Effect of Substrate Roughness and Contact Scale on the Tribological Performance of MoS2 Coatings
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Details
2.1. Substrate Preparation
2.2. FE model Description
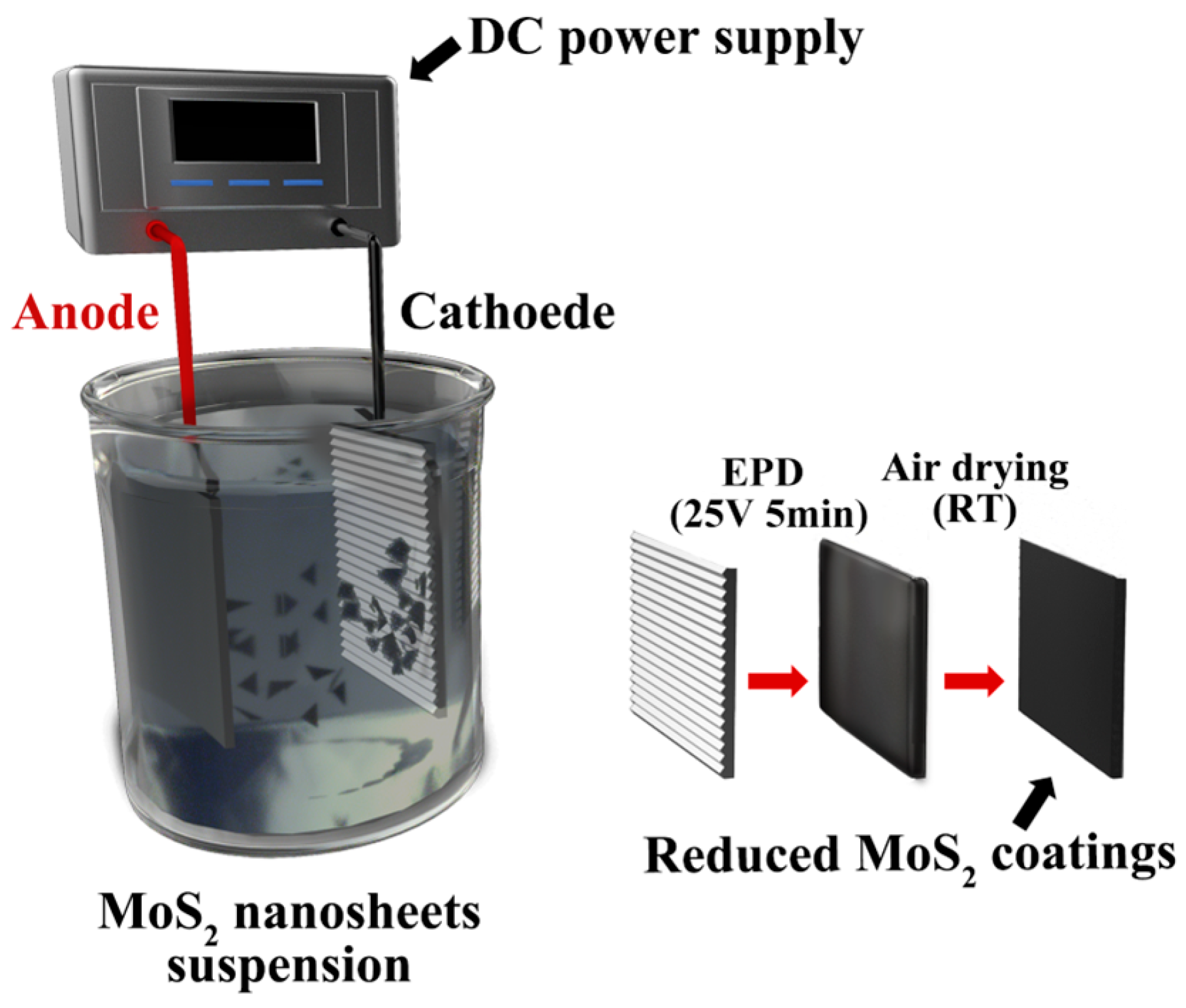
2.3. MoS2 Coating Deposition
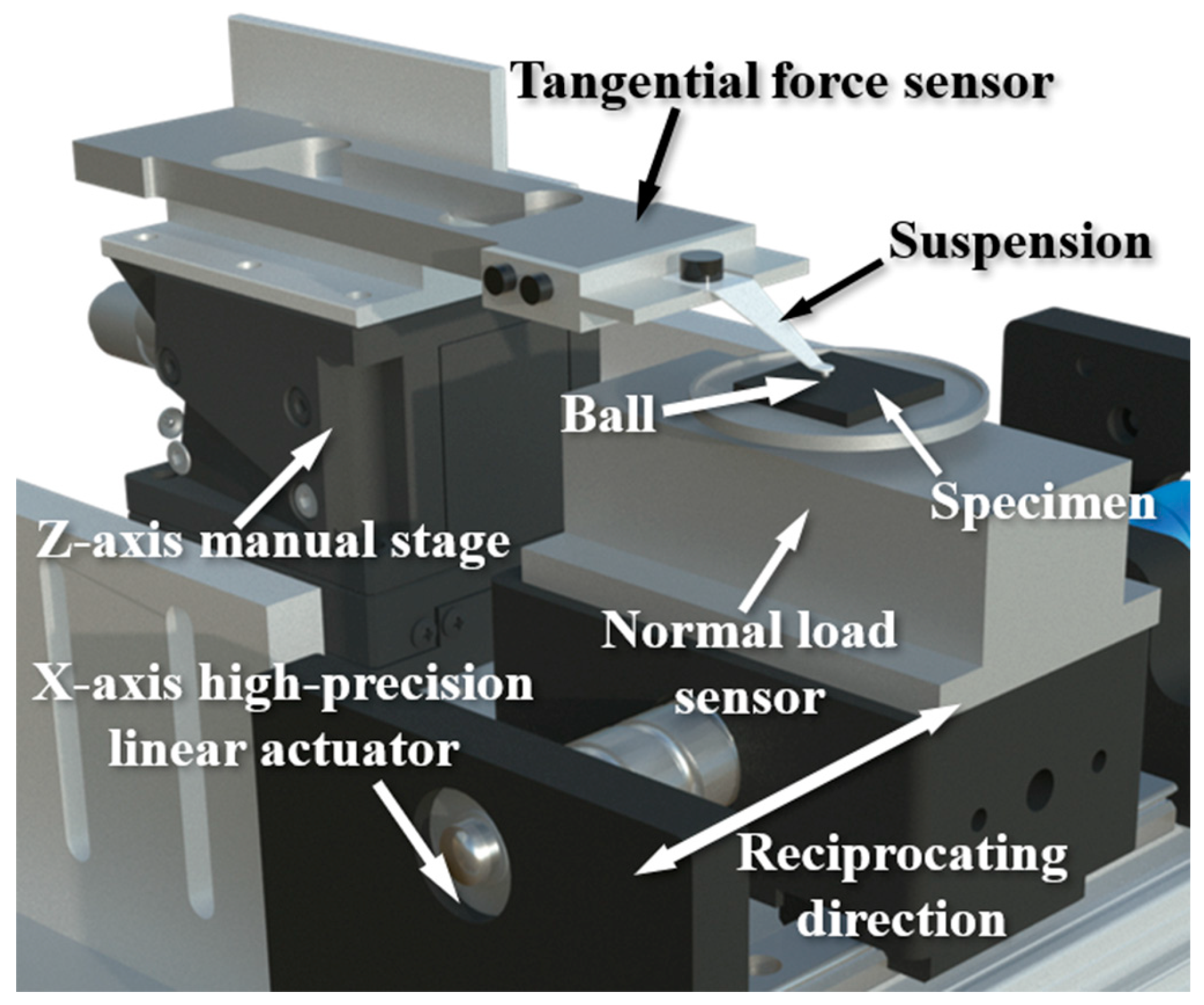
2.4. Tribotest
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Simulation Result
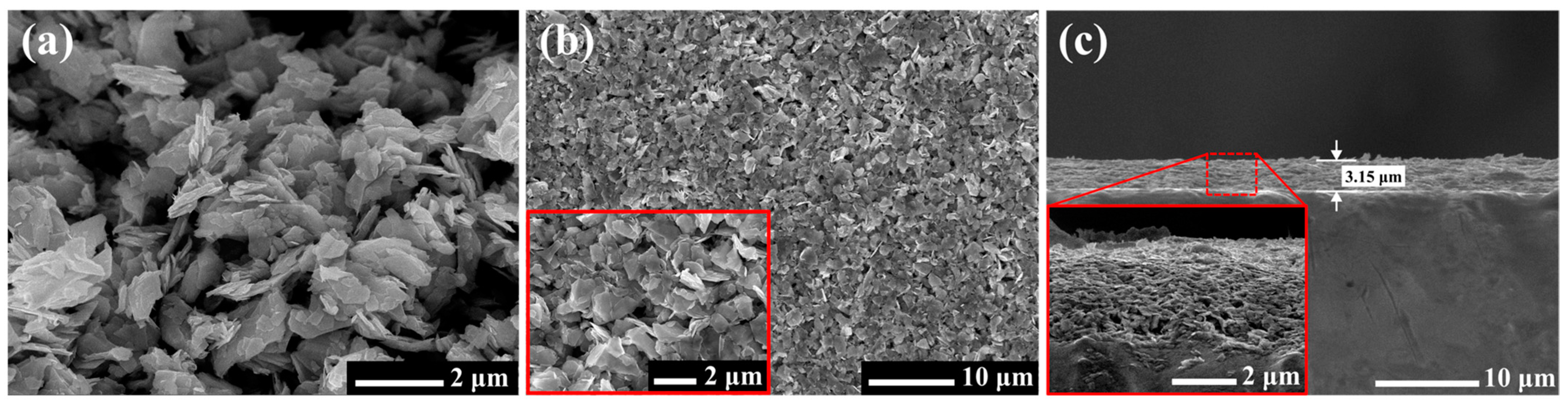
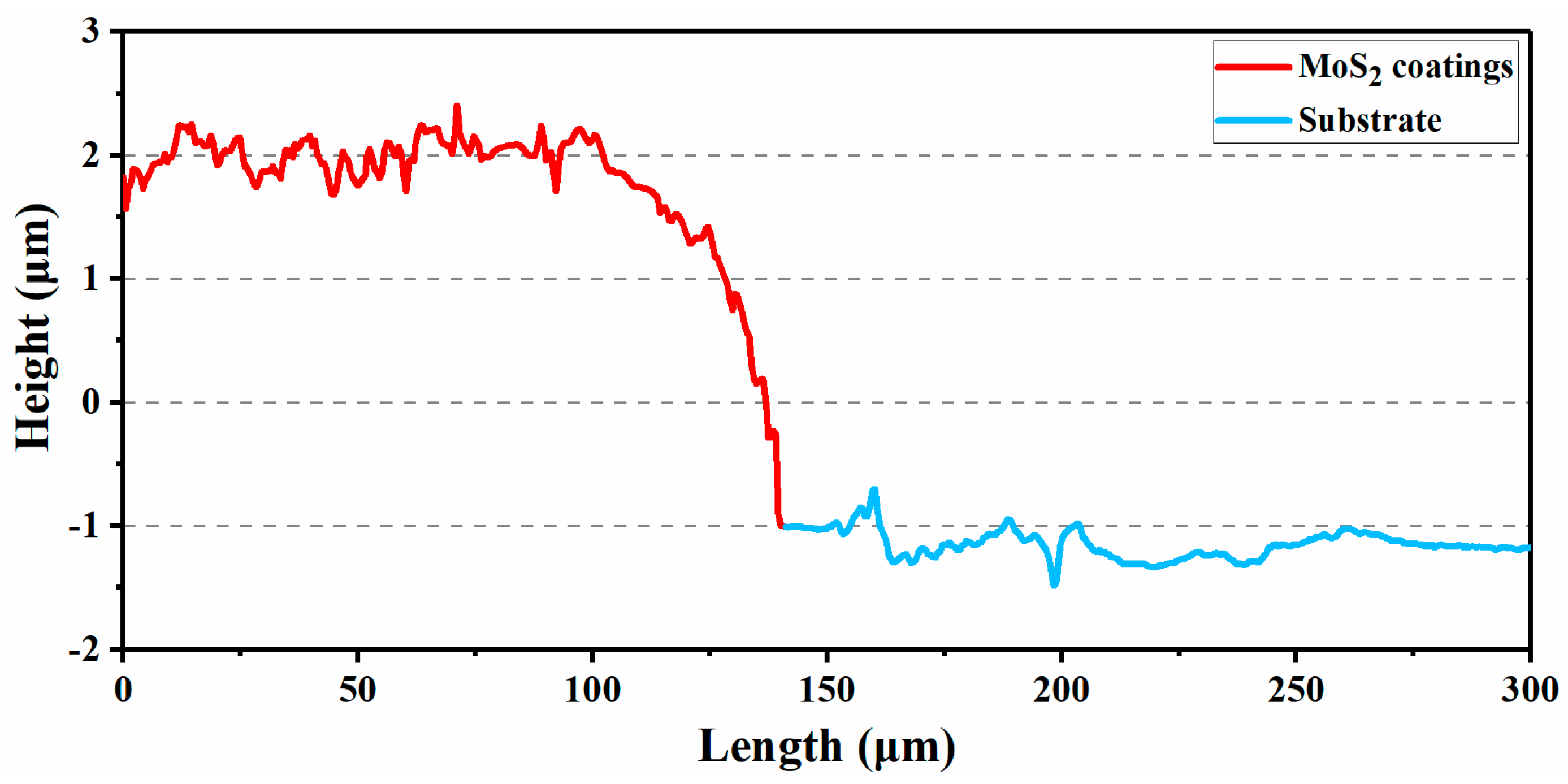
3.2. Characteristics of the MoS2 Coatings
3.3. Effects of Surface Roughness on the Tribological Properties
3.4. Compositional and Morphological Analysis of the Wear Tracks
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Van Kessel, P.; Hornbeck, L.J.; Meier, R.E.; Douglass, M.R. A MEMS-based projection display. Proc. IEEE 1998, 86, 1687–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amontons, G. De la résistance causée dans les machines. In Mémoires de l’Académie Royale A; Chez Gerard Kuyper: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1699; pp. 257–282. [Google Scholar]
- Bowden, E.; Tabor, D. The Friction and Lubrication of Solids; Oxford University Press: London, UK, 1954. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, J.; Luedtke, W.D.; Gourdon, D.; Ruths, M.; Israelachvili, J.N.; Landman, U. Frictional Forces and Amontons’ Law: From the Molecular to the Macroscopic Scale. J. Phys. Chem. B 2004, 108, 3410–3425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archard, J.F. Contact and Rubbing of Flat Surfaces. J. Appl. Phys. 1953, 24, 981–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenkranz, A.; Costa, H.L.; Baykara, M.Z.; Martini, A. Synergetic