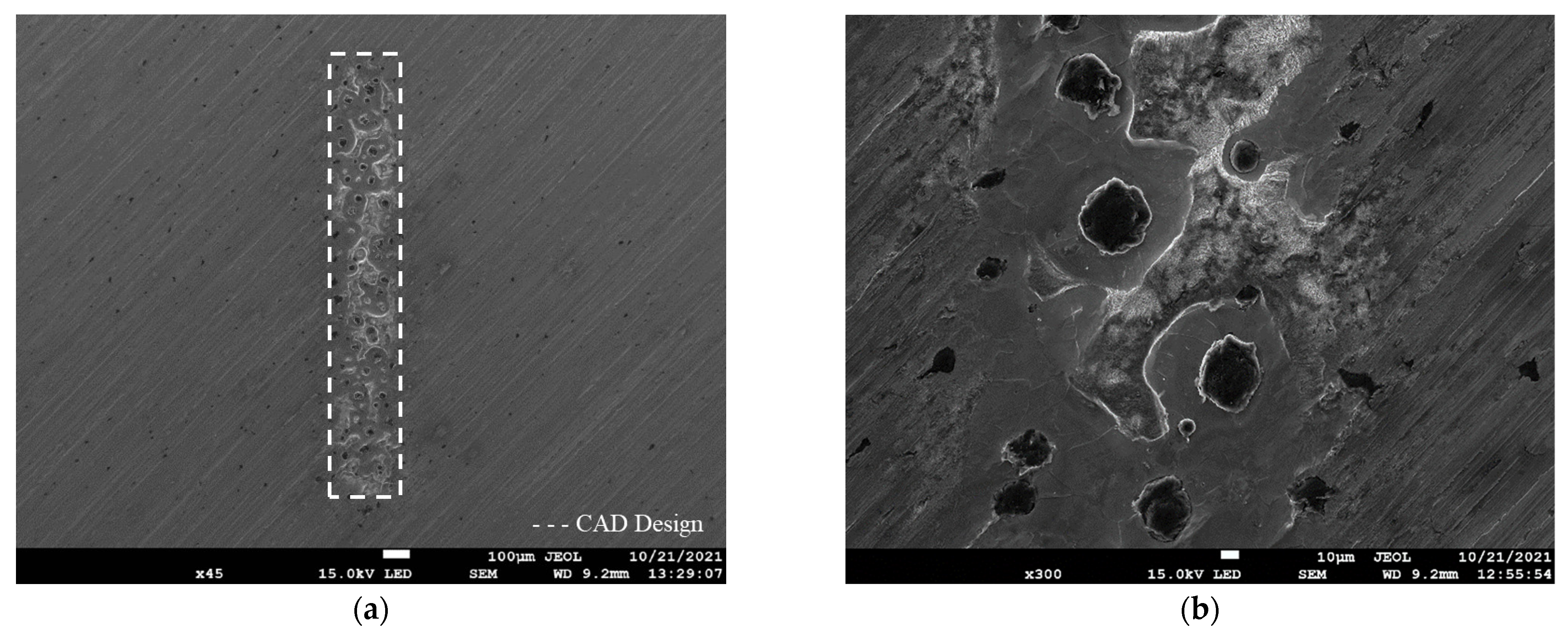
3.1.2. Textured Surface
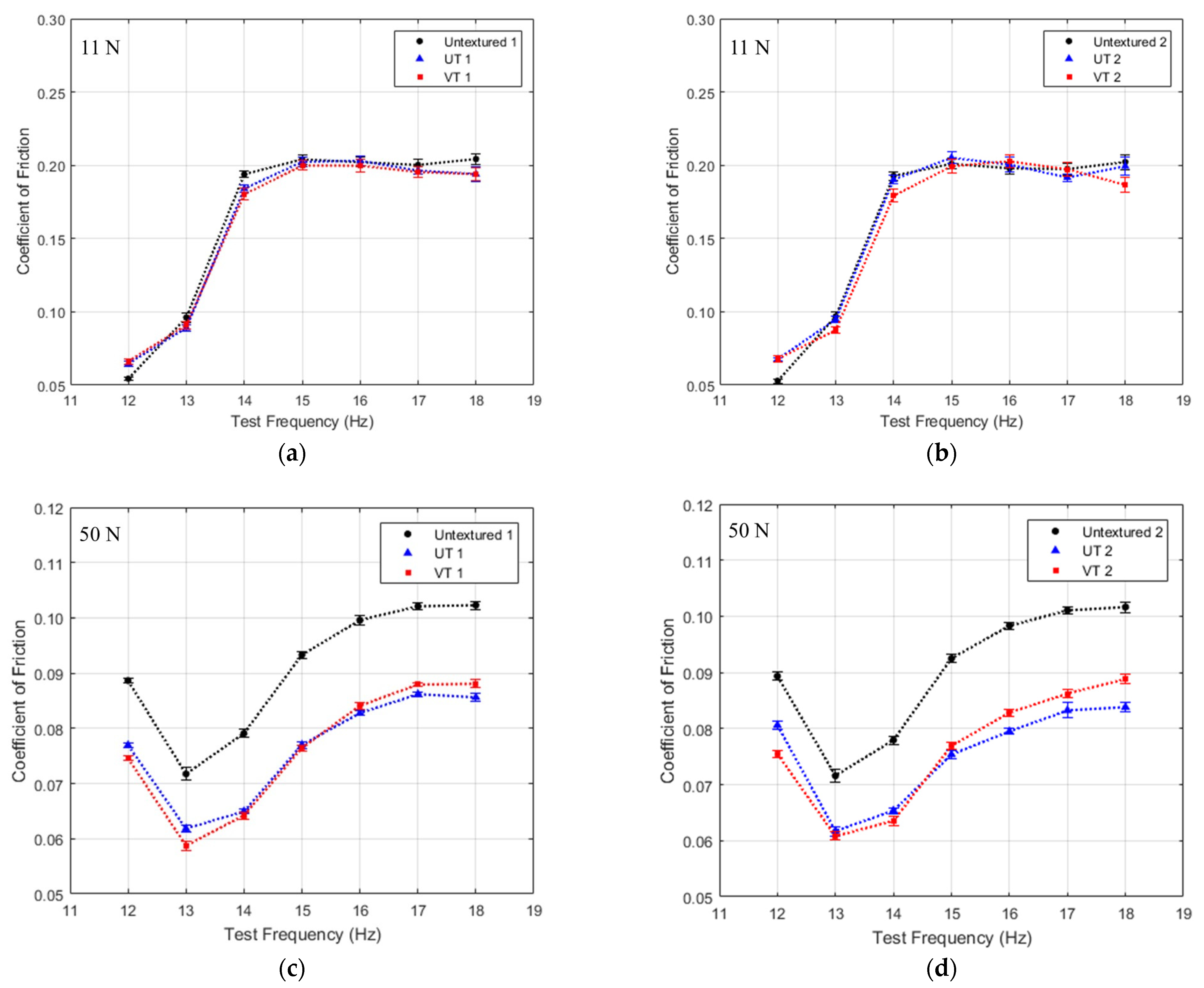
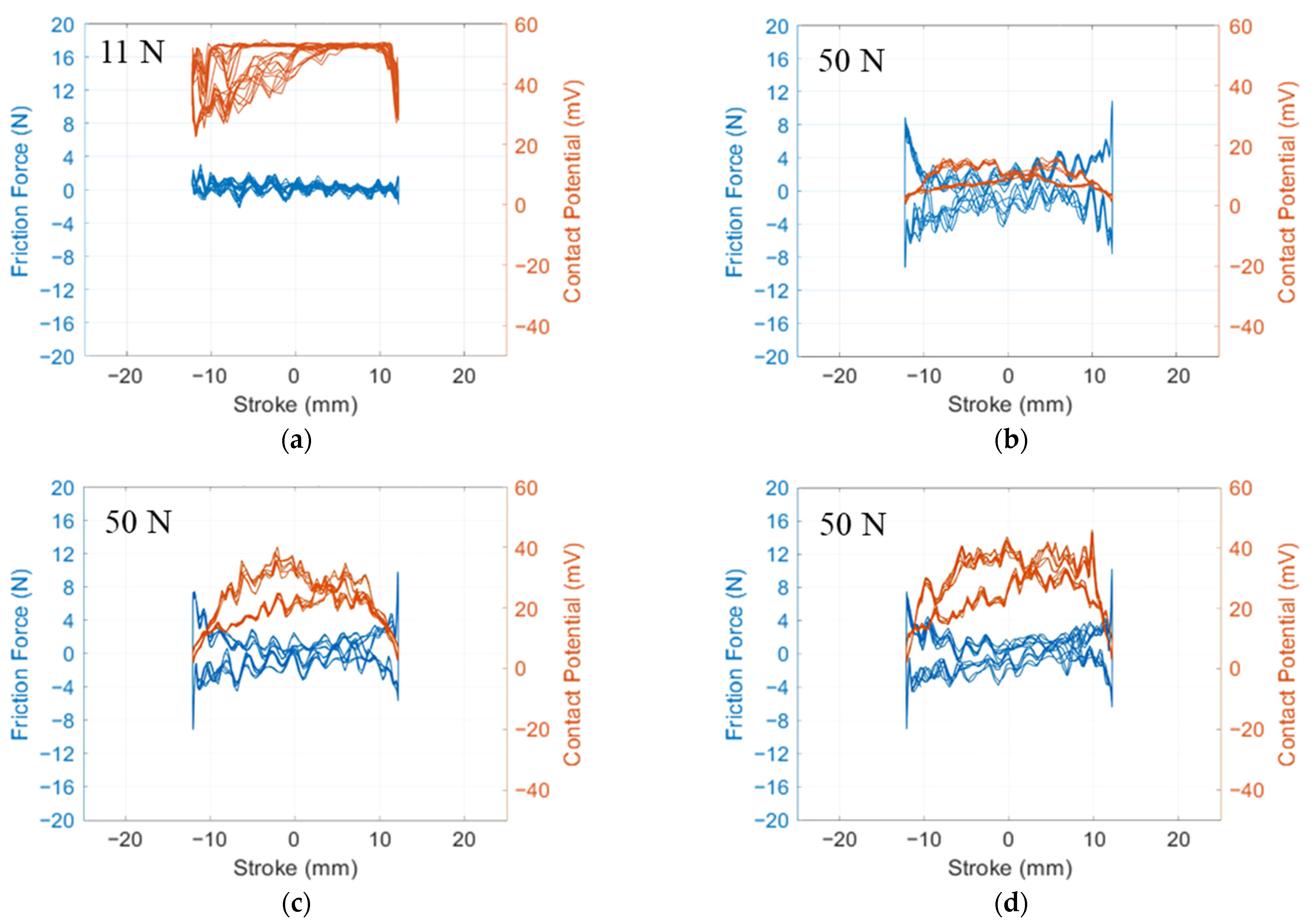
3.2. Tribological Results
3.2.1. Friction Behaviour
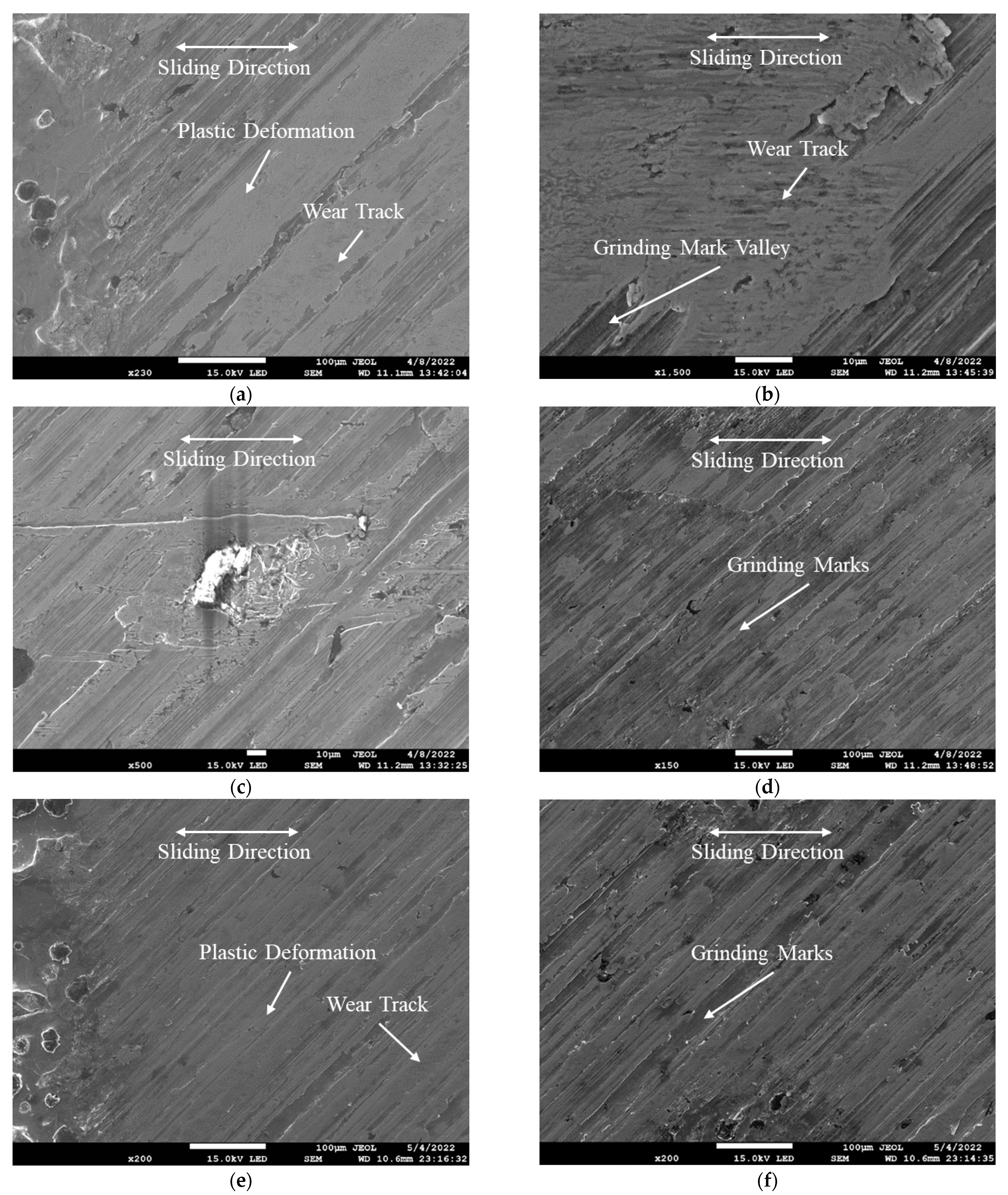
3.2.2. Coupon Surface Analysis
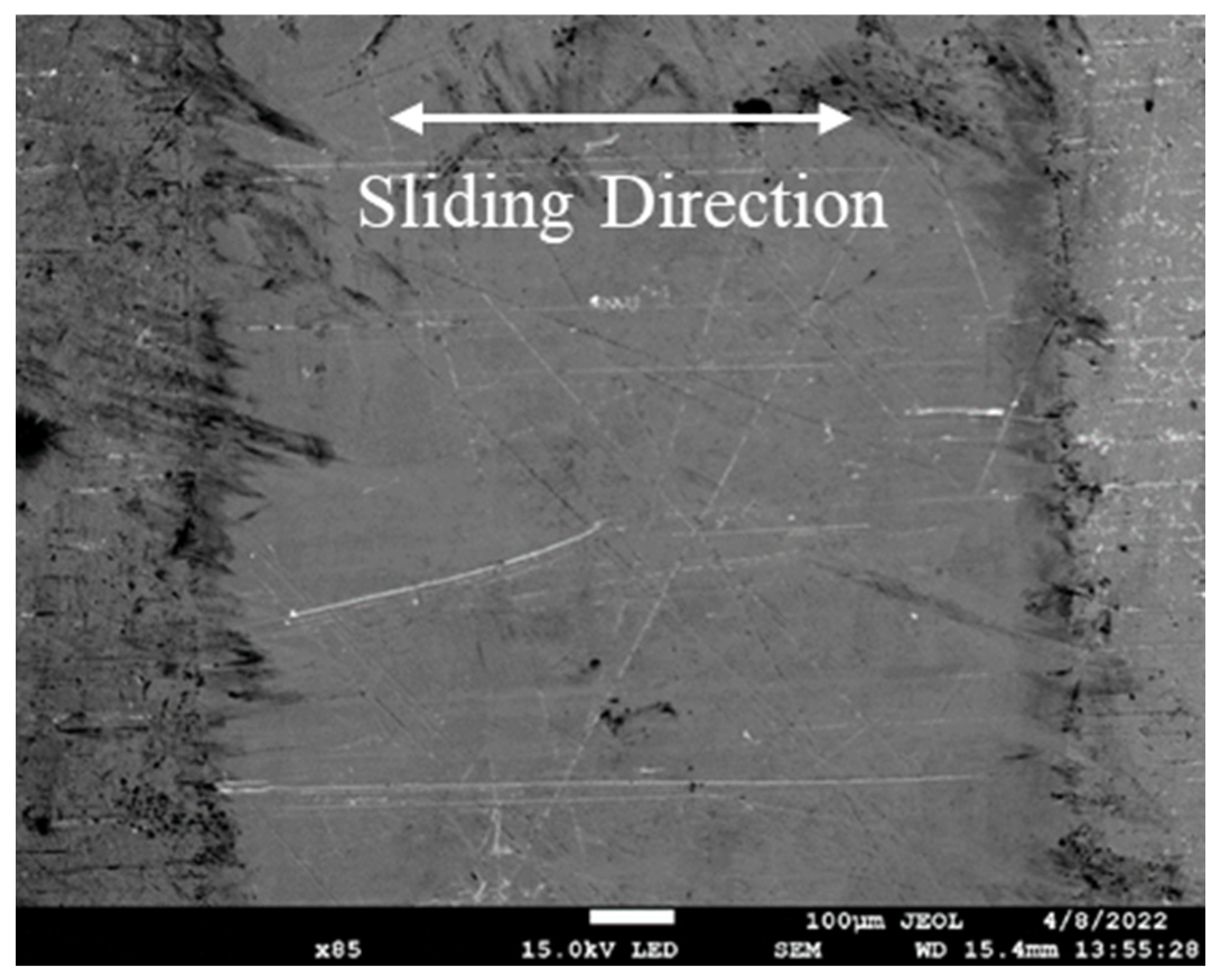
3.2.3. Countersurface Analysis
4. Summary
5. Conclusions
- EJM effectively produced precise uniform and variable groove patterns on cast iron surfaces without introducing thermal effects, burs, or lip formation.
- The selective dissolution process altered the surface topography, indicating that the final surface characteristics are influenced by the material composition, microstructure, and grain size.
- Textured surfaces exhibited a greater friction reduction at 50 N than at 11 N, with a consistent decrease of up to 18.8%.
- Optical and SEM analyses confirmed that plastic deformation and two-body abrasion were the primary wear mechanisms. Textured surfaces reduced wear by enhancing secondary lubrication and hydrodynamic effects.
- The VT surface proved more effective than the UT surface in reducing friction and wear under the mixed lubrication regime due to an improved secondary lubrication effect.
