Evaluation and Application of an Engineering Calculation Method of the Static Performance of an Aerostatic Journal Bearing with Multiple Orifice-Type Restrictors
Abstract
1. Introduction
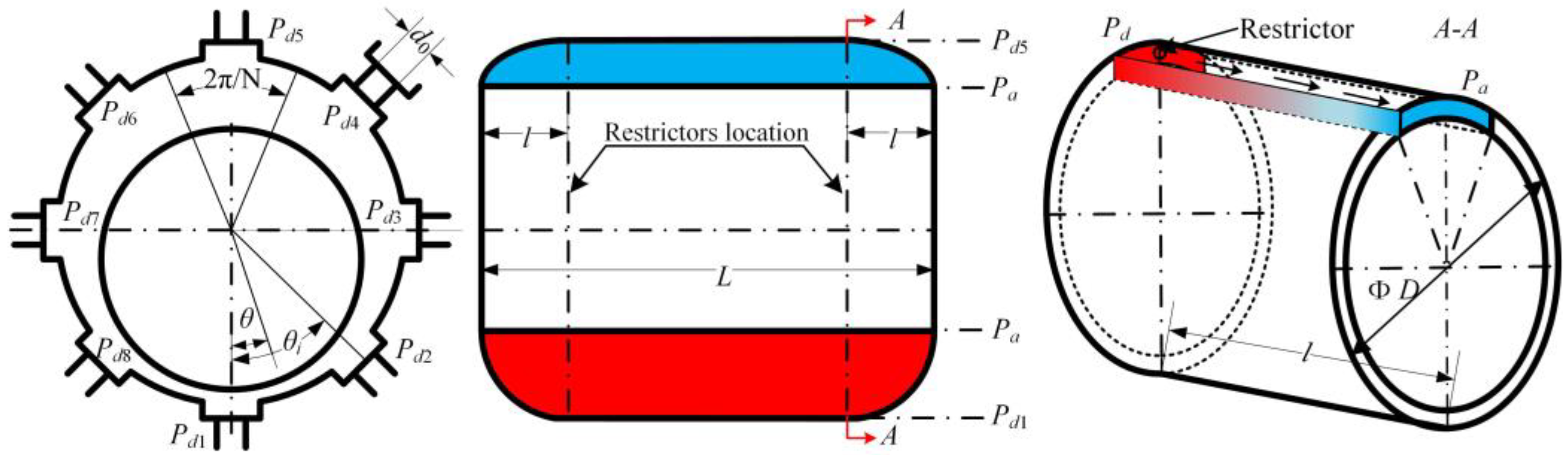
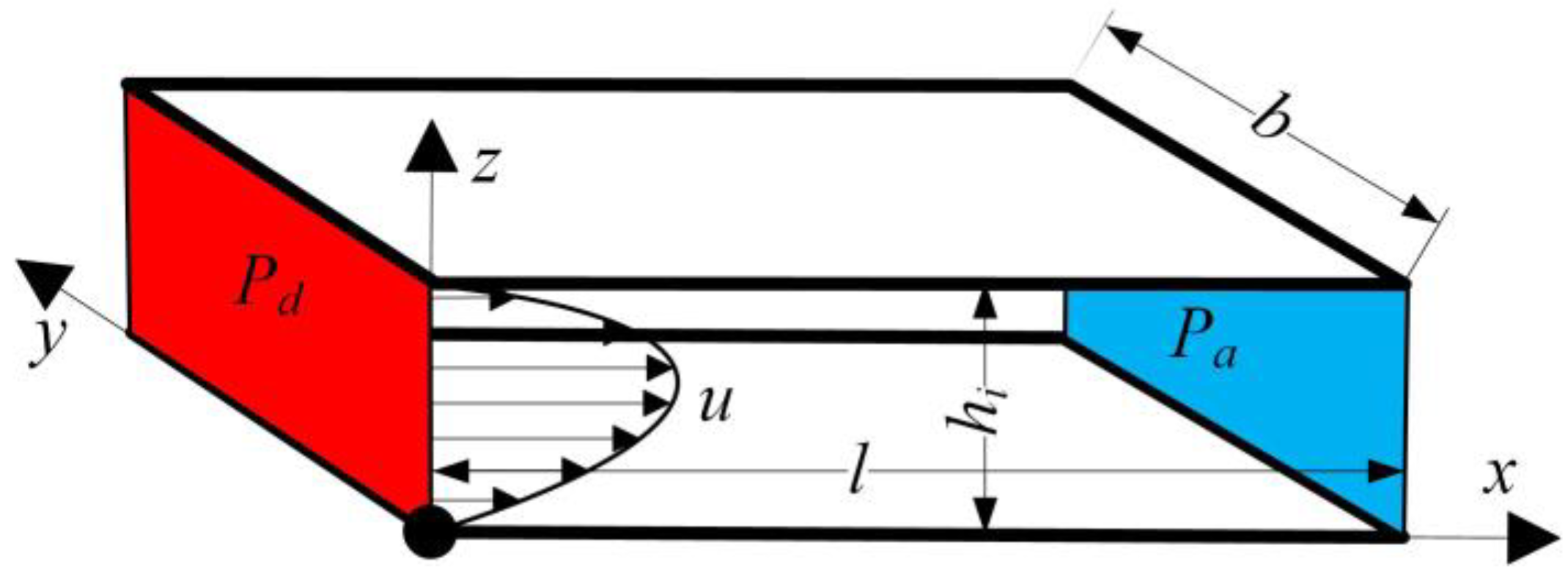
2. Principle of the Simplified Calculation Method
3. Calculation Procedures of the Simplified Calculation Method
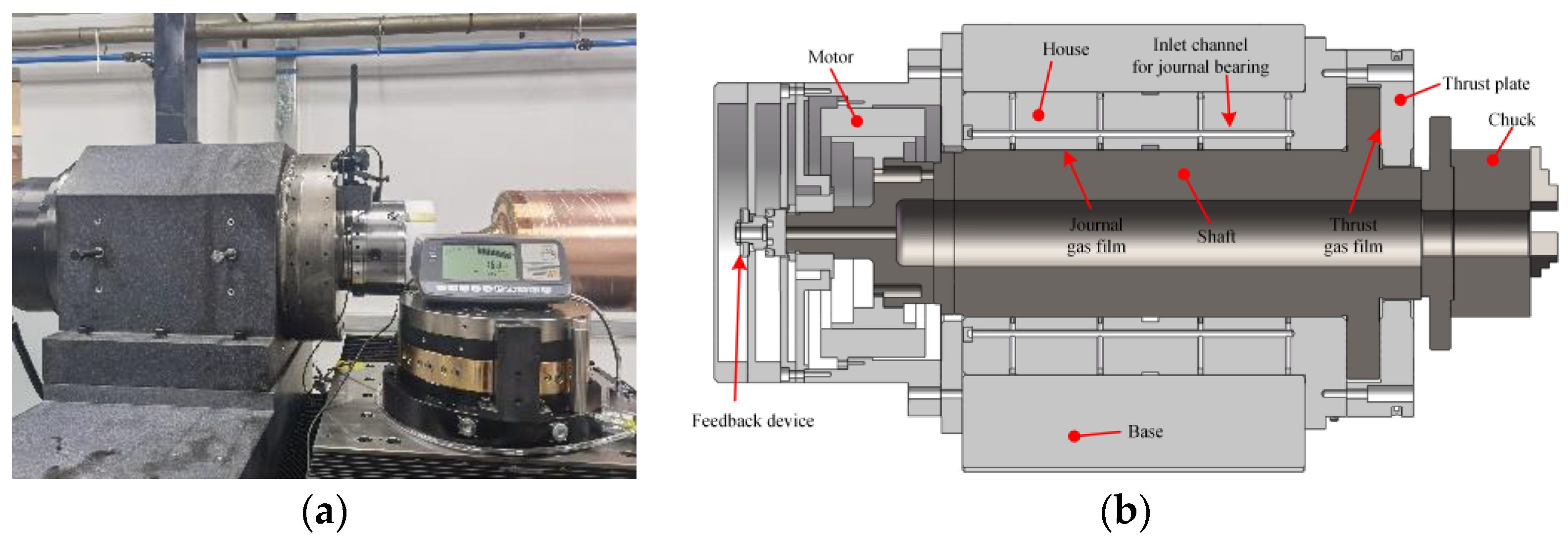
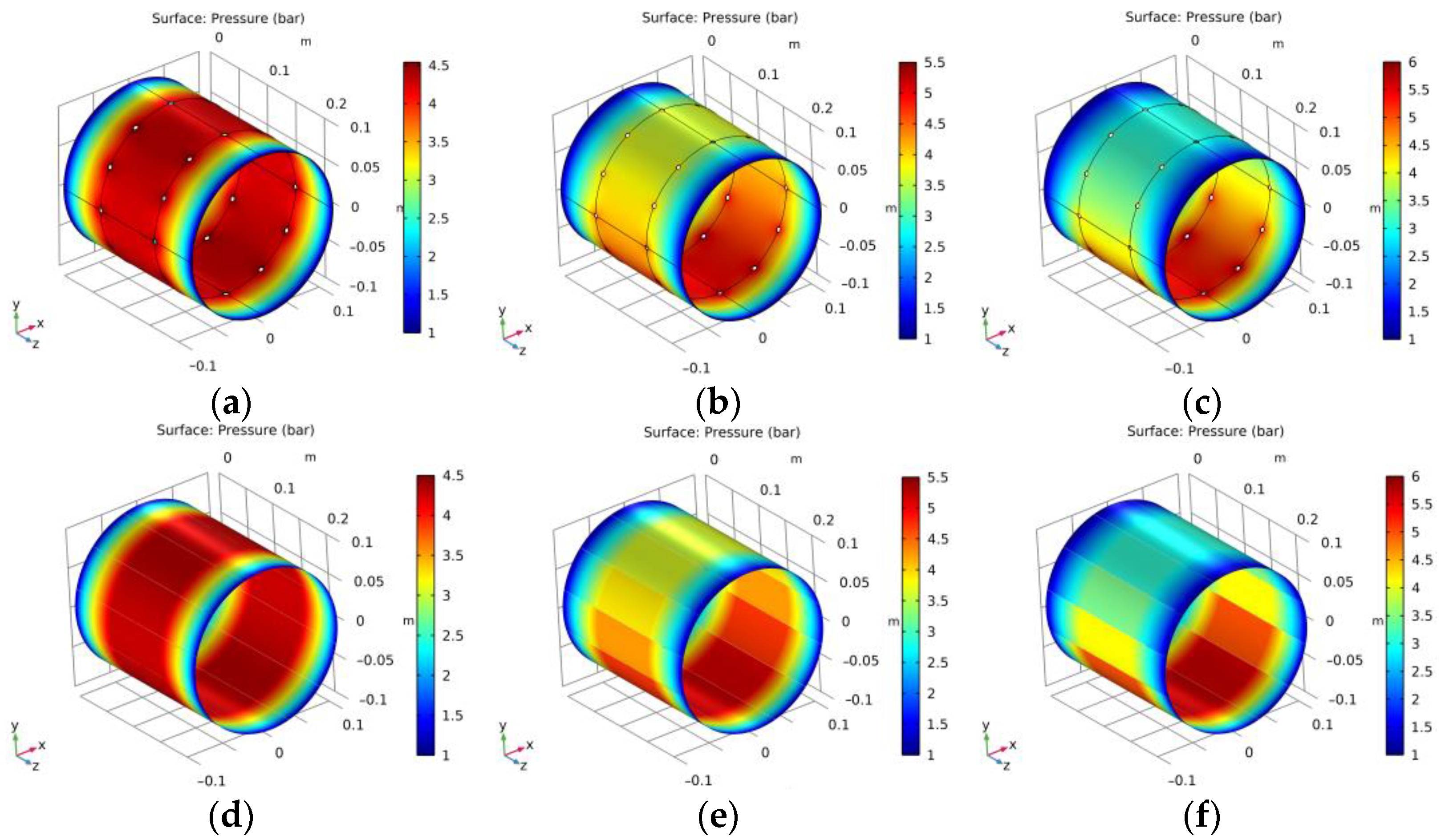
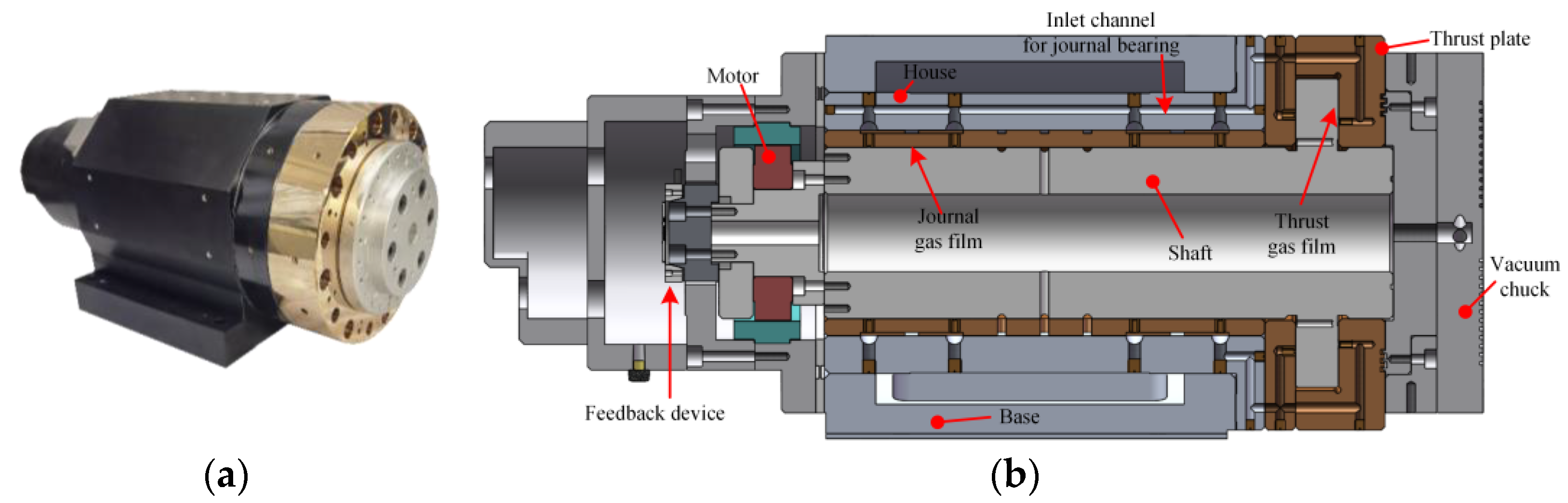
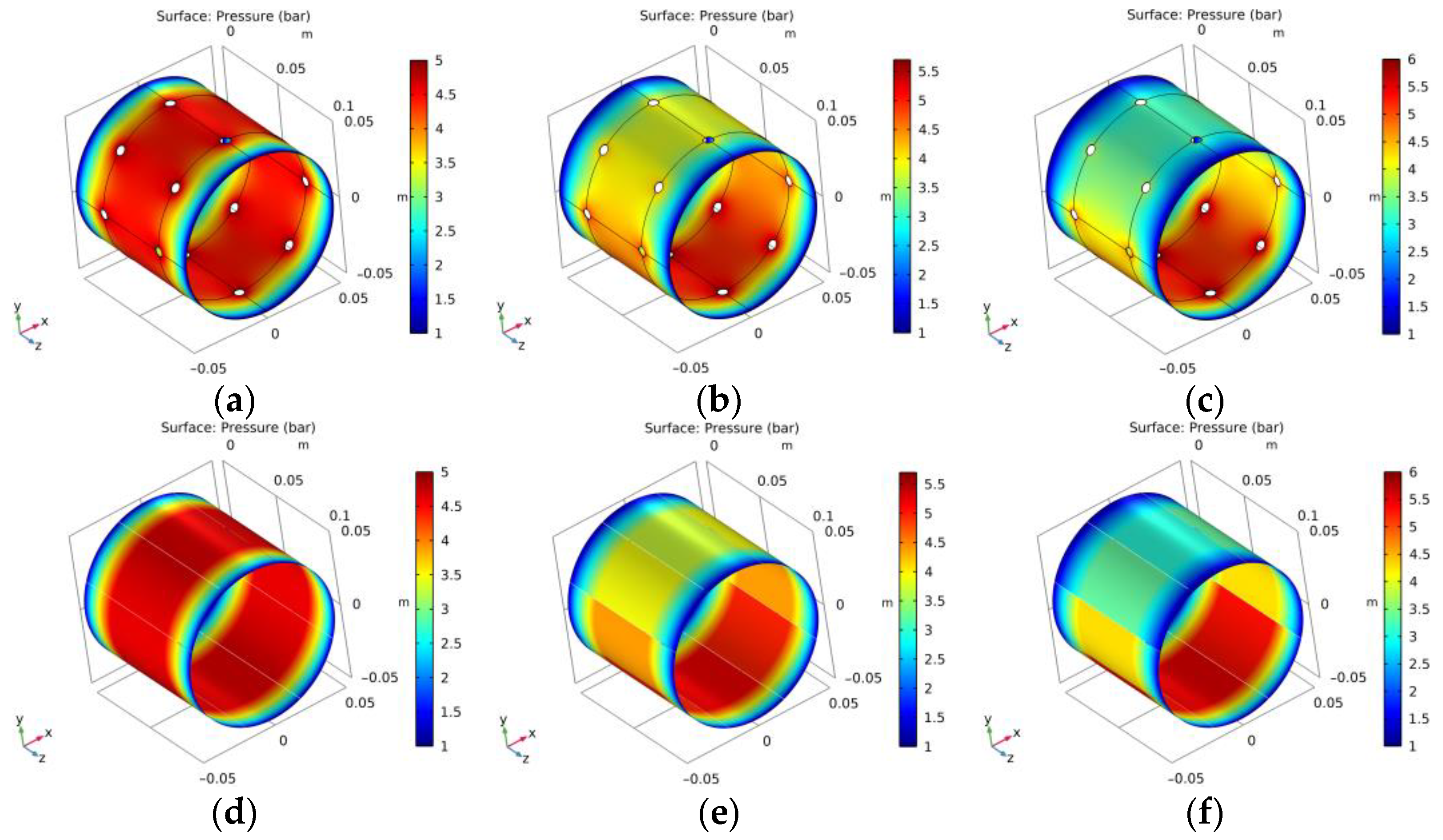
4. Application Case Study
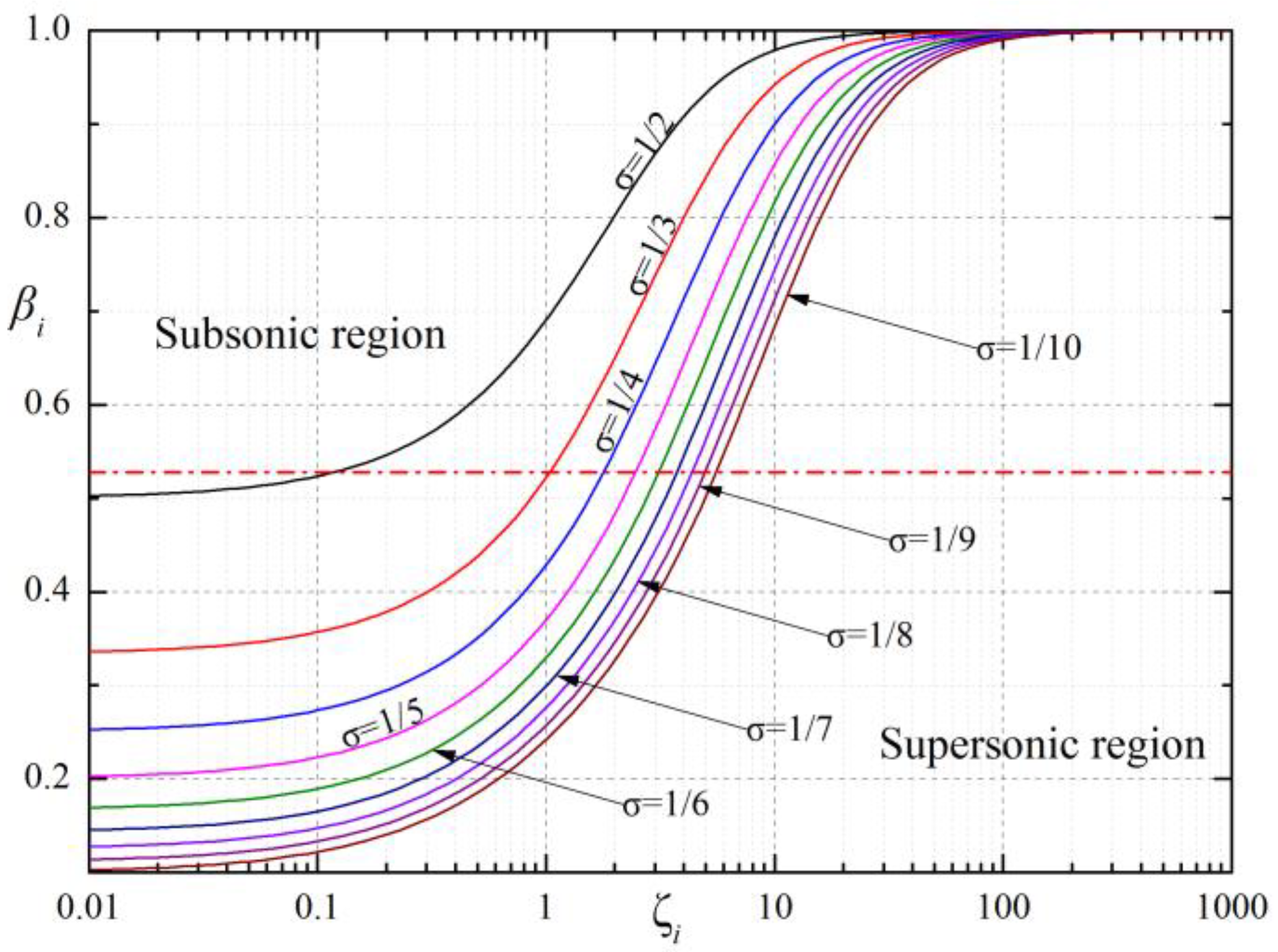
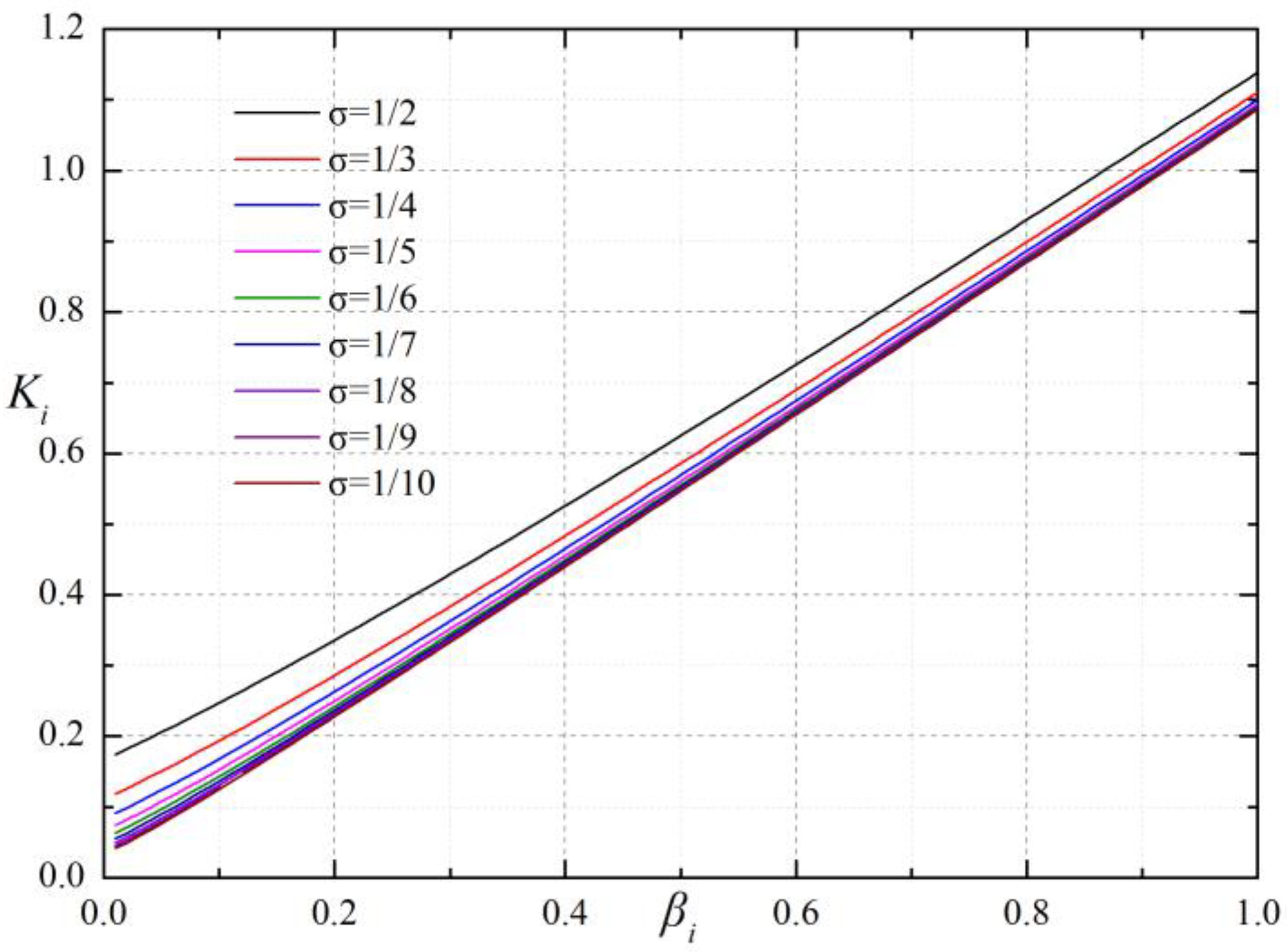
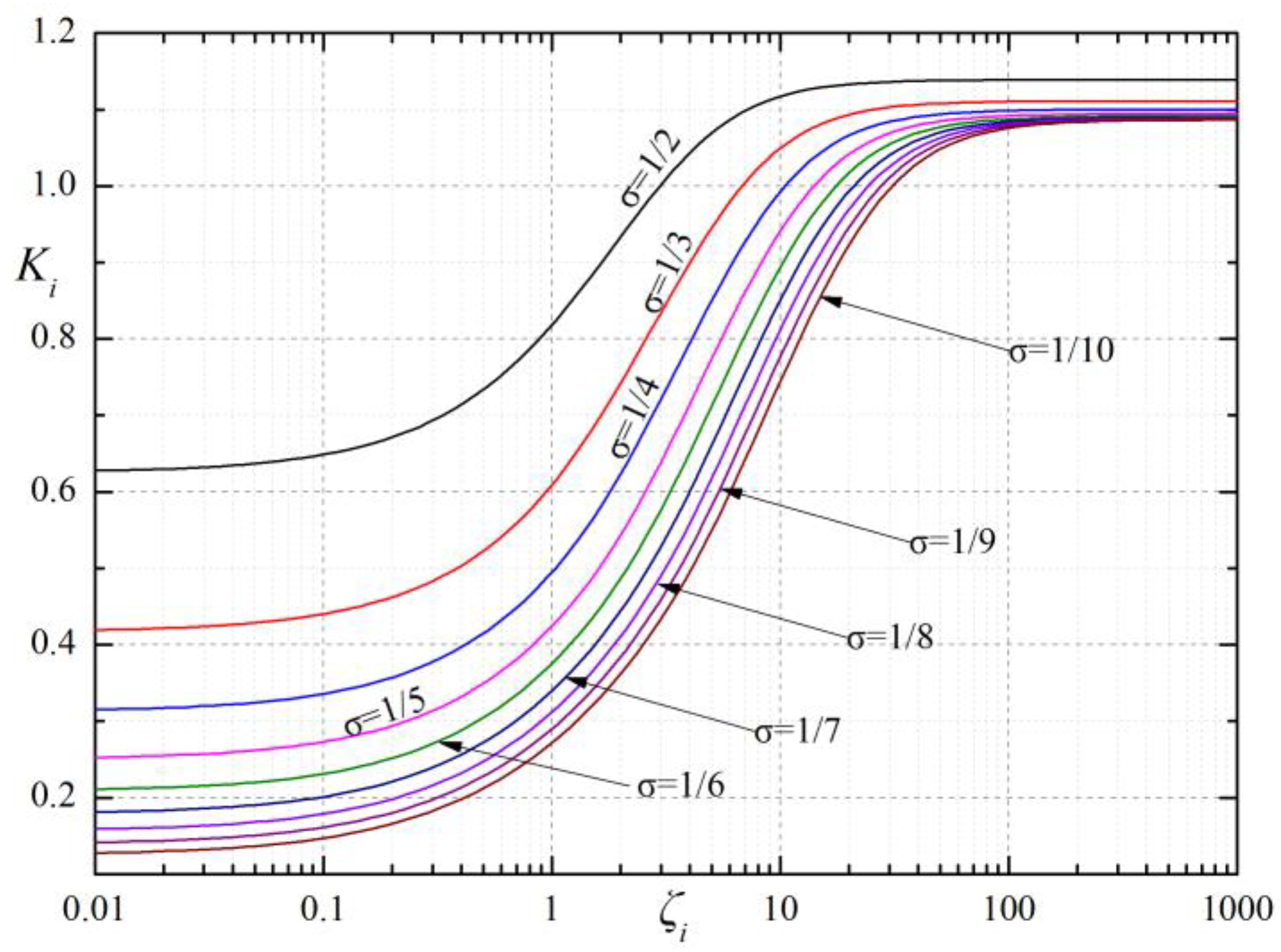
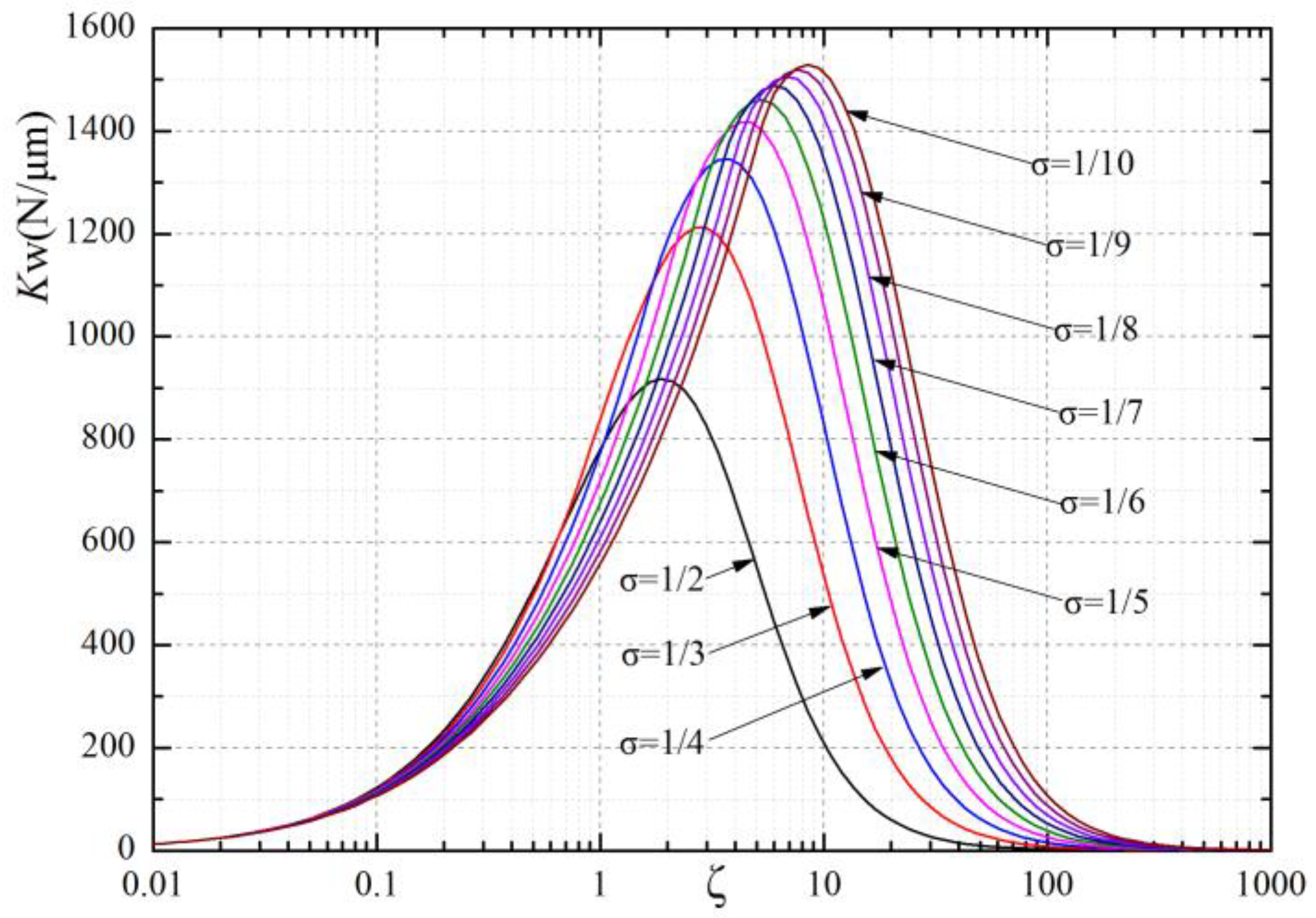
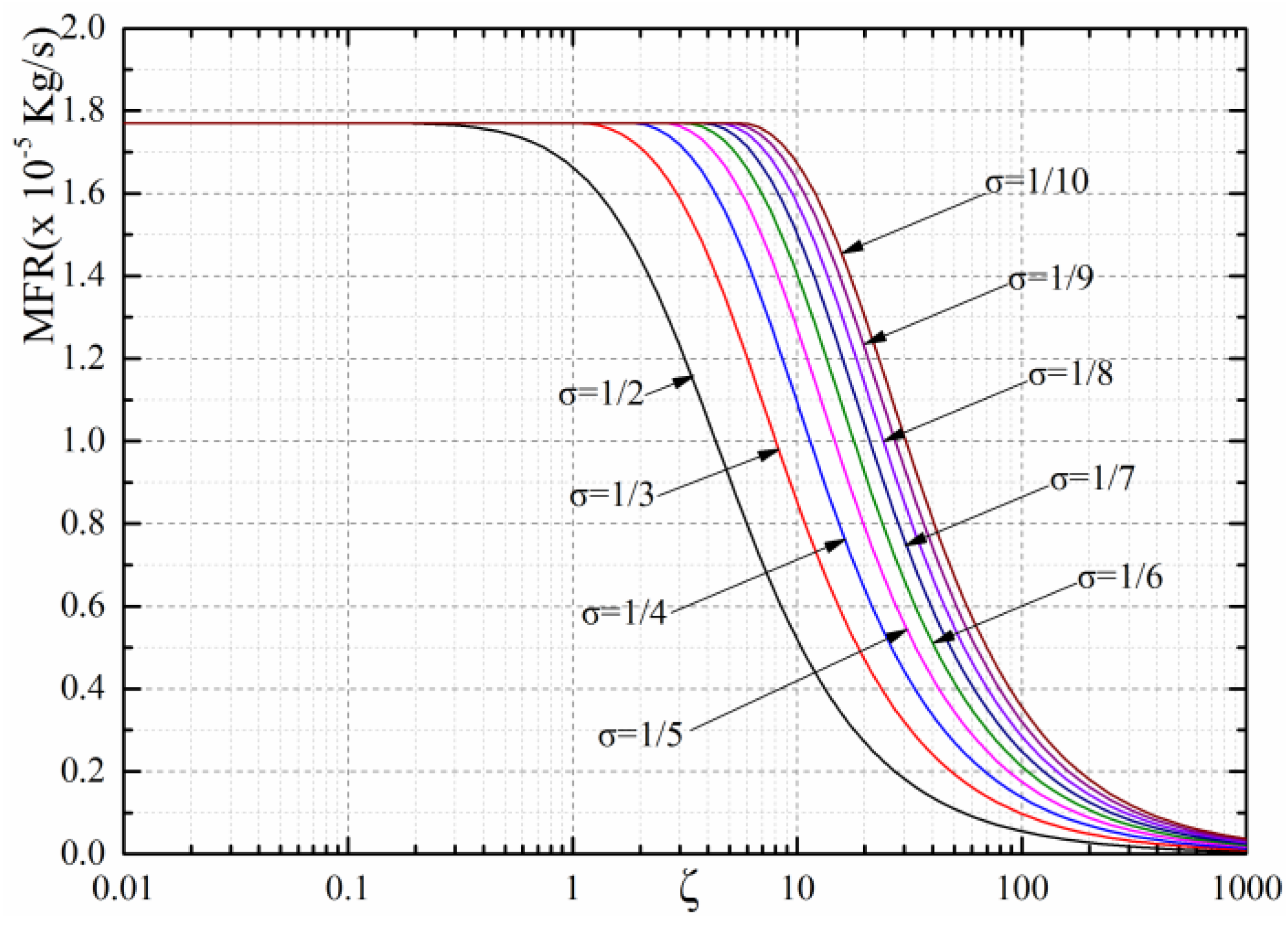
5. Impact of on a Bearing’s Performance
6. Conclusions
- (1)
- is a crucial parameter of the bearing’s performance. It can be assessed by the discharge correction factor , sectional area of the orifice A0, orifice number N, gas film thickness in the ith section hi, kinematic viscosity of air η, atmospheric density ρa, atmospheric pressure Pa, journal bearing diameter D, distance between orifices and gas film edge l, and journal bearing length L.
- (2)
- is the product of f1 (a gas-channel coefficient), f2 (a gas-lubricant coefficient) and f3 (a bearing structural coefficient). A bearing with better performance, such as LCC, stiffness and MFR, could be obtained if is in the range of 1~10.
- (3)
- With increasing, a bearing’s stiffness in each section will reach a maximal value and then decrease. Here, 0.4~0.6 MPa is an appropriate supply pressure range in most cases, as the bearing’s parameters are narrow at extremely high supply pressures to avoid shock waves.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| βi | |
| βα | Critical pressure ratio |
| η | Kinematic viscosity of air |
| ρ | Density of gas in the bearing |
| ρa | Atmospheric density |