effects of surface texturing and solid lubricants to tailor friction and wear—A review. Tribol. Int. 2021, 155, 106792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scharf, T.W.; Prasad, S.V. Solid lubricants: A review. J. Mater. Sci. 2012, 48, 511–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnet, C.; Erdemir, A. Historical developments and new trends in tribological and solid lubricant coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2004, 180–181, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Y.; Deng, J.; Wang, X.; Meng, R. Effect of laser surface textures combined with multi-solid lubricant coatings on the tribological properties of Al2O3/TiC ceramic. Wear 2015, 342–343, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Li, Z.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, G.; Ren, T.; Zhang, Y. Enhanced anticorrosion and antiwear properties of Ti–6Al–4V alloys with laser texture and graphene oxide coatings. Tribol. Int. 2020, 152, 106475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, P.; Huang, Z.; Chen, C. Effect of Substrate Roughness on the Friction and Wear Behaviors of Laser-Induced Graphene Film. Lubricants 2022, 10, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Li, S.; Huang, H.; Ding, C.; Wang, X. Experimental Investigation on Synergetic Effects of Micro Grooves and WSe2 in Sliding Contact. Lubricants 2022, 10, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luster, B.; Stone, D.; Singh, D.P.; to Baben, M.; Schneider, J.M.; Polychronopoulou, K.; Rebholz, C.; Kohli, P.; Aouadi, S.M. Textured VN coatings with Ag3VO4 solid lubricant reservoirs. