Finite Element Modelling of Wear Behaviors of Composite Laminated Structure
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Method
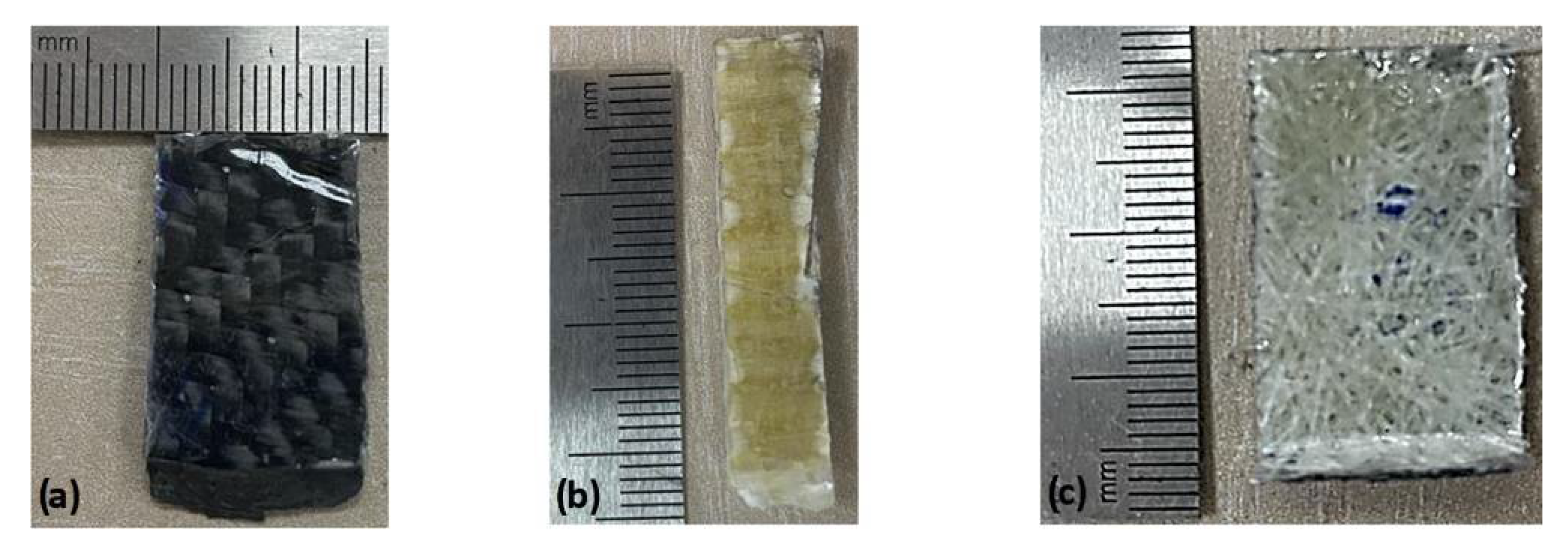
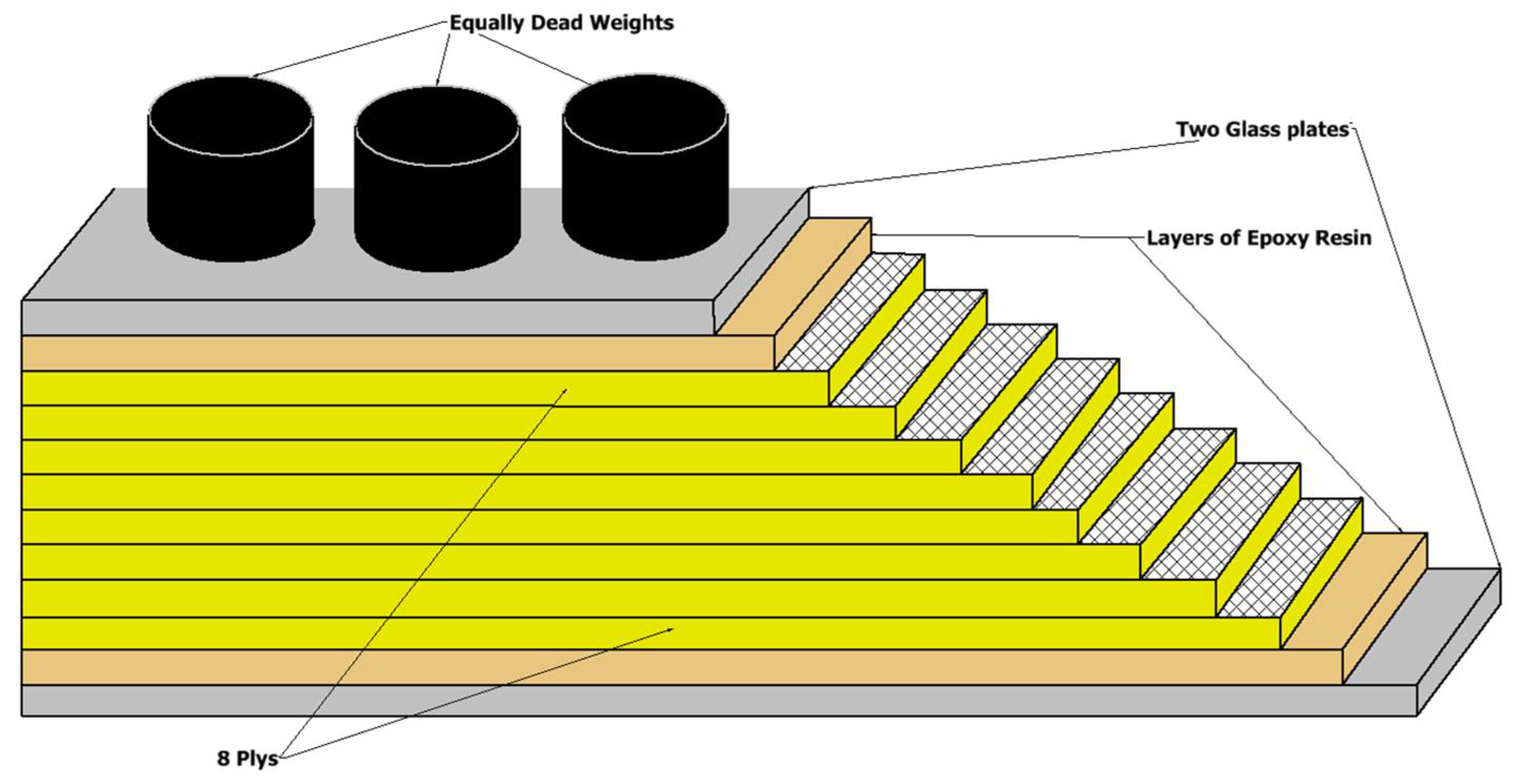
2.1. Material Preparation
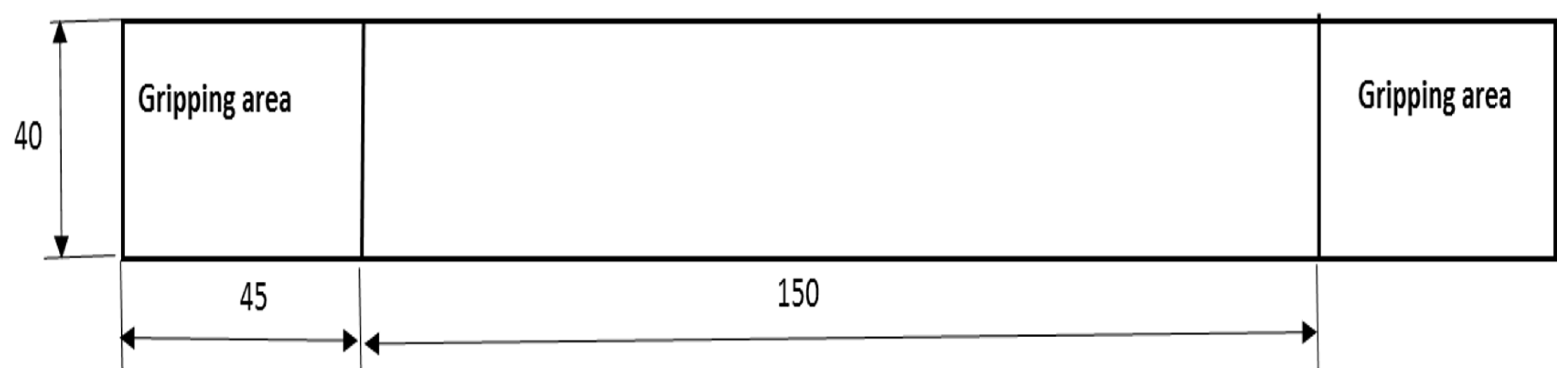
2.2. Tensile Test
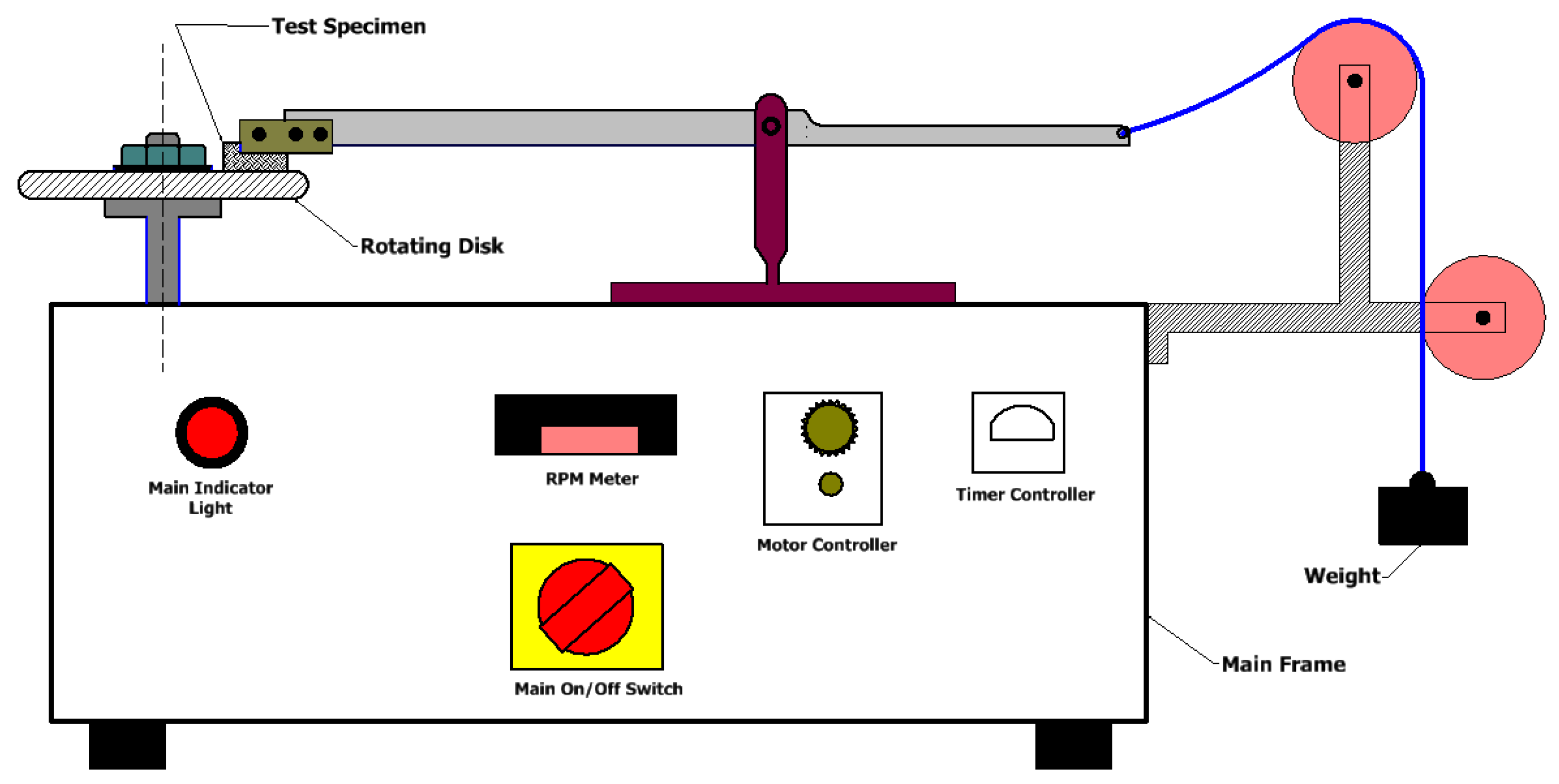
2.3. Wear Test
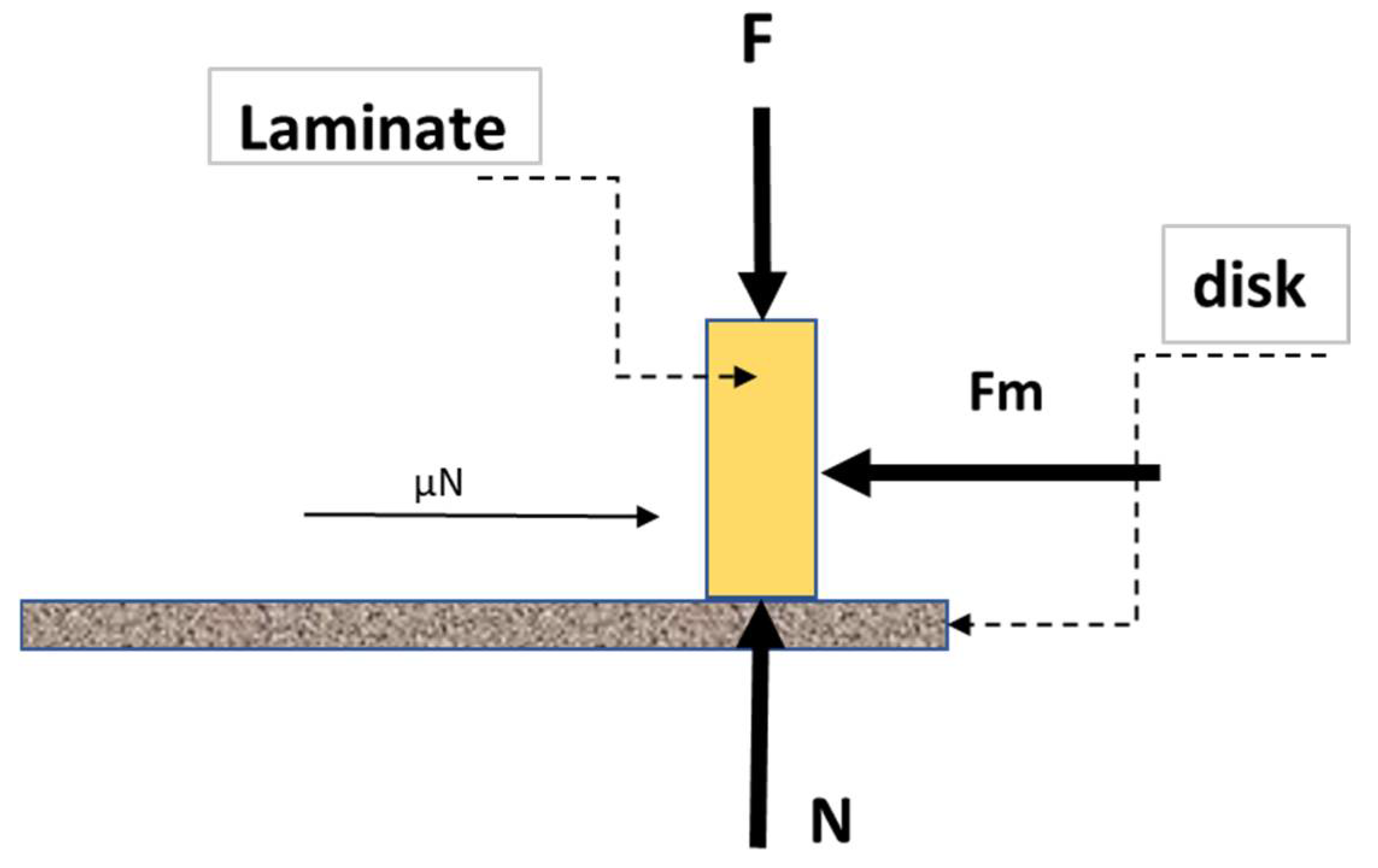
2.4. Friction Coefficient
2.5. Analytical Model
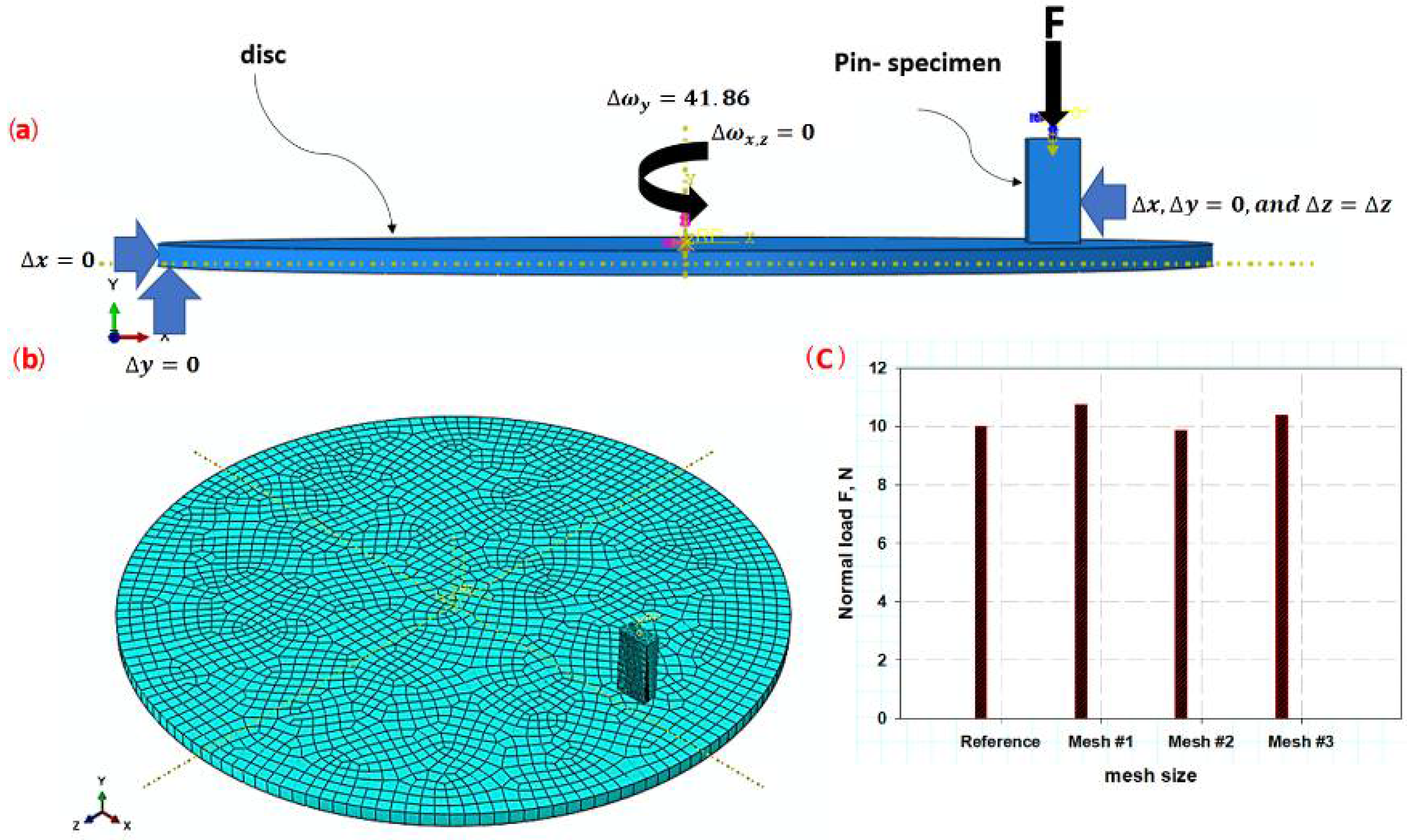
2.6. Finite Element Modeling
3. Results and Discussion
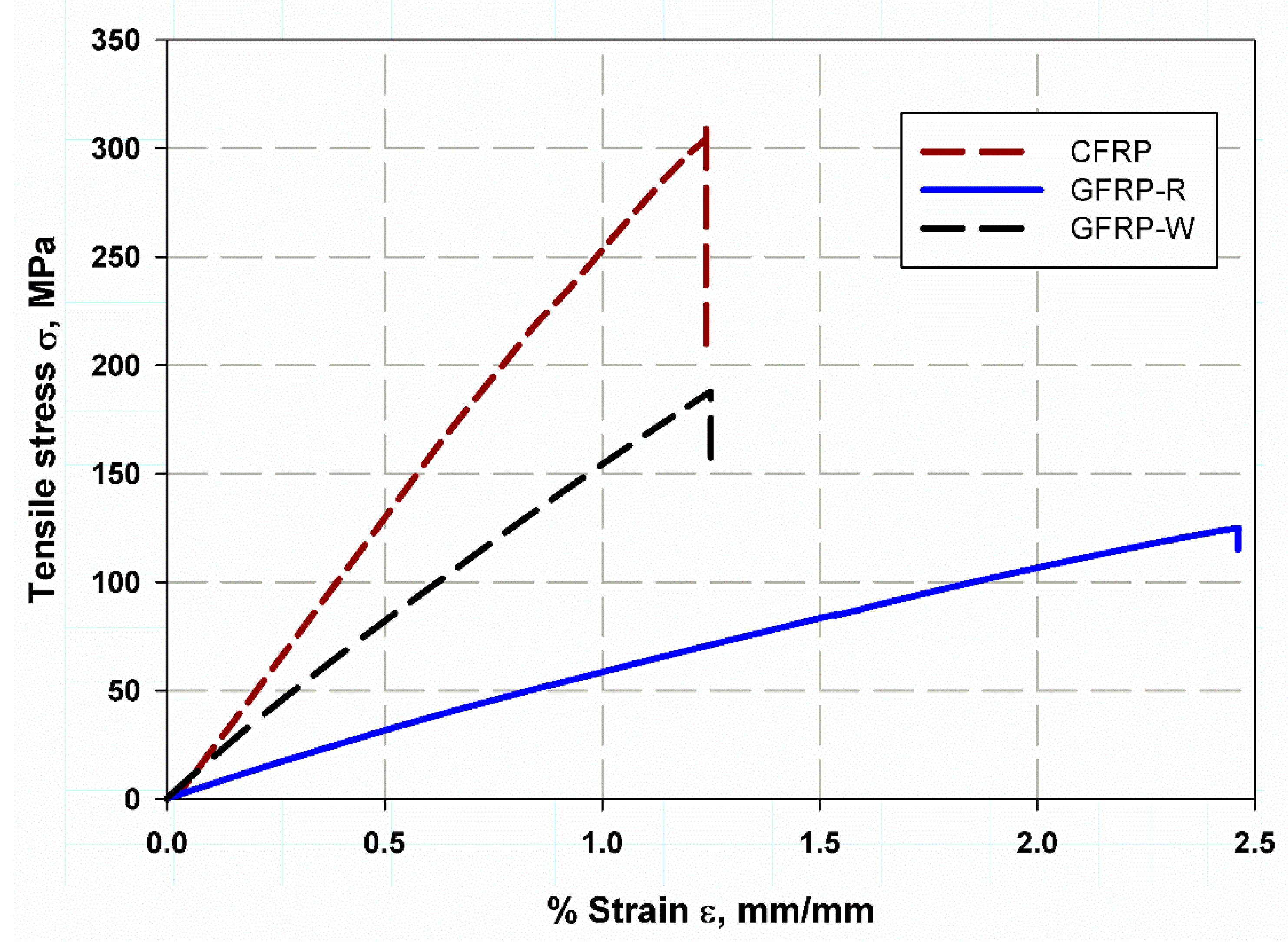
3.1. Tension Test
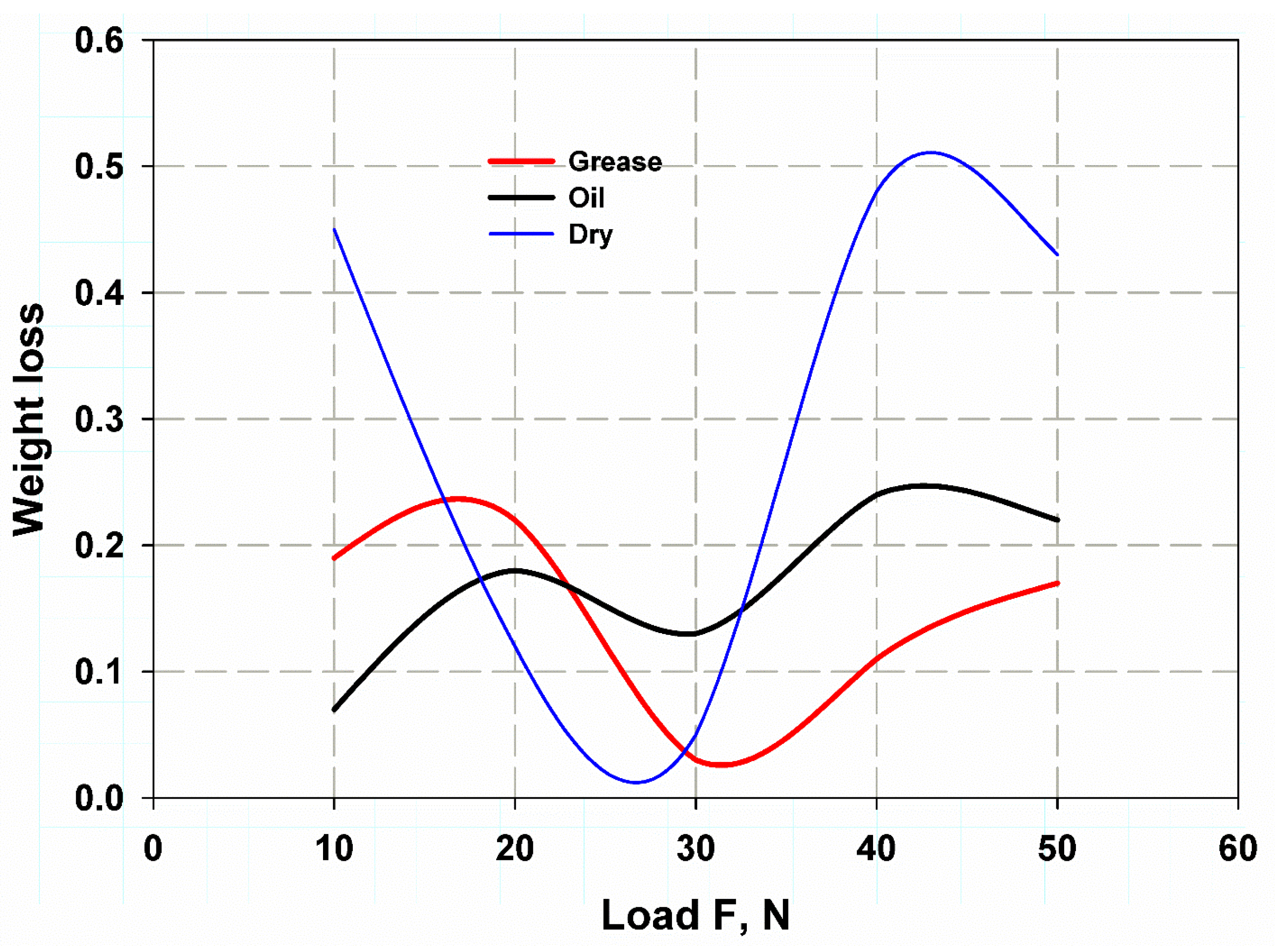
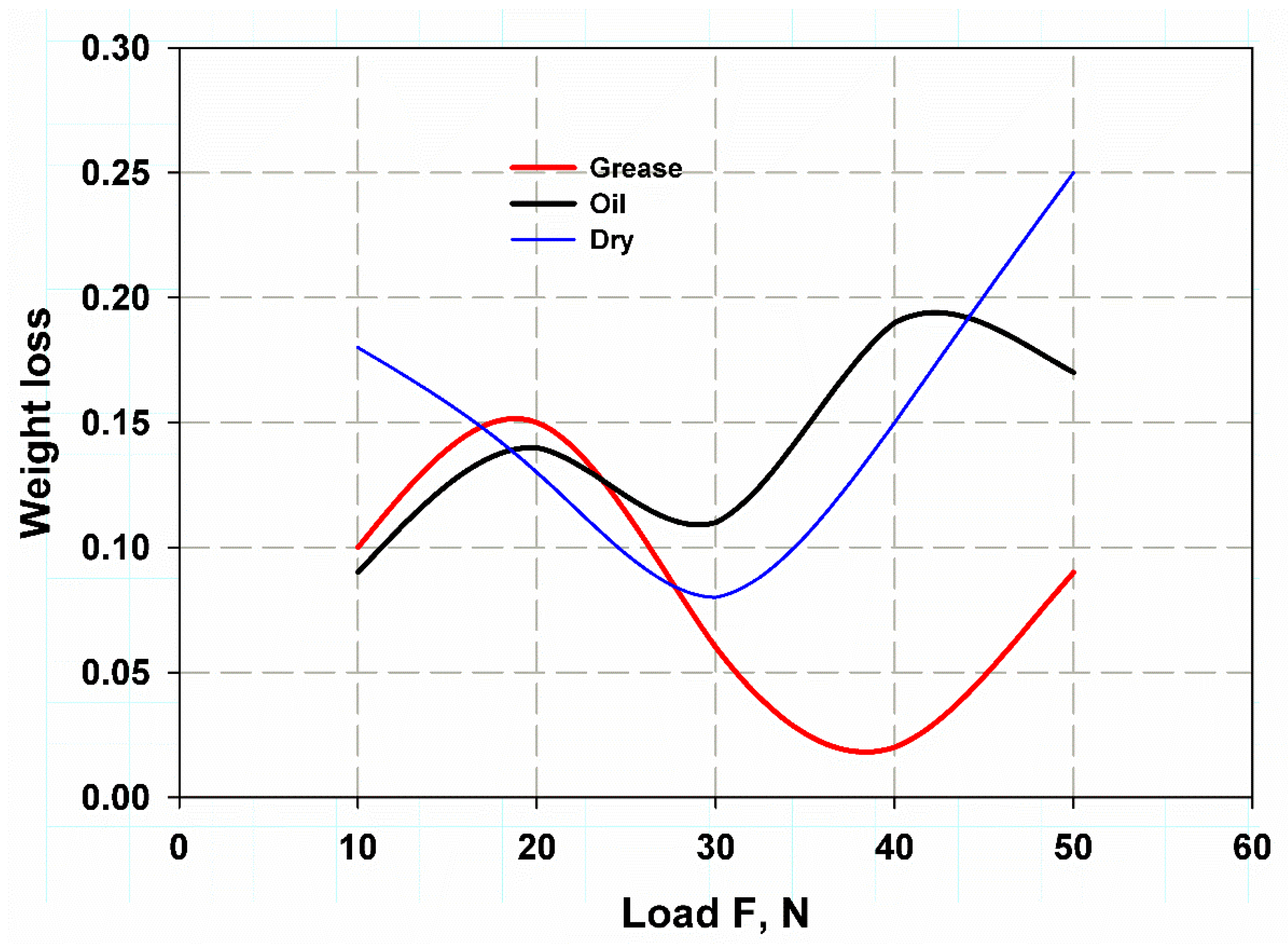
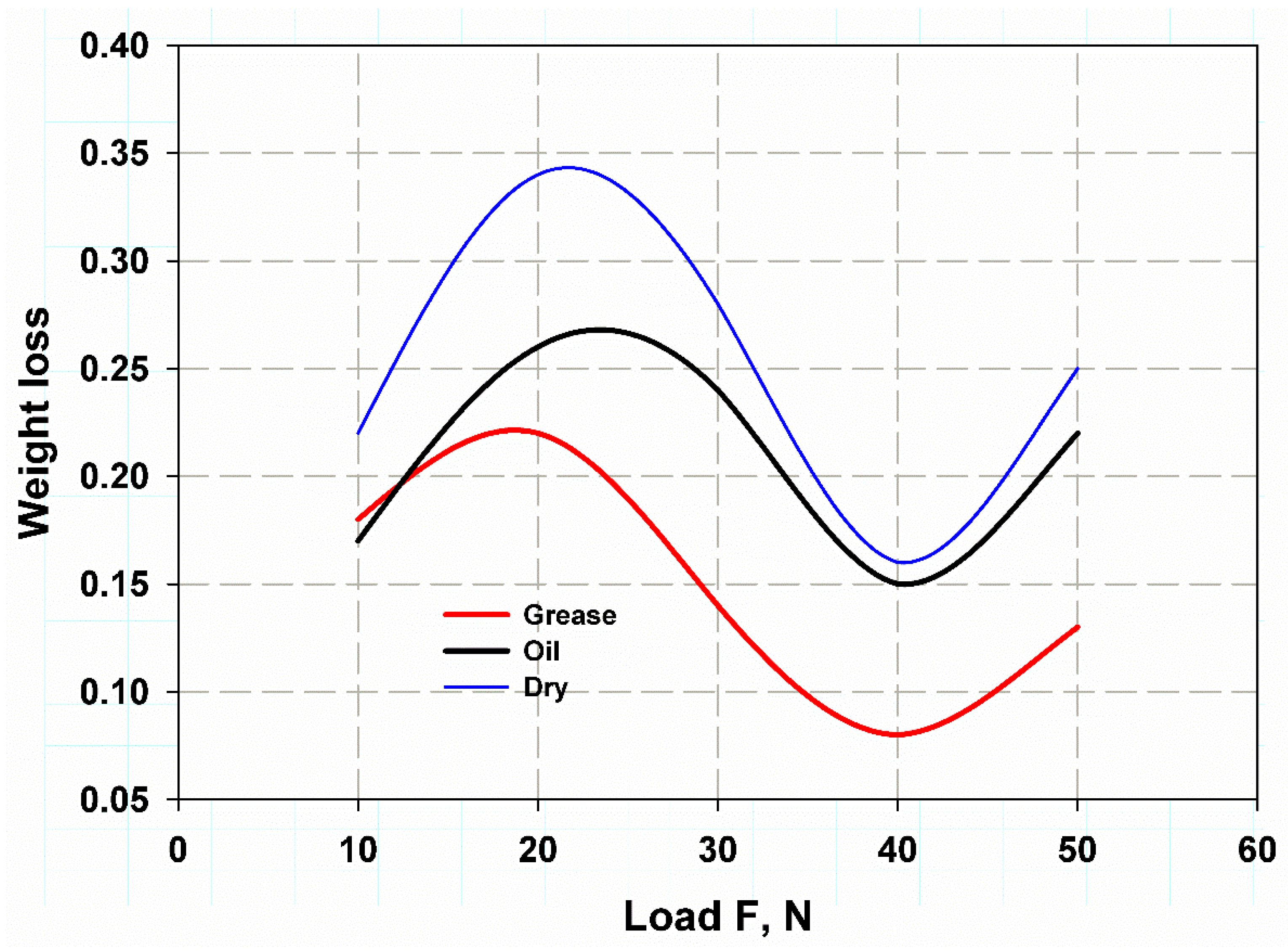
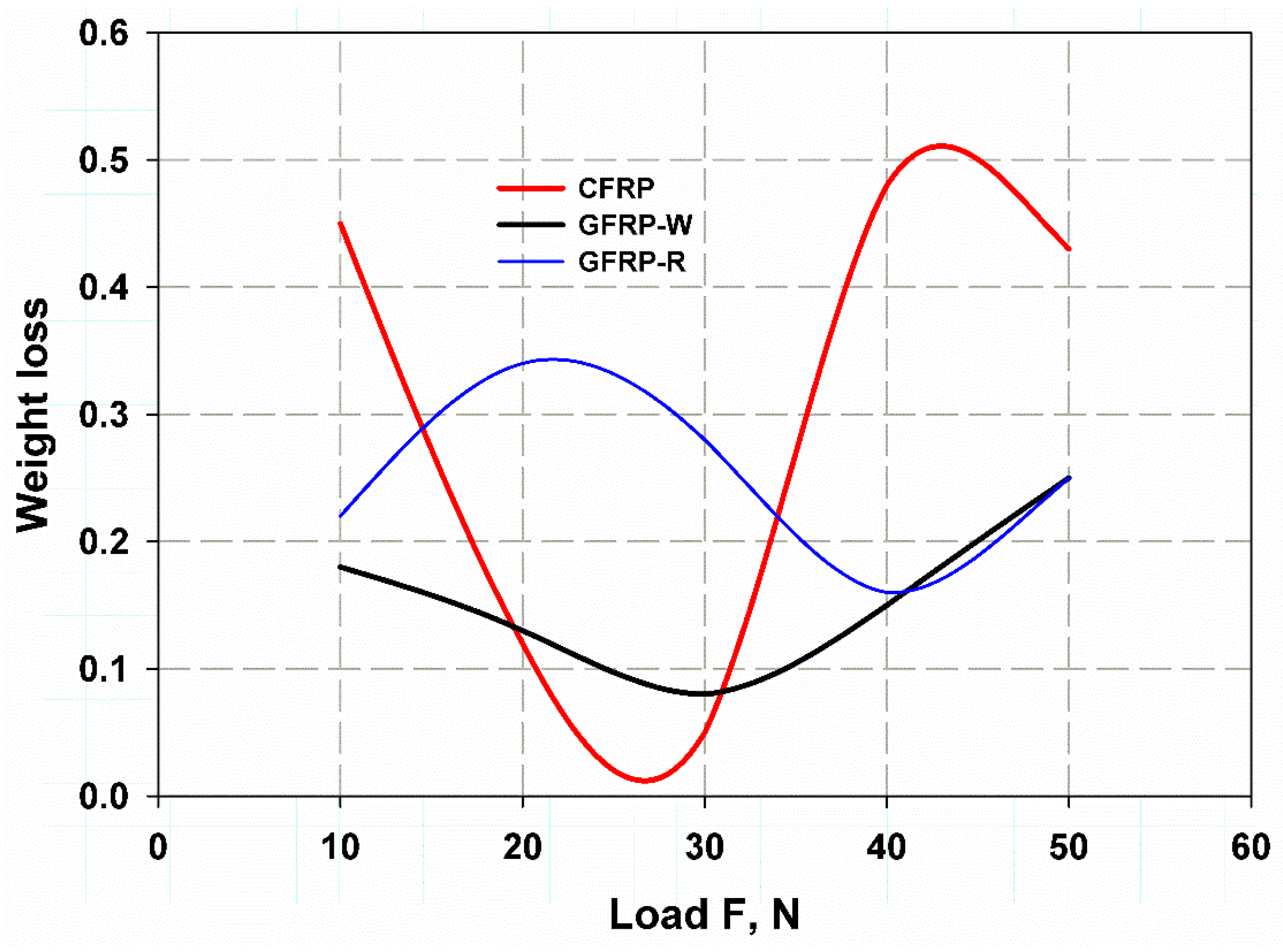
3.2. Wear Test
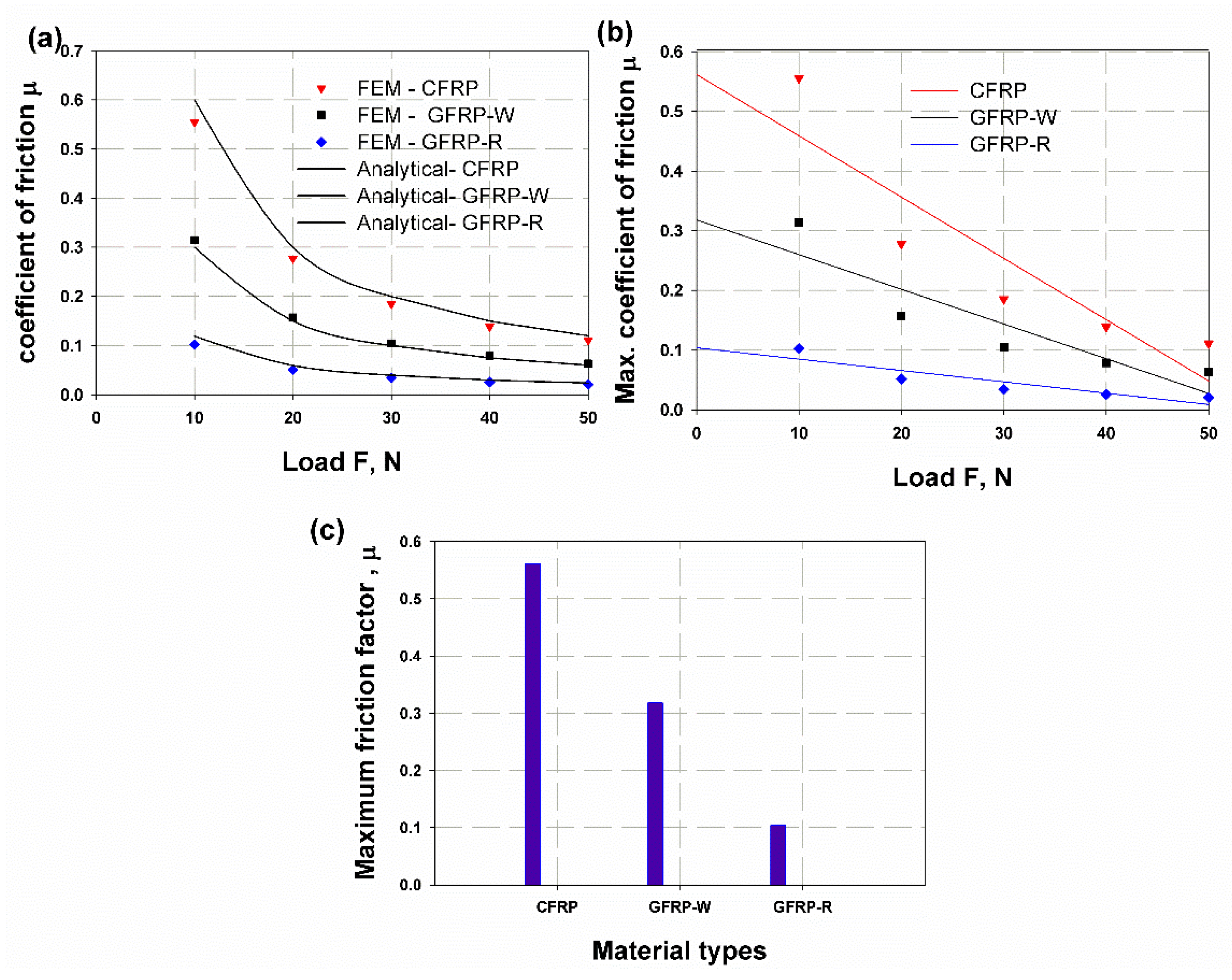
3.3. Comparison of the Results
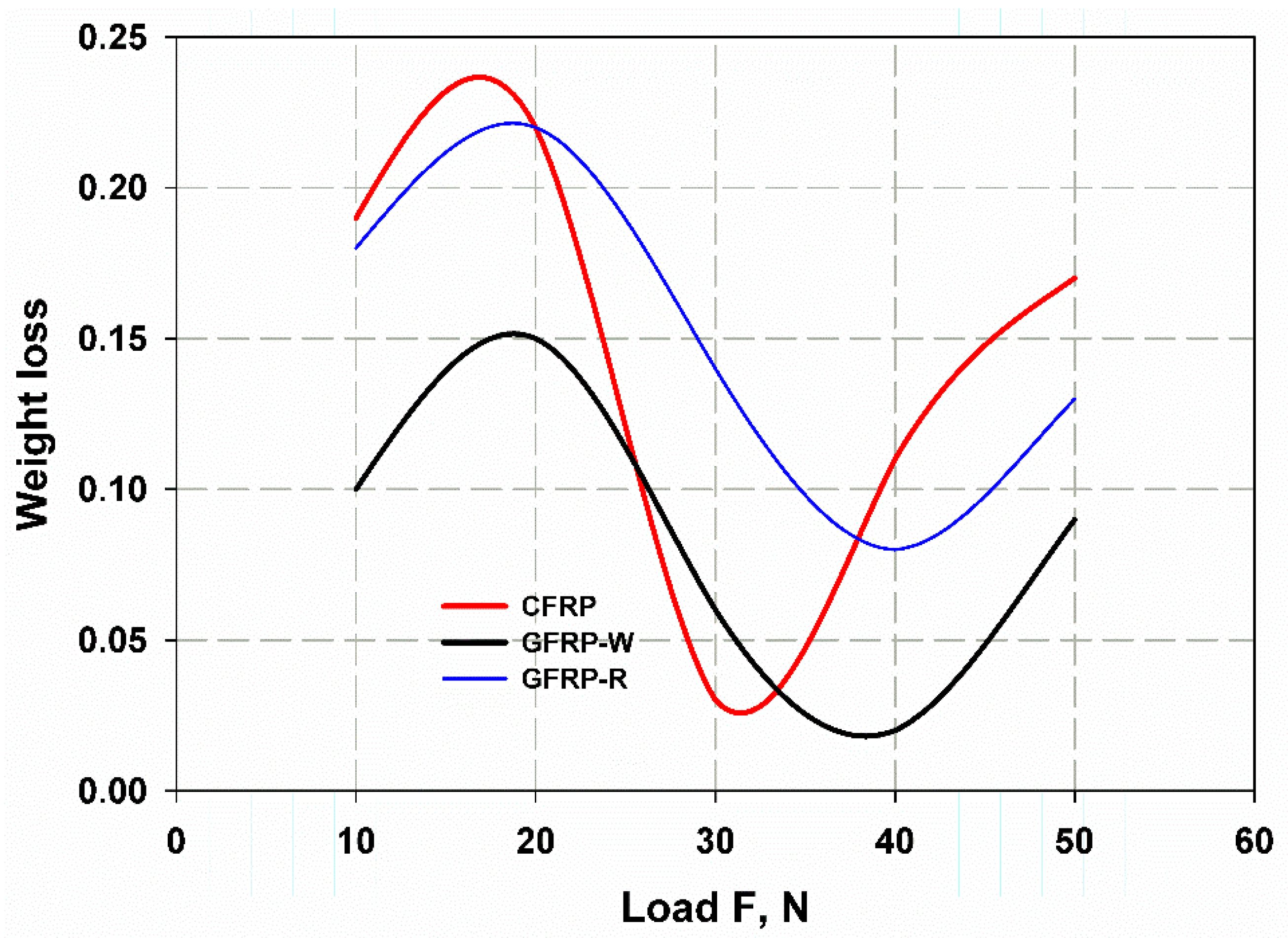
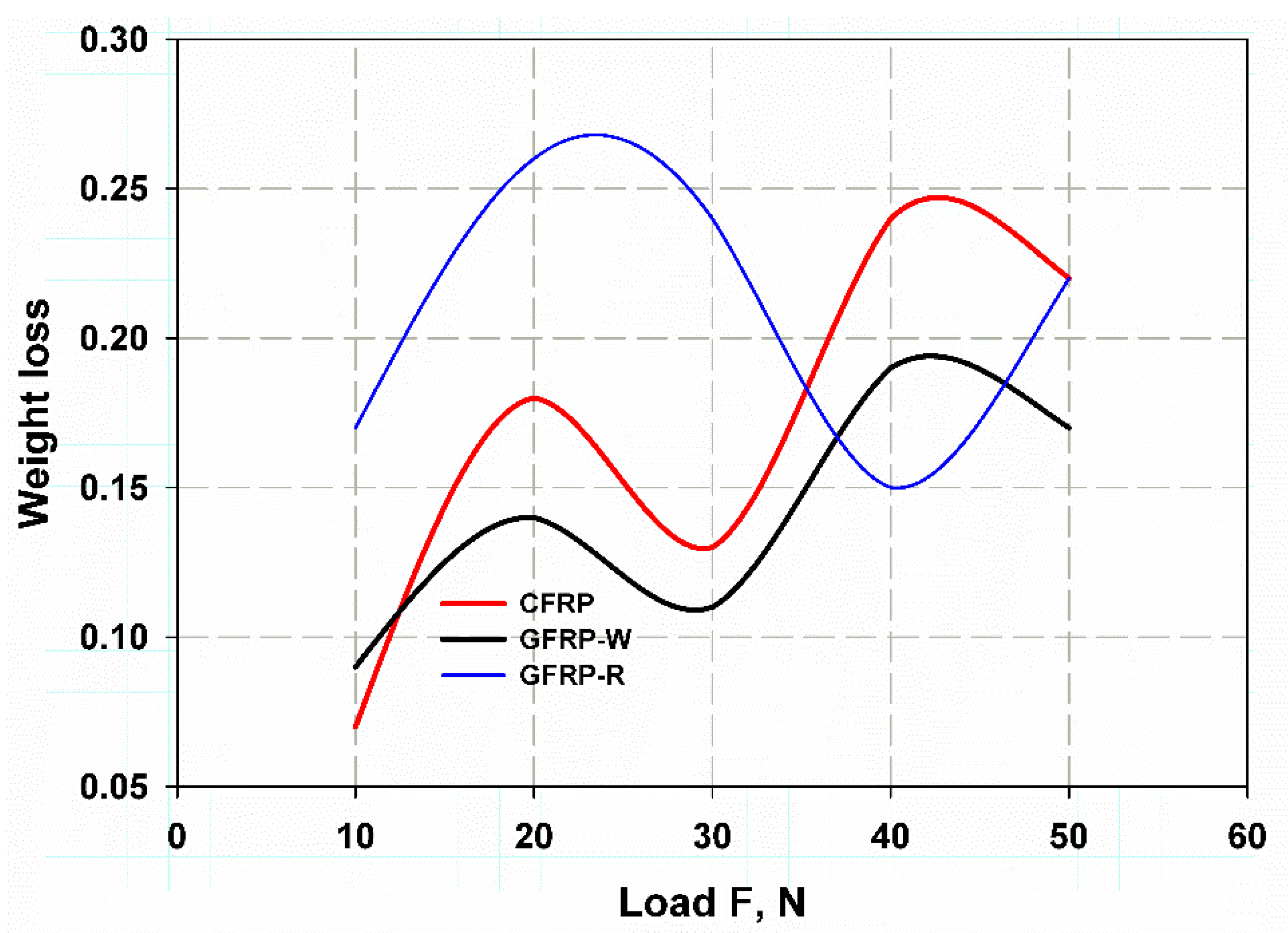
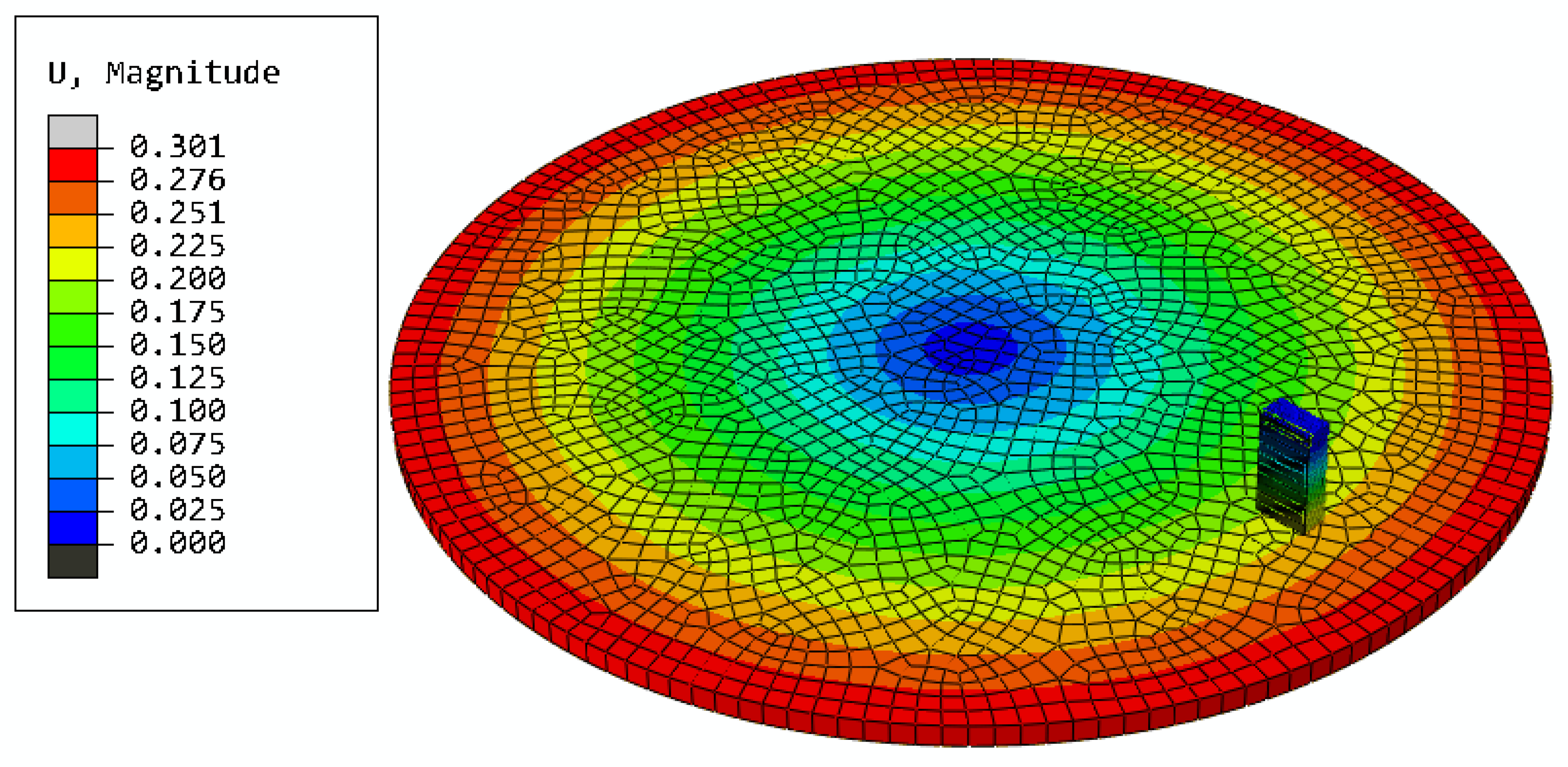
3.4. Finite Element Simulation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, C.; Yin, X.; Liu, Y.; Guo, R.; Xian, G. Long-term service evaluation of a pultruded carbon/glass