Abstract
Natural fiber-reinforced composites have become an important field of research due to their environment-friendly nature, low cost, lightweight, and excellent mechanical properties. In the current study, natural composites were fabricated by the hand layup technique to investigate the influence of pineapple leaf fiber (PALF) orientation on the mechanical properties and water absorption behaviors of epoxy composites. Pineapple leaf fibers, known for their natural fiber reinforcement capabilities, were incorporated into polymer matrices at various orientations (45°, 60°, 75°, and 90°) to evaluate their impact on the composite’s performance. Mechanical properties (tensile strength, flexural strength, impact energy, and micro-hardness) were assessed to understand how fiber alignment influences the overall structural integrity of the composite. Additionally, the water absorption characteristics of the fabricated composites were assessed by immersing specimens in water and measuring water uptake over time. Results revealed that fiber orientation plays a crucial role in enhancing mechanical strength and tribological properties, with composites reinforced with fibers aligned at 90° demonstrating efficient load transfer and reduced water absorption. Conversely, composites with fibers oriented at 45° showed relatively lower mechanical strength, higher water absorption, and lower tribological performance. These findings suggest that the optimization of fiber orientation in polymer composites can lead to enhanced performance and durability, making them suitable for an extensive range of eco-friendly and sustainable applications.
1. Introduction
Natural fibers are the fibers acquired from plants, animals, and geological processes. They have more benefits than synthetic fibers (such as polyethylene fiber, glass fiber, carbon fiber, and any other man-made fiber) in terms of flexibility, cost, and impact resistance, and they also are eco-friendly in nature and furnish a pollution-free environment because of their biodegradability. Natural fibers have attracted researchers throughout the globe because of their good mechanical properties, low cost, and ease of availability, among other reasons [1,2,3,4,5]. In recent decades, the consumption of natural fibers has increased significantly in composite manufacturing due to their sustainability, biodegradability, and eco-friendly properties. The pineapple is a widely cultivated tropical fruit, and fibers can be derived from its leaves. While the fruit itself can be consumed, the leaves, which are considered waste, have often been discarded. However, this unused by-product of pineapple cultivation, i.e., leaves, has recently gained the attention of researchers exploring the ways to utilize pineapple leaves for the development of innovative composite materials. The disposal of pineapple leaves contributes to environmental concerns, as large quantities of these leaves often go to waste and are not efficiently utilized. The persistence of such waste in landfills or open spaces can lead to an unpleasant odor, slow decomposition, and environmental pollution, due to the emission of harmful gases, including methane, during decomposition. To address these issues, researchers are currently focused on converting pineapple leaf waste into valuable resources, such as natural fiber composites. Incorporating pineapple leaf fibers (PALFs) into composite materials not only reduces the environmental burden caused by this waste but also provides an opportunity to produce eco-friendly and sustainable materials. The development of these PALF-based composites contributes to minimizing environmental problems by reducing waste accumulation and promoting the use of renewable resources. Furthermore, these composites offer a potential alternative to synthetic fibers, which are often non-biodegradable and harmful to the environment. Thus, by using PALFs, the composite industry can move toward more sustainable production practices while addressing the issues associated with pineapple leaf waste [6,7,8,9].
PALF has excellent mechanical properties, biodegradability, and cost-effectiveness, which make it valuable for diverse applications, especially in textiles, composites (mostly reinforced polymer composites), and even industrial uses. PALF exhibited high specific strength, durability, and stiffness, which are ascribed to its high cellulose content (70–80%) and comparably low microfibrillar angle [10,11,12,13]. In composite manufacturing, there are many factors that regulate the properties of fabricated composites, such as the content, length, orientation, and arrangement of fibers. Among these, fiber orientation plays a key role in altering the resultant properties of the pineapple-reinforced polymer composites developed. Several studies have explored the impact of fiber orientation of different fibers. Kumar et al. [14] explored the influence of basalt fiber orientation on the mechanical and water absorption behavior of developed laminate composites and found that the highest mechanical property was recorded in a 90° bidirectional basalt fiber orientation angle, among the 45°, 60°, and 90° basalt fiber orientated composites. The maximum tensile, flexural, and impact strength were recorded in the case of the 90° basalt fiber orientation, and the minimum was recorded for the 45° fiber orientation. Lasikun et al. [15] demonstrated that increasing the orientation angle of a zalacca midrib fiber-reinforced HDPE composite from 0° to 90° can lead to reduced impact and tensile strength. Bakir et al. [16] observed that maximum hardness was noted in discontinuous glass fiber orientation reinforced with epoxy, followed by the 90°, 0°, and 45° glass fiber orientations. The maximum tensile strength was found in the 90° glass fiber orientation, followed by the randomly orientated glass fiber in the 45° and 0° glass fiber orientations. Doddi et al. [17] observed that in the case of Pineapple leaf fibers hybridized with basalt fiber-reinforced epoxy composites, the tensile strength decreased with the increase in fiber orientation up to 45°; beyond that angle, increasing orientation correlated with increasing tensile strength. Almeida Jr et al. [18] investigated the shear behavior of glass fiber reinforced with epoxy composites and reported that 0° fiber orientation in composite had higher interlaminar shear strength, while it was at the lowest in the 90° fiber orientation. Cordin et al. [19] concluded that an increase in the orientation angle of a cellulose-type lyocell fiber reinforced with polypropylene from 0° to 90° could decrease the ultimate tensile strength and elastic modulus.
Many other studies have been performed on composites with different fiber orientations. Still, to the best of our knowledge, a study on the fiber orientation of PALF has not been explored yet. Considering the above, the present research focuses on developing green composite materials reinforced with PALF in different orientations such as 45°, 60°, 75°, and 90° using hand layup process. After that, the influence of the fiber orientation on the mechanical behavior (tensile strength, flexural strength, impact strength, micro-hardness) and water absorption behavior of the pineapple leaf natural fiber composites developed is further investigated.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
PALF is biodegradable, eco-friendly, and easily available, making it an attractive alternative to synthetic materials. The PALF used in this investigation was supplied by GoGreen Product Ltd., Chennai, India, in the form of a bidirectional mat. Detailed technical information, including the mechanical properties and chemical composition of the fiber to evaluate its suitability in composite materials, is provided in Table 1. Araldite LY 556 (chemically known as bisphenol A diglycidyl ether) and HY 951 (chemically known as N’-(2-aminoethyl)ethane-1,2-diamine) were selected as an epoxy resin and a curing agent, i.e., hardener, respectively, and were also purchased from GoGreen Product Ltd., Chennai, India. The basic properties of the epoxy resin and the curing agent are presented in Table 2.

Table 1.
Compositions and mechanical properties of PALF.

Table 2.
Characteristics of resin and hardener.
2.2. Fabrication of Composites
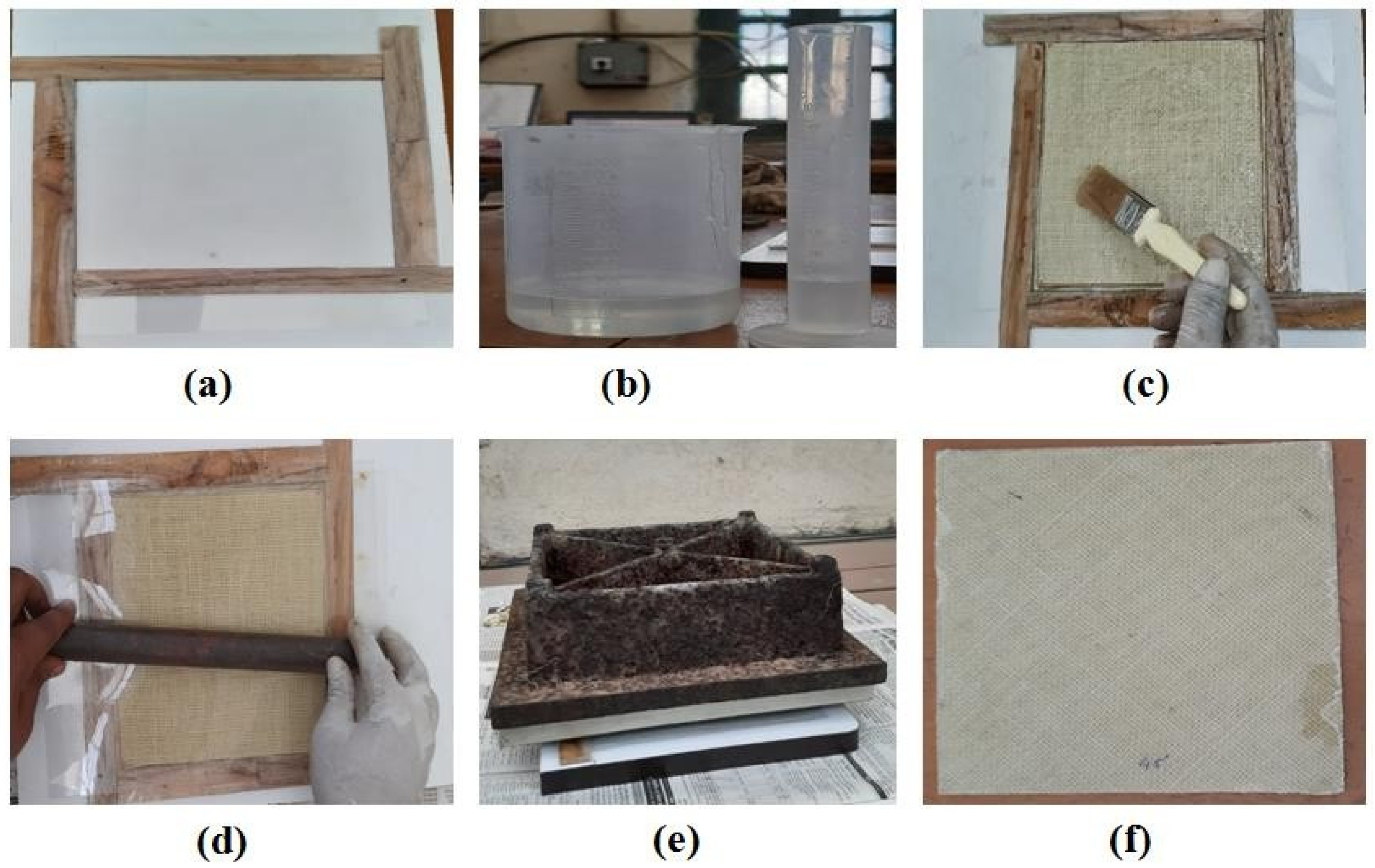
Figure 1 presents the complete methodology followed to fabricate PALF-reinforced polymer composites. The composite materials were fabricated via a hand layup process using the wooden mold box of size 180 × 180 × 5 mm3, as shown in Figure 1a. Matrix material, i.e., epoxy resin, is thermosetting in nature. The epoxy and hardener were poured into the beaker in a ratio of 10:1 after measuring with a measuring cylinder, as shown in Figure 1b, and mixed thoroughly with the help of a mechanical stirrer. Mold-releasing wax coated on a Teflon sheet was put at the bottom of the mold to avoid the sticking composite sample on the mold box after drying. Afterward, the epoxy–hardener mixture was applied uniformly on the entire mold box, and this mixture was spread thoroughly with the help of a hand brush. After that, a layer of PALF was placed over in the selected orientation (45°, 60°, 75°, and 90°), followed by another layer of the epoxy–hardener mixture, which was applied on the fiber mat and spread uniformly using a hand brush, as shown in Figure 1c. This process was repeated to create six layers of the bidirectional pineapple fiber mat.