| ε | Eccentricity ratio |
| Discharge correction factor | |
| Discharge coefficient | |
| Product of three coefficients | |
| A0 | Sectional area of the orifice |
| b | Width of 1-D gas film |
| CFD | Computational fluid dynamics |
| d0 | Diameter of the orifice |
| D | Journal bearing diameter |
| f1i | Gas channel coefficient |
| f2 | Lubricant physical coefficient |
| f3 | Bearing structural coefficient |
| FEM | Finite element method |
| h0 | Designed gas film thickness |
| hi | Gas film thickness in ith section |
| Δh | Film thickness changing value |
| k | Gas specific heat ratio |
| Kw | Bearing stiffness |
| l | Distance between orifices and gas film edge |
| L | Journal bearing length |
| LCC, W | Load carrying capacity |
| LCCE, Cw | LCC coefficient |
| MFR | Mass flow rate |
| MPOTRs | Multiple pocketed orifice-type restrictors |
| Mass flow rate through the orifice | |
| Bearing mass flow rate | |
| N | Orifice number |
| P | Pressure in the bearing |
| Pa | Atmospheric pressure |
| Pd | Pressure at orifice outlet |
| P0 | Supply pressure |
References
- Shinno, H.; Yoshioka, H.; Taniguchi, K. A Newly Developed Linear Motor-Driven Aerostatic X-Y Planar Motion Table System for Nano-Machining. CIRP Ann. Manuf. Technol. 2007, 56, 369–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Ju, B.; Fang, H.; Chen, Y.; Yu, N.; Wan, Y. Air bearing: Academic insights and trend analysis. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2019, 106, 1191–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Chang, Y.; Chen, P.; Zhuang, H.; Ding, Y.; Lu, H.; Chen, Y. Dynamic modeling of ultra-precision fly cutting machine tool and the effect of ambient vibration on its tool tip response. Int. J. Extrem. Manuf. 2020, 2, 025301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raniachandra, S. A solution of Reynolds equation for a full finite journal bearing. J. Fluids Eng. 1961, 83, 589–593. [Google Scholar]
