Abstract
Stern tube lubricants are essential in maritime operations, safeguarding ship propeller shafts from wear and corrosion while ensuring efficient propulsion. Their role in reducing friction and maintaining system integrity is critical. With growing environmental concerns, the adoption of environmentally acceptable lubricants (EALs) for stern tubes has gained importance, balancing operational performance with environmental protection. This study investigates the rheological and tribological properties of EALs formulated for ship propeller stern tube applications. The primary focus is on comparing these EALs with conventional mineral oils to assess their suitability in marine environments. EALs are increasingly favored due to their biodegradability and reduced environmental impact. Key parameters such as shear stability, friction factor, and temperature dependency were evaluated using a range of experimental methods including rotational viscometry and tribological analysis. The results indicate that the newly formulated EALs based on synthetic esters exhibit the highest viscosity index, a higher range of shear stability, and lower friction factors, compared to commercially available mineral oils, especially under varying operational conditions. These findings contribute to the ongoing efforts to promote eco-friendly lubricants in maritime industries, aligning with global environmental protection initiatives.
1. Introduction
The loss of lubrication in ship propellers leads to oil seepage into adjacent waters. Despite the typically small magnitude of these leaks, they pose significant ecological ramifications, contributing substantially to marine pollution on a global scale. Recent efforts to mitigate the loss of lubrication in ship propellers have prioritized the substitution of traditional mineral lubricants with environmentally acceptable lubricants (EALs) [1].
The mandate for safeguarding both human health and the environment falls within the purview of the United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). In 2013, the EPA promulgated regulations known as the Vessel General Permit (VGP) [2], delineating guidelines for lubricant usage within the maritime sector. Under this regulatory framework, commercial vessels exceeding 79 feet are prohibited from entering American waters if they employ non-compliant lubricants. This directive is gradually garnering support from an increasing number of states.
EALs are currently quite readily available on the market. Their biodegradability and minimal environmental impact associated with their use represent the primary competitive advantage over mineral lubricants. EALs consist of base oils, typically of ester origin or biobased oils, and additives that enhance their selected properties. It is crucial to have a suitable combination of additives to ensure the desired oil properties. One of the major drawbacks of EALs is the significant viscosity change with variations in pressure and temperature, which can lead to the inadequate lubrication of components, subsequent rapid wear, or even the destruction of ship propeller bearings under high loads and shear rates [1,3,4,5,6]. Therefore, the goal is to develop a sustainable lubricant with the highest possible viscosity index, which will maintain stable viscosity over a wide range of shear rates while exhibiting the lowest possible coefficient of friction. This work presents a comparative experimental study of one commercially available mineral oil, one commercially available environmentally acceptable lubricant (EAL), and one newly formulated EAL. Comprehensive chemical analyses reveal the differences in the composition of these oils. Furthermore, the analyses of their transport properties demonstrate their suitability for lubricating stern tubes. By comparing these distinct types of lubricants, this study provides valuable insights into their respective chemical and functional characteristics, contributing to the understanding of their performance in maritime applications. The findings highlight the potential advantages of the newly formulated EAL, particularly in terms of its compatibility and efficiency in stern tube lubrication, while also considering the environmental benefits.
1.1. Background of Stern Tube Lubrication
In ship propulsion systems, the interaction between the propeller device and its surroundings plays a critical role [7]. Over time, these systems, which have been in use for many years, are prone to wear and require efficient solutions to maintain performance. Bioproducts have emerged as viable options for various components of the propeller device [8]. Fluid motions in ships can lead to significant torsional forces, particularly when there are subtle yet critical differences between the propeller screw and the center of steering [9]. These forces contribute to a more accurate prediction of friction resistance compared to traditional research methods [7]. However, validating mathematical models developed for such complex systems remains challenging [7].
Additionally, lubrication occurs between the stern tube and the surrounding liquid. Drops in pressure around the outer hole of the connected shaft may indicate the presence of air, leading to the formation of bubbles that pass through the axial water system to lubricate the horizontal seal [10]. This bubble formation is facilitated by the pressure differential between the gas in the water and the surrounding air, along with the rotational motion of the follower and the influx of new water [11].
To improve efficiency and reduce fuel consumption, propulsion-improving devices (PIDs) such as ducts, pre-swirl fins, and contra-rotating propellers are employed [7,12,13,14]. These modifications enhance the flow around the hull or propeller. Pre-swirl devices improve the propeller inflow conditions, while post-swirl devices recover parts of the rotational energy in the propeller slipstream [13,14].
1.2. Importance of Biolubricants in Marine Applications
Marine oil spills present significant environmental and health risks, stemming from both the loss of mineral oils stored on ships during routine operations and the potential harm to marine ecosystems, which can impact biodiversity [12,15]. Exposure to these fluids can lead to various health issues, ranging from minor irritations to more serious conditions. Moreover, friction, wear, and the release of oil from machinery can directly affect marine life and, by extension, human health [16]. Studies have also highlighted the detrimental effects of emissions from marine vessels on air quality [17,18,19,20]. Consequently, the European Union (EU), the International Maritime Organization (IMO), and other global bodies have collaborated on legislative initiatives to promote the use of eco-compatible lubricants [12].
In September 2005, Directive 2005/35/EC was enacted, mandating the adoption of eco-compatible lubricants across all ship types [21]. In a broader global context prioritizing environmental protection, it is crucial to implement measures aimed at reducing pollution from human activities. One such measure involves the development and utilization of environmentally friendly products, such as biolubricants. As part of this global effort, significant regulations are being enacted to promote safer, greener, and healthier societies, with particular emphasis on reducing pollution in the marine environment [22]. Organizations like the Committee for the Protection of the Sea (CPS) and the IMO have specifically targeted the reduction in marine pollution, particularly from oils, as a critical objective [23].
This study concentrates on examining the rheological and tribological characteristics of newly formulated biolubricants derived from synthetic esters. In conducting comparative analyses, commercially accessible environmentally acceptable lubricants (EALs) and conventional mineral oil were employed for stern tube lubrication. The primary emphasis was placed on assessing shear stability and constructing Stribeck curves under various loads. Additionally, the investigation delved into the influence of temperature variations within the marine operational spectrum.
1.3. Shear Stability
Capillary viscometers and rotational rheometers are instrumental in measuring viscosity at a wide range of shear rates [24,25,26,27,28]. Capillary viscometers are particularly vital for evaluating high-temperature high-shear (HTHS) characteristics, which are critical for engine oils operating at elevated temperatures [29]. In the context of marine applications, especially for lubricating ship propellers where lubricant temperatures can reach up to 100 °C, rotary rheometers with narrow gaps (~100 μm or less) are recommended [30].
The propeller’s direct contact with seawater and its construction from thermally conductive metals mean the lubricant’s temperature matches that of the surrounding water when the vessel is stationary. During navigation, the lubricant’s temperature increases, with a maximum limit of 80 °C [31]. Both mineral oils and environmentally acceptable lubricants (EALs) used in ship propeller lubrication exhibit Newtonian fluid behavior under standard conditions, where dynamic viscosity is temperature-dependent and linearly related to shear stress and shear rate [32]. However, during specific maneuvers such as starting or turning, the gap between the propeller shaft and bearing narrows, leading to a significant local increase in the shear rate [31]. Thus, understanding the behavior of lubricants under these conditions is essential for ensuring effective lubrication and preventing equipment damage [29,31,32,33,34,35,36].
1.4. Friction Factor
The stern tube of a marine vessel encases the propeller shaft as it traverses the hull, incorporating bearings for support and a sealing mechanism to prevent water ingress and lubricant escape [37]. Effective lubrication is paramount to mitigate friction and wear between the rotating shaft and bearings [38]. The friction coefficient plays a pivotal role in stern tube lubrication, influencing the efficiency, reliability, and longevity of the bearing system aboard ships [39].
A lower friction coefficient indicates diminished resistance between the shaft and bearings, resulting in decreased energy consumption by the propulsion system [38]. Optimal lubrication sustains a lower friction coefficient, translating into fuel savings and reduced operational expenses [39]. Additionally, friction generates heat, with elevated coefficients potentially causing excessive heat accumulation within the stern tube [34]. Adequate lubrication curtails friction, thereby managing temperatures and averting overheating that may jeopardize bearings and seals [37].
Reduced friction coefficients also curtail wear on stern tube components, extending their operational lifespan and diminishing maintenance costs and downtime [38]. The selection of lubricants capable of maintaining low friction coefficients under operational conditions assumes critical importance. High-quality lubricants form stable films that minimize metal-to-metal contact, thereby lowering friction coefficients [39].
Efficient lubrication with minimal friction coefficients mitigates the risks of lubricant leakage and water contamination, crucial for compliance with environmental regulations and for safeguarding marine ecosystems [37]. In summary, the friction coefficient profoundly impacts the efficiency, durability, and environmental adherence of stern tube lubrication systems in marine vessels [38].