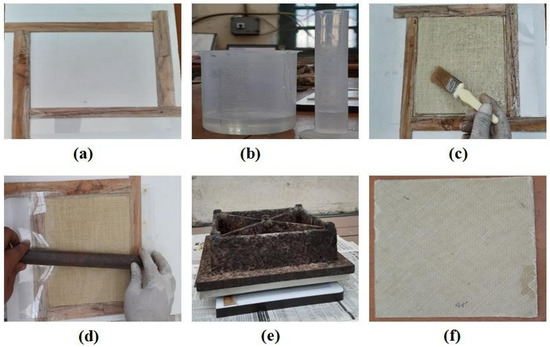
Figure 1.
Process followed to fabricate PALF-reinforced polymer composites: (a) wooden mold, (b) measured epoxy and hardener, (c) hand layup process, (d) rolling process after hand layup process, (e) load applied on the mold, and (f) final fabricated composite plates.
After incorporating the six layers of fiber mat, a Teflon sheet coated with mold-releasing wax was put over it and rolled with a roller, as shown in Figure 1d. The rolling helped achieve a uniform distribution of the epoxy–hardener mixture across the incorporated fiber layers, along with the removal of any air bubbles that existed in between the fiber mat layers. Finally, a 40 kg weight was placed over the layers and left for about 24 h for curing, as shown in Figure 1e. After 24 h, the fabricated composite plates, as shown in Figure 1f, were taken out, and samples were cut accordingly for mechanical and water absorption testing. The PALF-reinforced polymer composites were each fabricated using the above-mentioned process for different orientations (45°, 60°, 75°, and 90°) of the PALF.
2.3. Assessment of the Mechanical Properties of the Fabricated Composites
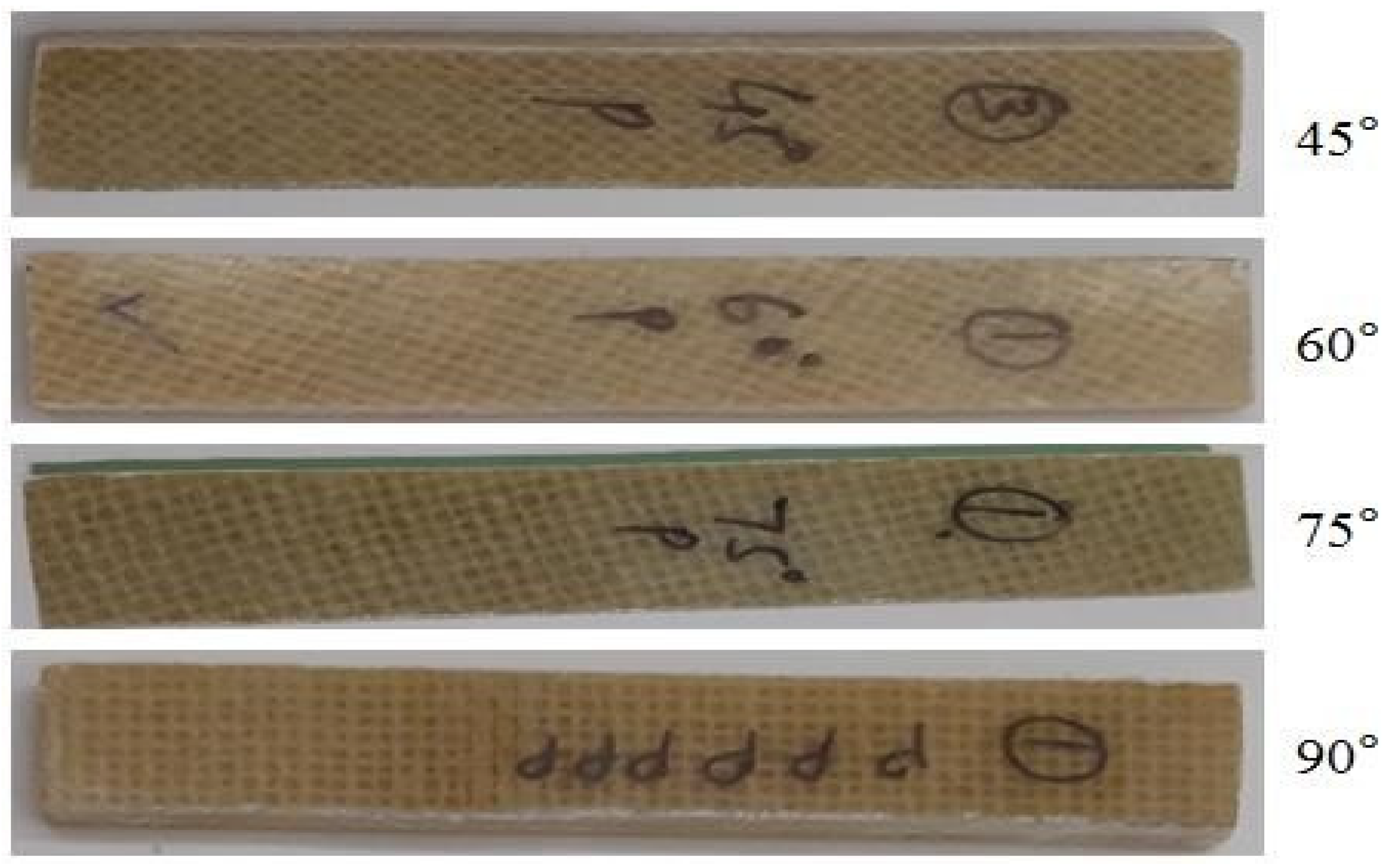
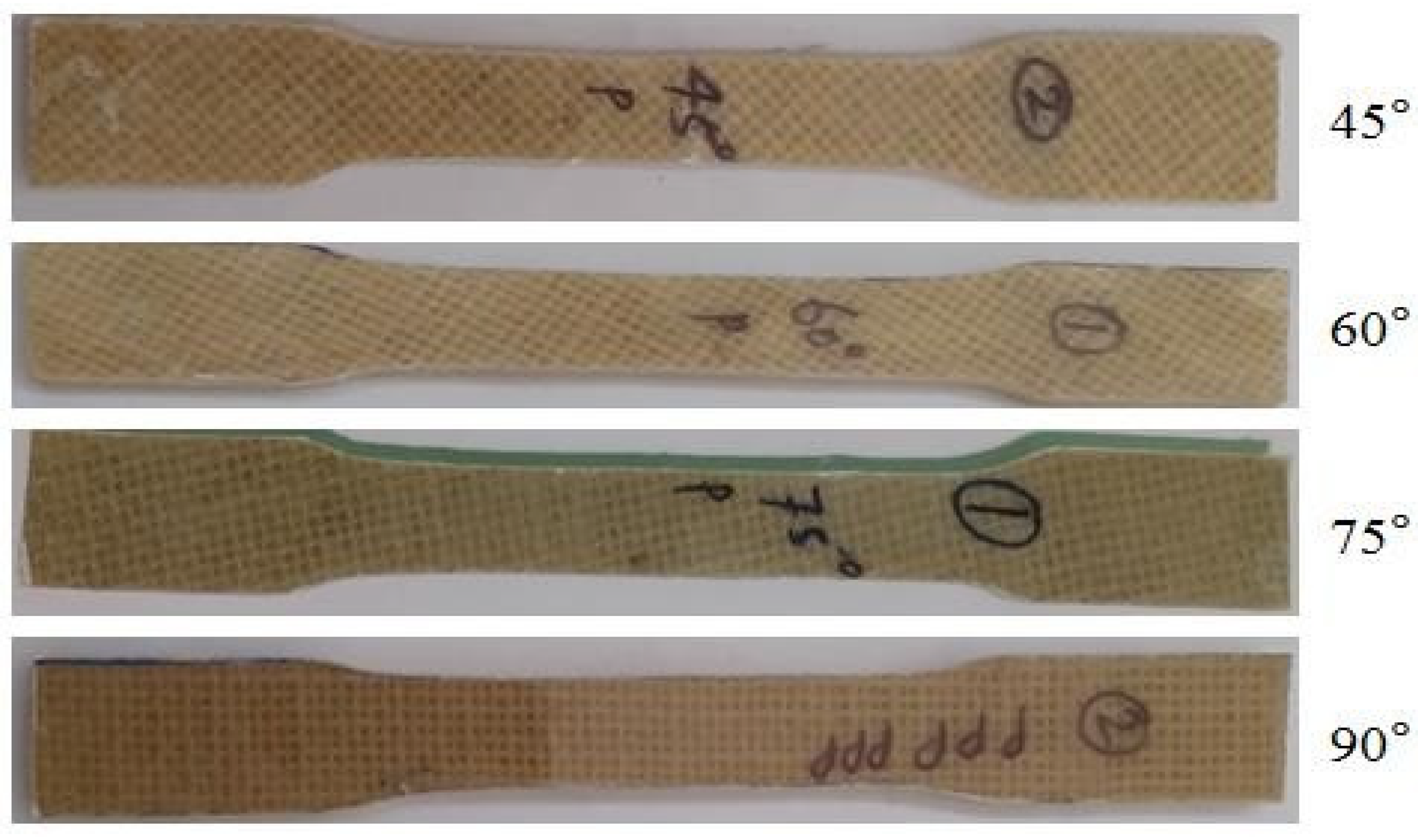
Tensile test: Tensile tests were executed on the Zwick/Roell UTM Machine (UTM Z250, Chennai, India). The specimens for the tensile test were prepared in the shape of a dog bone—as per the ASTM D638-22 standard [20]—with a length of 165 mm, a gauge length of 50 mm, and a thickness of 5 mm, as shown in Figure 2. The tensile tests were conducted under atmospheric conditions, with a surrounding temperature of ~30 °C and relative humidity (RH) of 50 ± 5%. Clamps were used to carry the samples in the longitudinal direction, and the load was applied to the specimen with a cross-head speed of 1 mm/min. For each orientation, five specimens were examined and the average values of each were reported.