- Pandian, M.C. A new method for the numerical solution of the Reynolds equation for gas-lubricated slider bearings. J. Eng. Math. 1985, 19, 3–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anaya-Dufresne, M.; Sinclair, G.B. Some Exact Solutions of Reynolds Equation. J. Tribol. 1995, 117, 560–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, J.W. The Design of Aerostatic Bearings; The Machinery Publishing Co., Ltd.: London, UK, 1970; pp. 68–112. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Ding, H. A simplified calculation method on the performance analysis of aerostatic thrust bearing with multiple pocketed orifice-type restrictors. Tribol. Int. 2012, 56, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, I.C.; Gross, W.A. Analysis and Design of Externally Pressurized Gas Bearings. Tribol. Trans. 1962, 5, 261–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jason, R.L. Analytical and Experimental Study of Externally Pressurized Air Lubricated Journal Bearings. J. Basic Eng. 1962, 84, 159–165. [Google Scholar]
- Colombo, F.; Raparelli, T.; Trivella, A.; Viktorov, V. Lumped parameters models of rectangular pneumatic pads: Static analysis. Precis. Eng. 2015, 42, 283–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, H.; Yabe, H. Analysis of Externally Pressurized Circular Thrust Gas-Bearing with Multiple Supply Holes. Tribol. Trans. 1964, 7, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, H.; Yabe, H.; Ohnishi, K. Analysis of Externally Pressurized Rectangular Pads with Multiple Supply Holes. Tribol. Trans. 1966, 9, 391–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddi, M.M. Finite-Element Solution of the Incompressible Lubrication Problem. J. Lubr. Technol. 1969, 91, 524–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddi, M.M.; Chu, T.Y. Finite Element Solution of the Steady-State Compressible Lubrication Problem. J. Lubr. Technol. 