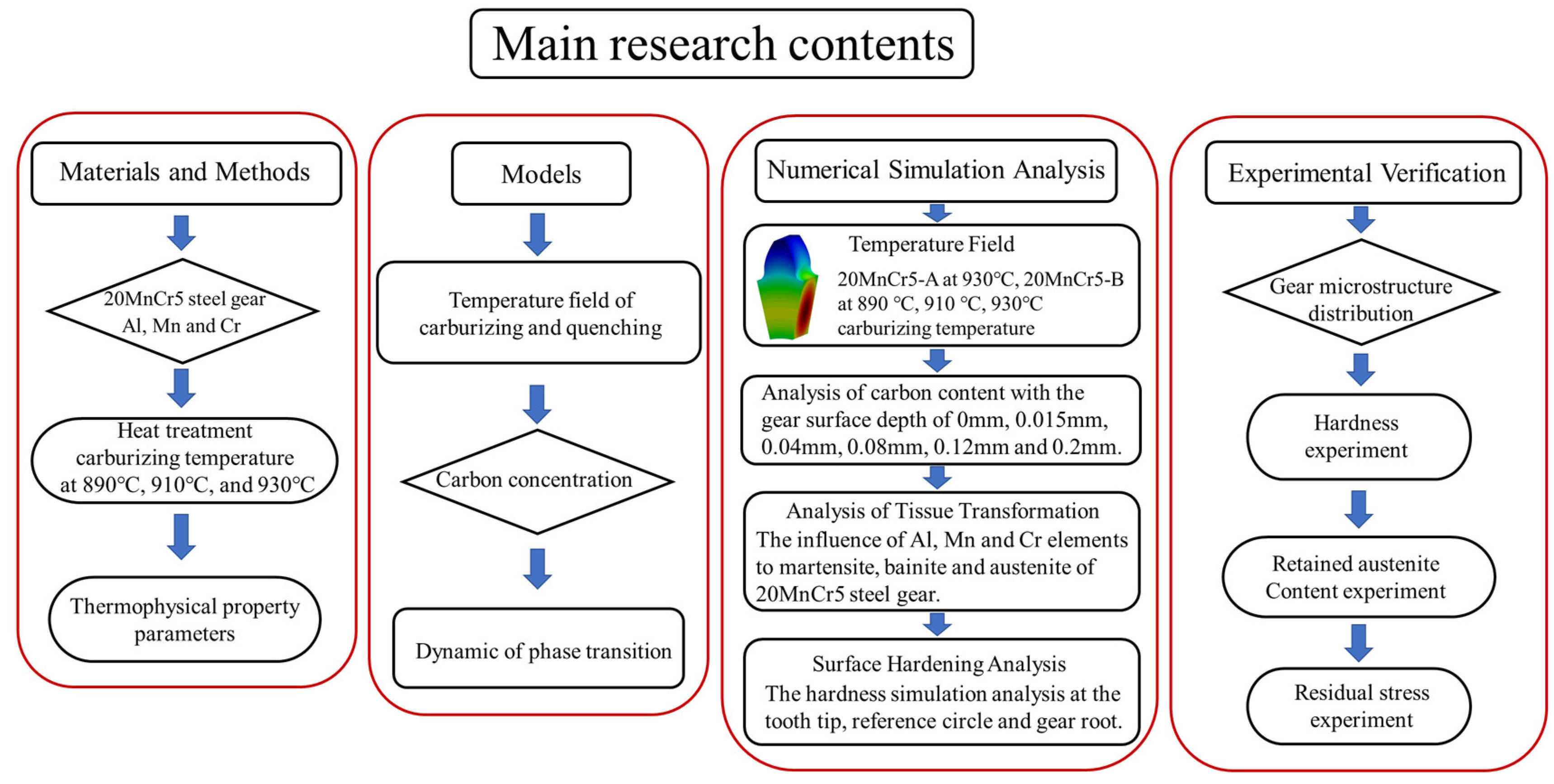
Study of the Effect of Regulating Alloying Elements and Optimizing Heat Treatment Processes on the Microstructure Properties of 20MnCr5 Steel Gears
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
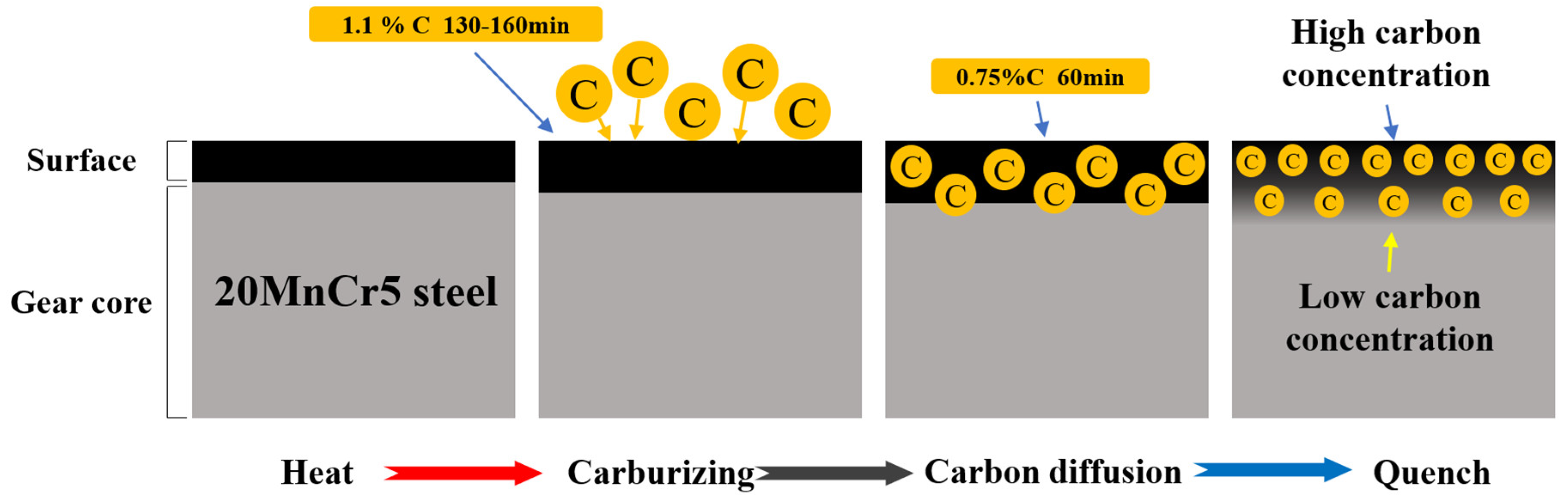
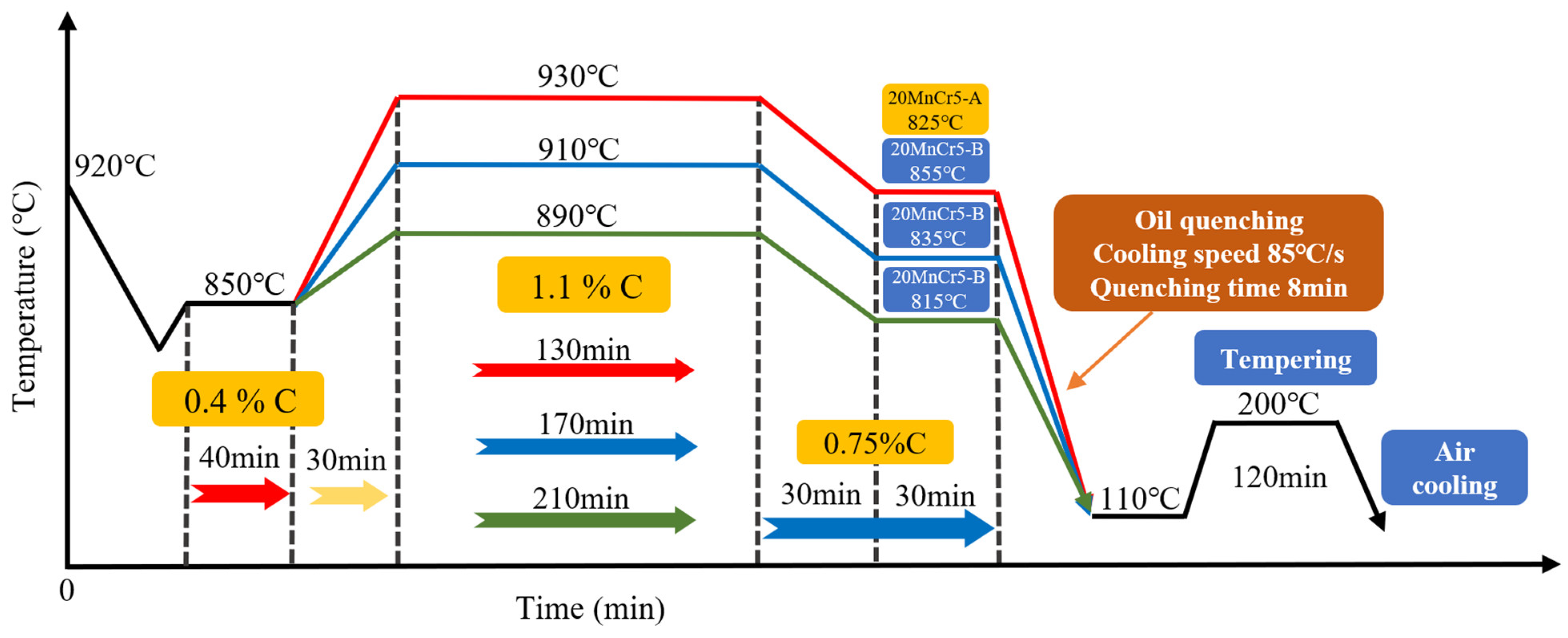
2.1. Heat Treatment
2.2. Materials