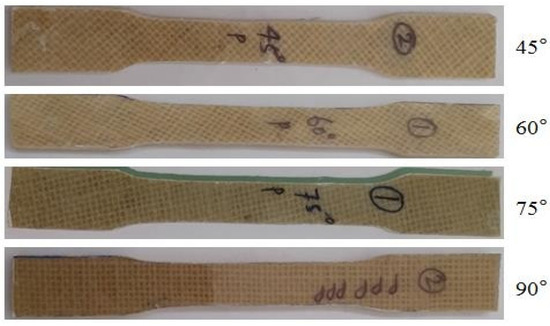
Figure 2.
Specimens prepared for tensile test.
Flexural strength test: Flexural strength tests were also executed on the same Zwick/Roell UTM Machine used for the tensile test. For flexural testing, the samples were prepared as per the ASTM D790-17 standard [21], with a length of 100 mm, width of 20 mm, and thickness of 5 mm, as shown in Figure 3. The cross-head speed of 1 mm/min was applied during the flexural test. The specimens remained loaded until the core broke, at which point the bending load was registered. For each orientation, five specimens were examined and the average values of each were reported.

Figure 3.
Specimens prepared for flexural strength test.
Impact test: The impact test was performed on a standard impact pendulum-mounted hammer. The specimens were prepared according to ASTM D6110-18 [22] for the Charpy impact test. The sample measured 64 mm × 13 mm × 5 mm in size and was notched (V-notch, 2 mm) at the center. The test sample was attached to a vertical, simply supported beam and damaged by a single pendulum swing; the corresponding impact energy was recorded. For each orientation, five specimens were examined and the average values of each were reported.
Micro-hardness test: The composite specimens were prepared according to the ASTM E384-22 [23] for micro-hardness testing. A load of 100 g was applied for 10 s using a diamond indenter. At least 10 readings were taken for each specimen of different orientations of fibers, and the mean value was reported.
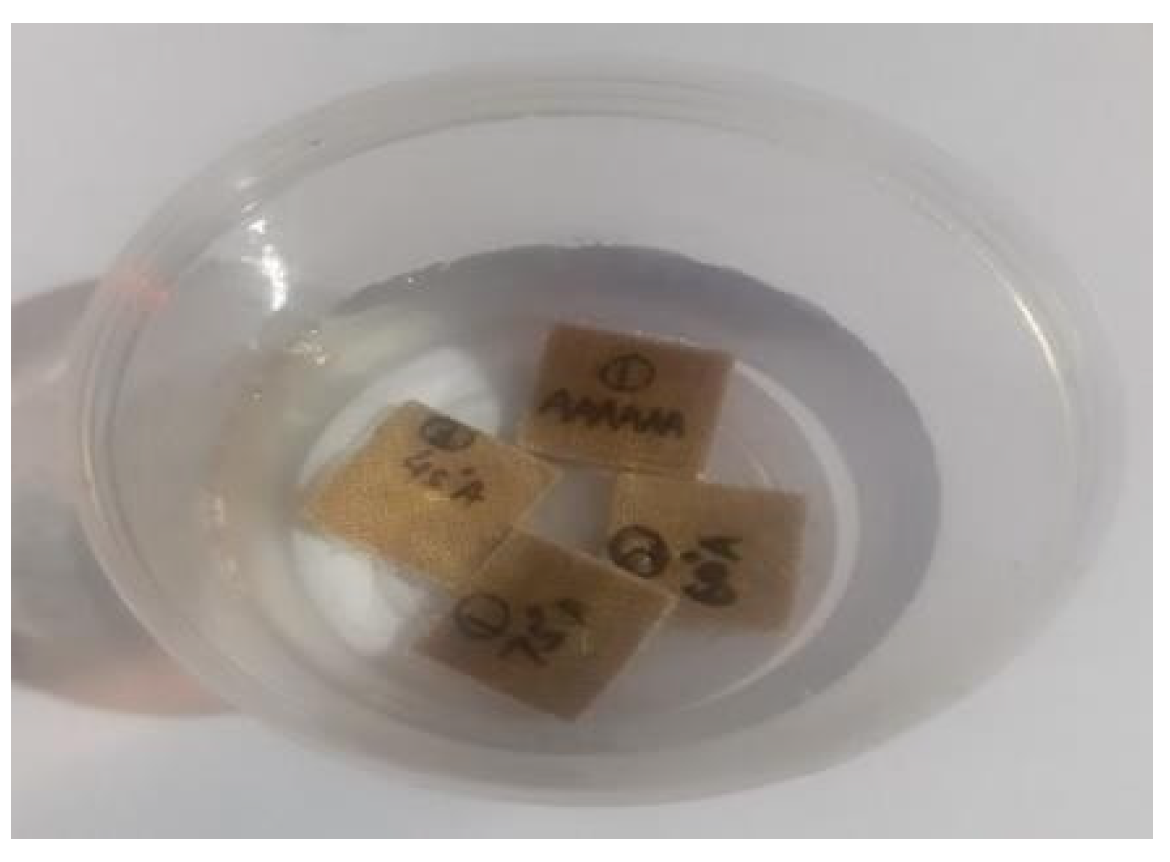
2.4. Water Absorption Test
The water absorption test was carried out according to ASTM D570-22 standard [24] at room temperature. All the test specimens were dried in a hot air oven at a temperature of 50 °C to remove any humidity present before starting the test. Dry specimen weight was determined using an electronic weighing machine with a precision of 0.001 g. All the samples were dipped into water under normal atmospheric conditions, as shown in Figure 4. The specimens were withdrawn from the water tank at specified time intervals, cleaned with cotton to remove any water droplets present on the surface, and weighed using a digital weighing machine. This process was repeated until all the specimens reached a saturation state. The percentages of water absorption of specimens were evaluated using the following formula:
where is the weight before water dipping in water, and is the weight of the composite after water absorption.
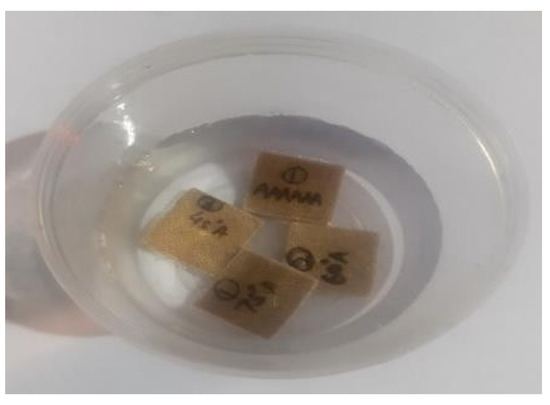

Figure 4.
Specimens immersed in water for water absorption test.