- Countersurface analysis revealed reduced wear when sliding against textured specimens, showing less two-body abrasion and no observable material transfer.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Coblas, D.G.; Fatu, A.; Maoui, A.; Hajjam, M. Manufacturing textured surfaces: State of art and recent developments. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part J J. Eng. Tribol. 2014, 229, 3–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, V.W.; Tung, S.C. Overview of automotive engine friction and reduction trends–Effects of surface, material, and lubricant-additive technologies. Friction 2016, 4, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakuda, M.; Yamauchi, Y.; Kanzaki, S.; Yasuda, Y. Effect of surface texturing on friction reduction between ceramic and steel materials under lubricated sliding contact. Wear 2003, 254, 356–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, J.C.; Kamps, T.J.; Lam, J.W.; Mitchell-Smith, J.; Clare, A.T. Tribological behaviour of an electrochemical jet machined textured Al-Si automotive cylinder liner material. Wear 2017, 376–377, 1611–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, J.C.; Cinti, S.; Kamps, T.J.; Mitchell-Smith, J.; Clare, A.T. Influence of contact area on the sliding friction and wear behaviour of an electrochemical jet textured Al-Si alloy. Wear 2019, 426–427, 1336–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varenberg, M.; Halperin, G.; Etsion, I. Different aspects of the role of wear debris in fretting wear. Wear 2002, 252, 902–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Jing, D.; Hu, J.; Ding, X.; Yao, Z. Numerical investigation of the tribological performance of micro-dimple textured surfaces under hydrodynamic lubrication. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2017, 8, 2324–2338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fesanghary, M.; Khonsari, M.M. On the optimum groove shapes for load-carrying capacity enhancement in parallel flat surface bearings: Theory and experiment. Tribol. Int. 2013, 67, 254–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etsion, I. Improving Tribological Performance of Mechanical Components by Laser Surface Texturing. Tribol. Lett. 2004, 17, 733–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Wang, X.; Zhou, F. Geometric Shape Effects of Surface Texture on the Generation of Hydrodynamic Pressure Between Conformal Contacting Surfaces. Tribol. Lett. 2009, 37, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlădescu, S.-C.; Medina, S.; Olver, A.V.; Pegg, I.G.; Reddyhoff, T. The Transient Friction Response of a Laser-Textured, Reciprocating Contact to the Entrainment of Individual Pockets. Tribol. Lett. 2016, 62, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghani, J.A.; Mohd Nasir, F.F.; Rahman, H.A.; Hakim Wan Zamri, W.F.; Kasim, M.S.; Muhamad, S.S. Computational fluid dynamic analysis on tribological performance under hydrodynamic lubrication of dimple textured surface produced using turning process. Wear 2021, 477, 203898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronen, A.; Etsion, I.; Kligerman, Y. Friction-Reducing Surface-Texturing in Reciprocating Automotive Components. Tribol. Trans. 2001, 44, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etsion, I.; Burstein, L. A Model for Mechanical Seals with Regular Microsurface Structure. Tribol. Trans. 1996, 39, 677–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etsion, I.; Kligerman, Y.; Halperin, G. Analytical and Experimental Investigation of Laser-Textured Mechanical Seal Faces. Tribol. Trans. 1999, 42, 511–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etsion, I. State of the Art in Laser Surface Texturing. J. Tribol. 2005, 127, 248–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etsion, I.; Sher, E. Improving fuel efficiency with laser surface textured piston rings. Tribol. Int. 2009, 42, 542–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etsion, I. Modeling of surface texturing in hydrodynamic lubrication. Friction 2013, 1, 195–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruzzone, A.A.G.; Costa, H.L.; Lonardo, P.M.; Lucca, D.A. Advances in engineered surfaces for functional performance. CIRP Ann. 2008, 57, 750–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, H.L.; Hutchings, I.M. Hydrodynamic lubrication of textured steel surfaces under reciprocating sliding conditions. Tribol. Int. 2007, 40, 1227–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, H.L.; Hutchings, I.M. Development of a maskless electrochemical texturing method. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2009, 209, 3869–3878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, H.L.; Hutchings, I.M. Some innovative surface texturing techniques for tribological purposes. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part J J. Eng. Tribol. 2014, 229, 429–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vladescu, S.-C.; Olver, A.V.; Pegg, I.G.; Reddyhoff, T. The effects of surface texture in reciprocating contacts—An experimental study. Tribol. Int. 2015, 82, 28–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlădescu, S.-C.; Medina, S.; Olver, A.V.; Pegg, I.G.; Reddyhoff, T. Lubricant film thickness and friction force measurements in a laser surface textured reciprocating line contact simulating the piston ring–liner pairing. Tribol. Int. 2016, 98, 317–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlădescu, S.