UV Spectroscopy of Massive Stars
Abstract
1. Introduction
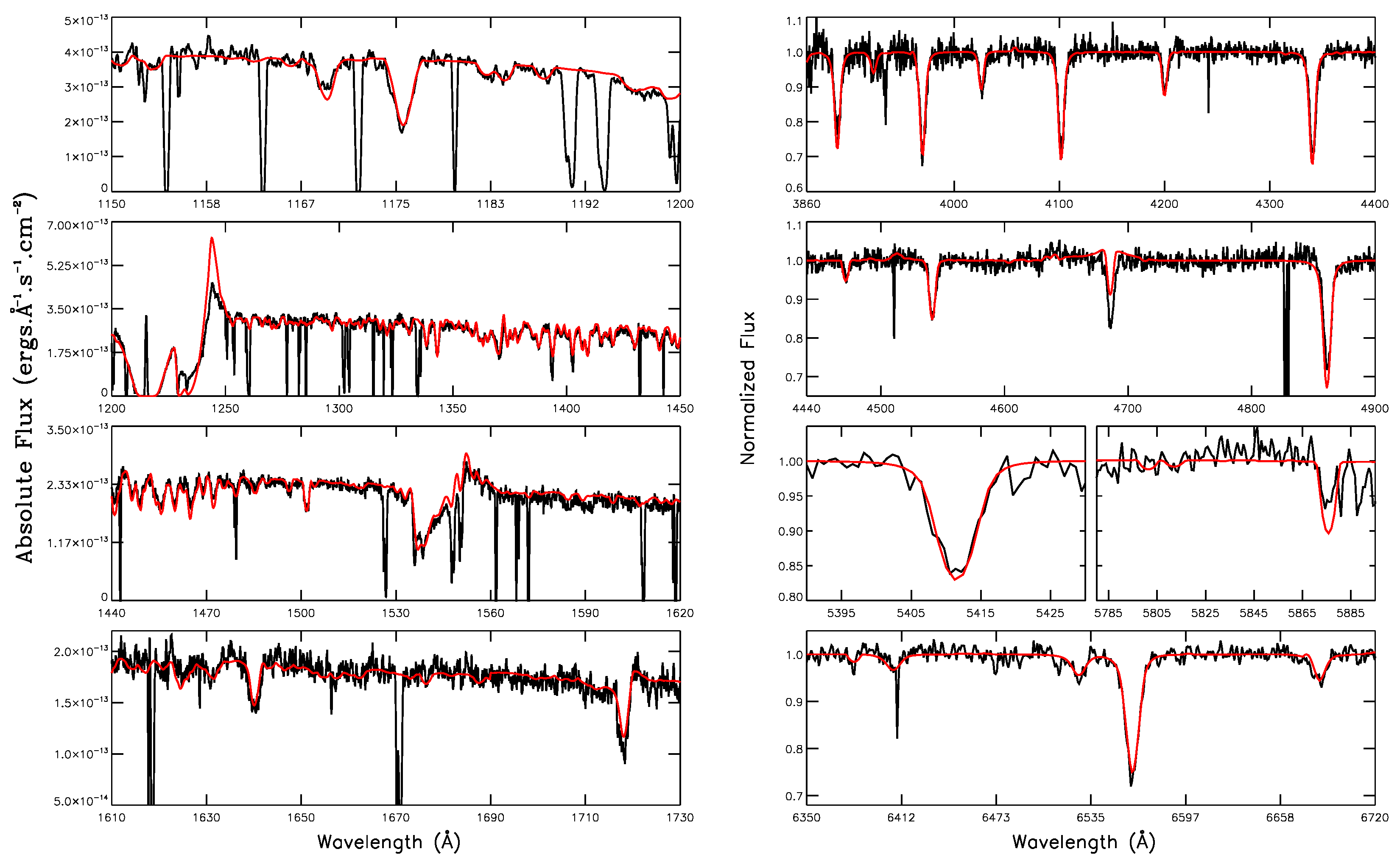
2. Spectral Atlases
2.1. OB Stars
2.2. Wolf–Rayet Stars
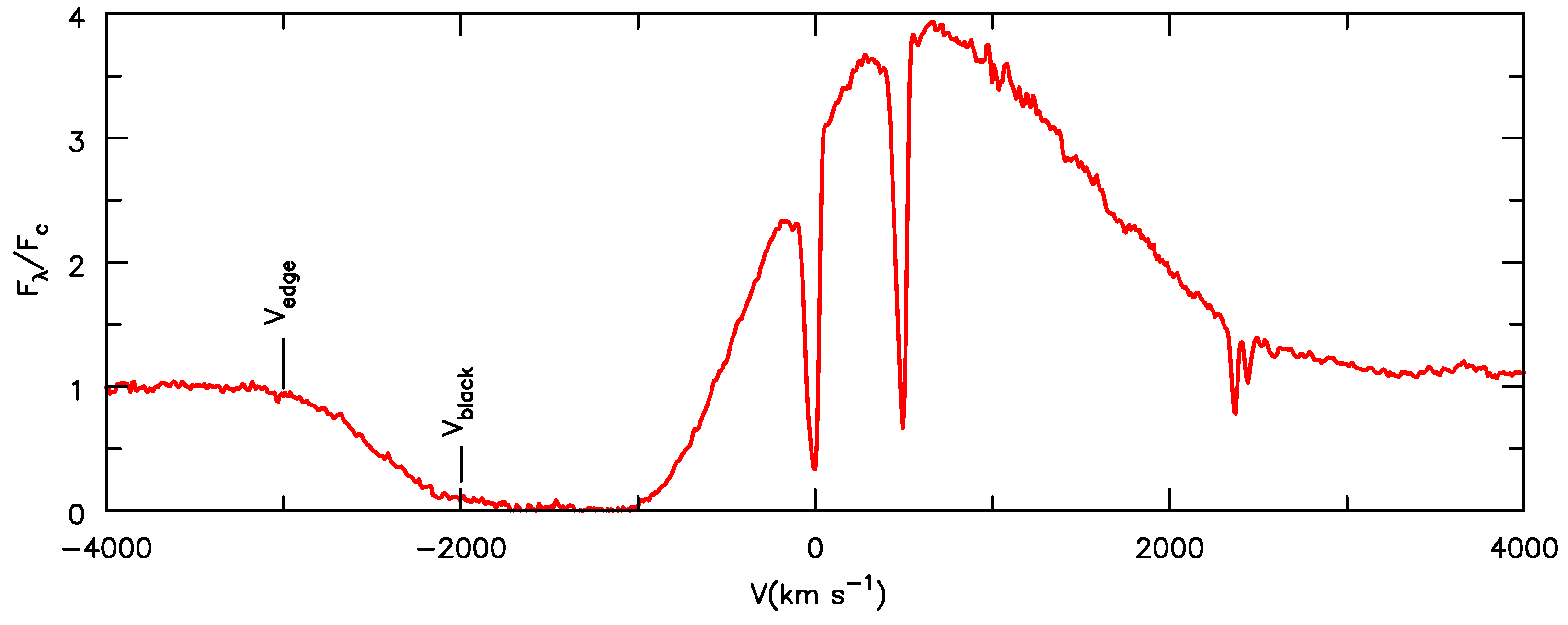
3. Structure of Hot Star Winds
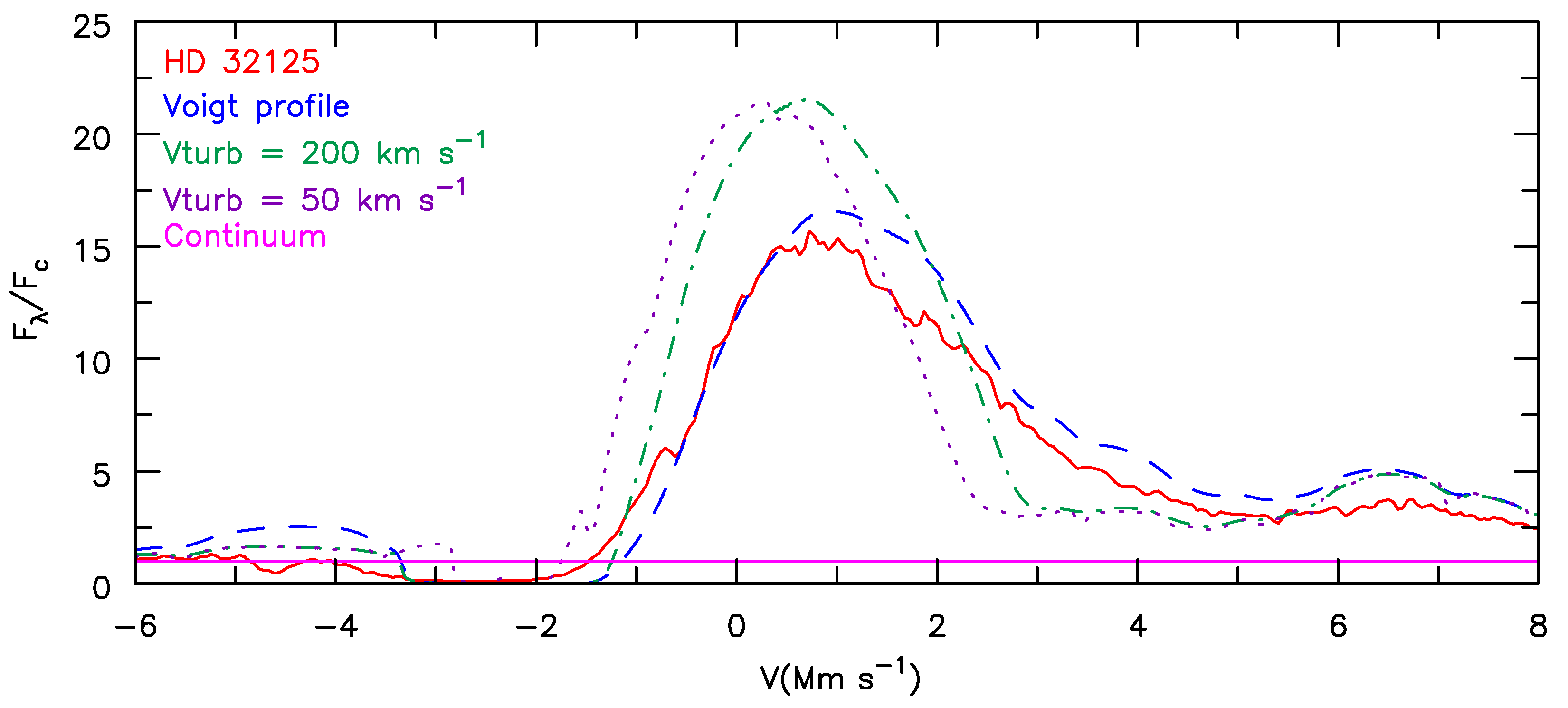
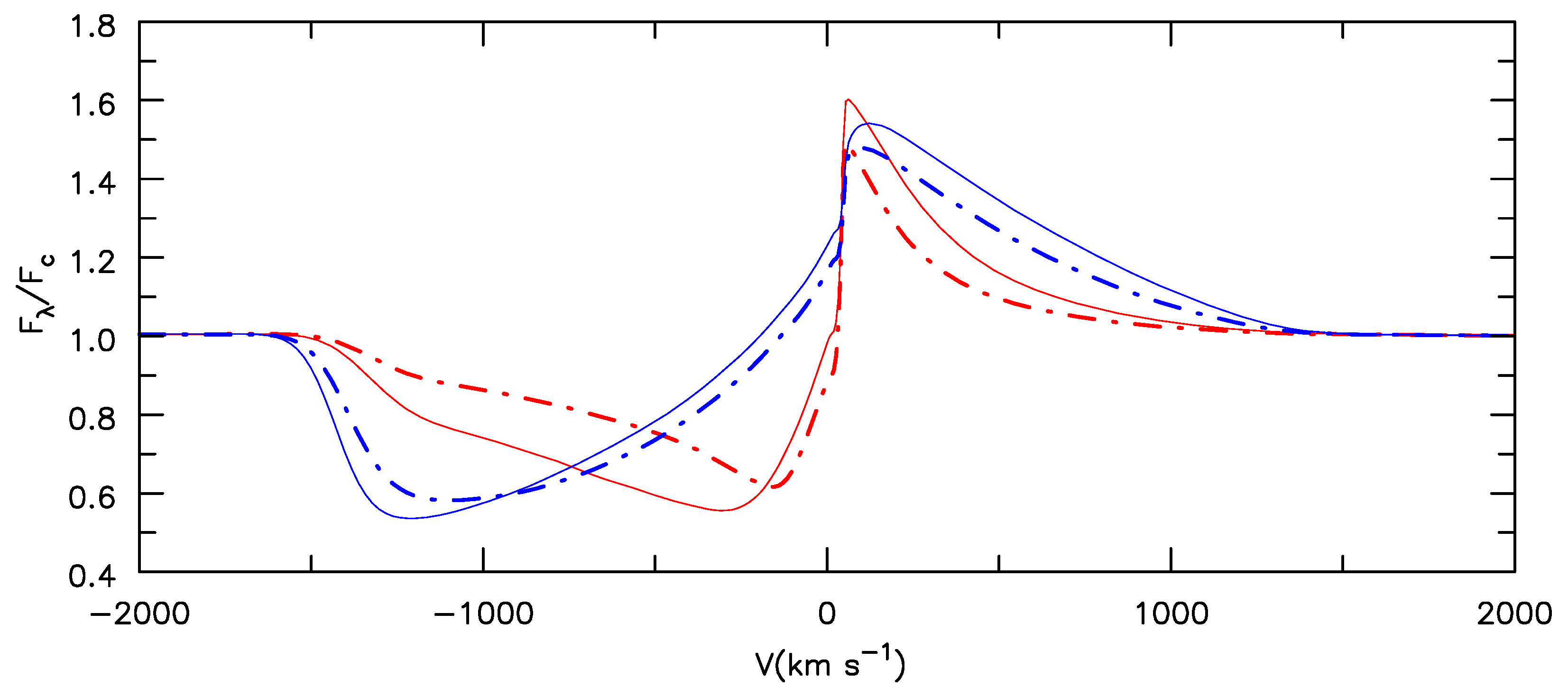
4. Modelling of the UV Spectra
4.1. Single Stars
4.2. Models with Rotation
4.3. Binaries
5. UV Nuggets
5.1. Mass-Loss Diagnostics Using UV Spectral Lines
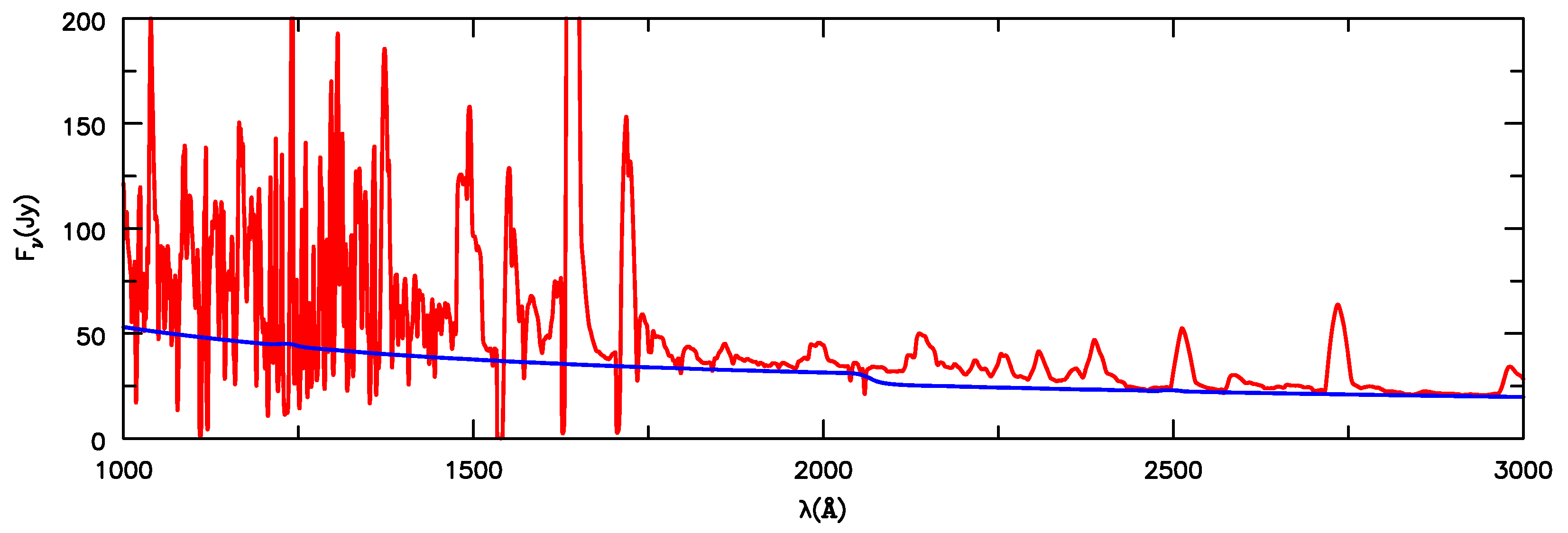
5.2. The Extreme Ultraviolet
5.3. Weak Winds
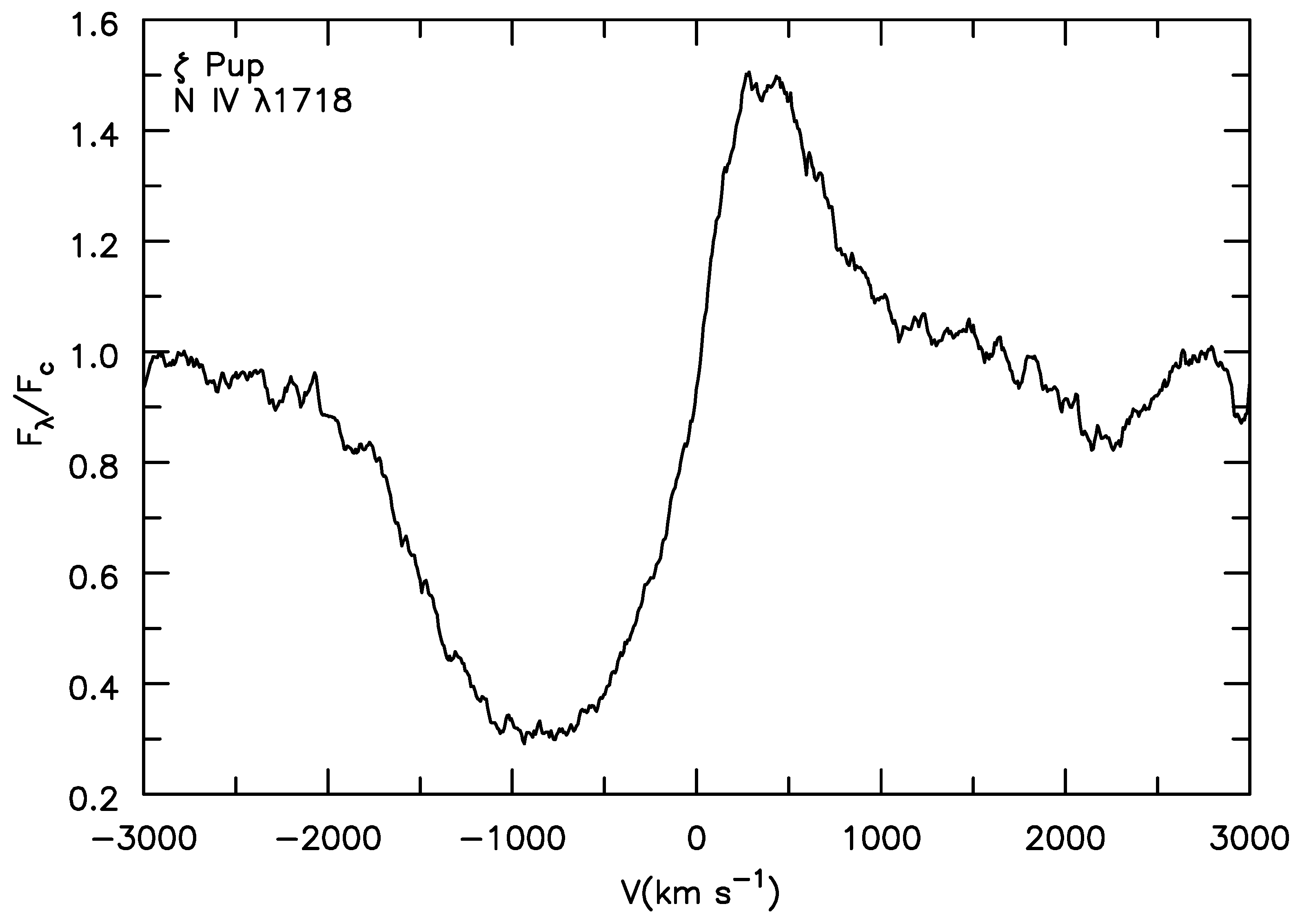
5.4. Superions
5.5. Non Galactic/Magellanic Studies
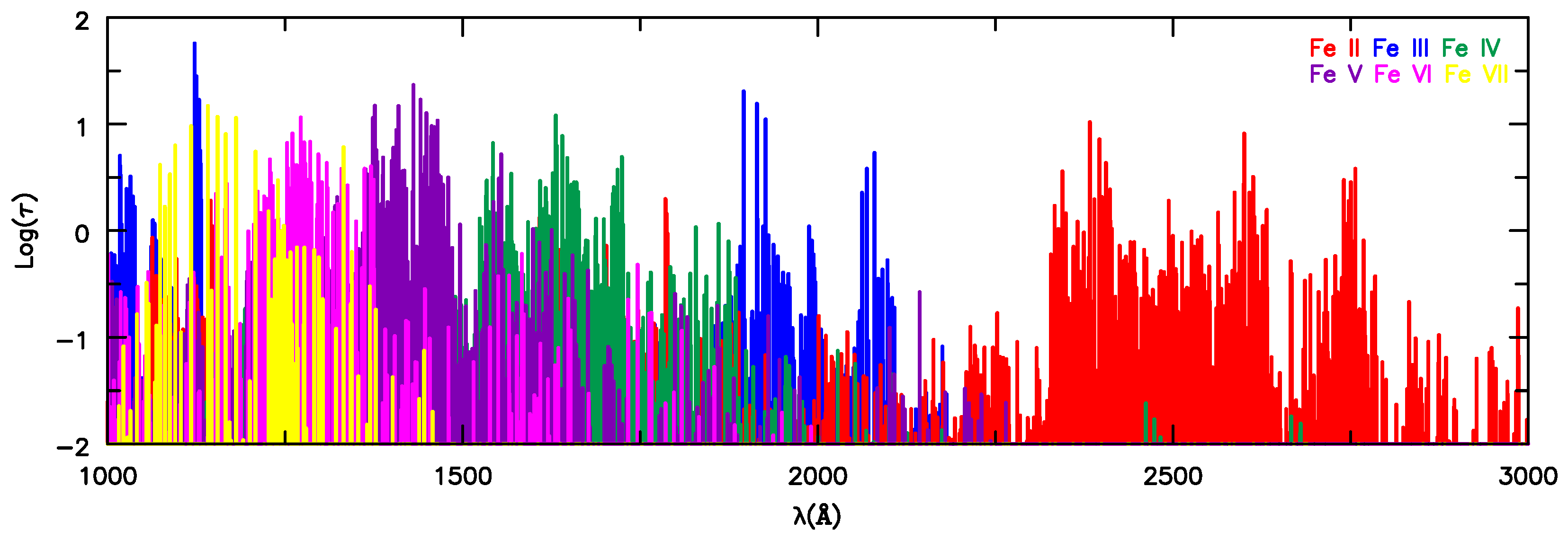
5.6. The Iron Forest
6. Other Classes of Massive Stars
6.1. Modelling of Wolf–Rayet Stars
6.2. O Stars with Strong Magnetic Fields
6.3. LBVs
7. Inferences from the UV
7.1. and
7.2. On the Accuracy of UV Mass-Loss Rates
8. Conclusions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CAK | Castor, Abbott, and Klein |
| CV | cataclysmic variable |
| DACs | discrete absorption components |
| BSG | blue supergiant |
| FUSE | Far Ultraviolet Spectroscopic Explorer |
| HR | Hertzsprung-Russell |
| IUE | International Ultraviolet Explorer |
| LBV | luminous blue variable |
| LMC | Large Magellanic Cloud |
| MC | Monte Carlo |
| RSG | red supergiant |
| SMC | Small Magellanic Cloud |
| SN(e) | supernova(e) |
| ULLYSES | Ultraviolet Legacy Library of Young Stars as Essential Standards |
| YSG | yellow supergiant |
| WR | Wolf–Rayet |
| ZAMS | zero-age main sequence |
References
- Morton, D.C.; Spitzer, L., Jr. Line Spectra of Delta and pi Scorpii in the Far-Ultraviolet. Astrophys. J. 1966, 144, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morton, D.C. The Far-Ultraviolet Spectra of Six Stars in Orion. Astrophys. J. 1967, 147, 1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beals, C.S. The Spectra of the P Cygni Stars. Publ. Dom. Astrophys. Obs. Vic. 1953, 9, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groh, J.H.; Meynet, G.; Georgy, C.; Ekström, S. Fundamental properties of core-collapse supernova and GRB progenitors: Predicting the look of massive stars before death. Astron. Astrophys. 2013, 558, A131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smartt, S.J. Progenitors of Core-Collapse Supernovae. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 2009, 47, 63–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smartt, S.J. Observational Constraints on the Progenitors of Core-Collapse Supernovae: The Case for Missing High-Mass Stars. Publ. Astron. Soc. Australia 2015, 32, e016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, B.; Beasor, E.R. ’On the red supergiant problem’: A rebuttal, and a consensus on the upper mass cut-off for II-P progenitors. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2020, 496, L142–L146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrell, E.J.; Groh, J.H.; Meynet, G.; Eldridge, J.J. The uncertain masses of progenitors of core-collapse supernovae and direct-collapse black holes. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2020, 494, L53–L58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dessart, L.; Hillier, D.J. The difficulty of inferring progenitor masses from type-II-Plateau supernova light curves. Astron. Astrophys. 2019, 625, A9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, E.; Ott, C.D. Black Hole Formation in Failing Core-Collapse Supernovae. Astrophys. J. 2011, 730, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukhbold, T.; Woosley, S.E. The Compactness of Presupernova Stellar Cores. Astrophys. J. 2014, 783, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meynet, G.; Chomienne, V.; Ekström, S.; Georgy, C.; Granada, A.; Groh, J.; Maeder, A.; Eggenberger, P.; Levesque, E.; Massey, P. Impact of mass-loss on the evolution and pre-supernova properties of red supergiants. Astron. Astrophys. 2015, 575, A60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, L.F. A revised spectral classification system and a new catalogue for galactic Wolf–Rayet stars. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1968, 138, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, A.V.; Conti, P.S.; Massey, P. Spectroscopic studies of Wolf–Rayet stars. III—The WC subclass. Astrophys. J. 1986, 300, 379–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conti, P.S.; Leep, M.E.; Perry, D.N. The spectra of Wolf–Rayet stars. I. Optical line strengths and the hydrogen-to-helium ratios in WN type stars. Astrophys. J. 1983, 268, 228–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massey, P.; Hunter, D.A. Star