hybrid rod exposed to elevated temperature, hydraulic pressure and fatigue load coupling. Int. J. Fatigue 2020, 134, 105480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Xian, G.; Li, H. Effect of postcuring immersed in water under hydraulic pressure on fatigue performance of large-diameter pultruded carbon/glass hybrid rod. Fatigue Fract. Eng. Mater. Struct. 2019, 42, 1148–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Yan, D. Study on the durability of GFRP bars and carbon/glass hybrid fiber reinforced polymer (HFRP) bars aged in alkaline solution. Compos. Struct. 2021, 261, 113285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthik, K.; Rajamani, D.; Manimaran, A.; Prakash, J.U. Wear behaviour of hybrid polymer matrix composites using Taguchi technique. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 33, 3186–3190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suresha, B.; Chandramohan, G.; Siddaramaiah; Samapthkumaran, P.; Seetharamu, S. Three-body abrasive wear behaviour of carbon and glass fiber reinforced epoxy composites. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2007, 443, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harirao, A.N. Investigation of Dry Wear Behaviour of Silicon-Eglass-Epoxy composite Material. Silicon 2017, 9, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahesha, G.T.; Satish Shenoy, B.; Vijaya Kini, M.; Padmaraj, N.H. Wear behaviour studies on Grewia Serrulata bast fibre reinforced polymer composites. Cogent Eng. 2018, 5, 1517580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arthanarieswaran, V.; Kumaravel, A.; Kathirselvam, M. Evaluation of mechanical properties of banana and sisal fiber reinforced epoxy composites: Influence of glass fiber hybridization. Mater. Des. 2014, 64, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M.K.; Mohamed, A.F.; Khalil, K.A.; Abdellah, M.Y. Numerical and Experimental Evaluation of Mechanical and Ring Stiffness Properties of Preconditioning Underground Glass Fiber Composite Pipes. J. Compos. Sci. 2021, 5, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, K.S.; Varadarajan, Y.; Rajendra, N. Erosive Wear Behaviour of Carbon Fiber-reinforced Epoxy Composite. Mater. Today Proc. 2015, 2, 2975–2983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bijwe, J.; Indumathi, J.; Ghosh, A. On