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2011, 206, 1932–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdemir, A. Review of engineered tribological interfaces for improved boundary lubrication. Tribol. Int. 2005, 38, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettersson, U.; Jacobson, S. Influence of surface texture on boundary lubricated sliding contacts. Tribol. Int. 2003, 36, 857–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Liu, K.; Gao, T.; Qiao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, W.; Ye, J. The unrecognized importance of roughness directionality to polymer wear. Wear 2021, 486–487, 204084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawari, C.K.; Haq, I.; Mönkkönen, K.; Suvanto, M.; Saarinen, J.J. Reduced sliding friction on flat and microstructured metal injection molded (MIM) WC-Co hard metals with MoS2 composite lubricants. Tribol. Int. 2021, 160, 107020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Ju, P.; Ji, L.; Li, H.; Liu, X.; Chen, L.; Zhou, H.; Chen, J. Toward Robust Macroscale Superlubricity on Engineering Steel Substrate. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, e2002039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bijani, D.; Deladi, E.L.; Akchurin, A.; De Rooij, M.B.; Schipper, D.J. The Influence of Surface Texturing on the Frictional Behaviour of Parallel Sliding Lubricated Surfaces under Conditions of Mixed Lubrication. Lubricants 2018, 6, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arenas, M.A.; Ahuir-Torres, J.I.; García, I.; Carvajal, H.; de Damborenea, J. Tribological behaviour of laser textured Ti6Al4V alloy coated with MoS2 and graphene. Tribol. Int. 2018, 128, 240–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Patel, D.S.; Ramkumar, J.; Balani, K. Single step laser surface texturing for enhancing contact angle and tribological properties. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2018, 100, 1253–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Guan, Y.; Ramakrishna, S. Tribological behavior of femtosecond laser-textured leaded brass. Tribol. Int. 2021, 162, 107115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grützmacher, P.G.; Profito, F.J.; Rosenkranz, A. Multi-Scale Surface Texturing in Tribology—Current Knowledge and Future Perspectives. Lubricants 2019, 7, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, M.-S.; Chae, Y.-H.; Kim, S.-S.; Hinoki, T.; Kohyama, A. Effect of geometrical parameters in micro-grooved crosshatch pattern under lubricated sliding friction. Tribol. Int. 2010, 43, 1508–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, J.; Braun, D.; Greiner, C. Laser Textured Surfaces for Mixed Lubrication: Influence of Aspect Ratio, Textured Area and Dimple Arrangement. Lubricants 2017, 5, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Sai, Q.; Wang, S.; Williams, J. Effects of Laser Surface Texturing and Lubrication on the Vibrational and Tribological Performance of Sliding Contact. Lubricants 2022, 10, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schäfer, C.; Reinert, L.; MacLucas, T.; Grützmacher, P.; Merz, R.; Mücklich, F.; Suarez, S. Influence of Surface Design on the Solid Lubricity of Carbon Nanotubes-Coated Steel Surfaces. Tribol. Lett. 2018, 66, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maclucas, T.; Daut, L.; Grützmacher, P.; Guitar, M.A.; Presser, V.; Gachot, C.; Suarez, S.; Mücklich, F. Influence of structural depth of laser-patterned steel surfaces on the solid lubricity of carbon nanoparticle coatings. Friction 2023, 11, 1276–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherif, H.A.; Kossa, S. Relationship between normal and tangential contact stiffness of nominally flat surfaces. Wear 1991, 151, 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahouani, H.; Mezghani, S.; Pailler-Mattei, C.; Elmansori, M. Effect of roughness scale on contact stiffness between solids. Wear 2009, 266, 589–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellgren, U.; Björklund, S.; Andersson, S. A finite element-based model of normal contact between rough surfaces. Wear 2003, 254, 1180–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ripoll, M.R.; Podgornik, B.; Vižintin, J. Finite element analysis of textured surfaces under reciprocating sliding. Wear 2011, 271, 952–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komvopoulos, K.; Choi, D.-H. Elastic Finite Element Analysis of Multi-Asperity Contacts. J. Tribol. 1992, 114, 823–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasarekar, A.T.; Bolander, N.W.; Sadeghi, F.; Tseregounis, S. Modeling of fretting wear evolution in rough circular contacts in partial slip. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2007, 49, 690–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, A.; Sadeghi, F. A novel approach to model effects of surface roughness parameters on wear. Wear 2015, 338–339, 73–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Li, F.; Chen, X.; Li, H.; Chen, W.; Zhang, P. Effect