Abstract
A water lubricating axial piston pump (WLPP) is the core power component of a green and environmentally friendly water hydraulic system. The friction and wear of the friction pairs of a WLPP are the key factors that restrict its development. In order to explore the friction and wear mechanism of materials, the tribological properties of CFRPEEK against 316L and 1Cr17Ni2 under water lubrication were investigated in a friction testing machine and an axial piston pump, respectively. An environmental scanning electron microscope (ESEM), confocal laser scanning microscopy and a surface profiler were used to analyze the morphology of the samples. In a friction testing machine, two different metals are paired with CFRPEEK, and the friction coefficient and wear rate barely show any differences. The wear rate of CFRPEEK is two orders of magnitude higher than that of metal. In the WLPP, 316L can hardly be paired with CFRPEEK, while 1Cr17Ni2 works well. The wear of 1Cr17Ni2 in the WLPP is greater than that of CFRPEEK. The high-pressure water film lubrication friction pairs cause the wear of the metal and show the difference in these two test methods. The wear mechanism is mainly abrasive wear. Improving the wear resistance of metals is very important for the development of WLPP.
1. Introduction
Water hydraulics, which uses tap/sea water instead of traditional mineral oil as the working medium, has the advantages of environmental protection, non-combustion, compatibility with the environment and accessibility. This technology is widely used in seawater desalination [1,2], submersible buoyancy regulation [3,4], fire protection [5] and other fields. A water lubricating axial piston pump (WLPP), which increases the pressure of the working medium, is the core component of a water hydraulic system.
Figure 1 shows the structure of a WLPP. Its working principle is as follows. The rotating shaft drives the slipper to slide on the surface of the swashplate. The piston also rotates with the shaft and reciprocates in the cylinder sleeve. At the same time, the rotating shaft drives the floating plate to slide on the surface of the valve plate. Under the action of this motion and the hydraulic pressure, it forms three major friction pairs of the water pump, namely, the slipper/swashplate pair, the piston/cylinder sleeve pair and the valve plate/floating plate pair. These three friction pairs perform bearing and sealing functions [6]. However, compared with mineral oil, water has low viscosity, strong corrosion, high vaporization pressure and other physical and chemical properties [7], which make the friction pairs of a WLPP face serious friction and lubrication problems.
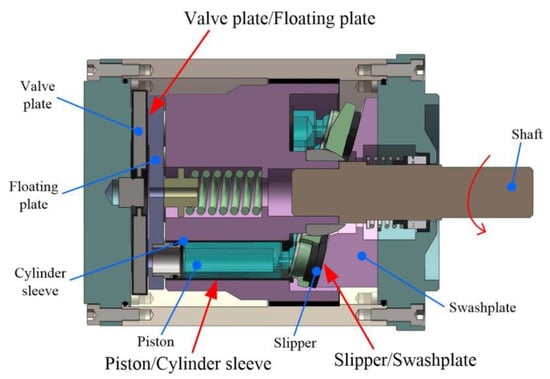
Figure 1.
Structure of WLPP.
Therefore, the materials of water-lubricated friction pairs have been researched. Generally, friction pair materials for a WLPP require corrosion resistance, good mechanical properties and tribological properties [8,9]. At present, the materials of water-lubricated friction pairs are mainly stainless steel [10], engineering plastics [11] and ceramics [12,13]. Ceramics are characterized by high strength, large elastic modulus, wear resistance and corrosion resistance, and are suitable to use under high-speed and heavy-load conditions. Nevertheless, the toughness and fatigue resistance of ceramics are poor. The main failure modes of ceramic parts are brittle fracture and fatigue spalling [14]. Furthermore, ceramics are difficult to process and are not the best material for making the friction pairs of a WLPP. In comparison, engineering plastics and stainless steel are more suitable for the friction pairs.
Among many engineering plastics, Poly ether ether ketone (PEEK) is a promising polymer with high mechanical and tribological properties, such as high temperature resistance, corrosion resistance, self-lubrication and dimensional stability, which is widely used in the fields of automobiles, aerospace, nuclear power and medical equipment [15,16,17,18]. Many researchers have studied the friction and wear properties of PEEK/modified PEEK under water lubrication. Chen et al. [19] studied the tribological behaviors of CF/PEEK under seawater lubrication, with sliding speeds of 0.5 m/s–1 m/s and normal loads of 200 N–600 N. The results showed that the incorporation of CF can greatly improve the wear resistance of PEEK. Li et al. [20] investigated the effect of different temperatures (0–50 °C) on the friction and wear properties of CFRPEEK against AISI 431 steel under water lubrication, using a disc-on-disc tester under sliding speeds of 0.68–1.36 m/s and loads of 0.61–1.83 MPa. It was found that the increasing lubricant temperature will lead to the deterioration of tribological properties of the materials. Davim et al. [21,22,23] used a pin-on-disc machine to research the effects of the PV factors (0.5–3 MPa·m/s) and the sliding distance on the tribological behaviors of CF/PEEK and AISI 316L under dry friction and water lubrication. Li et al. [24] investigated the friction and wear behaviors of PEEK filled with short carbon fibers and SiO2 against GCr15 under dry sliding conditions, with PV factors ranging from 1 to 12 MPa·m/s. Moreover, under high hydrostatic pressure, the friction and wear behavior of materials have been studied by scholars. Liu et al. [25] Studied the tribological behavior of different polymer materials under 0–40 MPa hydrostatic pressure. It was found that the wear behavior of thermoplastic polymers sliding in seawater is strongly dependent on the hydrostatic pressure. Wu et al. [26] have developed a disc-on-disc friction testing machine that can simulate hydrostatic pressure up to 80 MPa. In their follow-up work [27], the friction and wear characteristics of CF/PEEK against 431 stainless steel under high hydrostatic pressure were investigated. The results showed that hydrostatic pressure helps reduce the wear rates of CF/PEEK and 431 stainless steel.