1.4.1. Measuring and Controlling Friction Factor
The friction factor in stern tube lubrication is a crucial parameter that can be managed through the careful selection of lubricants, continuous monitoring, and thoughtful design considerations. Lubricants are chosen based on their viscosity and specific additives, such as anti-wear agents, friction modifiers, and corrosion inhibitors, which help maintain a low friction factor under varying operational loads and temperatures. Regular inspections, including oil analysis and vibration monitoring, are essential to evaluate lubricant condition and bearing wear, ensuring the optimal performance of the lubrication system. Timely top-up and replacement of the lubricant are necessary to maintain its effectiveness in minimizing friction [39,40,41,42].
Additionally, the choice of bearing materials and their surface finish plays a significant role in influencing the friction factor. Materials with superior tribological properties and smooth surface finishes contribute to reduced friction. In summary, the friction factor’s influence on energy efficiency, heat generation, wear and tear, lubricant performance, and environmental impact necessitates its effective management. Proper lubricant selection, regular monitoring, and maintenance are vital to ensuring the reliable and efficient operation of the stern tube-bearing system [39,40,41,42].
1.4.2. Experimental Methods for Measuring the Friction Factor
Experimental methods for measuring the friction factor involve various techniques and equipment to accurately determine the frictional resistance between surfaces under specific conditions. Available methods with brief descriptions and typical applications are listed in Table 1.

Table 1.
Summary of different types of tribometers and related instruments.
2. Materials and Methods
The experiments were aimed at determining the temperature dependence of the viscosity of the tested oils, their viscosity index, shear stability, and the determination of the friction factor as a function of temperature and load on the measuring cell. Kinematic viscosity and viscosity index were determined on a Stabinger viscometer (Anton Paar, Graz, Austria). The temperature dependence of the dynamic viscosity was also determined on a MARS 60 rheometer, mainly to set the upper limits of the measurement program at high shear rates. The limiting factor was the maximum unsurpassed rotor speed and the maximum torque. The aim was to use the sensor within the maximum possible range.
Based on the viscosity measurements, the Results section reveals the stable viscosity region and evaluates the influence of secondary flow on the different geometries. From the friction coefficient measurements, Stribeck curves were constructed, and the shear rates at which the transition from mixed to hydrodynamic lubrication regime occurred were determined. Three samples were tested: one mineral standard, one EAL standard, and a new fully additive EAL formulation based on the saturated esters.
2.1. Materials
Three samples of propeller lubrication oils were tested: a commercial mineral oil (C-MIN), a commercial environmentally acceptable oil (C-EAL), and a fully formulated environmentally acceptable synthetic ester-based bio lubricant (N-EAL-A1X). C-MIN is an oil of Group I based on paraffinic hydrocarbons. C-EAL is an oil based on synthetic esters with minimum additives. N-EAL-A1X is an oil based on a narrow cut of branched synthetic esters. The basic available characteristics of tested oils are given in Table 2.

Table 2.
Labeling and characteristics of the tested oils (base oil type, presence of additives and antioxidants, and viscosity grade).
The newly formulated sample, N-EAL-A1X, is composed of a saturated ester base oil (92 wt%) characterized by an iodine value below 5, an acid number below 0.5, and a viscosity index of 165. The primary components are a polymer mixture of adipic acid ester and diisotridecyl adipate (CAS# 26401-35-4). To enhance performance, a premium additive package, certified by Ecolabel for industrial gear oils, was incorporated at 3 wt%. The key components of this additive package include 1,3,4-thiadiazolidine-2,5-dithione; reaction products with hydrogen peroxide and tert-nonanethiol (ES# 293-927-7); reaction products of diphosphorus pentaoxide and alcohol C7-9-iso; C8 rich, salted with 2-ethylhexylamine (ES# 942-466-6); and isooctadecanoic acid, the reaction product with tetraethylenepentamine (ES# 701-204-9). This package provides excellent protection under extreme pressure (EP) conditions, superior load-carrying capacity, resistance to micro-pitting, and strong bearing protection.
Additionally, the formulation includes sulfurized linear polymer (inactive sulfur) as an extreme pressure additive at 2 wt% (EP), amine-neutralized phosphoric acid ester polymer containing 5% phosphorus and 2.5% nitrogen as an anti-wear additive at 1 wt% (AW), high-molecular-weight phenolic antioxidant (3,5-Bis(1,1-dimethylethyl)-4-hydroxy-benzenepropanoic acid C7-9-branched alkyl esters, CAS# 125643-61-0) at 1 wt%, yellow metal corrosion inhibitor, based on tolyltriazole sodium salt (CAS# 64665-57-2) at 0.3 wt% (CI), alkyl methacrylate polymer dispersed in mineral oil at 0.3 wt% as a pour-point depressant (PPD), and a blend of silicone–polyacrylate and synthetic hydrocarbons at 0.05 wt% as a defoamer.
2.2. Methods
The comparison of the tested oils based on their chemical composition and the nature of their base oils was conducted using Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) analysis. The FTIR spectra of the liquids were measured using an IS5 instrument by Nicolet (Prague, Czech Republic) with an ATR (attenuated total reflectance) attachment, facilitating accurate spectral analysis.
Chemical composition was also analyzed by high-pressure liquid chromatography and mass spectroscopy (HPLC-MS). For this purpose, the oil samples were diluted in a mixture of hexane and isopropanol (2:1, volumetrically). Chromatographic separation was performed on Dionex UltiMate 3000 (Thermo Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). The XBridge BEH (Bridged Ethyl Hybrid, Milford, MA, USA) C18 column, 130 Å, 3.5 μm, 4.6 mm × 150 mm, and XBridge BEH C18 column, 130 Å, 3.5 μm, 4.6 mm × 250 mm, connected into series, were used to separate the compounds of interest. The mobile phase consisted of 0.1% formic acid in acetonitrile (solvent A) and isopropanol (solvent B). The linear gradient elution was set as follows: 0 min, 100:0 (A:B); 106 min, 69:31; 109 min, 0:100; 110 min, 100:0. The flow rate was set at 1 mL/min, and the injection volume was 10 μL. The HPLC system was coupled with a mass spectrometer micrOTOF-Q III (Bruker, Billerica, MA, USA) equipped with an APCI (Atmospheric Pressure Chemical Ionization) source in positive ionization mode. The parameters were set as follows: vaporization temperature 400 °C, dry temperature 200 °C, dry gas flow rate 7 L/min, nebulizer gas pressure 3 bar, capillary voltage 4000 V, end-plate offset −500 V, corona needle current 3000 nA, ion energy 3 eV, collision energy 7 eV, and m/z scan range 100–1500.
The viscosity index, kinematic viscosity, and density at 40 °C and 100 °C were determined using a Stabinger-type viscometer SVM 3001 from AntonPaar (Graz, Austria). This instrument provided precise measurements of these viscosity-related parameters.
For comprehensive rheological characterization, a Rheometer MARS 60 by Haake–Thermo (Waltham, MA, USA) was utilized. The rheometer was equipped with various specialized cells, including a standard Couette cell, a high-shear measuring cell, and a triborheology cell featuring a ball on three plates setup; see Figure 1. Rheological tests were performed under controlled rate (CR) mode, and flow curves were recorded at temperatures of 10, 20, 40, and 80 °C.
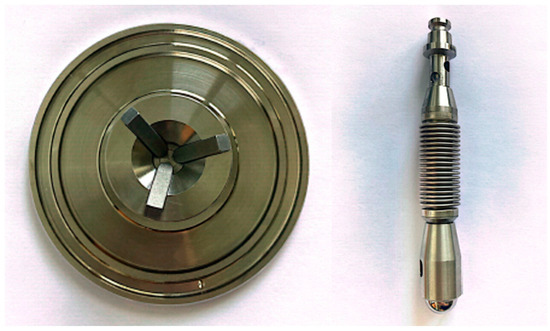
Figure 1.
Tribocell-measuring geometry (right—rotor with a flexible shaft and ball holder; left—the bottom holder with replaceable plates on adapter plate).
Friction factor measurements were conducted at the same temperatures using the same rheometer setup, applying four different loads (0.5 N, 1 N, 3 N, and 6 N of normal force).
In addition to the comprehensive rheological characterization described previously, the Rheometer MARS 60 by Haake–Thermo also facilitated high-shear and tribology experiments over a wide range of speeds. This instrument allowed for the precise control of rotational speeds, ranging from zero up to the maximum available speed, enabling detailed investigations into the viscosity and tribological properties of the tested oils under varying shear conditions. High-shear experiments were particularly crucial for assessing the oil’s performance in extreme operating conditions, simulating scenarios where shear rates are significant, such as in mechanical components under high-speed rotation or shear-sensitive applications. These experiments provided valuable insights into how the oils behave under different operational speeds, contributing to a comprehensive understanding of their suitability for various industrial and engineering applications.
The pin-on-disc method was employed to monitor wear. The tests were conducted at room temperature with a normal force of 20 N, generating an initial contact pressure greater than 1 GPa. The tests were carried out for thirty minutes at a rotational speed of forty revolutions per minute, with a rotation radius of 12 mm. Subsequently, photographic documentation was taken, and profilometry was performed in four different planes. An illustrative photo of the used apparatus is shown in Figure 2.