1970, 92, 495–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wadhwa, S.; Sinhasan, R.; Singh, D. Analysis of externally pressurized gas bearings by an incremental finite element method. Wear 1981, 69, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, S.H. p-Version Finite Element Analysis of Gas Bearings of Finite Width. J. Tribol. 1991, 113, 417–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, C.-Y.; Wang, C.-C.; Lee, Y.-H. Performance analysis of high-speed spindle aerostatic bearings. Tribol. Int. 2005, 38, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Chang, C. An Application of Newton’s Method to the Lubrication Analysis of Air-Lubricated Bearings. Tribol. Trans. 1999, 42, 419–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wadhwa, S.; Sinhasan, R.; Singh, D. Analysis of orifice compensated externally pressurized gas bearings. Tribol. Int. 1983, 16, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.; Gong, W.; Zheng, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, W.; Jiang, Z. A simplified FEM analysis on the static performance of aerostatic journal bearings with orifice restrictor. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part J J. Eng. Tribol. 2020, 235, 1379–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.T.; Ding, H. Design analysis and experimental study of aerostatic linear guideways used in a high acceleration and high precision xy stage. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part J J. Eng. Tribol. 2007, 221, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charki, A.; Bigaud, D.; Guérin, F. Behavior analysis of machines and system air hemispherical spindles using finite element modeling. Ind. Lubr. Tribol. 2013, 65, 272–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.; Xia, H.; Lei, D.; Zhang, X.; Jiang, Z. A Calculation Method to Investigate the Effects of Geometric Parameters and Operational Conditions on the Static Characteristics of Aerostatic Spherical Bearings. J. Tribol. 