2.5. Tribological Performance Assessment
The friction and wear behaviors were assessed using a pin-on-disc tribometer (Ducom, Bengaluru, India; TR-20LE-PMH-200) through the unidirectional (rotating) sliding test under dry conditions. The test specimens were prepared according to the ASTM G99-23 standards [25] for developing composites with different fiber orientations. Before conducting the test, the sliding disc (EN 31, Hardness < 62 HRC, Roughness ~ 0.05 µm) and composite specimen’s surfaces were polished with silicon carbide emery paper to ensure proper contact with the specimens on the disc (surface roughness~0.2 µm) and then cleaned with acetone and isopropanol. The tests were conducted at different sliding speeds (1, 2, and 3 m/s) under a load of 20 N for a sliding distance of 3000 m at room temperature. Each test was repeated 4 times, and the average COF was reported. The initial (before friction test) and final (after friction test) weights of all the samples were measured using a high accuracy and precision digital electronic weighing machine, with an accuracy of 0.001 gm, and the wear loss was measured. The surface was examined under FESEM (ZEISS EVO, Oberkochen, Germany) to explore the worn morphologies of the surfaces after the friction test.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effect of Different Orientations of Fibers on Tensile Strength
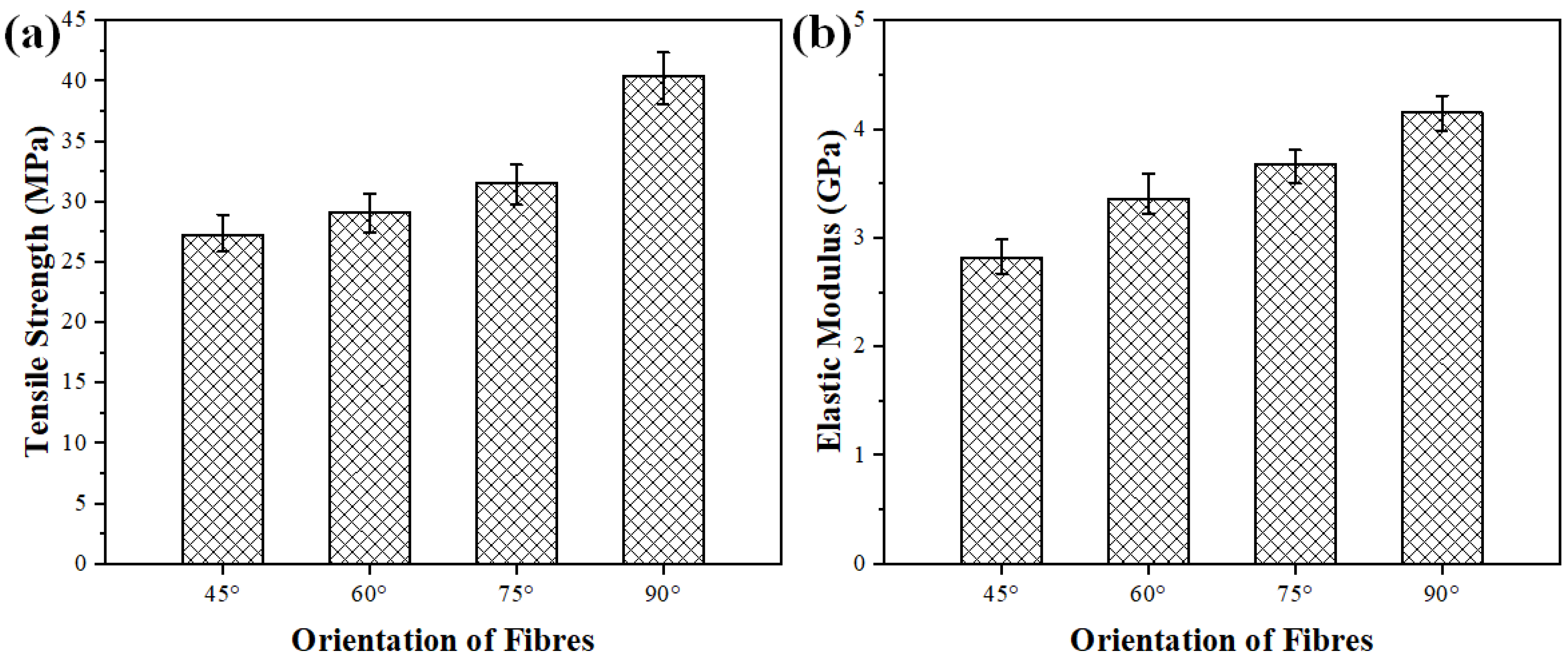
The tensile strength of the fiber-reinforced polymer composites is highly influenced by the orientation of the fibers within the composite structure. In bidirectional mats, the fibers are oriented at specific angles relative to the direction of the applied stress, and this orientation significantly affects how the material responds to tensile forces. The tensile strength and elastic modulus of the fabricated composites with different PALF orientations, such as 45°, 60°, 75° and 90°, are demonstrated in Figure 5. The results reveal that tensile strength and elastic modulus gradually increase with an increase in the fiber orientation from 45° to 90°. The minimum average tensile strength is ~27.17 MPa, with an orientation angle of 45°, and the maximum average tensile strength is an orientation angle of ~40.42 MPa at a 90° fiber orientation. From the results, it is evident that the composites with a 90° PALF orientation have ~49% higher tensile strength as compared to the composites with a 45° PALF orientation. For the 45°, 60°, and 75° fiber orientations, the fiber length is shorter, and the applied load is resolved into two components, leading to forces acting in two different directions. On the other hand, for the 90° fiber orientation, the load is applied along the fiber length, resulting in only one component of force aligned with its orientation; thus, it displays the highest tensile strength and elastic modulus among all the above-mentioned fiber orientations. Kumar et al. [14] explored the influence of bidirectional basalt fiber orientation, such as 45°, 60°, and 90°, on mechanical properties and found that the 90° basalt fiber-reinforced epoxy matrix composites had excellent mechanical characteristics as compared to the 45°and 60° basalt fiber-reinforced epoxy composites, similar to the findings of the current investigation.
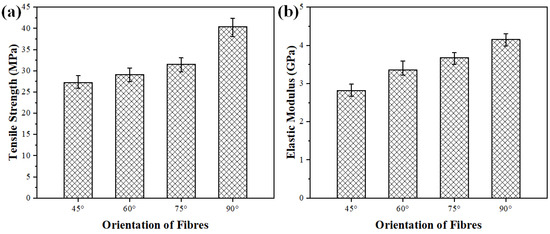
Figure 5.
(a) Tensile strength and (b) elastic modulus of PALF composites fabricated with different orientations of fibers.
3.2. Effect of Different Orientations of Fibers on Flexural Strength
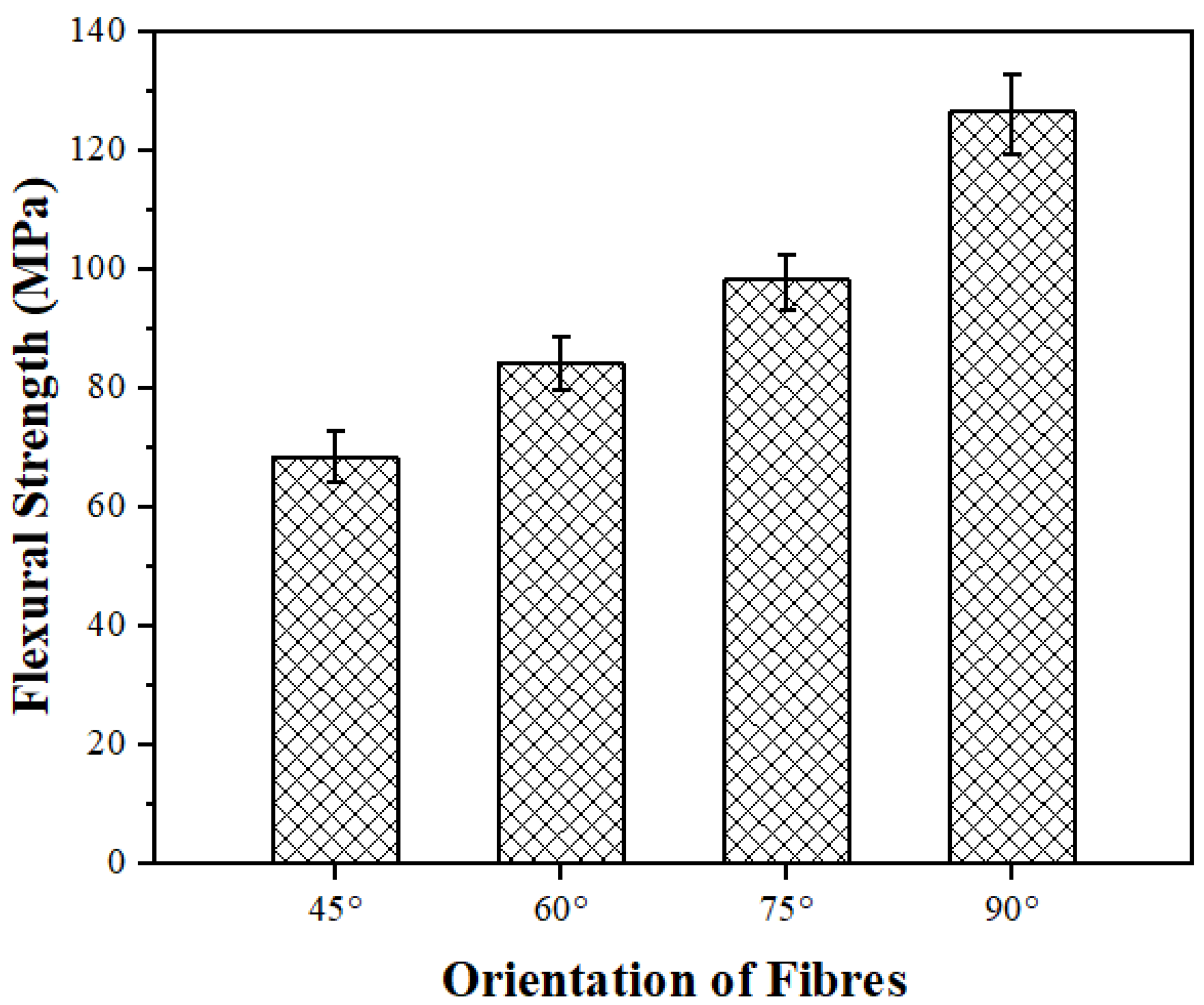
The flexural strength of the fiber-reinforced polymer composites is a crucial property that affects the material’s ability to resist bending or flexing under applied loads. It is strongly influenced by the orientation of the fibers, as the fibers are the primary load-bearing elements in the composite. In bidirectional mats, the fibers are arranged at specific angles, and this arrangement plays a critical role in determining the flexural strength of the composite. The flexural strengths of 45°, 60°, 75°, and 90° PALF-reinforced epoxy matrix composites are presented in Figure 6. The flexural strength increases with the increase in fiber orientation from 45° to 90°. The maximum flexural strength is ~126.42 MPa in the case of the 90° PALF orientation, and the minimum flexural strength is ~68.33 MPa in the 45° PALF orientation. From the results, it is evident that the composites with a 90° PALF orientation demonstrate ~85% higher flexural strength as compared to those with the 45° PALF orientation. This is because of the fiber orientation angles, which directly affect each layer’s strain. The strain of each layer is directly proportional to its distance from the neutral layers under the bending. Doddi et al. [17] found similar results in terms of the effect of basalt fiber orientation on dynamic mechanical behaviors and concluded that fiber orientation angle had a more significant impact on the dynamic and static properties.