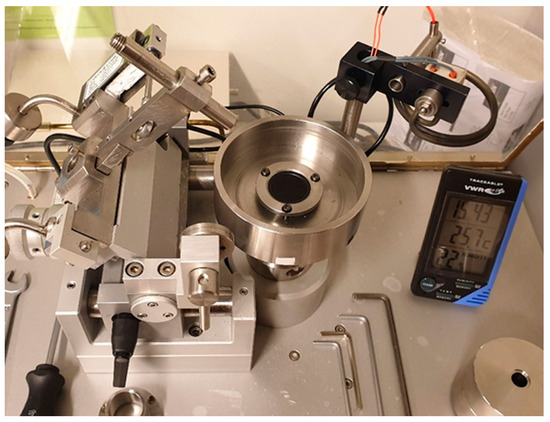
Figure 2.
Pin-on-disc apparatus used for wear testing.
3. Results
3.1. Oil Characterization by FTIR
The collected ATR-FITR spectra of oils are presented in Figure 3. In the case of C-MIN oil, no characteristic peak was detected at a wavelength of 1743 cm−1, indicating the absence of a functional ester group. By contrast, C-EAL and N-EAL-A1X exhibit this peak, confirming the ester origin of these oils. Additionally, the absence of peaks characteristic of a double bond in all samples indicates the use of saturated esters in the case of N-EAL-A1X and C-EAL. Similarly, for C-MIN, it can be deduced that it is composed of saturated hydrocarbons with minimal oxygen content, which confirms the absence of peaks from oxygenated functional groups in the region of 800–1300 cm−1; see Figure 3. Table 3 lists all key functional groups and their identification in the lubricants examined within the measured wavelength range.
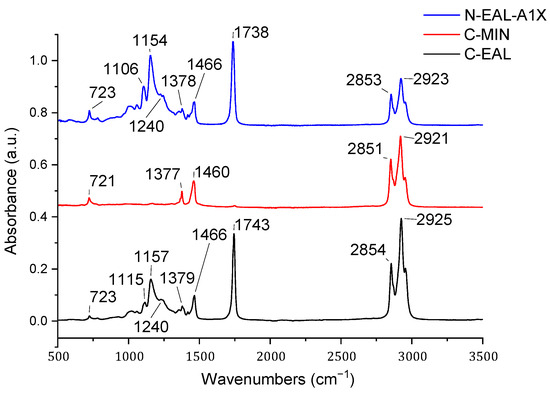
Figure 3.
FTIR spectra of tested oils.

Table 3.
Characteristic peaks detected in the FTIR spectra and their indication in tested oils.
3.2. Oil Characterization by HPLC-MS
The HPLC-MS chromatograms collected are shown in Figure 4 except for C-MIN mineral oil. Mineral oil was not suitable for the APCI ionization used for the HPLC-MS analysis because the C-MIN oil contained mainly saturated hydrocarbons (see FTIR analysis, Figure 3) which were not ionized. The chromatograms of both EALs were very similar. Evaluated details are listed in Table 4.
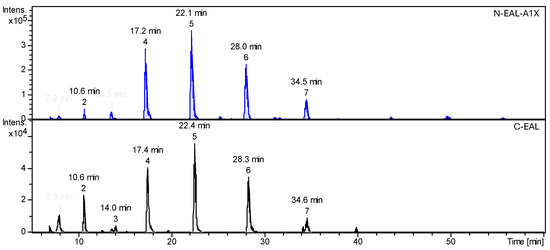
Figure 4.
HPLC-MS chromatograms of N-EAL-A1X and C-EAL.

Table 4.
HPLC-MS analysis of EALs: retention time (RT), maximal ion mass (m/z), and mass fraction on the basis of peak area.
3.3. Kinematic Viscosity and Viscosity Index
Kinematic viscosity measurements at temperatures of 40 °C and 100 °C, along with the density at 40 °C, were conducted using an Anton Paar 3001 viscometer, a reliable instrument known for its precision in viscosity and density determinations. These measurements provide crucial data points that characterize the flow behavior and density of the oils under standardized thermal conditions, reflecting their viscosity–temperature relationship and thermal stability. Additionally, the viscosity index (VI) of each oil sample was calculated, which serves as a key indicator of how viscosity changes with temperature variations. The results of these measurements are summarized in Table 5.

Table 5.
Basic characteristics of the tested oils.
Oils are categorized into viscosity grades based on their kinematic viscosity at 40 °C ± 10%. Experimental verification confirmed that the tested samples align with the specified viscosity grades according to ISO 3448 VG standards [83]. Among the lubricants used for ship propellers, VG100 mineral oils are prevalent. However, an essential criterion in lubricant selection extends beyond viscosity alone to include the viscosity index. A higher viscosity index indicates reduced viscosity sensitivity to temperature changes, highlighting the importance of finding an optimal balance between viscosity and viscosity index for effective lubrication performance. In this context, the newly formulated oil A1X was tailored to meet VG100 specifications while exhibiting a sufficiently elevated viscosity index. Contrastingly, the tested commercial mineral oil and commercial EAL demonstrated lower viscosity indexes, with the mineral oil notably lower in comparison.
3.4. Temperature Dependence of Viscosity
The operational temperature window for lubricating ship propellers ranges from 10 °C to 80 °C. Within this range, the temperature dependence of the dynamic viscosity of the tested oils was determined. The tests were conducted using a Haake Mars 60 rotational viscometer equipped with coaxial cylinder geometry. The temperature dependence of the dynamic viscosity of the tested oils is shown in Figure 5a. The data were interpreted using the power-law model ln (η) = (A/T)B, and its parameters were identified. The power-law data are presented in Figure 5b, and the model parameters are listed in Table 6. These plots demonstrate the rheological behavior of the oils under different thermal conditions, offering insights into viscosity trends across temperature ranges.
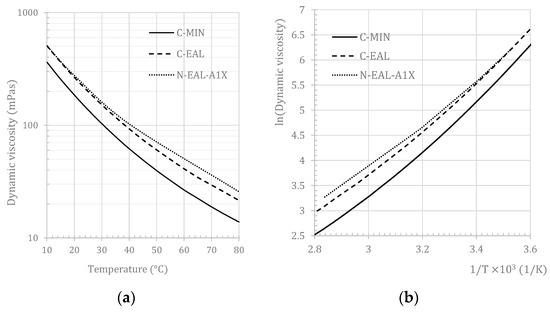
Figure 5.
Dynamic viscosity as a function of temperature: (a) dynamic viscosity is plotted against temperature, showcasing the variation of viscosity with changing temperature; (b) the natural logarithm of dynamic viscosity plotted against the reciprocal of the absolute thermodynamic temperature. The data were interpreted using the power-law model, and the parameters are listed in Table 6.

Table 6.
Parameters of the power-law model.
Parameter A provides a baseline for viscosity measurements and depends on the molecular structure and composition of the fluid. It can be influenced by factors such as molecular weight, intermolecular forces, and specific interactions within the fluid. The second parameter B describes how sensitive the viscosity is to changes in temperature. A higher absolute value of B indicates greater sensitivity of viscosity to temperature changes. If B > 0, the viscosity decreases with an increase in temperature, which is typical for most fluids as they become less viscous when heated. If B < 0, the viscosity increases with an increase in temperature, which is less common but can occur in certain complex fluids or conditions. If B = 0, the viscosity is constant and does not change with temperature, indicating a Newtonian fluid with no temperature dependence.
3.5. Shear Stability
The geometry suitable for determining viscosity at high shear rates is characterized by a very narrow gap. The evaluation of the shear stability of oils is based on comparing viscosity data measured under standard conditions with data measured at high shear rates. As the shear rate increases, a deviation of the flow curve from linearity can be observed, indicating a reversible reduction in oil viscosity. The data were processed using the following procedure. Flow Curve Construction: A flow curve was constructed for standard conditions, confirming its linear character and thereby the Newtonian behavior of the oils within the tested range of shear rates. High-Shear Data Plotting: High-shear data were then plotted on the same graph. Critical Shear Stability Point Identification: The critical shear stability point (the critical shear rate and critical shear stress) was identified for each temperature and oil where the high-shear data deviated from linear behavior by more than 5%; see Figure 6 and Figure 7. The determined critical values are shown in Table 7.
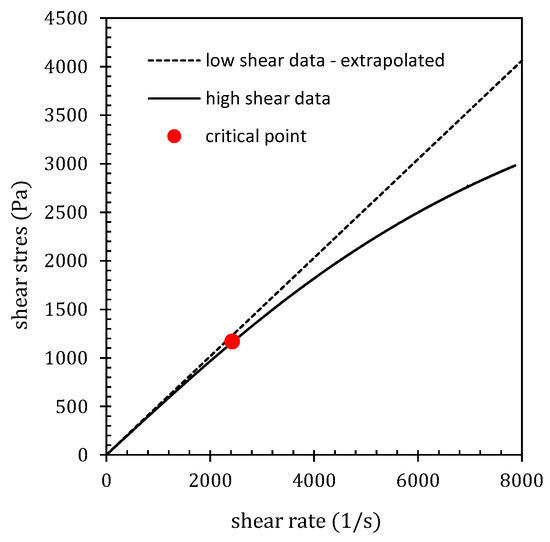
Figure 6.
