Extensive Stability Assessment of TiO2/Polyvinyl Ether Nanolubricant with Physical Homogenization
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Material Properties and Preparation
2.2. Material Properties and Preparation
2.2.1. High-Speed Homogenizer
2.2.2. Ultrasonication Bath Homogenization
2.3. Stability Evaluation of Nanolubricant
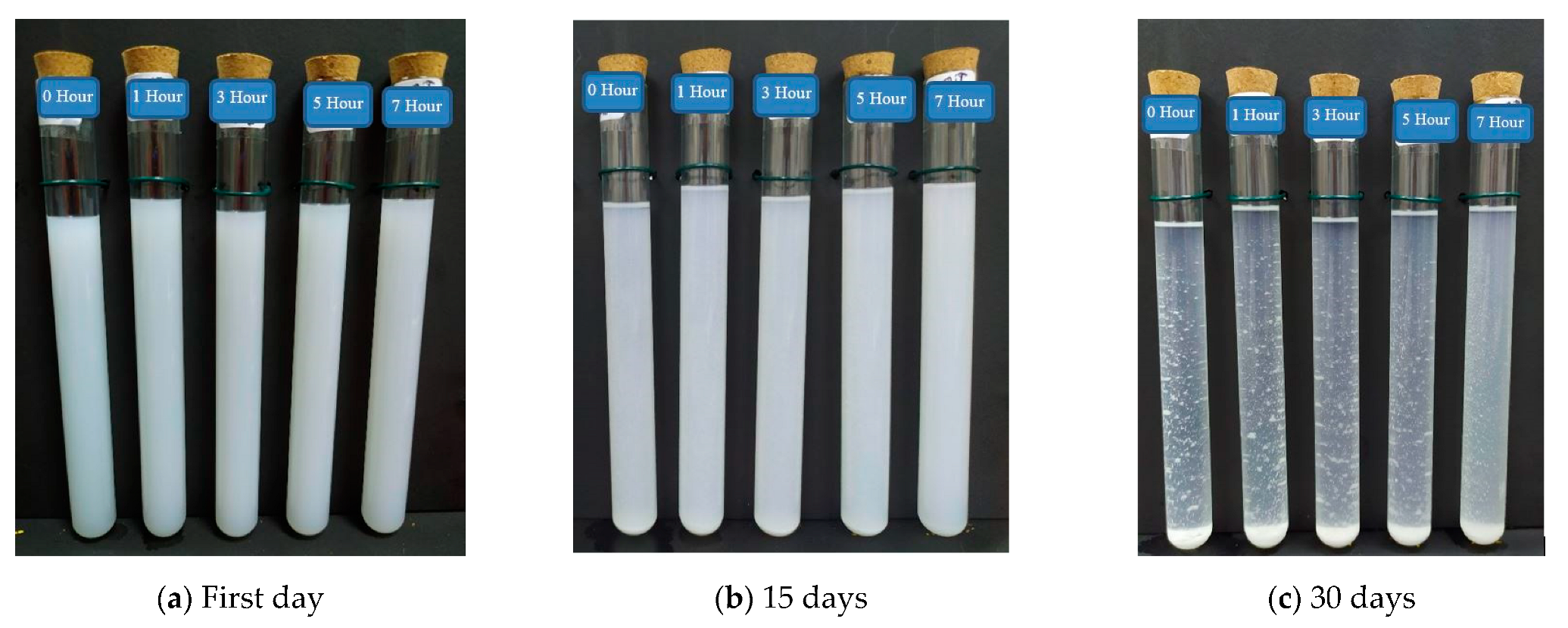
2.3.1. Photo Capturing
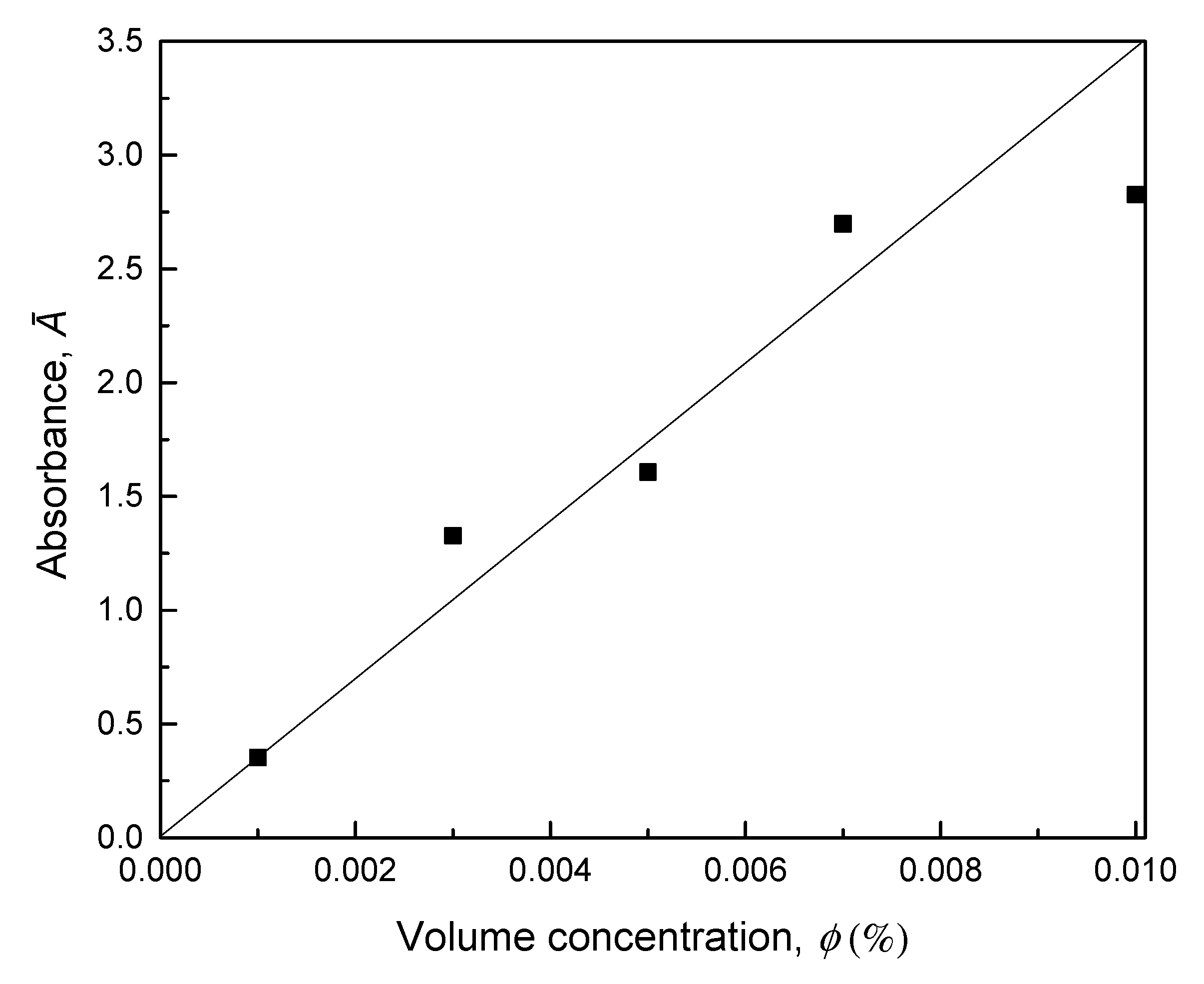
2.3.2. UV-Vis Spectrophotometer
2.3.3. Zeta Potential and Zeta Sizer
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Photo Capturing Observation
3.2. UV-Vis Spectrophotometer Evaluation
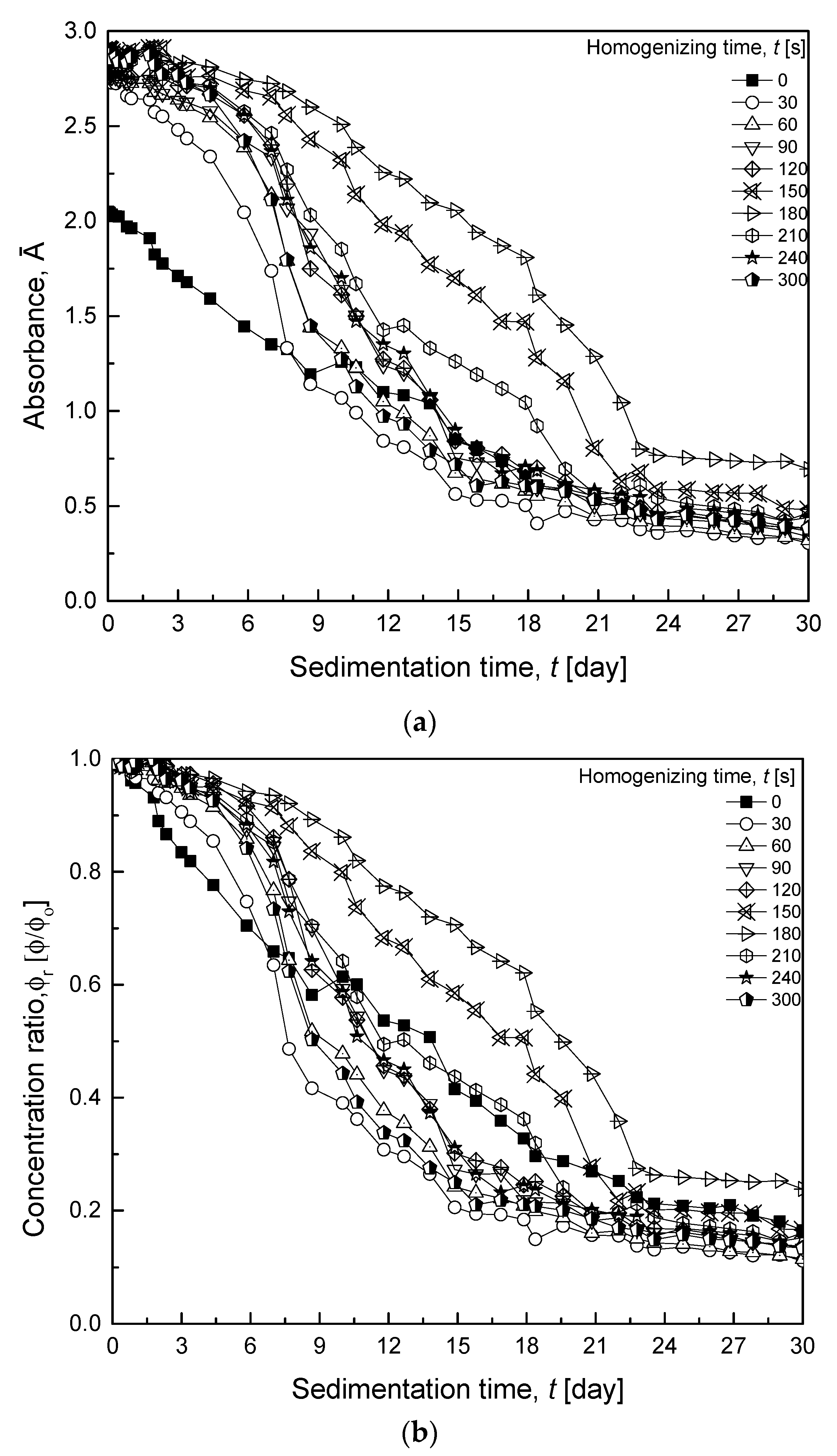
3.2.1. Various HSH Times
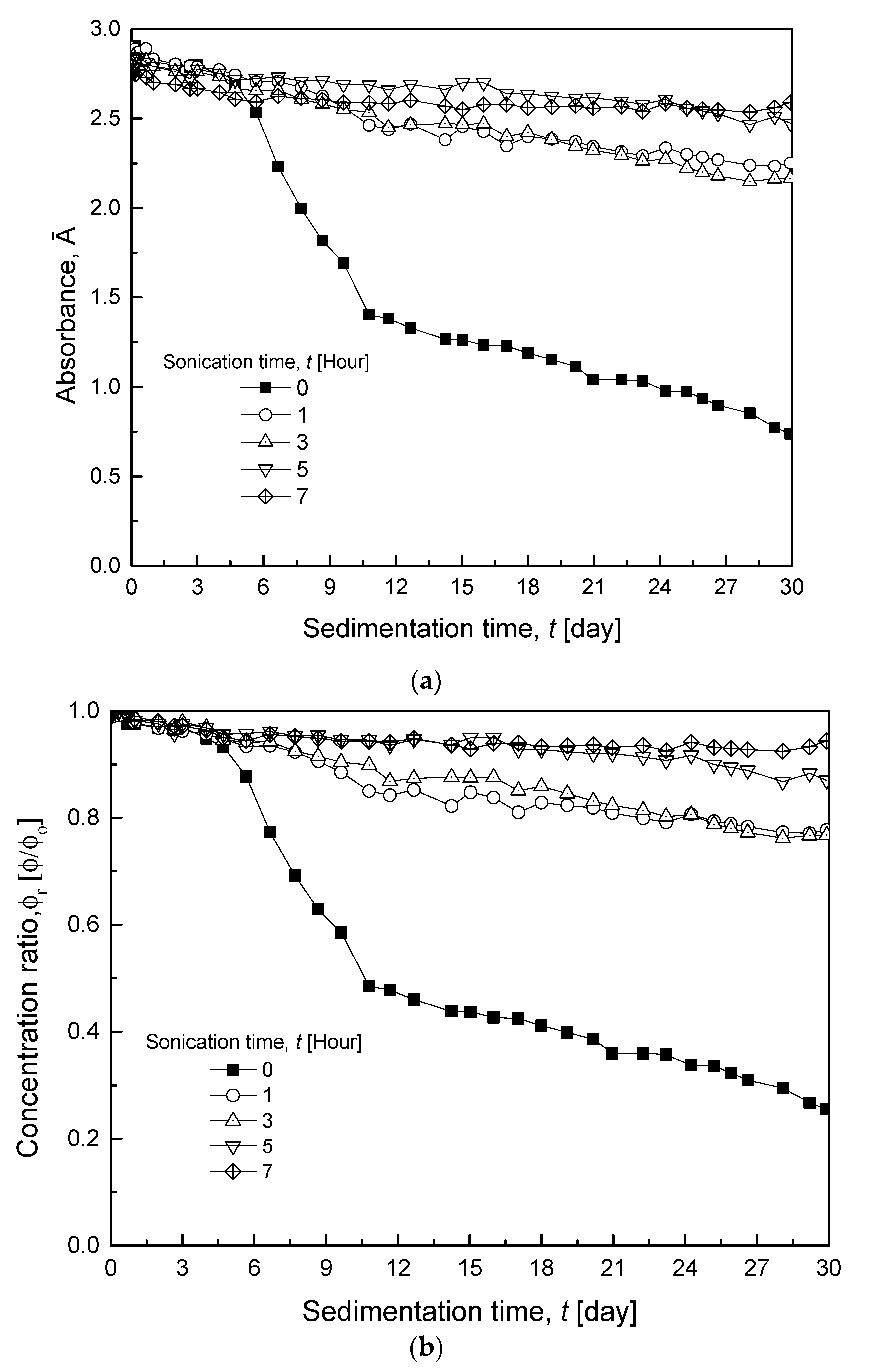
3.2.2. Various Sonication Times
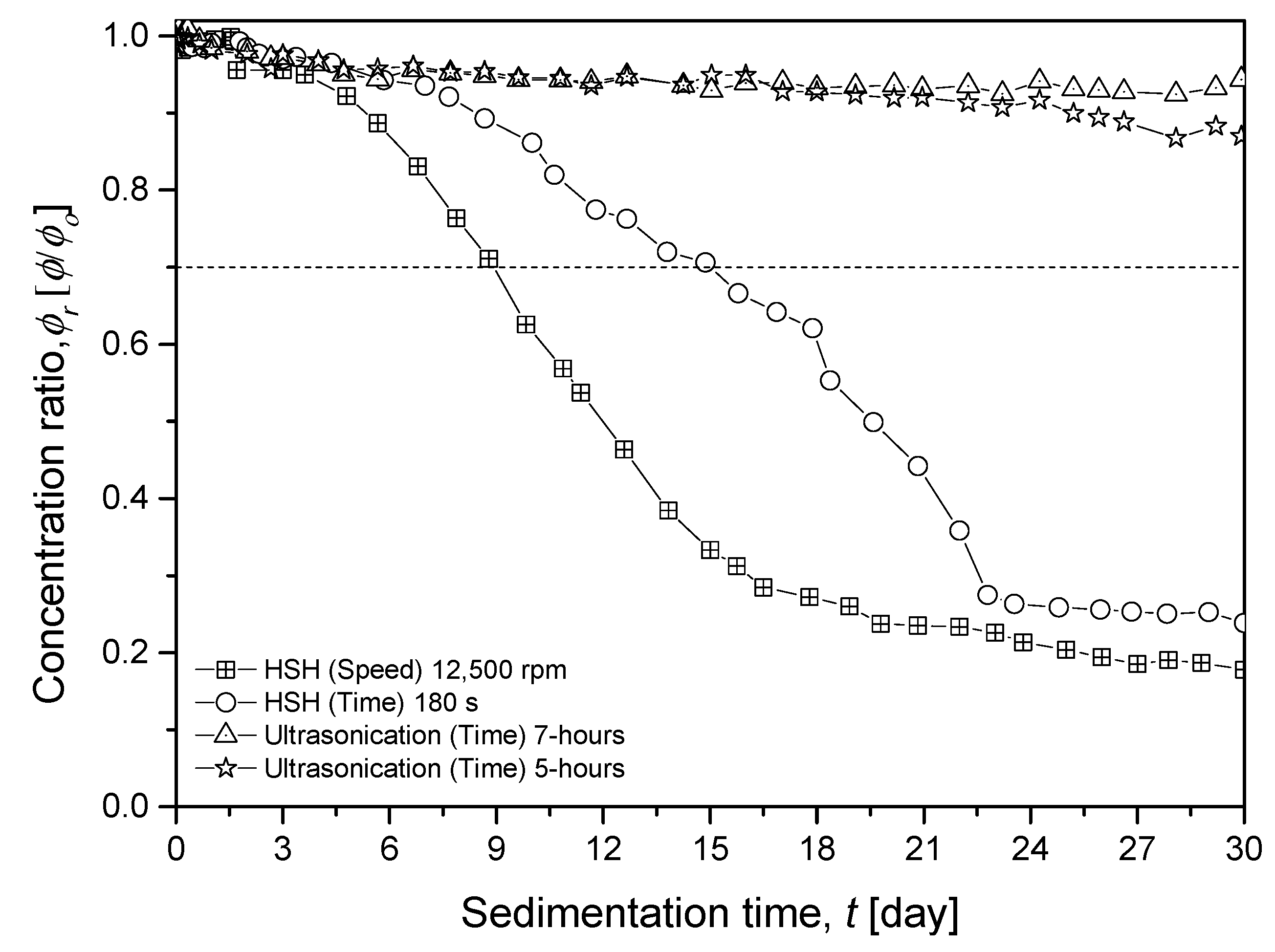
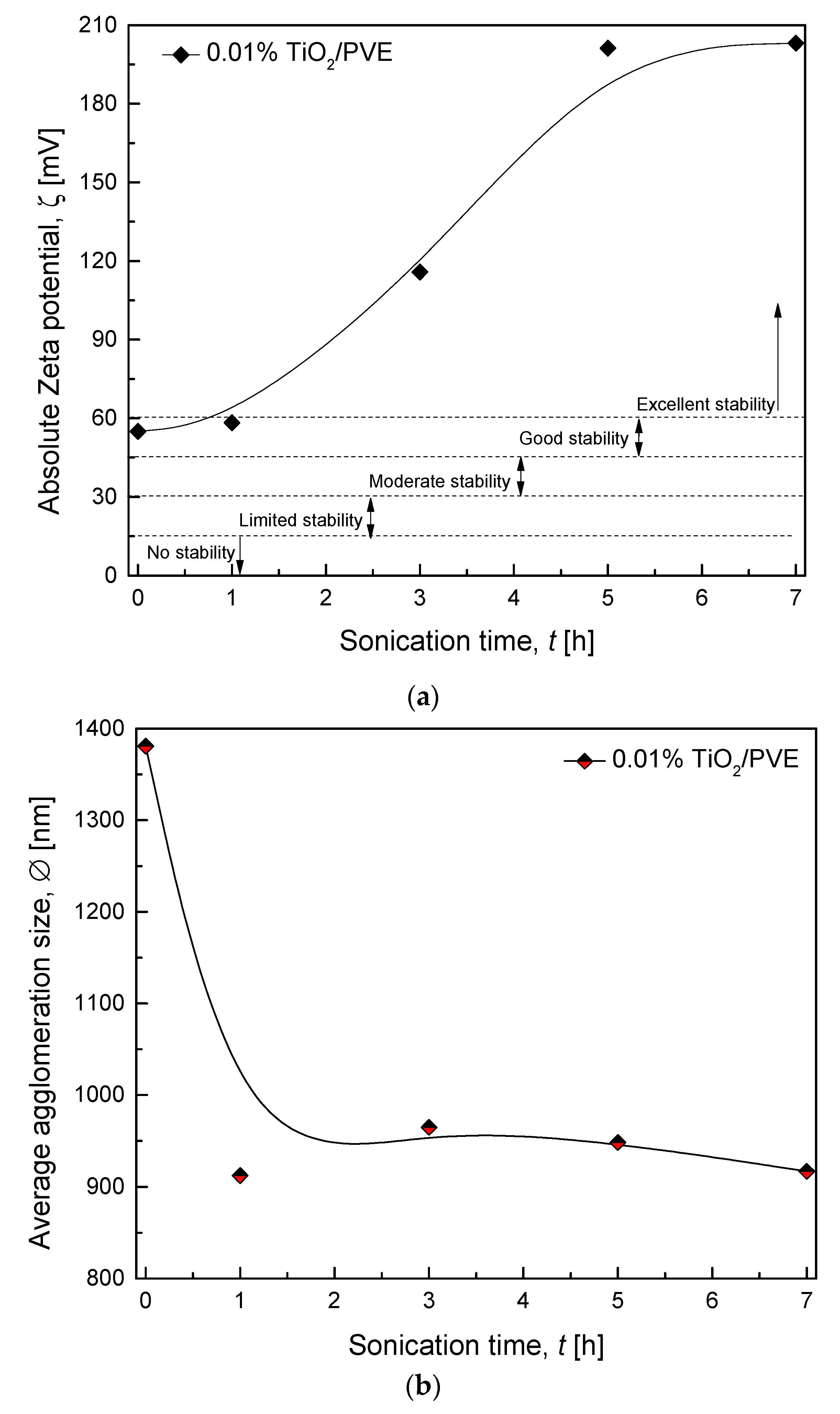
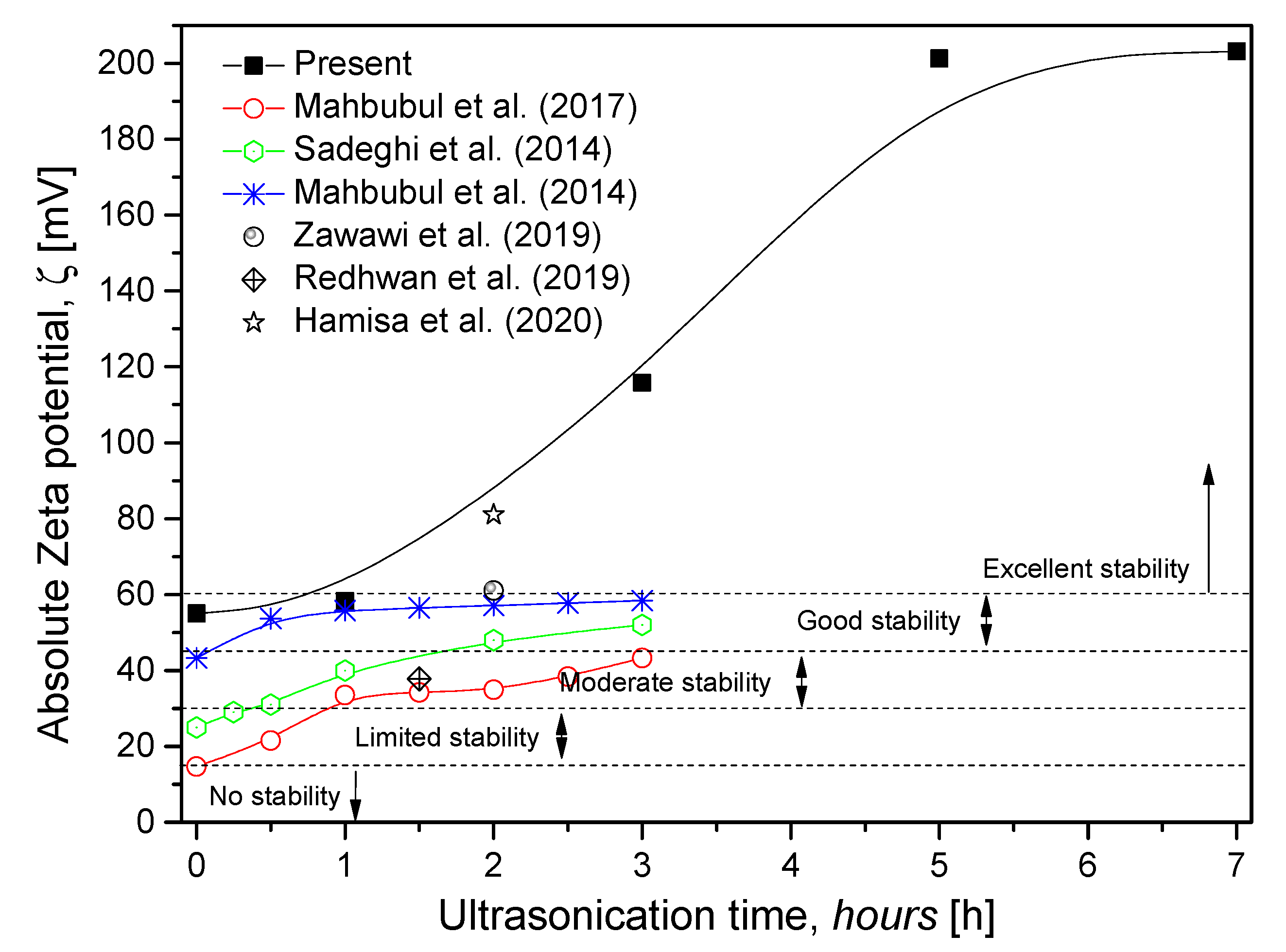
3.3. Zeta Potential and Zeta Sizer Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ahmed, M.S.; Elsaid, A.M. Effect of hybrid and single nanofluids on the performance characteristics of chilled water air conditioning system. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2019, 163, 114398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masuda, H.; Ebata, A.; Teramae, K.; Hishinuma, N. Alteration of thermal conductivity and viscosity of liquid by dispersing ultra-fine particles. Dispersion of Al2O3, SiO2 and TiO2 ultra-fine particles. Netsu Bussei 1993, 7, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.U.S.; Eastman, J.A. Enhancing thermal conductivity of fluids with nanoparticles. In Proceedings of the ASME International Mechanical Engineering Congress & Exposition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 1 October 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.; Jiang, W.; Ji, W.; Mahian, O.; Bazri, S.; Sadri, R.; Badruddin, I.A.; Wongwises, S. A review of heating/cooling processes using nanomaterials suspended in refrigerants and lubricants. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2020, 153, 119611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, E.J.; Lee, J.; Jung, D.; Shim, S.E. Dispersion Stability of Fluorinated Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes in FC-27 Refrigerant. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2011, 32, 1485–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alawi, O.A.; Sidik, N.A.C.; Mohammed, H.A. A comprehensive review of fundamentals, preparation and applications of nanorefrigerants. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2014, 54, 81–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, T.A.; Moreira, D.C.; Ribatski, G. Nanofluids for heat transfer applications: A review. J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 2018, 40, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghavalu, K.V.; Rasu, N.G. Review on Applications of NanoFluids used in Vapour Compression Refrigeration System for Cop Enhancement. In Proceedings of the IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2018; p. 012112. [Google Scholar]
- Ismail, M.F.; Wan Hamzah, W.A. Performance Investigation of R32 and R410a Refrigerants with Different Compressor Lubricants. In Proceedings of the 2nd Energy Security and Chemical Engineering Congress, Singapore, 3–5 November 2021; pp. 259–269. [Google Scholar]
- Bi, S.; Guo, K.; Liu, Z.; Wu, J. Performance of a domestic refrigerator using TiO2-R600a nano-refrigerant as working fluid. Energy Convers. Manag. 2011, 52, 733–737. [Google Scholar]