the abrasive wear behaviour of fabric-reinforced polyetherimide composites. Wear 2002, 253, 768–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Suresha, B.; Siddaramaiah; Kishore; Seetharamu, S.; Kumaran, P.S. Investigations on the influence of graphite filler on dry sliding wear and abrasive wear behaviour of carbon fabric reinforced epoxy composites. Wear 2009, 267, 1405–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alpas, A.; Embury, J. The role of subsurface deformation and strain localization on the sliding wear behaviour of laminated composites. Wear 1991, 146, 285–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korim, N.S.; Abdellah, M.Y.; Dewidar, M.; Abdelhaleem, A.M. Crushable finite element modeling of mechanical properties of titanium foam. Int. J. Sci. Eng. Res. 2015, 6, 1221–1227. [Google Scholar]
- Põdra, P.; Andersson, S. Simulating sliding wear with finite element method. Tribol. Int. 1999, 32, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benabdallah, H.; Olender, D. Finite element simulation of the wear of polyoxymethylene in pin-on-disc configuration. Wear 2006, 261, 1213–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doddamani, R.A.S.; Bharath, K. Dry sliding wear simulation of hybrid aluminum metal matrix composites. Adv. Compos. Hybrid Mater. 2020, 3, 120–126. [Google Scholar]
- Pradhan, P.; Satapathy, A. Investigation on sliding wear behaviour of walnut shell powder (WSP) filled polyester composites using finite element method. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 44, 4190–4195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, A.; Van Paepegem, W.; De Baets, P.; Ost, W.; Degrieck, J. Adaptive finite element simulation of wear evolution in radial sliding bearings. Wear 2012, 296, 660–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, R.M. Mechanics of Composite Materials; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Mallick, P.K. Composites Engineering Handbook; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Khashaba, U. In-plane shear properties of cross-ply composite laminates with different off-axis angles. Compos. Struct. 