The research on the tribological properties of PEEK and its poly composites focus on sliding speed, loads, lubricating temperature, material modification and hydrostatic pressure. The test method is usually conducted with a friction and wear testing machine with normal-pressure water lubrication. These studies focus more on the tribological characteristics of PEEK, and suggest that the strength and hardness of the metals are much greater than PEEK, while ignoring the wear issue of the metal materials. However, the WLPP works at 14 MPa and 1500 rpm, which makes the load of its friction pairs as high as 6.7 m/s and 4.1 MPa. Moreover, the friction pairs of the WLPP are lubricated by high-pressure water, which lead to the materials’ deformation [28]. Hence, the wear mechanism of PEEK and steel will be different when the lubrication conditions change. It is necessary to study the tribological behaviors of PEEK and stainless steel under real conditions for the design of WLPP.
In this work, the difference in tribological characteristics between CFRPEEK and stainless steel, under water lubrication in a friction testing machine and an axial piston pump, was studied. The friction coefficients and wear rates of CFRPEEK and stainless steel were measured, and the worn surface morphology was obtained. In particular, the wear mechanism of metals was analyzed using a friction testing machine and high-pressure lubrication in the WLPP. This study has instructive significance for the design and material selection of the friction pair of the water hydraulic pump.
2. Experimental
2.1. Sample Preparation
2.1.1. Sample for Friction Testing Machine
The materials of the upper samples are 316L (ASTM A240M-15a) and 1Cr17Ni2 (GB/T 1221-2007). The 316L sample is austenitic stainless steel, which is corrosion-resistant and is generally used in a corrosive environment. It has low strength and its hardness cannot be improved via heat treatment. Its hardness is usually lower than 187 HB. The 1Cr17Ni2 sample is martensitic stainless steel with high strength, and is widely used in ships, steam turbines and other harsh environments. After heat treatment, its hardness is HRC41–44 (~400 HB). These two materials have good water corrosion resistance and are commonly used to make parts of water hydraulic piston pumps [20,29]. The main mechanical properties of the two stainless steel materials are shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Mechanical properties of the two stainless steels.
CFRPEEK was selected to make the lower sample, which is made of 70% PEEK matrix and 30% carbon fibers. This material was commercially obtained from Ensinger Co., Ltd. (Nufringen, Germany). The main performance parameters of CFRPEEK are shown in Table 2.

Table 2.
Properties of CFRPEEK [30].
2.1.2. Samples of WLPP
As shown in Figure 2, the friction surface of slippers is coated with CFRPEEK by injection molding process, and its roughness and flatness are not greater than 0.8 μm and 0.003 mm, respectively. The swashplate parts are made of 316L and 1Cr17Ni2, and the heat treatment process is the same as that of the upper samples. The roughness and flatness of swashplate parts are less than 0.8 μm and 0.01 mm, respectively.

Figure 2.
Slipper and swashplate parts of WLPP.
2.2. Tribology Tests
2.2.1. Tribology Tests in Friction Testing Machine
A pin-on-disc friction testing machine (MMU–10, SHIJIN, Jinan, China) was utilized for tribological tests. As shown in Figure 3, the upper sample (stainless steel pin) and the lower sample (CFRPEEK disc) were installed in the sample box. Circulating water flowed into the sample box from the inlet and flowed out from the outlet for lubrication. The temperature of water was kept between 22–25 °C.
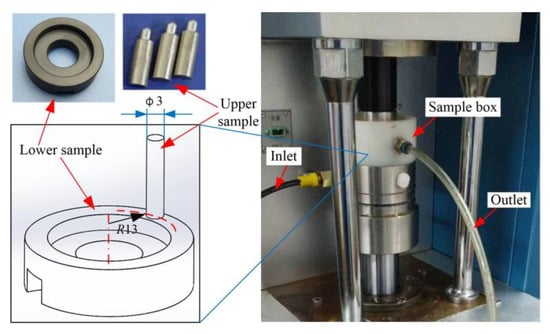
Figure 3.
Pin-on-disc friction testing machine.
The surfaces of pin-on-disc samples were polished with abrasive papers. The surface roughnesses of the pin-on-disc samples were less than 0.1 μm and 0.2 μm. Before and after the test, the samples were ultrasonically cleaned in industrial alcohol for 5 min and dried with a blower for 3 min. Then, the mass of samples was measured by an analytical balance (MS105, 0.01 mg, Mettler-toledo, Zurich, Switzerland). The weight difference of the samples before and after the test was the wear amount. The wear rate (w) and wear amount of the sample could be calculated by the following formula:
where Δm is the mass loss of the sample (g), ρ is the density (g/mm3), N is the load (N), and L is the sliding distance (m). Repeated tests were carried out for each group.