Critical shear stability point identification for commercial EAL at 10 °C.
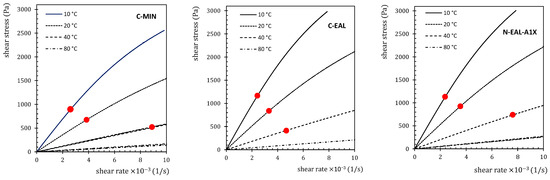
Figure 7.
Flow curves of tested oils with shear stability points at different temperatures.

Table 7.
The evaluated critical values of shear rates, shear stress, and dynamic viscosity indicate the shear stability region.
Similarly, viscosity curves are shown. Figure 6 displays the viscosities of a commercial EAL at temperatures of 10 °C, 20 °C, 40 °C, and 80 °C. It is observed that as the measurement temperature increases, the viscosity of the oil decreases, and the stable viscosity range widens. This means that the critical shear rate, where oils lose their Newtonian behavior, also increases. At 80 °C, the viscosity of the tested oils is already so low that, at high shear rates, secondary flow begins to form, negatively impacting viscosity determination. Viscosity curves of the tested oils with shear stability points at different temperatures are illustrated in Figure 8.
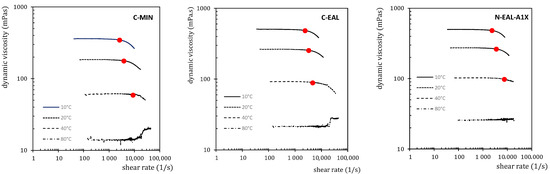
Figure 8.
Viscosity curves of the tested oils with shear stability points at different temperatures.
Values of critical shear stress and critical shear rates can be interpreted as functions of temperature. The critical shear stress as a function of temperature is shown in Figure 9. Data were approximated by the power-law model τ = ATB. Critical shear rates as a function of temperature are shown in Figure 10. Data were approximated by an exponential model γ = Aexp (BT). The optimized parameters of the exponential model are listed in Table 8.
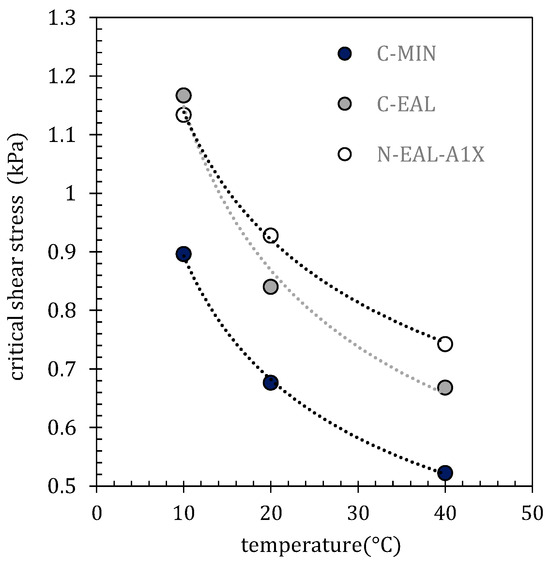
Figure 9.
Critical shear stress as a function of temperature approximated by the power-law model (model parameters are listed in Table 8).
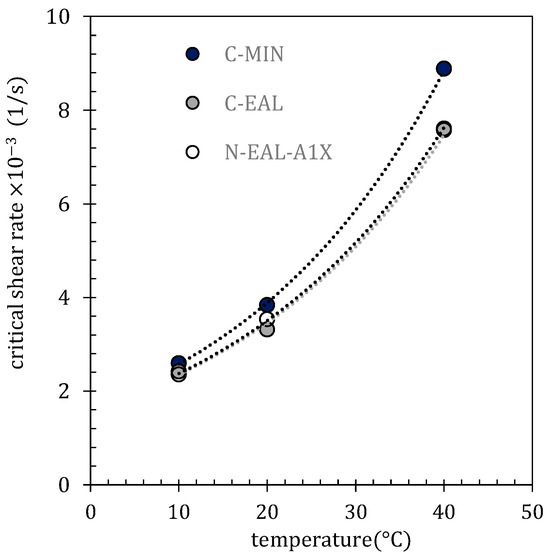
Figure 10.
Critical shear rate as a function of temperature approximated by the exponential model (model parameters are listed in Table 8).

Table 8.
Parameters of power-law and exponential models for critical shear stress resp critical shear rate representation as a function of temperature.
3.6. Friction Factor
The tests were conducted using a rotational viscometer equipped with a tribological cell in a ball-on-three-plate configuration. The contact force of the rotating ball was varied in steps of 0.5, 1, 3, and 6 N. Additionally, the influence of temperature was studied within the same temperature range as the rheological tests, namely 10, 20, 40, and 80 °C. Measurements were performed in the CR (control rate) mode with a gradual increase in rotation speed from 1 up to 800 mm·s−1. From the measured data, the dependencies of the friction coefficient on the rotation speed were constructed for all temperatures and contact forces; see Figure 11 and Figure 12.
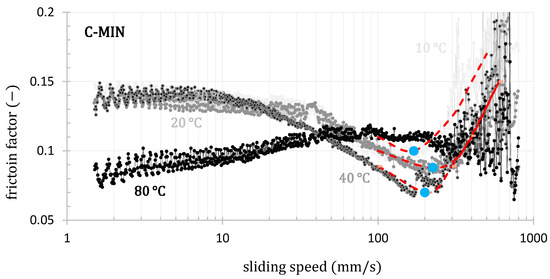
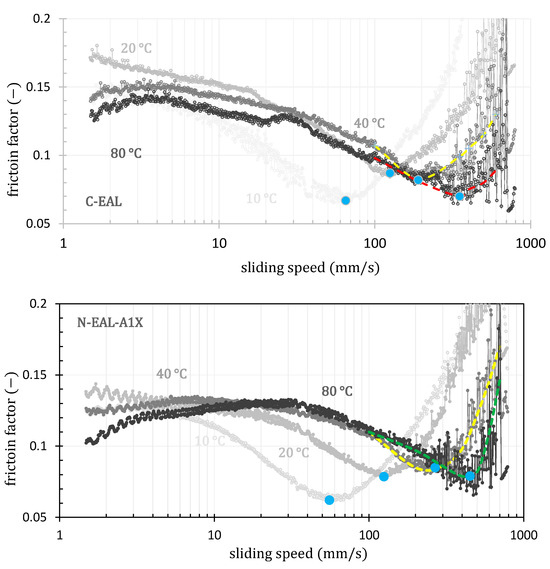
Figure 11.
The influence of temperature on the lubrication regime for all tested samples at normal force of 0.5 N. Blue circles indicate the transition from the mixed to the hydrodynamic regime of lubrication.
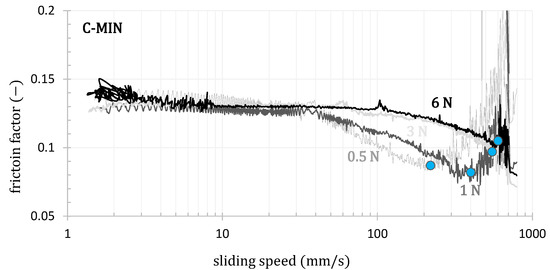
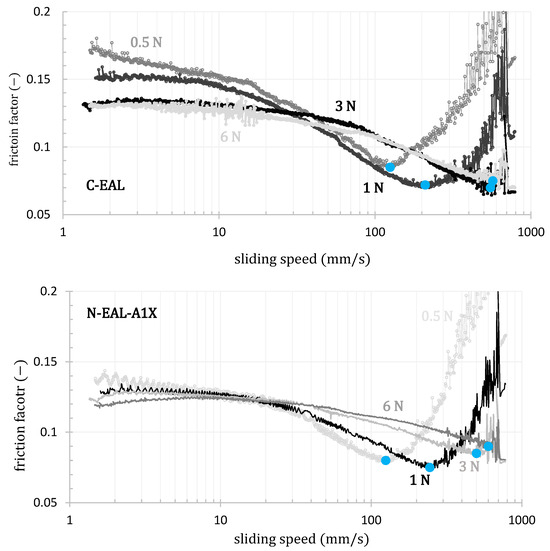
Figure 12.
The influence of load on the lubrication regime for all tested samples at 20 °C. Blue circles indicate the transition from the mixed to the hydrodynamic regime of lubrication.