2.2.1. Chemical Composition of Materials
2.2.2. Material Phase Change Parameters
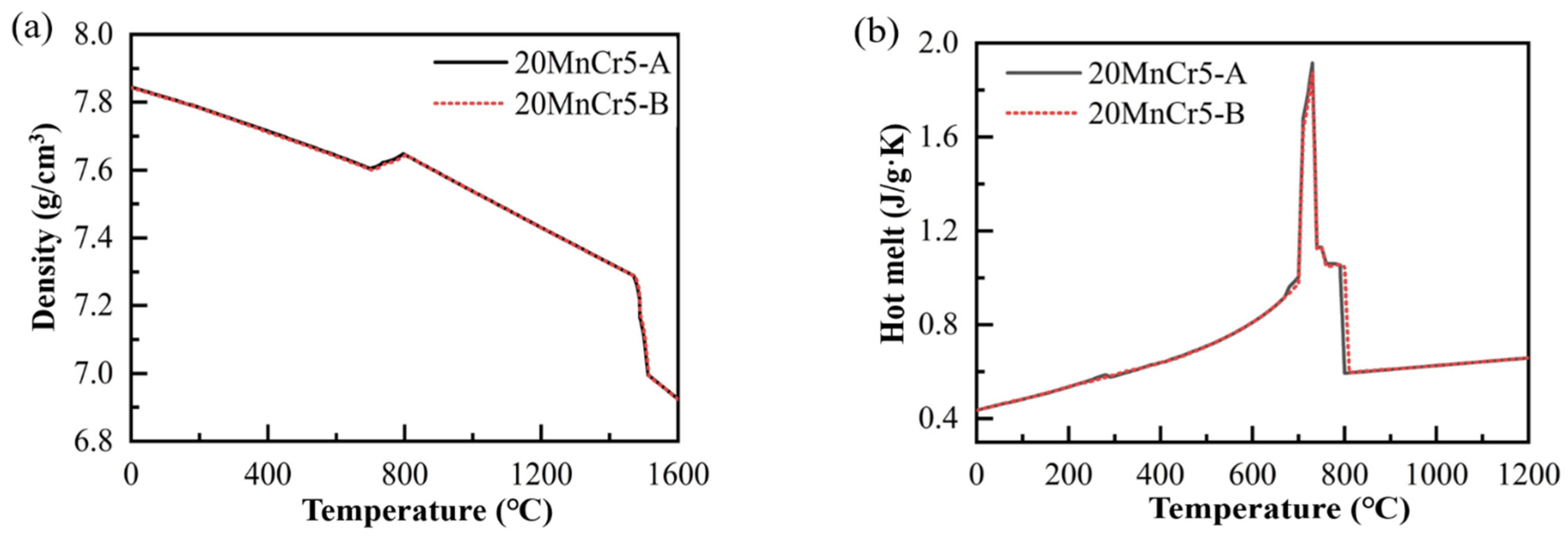
2.2.3. Thermophysical Property Parameters
3. Models
3.1. Temperature Field of Carburizing and Quenching
3.2. Carbon Concentration
3.3. Dynamic of Phase Transition
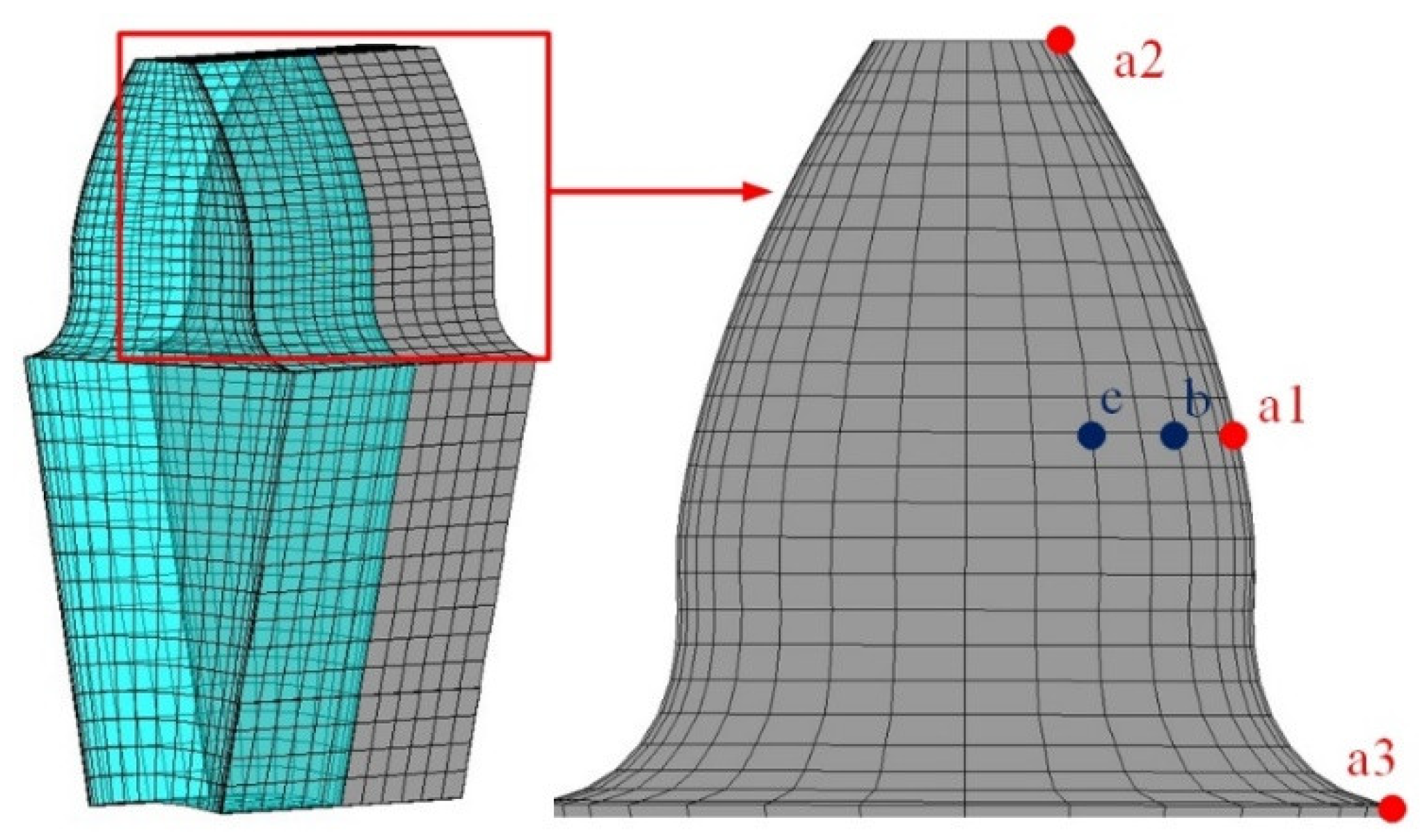
4. Numerical Simulation Analysis