of Two Graphene Coatings on the Friction and Wear of Sliding Electrical Contact Interface. Lubricants 2022, 10, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orgeldinger, C.; Tremmel, S. Understanding Friction in Cam–Tappet Contacts—An Application-Oriented Time-Dependent Simulation Approach Considering Surface Asperities and Edge Effects. Lubricants 2021, 9, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichert, S.; Lorentz, B.; Albers, A. Influence of flattening of rough surface profiles on the friction behaviour of mixed lubricated contacts. Tribol. Int. 2016, 93, 614–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, W.; Jin, X.; Kirk, A.; Shipway, P.; Sun, W. Effects of surface roughness on local friction and temperature distributions in a steel-on-steel fretting contact. Tribol. Int. 2018, 120, 350–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, L.; Hyun, S.; Molinari, J.; Robbins, M.O. Finite element modeling of elasto-plastic contact between rough surfaces. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2005, 53, 2385–2409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juettner, M.; Bartz, M.; Tremmel, S.; Correns, M.; Wartzack, S. Edge Pressures Obtained Using FEM and Half-Space: A Study of Truncated Contact Ellipses. Lubricants 2022, 10, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenwood, J.A.; Williamson, J.B.P. Contact of nominally flat surfaces. Proc. R. Soc. Lund. Ser. A Math. Phys. Sci. 1966, 295, 300–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenkranz, A.; Heib, T.; Gachot, C.; Mücklich, F. Oil film lifetime and wear particle analysis of laser-patterned stainless steel surfaces. Wear 2015, 334–335, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinert, L.; Lasserre, F.; Gachot, C.; Grützmacher, P.; MacLucas, T.; Souza, N.; Mücklich, F.; Suarez, S. Long-lasting solid lubrication by CNT-coated patterned surfaces. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rapoport, L.; Moshkovich, A.; Perfilyev, V.; Lapsker, I.; Halperin, G.; Itovich, Y.; Etsion, I. Friction and wear of MoS2 films on laser textured steel surfaces. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2008, 202, 3332–3340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Han, J.-H.; Wang, T.; Hwang, Y.-H.; Xu, S.; Liu, W.; Kim, D.-E. Tribochemical reaction and wear mechanism of MoDTC based friction modifier. Tribol. Int. 2022, 165, 107302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Shin, D.-G.; Xu, S.; Kim, C.-L.; Kim, D.-E. Understanding of the lubrication mechanism of reduced graphene oxide coating via dual in-situ monitoring of the chemical and topographic structural evolution. Carbon 2021, 173, 941–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
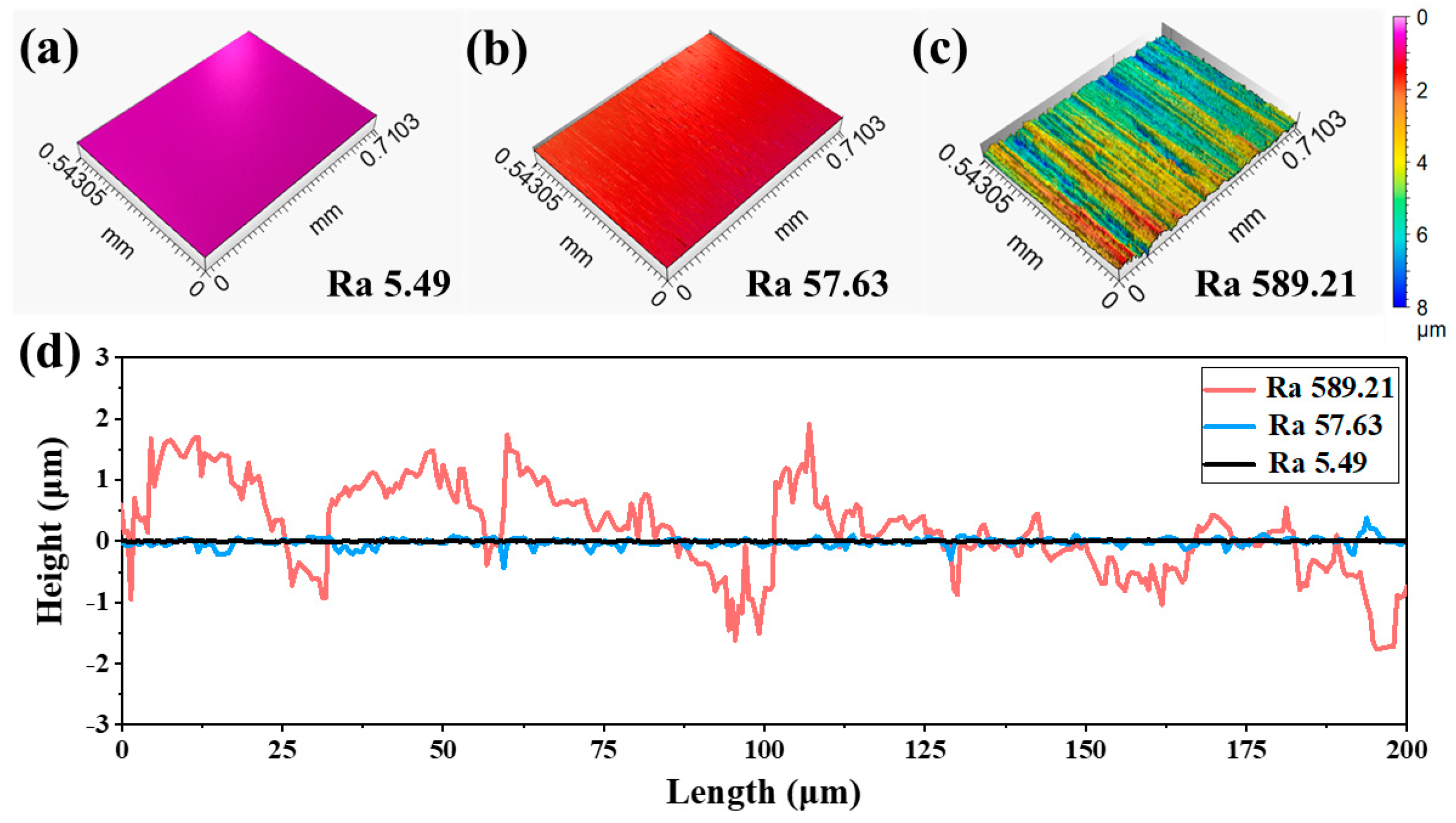

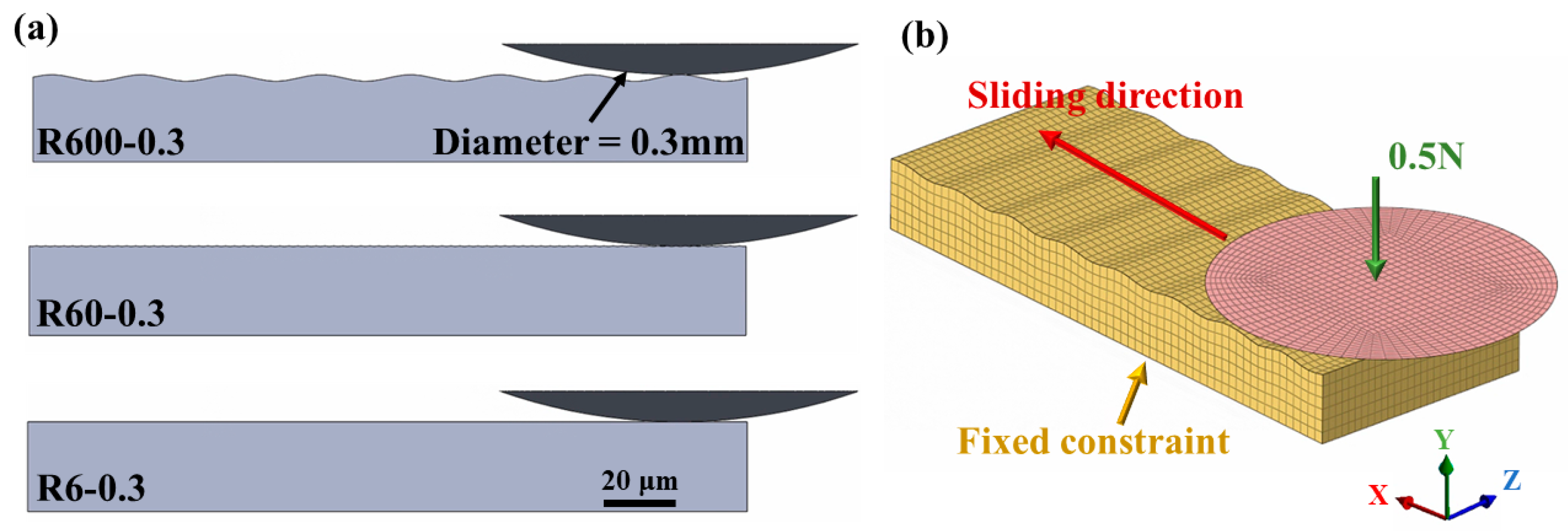
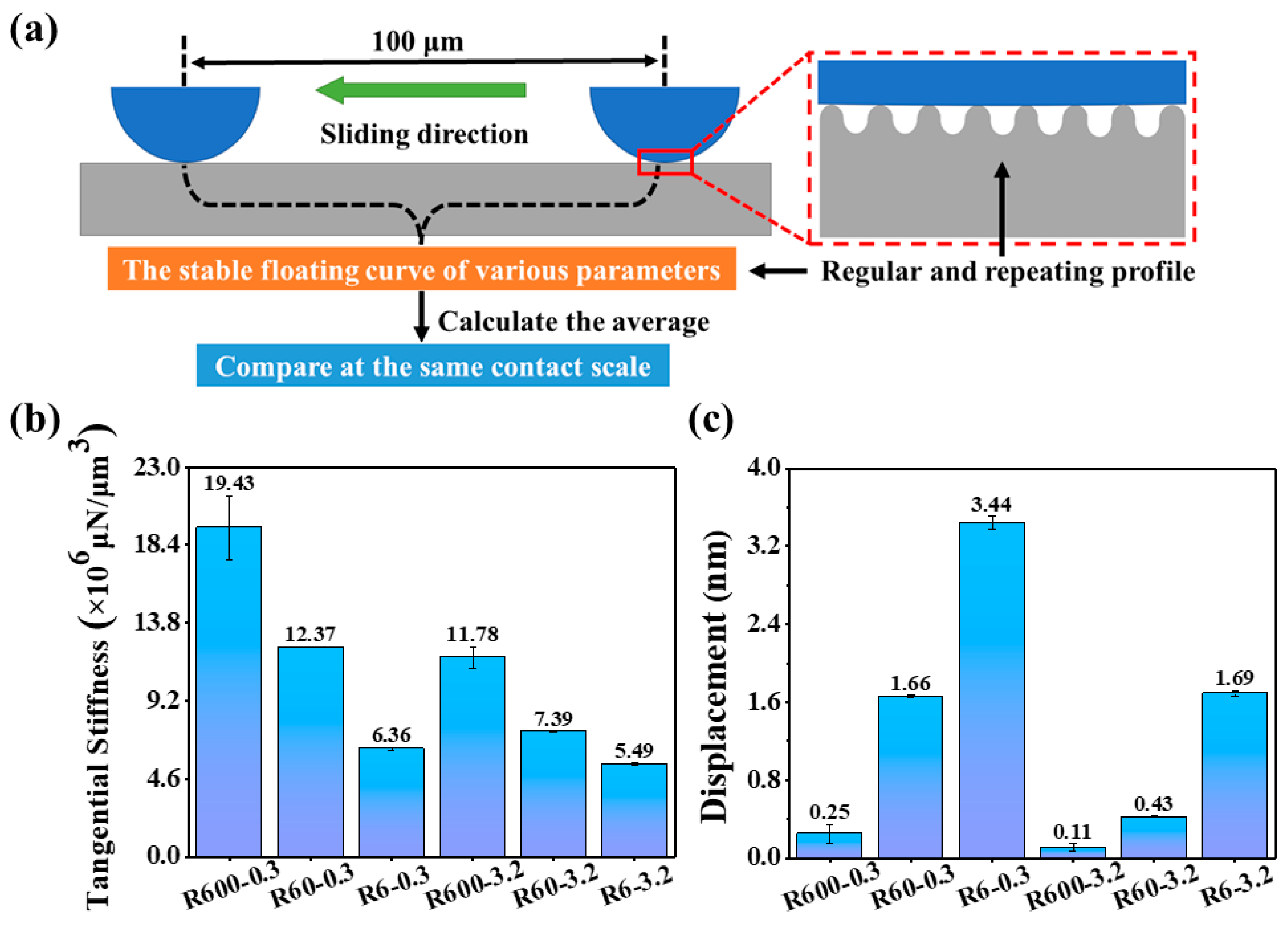
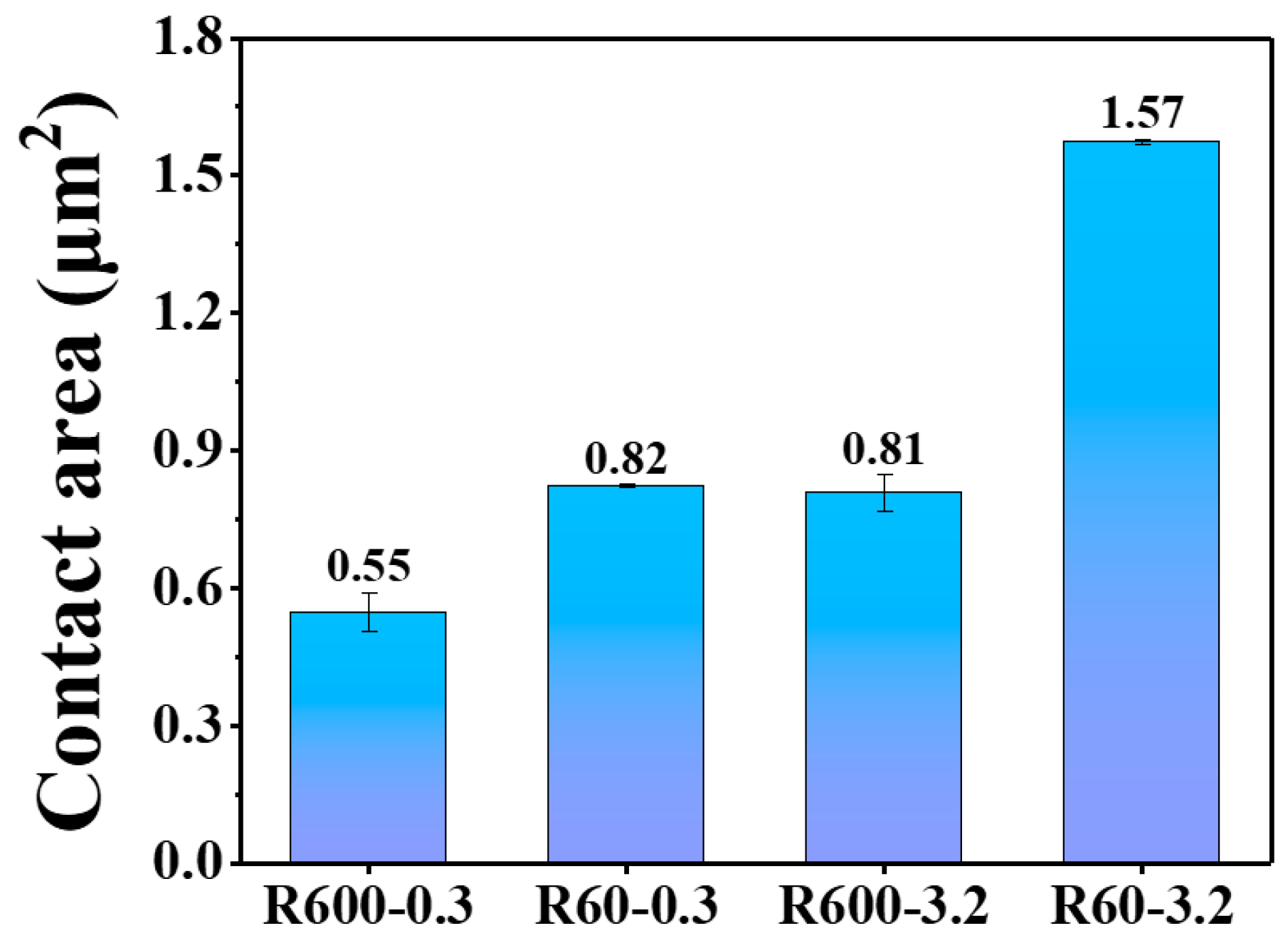

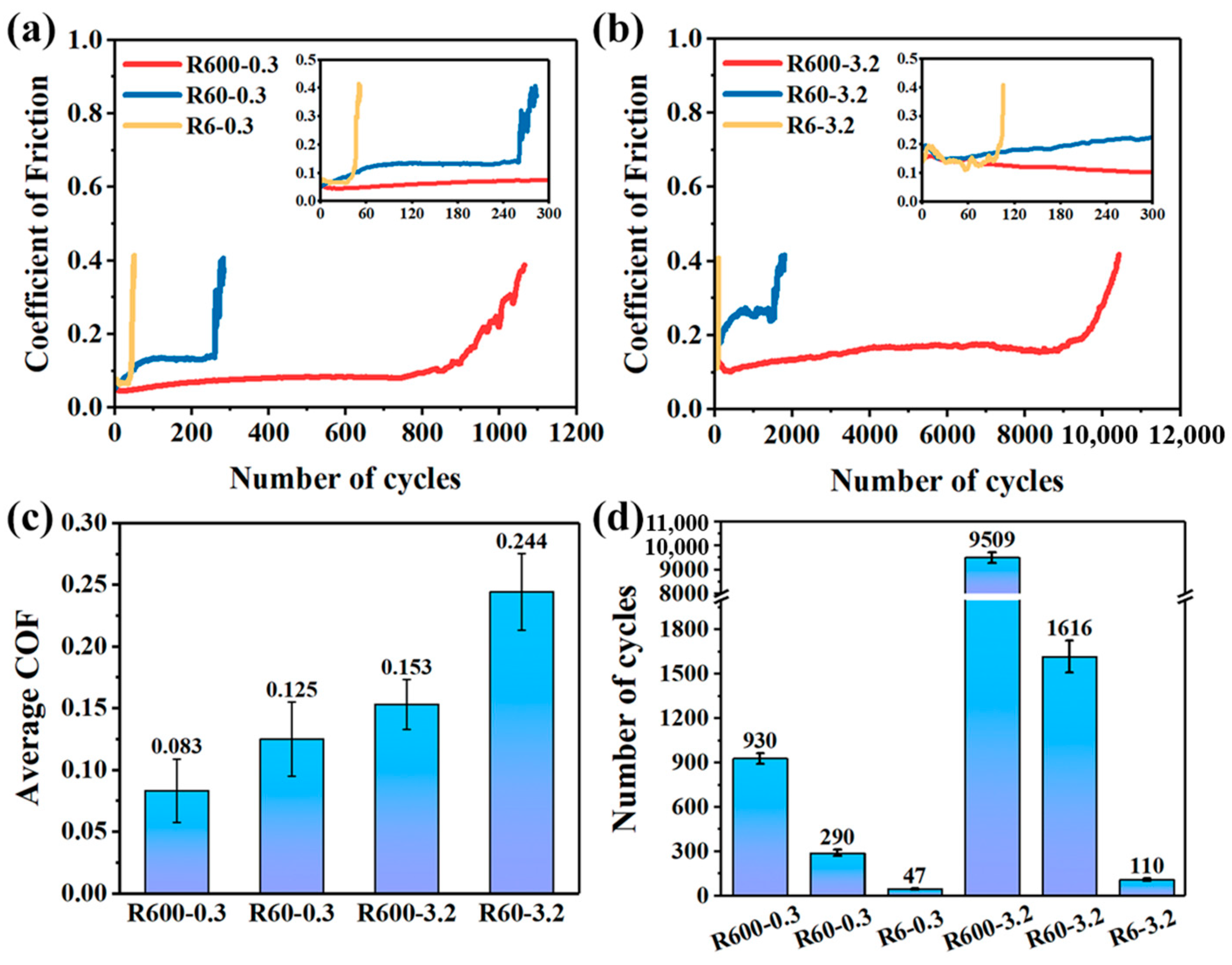
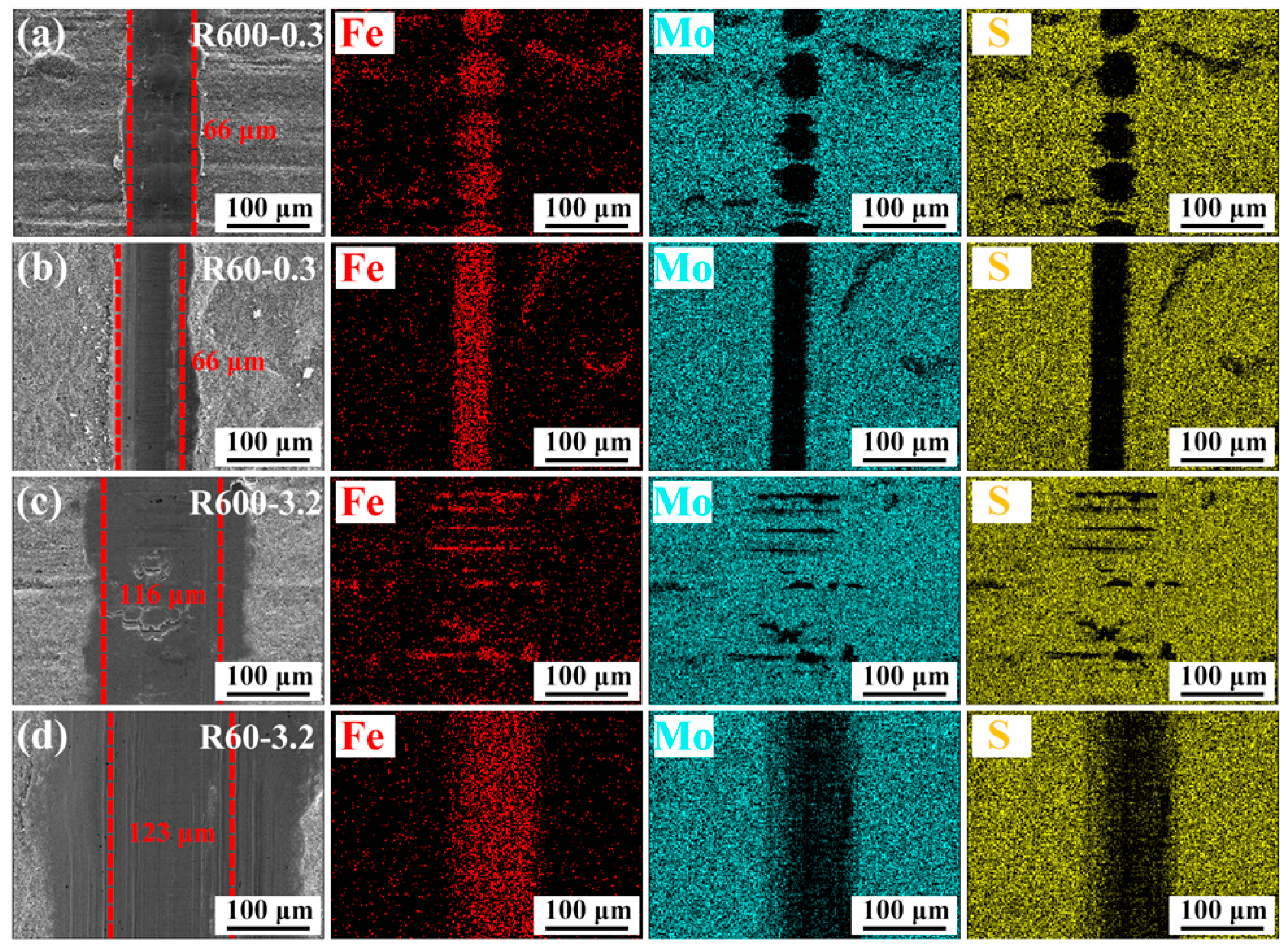
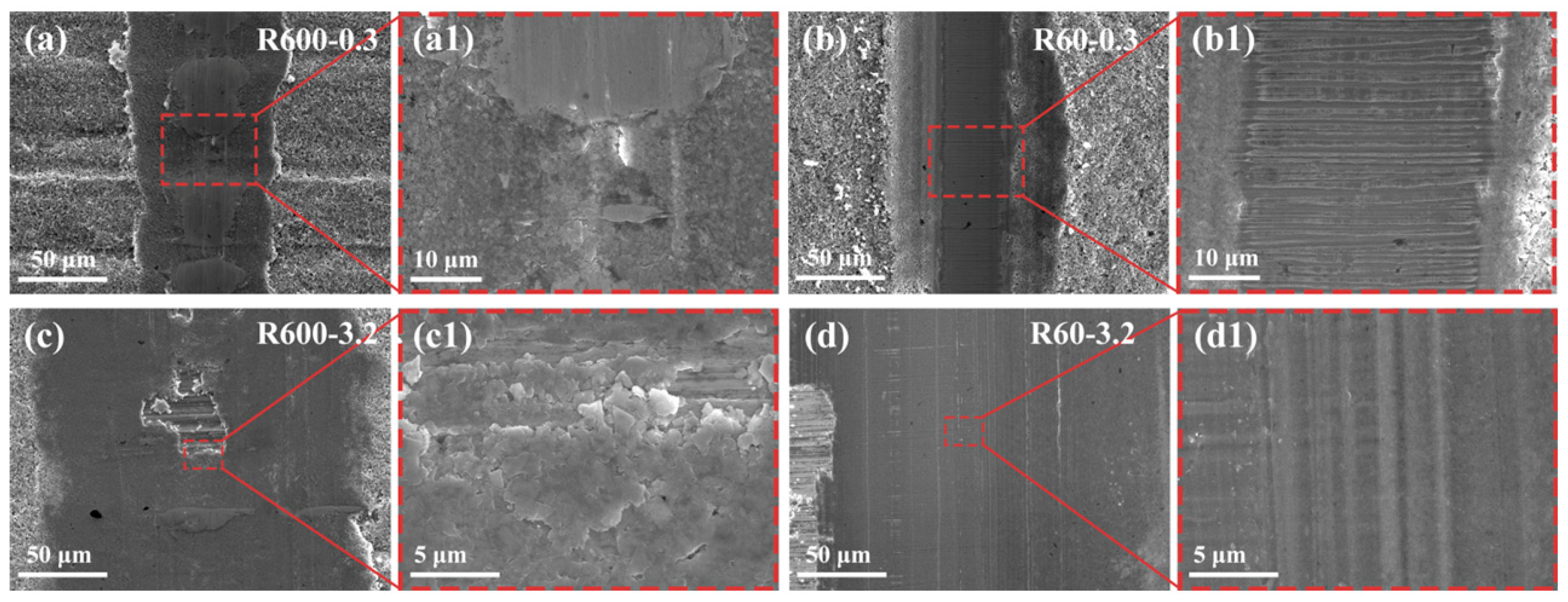
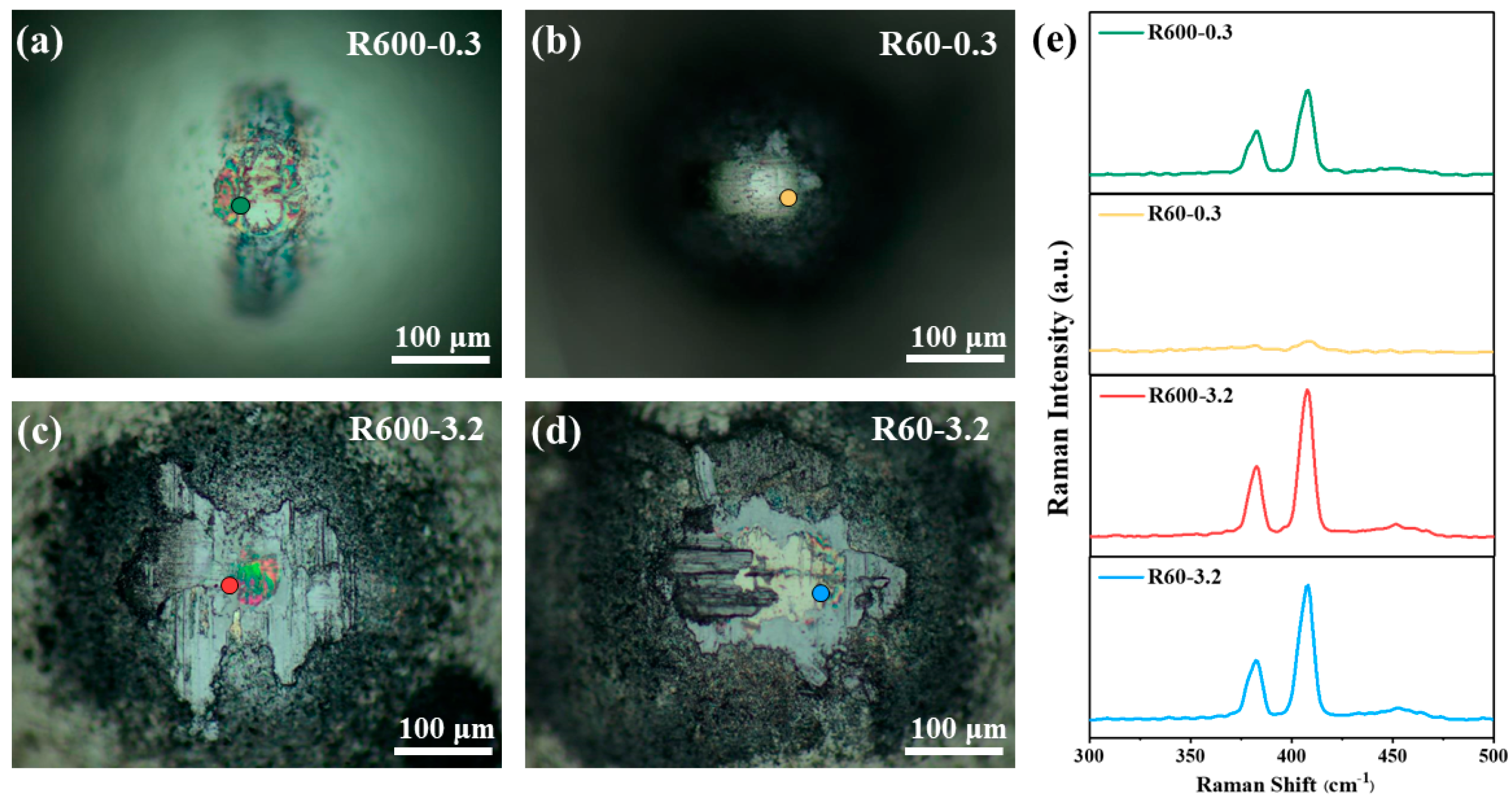
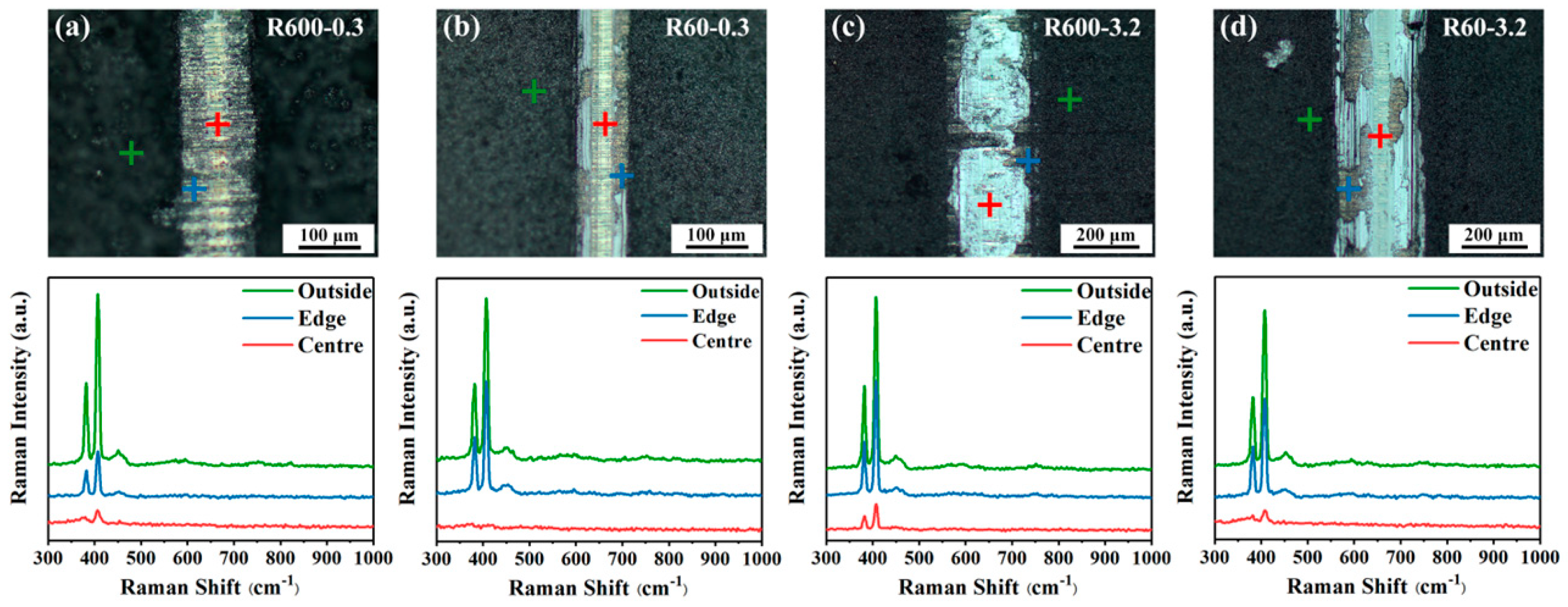
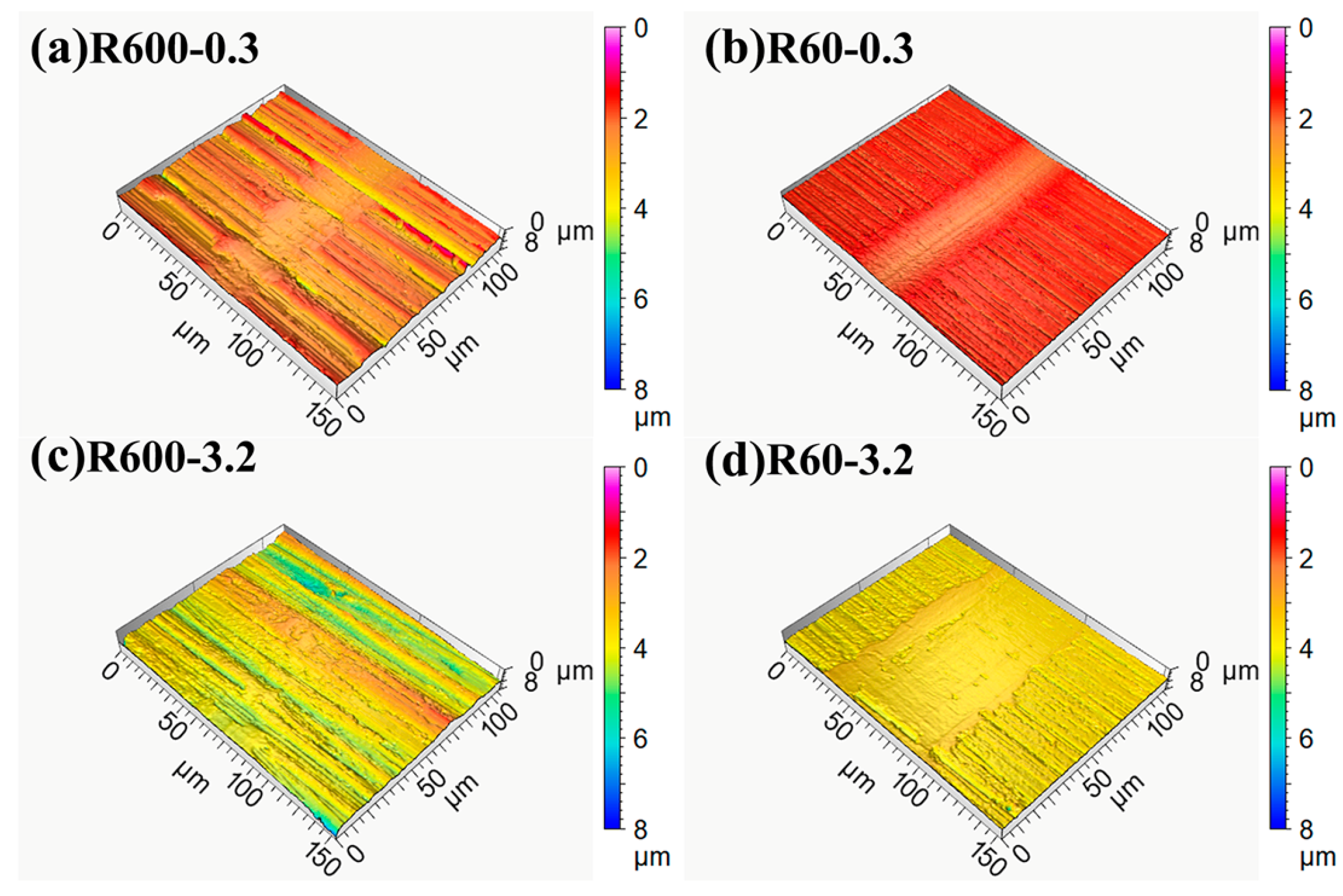
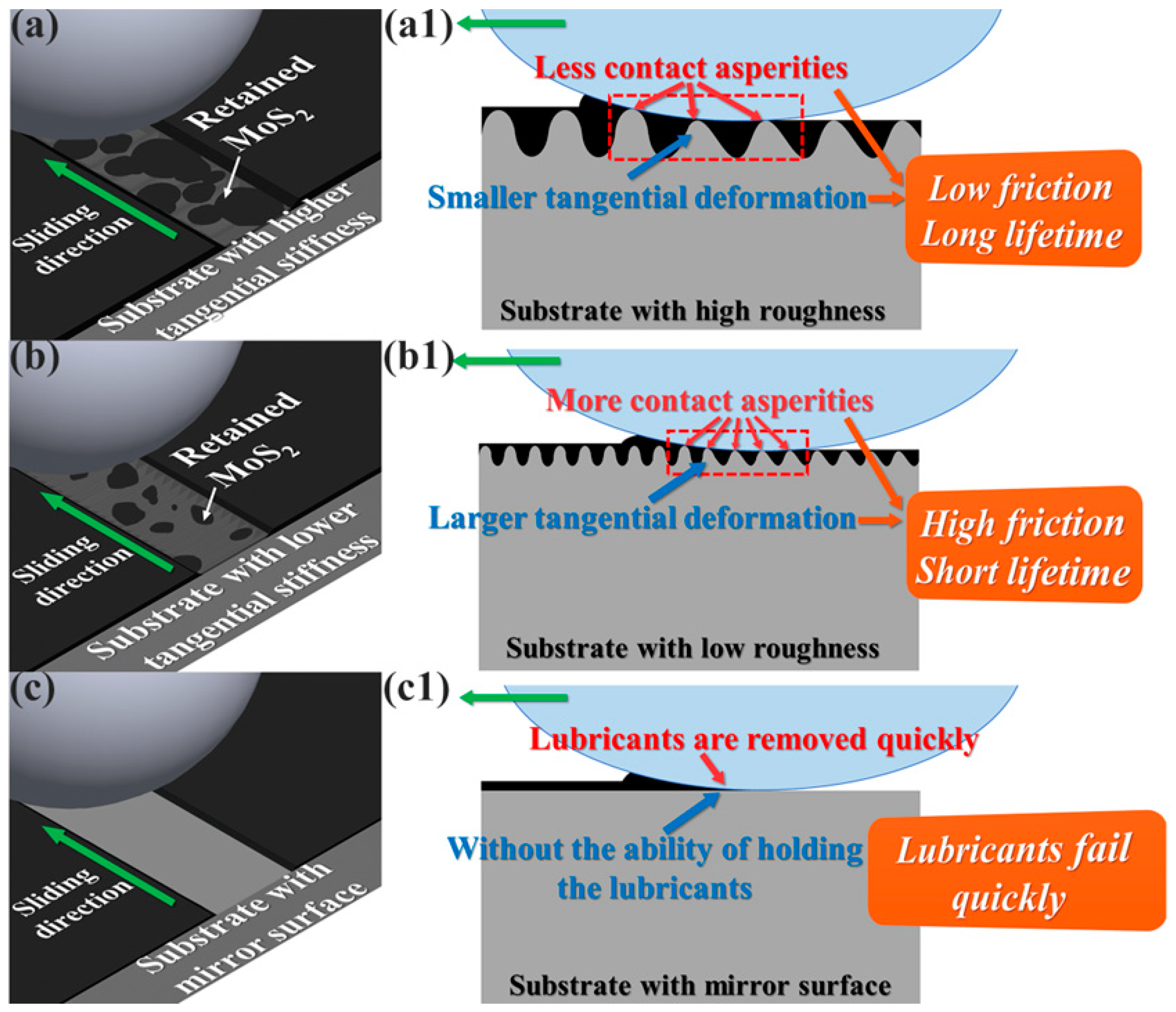
| Substrate | Sine Curve Equation (μm) | Ra (μm) | Amplitude (μm) | Wavelength (μm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| R600 | 0.942*sin (0.25*x) | 0.6 | 0.942 | 25 |