2018, 141, 021101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Qiao, Z.; Xue, J.; Wang, B.; Chen, W. A newly treated boundary conditions to enhance accuracy of finite element analysis for orifice-type aerostatic bearings. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2022, 173, 103277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Ge, Y.; Lu, Q.; Zhang, W.; Wang, S. Air film pressure field characteristics of aerostatic thrust bearing with orifice blockage. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajdeep, D.; Andreas, H.; Dirk, W.; Patrick, J.; Beat, H.M. Numerical modeling and design decisions for aerostatic bearings with relatively large nozzle sizes in Magic-Angle Spinning (MAS) systems. Tribol. Int. 2022, 175, 107855. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, H.-L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, B.-R.; Yang, H.; Xia, H. Numerical Simulation and Experimental Verification of the Stiffness and Stability of Thrust Pad Aerostatic Bearings. Chin. J. Mech. Eng. 2018, 31, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Wang, B.; Luo, X.; Qiao, Z. Design and analysis of aerostatic spindle with high load characteristics for large ultra-precision drum lathe. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part J J. Eng. Tribol. 2015, 229, 1425–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belforte, G.; Raparelli, T.; Viktorov, V.; Trivella, A. Discharge coefficients of orifice-type restrictor for aerostatic bearings. Tribol. Int. 2007, 40, 512–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belforte, G.; Colombo, F.; Raparelli, T.; Trivella, A.; Viktorov, V. A new identification method of the supply hole discharge coefficient of gas bearings. Tribol. Des. WIT Trans. Eng. Sci. 2010, 66, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belforte, G.; Raparelli, T.; Trivella, A.; Viktorov, V. Identification of Discharge Coefficients of Orifice-Type Restrictors for Aerostatic Bearings and Application