2.2.2. Tribology Tests in WLPP
Figure 4 shows the principle of the experimental system for testing the slipper/swashplate pairs of the WLPP. Slipper/swashplate pairs of different materials were installed in the tested pump to evaluate their tribological performance under real working conditions. A safety valve (4) was used to prevent system overpressure. The outlet pressure of the tested pump was regulated by the throttle valve (9), and measured by the pressure sensor (8, range: 0–25 MPa, accuracy: ±0.25% FS). The outlet flow was measured by flowmeter (10, range: 1–10 m3/h, accuracy: ±1% FS). The input speed and torque of the tested pump were measured by the tacho-torquemeter (5, range: 0–200 Nm, 0–5000 rpm, accuracy: ±0.1% FS). The change in pump volumetric efficiency could indirectly represent the wear of internal parts [31,32]. Its volumetric efficiency (ηv) could be expressed as follows:
where q is the outlet flow of the WLPP (L/min), qt is the theoretical flow of the WLPP (L/min), qt = 85n/1000, and n is the speed of the WLPP (r/min). Moreover, the wear of parts, including the macro size and macro morphology, was measured directly by measuring instruments.
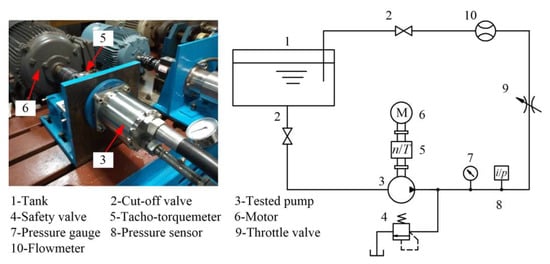
Figure 4.
Principle of the experimental system for testing the slipper/swashplate pairs of WLPP.
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Tribological Behaviors and Surface Topography within Friction Testing Machine
3.1.1. Tribological Behaviors of the Samples
In order to observe the friction and wear of materials in a short timeframe, the testing conditions in the friction testing machine were set to a contact pressure of 10 MPa and a sliding speed of 2 m/s. Each group of tests was carried out continuously for 180 min. The change in friction coefficients of the 316L/CFRPEEK and 1Cr17Ni2/CFRPEEK pairs, with time elapsed, is shown in Figure 5a. Both pairs have a running-in stage, after which the friction coefficient is stable. In order to compare the friction coefficient difference between the two materials, the average value of multiple sets of data is calculated, as shown in Figure 5b. Although the materials matched with CFRPEEK are different, the friction coefficients of the two pairs are slightly different. This means that different metal materials have little influence on the friction coefficient within the friction testing machine.
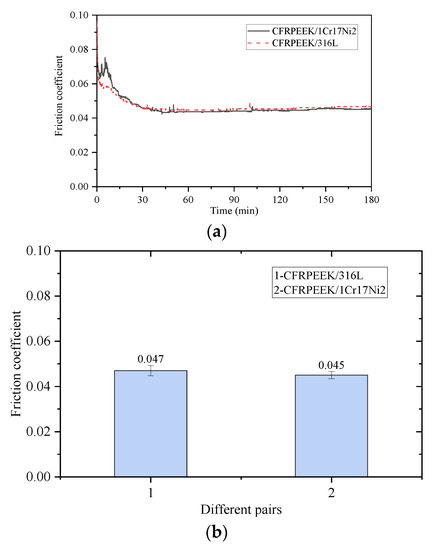
Figure 5.
Friction coefficient of different pairs. (a) Friction coefficients with sliding time; (b) average friction coefficients.
Furthermore, the wear rates of CFRPEEK and the two metals are also tested, as shown in Figure 6. In these two pairs, the wear rates of CFRPEEK have little difference, with the order of 10−7, which is similar to the results from previous studies [20,33]. Similarly, the wear rates of the two metals are similar, but are far less than the difference in CFRPEEK, with the order of 10−9. This means that the two metals are more wear-resistant than CFRPEEK.
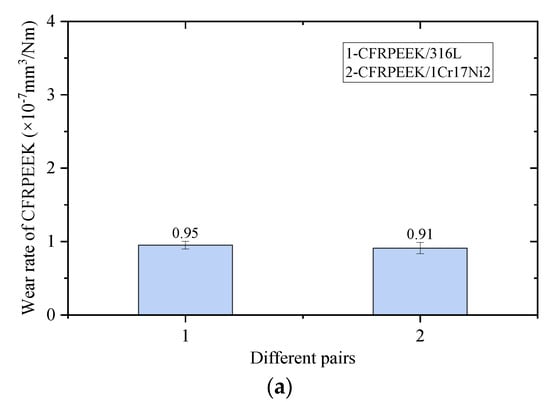
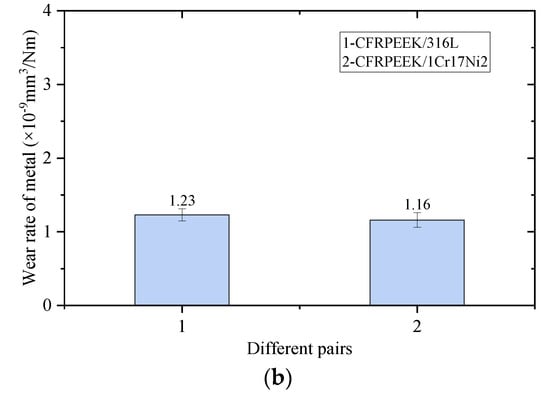
Figure 6.
Wear rates of different pairs. (a) Wear rates of CFRPEEK; (b) wear rates of metals.
