The Influence of Phosphate-Ester-Based Additives on Metal Cutting Fluid Behavior during the Machining of Titanium Alloy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Procedure
3. Experiment Results
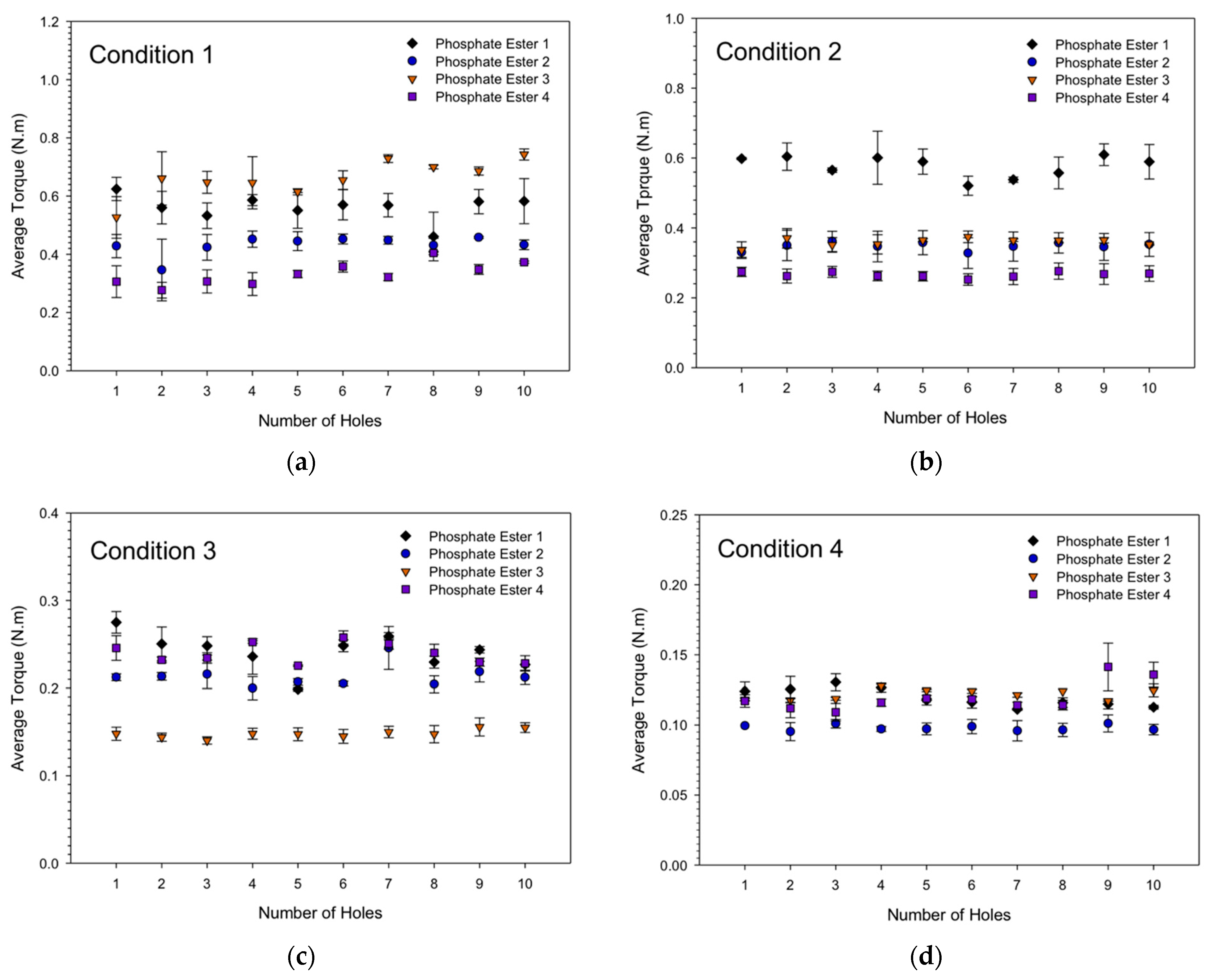
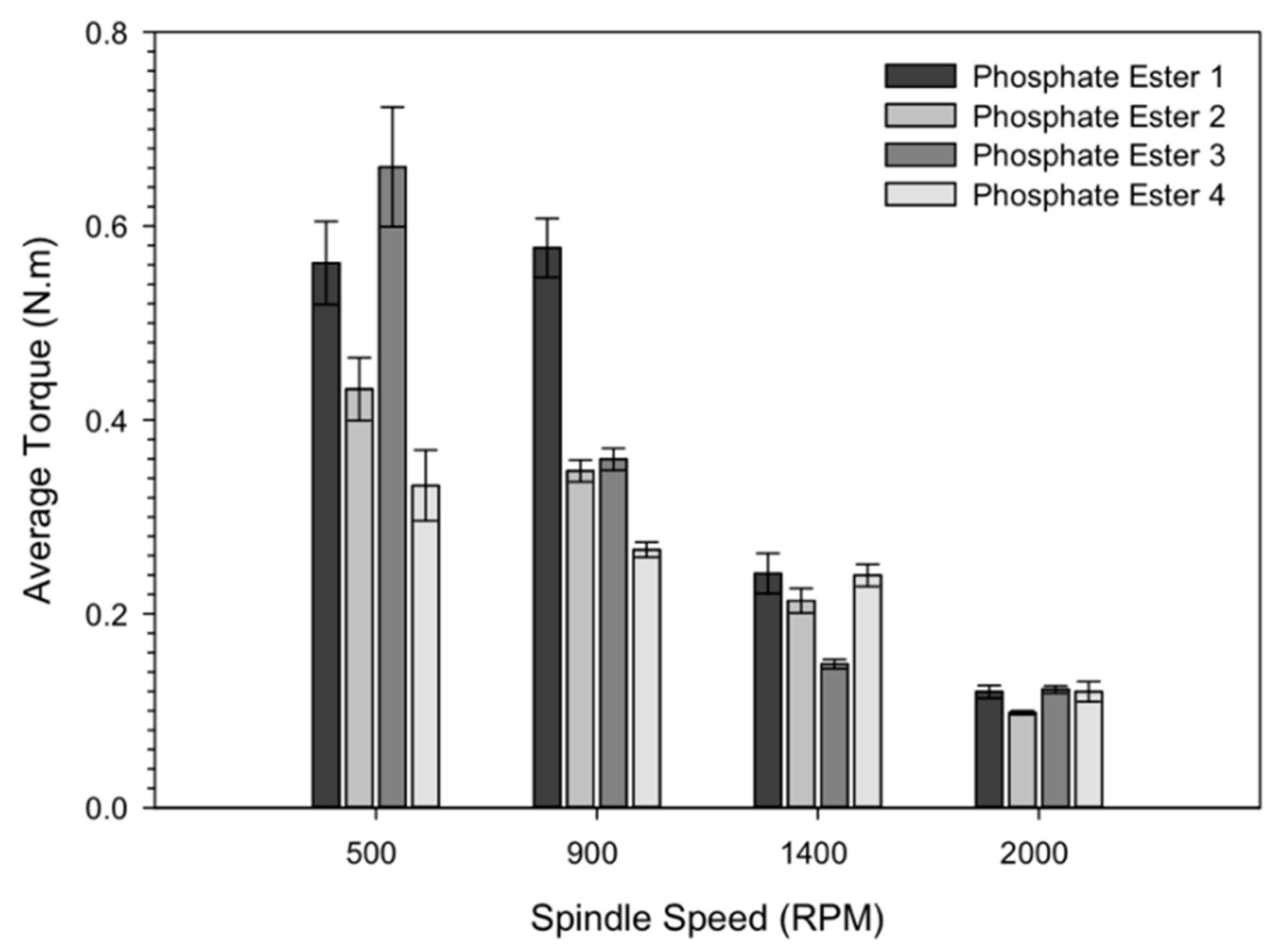
3.1. Average Torque
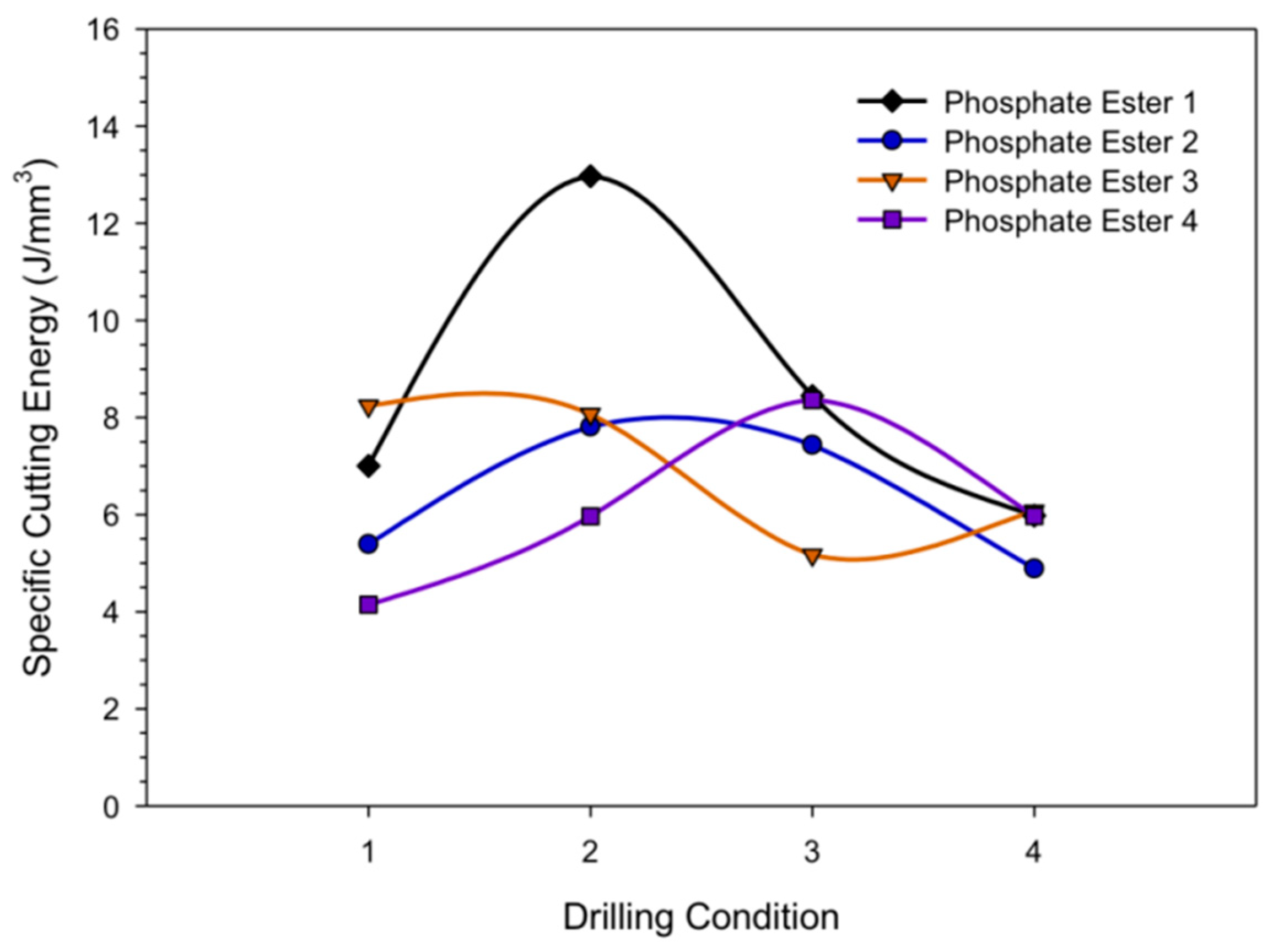
3.2. Special Cutting Energy (SCE)
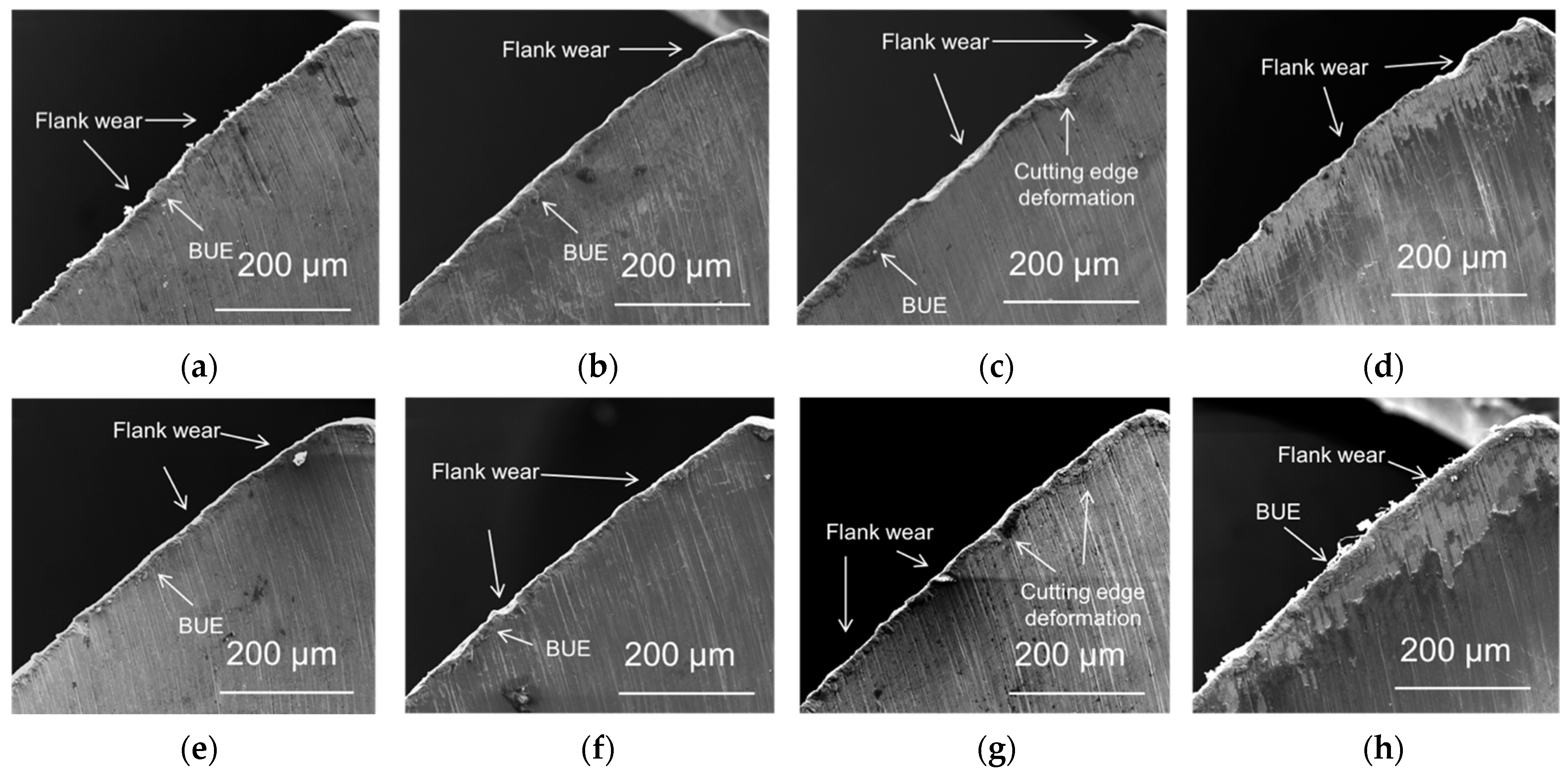