Examples. New Tribol. Ways 2011, 359–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belforte, G.; Raparelli, T.; Trivella, A.; Viktorov, V.; Visconte, C. CFD Analysis of a Simple Orifice-Type Feeding System for Aerostatic Bearings. Tribol. Lett. 2015, 58, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renn, J.-C.; Hsiao, C.-H. Experimental and CFD study on the mass flow-rate characteristic of gas through orifice-type restrictor in aerostatic bearings. Tribol. Int. 2004, 37, 309–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimoto, S.; Yamamoto, M.; Toda, K. Numerical Calculations of Pressure Distribution in the Bearing Clearance of Circular Aerostatic Thrust Bearings With a Single Air Supply Inlet. J. Tribol. 2006, 129, 384–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eleshaky, M.E. CFD investigation of pressure depressions in aerostatic circular thrust bearings. Tribol. Int. 2009, 42, 1108–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.; Chan, C.; Jeng, Y. Numerical analysis of discharge coefficients in aerostatic bearings with orifice-type restrictors. Tribol. Int. 2015, 90, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ting, G.-C.; Lee, Y.-H.; Huang, K.-Y. Development and experimental verification of radial-axial integrated cup-shaped aerostatic bearing for miniature turbine of dental handpiece. Tribol. Int. 2022, 174, 107740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Wang, G.; Feng, K.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, P. CFD-based investigation and experimental study on the performances of novel back-flow channel aerostatic bearings. Tribol. Int. 2021, 165, 107319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neves, M.; Schwarz, V.; Menon, G. Discharge coefficient influence on the performance of aerostatic journal bearings. Tribol. Int. 2010, 43, 746–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Chen, X.; Chen, H. A hybrid approach to the