-C.; Olver, A.V.; Pegg, I.G.; Reddyhoff, T. Combined friction and wear reduction in a reciprocating contact through laser surface texturing. Wear 2016, 358–359, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlădescu, S.-C.; Ciniero, A.; Tufail, K.; Gangopadhyay, A.; Reddyhoff, T. Optimization of Pocket Geometry for Friction Reduction in Piston–Liner Contacts. Tribol. Trans. 2017, 61, 522–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlădescu, S.-C.; Ciniero, A.; Tufail, K.; Gangopadhyay, A.; Reddyhoff, T. Looking into a laser textured piston ring-liner contact. Tribol. Int. 2017, 115, 140–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Profito, F.J.; Vlădescu, S.-C.; Reddyhoff, T.; Dini, D. Transient experimental and modelling studies of laser-textured micro-grooved surfaces with a focus on piston-ring cylinder liner contacts. Tribol. Int. 2017, 113, 125–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmer, M.; Vlădescu, S.-C.; Mattsson, L.; Fowell, M.; Reddyhoff, T. Shear-area variation: A mechanism that reduces hydrodynamic friction in macro-textured piston ring liner contacts. Tribol. Int. 2021, 161, 107067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gropper, D.; Wang, L.; Harvey, T.J. Hydrodynamic lubrication of textured surfaces: A review of modeling techniques and key findings. Tribol. Int. 2016, 94, 509–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gachot, C.; Rosenkranz, A.; Hsu, S.M.; Costa, H.L. A critical assessment of surface texturing for friction and wear improvement. Wear 2017, 372–373, 21–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhu, H.; Tang, W.; Ma, C.; Zhang, W. Development of the theoretical model for the optimal design of surface texturing on cylinder liner. Tribol. Int. 2012, 52, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arslan, A.; Masjuki, H.H.; Kalam, M.A.; Varman, M.; Mufti, R.A.; Mosarof, M.H.; Khuong, L.S.; Quazi, M.M. Surface Texture Manufacturing Techniques and Tribological Effect of Surface Texturing on Cutting Tool Performance: A Review. Crit. Rev. Solid State Mater. Sci. 2016, 41, 447–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryk, G.; Kligerman, Y.; Etsion, I. Experimental Investigation of Laser Surface Texturing for Reciprocating Automotive Components. Tribol. Trans. 2002, 45, 444–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kligerman, Y.; Etsion, I.; Shinkarenko, A. Improving Tribological Performance of Piston Rings by Partial Surface Texturing. J. Tribol. 2005, 127, 632–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovalchenko, A.; Ajayi, O.; Erdemir, A.; Fenske, G.; Etsion, I. The Effect of Laser Texturing of Steel Surfaces and Speed-Load Parameters on the Transition of Lubrication Regime from Boundary to Hydrodynamic. Tribol. Trans. 2004, 47, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natsu, W.; Ikeda, T.; Kunieda, M. Generating complicated surface with electrolyte jet machining. Precis. Eng. 2007, 31, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, L.R.R.; Costa, H.L. Tribological behavior of gray cast iron textured by maskless electrochemical texturing. Wear 2017, 376–377, 1601–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell-Smith, J.; Speidel, A.; Gaskell, J.; Clare, A.T. Energy distribution modulation by mechanical design for electrochemical jet processing techniques. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2017, 122, 32–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clare, A.T.; Speidel, A.; Bisterov, I.; Jackson-Crisp, A.; Mitchell-Smith, J. Precision enhanced electrochemical jet processing. CIRP Ann. 2018, 67, 205–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell-Smith, J.; Speidel, A.; Clare, A.T. Transitory electrochemical masking for precision jet processing techniques. J. Manuf. Process. 2018, 31, 273–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abedi, H.; Fareghi, A.; Saghafian, H.; Kheirandish, S. Sliding wear behavior of a ferritic–pearlitic ductile cast iron with different nodule count. Wear 2010, 268, 622–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamps, T.J.; Walker, J.C.; Wood, R.J.; Lee, P.M.; Plint, A.G. Reproducing automotive engine scuffing using a lubricated reciprocating contact. Wear 2015, 332–333, 1193–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamps, T.; Walker, J.; Wood, R.; Lee, P.; Plint, A. Scuffing mechanisms of EN-GJS 400-15 spheroidal graphite cast iron against a 52100 bearing steel in a PAO lubricated reciprocating contact. Wear 2017, 376, 1542–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, J.C.; Barnes, Z.; Shehata, A.; Jiang, P.; Kamps, T.J. Variable pressure scuffing of a flake graphite cast iron diesel cylinder liner. Tribol. Int. 2023, 179, 108155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, J.C.; Jones, H.G.; Kamps, T.J. Dynamic pressure scuffing initiation of a grade 250 flake graphite cast iron. Wear 2023, 523, 204864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Lv, Y.; Li, B.; Huang, R.; Yu, B.; Wang, W.; Li, C.; Xu, J. Reciprocating electrolyte jet with prefabricated-mask machining micro-dimple arrays on cast iron cylinder liner. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2019, 266, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Yu, B.; Ye, B.; Shen, Y.; Huang, R.; Du, F. Effects of Cast-Iron Surface Texturing on the Anti-Scuffing Performance under Starved Lubrication. Materials 2019, 12, 1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EN GJS 400-15; Spheroidal Graphite Iron Datasheet. West Yorkshire Steel: Leeds, UK, 2025.