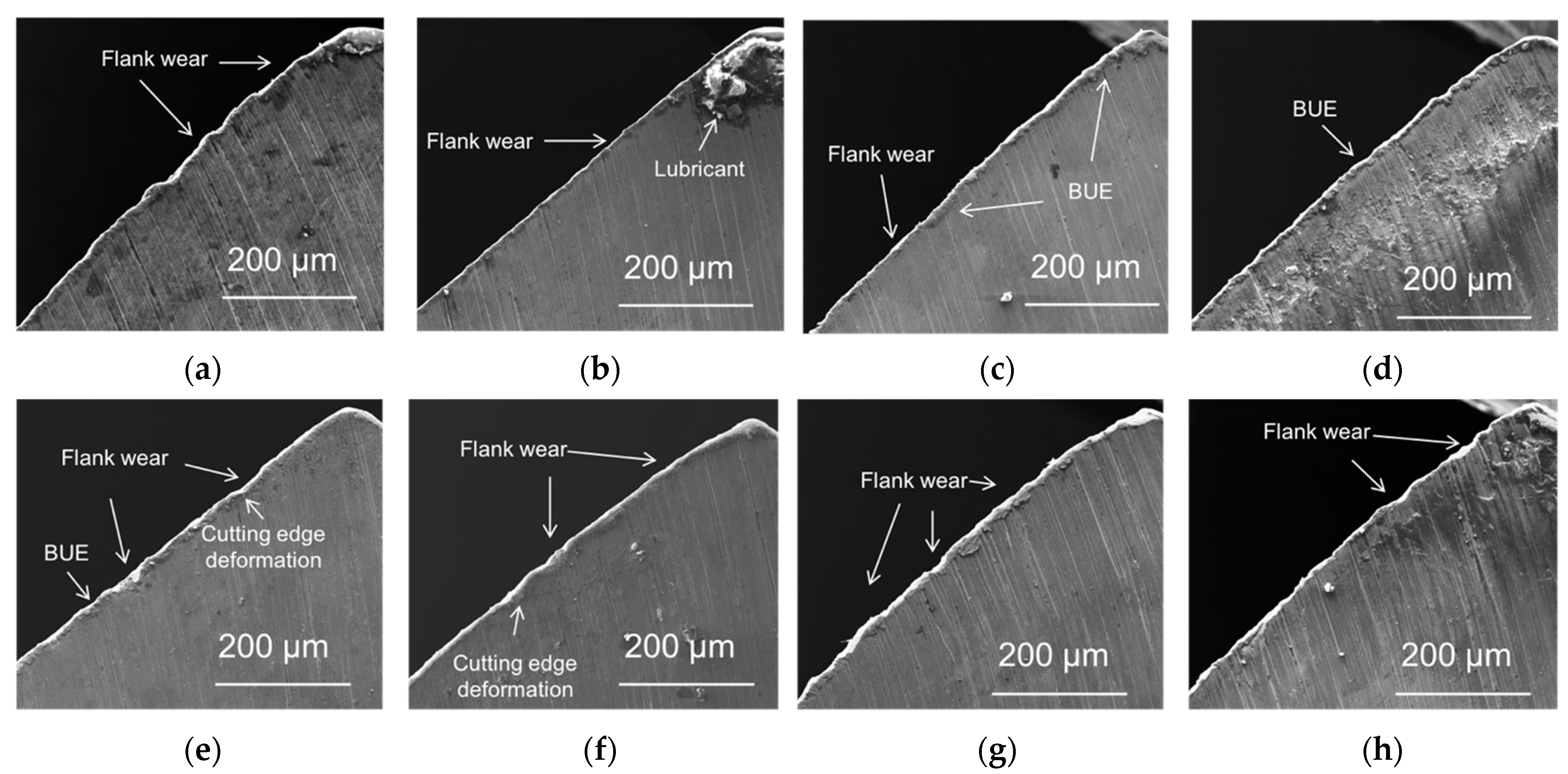
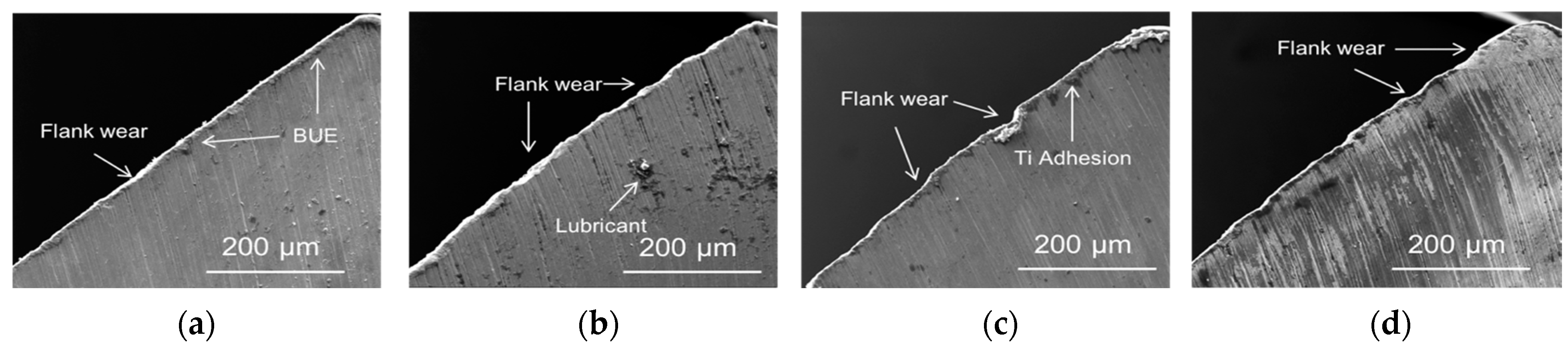
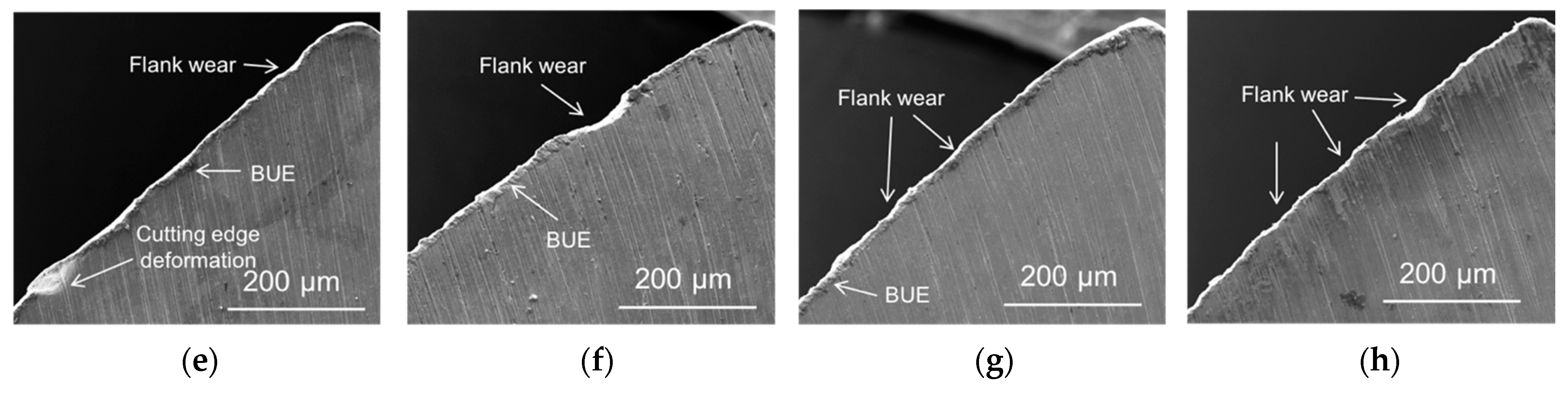
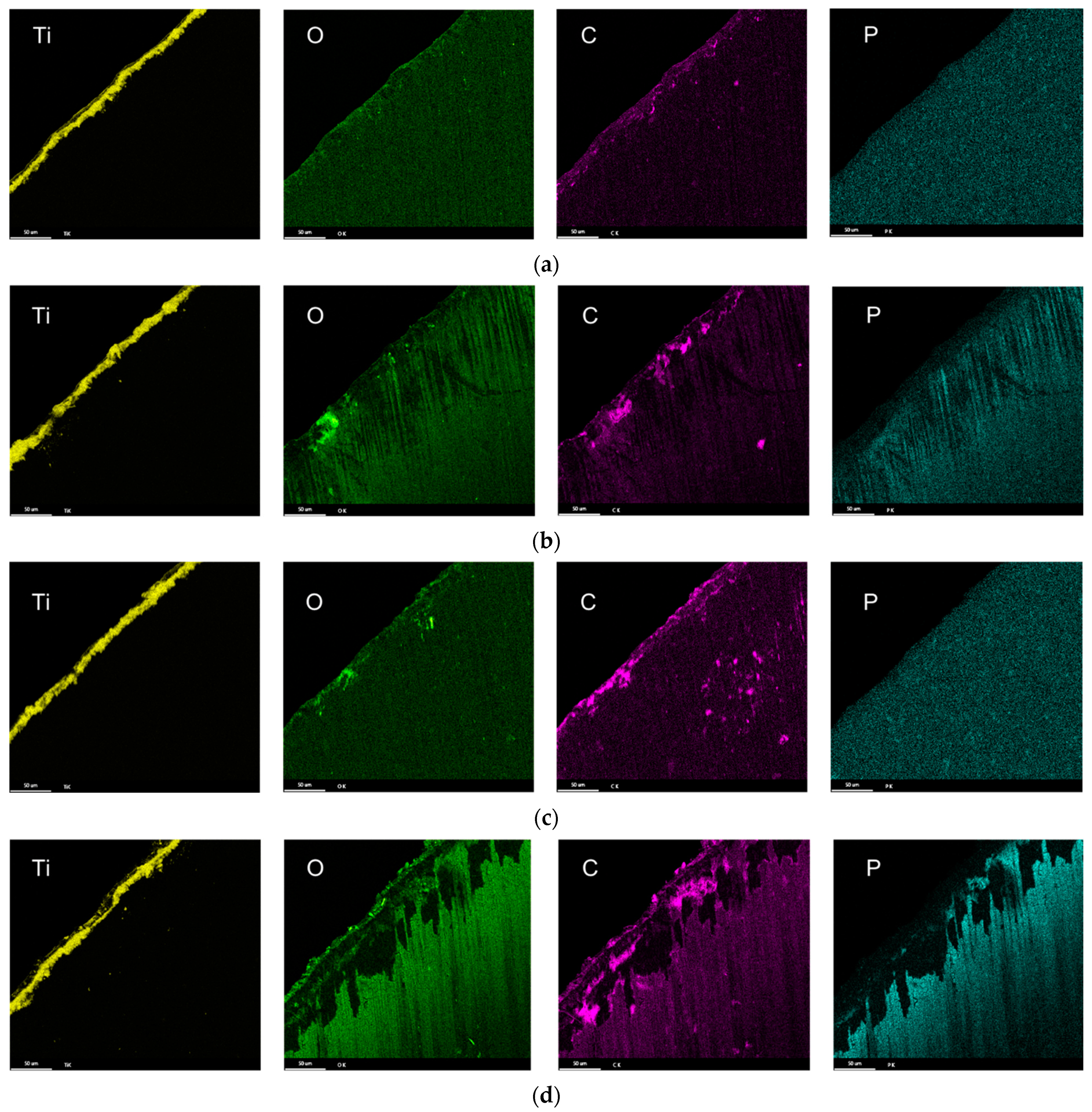
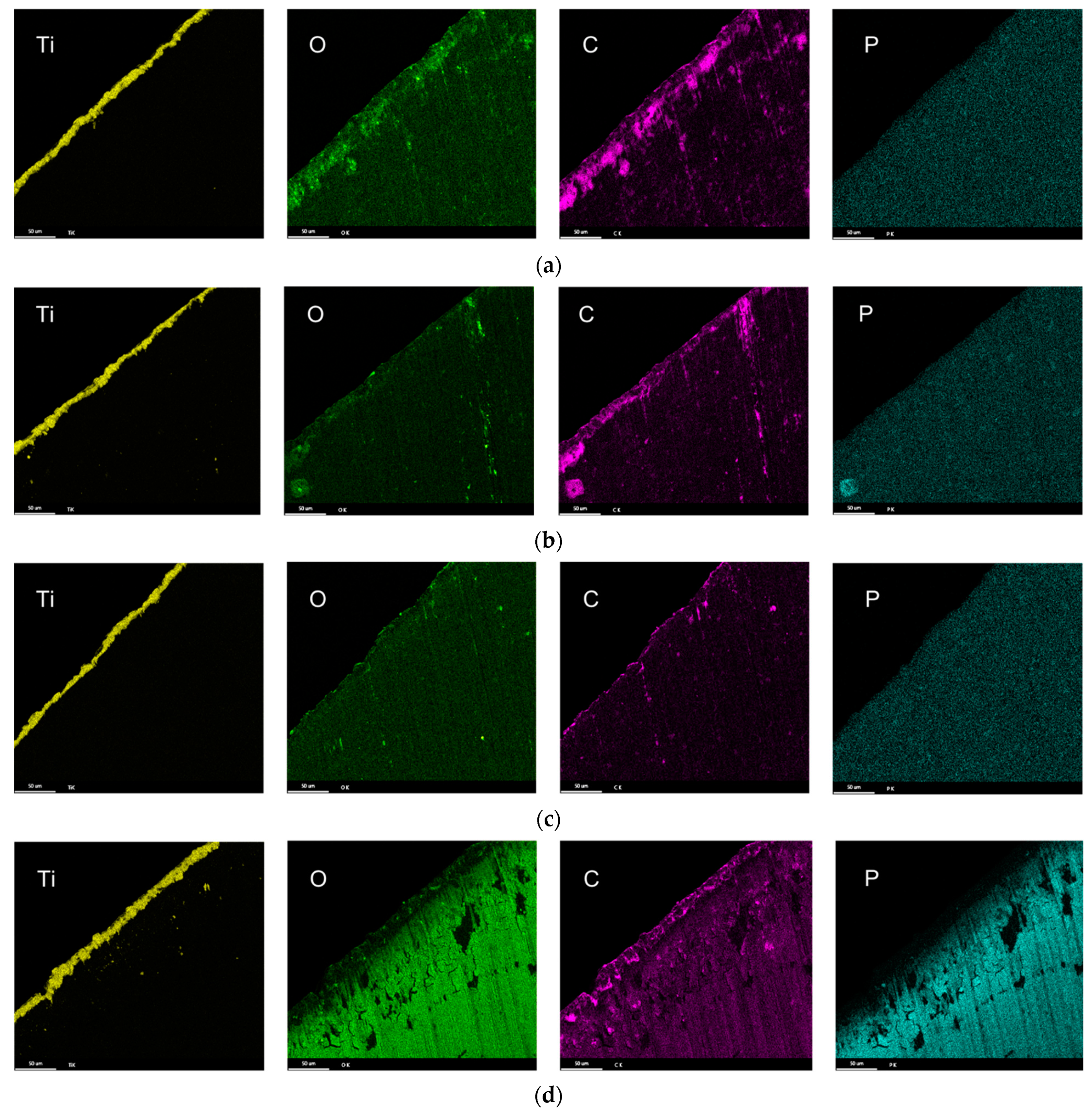
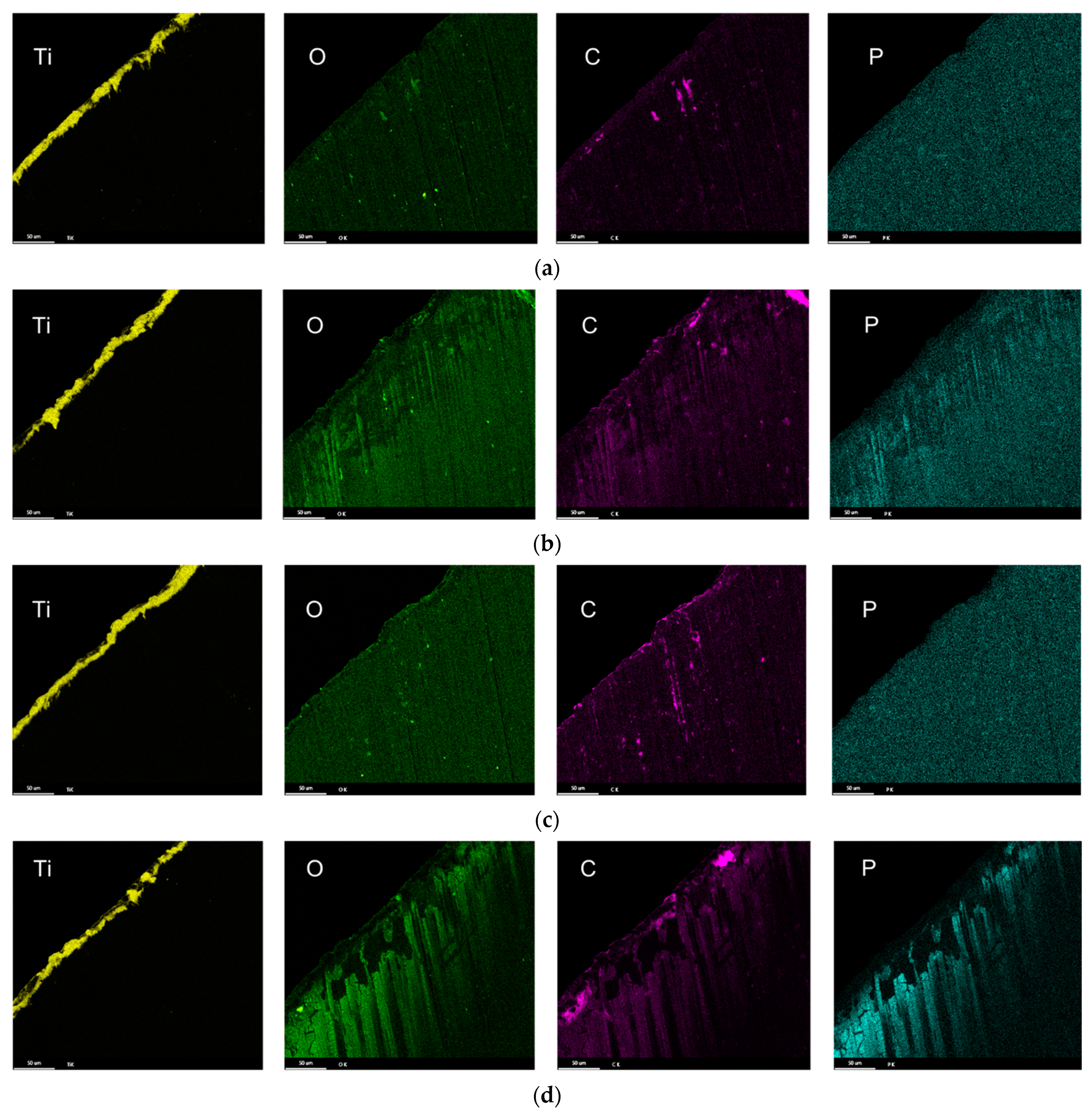