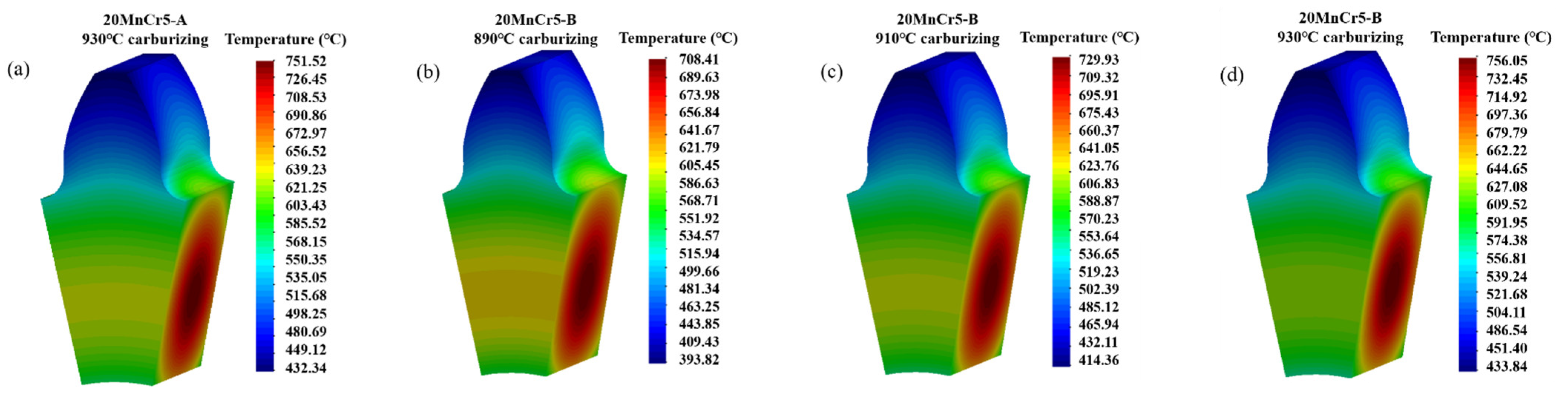
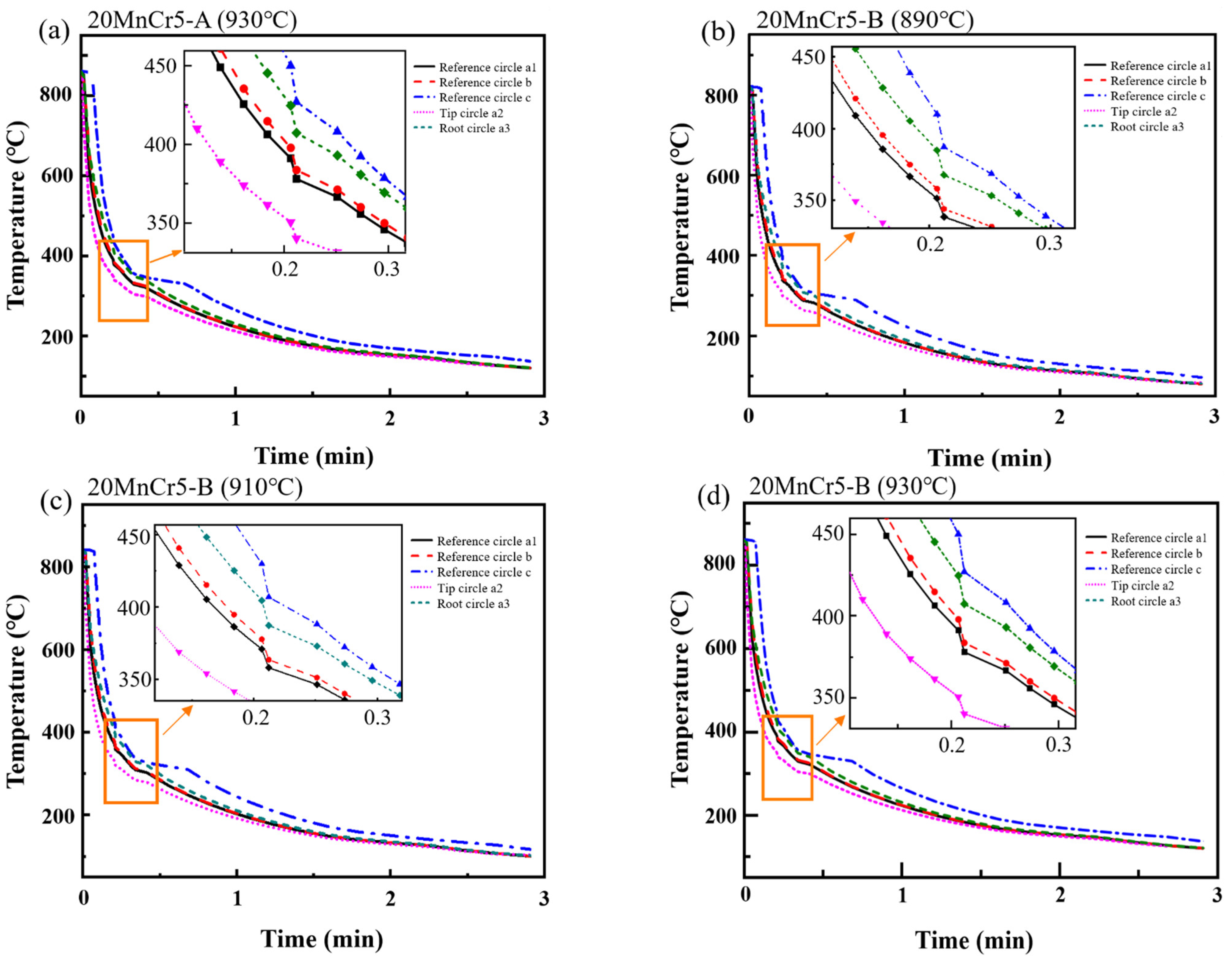
4.1. Temperature Field
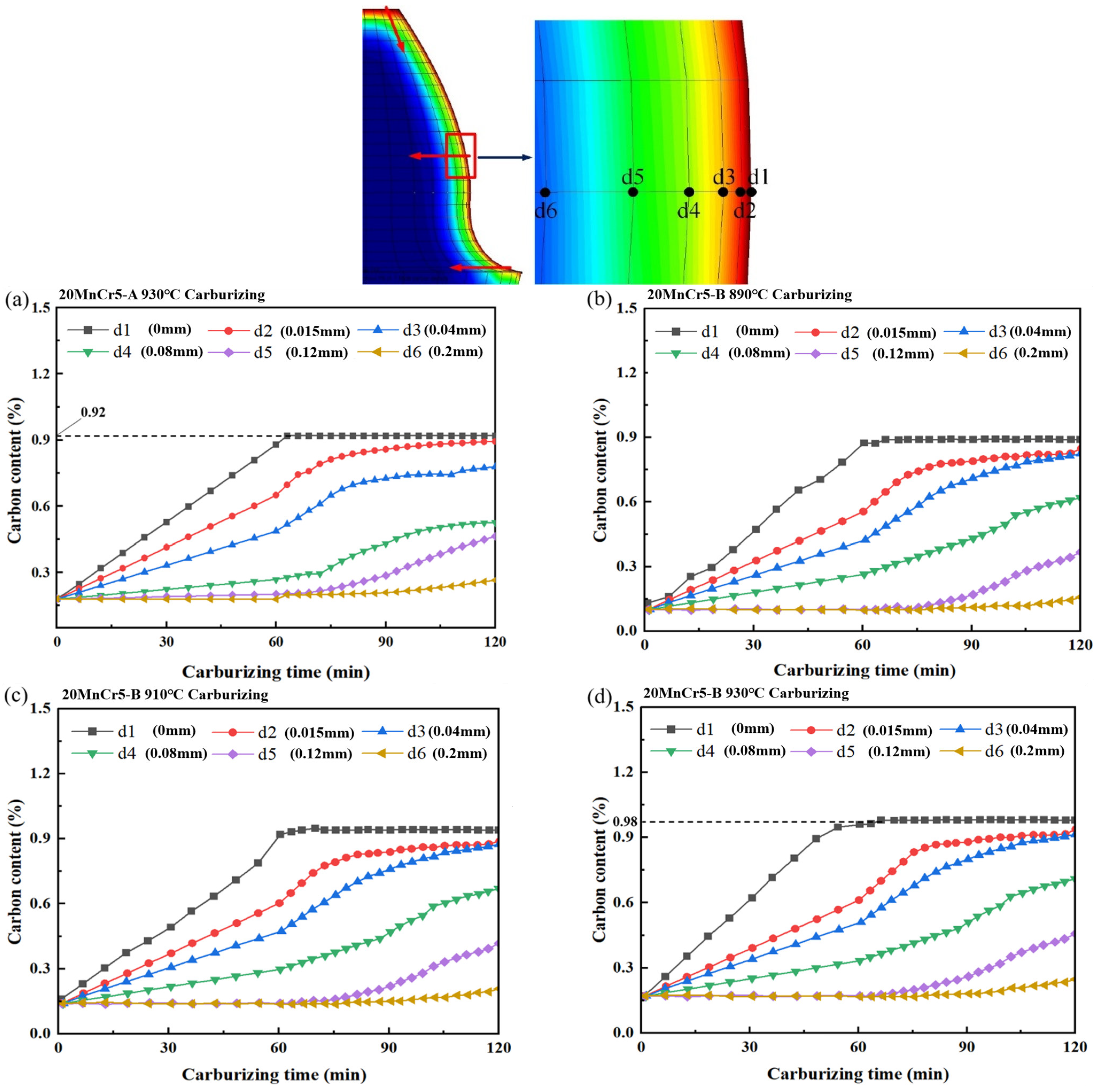
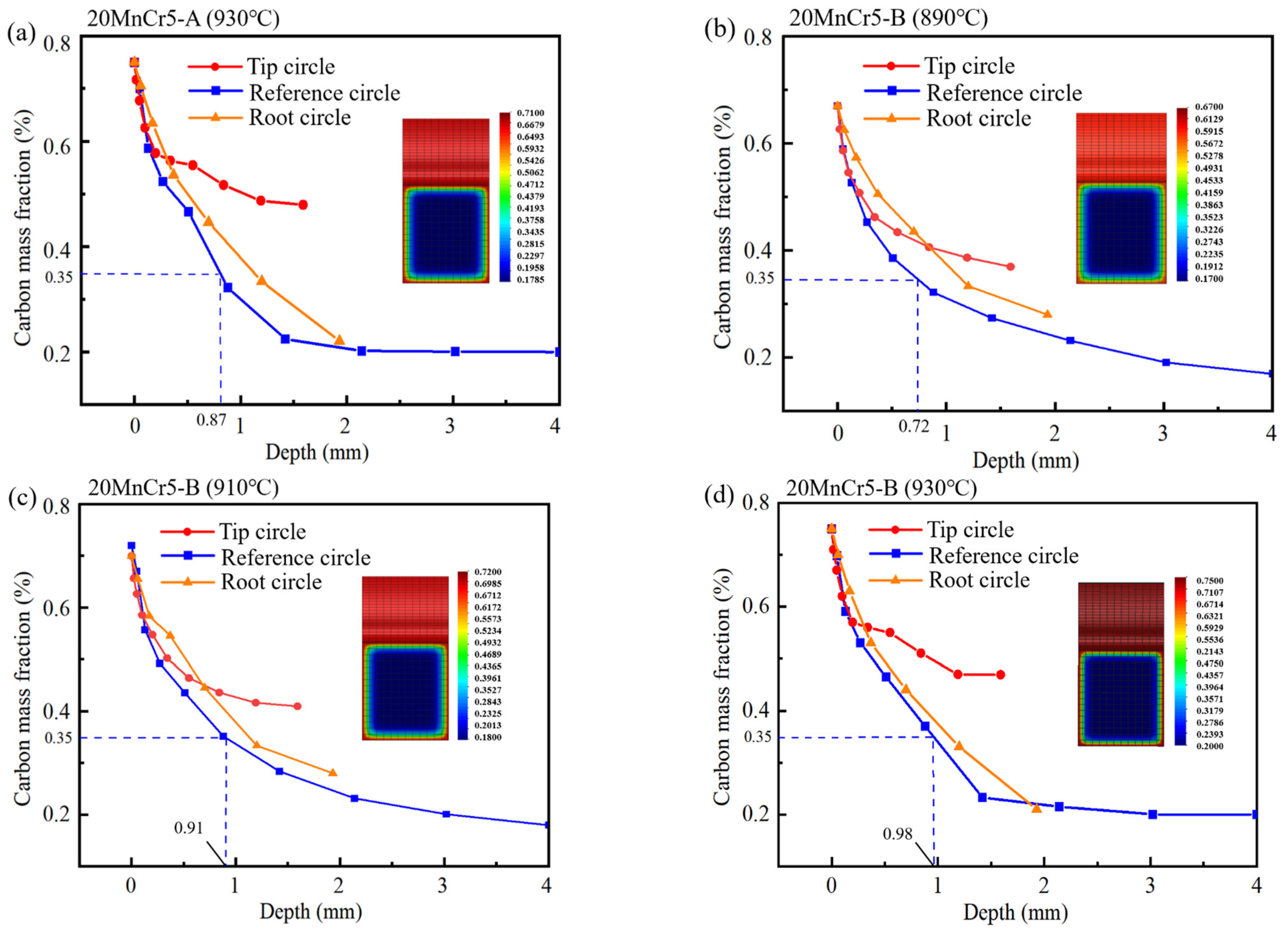
4.2. Analysis of Carbon Content
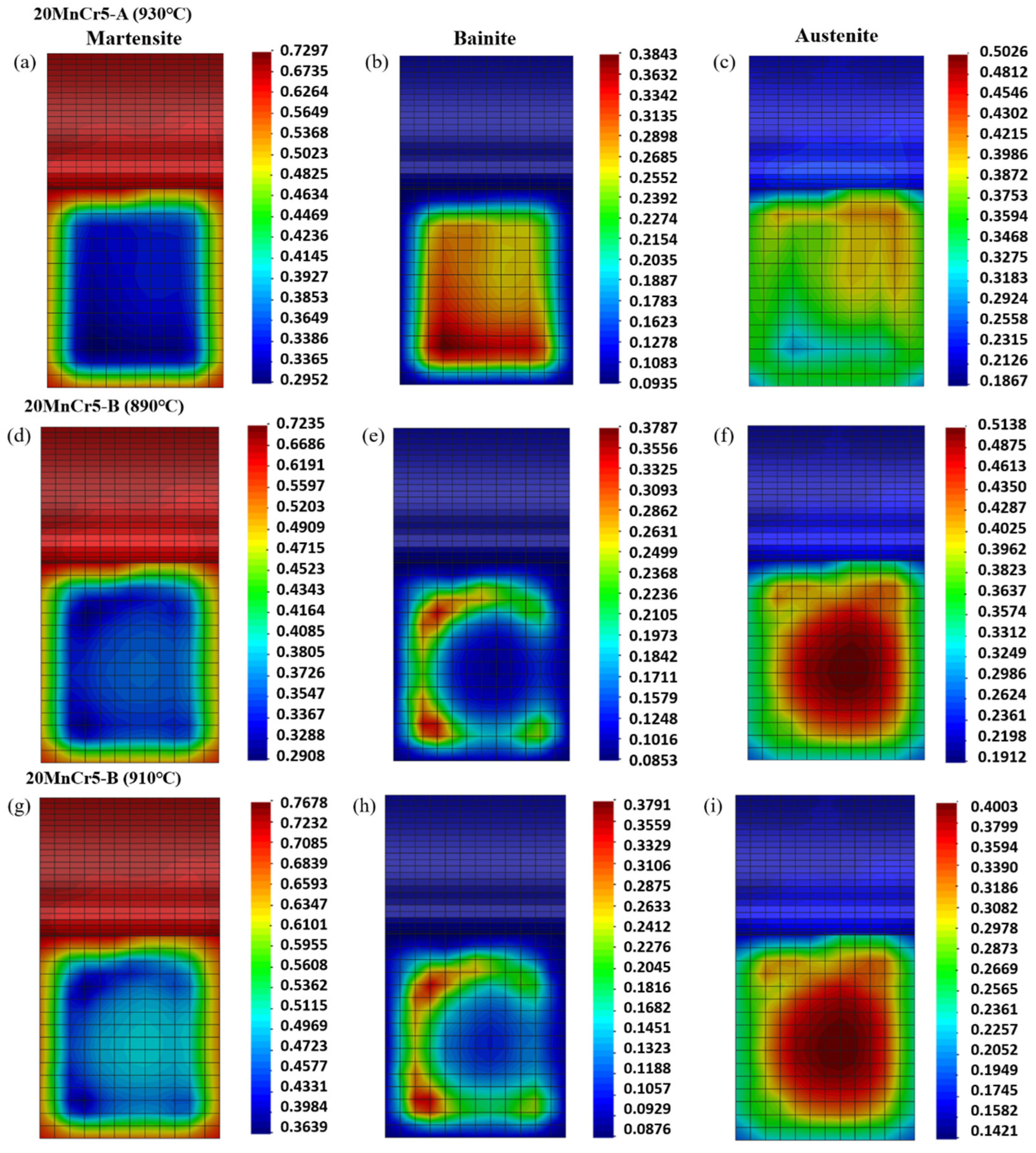
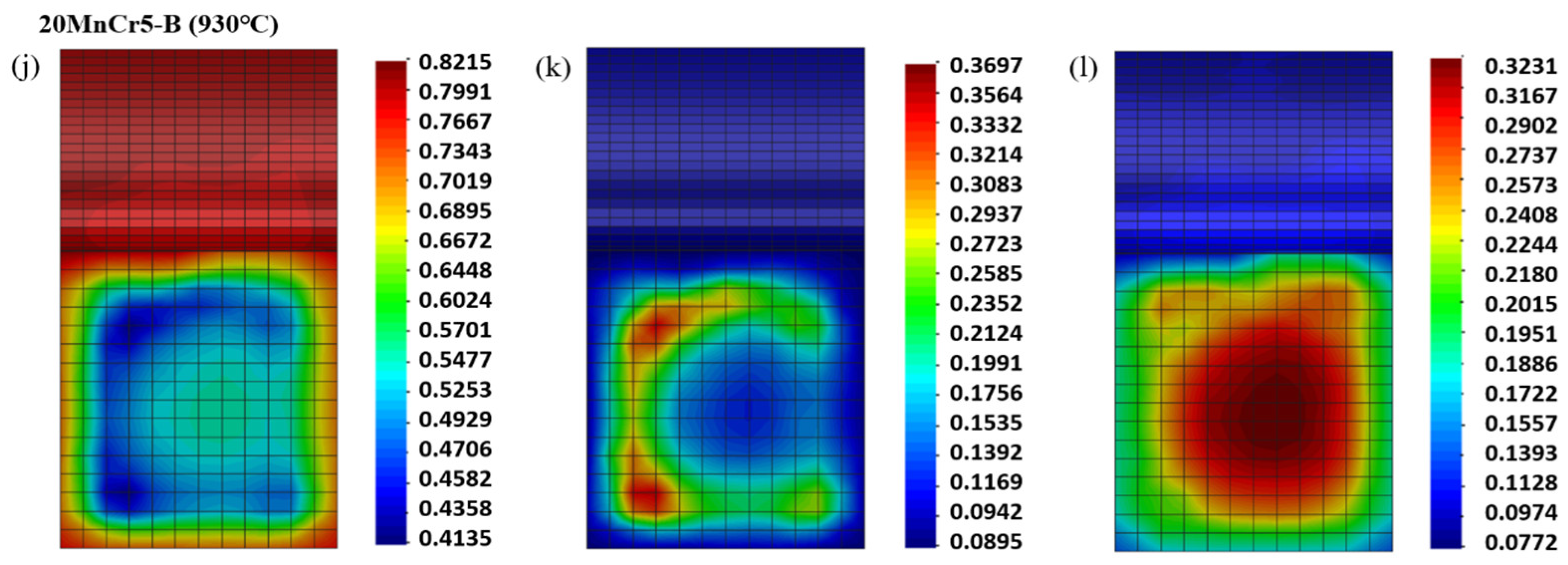
4.3. Analysis of Tissue Transformation
4.4. Surface Hardening Analysis