2004, 65, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, Y.; Hassan, M.K.; Abu El-Ainin, H.; Hashem, A.M. Effect of stacking sequence and geometric scaling on the brittleness number of glass fiber composite laminate with stress raiser. Sci. Eng. Compos. Mater. 2014, 21, 281–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M.K.; Mohammed, Y.; Salem, T.; Hashem, A. Prediction of nominal strength of composite structure open hole specimen through cohesive laws. Int. J. Mech. Mech. Eng. IJMME-IJENS 2012, 12, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Khashaba, U.; Aldousari, S.; Najjar, I. Behavior of [0]8 woven composites under combined bending and tension loading: Part—I experimental and analytical. J. Compos. Mater. 2012, 46, 1345–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrie, E.M. Epoxy Adhesive Formulations; McGraw Hill Professional: New York, NY, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- STD/D3171; Standard Test Methods for Constituent Content of Composite Materials. ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2011.
- Abdellah, M.Y. Essential work of fracture assessment for thin aluminium strips using finite element analysis. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2017, 179, 190–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagnestål, A.; Sellgren, U.; Andersson, K. Durable winch-based point absorbers. In Proceedings of the 12th European Wave and Tidal Energy Conference, EWTEC 2017, Cork, Ireland, 27 August–1 September 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Shukla, M.J.; Kumar, D.S.; Mahato, K.K.; Rathore, D.; Prusty, R.K.; Ray, B.C. A comparative study of the mechanical performance of Glass and Glass/Carbon hybrid polymer composites at different temperature environments. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2015, 75, 012002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minus, M.; Kumar, S. The Processing, Properties, and Structure of Carbon Fibers. JOM 2005, 57, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM D3039/D 3039M; Standard Test Method for Tensile Properties of Polymer Matrix Composite Materials. ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 1995.
- Available online: https://www.zwickroell.com/products/static-materials-testing-machines/universal-testing-machines-for-static-applications/materials-testing-machine-with-hydraulic-drive/ (accessed on 15 May 2022).