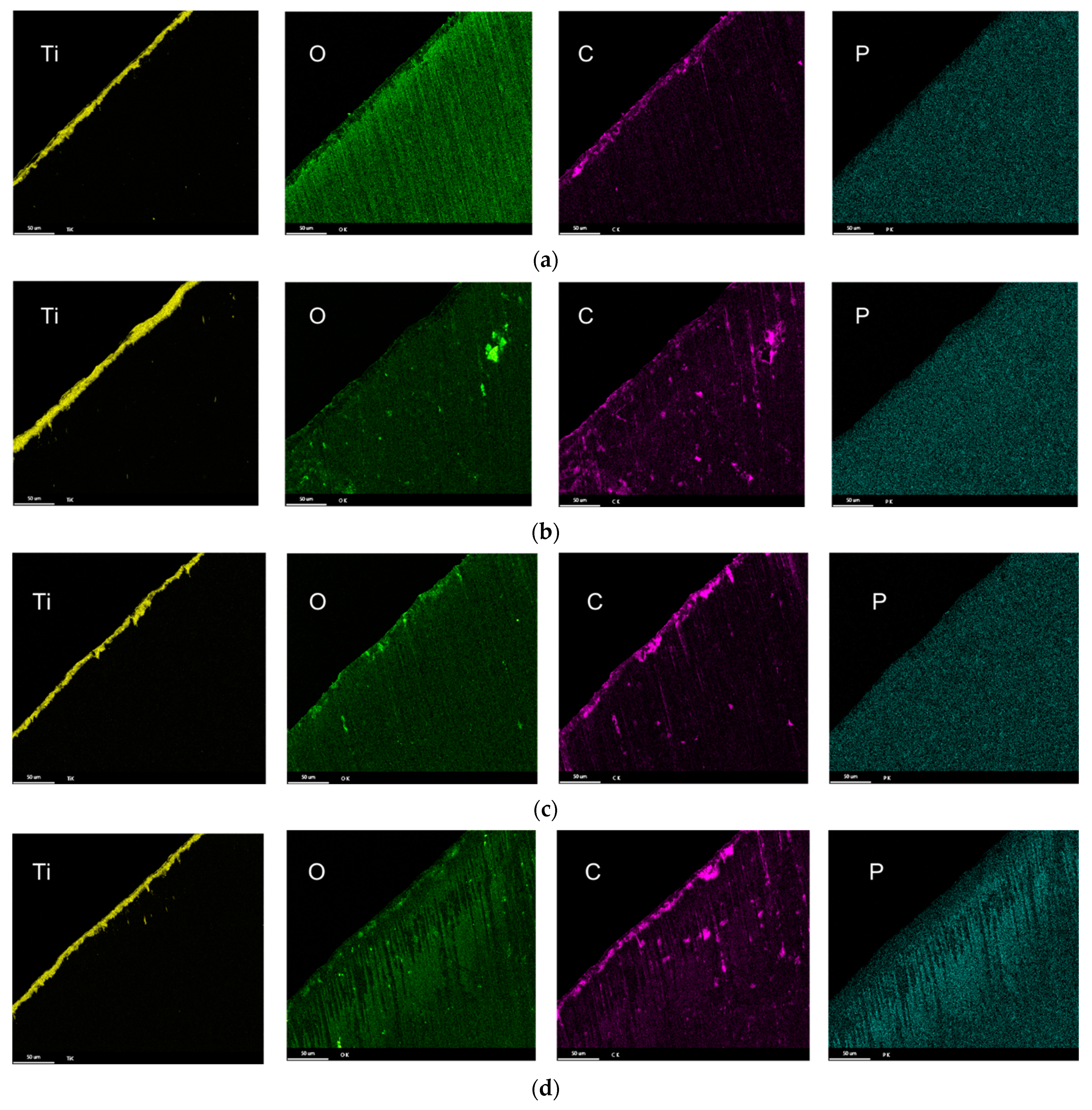
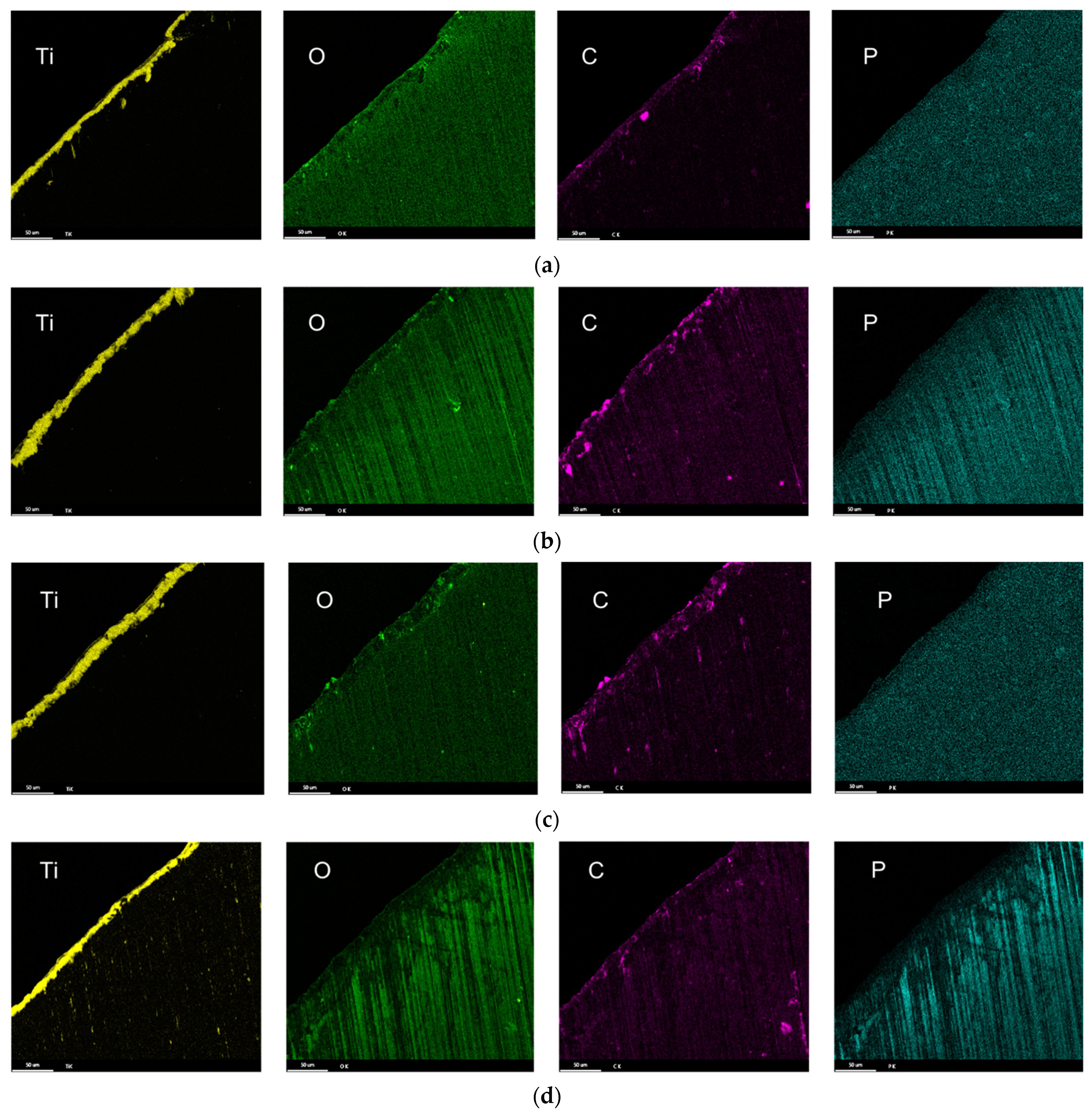
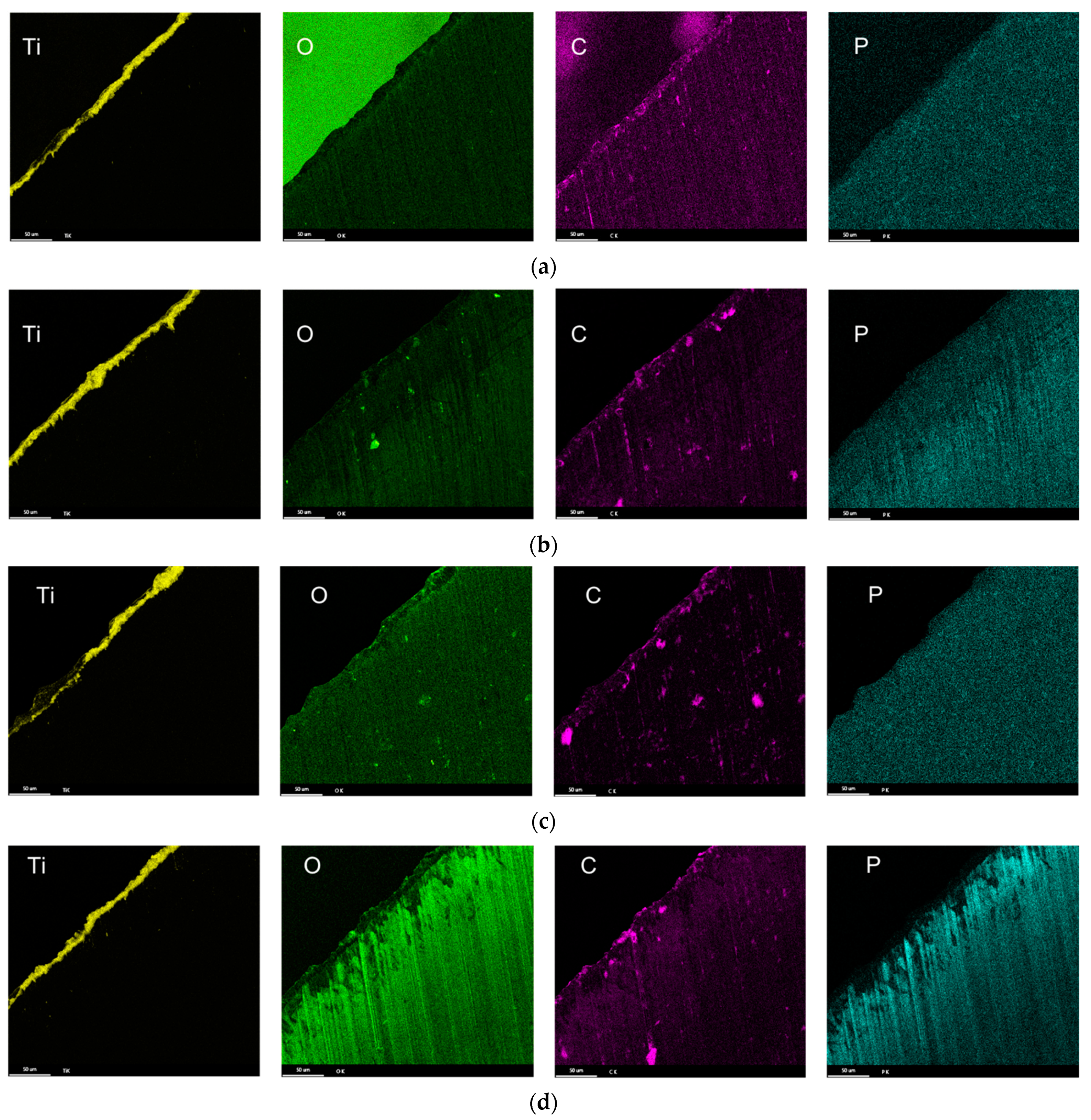
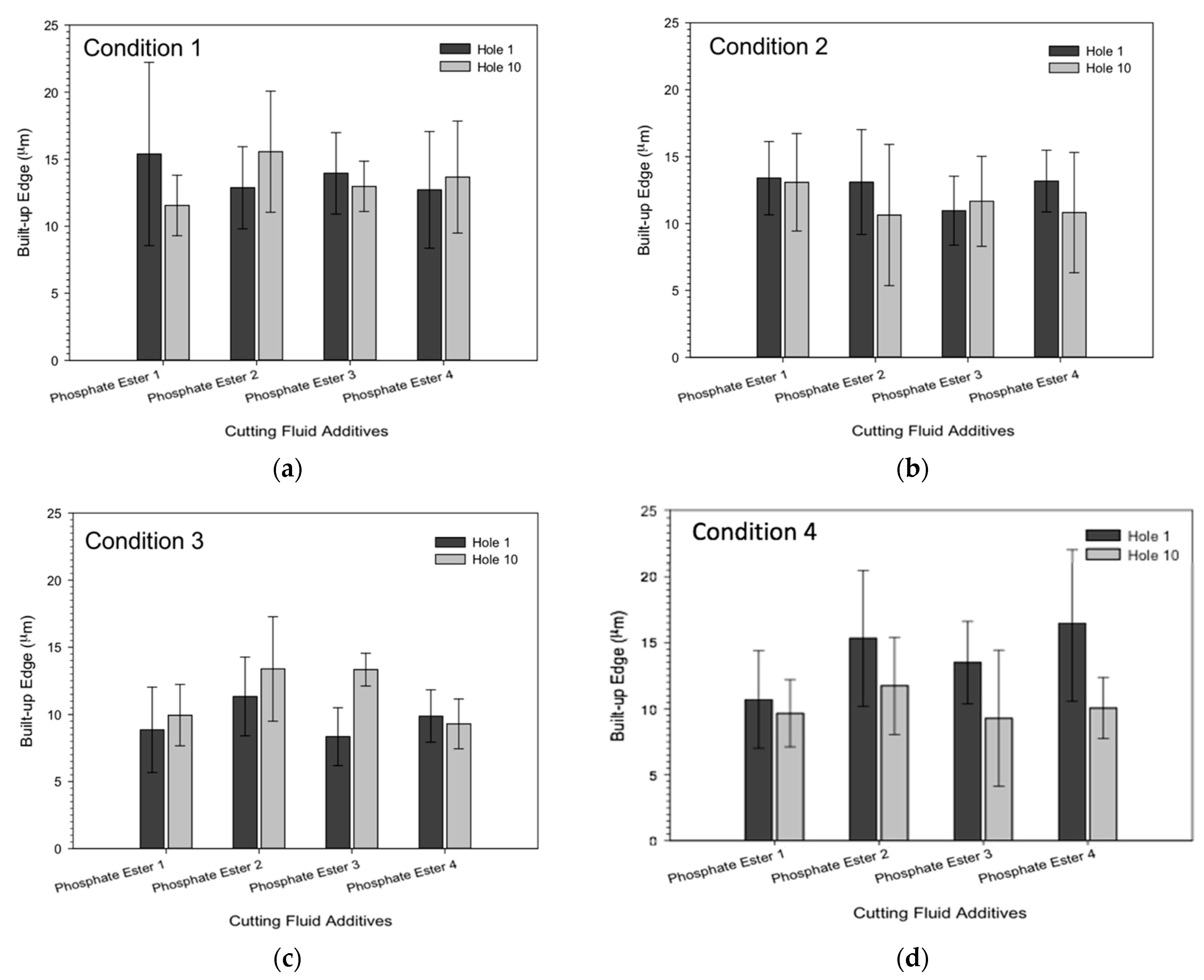
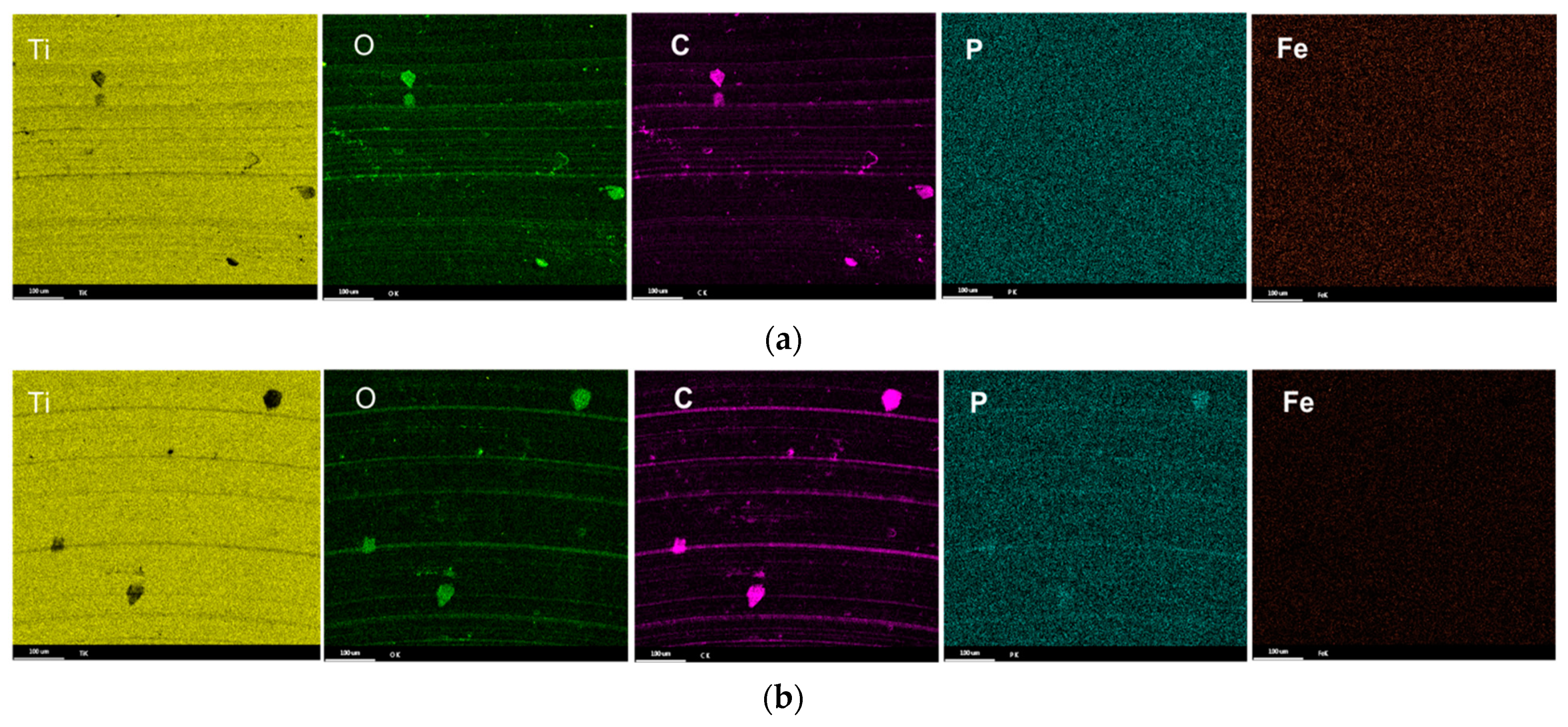