3.1.2. Surface Topography of the Samples
The surface morphology of the 316L/CFRPEEK pair is similar to that of the 1Cr17Ni2/CFRPEEK pair after testing. An environmental scanning electron microscope (ESEM, FEI Quanta 200) was used to analyze the morphology of the samples. Due to the non-conductivity of CFRPEEK, the CFRPEEK samples were subjected to a gold-plating treatment before the morphology was calculated. Only the ESEM image of the 1Cr17Ni2/CFRPEEK pair is analyzed below. As shown in Figure 7a, there are some cavities on the surface of the unused CFRPEEK, which may be formed by the fracture and extraction of carbon fibers caused by mechanical cutting and the sanding with the abrasive paper. Compared with the worn CFRPEEK surface (see Figure 7b), the cavities on unused CFRPEEK surface disappear due to wear. Furthermore, the carbon fibers thin and break due to wear. More significantly, the carbon fibers are separated and pulled out from the PEEK matrix [20]. The wear mechanisms of CFRPEEK are mainly surface fatigue wear and adhesive wear [34].
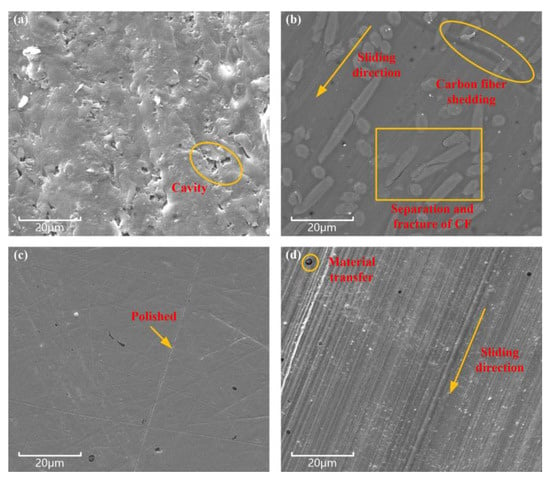
Figure 7.
Surface topography of the samples. (a) Unused CFRPEEK; (b) worn CFRPEEK; (c) unused 1Cr17Ni2; (d) worn 1Cr17Ni2.
The wear morphology of 1Cr17Ni2 is different from that of CFRPEEK. As shown in Figure 7c, the surface of the unused 1Cr17Ni2 sample is flat, and there are some crisscross, fine textures present after polishing. As shown in Figure 7d, there are clear abrasion marks along the sliding direction on the worn 1Cr17Ni2 surface. At the same time, some PEEK materials have adhered to the 1Cr17Ni2 metal surface. The wear mechanism of CFRPEEK and 1Cr17Ni2 metal is as follows. The mechanical properties of the PEEK matrix are increased by filling carbon fibers; that is, carbon fibers improve the bearing capacity of the PEEK matrix. However, under high contact pressure and sliding speed, the carbon fiber is worn and peeled off. Due to the high hardness and strength of carbon fiber, it causes metal surface wear. The PEEK matrix is worn off and transferred to the 1Cr17Ni2 metal surface in a small amount, which reduces wear to a certain extent. These wear mechanisms also verify previous research [35,36].
3.2. Wear Analysis of Slipper/Swashplate Pair of WLPP
3.2.1. Volumetric Efficiency of WLPP
In the test system shown in Figure 4, the 316L and 1Cr17Ni2 swashplates are installed in the tested pump to test volumetric efficiency. At the beginning of the test, the tested pump speed was adjusted to 1500 rpm, and the outlet pressure was set to 14 MPa. Then, the tested pump was operated under this working condition. The tested pump with the 316L swashplate was operated continuously for 20 min at 1500 rpm and with no load (~0.5 MPa). The temperature of the pump shell was high and the vibration and noise were abnormal. Therefore, the volumetric efficiency of the pump could not be tested at high outlet pressure.
For the tested pump with the 1Cr17Ni2 swashplate, the vibration, noise and shell temperature were normal during the test. Under the working conditions of 14 MPa and 1500 rpm, the tested pump was worked for 6–8 h every day, with a total final testing time of 500 h. Its volumetric efficiency was tested. The volumetric efficiency of the pump changed with time elapsed, as shown in Figure 8. The volumetric efficiency of the pump decreased gradually with the increase in operation time, from 92.5% at the beginning to 88.6% at 500 h. This indirectly reflected the wear of the moving parts, which increased the fit or seal clearance, resulting in increased leakage and reduced volumetric efficiency [37].
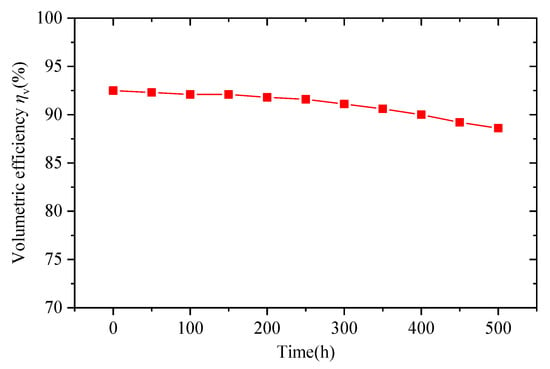
Figure 8.
The volumetric efficiency of WLPP (installed with 1Cr17Ni2 swashplate) changes with time.
During the test of the WLPP, the 1Cr17Ni2/CFRPEEK and 316L/CFRPEEK friction pairs showed obvious differences. The results showed that the 316L/CFRPEEK friction pair cannot be used in the WLPP, while the 1Cr17Ni2/CFRPEEK friction pair can operate for a long time at a high speed and with a heavy load. This is significantly different from the tribological characteristics of the two in the friction testing machine.