- Hassan, M.K.; Mohammed, Y.; Abu, E. Improvement of Al-6061 alloys mechanical properties by controlling processing parameters. Int. J. Mech. Mechatron. Eng. 2012, 12, 14–18. [Google Scholar]
- The Editors of Encyclopaedia Britannica. Argon. In Encyclopedia Britannica; Encyclopedia Britannica: London, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Plesha, M.E.; Gray, G.L.; Costanzo, F. Engineering Mechanics: Statics; McGraw-Hill Higher Education: New York, NY, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Ghatrehsamani, S.; Akbarzadeh, S. Predicting the wear coefficient and friction coefficient in dry point contact using continuum damage mechanics. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part J J. Eng. Tribol. 2019, 233, 447–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdellah, M.Y. An approximate analytical model for modification of size effect law for open-hole composite structure under biaxial load. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part C J. Mech. Eng. Sci. 2021, 235, 3570–3583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soutis, C.; Filiou, C. Stress Distributions around Holes in Composite Laminates Subjected to Biaxial Loading. Appl. Compos. Mater. 1998, 5, 365–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soutis, C. Fibre reinforced composites in aircraft construction. Prog. Aerosp. Sci. 2005, 41, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inal, O.; Katnam, K.; Potluri, P.; Soutis, C. Progress in interlaminar toughening of aerospace polymer composites using particles and non-woven veils. Aeronaut. J. 2022, 126, 222–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouad, H.; Mourad, A.H.I.; Al Shammari, B.A.; Hassan, M.K.; Abdallah, M.Y.; Hashem, M. Fracture toughness, vibration modal analysis and viscoelastic behavior of Kevlar, glass, and carbon fiber/epoxy composites for dental-post applications. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2020, 101, 103456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubin, G. Handbook of Composites; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Nuruzzaman, D.M.; Chowdhury, M.A.; Rahaman, M.L. Effect of duration of rubbing and normal load on friction coefficient for polymer and composite materials. Ind. Lubr. Tribol. 2011, 63, 320–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mimaroglu, A.; Unal, H.; Arda, T. Friction and wear performance of pure and glass fibre reinforced poly-ether-imide on polymer and steel counterface materials. Wear 2007, 262, 1407–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, M.A.; Helali, M. The effect of amplitude of vibration on the coefficient of friction for different materials. Tribol. Int. 2008, 41, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhushan, B. Tribology and Mechanics of Magnetic Storage Devices; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Blau, P.J. Scale effects in sliding friction: An experimental study. In Fundamentals of Friction: Macroscopic and Microscopic Processes; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1992; pp. 523–534. [Google Scholar]
- Chowdhury, M.; Khalil, M.K.; Nuruzzaman, D.M.; Rahaman, M.L. The effect of sliding speed and normal load on friction and wear property of aluminum. Int. J. Mech. Mechatron. Eng. 2011, 11, 45–49. [Google Scholar]
- Chowdhury, M.; Nuruzzaman, D.M.; Mia, A.H.; Rahaman, M.L. Friction coefficient of different material pairs under different normal loads and sliding velocities. Tribol. Ind. 2012, 34, 18. [Google Scholar]


| Property | E-Glass | AS4-Carbon Fiber | Kemapoxy (150 RGL) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Density (kg/m3) | 2600 | 1790 | 1.2 |
| Tensile strength (MPa) | 3450 | 4270 | 85 |
| Modulus of Elasticity (GPa) | 80 | 228 | 2.5 |
| Passion’s ratio | 0.25 | 0.34 | 0.35 |
| In plane shear modulus (GPa) | 30.8 | 25 | 1.24 |
| Material | Thickness t, mm | Width w, mm | Area A, mm | Number of Fibers |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 (CFRP) | 2.2 | 14 | 33 | 800 |
| S2 (GFRP-W) | 5 | 5.2 | 26 | 800 |
| S3 (GFRP-R) | 2 | 16 | 32 | 210 |
| Specimens | E (GPa) | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Elongation (Comparative Measure) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average Value | Std. Dev. | Average Value | Std. Dev. | ||
| S1 (CFRP) | 27.13 | 1.7 | 303 | 17.98 | lower |
| S2 (GFRP-W) | 15.36 | 1.2 | 187.5 | 10.5 | intermediate |
| S3 (GFRP-R) | 5.01 | 1.5 | 125 | 2.5 | higher |
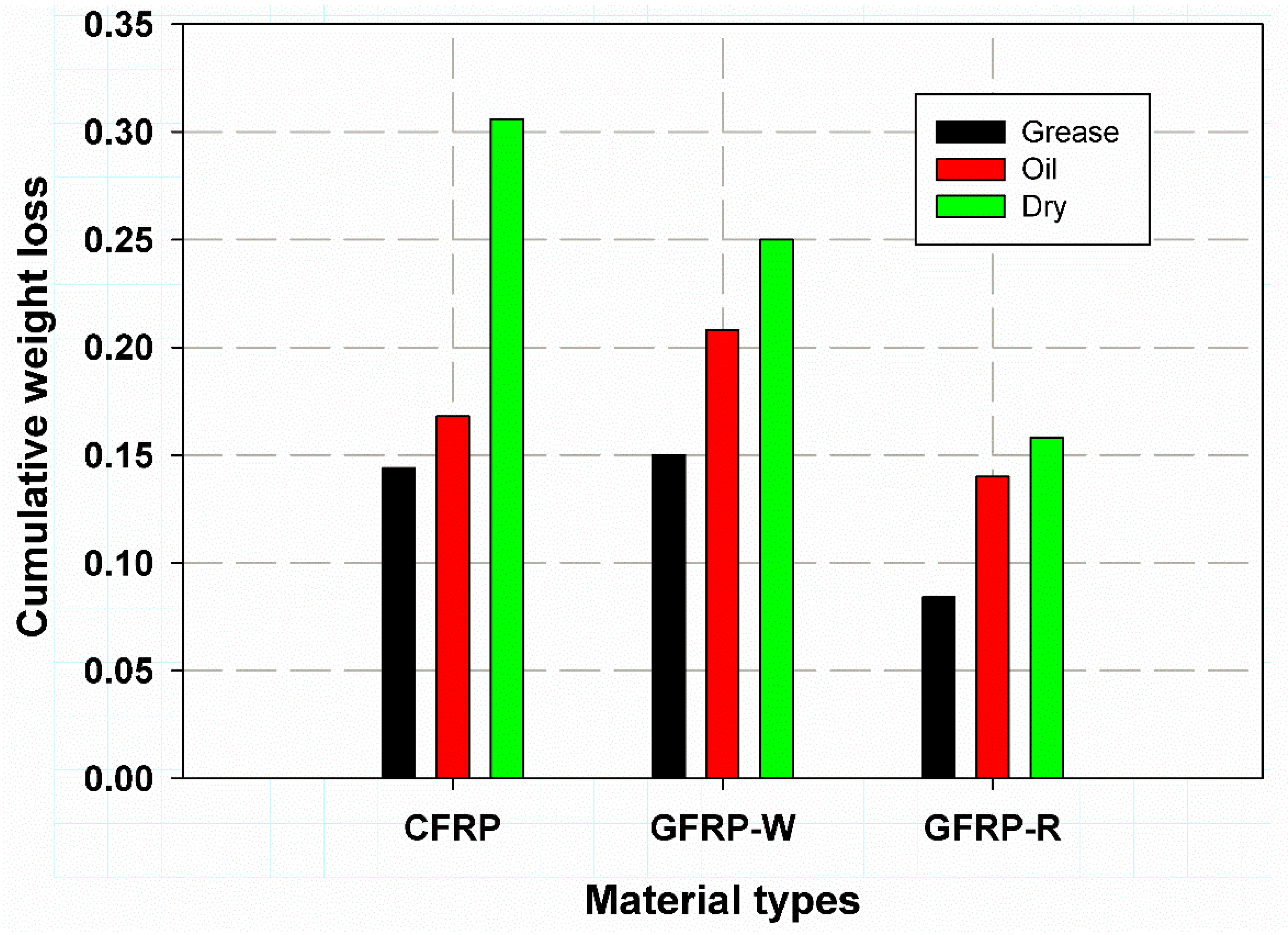
| Laminate Types | Grease | Oil | Dry |
|---|---|---|---|
| CFRP | 0.144 | 0.168 | 0.306 |
| GFRP-W | 0.15 | 0.208 | 0.25 |
| GFRP-R | 0.084 | 0.14 | 0.158 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abdellah, M.Y.; Hassan, M.K.; AlMalki, A.-A.; Mohamed, A.F.; Backar, A.H. Finite Element Modelling of Wear Behaviors of Composite Laminated Structure. Lubricants 2022, 10, 317. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants10110317
Abdellah MY, Hassan MK, AlMalki A-A, Mohamed AF, Backar AH. Finite Element Modelling of Wear Behaviors of Composite Laminated Structure. Lubricants. 2022; 10(11):317. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants10110317
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbdellah, Mohammed Y., Mohamed K. Hassan, Abdel-Aziz AlMalki, Ahmed F. Mohamed, and Ahmed H. Backar. 2022. "Finite Element Modelling of Wear Behaviors of Composite Laminated Structure" Lubricants 10, no. 11: 317. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants10110317
APA StyleAbdellah, M. Y., Hassan, M. K., AlMalki, A.-A., Mohamed, A. F., & Backar, A. H. (2022). Finite Element Modelling of Wear Behaviors of Composite Laminated Structure. Lubricants, 10(11), 317. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants10110317