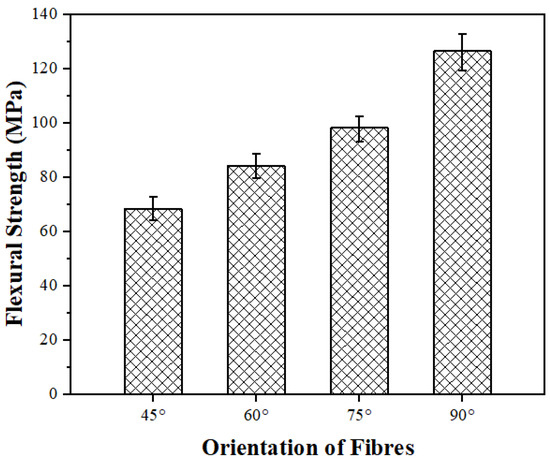
Figure 6.
Flexural strength of PALF composites fabricated with different orientations of fibers.
3.3. Effect of Different Orientations of Fibers on Impact Strength
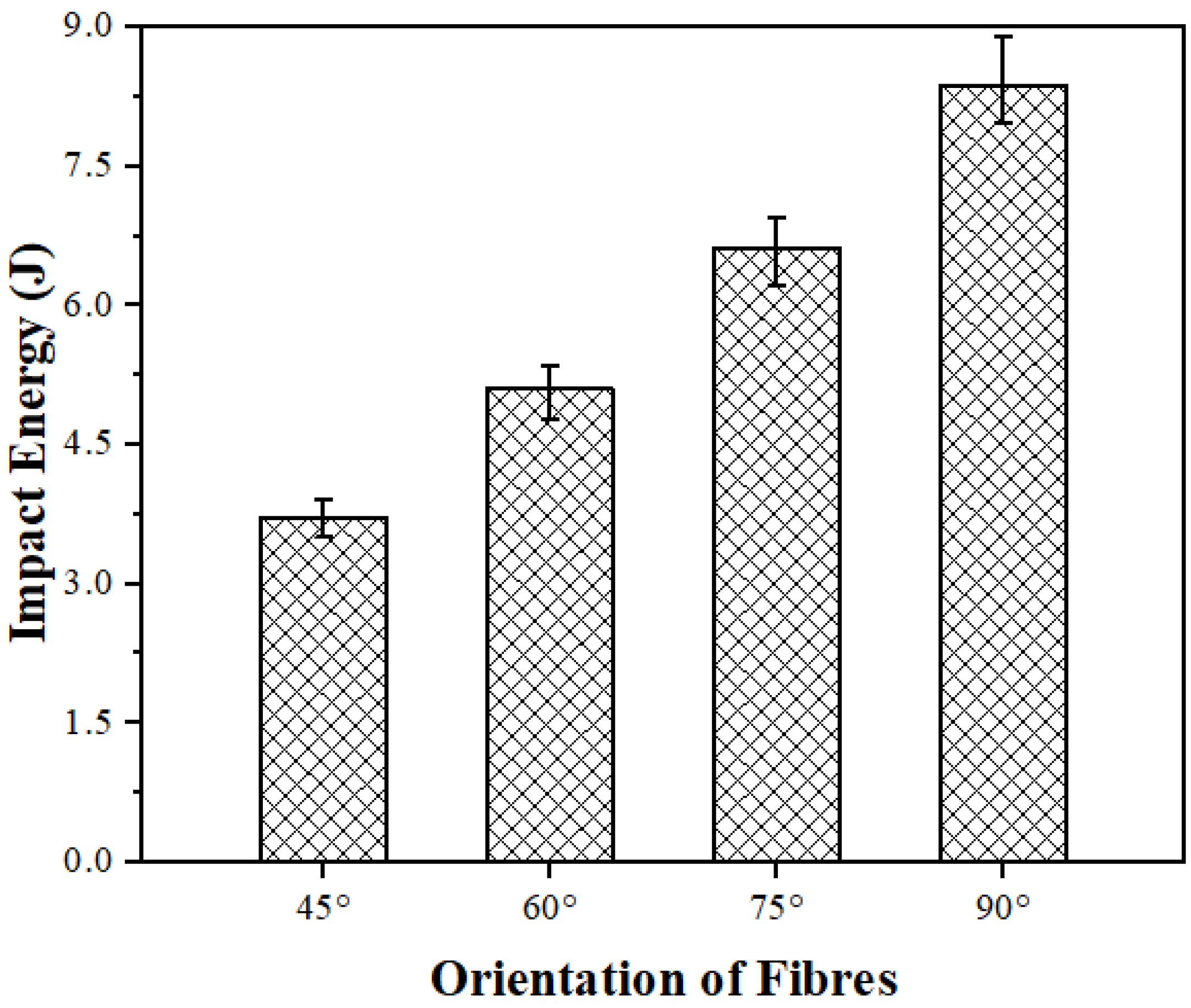
Impact strength is the measure of a material’s ability to sustain sudden forces or shocks without fracturing. In bidirectional mats, the fibers are arranged at different angles relative to the applied load, and this affects how the material distributes stress, absorbs energy, and resists failure under impact conditions. In the impact testing, V-notched samples were prepared, because the failure of a sample typically initiates at the notch point during impact testing. The impact energy observed for the different composites in the Charpy test is shown in Figure 7. The highest impact energy was observed in the composites with a 90° fiber orientation. As depicted in Figure 7, the optimum impact energy of 8.37 J was achieved for the 90° fiber orientation, while the lowest impact energy of 3.71 J was recorded for the composites with a 45° fiber orientation. The results clearly indicate that the composites with a 90° PALF orientation exhibited an impact strength that was ~126% higher than that of the composites with a 45° fiber orientation. Kumar et al. [26] investigated the influence of the orientation of aloe vera natural fibers on the mechanical properties of epoxy composites, such as impact strength, and found that fiber orientation significantly influenced the impact strength. It was clearly mentioned that composites with a 90° aloe vera fiber orientation obtained maximum impact strength, while those with a 45° aloe vera fiber orientation obtained minimum impact strength.
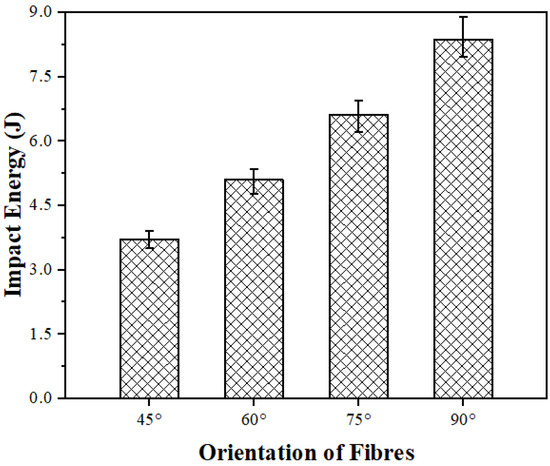
Figure 7.
Impact strength of PALF composites fabricated with different orientations of fibers.