Formation in R136: A Cluster of O3 Stars Revealed by Hubble Space Telescope Spectroscopy. Astrophys. J. 1998, 493, 180–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamann, W.R.; Gräfener, G.; Liermann, A.; Hainich, R.; Sander, A.A.C.; Shenar, T.; Ramachand ran, V.; Todt, H.; Oskinova, L.M. The Galactic WN stars revisited. Impact of Gaia distances on fundamental stellar parameters. Astron. Astrophys. 2019, 625, A57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crowther, P.A.; Hillier, D.J.; Smith, L.J. Fundamental parameters of Wolf–Rayet stars. II. Tailored analyses of Galactic WNL stars. Astron. Astrophys. 1995, 293, 403–426. [Google Scholar]
- Hamann, W.R.; Gräfener, G.; Liermann, A. The Galactic WN stars. Spectral analyses with line-blanketed model atmospheres versus stellar evolution models with and without rotation. Astron. Astrophys. 2006, 457, 1015–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, C.; Müller, B.; Heger, A.; Pakmor, R.; Springel, V. Black Hole Formation and Fallback during the Supernova Explosion of a 40 M⊙ Star. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2018, 852, L19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ensman, L.M.; Woosley, S.E. Explosions in Wolf–Rayet stars and Type Ib supernovae. I—Light curves. Astrophys. J. 1988, 333, 754–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dessart, L.; Hillier, D.J.; Li, C.; Woosley, S. On the nature of supernovae Ib and Ic. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2012, 424, 2139–2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taddia, F.; Stritzinger, M.D.; Bersten, M.; Baron, E.; Burns, C.; Contreras, C.; Holmbo, S.; Hsiao, E.Y.; Morrell, N.; Phillips, M.M.; et al. The Carnegie Supernova Project I. Analysis of stripped-envelope supernova light curves. Astron. Astrophys. 2018, 609, A136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podsiadlowski, P.; Joss, P.C.; Hsu, J.J.L. Presupernova evolution in massive interacting binaries. Astrophys. J. 1992, 391, 246–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippenko, A.V. Optical Spectra of Supernovae. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 1997, 35, 309–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuncarayakti, H.; Anderson, J.P.; Galbany, L.; Maeda, K.; Hamuy, M.; Aldering, G.; Arimoto, N.; Doi, M.; Morokuma, T.; Usuda, T. Constraints on core-collapse supernova progenitors from explosion site integral field spectroscopy. Astron. Astrophys. 2018, 613, A35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woosley, S.E.; Heger, A. The Progenitor Stars of Gamma-Ray Bursts. Astrophys. J. 2006, 637, 914–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najarro, F.; Herrero, A.; Verdugo, E. Massive stars in the UV. Astrophys. Space Sci. 2006, 303, 153–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, F. UV, optical and near-IR diagnostics of massive stars. Bull. De La Soc. R. Des Sci. De Liege 2011, 80, 29–41. [Google Scholar]
- Crowther, P.A. Physical Properties of Wolf–Rayet Stars. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 2007, 45, 177–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puls, J.; Vink, J.S.; Najarro, F. Mass loss from hot massive stars. Astron. Astrophys. Rev. 2008, 16, 209–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, F. Empirical Properties of Very Massive Stars. In Very Massive Stars in the Local Universe; Vink, J.S., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; Volume 412, pp. 9–42. [Google Scholar]
- Walborn, N.R.; Fitzpatrick, E.L. The OB Zoo: A Digital Atlas of Peculiar Spectra. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 2000, 112, 50–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snow, T.P., Jr.; Morton, D.C. Copernicus ultraviolet observations of mass-loss effects in O and B stars. Astrophys. J. Suppl. 1976, 32, 429–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snow, T.P., Jr.; Jenkins, E.B. A catalog of 0.2 Å resolution far-ultraviolet stellar spectra measured with Copernicus. Astrophys. J. Suppl. 1977, 33, 269–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walborn, N.R.; Bohlin, R.C. An Atlas of OB Spectra from 1000A to 1200A. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 1996, 108, 477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walborn, N.R.; Nichols-Bohlin, J.; Panek, R.J. International Ultraviolet Explorer Atlas of O-Type Spectra from 1200 to 1900 Å. NASA Ref. Publ.; 1985; 1155. Available online: https://ui.adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/1995NASRP1363.....W/abstract (accessed on 12 August 2020).