numerical solution of air flow field in aerostatic thrust bearings. Tribol. Int. 2016, 102, 444–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.; Cheng, K.; Ding, H.; Chen, S. Analysis on discharge coefficients in FEM modeling of hybrid air journal bearings and experimental validation. Tribol. Int. 2018, 119, 549–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyatake, M.; Yoshimoto, S. Numerical investigation of static and dynamic characteristics of aerostatic thrust bearings with small feed holes. Tribol. Int. 2010, 43, 1353–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gero, L.R.; Ettles, C.M.M. An Evaluation of Finite Difference and Finite Element Methods for the Solution of the Reynolds Equation. ASLE Trans. 1986, 29, 166–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belforte, G.; Colombo, F.; Raparelli, T.; Trivella, A.; Viktorov, V. Performance of Externally Pressurized Grooved Thrust Bearings. Tribol. Lett. 2009, 37, 553–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Cheng, K.; Chen, S.; Ding, H.; Fu, H. CFD based investigation on influence of orifice chamber shapes for the design of aerostatic thrust bearings at ultra-high speed spindles. Tribol. Int. 2015, 92, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Term | Specification |
|---|---|
| 225 mm | |
| Diameter of spindle rotor, D | 200 mm |
| Orifice-end distance, l | 65 mm |
| Orifice diameter, d0 | 0.2 mm |
| Gas film thickness, h0 | 20 μm |
| 0.5 MPa | |
| Number of orifices in each row, N | 12 |
| Lubricant | Clean air |
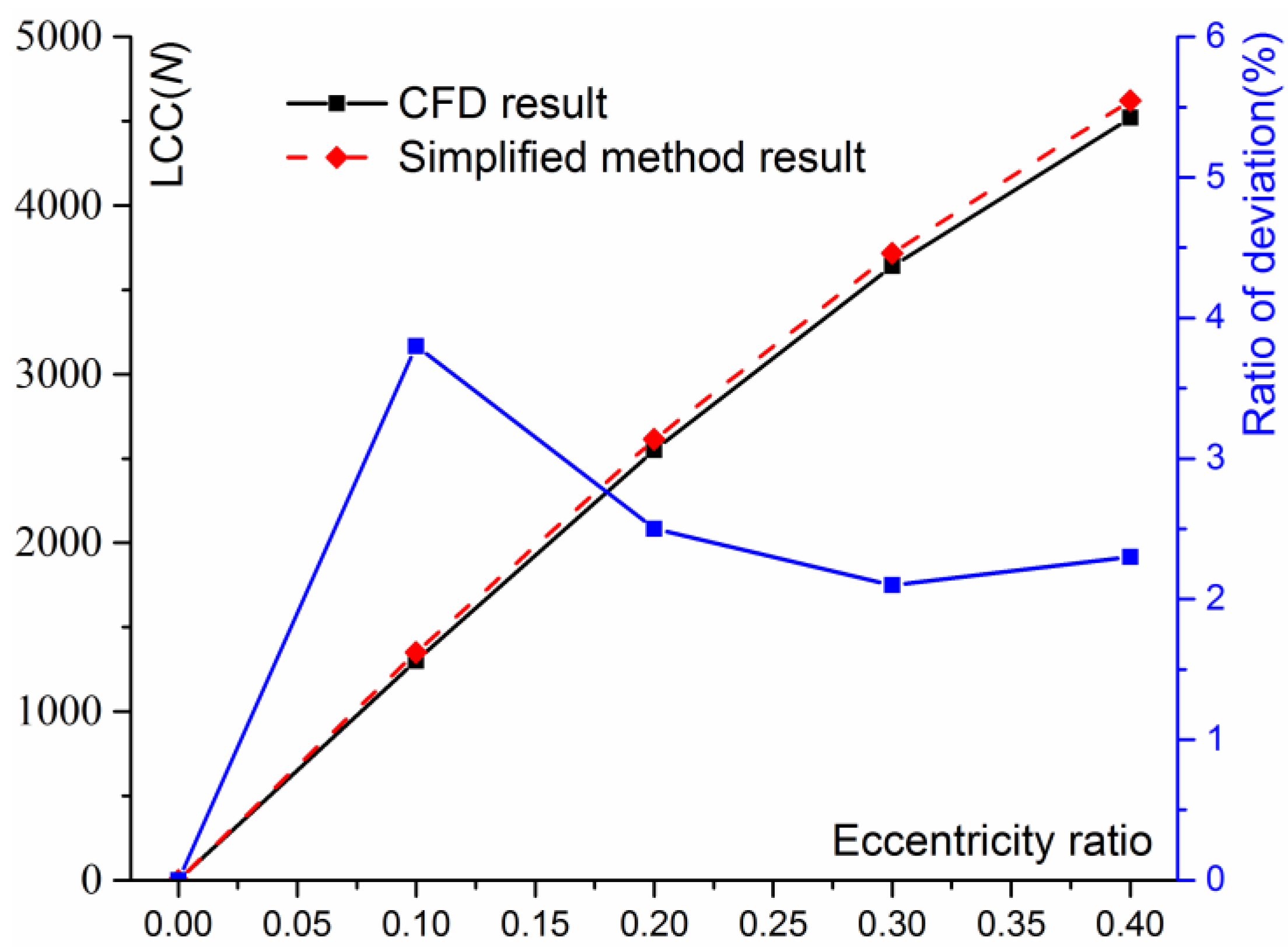
| Eccentricity Ratio | Eccentricity Value | CFD Result | Simplified Method Result | Ratio of Deviation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 μm | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0.1 | 2 μm | 1300 N | 1350 N | 3.8% |
| 0.2 | 4 μm | 2550 N | 2614 N | 2.5% |
| 0.3 | 6 μm | 3640 N | 3717 N | 2.1% |
| 0.4 | 8 μm | 4520 N | 4622 N | 2.3% |