- Fuskele, V.; Sarviya, R.M. Recent developments in Nanoparticles Synthesis, Preparation and Stability of Nanofluids. Mater. Today Proc. 2017, 4, 4049–4060. [Google Scholar]
- Sezer, N.; Atieh, M.A.; Koc, M. A comprehensive review on synthesis, stability, thermophysical properties, and characterization of nanofluids. Powder Technol. 2019, 344, 404–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verwey, E.J.W. Theory of the Stability of Lyophobic Colloids. J. Phys. Colloid Chem. 1947, 51, 631–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Zhu, H.; Wang, L.; Liu, L. Critical issues in nanofluids preparation, characterization and thermal conductivity. Curr. Nanosci. 2009, 5, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.I.; Valan Arasu, A. A review of influence of nanoparticle synthesis and geometrical parameters on thermophysical properties and stability of nanofluids. Therm. Sci. Eng. Prog. 2019, 11, 334–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che Sidik, N.A.; Mahmud Jamil, M.; Aziz Japar, W.M.A.; Muhammad Adamu, I. A review on preparation methods, stability and applications of hybrid nanofluids. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 80, 1112–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heris, S.Z.; Razbani, M.A.; Estelle, P.; Mahian, O. Rheological Behavior of Zinc-Oxide Nanolubricants. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2015, 36, 1073–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghadimi, A.; Saidur, R.; Metselaar, H.S.C. A review of nanofluid stability properties and characterization in stationary conditions. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2011, 54, 4051–4068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, M.; Dadvar, M.; Dabir, B. Application of response surface methodology for optimization of the stability of asphaltene particles in crude oil by TiO2/SiO2 nanofluids under static and dynamic conditions. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2018, 39, 431–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharif, M.Z.; Azmi, W.H.; Redhwan, A.A.M.; Mamat, R. Investigation of thermal conductivity and viscosity of Al2O3/PAG nanolubricant for application in automotive air conditioning system. Int. J. Refrig. 2016, 70, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redhwan, A.A.M.; Azmi, W.H.; Sharif, M.Z.; Mamat, R.; Zawawi, N.N.M. Comparative study of thermo-physical properties of SiO2 and Al2O3 nanoparticles dispersed in PAG lubricant. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2017, 116, 823–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zawawi, N.N.M.; Azmi, W.H.; Sharif, M.Z.; Najafi, G. Experimental investigation on stability and thermo-physical properties of Al2O3-SiO2/PAG nanolubricants with different nanoparticle ratios. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2019, 135, 1243–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, J.; Singh, J.; Ohunakin, O.S.; Adelekan, D.S. Energy analysis of a domestic refrigerator system with ANN using LPG/TiO2–lubricant as replacement for R134a. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2018, 135, 475–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanka, S.; Alexandrova, E.; Kozhukhova, M.; Hasan, M.S.; Nosonovsky, M.; Sobolev, K. Tribological and wetting properties of TiO2 based hydrophobic coatings for ceramics. J. Tribol. 2019, 141, 101301. [Google Scholar]
- Borras, A.; Lopez, C.; Rico, V.; Gracia, F.; Gonzalez-Elipe, A.R.; Richter, E.; Battiston, G.; Gerbasi, R.; McSporran, N.; Sauthier, G. Effect of visible and UV illumination on the water contact angle of TiO2 thin films with incorporated nitrogen. J. Phys. Chem. C 2007, 111, 1801–1808. [Google Scholar]
- Balajka, J.; Hines, M.A.; DeBenedetti, W.J.; Komora, M.; Pavelec, J.; Schmid, M.; Diebold, U. High-affinity adsorption leads to molecularly ordered interfaces on TiO2 in air and solution. Science 2018, 361, 786–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.Y. How titanium dioxide cleans itself. Science 2018, 361, 753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouikhalfan, M.; Labihi, A.; Belaqziz, M.; Chehouani, H.; Benhamou, B.; Sarı, A.; Belfkira, A. Stability and thermal conductivity enhancement of aqueous nanofluid based on surfactant-modified TiO2. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2020, 41, 374–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idemitsu Kosan, C.L. Material Safety Data Sheet -Daphne Hermetic Oil FVC68D. In Material Safety Data Sheet; Idemitsu: Tokyo, Japan, 2010; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Hongwu International Group Ltd. Anatase Nano TiO2 Titanium Dioxide Powders. Available online: www.hwnanomaterial.com/anatase-nano-tio2-titanium-dioxide-powders_p49.html(accessed on 25 September 2021).