- Walborn, N.R.; Parker, J.W.; Nichols, J.S. International Ultraviolet Explorer Atlas of B-Type Spectra from 1200 to 1900 Å. NASA Ref. Publ.; 1995; 1363. Available online: Phttps://ui.adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/1985NASRP1155.....W/abstract (accessed on 12 August 2020).
- Walborn, N.R.; Nichols-Bohlin, J. Ultraviolet spectral morphology of the O stars. IV. The OB supergiantsequence. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 1987, 99, 40–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellerin, A.; Fullerton, A.W.; Robert, C.; Howk, J.C.; Hutchings, J.B.; Walborn, N.R.; Bianchi, L.; Crowther, P.A.; Sonneborn, G. An Atlas of Galactic OB Spectra Observed with the Far Ultraviolet Spectroscopic Explorer. Astrophys. J. Suppl. 2002, 143, 159–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walborn, N.R.; Fullerton, A.W.; Crowther, P.A.; Bianchi, L.; Hutchings, J.B.; Pellerin, A.; Sonneborn, G.; Willis, A.J. Far Ultraviolet Spectroscopic Explorer Atlas of OB Stars in the Magellanic Clouds. Astrophys. J. Suppl. 2002, 141, 443–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crowther, P.A.; Hillier, D.J.; Evans, C.J.; Fullerton, A.W.; De Marco, O.; Willis, A.J. Revised Stellar Temperatures for Magellanic Cloud O Supergiants from Far Ultraviolet Spectroscopic Explorer and Very Large Telescope UV-Visual Echelle Spectrograph Spectroscopy. Astrophys. J. 2002, 579, 774–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massa, D.; Fullerton, A.W.; Sonneborn, G.; Hutchings, J.B. Constraints on the Ionization Balance of Hot-Star Winds from FUSE Observations of O Stars in the Large Magellanic Cloud. Astrophys. J. 2003, 586, 996–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fullerton, A.W.; Massa, D.L.; Prinja, R.K. The Discordance of Mass-Loss Estimates for Galactic O-Type Stars. Astrophys. J. 2006, 637, 1025–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walborn, N.R.; Lennon, D.J.; Heap, S.R.; Lindler, D.J.; Smith, L.J.; Evans, C.J.; Parker, J.W. The Ultraviolet and Optical Spectra of Metal-deficient O Stars in the Small Magellanic Cloud. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 2000, 112, 1243–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dean, C.A.; Bruhweiler, F.C. An ultraviolet line list for O star spectra. Astrophys. J. Suppl. 1985, 57, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayres, T.R.; The ASTRAL I & II Science Teams. The Advanced Spectral Library (ASTRAL) Project. In American Astronomical Society Meeting Abstracts; American Astronomical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 2014; Volume 223, p. 254.37. [Google Scholar]
- Willis, A.J.; van der Hucht, K.A.; Conti, P.S.; Garmany, D. An atlas of high resolution IUE ultraviolet spectra of 14 Wolf–Rayet stars. Astron. Astrophys. Suppl. 1986, 63, 417–599. [Google Scholar]
- Schulte-Ladbeck, R.E.; Hillier, D.J.; Herald, J.E. The Hopkins Ultraviolet Telescope Far-Ultraviolet Spectral Atlas of Wolf–Rayet Stars. Astrophys. J. Lett. 1995, 454, L51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willis, A.J.; Crowther, P.A.; Fullerton, A.W.; Hutchings, J.B.; Sonneborn, G.; Brownsberger, K.; Massa, D.L.; Walborn, N.R. An Atlas of Far-Ultraviolet Spectra of Wolf–Rayet Stars from the FUSE Satellite. Astrophys. J. Suppl. 2004, 154, 651–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucy, L.B.; Solomon, P.M. Mass Loss by Hot Stars. Astrophys. J. 1970, 159, 879–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owocki, S.P.; Castor, J.I.; Rybicki, G.B. Time-dependent models of radiatively driven stellar winds. I— Nonlinear evolution of instabilities for a pure absorption model. Astrophys. J. 1988, 335, 914–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantiello, M.; Langer, N.; Brott, I.; de Koter, A.; Shore, S.N.; Vink, J.S.; Voegler, A.; Lennon, D.J.; Yoon, S.C. Sub-surface convection zones in hot massive stars and their observable consequences. Astron. Astrophys. 2009, 499, 279–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantiello, M.; Braithwaite, J.; Brandenburg, A.; Del Sordo, F.; Käpylä, P.; Langer, N. 3D MHD simulations of subsurface convection in OB stars. In Active OB Stars—Structure, Evolution, Mass Loss, and Critical Limits, IAU Symposium 272; Neiner, C., Wade, G., Meynet, G., Peters, G., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2011; pp. 32–37. [Google Scholar]
- Hillier, D.J.; Miller, D.L. Constraints on the Evolution of Massive Stars through Spectral Analysis. I. The WC5 Star HD 165763. Astrophys. J. 1999, 519, 354–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundqvist, J.O.; Puls, J.; Owocki, S.P. Mass loss from inhomogeneous hot star winds. III. An effective-opacity formalism for line radiative transfer in accelerating, clumped two-component media, and first results on theory and diagnostics. Astron. Astrophys. 2014, 568, A59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owocki, S.P. Dynamical simulation of the “velocity-porosity” reduction in observed strength of stellar wind lines. In Clumping in Hot-Star Winds; Hamann, W.R., Feldmeier, A., Oskinova, L.M., Eds.; Universitätsverlag Potsdam: Potsdam, Germany, 2008; pp. 121–124. [Google Scholar]
- Owocki, S.P.; Cohen, D.H. The Effect of Porosity on X-ray Emission-Line Profiles from Hot-Star Winds. Astrophys. J. 2006, 648, 565–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oskinova, L.M.; Hamann, W.R.; Feldmeier, A. Neglecting the porosity of hot-star winds can lead to underestimating mass-loss rates. Astron. Astrophys. 2007, 476, 1331–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šurlan, B.; Hamann, W.R.; Aret, A.; Kubát, J.; Oskinova, L.M.; Torres, A.F. Macroclumping as solution of the discrepancy between Hα and P v mass loss diagnostics for O-type stars. Astron. Astrophys. 2013, 559, A130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundqvist, J.O.; Puls, J. Atmospheric NLTE models for the spectroscopic analysis of blue stars with winds. IV. Porosity in physical and velocity space. Astron. Astrophys. 2018, 619, A59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eversberg, T.; Lépine, S.; Moffat, A.F.J. Outmoving Clumps in the Wind of the Hot O Supergiant ζ Puppis. Astrophys. J. 1998, 494, 799–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchenko, S.V.; Moffat, A.F.J.; Eversberg, T.; Morel, T.; Hill, G.M.; Tovmassian, G.H.; Seggewiss, W. A comprehensive variability study of the enigmatic WN8 stars—Final results. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1998, 294, 642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lépine, S.; Moffat, A.F.J. Wind Inhomogeneities in Wolf–Rayet Stars. II. Investigation of Emission-Line Profile Variations. Astrophys. J. 1999, 514, 909–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaper, L.; Henrichs, H.F.; Nichols, J.S.; Snoek, L.C.; Volten, H.; Zwarthoed, G.A.A. Long- and short-term variability in O-star winds. I. Time series of UV spectra for 10 bright O stars. Astron. Astrophys. Suppl. 