3.2.2. Wear Analysis of Slipper and Swashplate Pairs
In order to study the wear mechanism of the swashplate and slipper friction pairs made of two materials, the worn appearances of the swashplate and the slipper were measured. A camera was used to take photos of the friction surface in order to observe the wear from a macro perspective. The wear profile of the swashplate was measured along the normal direction of the sliding direction with a profiler. This model is the MarSurf LD130 (Mahr, Gottingen, Germany), with a resolution of 0.8 nm. The three-dimensional morphology of the swashplate wear area was measured by confocal laser scanning microscopy (LSM800, Zeiss, Oberkochen, Germany). The wear of the friction surface of the swashplate parts is shown in Figure 9.
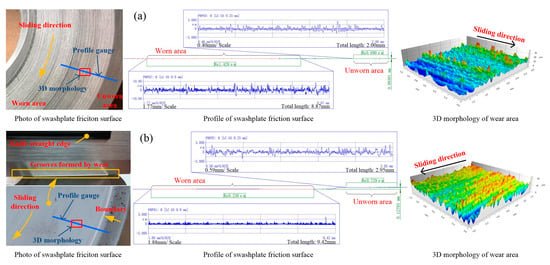
Figure 9.
Wear of friction surface of swashplate parts. (a) The 316L swashplate; (b) the 1Cr17Ni2 swashplate.
The wear photo shows that the 316L swashplate friction surface (see Figure 9a) is severely worn after a short period of no-load operation. Along the sliding direction of the slipper, the wear forms a dense groove, which makes a clear boundary between the wear area and the non-wear area. From the profile measurement results showing the sliding direction of the slipper, it can be seen that the surface roughness increases significantly, from Ra0.69 μm before the test to Ra1.43 μm after the test. The height difference between the worn area and the non-worn area is 3 μm, which is the depth of the wear marks on the 316L swashplate surface. The 3D morphology of the wear area shows that the maximum height of the peaks and troughs formed by the wear mark is more than 30 μm, and the surface roughness is Sa2.99 μm.
By comparison, the friction surface of the 1Cr17Ni2 swashplate is much smoother, as shown in Figure 9b; however, due to the wear caused by long-time operation under high pressure, there are an grooves on the swashplate surface. Similarly, a clear boundary (step) is formed between the worn area and the non-worn area. The profile of the 1Cr17Ni2 swashplate was tested with the same method and position. The wear area is smoother than the non-wear area, and the roughness is reduced from Ra0.729 μm to Ra0.238 μm. This means that the 1Cr17Ni2 swashplate is polished by CFRPEEK. The 3D morphology observation results also show that the maximum contour height difference is less than 20 μm, and the surface roughness is Sa2.35 μm. Nevertheless, the depth of the wear marks on the swashplate surface reaches 0.128 mm, and the metal is considerably worn away, which is obviously different from the wear rate results obtained using the friction testing machine.
The wear of the CFRPEEK slippers matched with the different stainless steels was evaluated and analyzed. A micrometer was used to measure the height difference of the slipper friction surface before and after the test. Each slipper friction surface was measured at three points at equal intervals and averaged to reduce error. The CFRPEEK slipper matched with the 316L swashplate was worn 0.005 mm, and it was worn 0.103 mm when matched with the 1Cr17Ni2 swashplate. Although the wear of the former was much less than that of the latter, the wear rate of the former was also much greater than that of the latter. This is because the former had been operated for nearly 20 min under no load (~0.5 MPa), and the latter had been operated for 500 h under a rated load (14 MPa).
The wear morphology of the CFRPEEK slippers matched with different stainless steels was measured, as shown in Figure 10. When matched with the 316L swashplate, the slipper friction surface becomes very rough after a short time of operation (see Figure 10a). The friction surface is covered with dense and staggered grooves. As shown in Figure 10b, the PEEK matrix is embedded with a certain amount of metal debris. At the same time, the carbon fibers are broken or even pulled out, which causes some cavities on the surface of CFRPEEK. This is because the strength and hardness of carbon fiber are much higher than that of 316L stainless steel. When the two of them rub against each other, the carbon fibers cut 316L metal to form large abrasive debris. Due to the low strength and hardness of the PEEK matrix, it is embedded with metal debris under the action of the load and speed [33,34].
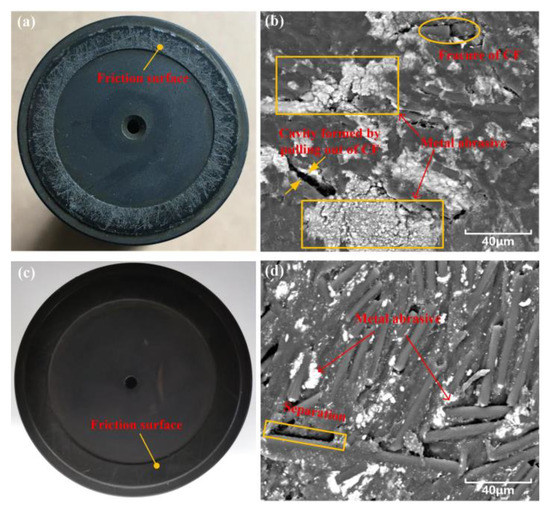
Figure 10.
Wear of friction surface of slipper parts. (a) Photo of slipper after sliding with 316L swashplate; (b) ESEM morphology of slipper after sliding with 316L swashplate; (c) photo of slipper after sliding with 1Cr17Ni2 swashplate; (d) ESME morphology of slipper after sliding with 1Cr17Ni2 swashplate.