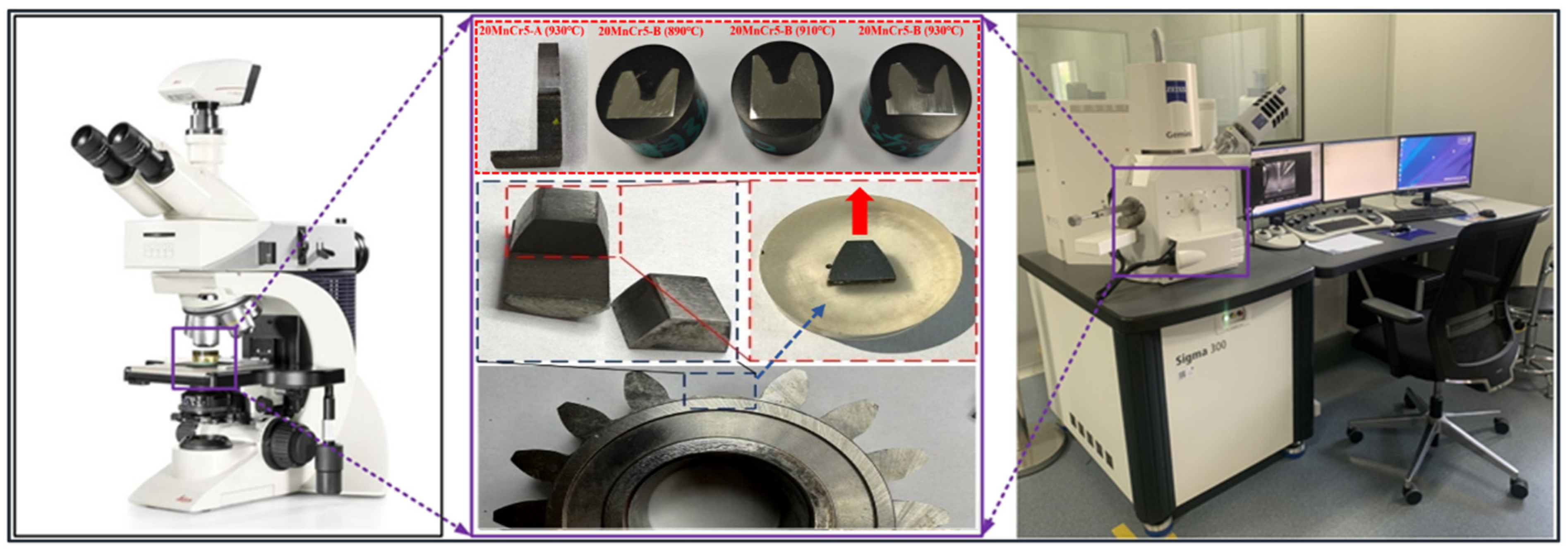
5. Experimental Verification
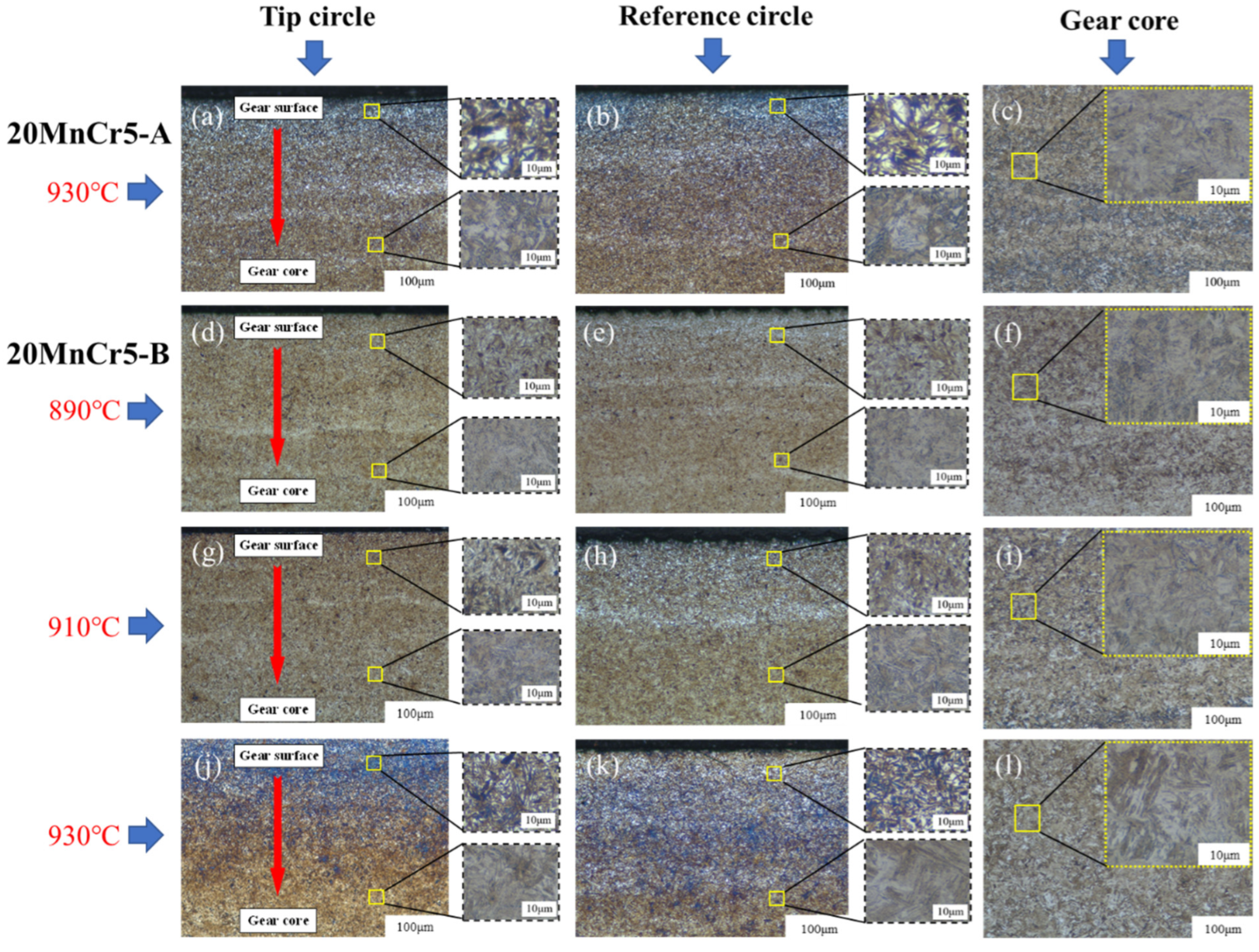
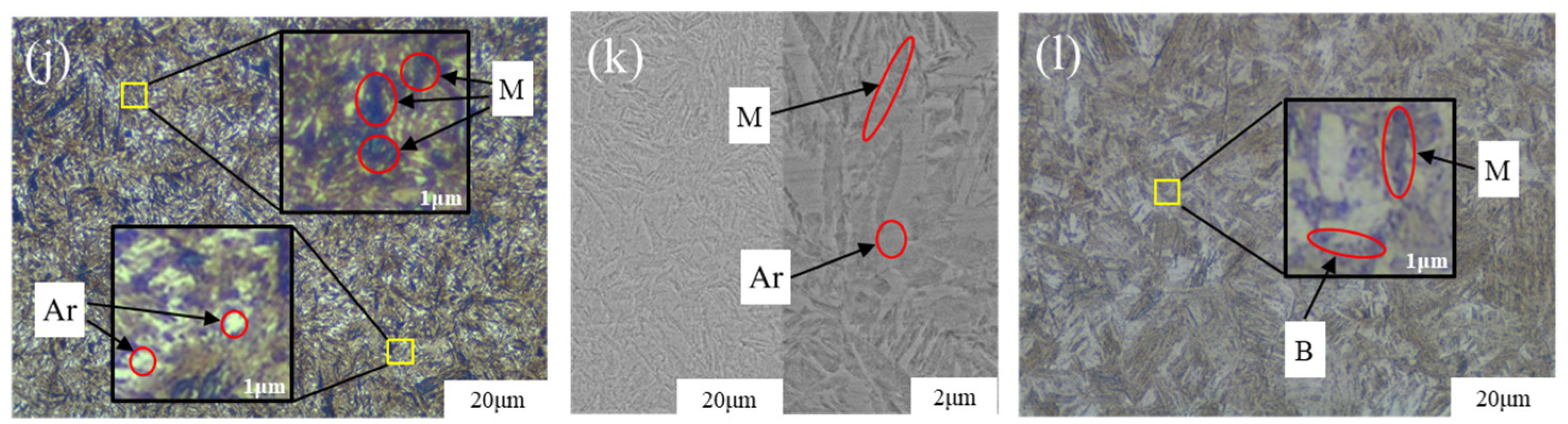
5.1. Gear Microstructure
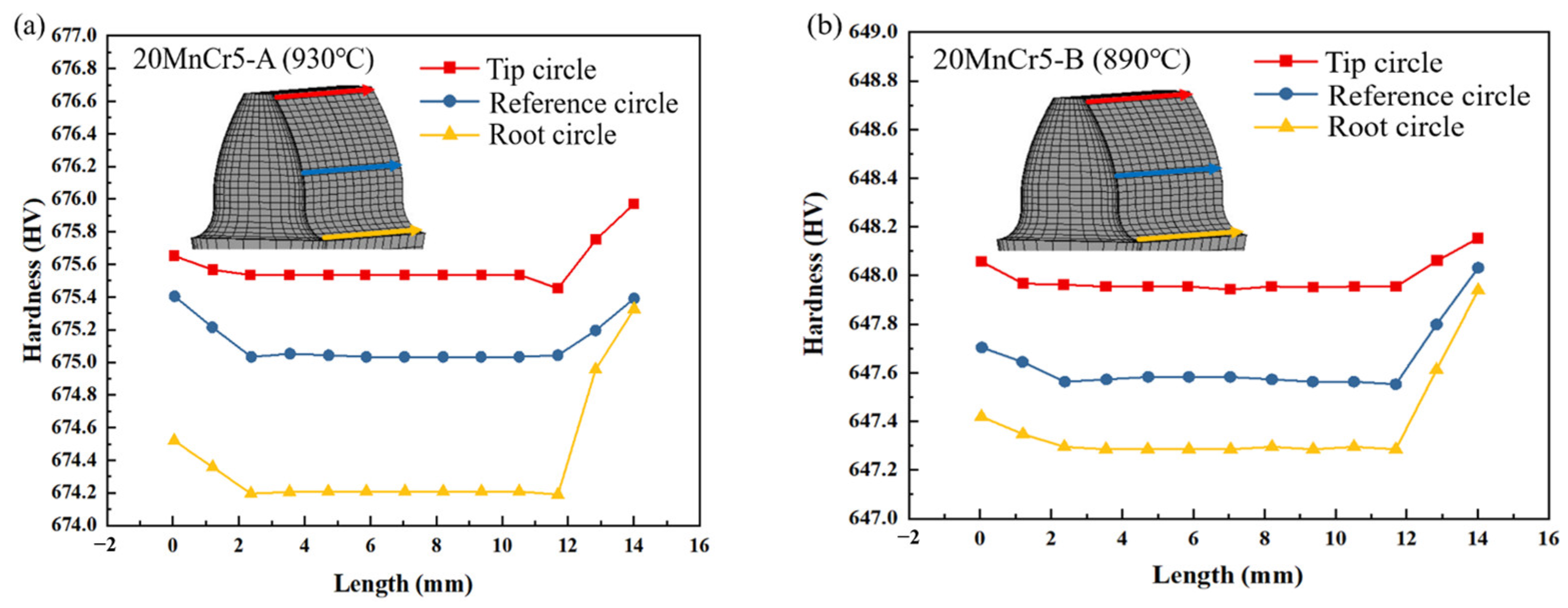
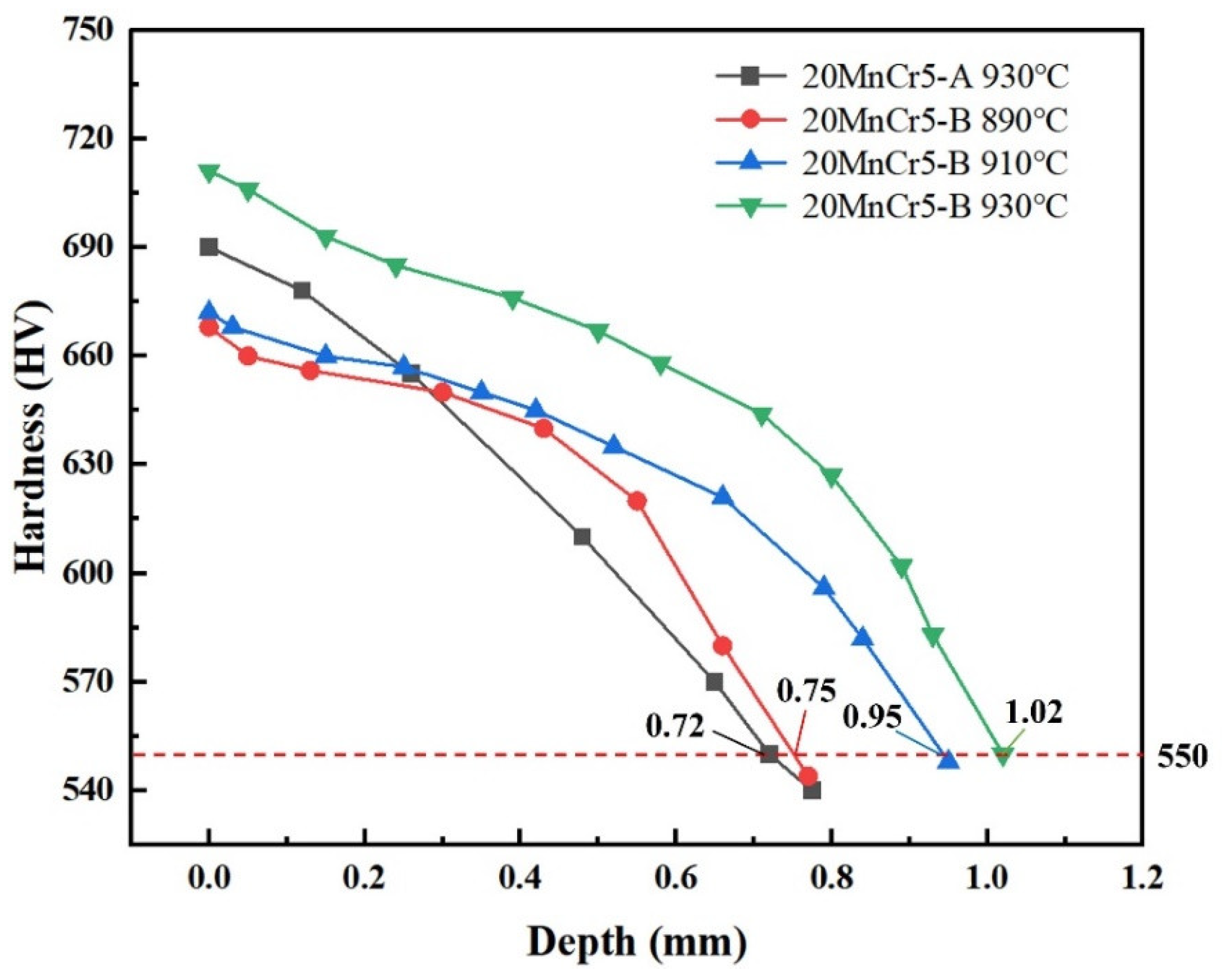
5.2. Hardness
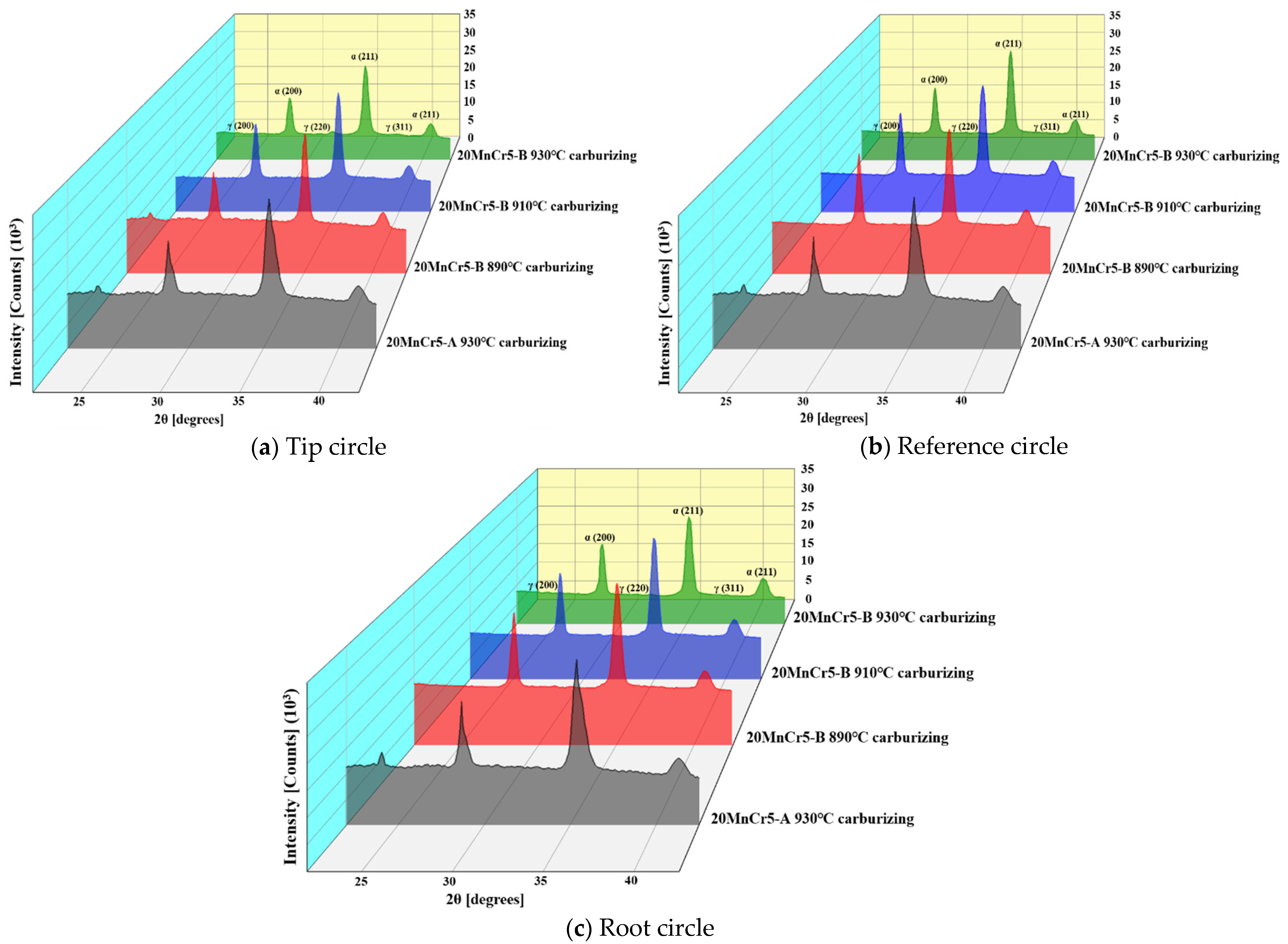
5.3. Retained Austenite