The shape of the curves shows that, in most cases, the experiments capture all three lubrication regimes. In the lower speed range, the friction factor is almost constant in the boundary lubrication regime. It then decreases to a minimum in the mixed lubrication regime before increasing again in the hydrodynamic lubrication regime. In the speed range of 100 to 800 mm·s−1 at temperatures of 40 and 80 °C, we observe significant data noise caused by high rotation speeds under low load. The data in this range were fitted with a second-degree polynomial, from which the minimum was subsequently estimated.
As the temperature increases, the transition to the hydrodynamic lubrication regime shifts to higher rotational speeds (blue points; see Figure 10). This means that a stable lubrication film forms at higher rotational speeds due to the reduced viscosity at higher temperatures.
3.7. Wear
The wear performance of three different samples—C-MIN, C-EAL, and N-EAL-A1X—was assessed under identical conditions of 20 N normal load, 40 RPM, and a test duration of 30 min. Photographic documentation and profilometry were used to quantify wear scars and analyze surface degradation.
4. Discussion
4.1. Oil Characterization by FTIR and HPLC-MS
The absence of a characteristic peak at 1746 cm−1 in C-MIN oil suggests the absence of a functional ester group, consistent with its composition predominantly comprising hydrocarbons with minimal oxygen content; see Figure 3. This finding is supported by the lack of peaks corresponding to oxygenated functional groups in the 800–1300 cm−1 spectral region [84,85]. In contrast, both C-EAL and N-EAL-A1X oils exhibit a prominent peak at 1746 cm−1, indicative of their ester-based composition and the presence of carbonyl groups (C=O) in esters [86,87]. The identification of these functional groups using FTIR spectroscopy provides valuable insights into the chemical distinctions between mineral-based and ester-based oils [84,85]. These findings underscore the utility of FTIR spectroscopy for characterizing lubricant formulations based on their chemical composition and functional groups [86,87,88,89,90].
4.2. Oil Characterization by HPLC-MS
The HPLC-MS chromatograms contained about seven individual peaks of significant area, many of them of similar maximal mass (m/z) in their mass spectrum; see Table 4. The highest fraction in both EALs had a compound with RT 22,1 min of [M + H] mass of 397.33. There were two other different peaks identified in the chromatogram of the same fragment mass with RT 10.6 and 28.0 min. This suggests that there are different isomers of the same compound having the same mass. Interestingly, all components of mass 397.33 had a total mass fraction of 62.6% in both EALs. Deducing from the FTIR analysis that the oil components were most likely saturated esters, ethylene glycol and capric acid diester (M = 396.55 g/mol) matched the measured mass almost perfectly ([M + H] = 396.55 + 1 ≅ 397.33). The second-highest content was a compound of (m/z) 369.30 with RT 7.9 and 17.2 min. For this mass, the diester of ethylene glycol with caprylic (C8) and myristic acid (C14) provided the closest match to the measured value of (m/z) 369.30 with a slightly higher molecular mass of 370.56 g/mol. The component of the third-highest fraction had (m/z) 425.3 with retention times of 14.0 and 34.5 min. The diester of ethylene glycol and two lauric acids (C12) or the diester of ethylene glycol and myristic (C14) and capric (C10) acids provides the closest match to the measured (m/z) 425,3 with a slightly higher molecular mass of 426 g/mol. The component of (m/z) 341.27 with RT 13.5 was identified only in N-EAL-A1X; the estimation of the possible molecular structure based on the measured ion mass was not successful.
4.3. Kinematic Viscosity and Viscosity Index
Verification measurements of kinematic viscosity conducted using the Anton Paar 3001 apparatus [91] confirmed the classification of oils into their respective viscosity grades with adherence to ISO 3448 VG standards for viscosity grades based on kinematic viscosity at 40 °C ± 10% [92,93]. Additionally, the viscosity index, which indicates the temperature dependence of viscosity, was calculated from the measured data [94].
VG100 mineral oils are extensively utilized among ship propeller lubricants due to their favorable viscosity characteristics [85]. However, the viscosity index emerges as a critical criterion in lubricant selection, highlighting the importance of balancing viscosity with temperature sensitivity [87]. The development of the newly formulated oil A1X aimed to meet VG100 specifications while achieving a notably elevated viscosity index [93]. It was found that the newly formulated oil N-EAL-A1X has the highest viscosity index among all tested samples, as shown in Table 5, indicating that its viscosity is the least affected by temperature [83,95,96,97,98].
4.4. Temperature Dependence of Viscosity
The operational efficiency of lubricating ship propellers depends on temperature conditions typically ranging from 10 °C to 80 °C [98]. Dynamic viscosity measurements across this temperature range were meticulously performed using a Haake Mars 60 rotational viscometer equipped with coaxial cylinder geometry [93,99,100,101]. Figure 5a illustrates the temperature-dependent profiles of dynamic viscosity for the tested oils, showing a decline in dynamic viscosity across the specified temperature window. The most significant drop in dynamic viscosity was observed for C-MIN, followed by C-EAL, while the newly formulated lubricant N-EAL-A1X exhibited the smallest decrease in dynamic viscosity within the tested temperature range. These findings are consistent with the measured viscosity index values of the tested fluids, confirming the reliability of the results.
The temperature profiles were fitted to a power-law model, with the resulting parameters presented in Table 6. Parameter A reflects the baseline level of dynamic viscosity, with its numerical values supporting the observation that C-MIN has the lowest dynamic viscosity, while N-EAL-A1X has the highest. Parameter B quantifies the temperature dependence of dynamic viscosity, where higher values indicate a greater reduction in viscosity with increasing temperature. The numerical values show that C-MIN displays the strongest temperature dependence, while N-EAL-A1X shows the weakest, corresponding to the observed viscosity index values.
4.5. Shear Stability
The evaluation of viscosity at high shear rates required the use of narrow-gap geometry, which was crucial for assessing oil stability [86,87,93]. The measurements of the shear stress–shear rate dependence under standard conditions confirmed Newtonian behavior for all tested oils within the tested range of shear rates [84,92]. Utilizing a narrow-gap measuring cell enabled access to a much broader range of shear rates, allowing for the detection of reversible viscosity reduction in the oil [99]. Comparing viscosity data obtained under standard conditions with the data collected at high shear rates allows for the identification of the shear rate and shear stress at which reversible viscosity reduction begins to manifest. In this study, we defined an acceptable viscosity reduction threshold of 5%. The shear rate and shear stress, at which the dynamic viscosity decreases by more than 5% from the original value, are referred to as critical values, and these are presented in Table 7 [85].
Figure 6 shows the trend of low-shear data alongside full high-shear data. The point at which the high-shear data deviate from the linear trend of the low-shear data is marked in red, with the vertical coordinate indicating the critical shear stress and the horizontal coordinate representing the critical shear rate. All tested oils were evaluated in the same manner at temperatures of 10 °C, 20 °C, 40 °C, and 80 °C, as shown in Figure 7, with a detailed example for sample C-EAL. These critical points obtained for different oils and temperatures illustrate the transition between lubrication regimes with changing shear rates and temperatures [86,87].
In the viscosity–shear rate dependency trends, the critical values manifest as a decrease in viscosity, indicated by the downward bend of the horizontal line, as shown in Figure 8. Higher temperatures expand the stable viscosity range in the tested oils, suggesting an increase in critical shear rates where the oils lose their Newtonian behavior [87].
The relationship between the identified critical shear stresses and temperature for all tested oils can be well approximated by a power-law model, with a decreasing trend in shear stresses as the temperature increases, as illustrated in Figure 9 [93]. For the critical shear rates, an increasing exponential trend was observed with rising temperature, as seen in Figure 10 [92]. These data elucidate the temperature-dependent shear behavior of the tested oils and can be advantageously used to estimate the functional performance parameters of lubrication, including applications such as ship propeller lubrication [99].
4.6. Friction Factor
This study employed a rotational viscometer equipped with a ball-on-three-plate tribological cell to investigate the frictional behavior of lubricants under various conditions [86]. The tests involved altering the contact force applied to the rotating ball in increments of 0.5, 1, 3, and 6 N while examining the temperature influence across a range of 10, 20, 40, and 80 °C.
The control rate (CR) mode facilitated systematic increases in rotational speeds from 1 to 800 mm·s−1, allowing for the analysis of friction coefficient dependencies on rotational speed. The measured data reveal the presence of all three lubrication regimes: boundary, mixed, and hydrodynamic [84]. At lower speeds, the friction coefficient remains relatively constant in the boundary lubrication regime before decreasing to a minimum in the mixed lubrication regime. Subsequently, it increases again in the hydrodynamic regime as the speed rises.
In the case of mineral oil, the transition to the hydrodynamic lubrication regime is virtually independent of temperature, with temperature primarily affecting the friction coefficient. In contrast, for the tested environmentally acceptable lubricants, a notable shift of the transition to the hydrodynamic regime toward higher rotational speeds was observed with increasing temperature. Additionally, this regime is achieved at lower temperatures compared to the tested mineral oil, which is advantageous for the final application in ship propeller lubrication [102]. These trends are documented in Figure 11. In contrast to the varying temperature effects, it is evident that an increased contact force shifts the onset of the hydrodynamic lubrication regime for all tested oils to higher sliding speeds, as illustrated in Figure 12.