- Zawawi, N.N.M.; Azmi, W.H.; Redhwan, A.A.M.; Sharif, M.Z.; Sharma, K.V. Thermo-physical properties of Al2O3-SiO2/PAG composite nanolubricant for refrigeration system. Int. J. Refrig. 2017, 80, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharif, M.Z.; Azmi, W.H.; Redhwan, A.A.M.; Zawawi, N.N.M. Improvement of nanofluid stability using 4-step UV-vis spectral absorbency analysis. J. Mech. Eng. 2017, 4, 233–247. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, W.; Xie, H. A review on nanofluids: Preparation, stability mechanisms, and applications. J. Nanomater. 2012, 2012, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharif, M.Z.; Azmi, W.H.; Redhwan, A.A.M.; Mamat, R.; Yusof, T.M. Performance analysis of SiO2/PAG nanolubricant in automotive air conditioning system. Int. J. Refrig. 2017, 75, 204–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redhwan, A.A.M.; Azmi, W.H.; Sharif, M.Z.; Mamat, R.; Samykano, M.; Najafi, G. Performance improvement in mobile air conditioning system using Al2O3/PAG nanolubricant. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2019, 135, 1299–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamisa, A.H.; Yusof, T.M.; Azmi, W.H.; Mamat, R.; Sharif, M.Z. The stability of TiO2/POE nanolubricant for automotive air-conditioning system of hybrid electric vehicles. In Proceedings of the IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2020; p. 012050. [Google Scholar]
- Mahbubul, I.M.; Elcioglu, E.B.; Saidur, R.; Amalina, M.A. Optimization of ultrasonication period for better dispersion and stability of TiO2–water nanofluid. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2017, 37, 360–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadeghi, R.; Etemad, S.G.; Keshavarzi, E.; Haghshenasfard, M. Investigation of alumina nanofluid stability by UV–vis spectrum. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 2014, 18, 1023–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahbubul, I.M.; Chong, T.H.; Khaleduzzaman, S.S.; Shahrul, I.M.; Saidur, R.; Long, B.D.; Amalina, M.A. Effect of Ultrasonication Duration on Colloidal Structure and Viscosity of Alumina–Water Nanofluid. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 6677–6684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Property | PVE |
|---|---|
| Density, g/cm3 (@ 15 °C) | 0.9369 |
| Dynamic viscosity, Pa·s @ 40 °C | 62.37 × 10−3 |
| Dynamic viscosity, Pa·s @ 100 °C | 7.53 × 10−3 |
| Viscosity index | 84 |
| Pour point, °C | −37.5 |
| Flashpoint, °C | 204 |
| Total acid number (mg KOH/g) | >0.01 |
| Volumetric resistivity (RT) (Ω·cm) | 6 × 1013 |
| Copper corrosion (100 °C, 1 h) | 1 (1B) |
| Water content (ppm) | >150 |
| Property | TiO2 |
|---|---|
| Molecular mass, g/mol | 79.87 |
| Average particle diameter, nm | 50 |
| Density, kg/m | 4230 |
| Thermal conductivity, W/m·K | 8.4 |
| Specific heat, J/kg·K | 692 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ismail, M.F.; Azmi, W.H.; Mamat, R.; Sharma, K.V.; Ali, H.M. Extensive Stability Assessment of TiO2/Polyvinyl Ether Nanolubricant with Physical Homogenization. Lubricants 2023, 11, 67. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants11020067
Ismail MF, Azmi WH, Mamat R, Sharma KV, Ali HM. Extensive Stability Assessment of TiO2/Polyvinyl Ether Nanolubricant with Physical Homogenization. Lubricants. 2023; 11(2):67. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants11020067
Chicago/Turabian StyleIsmail, Mohd Farid, Wan Hamzah Azmi, Rizalman Mamat, Korada Viswanatha Sharma, and Hafiz Muhammad Ali. 2023. "Extensive Stability Assessment of TiO2/Polyvinyl Ether Nanolubricant with Physical Homogenization" Lubricants 11, no. 2: 67. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants11020067
APA StyleIsmail, M. F., Azmi, W. H., Mamat, R., Sharma, K. V., & Ali, H. M. (2023). Extensive Stability Assessment of TiO2/Polyvinyl Ether Nanolubricant with Physical Homogenization. Lubricants, 11(2), 67. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants11020067