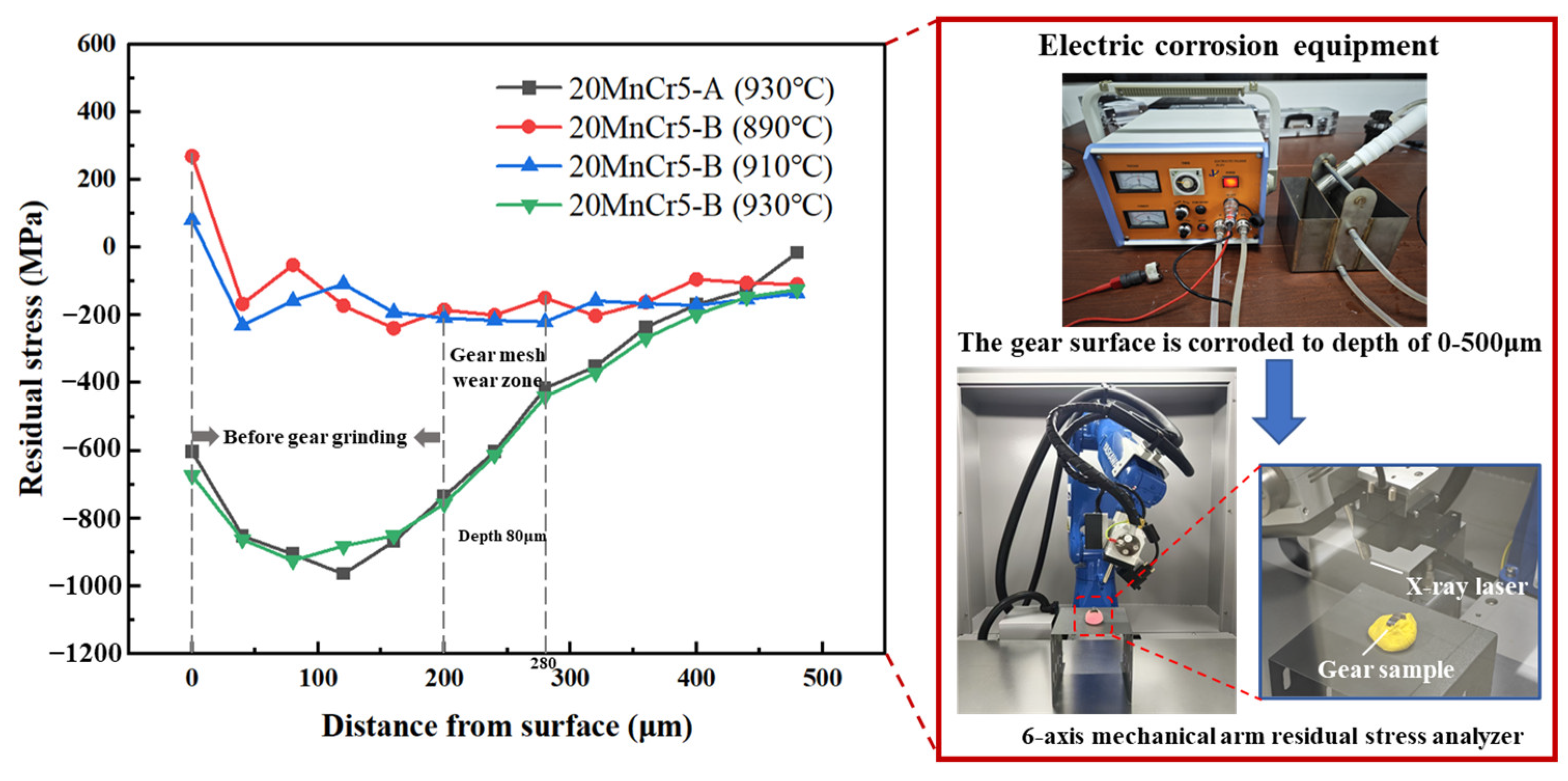
5.4. Residual Stress
6. Conclusions
- (1)
- Regulating the content of Al, Mn and Cr elements makes the gear reach the carburizing temperature faster and improve the quenching rate. After carburizing heat treatment at 930 °C, the 20MnCr5-A and 20MnCr5-B steel gears have a carbon content on the gear surface of 0.92% and 0.98%, and have a carburized layer depth at the reference circle of 0.87 mm and 0.98 mm, respectively. The error between the simulated hardness and the test value is less than 4%.
- (2)
- Compared with the 20MnCr5-A steel gear, the 20MnCr5-B steel gear obtains finer martensite and fine sheet bainite after carburizing at 930 °C for 130 min and tempering at 200 °C for 120 min by increasing Al element to 0.032%. The bainite divides the retained austenite into thin films, greatly reducing the volume of retained austenite and grain size. The retained austenite volume at the tooth tip, reference circle and gear root is less than 8.3%. The error between the simulated retained austenite volume and the test value is less than 5%.