3.4. Effect of Different Orientations of Fibers on Micro-Hardness
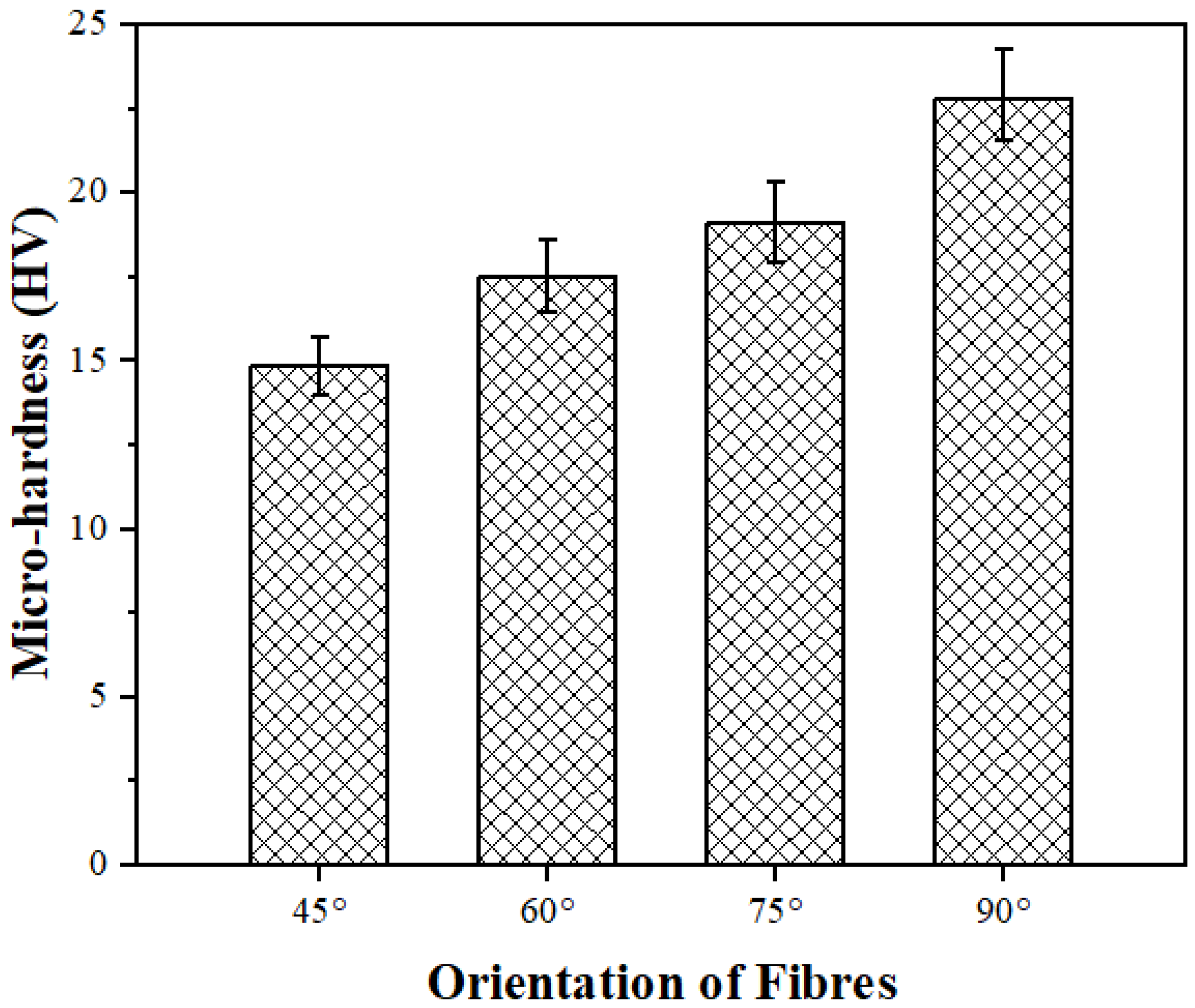
In fiber-reinforced polymer composites, the orientation of the fibers plays a crucial role in determining the material’s micro-hardness because it influences the distribution of stress and load-carrying capacity within the composite structure. Figure 8 illustrates the micro-hardness of the PALF composites fabricated with different orientations of fibers. One can observe that the micro-hardness increases as the orientation of fibers changes from 45° to 90°. The micro-hardness of the fabricated composites with a 45° fiber orientation revealed the minimum hardness, as the fibers may not be aligned with the applied load direction. Increasing the orientation angle can balance the load transfer between the matrix and fibers thus improving the micro-hardness of the composites with high orientation angles. The highest micro-hardness value of 21.63 HV was achieved for the composites with a 90° fiber orientation, while the lowest value of 14.71 HV was recorded for the composites with a 45° fiber orientation. These results clearly demonstrate that fiber orientation plays a significant role in influencing the micro-hardness properties of composite materials. The micro-hardness of the composites with a 90° fiber orientation was ~47% higher than that of the composites with a 45° fiber orientation, highlighting the impact of fiber alignment on the hardness performance.
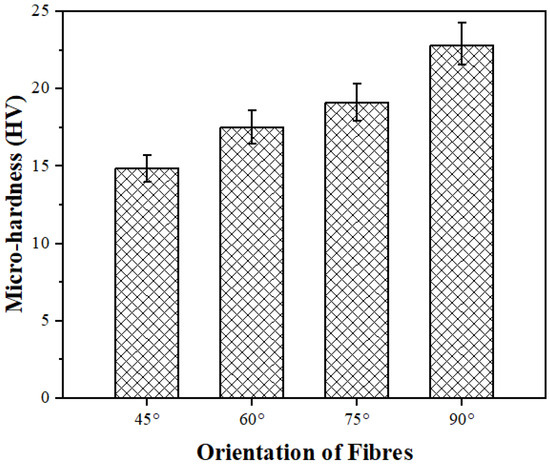
Figure 8.
Micro-hardness of PALF composites fabricated with different orientations of fibers.
3.5. Effect of Orientations of Fibers on Water Absorption
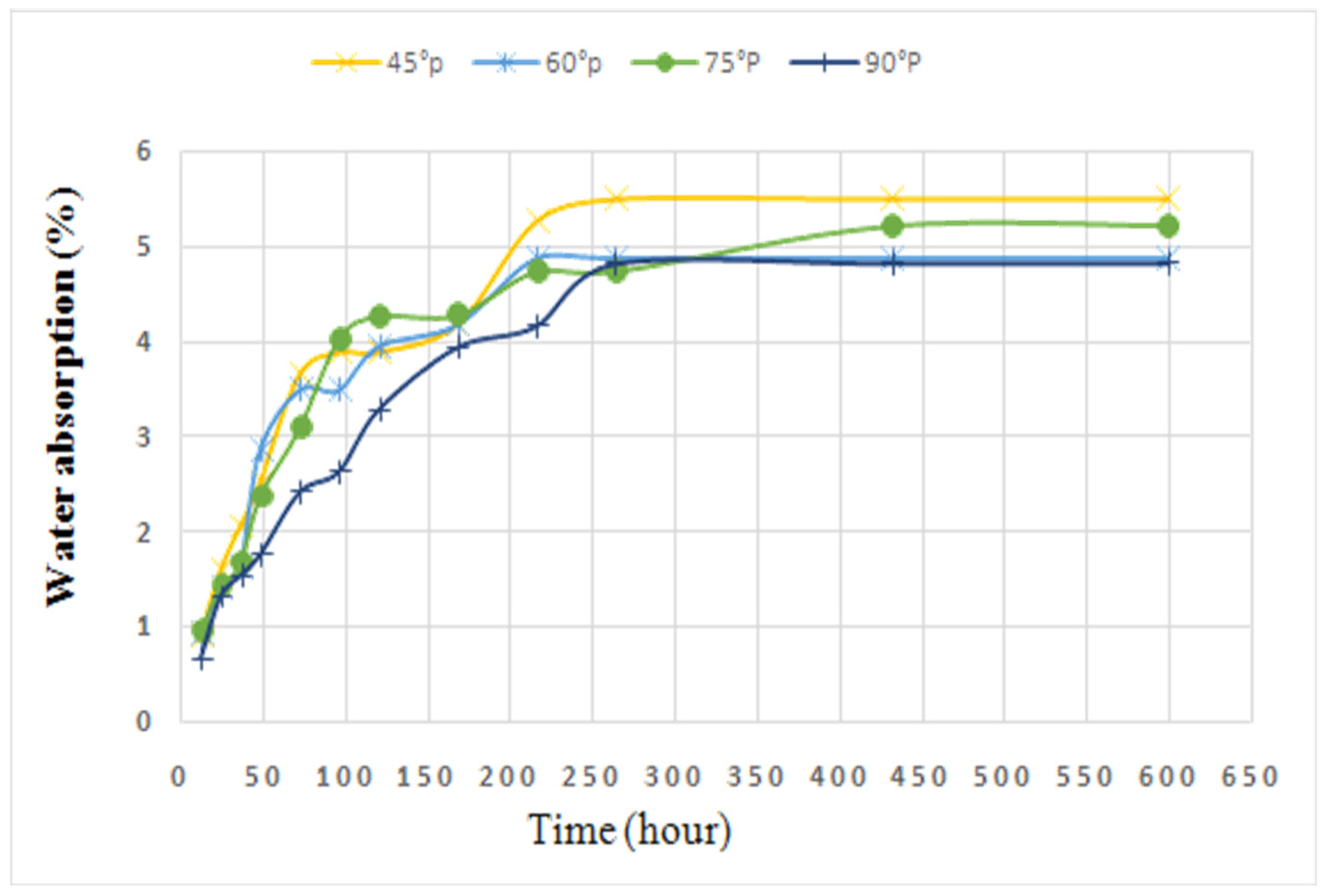
Natural fibers like PALF are highly susceptible to moisture absorption due to their hydrophilic nature (high cellulose content). Water absorption can degrade the mechanical properties of polymer composites, especially when the fibers swell. It can lead to the development of internal stress and a reduction in adhesion between the fibers and the matrix. The fiber orientation in a composite material plays a significant role in determining its water absorption behavior. The water absorption behavior of PALF-reinforced polymer composites fabricated with different orientations of fibers is illustrated in Figure 9. Among all the fabricated composites, the composite with the 45° fiber orientation exhibited the highest water absorption after 250 h compared to the composites with the 60°, 75°, and 90° fiber orientations, as the chance of water penetration is higher at this orientation. Initially, water absorption increased rapidly over time, reaching its peak at around 250 h. After this point, the rate of water absorption slowed significantly between 250 and 600 h. Beyond 600 h, the water absorption reached a plateau, indicating that the material had reached saturation. The composites with the 60° and 75° fiber orientations demonstrated moderate water absorption. Moreover, the composite with the 90° fiber orientation exhibited the lowest water absorption overall, suggesting that water could not diffuse easily into the fibers and matrix.