4.7. Wear
The pin-on-disk method was used to test wear resistance. Contact between the loaded pin and the disk creates a wear scar that reflects the lubricating properties of the oils tested. This process develops through dynamic contact between the two surfaces, leading to unstable movements along the sliding track. In the initial friction phase, a significant increase in contact force was observed, caused by the detachment of the surface layers from both materials of the tribological pair. These layers can create specific roughness values, resulting in a smaller contact area between the pin and the disk and consequently higher contact pressures. The action of high contact pressures on rough surfaces tends to remove soft layers, facilitating the release of wear debris on the sliding track and resulting in high amplitude values in the abrasive wear scar profile [103]. Photographs of the resulting scars are provided along with the profiles in Figure 13.
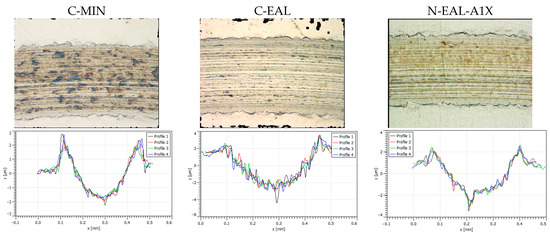
Figure 13.
The wear tracks and profilometry results after testing with commercial mineral oil (C-MIN), commercial EAL (C-EAL), and newly formulated EAL (N-EAL-A1X) at room temperature.
It appears that the scar under mineral oil lubrication has a narrower but significantly shallower profile compared to the scar of commercial C-EAL. From the comparison of the tested EALs, it is evident that the commercially available C-EAL has a slightly wider scar but is nearly a quarter deeper than the newly formulated N-EAL-A1X, which has a profile comparable to that of commercial mineral oil.
5. Conclusions
This study provides comprehensive insights into the characterization and performance of various lubricants through a series of analytical and experimental approaches. FTIR spectroscopy revealed distinct chemical compositions between mineral and ester-based oils, highlighting the presence of ester functional groups in C-EAL and N-EAL-A1X, while C-MIN lacked these groups. HPLC-MS analysis further identified the key compounds in the ester-based lubricants, confirming their ester-based nature and supporting the FTIR findings.
The kinematic viscosity tests and viscosity index calculations confirmed that the newly formulated oil N-EAL-A1X achieved the highest viscosity index among the tested samples, indicating superior temperature stability. This was further validated by dynamic viscosity measurements, where N-EAL-A1X exhibited the smallest decrease in viscosity across a broad temperature range, outperforming both, mineral and commercial ester-based oils.
Shear stability evaluations showed that N-EAL-A1X also maintained its performance under high shear rates better than other oils, with critical shear stress and shear rate data demonstrating its robust stability across different temperatures. Friction factor analysis revealed that all tested oils transitioned through the boundary, mixed, and hydrodynamic lubrication regimes, with N-EAL-A1X achieving the hydrodynamic regime at lower temperatures compared to mineral oil, which is advantageous for applications requiring stable lubrication at varying operational conditions.
Wear resistance tests indicated that N-EAL-A1X exhibited a wear scar profile comparable to that of commercial mineral oil, while C-EAL showed a deeper scar, suggesting higher wear under similar conditions. These findings underscore N-EAL-A1X’s potential benefits for lubrication applications, particularly in scenarios requiring high performance across temperature variations and shear conditions.
Overall, the newly formulated N-EAL-A1X demonstrated superior lubrication performance, stability, and wear resistance, making it a promising candidate for applications such as ship propeller lubrication, where robust and reliable lubrication is critical.
The use of sustainable lubricants for stern tube applications presents several notable advantages over conventional lubricants. Environmentally acceptable lubricants (EALs) are biodegradable and less toxic, significantly reducing the environmental impact in the event of a leakage and thereby minimizing harm to marine ecosystems. Additionally, these lubricants facilitate compliance with stringent environmental regulations, such as those set by the International Maritime Organization (IMO) and various national authorities, thereby mitigating legal risks and potential fines. Sustainable lubricants also lower environmental liability, as their reduced toxicity lessens the costs and complexities associated with spill cleanup and damage control. Furthermore, adopting these lubricants enhances corporate social responsibility, improving a company’s reputation as an environmentally conscientious entity. In terms of performance, many sustainable lubricants offer lubrication properties that are comparable to, or even exceed, those of conventional products under extreme conditions. Although the initial expense of sustainable lubricants may be higher, the long-term savings associated with reduced environmental and compliance costs can be substantial. Ultimately, the use of sustainable lubricants aligns with global sustainability goals and supports broader efforts to minimize environmental impact in the maritime industry.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.V. and P.S.; methodology, M.V.; formal analysis, S.A. and L.Z.; investigation, M.V. and P.S.; resources, M.V.; data curation, S.K.; writing—original draft preparation, M.V.; writing—review and editing, M.V.; visualization, M.V.; supervision, M.V.; project administration, M.V.; funding acquisition, M.V. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The presented results and methodology are based on the research project “Novel Routes for Cost-effective Environmentally Acceptable Lubricants” no. TO01000250 is supported by Norway grants and the Technology Agency of the Czech Republic.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available upon request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank TAČR and other team members for their support and creative and financial contributions to the project.
Conflicts of Interest
Author L. Zelenka was employed by Biona a. s., a producer of EALs, responsible for the lubricant formulation. The lubricant tests and analyses presented in this work were performed outside Biona a. s. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Frost, J.; Frycz, M.; Kowalski, J.; Wodtke, M.; Litwin, W. Environmentally acceptable lubricants (EAL) compared with a reference mineral oil as marine stern tube bearing lubricant—Experimental and theoretical investigations. Tribol. Int. 2023, 189, 109001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United States Environmental Protection Agency. Vessel General Permit for Discharges Incidental to the Normal Operation of Vessels (VGP). Fed. Regist. 2013. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/vessels-marinas-and-ports/vessels-vgp (accessed on 26 June 2024).
- Pichler, J.; Eder, M.R.; Besser, C.; Pisarova, L.; Dörr, N.; Marchetti-Deschmann, M.; Frauscher, M. A comprehensive review of sustainable approaches for synthetic lubricant components. Green Chem. Lett. Rev. 2023, 16, 2185547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mang, T.; Dresel, W. Lubricants and Lubrication, 3rd ed.; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA: Weinheim, Germany, 2017; ISBN 978-3-527-32670-9. [Google Scholar]
- Rudnick, L.R. Lubricant Additives: Chemistry and Applications; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017; ISBN 978-1-4987-3172-0. [Google Scholar]
- Večeř, M.; Krčková, S. Shear stability of base fluids for environmentally acceptable lubricants for stern tube application. AIP Conf. Proc. 2023, 2997, 040007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiong, M.-C.; Kang, H.-S.; Shaharuddin, N.M.R.; Mat, S.; Quen, L.K.; Ten, K.-H.; Ong, M.C. Challenges and opportunities of marine propulsion with alternative fuels. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 149, 111397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, D.C.; Kock, F. The EAL-Mystery: Facts and findings from the perspective of a classification society. In Proceedings of the SNAME 14th Propeller and Shafting Symposium, PSS 2015, Norfolk, VA, USA, 15–16 September 2015; p. 172236. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, C.; Cai, H.-P.; Qian, Z.-F.; Chen, K. The design of propeller and propeller boss cap fins (PBCF) by an integrative method. J. Hydrodyn. 2014, 26, 586–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borras, F.X.; van den Nieuwendijk, R.; Ramesh, V.; de Rooij, M.B.; Schipper, D.J. Stern tube seals operation: A practical approach. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2021, 13, 1687814021994404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saettone, S.; Regener, P.B.; Andersen, P. Pre-swirl stator and propeller design for varying operating conditions. In Proceedings of the 13th International Symposium on Practical Design of Ships and Other Floating Structures (PRADS2016), Copenhagen, Denmark, 4–8 September 2016; Technical University of Denmark: Kongens Lyngby, Denmark, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Middlebrook, A.M.; Murphy, D.M.; Ahmadov, R.; Atlas, E.L.; Bahreini, R.; Blake, D.R.; Brioude, J.; de Gouw, J.A.; Fehsenfeld, F.C.; Frost, G.J.; et al. Air quality implications of the Deepwater Horizon oil spill. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 109, 20280–20285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norse, E.A.; Amos, J. Impacts, perception, and policy implications of the BP/deepwater horizon oil and gas disaster. Environ. Law Rep. 2010, 40, 11058–11073. [Google Scholar]
- Asif, Z.; Chen, Z.; An, C.; Dong, J. Environmental impacts and challenges associated with oil spills on shorelines. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumaila, U.R.; Cisneros-Montemayor, A.M.; Dyck, A.; Huang, L.; Cheung, W.; Jacquet, J.; Kleisner, K.; Lam, V.; McCrea-Strub, A.; Swartz, W.; et al. Impact of the Deepwater Horizon well blowout on the economics of U.S. Gulf fisheries. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2012, 69, 499–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HEALTH EFFECTS. In Toxicological Profile for Hydraulic Fluids; Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (US): Atlanta, GA, USA, 2 September 1997. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK595479/ (accessed on 26 June 2024).