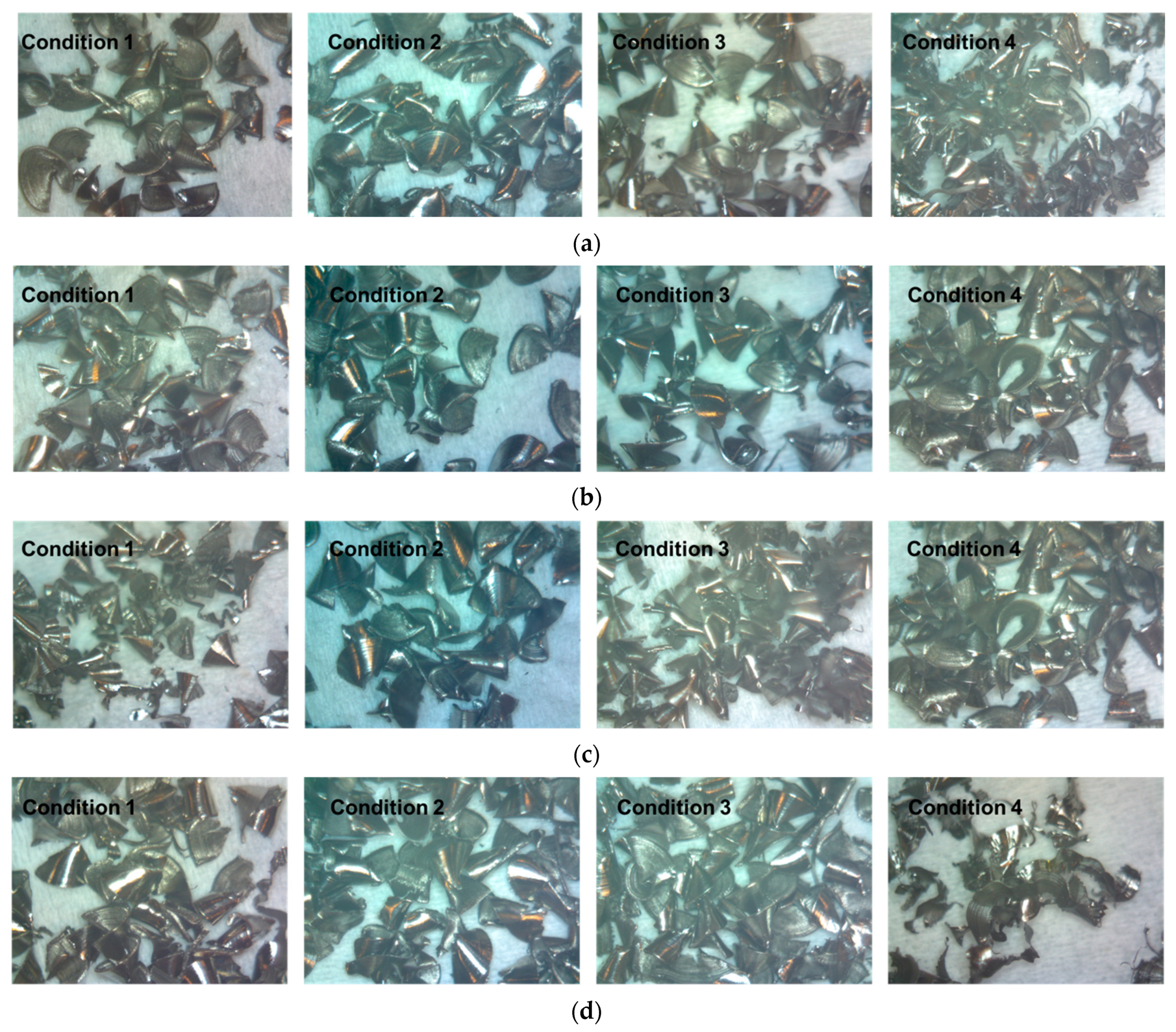
3.3. Characterization of Drill Bit
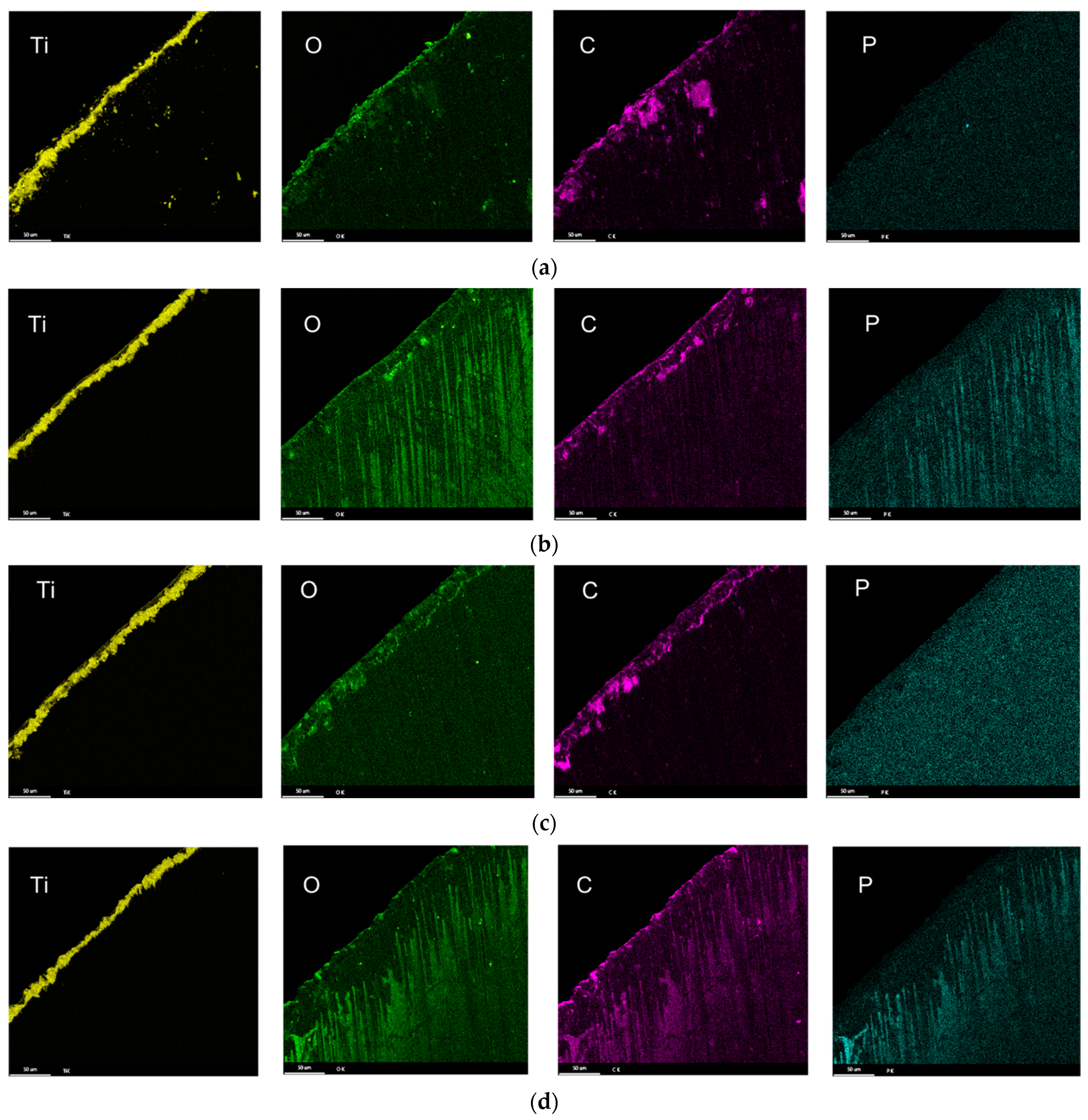
3.4. Drill Bit Surface Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- The drilling performance of the phosphorus esters additives was associated with the drilling condition employed under the constant MRR. The very-high-phosphorous-level phosphate ester performance was more sustainable than the other additives under lower drilling conditions, while under higher drilling conditions, the high-phosphorous-level phosphate ester additive and the medium-phosphorous-level phosphate ester additives provided better lubrication.