As shown in Figure 10c, when matched with the 1Cr17Ni2 swashplate, the slipper friction surface is relatively flat after high-pressure operation for a long time. The enlarged scanning electron microscope shows (Figure 10d) that the carbon fibers are densely distributed on the surface, and a few parts are separated from the PEEK matrix. Moreover, wear debris of a small size is embedded into the PEEK matrix around the carbon fiber.
However, when CFRPEEK slippers are paired with the 316L and 1Cr17Ni2 swashplate in the WLPP, the wear rates of the metals are very different. The wear rate of 316L is much greater than that of the 1Cr17Ni2. At the same time, the depth of the the 1Cr17Ni2 swashplate wear mark is greater than that of the CFRPEEK slipper. This means that CFRPEEK is more wear-resistant than the metals. These results are completely different from the results of the friction testing machine.
In summary, due to the low strength and hardness of 316L, the swash plate made of this material is microcut by carbon fibers with a high hardness. The wear mechanisms of 316L are mainly severe abrasive wear [34] and slight adhesive wear. However, with the higher strength and hardness of 1Cr17Ni2, the swash plate made of this material has a certain polishing effect. Its wear mechanism is slight abrasive wear. As for CFRPEEK, carbon fibers break and fall off on the surface, and the PEEK matrix is embedded with metal abrasive debris. The wear mechanisms of CFRPEEK are mainly abrasive wear [23], surface fatigue wear and adhesive wear [20,38].
3.3. Analysis of Tribological Differences under Two Test Methods
The cause of the difference in the friction tests between CFRPEEK and the two stainless steels in the friction testing machine and the axial piston pump is the pressure of the lubricating water. Atmospheric pressure water lubrication is used in the friction testing machine, while high-pressure (~14 MPa) water lubrication is used in the WLPP. The wear mechanisms of CFRPEEK and the metals under the two test methods are shown in Figure 11.
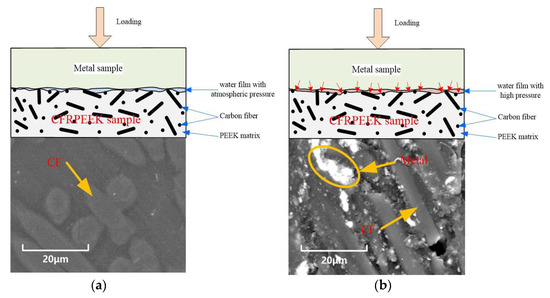
Figure 11.
Wear mechanisms of CFRPEEK and metals. (a) Atmospheric pressure water lubrication in friction testing machine; (b) high-pressure water lubrication in WLPP.
Figure 11a shows the wear mechanism of CFRPEEK against two stainless steels under atmospheric pressure water lubrication, which is used to analyze the wear condition in the friction testing machine. Under the action of the test load, contact stress is generated between the metal sample and the CFRPEEK sample. The carbon fibers and the PEEK matrix in the contact area jointly bear the contact stress. Because the lubricating water is at atmospheric pressure, it cannot cause microdeformation on the surface of the carbon fibers or the PEEK matrix, but it still plays the role of lubrication and cooling. With the low hardness and strength of CFRPEEK, its wear rate is larger than that of metal. The worn surface of CFRPEEK is also relatively flat.
Figure 11b shows the wear mechanism of CFRPEEK against two stainless steels under high-pressure water lubrication, which is used to analyze the wear condition in the WLPP. The tensile strength and modulus of carbon fibers exceed 3.0 GPa and 230 GPa, respectively. Its hardness is second only to diamond, and more than 10 times that of the metals [39]. However, the hardness and elastic modulus of the PEEK matrix are 85 (shore D) and 3.5 GPa [30], respectively. Based on the diameter of the carbon fibers (~8 μm) [30], the deformations of the carbon fibers and the PEEK matrix are 0.5 × 10−3 μm and 32 × 10−3 μm, respectively, under the pressure of 14 MPa. Therefore, under the condition of high-pressure water lubrication, the deformation of the PEEK matrix is larger than that of the carbon fibers. The difference deformation increases the amount of the carbon fibers’ contact with the metal and makes them bear a greater load. Due to the extremely high hardness of carbon fibers, the wear of the metal increases when rubbed against them. In this case, the strength and hardness of the metal materials affect their wear rates. Generally, the higher the strength and hardness of metal materials, the lower the wear rates. Due to the low strength and hardness of 316L, the wear of the 316L swashplate is serious. With the high strength and hardness of 1Cr17Ni2, the surface of the 1Cr17Ni2 swashplate is smooth after rubbing against carbon fibers. The micro surface of CFRPEEK matched with the metal is relatively rough. Metal wear debris is embedded into the PEEK matrix with low hardness between carbon fibers.
4. Conclusions
In this work, the tribological characteristics of CFRPEEK sliding against 316L and 1Cr17Ni2 stainless steel under water lubrication in a friction testing machine and an axial piston pump were investigated. Based on the study, the following conclusions can be drawn:
(1) Metal (316L or 1Cr17Ni2) is more wear-resistant than CFRPEEK within a friction testing machine. When tested with a friction testing machine, the friction coefficient and wear rates of the CFRPEEK/316L and CFRPEEK/1Cr17Ni2 friction pairs have no significant difference. The wear rate of CFRPEEK is on the order of 10−7, while that of metal is on the order of 10−9.