| R60 | 0.094*sin (2.5*x) | 0.06 | 0.094 | 2.5 |
| Designations | R600-0.3 | R60-0.3 | R6-0.3 | R600-3.2 | R60-3.2 | R6-3.2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Roughness | Ra 600.46 nm | Ra 59.82 nm | / | Ra 600.46 nm | Ra 59.82 nm | / |
| Counter ball diameter | 0.3 mm | 0.3 mm | 0.3 mm | 3.2 mm | 3.2 mm | 3.2 mm |
| Normal load | 0.5 N | 0.5 N | 0.5 N | 0.5 N | 0.5 N | 0.5 N |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, C.; Zhang, J.; Le, K.; Niu, Y.; Gao, X.; Che, Q.; Xu, S.; Liu, Y.; Liu, W. Effect of Substrate Roughness and Contact Scale on the Tribological Performance of MoS2 Coatings. Lubricants 2023, 11, 191. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants11050191
Wang C, Zhang J, Le K, Niu Y, Gao X, Che Q, Xu S, Liu Y, Liu W. Effect of Substrate Roughness and Contact Scale on the Tribological Performance of MoS2 Coatings. Lubricants. 2023; 11(5):191. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants11050191
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Chen, Jianjun Zhang, Kai Le, Yuqi Niu, Xiaoming Gao, Qinglun Che, Shusheng Xu, Yuzhen Liu, and Weimin Liu. 2023. "Effect of Substrate Roughness and Contact Scale on the Tribological Performance of MoS2 Coatings" Lubricants 11, no. 5: 191. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants11050191
APA StyleWang, C., Zhang, J., Le, K., Niu, Y., Gao, X., Che, Q., Xu, S., Liu, Y., & Liu, W. (2023). Effect of Substrate Roughness and Contact Scale on the Tribological Performance of MoS2 Coatings. Lubricants, 11(5), 191. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants11050191