- Saliba, M.; Azzopardi, F.; Muscat, R.; Grima, M.; Smyth, A.; Jalkanen, J.-P.; Johansson, L.; Deidun, A.; Gauci, A.; Galdies, C.; et al. Trends in vessel atmospheric emissions in the central mediterranean over the last 10 years and during the COVID-19 outbreak. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, B.N.; Sonntag, D.; Seltzer, K.M.; Pye, H.O.T.; Allen, C.; Murray, E.; Toro, C.; Gentner, D.R.; Huang, C.; Jathar, S.; et al. Reactive organic carbon air emissions from mobile sources in the United States. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2023, 23, 13469–13483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, J.; Wang, X.; Wei, Z.; Wang, L.; Wang, C.; Chen, Z. A review of NOx and SOx emission reduction technologies for marine diesel engines and the potential evaluation of liquefied natural gas fuelled vessels. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 766, 144319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Wang, L.; Du, W.; Chen, Y.; Yun, X.; Chen, Y.; Shen, G.; Shen, H.; Yang, X.; Tao, S. Emission factors of oxygenated polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from ships in China. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 337, 122483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Directive 2005/35/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 7 September 2005 on Ship-Source Pollution and on the Introduction of Penalties, Including Criminal Penalties, for Pollution Offences. Available online: http://data.europa.eu/eli/dir/2005/35/2009-11-16 (accessed on 26 June 2024).
- Hughes, E. FuelEU Maritime—Avoiding Unintended Consequences. European Community Shipowners’ Associations (ECSA) 2021. Available online: https://www.ics-shipping.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/05/FuelEU-Maritime-Avoiding-Unintended-Consequences-1.pdf (accessed on 4 July 2024).
- Hwang, D.J. The IMO Action Plan to Address Marine Plastic Litter from Ships and Its Follow-Up Timeline. J. Int. Marit. Saf. Environ. Aff. Shipp. 2020, 4, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMillan, M.L.; Murphy, C.K. Temporary viscosity loss and its relationship to journal bearing performance. SAE Spec. Publ. 1978, 429, 63–77. [Google Scholar]
- Duda, J.L.; Klaus, E.E.; Lin, S.C.; Lee, F.L. High-shear viscosity studies of polymer-containing lubricants. Tribol. Ser. 1987, 11, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyle, W.P. High pressure, high shear rate capillary viscometer. S. Afr. Mech. Eng. 1976, 26, 78–86. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, Y.I.; Choi, E.; Kirkland, W.H. The rheology and hydrodynamic analysis of grease flows in a circular pipe. Tribol. Trans. 1993, 36, 545–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, P.L.; Lingard, S.; Cameron, A. High Pressure Viscosity and Shear Response of Oil using the Rotating Optical Micro-Viscometer. Tribol. Ser. 1995, 30, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, R.; Chen, R.; Bala, V. Viscosity Measurement at High Temperature and Varying Shear Rates for Engine Lubricants. Petro Industry News. 2020. Available online: https://www.petro-online.com/article/analytical-instrumentation/11/koehler-instrument-company/viscosity-measurement-at-high-temperature-and-varying-shear-rates-for-engine-lubricants/2774 (accessed on 4 July 2024).
- Wolak, A.; Zając, G.; Fijorek, K.; Janocha, P.; Matwijczuk, A. Experimental investigation of the viscosity parameters ranges—Case study of engine oils in the selected viscosity grade. Energies 2020, 13, 3152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alnes, Ø.Å.; Sethumadhavan, A. Environmentally Acceptable Stern Tube Lubricants—How to Avoid Costly Failures DNV-GL. 2019. Available online: https://www.dnv.com/maritime/webinars-and-videos/on-demand-webinars/access/eal/ (accessed on 16 September 2024).
- Khonsari, M.M.; Booser, E.R. Applied Tribology: Bearing Design and Lubrication, 2nd ed.; Wiley-Interscience: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017; ISBN 978-1118700280. [Google Scholar]
- Lugt, P.M. Grease Lubrication in Rolling Bearings; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013; ISBN 978-1118353912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spikes, H.A.; Olver, A.V. Basics of mixed lubrication. Lub. Sci. 2003, 16, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stachowiak, G.W.; Batchelor, A.W. Engineering Tribology, 4th ed.; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 2014; ISBN 978-012-397047-3. [Google Scholar]
- Dowson, D. A generalized Reynolds equation for fluid-film lubrication. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 1962, 4, 9–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barszczewska, A.; Piątkowska, E.; Litwin, W. Selected problems of experimental testing marine stern tube bearings. Pol. Mar. Res. 2019, 26, 142–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litwin, W. Experimental research on marine oil-lubricated stern tube bearing. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part J J. Eng. Tribol. 2019, 233, 1773–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Ouyang, W.; Liang, X.; Yan, X.; Yuan, C.; Zhou, X.; Guo, Z.; Dong, C.; Liu, Z.; Jin, Y.; et al. Review of the evolution and prevention of friction, wear, and noise for water-lubricated bearings used in ships. Friction 2024, 12, 1–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, H.; Yang, C.; Zhu, H.; Li, X.; Li, Z.; Xu, X. Experimental analysis on friction-induced vibration of water-lubricated bearings in a submarine propulsion system. Ocean Eng. 2020, 203, 107239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, C.; Guo, Z.; Tao, W.; Dong, C.; Bai, X. Effects of different grain sized sands on wear behaviours of NBR/casting copper alloys. Wear 2017, 384–385, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Z.; Guo, Z.; Yuan, C. Effect of Material Hardness on Water Lubrication Performance of Thermoplastic Polyurethane under Sediment Environment. J. Mat. Eng. Perform. 2021, 30, 7532–7541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, J.; Nagdeve, L.; Kumar, H. Tribological investigations into pin-on-disc tribometer under dry sliding conditions at various temperature ranges. J. Proc. Mech. Eng. 2022, 236, 178–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Samarai, R.A.; Haftirman, K.R.A.; Al-Douri, Y. The Influence of Roughness on the Wear and Friction Coefficient under dry and lubricated sliding. Int. J. Sci. Eng. Res. 2012, 3, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Archard, J.F. Contact and rubbing of flat surfaces. J. App. Phys. 1953, 24, 981–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soundararajan, S.; Muthukutti, G.P.; Kumarasamy, S.P.; Vijayananth, K.; Barik, D.; Sharma, P.; Paramasivam, P. Investigating the tribological characteristics of copper surface composites reinforced with high entropy alloy (AlCoCrCuFe) through friction stir processing. Sci Rep. 2023, 13, 22652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goti, E.; Mazza, L.; Mura, A.; Zhang, B. An early method for the technical diagnosis of pin-on-disk tribometers by reference friction measurements in EHL conditions. Measurement 2020, 166, 108169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scharf, T.W.; Prasad, S.V. Solid lubricants: A review. J. Mat. Sci. 2013, 48, 511–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tohyama, M.; Ohmiya, Y.; Hirose, M.; Matsuyama, H.; Toda, T.; Hasegawa, K.; Onizuka, T.; Sato, H.; Yokoi, M.; Sato, N. Measurement of Oil-Film Thickness and Observation of Oil Distribution in High-Speed Deep-Groove Ball Bearings. Tribol. Online 2024, 19, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahto, N.K.; Shafali, K.; Tyagi, R.; Sharma, O.P.; Khatri, O.P.; Sinha, S.K. Friction and wear of Ni3Al-based composites containing Ag and Cu modified hBN at elevated temperatures. Wear 2023, 530, 205065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trivedi, H.K.; Bhatt, D.V. Effect of Lubricating Oil on Tribological behaviour in Pin on Disc Test Rig. Tribol. Ind. 2017, 39, 90–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Elagouz, A.; Ali, M.K.; Hou, X.; Abdelkareem, M.A.; Hassan, M.A. Frictional performance evaluation of sliding surfaces lubricated by zinc-oxide nano-additives. Surf. Eng. 2019, 36, 144–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanasarma, S.; Mohan, M.S.; Kuzhiveli, B.T. Comparative evaluation of physiochemical, rheological, tribological and thermal properties of nanoparticle loaded and bio-lube-blended polyolester lubricant. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2023, 148, 2905–2919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fayaz, S.D.; Wani, M.F. Evaluating Scuffing Failure in Dry Sliding Conditions of Monolayer Chromium Piston Ring/Bulk Grey Cast Iron Liner Interface. Tribol. Online 2020, 15, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biberger, J.; Füßer, H.J. Development of a test method for a realistic, single parameter-dependent analysis of piston ring versus cylinder liner contacts with a rotational tribometer. Trib. Int. 2017, 113, 111–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Castro Neves, M.G.; de Arruda, M.A.; Freitas, J.C.S.; Batista, E.A.; Prado, T.A.; Naka, M.H. Construction of a tribometer for tests with biolubricants. In Proceedings of the 10th IEEE/IAS International Conference on Industry Applications, Fortaleza, Brazil, 5–7 November 2012; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singhal, S.; Ritwik, A.; Rajan, K.; Dwivedi, R.K. Critical Review on Tribometers and Their Contact Mechanism. In Optimization of Industrial Systems; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM D5481-19; Standard Test Method for Measuring Apparent Viscosity at High-Temperature and High-Shear Rate by Multicell Capillary Viscometer. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2019. Available online: https://www.astm.org/d5481-20.html (accessed on 16 September 2024).