(2) The wear of 1Cr17Ni2 is greater than the wear of CFRPEEK in a WLPP. When tested in a water-lubricated axial piston pump, the CFRPEEK/316L and CFRPEEK/1Cr17Ni2 friction pairs show great differences. The wear rates of CFRPEEK against 316L are very high, and show that the pair can hardly be used in the pump. However, CFRPEEK against 1Cr17Ni2 can be used as friction pair materials in the pump for a long time. After 500 h in a high-pressure test, the CFRPEEK slipper and the 1Cr17Ni2 swashplate were worn by 0.103 mm and 0.128 mm, respectively. This is obviously different from the wear rate test results of metal and CFRPEEK in the friction testing machine.
(3) The amount of load borne by carbon fibers is the main reason for the difference in tribological properties between the different metals and CFRPEEK. The friction interface between metal (316L or 1Cr17Ni2) and CFRPEEK is lubricated by atmospheric pressure water in the friction testing machine, but it is lubricated by high-pressure water in the pump. This is the biggest difference between the two. The high-pressure water film causes the microdeformation of the PEEK matrix at the interface of CFRPEEK, which makes the carbon fibers bear more loads. High strength and high hardness carbon fibers cut metal to form grinding, resulting in the abrasive wear of the metal and CFRPEEK. The wear mechanism of CFRPEEK is mainly surface fatigue wear. The 316L with low strength and hardness rubs against carbon fibers, causing serious wear. The wear of 1Cr17Ni2 with higher strength and hardness is better.
Based on the above findings, it is necessary to study wear resistance methods for metals in the future to improve the performance of WLPPs.
Author Contributions
Methodology and writing—original draft preparation, D.L. and X.M.; test and data processing, S.W. and J.W.; project administration, F.Y.; checking and supervision, Y.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by National Natural Science Foundation of China, grant number 52105054, Key scientific and technological projects in Henan Province, grant number 222102220012 and 222102220073, Key scientific research projects of colleges and universities in Henan Province, 22A460004 and 22A460017.
Data Availability Statement
The data-supported results are included within this article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Lou, F.L.; Nie, S.L.; Yin, F.L.; Lu, W.; Ji, H.; Ma, Z.H.; Kong, X.L. Numerical and experimental research on the integrated energy recovery and pressure boost device for seawater reverse osmosis desalination system. Desalination 2022, 523, 115408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, F.L.; Nie, S.L.; Ji, H.; Lou, F.L. Numerical study of structure parameters on energy transfer and flow characteristics of integrated energy recovery and pressure boost device. Desalin. Water Treat. 2018, 131, 141–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.F.; Liu, Y.S.; Han, M.X.; Wu, D.F.; Li, D.L. Improving the performance of an AUV hovering system by introducing low-cost flow rate control into water hydraulic variable ballast system. Ocean Eng. 2016, 125, 155–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.S.; Li, D.L.; Tang, Z.Y.; Deng, Y.P.; Wu, D.F. Thermodynamic modeling, simulation and experiments of a water hydraulic piston pump in water hydraulic variable ballast system. Ocean Eng. 2017, 138, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.S.; Jiang, Z.; Wang, D.; Li, X.H. Experimental research on the water mist fire suppression performance in an enclosed space by changing the characteristics of nozzles. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 2014, 52, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.H.; Lyu, F.; Xu, B.; Huang, W.D.; Wu, W.; Guo, Z.M.; Xu, H.G.; Huang, X.C. Simulation and experimental investigation on low wear rate surface contour of piston/cylinder pair in an axial piston pump. Tribol. Int. 2021, 162, 107127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.B.; Wang, J.Z.; Yan, F.Y. Friction and Wear Behaviors of Several Polymers Sliding Against GCr15 and 316 Steel Under the Lubrication of Sea Water. Tribol. Lett. 2011, 42, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, F.L.; Kong, X.L.; Ji, H.; Nie, S.L.; Lu, W. Research on the pressure and flow characteristics of seawater axial piston pump considering cavitation for reverse osmosis desalination system. Desalination 2022, 540, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.S.; Cheng, Q.; Wang, Z.Y.; Pang, H.; Deng, Y.P.; Zhou, X.P.; Luo, X.H.; Cui, Y.; Wu, D.F. Seawater hydraulics: From the sea surface to depths of 11000 meters. Sci. China-Technol. Sci. 2022, 65, 2178–2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.P.; Guo, G.F.; Zhao, F.Y.; Wang, T.M.; Jim, B.; Wetzel, B.; Zhang, G.; Wang, Q.H. Tribological behaviors of epoxy composites under water lubrication conditions. Tribol. Int. 2016, 95, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, F.L.; Ji, H.; Nie, S.L. Tribological behavior of various ceramic materials sliding against CF/PTFE/graphite-filled PEEK under seawater lubrication. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part J-J. Eng. Tribol. 2019, 233, 1729–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brookes, C.A.; Fagan, M.J.; James, R.D.; Connachie, J.M. The Selection and Performance of Ceramic Components in a Sea-water Pump. In Proceedings of the JFPS International Symposium on Fluid Power, Yokohama, Japan, 12 November 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, M.; Kato, K.; Adachi, K. Friction and wear of self-mated SiC and Si3N4 sliding in water. Wear 2001, 250, 246–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.B.; Huang, C.Z.; Yuan, J.T.; Zou, B.; Liu, H.L.; Zhu, H.T. Cutting performance and life prediction of an Al2O3/TiC micro nano-composite ceramic tool when machining austenitic stainless steel. Ceram. Int. 2015, 41, 7059–7065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.H.; Tao, W.