- Mohamad, S.A.; Lu, X.; Zheng, Q. Numerical modeling of lubrication of piston ring of two-stroke marine diesel engine considering the effect of multi-scale grooves on the cylinder liner. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part J 2015, 229, 989–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.; Mohamad, S.A.; Lu, X.; Li, W. Numerical Analysis and Experimental Evaluation of Cylinder Liner Macro-Scale Surface Texturing. In Proceedings of the ASME 2015 Internal Combustion Engine Division Fall Technical Conference, Houston, TX, USA, 8–11 November 2015. [Google Scholar]
- ISO 4287:1997; Geometrical product specifications (GPS) — Surface texture: Profile method — Terms, definitions and surface texture parameters. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1997.
- ISO 16610-21:2011; Geometrical Product Specifications (GPS)—Filtration—Part 21: Linear profile filters: Gaussian filters. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011.
- Menezes, P.L.; Kailas, S.V. Role of surface texture and roughness parameters on friction and transfer film formation when UHMWPE sliding against steel. Biosurface Biotribology 2016, 2, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowell, M.; Olver, A.V.; Gosman, A.D.; Spikes, H.A.; Pegg, I. Entrainment and Inlet Suction: Two Mechanisms of Hydrodynamic Lubrication in Textured Bearings. J. Tribol. 2006, 129, 336–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilhena, L.; Sedlaček, M.; Podgornik, B.; Rek, Z.; Žun, I. CFD Modeling of the Effect of Different Surface Texturing Geometries on the Frictional Behavior. Lubricants 2018, 6, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahlin, F.; Glavatskih, S.B.; Almqvist, T.r.; Larsson, R. Two-Dimensional CFD-Analysis of Micro-Patterned Surfaces in Hydrodynamic Lubrication. J. Tribol. 2005, 127, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Zhu, H. An optimum design model for textured surface with elliptical-shape dimples under hydrodynamic lubrication. Tribol. Int. 2011, 44, 987–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Ni, H.; Chen, H.; Wang, P. Numerical simulation and experimental investigation on tribological performance of micro-dimples textured surface under hydrodynamic lubrication. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2019, 163, 105095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saurabh, A.; Joshi, K.; Manoj, A.; Verma, P.C. Process Optimization of Automotive Brake Material in Dry Sliding Using Taguchi and ANOVA Techniques for Wear Control. Lubricants 2022, 10, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gahr, K.-H.Z. Chapter 4 Classification of Wear Processes. In Tribology Series; Gahr, K.-H.Z., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1987; Volume 10, pp. 80–131. [Google Scholar]