- Wolak, A. Statistical Analysis of HTHS Viscosity Rating of Present-Day Engine Oils. Tribol. Trans. 2019, 62, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macián, V.; Tormos, B.; Ruiz, S.; Miró, G. Low viscosity engine oils: Study of wear effects and oil key parameters in a heavy duty engine fleet test. Tribol. Int. 2016, 94, 240–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bair, S. A more complete description of the shear rheology of high-temperature high-shear journal bearing lubrication. Tribol. Trans. 2006, 49, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zewdie, H.; Tibba, G.S.; Zeleke, D.S.; Perumal, V.; Castaneiras, P.D.R. A Review on the Impact of Bio-Additives on Tribological Behavior of Diesel Fuels. Adv. Tribol. 2024, 2024, 5530337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.B.; Du, Z.X.; Li, C.X.; Min, E. Study on the lubrication properties of biodiesel as fuel lubricity enhancers. Fuel 2005, 84, 1601–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drown, D.C.; Harper, K.; Frame, E. Screening vegetable oil alcohol esters as fuel lubricity enhancers. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2001, 78, 579–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wadumesthrige, K.; Ara, M.; Salley, S.O.; Ng, K.Y.S. Investigation of Lubricity Characteristics of Biodiesel in Petroleum and Synthetic Fuel. Energy Fuels 2009, 23, 2229–2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.F.; Wang, Q.J.; Hu, X.G.; Li, C.; Zhu, X.F. Characterization of the lubricity of bio-oil/diesel fuel blends by high frequency reciprocating test rig. Energy 2010, 35, 283–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM D6079-20; Standard Test Method for Evaluating Lubricity of Diesel Fuels by the High-Frequency Reciprocating Rig (HFRR). ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2023. Available online: https://www.astm.org/d6079-22.html (accessed on 16 September 2024).
- ASTM D2266-16; Standard Test Method for Wear Preventive Characteristics of Lubricating Grease (Four-Ball Method). ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2016. Available online: https://www.astm.org/d2266-91r96.html (accessed on 16 September 2024).
- Zulkifli, N.W.M.; Kalam, M.A.; Masjuki, H.H.; Shahabuddin, M.; Yunus, R. Wear prevention characteristics of a palm oil-based TMP (trimethylolpropane) ester as an engine lubricant. Energy 2013, 54, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, Y.; Sharma, A.; Singh, N.K.; Chen, W.H. Development of bio-based lubricant from modified desert date oil (balanites aegyptiaca) with copper nanoparticles addition and their tribological analysis. Fuel 2020, 259, 116259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Varun Chauhan, S. Analysis of tribological performance of biodiesel. J. Eng. Tribol. 2014, 228, 797–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, P.R.C.F.; do Nascimento, M.R.; Cavalcante, C.L.; de Luna, F.M.T. Synthesis and tribological properties of bio-based lubricants from soybean oil. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2024, 14, 20509–20521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadiq, I.O.; Suhaimi, M.A.; Sharif, S.; Yusof, N.M.; Hisam, M.J. Enhanced performance of bio-lubricant properties with nano-additives for sustainable lubrication. Indust. Lub. Trib 2022, 74, 995–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachchhav, B.; Bagchi, H. Effect of surface roughness on friction and lubrication regimes. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 38, 169–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, M.; Rahmani, R.; Dolatabadi, N.; Morris, N.; Jones, D.; Craig, C. An analytical friction model for point contacts subject to boundary and mixed elastohydrodynamic lubrication. Tribol. Int. 2024, 196, 109699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pogodina, N.V.; Amann, T.; Dold, C.; Metwalli, E.; Müller-Buschbaum, P.; Kailer, A.; Friedrich, C. Triborheology and orientational dynamics of ionic liquid crystals. J. Mol. Liq. 2014, 192, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duque-Ossa, L.C.; Ruiz-Pulido, G.; Medina, D.I. Triborheological Study under Physiological Conditions of PVA Hydrogel/HA Lubricant as Synthetic System for Soft Tissue Replacement. Polymers 2021, 13, 746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avilés-Castrillo, J.I.; Quintanar-Guerrero, D.; Aguilar-Pérez, K.M.; Medina, D.I. Biotriborheology of Shea Butter Solid Lipid Nanoparticles in a topical cream. Tribol. Int. 2021, 156, 106836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andablo-Reyes, E.; Vicente, J.D.; Hidalgo-Alvarez, R. On the nonparallelism effect in thin film plate-plate rheometry. J. Rheol. 2011, 55, 981–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briscoe, W.H. Aqueous boundary lubrication: Molecular mechanisms, design strategy, and terra incognita. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 27, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, Z.M.; Mueller, D.W.; Zhang, C.W.J. State of the art of friction modelling at interfaces subjected to elastohydrodynamic lubrication (EHL). Friction 2021, 9, 207–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagh, V.P.; Saboo, N.; Gupta, A. Tribology as emerging science for warm mix technology: A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 359, 129445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 3448; Petroleum Products—Determination of Kinematic Viscosity and Calculation of Dynamic Viscosity. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2013.
- Hamrock, B.J.; Schmid, S.R.; Jacobson, B.O. Fundamentals of Fluid Film Lubrication, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Totten, G.E. Handbook of Lubrication and Tribology: Volume I Application and Maintenance, 2nd ed.; Taylor & Francis: Abingdon, UK, 2006; ISBN 9780849320958. [Google Scholar]
- Stolarski, T.A. Tribology in Machine Design; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 2000; ISBN 0-7506-3623-8. [Google Scholar]
- Pirro, D.M.; Webster, M.; Daschner, E. Lubrication Fundamentals: Revised and Expanded, 3rd ed.; Taylor & Francis: Abingdon, UK, 2016; ISBN 9781498752909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van de Voort, F.R.; Sedman, J.; Pinchuk, D. An Overview of Progress and New Developments in FTIR Lubricant Condition Monitoring Methodology. In-Service Lubricant and Machine Analysis, Diagnostics, and Prognostics. J. ASTM Int. 2011, 1536, 55–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van De Voort, F.R.; Sedman, J. FTIR condition monitoring of in-service lubricants: Ongoing developments and future perspectives. Tribol. Trans. 2006, 49, 410–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van de Voort, F.R. FTIR Condition Monitoring of In-Service Lubricants: Analytical Role and Quantitative Evolution. Tribol. Online 2022, 17, 144–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anton Paar GmbH, Graz, Austria. Anton Paar 3001 Viscometer. Available online: https://www.anton-paar.com/corp-en/products/details/svm-series/?sku=105001 (accessed on 26 June 2024).
- Bird, R.B.; Armstrong, R.C.; Hassager, O. Dynamics of Polymeric Liquids, Volume 1: Fluid Mechanics, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1987; ISBN 978-0-471-80245-7. [Google Scholar]
- Barnes, H.A.; Hutton, J.F.; Walters, K. An Introduction to Rheology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1989; ISBN 9780444871404. [Google Scholar]
- Wichterle, K.; Večeř, M. Transport and Surface Phenomena; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; ISBN 9780128189948. [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava, S.P. Advances in Lubricant Additives and Tribology; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2009; ISBN 9788188305940. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, S.H. Tribology in Marine Diesel Engines. In Tribology of Machine Elements—Fundamentals and Applications; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, R.; Woydt, M.; Zhang, S. The Economic and Environmental Significance of Sustainable Lubricants. Lubricants 2021, 9, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draffin, N. An Introduction to Marine Lubricants; Petrospot Ltd.: Banbury, UK, 2017; ISBN 978-1-908663-27-6. [Google Scholar]
- Tanner, R.I. Engineering Rheology; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2000; ISBN 9780198564737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wein, O.; Vecer, M.; Havlica, J. End effects in rotational viscometry I. No-slip shear-thinning samples in the Z40 DIN sensor. Rheol. Acta 2007, 46, 765–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferry, J.D. Viscoelastic Properties of Polymers, 3rd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1980; ISBN 0-471-04894-1. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, T.V.V.L.N.; Kasolang, S.B.; Xie, G.; Katiyar, J.K.; Rani, A.M.A. (Eds.) Green Tribology: Emerging Technologies and Applications, 1st ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowson, D.; Higginson, G.R.; Whitaker, A.V.E. Elastohydrodynamic Lubrication: The Fundamentals of Roller and Gear Lubrication; Pergamon Press: Oxford, UK, 1966; ISBN 0080114725. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).