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, L.; Gu, J.W.; Jiang, Z.H. Continuous carbon fiber/crosslinkable poly(ether ether ketone) laminated composites with outstanding mechanical properties, robust solvent resistance and excellent thermal stability. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2018, 165, 148–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, Y.G.; Lee, J.A.; Kang, K.T. Prediction of Wear on Tibial Inserts Made of UHMWPE, PEEK, and CFR-PEEK in Total Knee Arthroplasty Using Finite-Element Analysis. Lubricants 2019, 7, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, M.X.; Tian, X.Y.; Peng, G.; Li, D.C.; Zhang, X.Y. High temperature rheological behavior and sintering kinetics of CF/PEEK composites during selective laser sintering. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2018, 165, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, D.; Negi, Y.S.; Sen Uppadhyaya, J.; Kumar, V. Synthesis and Modification of Poly(ether ether ketone) and their Properties: A Review. Polym. Rev. 2012, 52, 189–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.B.; Wang, J.Z.; Yan, F.Y. Comparative investigation on the tribological behaviors of CF/PEEK composites under sea water lubrication. Tribol. Int. 2012, 52, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Liu, Y.; Deng, Y.; Fang, M.; Wu, D. The Effect of Different Temperature on Friction and Wear Properties of CFRPEEK against AISI 431 Steel under Water Lubrication. Tribol. Trans. 2018, 61, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davim, J.P.; Cardoso, R. Thermo-mechanical model to predict the tribological behaviour of the composite PEEK-CF30/steel pair in dry sliding using multiple regression analysis. Ind. Lubr. Tribol. 2005, 57, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davim, J.P.; Cardoso, R. Tribological behaviour of the composite PEEK-CF30 at dry sliding against steel using statistical techniques. Mater. Des. 2006, 27, 338–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davim, J.P.; Cardoso, R. Effect of the reinforcement (carbon or glass fibres) on friction and wear behaviour of the PEEK against steel surface at long dry sliding. Wear 2009, 266, 795–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Qi, H.; Zhang, G.; Zhao, F.; Wang, T.; Wang, Q. Significant friction and wear reduction by assembling two individual PEEK composites with specific functionalities. Mater. Des. 2017, 116, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Wang, J.Z.; Jiang, P.F.; Yan, F.Y. Hydrostatic pressure-dependent wear behavior of thermoplastic polymers in deep sea. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2018, 29, 2410–2415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Guan, Z.; Cheng, Q.; Wei, G.; Tang, M.; Liu, Y. Development of a Friction Test Apparatus for Simulating the Ultra-High Pressure Environment of the Deep Ocean. Wear 2020, 452–453, 203294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Z.; Wu, D.; Cheng, Q.; Wang, Z.; Tang, M.; Liu, Y. Friction and Wear characteristics of CF/PEEK against 431 stainless steel under high hydrostatic pressure water lubrication. Mater. Des. 2020, 196, 109057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelosi, M.; Ivantysynova, M. A Geometric Multigrid Solver for the Piston-Cylinder Interface of Axial Piston Machines. Tribol. Trans. 2012, 55, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.N.; Gao, D.R.; Zhao, J.H. Tribological Properties of Friction Pair between 316L Stainless Steel and CF/PEEK with Nonsmooth Surface under Seawater Lubrication. Tribol. Trans. 2020, 63, 658–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ensinger. Available online: https://www.ensingerplastics.com/en/shapes/products/peek-tecapeek-cf30-black (accessed on 3 February 2023).
- Chao, Q.; Zhang, J.H.; Xu, B.; Wang, Q.N.; Lyu, F.; Li, K. Integrated slipper retainer mechanism to eliminate slipper wear in high-speed axial piston pumps. Front. Mech. Eng. 2022, 17, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.M.; Chen, J.; Li, J.; Li, Q.L.; Ren, C.Y. Wear analysis of swash plate/slipper pair of axis piston hydraulic pump. Tribol. Int. 2015, 90, 467–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.H.; Nie, S.L.; Yuan, S.H.; Liao, W.J. Comparative Evaluation of Tribological Characteristics of CF/PEEK and CF/PTFE/Graphite Filled PEEK Sliding against AISI630 Steel for Seawater Hydraulic Piston Pumps/Motors. Tribol. Trans. 2015, 58, 1096–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.Q.; Gao, D.R. Friction and wear properties of stainless steel sliding against polyetheretherketone and carbon-fiber-reinforced polyetheretherketone under natural seawater lubrication. Mater. Des. 2014, 53, 881–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mimaroglu, A.; Unal, H.; Ozel, A. Tribological Performance of Polyetheretherketone and its Composites under Water Environment. Macromol. Symp. 2013, 327, 108–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Q.G.; Chen, J.S.; Andrea, V. Tribological Behaviors of Carbon Fiber-Reinforced PEEK Sliding on Ion-Nitrided 2Cr13 Steel Lubricated with Tap Water. Tribol. Trans. 2015, 58, 691–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, S.L.; He, H.; Ji, H.; Nie, S.; Yan, X.P.; Yin, F.L. Failure analysis of auxiliary support bearing/shaft tribopair in seawater hydraulic axial piston pump. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2023, 146, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Fu, Q.; Wood, R.J.; Wu, J.; Wang, S. Influence of bionic non-smooth surface texture on tribological characteristics of carbon-fiber-reinforced polyetheretherketone under seawater lubrication. Tribol. Int. 2020, 144, 106100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newcomb, B.A. Processing, structure, and properties of carbon fibers. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2016, 91, 262–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).