1996, 116, 257–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snow, T.P., Jr. Long-term changes in ultraviolet P Cygni profiles observed with Copernicus. Astrophys. J. 1977, 217, 760–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massa, D.; Fullerton, A.W.; Nichols, J.S.; Owocki, S.P.; Prinja, R.K.; St-Louis, N.; Willis, A.J.; Altner, B.; Bolton, C.T.; Cassinelli, J.P.; et al. The IUE MEGA Campaign: Wind Variability and Rotation in Early-Type Stars. Astrophys. J. Lett. 1995, 452, L53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howarth, I.D.; Prinja, R.K.; Massa, D. The IUE MEGA Campaign: The Rotationally Modulated Wind of zeta Puppis. Astrophys. J. Lett. 1995, 452, L65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- St-Louis, N.; Dalton, M.J.; Marchenko, S.V.; Moffat, A.F.J.; Willis, A.J. The IUE MEGA Campaign: Wind Structure and Variability of HD 50896 (WN5). Astrophys. J. Lett. 1995, 452, L57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Prinja, R.K.; Massa, D.; Fullerton, A.W. The IUE MEGA Campaign: Modulated Structure in the Wind of HD 64760 (B0.5 Ib). Astrophys. J. Lett. 1995, 452, L61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berghoefer, T.W.; Baade, D.; Schmitt, J.H.M.M.; Kudritzki, R.P.; Puls, J.; Hillier, D.J.; Pauldrach, A.W.A. Correlated variability in the X-ray and Hα emission from the O4If supergiant ζ Puppis. Astron. Astrophys. 1996, 306, 899. [Google Scholar]
- Reid, A.H.N.; Howarth, I.D. Optical time-series spectroscopy of the O4 supergiant ζ Puppis. Astron. Astrophys. 1996, 311, 616–630. [Google Scholar]
- Schmutz, W.; Koenigsberger, G. Long uninterrupted photometric observations of the Wolf–Rayet star EZ CMa by the Toronto BRITE satellite reveal a very fast apsidal motion. Astron. Astrophys. 2019, 624, L3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koenigsberger, G.; Schmutz, W. The nature of the companion in the Wolf–Rayet system EZ Canis Majoris. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2005.06028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassinelli, J.P.; Swank, J.H. X-ray spectra of Orion OB supergiants. Astrophys. J. 1983, 271, 681–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, D.H.; Wollman, E.E.; Leutenegger, M.A.; Sundqvist, J.O.; Fullerton, A.W.; Zsargó, J.; Owocki, S.P. Measuring mass-loss rates and constraining shock physics using X-ray line profiles of O stars from the Chandra archive. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2014, 439, 908–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardelli, J.A.; Clayton, G.C.; Mathis, J.S. The relationship between infrared, optical, and ultraviolet extinction. Astrophys. J. 1989, 345, 245–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmutz, W. Observations Versus Atmospheric Models of WR Stars (review). In Wolf–Rayet Stars and Interrelations with Other Massive Stars in Galaxies, IAU Symposium 143; van der Hucht, K.A., Hidayat, B., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 1991; pp. 39–52. [Google Scholar]
- Lamers, H.J.G.L.M.; Cerruti-Sola, M.; Perinotto, M. The “SEI” Method for Accurate and Efficient Calculations of Line Profiles in Spherically Symmetric Stellar Winds. Astrophys. J. 1987, 314, 726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamann, W.R. Line formation in expanding atmospheres: On the validity of the Sobolev approximation. Astron. Astrophys. 1981, 93, 353–361. [Google Scholar]
- Sundqvist, J.O.; Puls, J.; Feldmeier, A. Mass loss from inhomogeneous hot star winds. I. Resonance line formation in 2D models. Astron. Astrophys. 2010, 510, A11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šurlan, B.; Hamann, W.R.; Kubát, J.; Oskinova, L.M.; Feldmeier, A. Three-dimensional radiative transfer in clumped hot star winds. I. Influence of clumping on the resonance line formation. Astron. Astrophys. 2012, 541, A37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurucz, R.L. Atlas: A Computer Program for Calculating Model Stellar Atmospheres; SAO Special Report #309; Smithsonian Institution, Astrophysical Observatory: Cambridge, UK, 1970. [Google Scholar]
- Kurucz, R.L. Model atmospheres for G, F, A, B, and O stars. Astrophys. J. Suppl. 1979, 40, 1–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubeny, I.; Lanz, T. Non-LTE line-blanketed model atmospheres of hot stars. 1: Hybrid complete linearization/accelerated lambda iteration method. Astrophys. J. 1995, 439, 875–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Przybilla, N.; Butler, K.; Becker, S.R.; Kudritzki, R.P.; Venn, K.A. Non-LTE line formation for neutral oxygen. Model atom and first results on A-type stars. Astron. Astrophys. 2000, 359, 1085–1106. [Google Scholar]
- Hummer, D.G. The effect of reflected and external radiation on stellar flux distributions. Astrophys. J. 1982, 257, 724–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauldrach, A.W.A.; Hoffmann, T.L.; Lennon, M. Radiation-driven winds of hot luminous stars. XIII. A description of NLTE line blocking and blanketing towards realistic models for expanding atmospheres. Astron. Astrophys. 2001, 375, 161–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gräfener, G.; Koesterke, L.; Hamann, W.R. Line-blanketed model atmospheres for WR stars. Astron. Astrophys. 2002, 387, 244–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sander, A.; Shenar, T.; Hainich, R.; Gímenez-García, A.; Todt, H.; Hamann, W.R. On the consistent treatment of the quasi-hydrostatic layers in hot star atmospheres. Astron. Astrophys. 2015, 577, A13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krtička, J.; Kubát, J. Comoving frame models of hot star winds. II. Reduction of O star wind mass-loss rates in global models. Astron. Astrophys. 2017, 606, A31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillier, D.J. WC stars—Hot stars with cold winds. Astrophys. J. 1989, 347, 392–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillier, D.J. An iterative method for the solution of the statistical and radiative equilibrium equations in expanding atmospheres. Astron. Astrophys. 1990, 231, 116–124. [Google Scholar]