- (3)
- By regulating the content of Al, Mn and Cr elements, the residual stress is increased by 2.9~5.6% at the depth of gear meshing wear between 200 and 280 μm. After carburizing at 930 °C for 130 min and tempering at 200 °C for 120 min, the residual stress in the meshing wear zone of the 20MnCr5-B steel gear increases by 200.4~362.2% compared with carburizing at 890 °C and 910 °C.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zaid, M.; Doquet, V.; Chiaruttini, V.; Depouhon, P.; Bonnand, V.; Pacou, D. On the influence of secondary branches on crack propagation in rolling contact fatigue. Int. J. Fatigue 2024, 182, 108211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koester, R.; Binder, A. Performance analysis of HTS excited 5 MW medium-speed wind turbine generators with different stator feeding concepts. IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 2024, 34, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhu, F.; Hao, N.; Cai, J.; Sun, W. Design optimization of external engagement cylindrical gear flowmeter under uncertainty. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 2024, 67, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, N.; Huang, X.; Huang, Y.; Tong, S.; Cong, F. Investigation of gear meshing vibration and meshing impact resonance intensity assessment. J. Comput. Nonlinear Dyn. 2024, 19, 051008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Sha, H.; Li, S.; Tong, Z.; Tong, S. Stochastic uncertain lubrication in gear transmission subjected to tribodynamic loading. Friction 2024, 12, 1741–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, S.; Tang, J.; Wei, Z.; Zhou, W.; Zhao, J.; Chen, H. Research on calculation of contact fatigue life of rough tooth surface considering residual stress. Eng. Fail. Anal 2022, 140, 106459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Liu, H.; Zhu, C.; Ge, Y. Simulation of the fatigue-wear coupling mechanism of an aviation gear. Friction 2021, 9, 1616–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Liu, H.; Zhu, C.; Li, Z. Numerical simulation of competing mechanism between pitting and micro- pitting of a wind turbine gear considering surface roughness. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2019, 104, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Guo, S.; He, G.; Jiang, B.; Zhou, L.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Y. Failure analysis of the carburized 20MnCr5 gear in fatigue working condition. Int. J. Fatigue 2022, 161, 106938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.; Zou, X.; Hua, S.; Zhou, Z.; Li, G.; Liu, H.; Tang, J. Carburizing effect-inspired bending fatigue forecasting model for spiral bevel gears. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2023, 242, 107987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Liu, H.; Zhu, C.; Sun, Z. Evaluation of contact fatigue life of a wind turbine carburized gear considering gradients of mechanical properties. Int. J. Damage Mech. 2019, 28, 1170–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; He, X.F.; Yu, W.C.; Shi, J.; Wang, M.Q.; Yao, K.F. Nano- and microhardness distribution in the carburized case of Nb-Microalloyed gear steel. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2020, 29, 4626–4630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Liu, H.; Zhu, C.; Bocher, P.; Liu, H.; Sun, Z. Evaluation of rolling contact fatigue of a carburized wind turbine gear considering the residual stress and hardness gradient. J. Tribol. 2018, 140, 061401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Liu, H.; Zhu, C.; Tang, J.; Jiang, C. Evaluation of contact fatigue risk of a carburized gear considering gradients of mechanical properties. Friction 2020, 8, 1039–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; He, X.; Yu, W.; Shi, J.; Wang, M.; Yao, K. Rotating bending fatigue properties of case carburized steel with different fractions of retained austenite. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2022, 32, 7960–7968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gencoglu, S.; Yazici, A. Surface Characteristics and distortion analysis of the case-hardened helical gears: A comparison of different case-hardening treatments. Trans. Indian Inst. Met. 2020, 73, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, H.; Wang, Z.; Liu, L.; Li, Y.; Guo, F. Regulation mechanism of cooling rate and RE (Ce, Y, Gd) on Mg17Al12 in AZ91 alloy and it’s role in fracture process. J. Mater. Res. Technol. JMRT 2022, 19, 3930–3941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Deng, X.; Wang, Z. Achieving excellent mechanical properties and wear resistance in Fe49Mn30Co10Cr10C1 interstitial high-entropy alloy via tuning composition and stacking fault energy by Nb doping. Wear 2023, 534, 205149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Li, D.Y. Influences of C, Si and Mn on the wear resistance of coiled tubing steel. Wear 2023, 524, 204854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Niu, Z.; Liu, H.; Xu, K.; Qin, S. Simulation of residual stress of V-Notch specimen treated by ultrasonic rolling. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2024, 34, 1232–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Xu, W.; Wan, S.; Luo, C.; Lin, Z.; Jiang, X. Determination of heat transfer coefficient by inverse analyzing for selective laser melting (SLM) of AlSi10Mg. Crystals 2022, 12, 1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iss, V.; Meis, J.; Rajaei, A.; Hallstedt, B.; Broeckmann, C. Fatigue strength evaluation of case-hardened components combining heat-treatment simulation and probabilistic approaches. Fatigue Fract. Eng. Mater. Struct. 2024, 47, 745–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Q.; Zhang, J.; Conejo, A.N.N.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Y. Investigation of methane decomposition and carburization with iron: The combination of a ReaxFF molecular dynamics simulation and experimental work. J. Mater. Sci. 2023, 58, 9420–9433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izowski, B.; Wojtyczka, A.; Motyka, M. Numerical simulation of low-pressure carburizing and gas quenching for pyrowear 53 steel. Metals 2023, 13, 371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, S.; Su, L.; Wang, F. Nucleation and coarsening behavior of aluminum nitride and its effect on abnormal grain growth in high-temperature carburizing process. Met. Mater. Trans. A 2024, 55, 910–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, X.; Tian, Y.; Wang, B.; Jia, T.; Wang, H.; Wang, Z. Prediction of the formation of carbide network on grain boundaries in carburizing of 18CrNiMo7-6 steel alloys. Surf. Coat. Tech. 2021, 421, 127348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, R.; Tian, G.; Gao, L.; Li, H. Optimization method for gear heat treatment process oriented to deformation and surface collaborative control. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2023, 33, 11376–11392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhao, J.; Tang, J.; Shao, W.; Sun, B. Simulation and experimental verification of die quenching deformation of aviation carburized face gear. Materials 2023, 16, 690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veronesi, P.; Balestri, A.; Colombini, E. Improvement in wear resistance of grade 37 titanium by microwave plasma oxy-carburizing. Technologies 2023, 11, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sondar, P.R.; Gurudath, B.; Ahirwar, V.; Hegde, S.R. Failure of hydraulic lathe chuck assembly. Eng. Fail. Anal 2022, 133, 106001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanamori, H.; Ju, D. Identification of heat transfer coefficients and simulation of quenching distortions on disk probe. Mater. Trans. 2020, 61, 884–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Deng, X.; Wang, H.; Zhou, L.; Xu, Y.; Ju, D. Modeling and simulation of vacuum low pressure carburizing process in gear steel. Coatings 2021, 11, 1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ju, D.; Cao, J.; Ishikawa, K. Analysis of the distortion of the bearing rings after quenching. Coatings 2023, 13, 1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Ju, D.; Li, M. Finite element modeling and experimental verification of nitriding process in S30C Steel. Mater. Res-Ibero-Am. J. 2017, 20, 509–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Jiang, J.; Chen, M.; Deng, X.; Wang, J.; Ju, D. Study on the mechanism of carbide precipitation by surface quenching treatment on GCr15 bearing rings based on the phase-field method. Front Mater. 2022, 9, 978025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biffi, C.A.; Fiocchi, J.; Tuissi, A. Selective laser melting of AlSi10 Mg: Influence of process parameters on Mg2Si precipitation and Si spheroidization. J. Alloy Compd. 2018, 755, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, H.F.; Druga, L.; Cojocaru, M.; Dumitru, C.; Ghinea, A. The structural evolution of refractory steel spare parts during the successive carburizing. U Politeh. Buch. Ser. B 2020, 82, 247–257. [Google Scholar]
- Vasic, M.M.; Zak, T.; Minic, D.M. Kinetics and influence of thermally induced crystallization of Fe, Ni-containing phases on thermomagnetic properties of Fe40Ni40B12Si8 amorphous alloy. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2022, 147, 3543–3551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zari, I.; Ali, F.; Khan, T.S.; Shafiq, A. Radiative Hiemenz flow towards a stretching Riga plate in hybrid nanofluid. Int. Commun. Heat Mass 2022, 139, 106492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Ge, Y.; Kahn, H.; Ernst, F.; Heuer, A.H. Diffusion profiles after nitrocarburizing austenitic stainless steel. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2015, 279, 180–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, D.Y.; Zhang, W.M.; Zhang, Y. Modeling and experimental verification of martensitic transformation plastic behavior in carbon steel for quenching process. Mat. Sci. Eng. A-Struct. 2006, 438, 246–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.Z.; Di, X.J.; Liu, Y.C.; Yu, L.M.; Yan, Z.S. Athermal martensite transformation of modified high Cr ferritic heat resistant steel undergoing different quenching temperatures. Mater. Res. Innov. 2012, 16, 198–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Ju, J.; Fu, H.; Ma, S.; Lin, J.; Lei, Y. Effect of chromium content on microstructure, hardness, and wear resistance of as-Cast Fe-Cr-B alloy. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2019, 28, 6428–6437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Type of Steel | C | Si | Mn | P | S | Cr | Ni | Mo | Cu | Al |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20MnCr5-A | 0.20 | 0.10 | 1.26 | 0.012 | 0.002 | 1.15 | 0.12 | 0.05 | 0.03 | — |
| 20MnCr5-B | 0.18 | 0.09 | 1.35 | 0.012 | 0.002 | 1.25 | 0.04 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.032 |
| Parameter | Driving Gear | Driven Gear |
|---|---|---|
| Number of teeth | 16 | 24 |
| Coefficient of displacement | 0.182 | 0.171 |
| Tip circle diameter/mm | 82.5 | 118.4 |
| Module/mm | 4.5 | |
| Pressure angle/(°) | 20 | |
| Tooth width/mm | 14 | |
| Retained Austenite Volume | Tip Circle (%) | Reference Circle (%) | Root Circle (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20MnCr5-A | 930 °C Carburizing | 18.2 | 18.9 | 19.4 |
| 20MnCr5-B | 890 °C Carburizing | 20.0 | 20.4 | 20.7 |
| 910 °C Carburizing | 14.9 | 16.0 | 16.2 | |
| 930 °C Carburizing | 7.5 | 8.1 | 8.3 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luo, L.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, F.; Hua, W.; Song, X.; Xu, Z.; Jia, Z. Study of the Effect of Regulating Alloying Elements and Optimizing Heat Treatment Processes on the Microstructure Properties of 20MnCr5 Steel Gears. Lubricants 2025, 13, 202. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants13050202
Luo L, Chen Y, Zhao F, Hua W, Song X, Xu Z, Jia Z. Study of the Effect of Regulating Alloying Elements and Optimizing Heat Treatment Processes on the Microstructure Properties of 20MnCr5 Steel Gears. Lubricants. 2025; 13(5):202. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants13050202
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuo, Li, Yong Chen, Fucheng Zhao, Weifeng Hua, Xu Song, Zhengyun Xu, and Zhicheng Jia. 2025. "Study of the Effect of Regulating Alloying Elements and Optimizing Heat Treatment Processes on the Microstructure Properties of 20MnCr5 Steel Gears" Lubricants 13, no. 5: 202. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants13050202
APA StyleLuo, L., Chen, Y., Zhao, F., Hua, W., Song, X., Xu, Z., & Jia, Z. (2025). Study of the Effect of Regulating Alloying Elements and Optimizing Heat Treatment Processes on the Microstructure Properties of 20MnCr5 Steel Gears. Lubricants, 13(5), 202. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants13050202