- Stachowiak, G.W.; Batchelor, A.W. Chapter 14 Fatigue Wear. In Engineering Tribology, 4th ed.; Stachowiak, G.W., Batchelor, A.W., Eds.; Butterworth-Heinemann: Boston, MA, USA, 2014; pp. 621–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
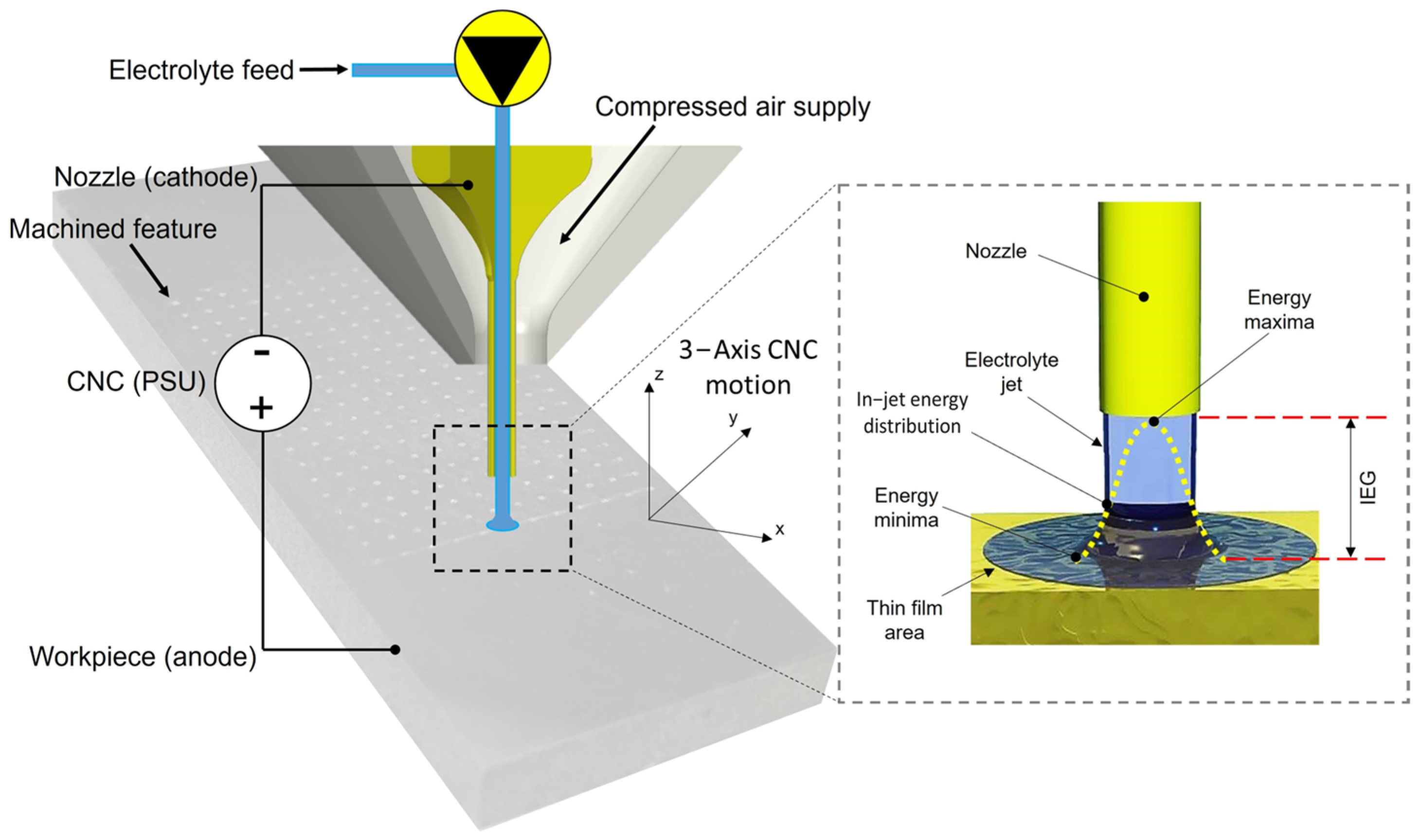





| Nominal composition | C | 3.4–3.85 |
| Si | 2.3–3.1 | |
| Mn | 0.1–0.3 | |
| P | ≤0.1 | |
| S | ≤0.02 | |
| Mg | ≤0.07 | |
| Fe | Bal. | |
| Mechanical properties | Tensile strength (N/mm2) | 400 |
| Elongation (%) | 15 | |
| Hardness (HB) | 120–180 |
| Electrolyte | NaCl @ 2.3 mol/L |
| Standoff | 500 µm |
| Nozzle ID | 150 µm |
| Current density | 288 Acm−2 |
| Flow rate | 80 mL/min |
| Translation speed | 50 mm/min |
| Sample | (µm) | (µm) | (mm) | (mm) | (mm) | Feature volume (mm3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UT | 8 ± 2.5 | 420 ± 27 | 1.8 ± 0.15 | 2 ± 0.047 | 2 ± 0.035 | 0.0030 |
| VT | 18 ± 2.4, | 420 ± 22 | 1.8 ± 0.17 | 2 ± 0.037 | 2 ± 0.045 | 0.0068, |
| 16 ± 2.4, | 0.0060, | |||||
| 14 ± 2.5, | 0.0053, | |||||
| 12 ± 1.9, | 0.0045, | |||||
| 10 ± 1.0, | 0.0038, | |||||
| 8 ± 2.5 | 0.0030 |
| Position | Stroke Reversals | Midstroke | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre/Post-Test | Pre (µm) | Post (µm) | Pre (µm) | Post (µm) | |
| 11 N | Untextured | 1.681 ± 0.034 | 1.447 ± 0.028 | 1.681 ± 0.034 | 1.484 ± 0.030 |
| UT | 1.458 ± 0.032 | 1.310 ± 0.029 | 1.458 ± 0.032 | 1.360 ± 0.034 | |
| VT | 1.447 ± 0.023 | 1.412 ± 0.039 | 1.460 ± 0.027 | 1.452 ± 0.030 | |
| 50 N | Untextured | 1.681 ± 0.034 | 1.084 ± 0.031 | 1.681 ± 0.034 | 1.404 ± 0.029 |
| UT | 1.458 ± 0.032 | 1.014 ± 0.040 | 1.458 ± 0.032 | 1.201 ± 0.050 | |
| VT | 1.447 ± 0.023 | 1.113 ± 0.044 | 1.460 ± 0.027 | 1.256 ± 0.034 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiang, P.; Mitchell-Smith, J.; Walker, J.C. Tribological Performance of Electrochemically Textured EN-GJS 400-15 Spheroidal Cast Iron. Lubricants 2025, 13, 203. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants13050203
Jiang P, Mitchell-Smith J, Walker JC. Tribological Performance of Electrochemically Textured EN-GJS 400-15 Spheroidal Cast Iron. Lubricants. 2025; 13(5):203. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants13050203
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiang, Peng, Jonathon Mitchell-Smith, and John Christopher Walker. 2025. "Tribological Performance of Electrochemically Textured EN-GJS 400-15 Spheroidal Cast Iron" Lubricants 13, no. 5: 203. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants13050203
APA StyleJiang, P., Mitchell-Smith, J., & Walker, J. C. (2025). Tribological Performance of Electrochemically Textured EN-GJS 400-15 Spheroidal Cast Iron. Lubricants, 13(5), 203. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants13050203