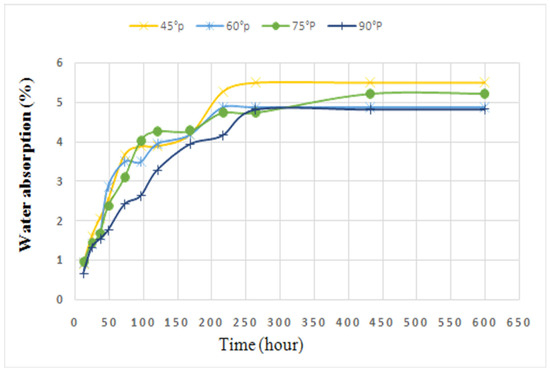
Figure 9.
Water absorption (%) of PALF composites fabricated with different orientations of fibers.
3.6. Effect of Orientations of Fibers on Tribological Behavior
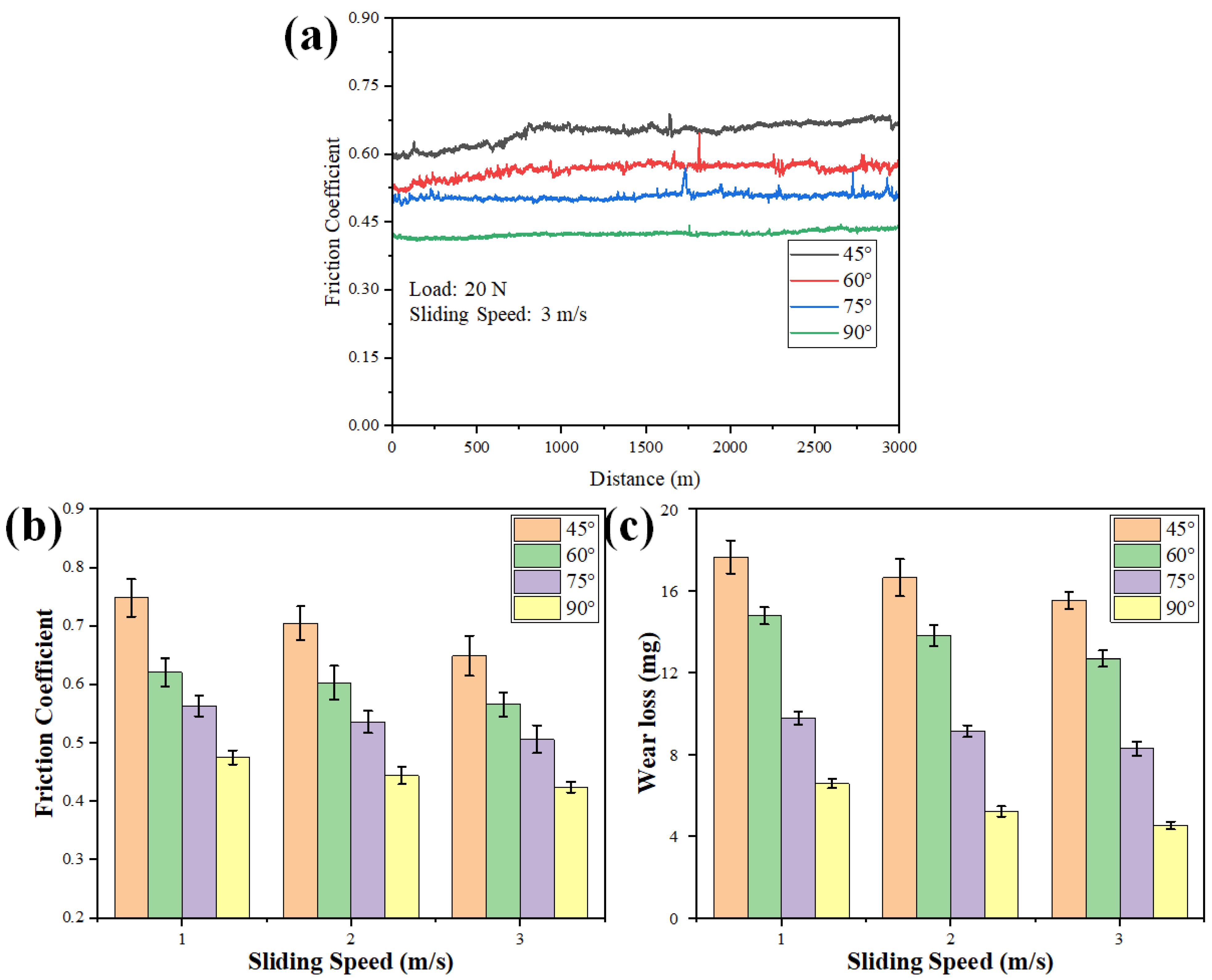
The effect of pineapple leaf fiber orientation on the tribological behavior of polymer composites was explored, as the proper fiber alignment could lead to enhanced wear resistance and frictional properties. Aligned fibers can result in a smoother contact surface, leading to reduced friction, while randomly oriented fibers may cause increased friction, due to their inconsistent interactions with the counterface. Figure 10 shows the variations in the friction coefficient for the different orientations at 3 m/s sliding speed under 20 N load, as well as the average COF and wear rate for the different orientations of fibers slid against EN31 steel disc; one can observe that as the orientation angle increases, the COF and wear rate decrease. The minimum COF and wear rate occur at 90°, while the maximum occurs at 45°. In short, for the the composites with fibers aligned in the sliding direction, friction and wear tend to be lower. Randomly oriented fibers can cause higher friction and wear rates because of their tendency to degrade more easily under stress. As the sliding speed increases, the friction coefficient and wear rate are found to reduce for the same sliding distance, which might be due to a decrease in the interaction time of the sliding surfaces.
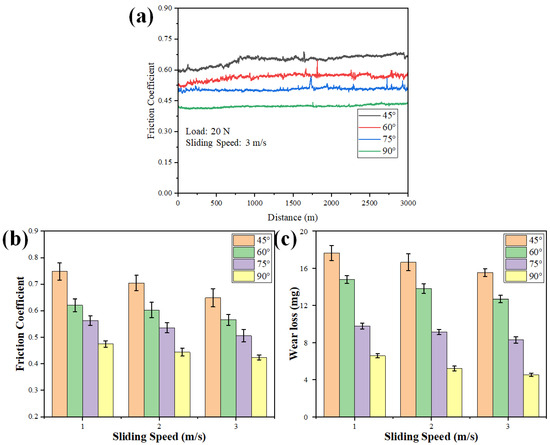
Figure 10.
(a) Variations in friction coefficient for different orientations at 3 m/s sliding speed under 20 N load. (b) Average friction coefficient and (c) wear loss (mg) of different polymer composites after the friction test.
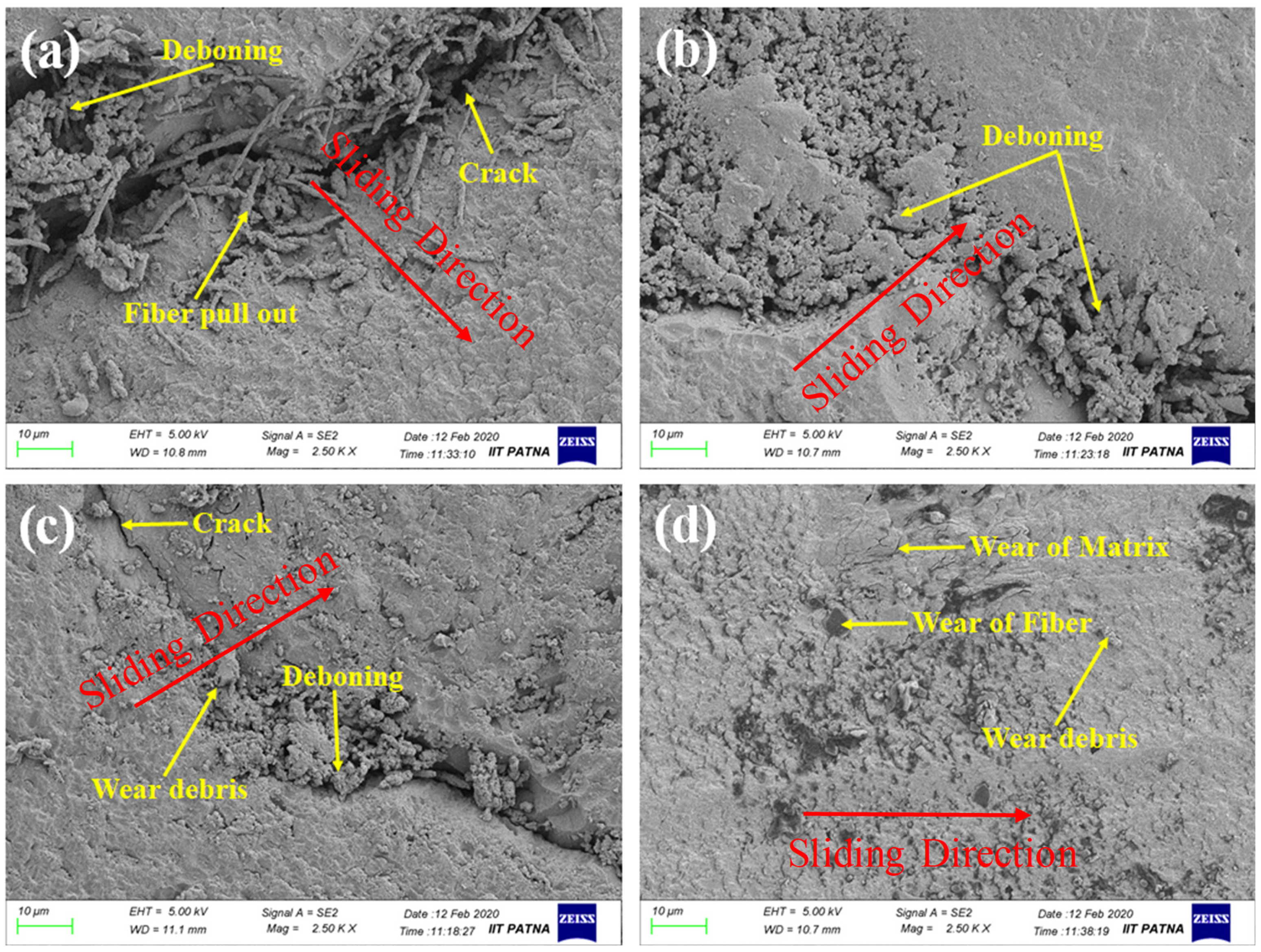
Figure 11 reveals the worn surface morphology of the different polymer composites slid at a 2 m/s sliding speed under 20 N. First, the matrix covering the fiber was worn; after that, the fiber was worn and pulled out. One can observe the deboning, fiber pull-out, and cracks across the surface of the composites with a 45° fiber orientation, which is possibly due to the misalignment of the fibers with the sliding direction. As observed in Figure 11, the composites with a 45° fiber orientation show the maximum damage to the surface. Increasing the orientation angle reduced the severity of the wear, and the minimum surface damage was observed for the composites with a 90° fiber orientation. So, it should be noted that if fibers are aligned in the direction of the sliding motion, they can provide more resistance to friction and wear.