- The phosphorus ester additives’ performance could be attributed to the behavior of the phosphorus-rich tribolayer formed on the surface of the cutting blade. The drilling performance of the low-phosphorous-level phosphate ester and high-phosphorous-level phosphate ester was related to the chemical dissolution of the tribolayer. However, the behavior of the phosphate ester with a very high phosphorous level and the medium-phosphorous-level phosphate ester additives was related to the sliding wear of the tribolayer formed on the cutting blades.
- The composition of the tribolayers was dependent on the type of phosphorous ester additives. The tribolayer formed from a low-phosphorous-level phosphate ester and high-phosphorous-level phosphate ester (with medium hydrocarbon chain length) was thin a phosphorus-rich layer, while the medium-phosphorous-level phosphate ester and very-high-phosphorous-level phosphate (with low hydrocarbon chain length) ester were observed to form thick organophosphate layers. Although most of the phosphate esters appeared to form mono-layered tribolayers, evidence of a multi-layered tribolayer was detected from the phosphate ester with the highest levels of phosphorus.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, W.; Zhu, Z.; Cheng, C.Y. A literature review of titanium metallurgical processes. Hydrometallurgy 2011, 108, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, J.; Machado, A.; Ezugwu, E.O. Performance of cutting fluids during face milling of steels. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2001, 116, 244–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, C.G.; Pramanik, A.; Basak, A.; Prakash, C.; Shankar, S. Drilling of titanium alloy (Ti6Al4V)—A review. Mach. Sci. Technol. 2021, 25, 637–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debnath, S.; Reddy, M.M.; Yi, Q.S. Environmental friendly cutting fluids and cooling techniques in machining: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2014, 83, 33–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinksmeier, E.; Meyer, D.; Huesmann-Cordes, A.; Herrmann, C. Metalworking fluids—Mechanisms and performance. CIRP Ann. 2015, 64, 605–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamil, N.; Azmi, A.; Fairuz, M. Coated carbide drill performance under soluble coconut oil lubricant and nanoparticle enhanced MQL in drilling AISI P20. In Proceedings of the IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 1 February 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Davim, J.P.; Gaitonde, V.; Karnik, S.J. Investigations into the effect of cutting conditions on surface roughness in turning of free machining steel by ANN models. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2008, 205, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, P.; Rong, Y.; Wang, G. The effect of cutting fluids applied in metal cutting process. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part B J. Eng. Manuf. 2016, 230, 19–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, T.; Kudaravalli, R.; Georgiou, G. Cryogenic machining through the spindle and tool for improved machining process performance and sustainability: Pt. I, system design. Procedia Manuf. 2018, 21, 266–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Outeiro, J.C.; Lenoir, P.; Bosselut, A. Thermo-mechanical effects in drilling using metal working fluids and cryogenic cooling and their impact in tool performance. Prod. Eng. 2015, 9, 551–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahim, E.; Sasahara, H. A study of the effect of palm oil as MQL lubricant on high speed drilling of titanium alloys. Tribol. Int. 2011, 44, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, M.K.; Song, Q.; Liu, Z.; Sarikaya, M.; Jamil, M.; Mia, M.; Khanna, N.; Krolczyk, G.M. Experimental characterisation of the performance of hybrid cryo-lubrication assisted turning of Ti–6Al–4V alloy. Tribol. Int. 2021, 153, 106582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, O.; Català, P.; Rodríguez, A.; Ostra, T.; Vivancos, J.; Rivero, A.; López-de-Lacalle, L.N. The use of hybrid CO2+ MQL in machining operations. Procedia Eng. 2015, 132, 492–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; An, Q.; Xu, J.; Chen, M.; Han, S. Wear performance of (nc-AlTiN)/(a-Si3N4) coating and (nc-AlCrN)/(a-Si3N4) coating in high-speed machining of titanium alloys under dry and minimum quantity lubrication (MQL) conditions. Wear 2013, 305, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamata, Y.; Obikawa, T. High speed MQL finish-turning of Inconel 718 with different coated tools. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2007, 192, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.Y.; Zhao, Z. Thermal aspects, material considerations and cooling strategies in cryogenic machining. Clean Prod. Process. 1999, 1, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, O.; Martín-Alfonso, J.; Rodríguez, A.; Calleja, A.; Fernández-Valdivielso, A.; De Lacalle, L.L. Sustainability analysis of lubricant oils for minimum quantity lubrication based on their tribo-rheological performance. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 164, 1419–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Hou, T.; Wang, W.; Zhang, G.; Gao, Y.; Wang, K. Tribological properties of black phosphorus nanosheets as oil-based lubricant additives for titanium alloy-steel contacts. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2020, 7, 200530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, B.; Wu, H.; Desanker, M.; Pickens, D.; Chung, Y.-W.; Wang, Q.J. Direct formation of lubricious and wear-protective carbon films from phosphorus-and sulfur-free oil-soluble additives. Tribol. Lett. 2018, 66, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, S.M.; Schroeter, R.B.; Bossardi, J.C.d.S.; Andrade, C.L.F.d. Influence of EP additive on tool wear in drilling of compacted graphite iron. J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 2011, 33, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Yao, X.; Zhang, T.; Jiang, F.; Shui, Y.; Xie, H.; Xiang, Z.; Li, Y.; Lin, L. Passivation Effect of the Chlorinated Paraffin Added in the Cutting Fluid on the Surface Corrosion Resistance of the Stainless Steel. Molecules 2023, 28, 3648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, P.R.; Patel, H. Using complex polymeric esters as multifunctional replacements for chlorine and other additives in metalworking. Tribol. Lubr. Technol. 1997, 53, 31. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, D.W. The Tribology and Chemistry of Phosphorus-Containing Lubricant Additives. IntechOpen: London, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J.; Mohammadi, J.; Zhou, Y.; Larsh, J.; Januszkiewicz, K.; Evans, R.; Zhao, Y.; Gali, O.A.; Riahi, R.A. An investigation into cutting fluid additives performance during machining processing of Ti-6Al-4V. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2020, 112, 977–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Gali, O.A.; Riahi, R.A. An Evaluation of the Tribological Behavior of Cutting Fluid Additives on Aluminum-Manganese Alloys. Lubricants 2021, 9, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Gali, O.A.; Riahi, R.A. An investigation into the tribological behaviour of cutting fluid additives on Ti-6Al-4V alloy. Lubr. Sci. 2022, 34, 331–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Mohammadi, J.; Gali, O.; Riahi, A. The Influence of Polymeric Ester-Type Additives on the Performance of Metal Cutting Fluids for Machining of Titanium Alloy. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2021, 31, 2057–2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantero, J.; Tardio, M.; Canteli, J.; Marcos, M.; Miguelez, M.J. Dry drilling of alloy Ti–6Al–4V. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2005, 45, 1246–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mistry, K.; Morina, A.; Erdemir, A.; Neville, A. Tribological performance of EP lubricants with phosphorus-based additives. Tribol. Trans. 2013, 56, 645–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Chemical Composition | Al | V | C | N | Fe | O | Ti |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weight (%) | 6.16 | 4.05 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.21 | 0.15 | balanced |
| Drilling Parameter | Condition 1 | Condition 2 | Condition 3 | Condition 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cutting Speed (m/s) | 0.105 | 0.188 | 0.293 | 0.419 |
| Feed Rate (mm/r) | 0.040 | 0.022 | 0.014 | 0.010 |
| Phosphorous Level | Hydrocarbon Chain | |
|---|---|---|
| PE 1 | Low | Very long |
| PE 2 | Medium | Long |
| PE 3 | High | Medium |
| PE 4 | Very high | Low |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, J.; Mohammadi, J.; Gali, O.A.; Riahi, R.A. The Influence of Phosphate-Ester-Based Additives on Metal Cutting Fluid Behavior during the Machining of Titanium Alloy. Lubricants 2023, 11, 301. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants11070301
Ma J, Mohammadi J, Gali OA, Riahi RA. The Influence of Phosphate-Ester-Based Additives on Metal Cutting Fluid Behavior during the Machining of Titanium Alloy. Lubricants. 2023; 11(7):301. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants11070301
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Junhui, Javad Mohammadi, Olufisayo A. Gali, and Reza A. Riahi. 2023. "The Influence of Phosphate-Ester-Based Additives on Metal Cutting Fluid Behavior during the Machining of Titanium Alloy" Lubricants 11, no. 7: 301. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants11070301
APA StyleMa, J., Mohammadi, J., Gali, O. A., & Riahi, R. A. (2023). The Influence of Phosphate-Ester-Based Additives on Metal Cutting Fluid Behavior during the Machining of Titanium Alloy. Lubricants, 11(7), 301. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants11070301