| Term | Specification |
|---|---|
| 100 mm | |
| Diameter of spindle rotor, D | 100 mm |
| Orifice-end distance, l | 25 mm |
| Orifice diameter, d0 | 0.2 mm |
| Gas film thickness, h0 | 15 μm |
| 0.5 MPa | |
| Number of orifices in each row, N | 8 |
| Lubricant | Clean air |
| Eccentricity Value | CFD Result | Simplified Method Result | Ratio of Deviation |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 μm | 0 N | 0 N | 0 |
| 1.2 μm | 242.8 N | 266.2 N | 9.6% |
| 2.4 μm | 476.3 N | 514.3 N | 8.0% |
| 3.6 μm | 673.5 N | 730.6 N | 8.5% |
| 4.8 μm | 838.7 N | 912.2 N | 8.7% |
| 6.0 | 968.8 N | 1061 N | 9.5% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, Y.; Qiao, Z.; Chen, W.; Xue, J.; Wang, B. Evaluation and Application of an Engineering Calculation Method of the Static Performance of an Aerostatic Journal Bearing with Multiple Orifice-Type Restrictors. Lubricants 2022, 10, 332. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants10120332
Wu Y, Qiao Z, Chen W, Xue J, Wang B. Evaluation and Application of an Engineering Calculation Method of the Static Performance of an Aerostatic Journal Bearing with Multiple Orifice-Type Restrictors. Lubricants. 2022; 10(12):332. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants10120332
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Yangong, Zheng Qiao, Wentao Chen, Jiadai Xue, and Bo Wang. 2022. "Evaluation and Application of an Engineering Calculation Method of the Static Performance of an Aerostatic Journal Bearing with Multiple Orifice-Type Restrictors" Lubricants 10, no. 12: 332. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants10120332
APA StyleWu, Y., Qiao, Z., Chen, W., Xue, J., & Wang, B. (2022). Evaluation and Application of an Engineering Calculation Method of the Static Performance of an Aerostatic Journal Bearing with Multiple Orifice-Type Restrictors. Lubricants, 10(12), 332. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants10120332