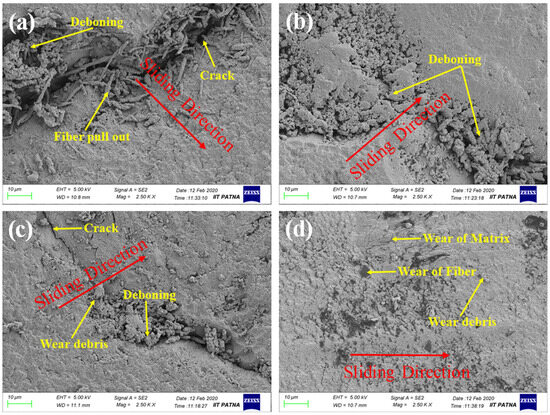
Figure 11.
Worn surface morphology of (a) 45°, (b) 60°, (c) 75°, and (d) 90°-oriented polymer composites after the friction test at 2 m/s sliding speed under 20 N.
4. Conclusions
In the current study, PALF-reinforced epoxy composites were fabricated with different orientations (45°, 60°, 75°, and 90°) of fibers in the epoxy matrix, using the cost-effective hand layup method, and the effects on the mechanical properties and water absorption behaviors were subsequently investigated. The orientation of the fibers in a composite material plays a key role in determining its mechanical properties. Increasing the angle of orientation of the PALF in the epoxy matrix can improve the tensile strength, flexural strength, impact strength, and hardness. The highest properties were recorded at an orientation of 90° and the lowest at a 45° orientation. As the fiber orientation increases (from 45° to 90°), the composite becomes more capable of withstanding sudden forces or impacts, providing stronger, more durable material properties. The alignment of the fibers plays a significant role in the material’s ability to resist surface damage, such as scratching or indentation. An increase in the hardness with the increase in fiber orientation suggests that the composite becomes more durable and resistant to localized surface deformation, enhancing its overall performance and wear resistance. Fiber orientation has a favorable effect on the water absorption behavior of PALF-reinforced composites, and the minimum water absorption was observed for the composites with a fiber orientation of 90°. While fiber orientation plays a significant role in mechanical properties like strength, its influence on how much water the composite absorbs is not as significant. Water absorption is more likely influenced by the diffusion of the water in the matrix. The composite with a 90° fiber orientation exhibited the lowest water absorption overall, suggesting that water may not diffuse easily into the fibers and matrix. Increasing the orientation angle reduced the friction coefficient and severity of the wear, which can be attributed to the alignment of the fiber orientation with the sliding direction. Overall, the composite fabricated with a fiber orientation of 90° emerged as the best composite among all considered in this study.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, N.K., S.S., A.S. and T.H.; Formal Analysis, N.K., S.S. and T.H.; Investigation, N.K. and S.S.; Methodology, N.K., S.S. and A.S.; Project Administration, A.S.; Software, N.K.; Supervision, A.S.; Validation, N.K. and S.S.; Visualization, N.K. and S.S.; Writing—Original Draft, N.K.; Writing—Review and Editing, S.S., A.S. and T.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
Dataset available on request from the authors.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Anand, P.B.; Lakshmikanthan, A.; Gowdru Chandrashekarappa, M.P.; Selvan, C.P.; Pimenov, D.Y.; Giasin, K. Experimental Investigation of Effect of Fiber Length on Mechanical, Wear, and Morphological Behavior of Silane-Treated Pineapple Leaf Fiber Reinforced Polymer Composites. Fibers 2022, 10, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemzadeh, B.; Duchesne, M.C.; Rodrigue, D. Mechanical, water absorption and aging properties of polypropylene/flax/glass fiber hybrid composites. J. Compos. Mater. 2015, 49, 3781–3798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijay, C.; Bajpai, P.K.; Maheshwari, S. Studies on mechanical and morphological characterization of developed jute/hemp/flax reinforced hybrid composites for structural applications. J. Nat. Fibers. 2018, 15, 80–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimah, A.; Ridho, M.R.; Munawar, S.S.; Adi, D.S.; Damayanti, R.; Subiyanto, B.; Fatriasari, W.; Fudholi, A. A review on natural fibers for development of eco-friendly bio-composite: Characteristics, and utilizations. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 13, 2442–2458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elfaleh, I.; Abbassi, F.; Habibi, M.; Ahmad, F.; Guedri, M.; Nasri, M.; Garnier, C. A comprehensive review of natural fibers and their composites: An eco-friendly alternative to conventional materials. Results Eng. 2023, 19, 101271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, M.I.; Kumar, M.A.; Raju, R.B. Tensile and Flexural properties of Jute, Pineapple leaf and Glass fiber Reinforced Polymer Matrix Hybrid Composites. Mater. Today Proc. 2018, 5, 458–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Singh, A.; Debnath, K. Influence of fiber weight ratio on the mechanical and water absorption performance of borassus/epoxy composites. Mater. Test. 2020, 9, 937–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sethupathi, M.; Khumalo, M.V.; Skosana, S.J.; Muniyasamy, S. Recent Developments of Pineapple Leaf Fiber (PALF) Utilization in the Polymer Composites—A Review. Separations 2024, 11, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asim, M.; Abdan Khalina Jawaid, M.; Nasir, M.; Dashtizadeh Zahra Ishak, M.R.; Hoque, M.E. A Review on Pineapple Leaves Fibre and Its Composites. Int. J. Polym. Sci. 2015, 2015, 950567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khumalo, M.V.; Sethupathi, M.; Skosana, S.J.; Muniyasamy, S. Melt-Extruded High-Density Polyethylene/Pineapple Leaf Waste Fiber Composites for Plastic Product Applications. Separations 2024, 11, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sezgin, H.; Enis, I.Y.; Berkalp, O.B. Impact of biaxial square woven jute fabric reinforcement on mechanical performance of polyester-based composites. Indian J. Fibre Text. Res. 2018, 43, 252–256. [Google Scholar]
- Jain, J.; Sinha, S. Pineapple leaf fiber polymer composites as a promising tool for sustainable, eco-friendly composite material. J. Nat. Fibers 2022, 19, 10031–10052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motaleb, K.A.; Shariful Islam, M.; Hoque, M.B. Improvement of physicomechanical properties of pineapple leaf fiber reinforced composite. Int. J. Biomater. 2018, 1, 7384360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Singh, A. Study the effect of fiber orientation on mechanical properties of bidirectional basalt fiber reinforced epoxy composites. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 39, 1581–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasikun, L.; Ariawan, D.; Surojo, E.; Triyono, J. Effect of fiber orientation on tensile and impact properties of Zalacca Midrib fiber-HDPE composites by compression molding. AIP Conf. Proc. 2018, 1931, 030060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakir, B.; Hashem, H. Effect of fiber orientation for fiber glass reinforced composite material on Mechanical properties. Int. J. Min. Metall. Mech. Eng. 2013, 1, 2320–4060. [Google Scholar]
- Doddi, P.R.; Chanamala, R.; Dora, S.P. Effect of fiber orientation on dynamic mechanical properties of PALF hybridized with basalt reinforced epoxy composites. Mater. Res. Express 2020, 7, 015329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, J., Jr.; Angrizani, C.C.; Botelho, E.C.; Amico, S.C. Effect of fiber orientation on the shear behaviour of glass fiber/epoxy composites. Mater. Des. 2015, 65, 789–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordin, M.; Bechtold, T.; Pham, T. Effect of fiber orientation on the mechanical properties of polypropylene–lyocell composites. Cellulose 2018, 25, 7197–7210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM D638-22; Standard Test Method for Tensile Properties of Plastics. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2022.
- ASTM D790-17; Standard Test Methods for Flexural Properties of Unreinforced and Reinforced Plastics and Electrical Insulating Materials. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2017.
- ASTM D6110-18; Standard Test Method for Determining the Charpy Impact Resistance of Notched Specimens of Plastics. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2018.
- ASTM E384-22; Standard Test Method for Microindentation Hardness of Materials. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2022.
- ASTM D570-22; Standard Test Method for Water Absorption of Plastics. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2022.
- ASTM G99-23; Standard Test Method for Wear and Friction Testing with a Pin-on-Disk or Ball-on-Disk Apparatus. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2023.
- Kumar, N.; Singh, A. Effect of aloe vera natural fiber orientation on the mechanical properties of epoxy composites. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2023, 9, 1859–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).