- Puls, J.; Urbaneja, M.A.; Venero, R.; Repolust, T.; Springmann, U.; Jokuthy, A.; Mokiem, M.R. Atmospheric NLTE-models for the spectroscopic analysis of blue stars with winds. II. Line-blanketed models. Astron. Astrophys. 2005, 435, 669–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carneiro, L.P.; Puls, J.; Hoffmann, T.L.; Holgado, G.; Simón-Díaz, S. Surface abundances of CNO in Galactic O-stars: A pilot study with FASTWIND. Astron. Astrophys. 2019, 623, A3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puls, J. FASTWIND reloaded: Complete comoving frame transfer for “all” contributing lines. In The Lives and Death-Throes of Massive Stars, IAU Symposium 329; Eldridge, J.J., Bray, J.C., McClelland, L.A.S., Xiao, L., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2017; p. 435. [Google Scholar]
- Sander, A.A.C.; Hamann, W.R.; Todt, H.; Hainich, R.; Shenar, T. Coupling hydrodynamics with comoving frame radiative transfer. I. A unified approach for OB and WR stars. Astron. Astrophys. 2017, 603, A86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sander, A.A.C.; Vink, J.S.; Hamann, W.R. Driving classical Wolf–Rayet winds: A Γ- and Z-dependent mass-loss. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2020, 491, 4406–4425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouret, J.C.; Lanz, T.; Martins, F.; Marcolino, W.L.F.; Hillier, D.J.; Depagne, E.; Hubeny, I. Massive stars at low metallicity. Evolution and surface abundances of O dwarfs in the SMC. Astron. Astrophys. 2013, 555, A1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauldrach, A.W.A.; Kudritzki, R.P.; Puls, J.; Butler, K.; Hunsinger, J. Radiation-driven winds of hot luminous stars. 12: A first step towards detailed UV-line diagnostics of O-stars. Astron. Astrophys. 1994, 283, 525–560. [Google Scholar]
- Pauldrach, A.W.A.; Kudritzki, R.P.; Puls, J.; Butler, K. Radiation driven winds of hot luminous stars. VII— The evolution of massive stars and the morphology of stellar wind spectra. Astron. Astrophys. 1990, 228, 125–154. [Google Scholar]
- Castor, J.I.; Abbott, D.C.; Klein, R.I. Radiation-driven winds in Of stars. Astrophys. J. 1975, 195, 157–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauldrach, A.; Puls, J.; Kudritzki, R.P. Radiation-driven winds of hot luminous stars—Improvements of the theory and first results. Astron. Astrophys. 1986, 164, 86–100. [Google Scholar]
- Gray, D.F. The Observation and Analysis of Stellar Photospheres, 2nd ed.; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Hillier, D.J.; Bouret, J.C.; Lanz, T.; Busche, J.R. The influence of rotation on optical emission profiles of O stars. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2012, 426, 1043–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjorkman, J.E.; Cassinelli, J.P. Equatorial disk formation around rotating stars due to Ram pressure confinement by the stellar wind. Astrophys. J. 1993, 409, 429–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owocki, S.P.; Cranmer, S.R.; Gayley, K.G. Inhibition FO Wind Compressed Disk Formation by Nonradial Line-Forces in Rotating Hot-Star Winds. Astrophys. J. Lett. 1996, 472, L115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owocki, S.P.; Gayley, K.G.; Cranmer, S.R. Effects of Gravity Darkening on Radiatively Driven Mass Loss from Rapidly Rotating Stars. In Boulder-Munich II: Properties of Hot Luminous Stars; ASP Conf. Ser.; Howarth, I., Ed.; Astronomical Society of the Pacific: San Francisco, CA, USA, 1998; Volume 131, pp. 237–244. [Google Scholar]
- Maeder, A. Stellar evolution with rotation IV: Von Zeipel’s theorem and anisotropic losses of mass and angular momentum. Astron. Astrophys. 1999, 347, 185–193. [Google Scholar]
- Simon, K.P.; Sturm, E. Disentangling of composite spectra. Astron. Astrophys. 1994, 281, 286–291. [Google Scholar]
- Palate, M.; Rauw, G. Spectral modelling of circular massive binary systems. Towards an understanding of the Struve-Sahade effect? Astron. Astrophys. 2012, 537, A119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Abdul-Masih, M.; Sana, H.; Conroy, K.E.; Sundqvist, J.; Prša, A.; Kochoska, A.; Puls, J. Spectroscopic patch model for massive stars using PHOEBE II and FASTWIND. Astron. Astrophys. 2020, 636, A59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eaton, J.A.; Cherepashchuk, A.M.; Khaliullin, K.F. Stratification of the Extended Atmosphere of the Wolf–Rayet Component of V444 Cygni. Astrophys. J. 1985, 297, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eaton, J.A.; Cherepashchuk, A.M.; Khaliullin, K.F. Stratification of the Extended Atmosphere of the Wolf–Rayet Component of V444 Cygni: Erratum. Astrophys. J. 1988, 334, 1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koenigsberger, G. Spectral variations in WNE Wolf–Rayet binaries: The Fe V + Fe VI pseudo-continuum. Rev. Mex. Astron. Astrofis. 1988, 16, 75–80. [Google Scholar]
- Koenigsberger, G. The Fe V/Fe VI ionization structure in WNE Wolf–Rayet winds. Astron. Astrophys. 1990, 235, 282. [Google Scholar]
- Stevens, I.R.; Blondin, J.M.; Pollock, A.M.T. Colliding Winds from Early-Type Stars in Binary Systems. Astrophys. J. 1992, 386, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, I.R.; Pollock, A.M.T. Stagnation-point flow in colliding-wind binary systems. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1994, 269, 226–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gayley, K.G.; Owocki, S.P.; Cranmer, S.R. Sudden Radiative Braking in Colliding Hot-Star Winds. Astrophys. J. 1997, 475, 786–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luehrs, S. A Colliding-Wind Model for the Wolf–Rayet System HD 152270. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 1997, 109, 504–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foellmi, C.; Koenigsberger, G.; Georgiev, L.; Toledano, O.; Marchenko, S.V.; Massey, P.; Dall, T.H.; Moffat, A.F.J.; Morrell, N.; Corcoran, M.; et al. New insights into the nature of the SMC WR/LBV binary HD 5980. Rev. Mex. De Astron. Y Astrofis. 2008, 44, 3–27. [Google Scholar]
- Hillier, D.J.; Koenigsberger, G.; Nazé, Y.; Morrell, N.; Barbá, R.H.; Gamen, R. The enigmatic binary system HD 5980. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2019, 486, 725–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, K.E.; Corcoran, M.F.; Gull, T.R.; Hillier, D.J.; Hamaguchi, K.; Ivarsson, S.; Lindler, D.J. η Carinae across the 2003.5 Minimum: Spectroscopic Evidence for Massive Binary Interactions. Astrophys. J. 2007, 660, 669–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Jerkstrand, A.; Fransson, C.; Kozma, C. The 44Ti-powered spectrum of SN 1987A. Astron. Astrophys. 2011, 530, A45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ergon, M.; Fransson, C.; Jerkstrand, A.; Kozma, C.; Kromer, M.; Spricer, K. Monte-Carlo methods for NLTE spectral synthesis of supernovae. Astron. Astrophys. 2018, 620, A156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shingles, L.J.; Sim, S.A.; Kromer, M.; Maguire, K.; Bulla, M.; Collins, C.; Ballance, C.P.; Michel, A.S.; Ramsbottom, C.A.; Röpke, F.K.; et al. Monte Carlo radiative transfer for the nebular phase of Type Ia supernovae. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2020, 492, 2029–2043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, K.S.; Knigge, C. Modeling the Spectral Signatures of Accretion Disk Winds: A New Monte Carlo Approach. Astrophys. J. 2002, 579, 725–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusterer, D.J.; Nagel, T.; Hartmann, S.; Werner, K.; Feldmeier, A. Monte Carlo radiation transfer in CV disk winds: Application to the AM CVn prototype. Astron. Astrophys. 2014, 561, A14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Parkinson, E.J.; Knigge, C.; Long, K.S.; Matthews, J.H.; Higginbottom, N.; Sim, S.A.; Hewitt, H.A. Accretion disc winds in tidal disruption events: Ultraviolet spectral lines as orientation indicators. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2020, 494, 4914–4929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carciofi, A.C.; Bjorkman, J.E. Non-LTE Monte Carlo Radiative Transfer. I. The Thermal Properties of Keplerian Disks around Classical Be Stars. Astrophys. J. 2006, 639, 1081–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clementel, N.; Madura, T.I.; Kruip, C.J.H.; Icke, V.; Gull, T.R. 3D radiative transfer in η Carinae: Application of the SIMPLEX algorithm to 3D SPH simulations of binary colliding winds. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2014, 443, 2475–2491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Clementel, N.; Madura, T.I.; Kruip, C.J.H.; Paardekooper, J.P.; Gull, T.R. 3D radiative transfer simulations of Eta Carinae’s inner colliding winds—I. Ionization structure of helium at apastron. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2015, 447, 2445–2458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hillier, D.J.; Lanz, T.; Heap, S.R.; Hubeny, I.; Smith, L.J.; Evans, C.J.; Lennon, D.J.; Bouret, J.C. A Tale of Two Stars: The Extreme O7 Iaf+ Supergiant AV 83 and the OC7.5 III((f)) star AV 69. Astrophys. J. 2003, 588, 1039–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prinja, R.K.; Massa, D.L. Signature of wide-spread clumping in B supergiant winds. Astron. Astrophys. 2010, 521, L55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Prinja, R.K.; Massa, D.L. Ultraviolet diagnostic of porosity-free mass-loss estimates in B stars. Astron. Astrophys. 2013, 559, A15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Cassinelli, J.P.; Cohen, D.H.; Macfarlane, J.J.; Drew, J.E.; Lynas-Gray, A.E.; Hoare, M.G.; Vallerga, J.V.; Welsh, B.Y.; Vedder, P.W.; Hubeny, I.; et al. EUVE Spectroscopy of epsilon Canis Majoris (B2 II) from 70 to 730 Angstrom. Astrophys. J. 1995, 438, 932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, D.H.; Hurwitz, M.; Cassinelli, J.P.; Bowyer, S. ORFEUS-SPAS II Extreme-Ultraviolet Spectroscopy of epsilon CMa (B2 II). Astrophys. J. Lett. 1998, 500, L51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najarro, F.; Kudritzki, R.P.; Cassinelli, J.P.; Stahl, O.; Hillier, D.J. Stellar winds and the EUV continuum excess of early B-giants. Astron. Astrophys. 1996, 306, 892. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, D.H.; Cassinelli, J.P.; Macfarlane, J.J.; Owocki, S.P. EUV/X-ray Emission and the Thermal and Ionization Structure of B Star Winds. In Thermal and Ionization Aspects of Flows from Hot Stars; ASP Conf. Ser.; Lamers, H., Sapar, A., Eds.; Astronomical Society of the Pacific: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2000; Volume 204, pp. 66–78. [Google Scholar]
- Kewley, L.J.; Nicholls, D.C.; Sutherland, R.S. Understanding Galaxy Evolution Through Emission Lines. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 2019, 57, 511–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morisset, C.; Schaerer, D.; Bouret, J.C.; Martins, F. Mid-IR observations of Galactic H II regions: Constraining ionizing spectra of massive stars and the nature of the observed excitation sequences. Astron. Astrophys. 2004, 415, 577–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stasińska, G.; Gräfener, G.; Pe na, M.; Hamann, W.R.; Koesterke, L.; Szczerba, R. Comprehensive modelling of the planetary nebula LMC-SMP 61 and its [WC]-type central star. Astron. Astrophys. 2004, 413, 329–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morisset, C.; Georgiev, L. A self-consistent stellar and 3D nebular model of planetary nebula IC 418. Astron. Astrophys. 2009, 507, 1517–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danehkar, A.; Todt, H.; Ercolano, B.; Kniazev, A.Y. Observations and three-dimensional photoionization modelling of the Wolf–Rayet planetary nebula Abell 48. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2014, 439, 3605–3615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Reyes-Pérez, J.; Morisset, C.; Pe na, M.; Mesa-Delgado, A. A consistent spectral model of WR 136 and its associated bubble NGC 6888. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2015, 452, 1764–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Walborn, N.R.; Blades, J.C. Spectral Classification of the 30 Doradus Stellar Populations. Astrophys. J. Suppl. 1997, 112, 457–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabín-Sanjulián, C.; Simón-Díaz, S.; Herrero, A.; Walborn, N.R.; Puls, J.; Maíz Apellániz, J.; Evans, C.J.; Brott, I.; de Koter, A.; Garcia, M.; et al. The VLT-FLAMES Tarantula Survey. XIII: On the nature of O Vz stars in 30 Doradus. Astron. Astrophys. 2014, 564, A39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouret, J.C.; Lanz, T.; Hillier, D.J.; Heap, S.R.; Hubeny, I.; Lennon, D.J.; Smith, L.J.; Evans, C.J. Quantitative Spectroscopy of O Stars at Low Metallicity: O Dwarfs in NGC 346. Astrophys. J. 2003, 595, 1182–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, F.; Schaerer, D.; Hillier, D.J.; Heydari-Malayeri, M. Puzzling wind properties of young massive stars in SMC-N81. Astron. Astrophys. 2004, 420, 1087–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, F.; Schaerer, D.; Hillier, D.J.; Meynadier, F.; Heydari-Malayeri, M.; Walborn, N.R. O stars with weak winds: The Galactic case. Astron. Astrophys. 2005, 441, 735–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Almeida, E.S.G.; Marcolino, W.L.F.; Bouret, J.C.; Pereira, C.B. Probing the weak wind phenomenon in Galactic O-type giants. Astron. Astrophys. 2019, 628, A36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oskinova, L.M.; Todt, H.; Ignace, R.; Brown, J.C.; Cassinelli, J.P.; Hamann, W.R. Early magnetic B-type stars: X-ray emission and wind properties. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2011, 416, 1456–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muijres, L.E.; Vink, J.S.; de Koter, A.; Müller, P.E.; Langer, N. Predictions for mass-loss rates and terminal wind velocities of massive O-type stars. Astron. Astrophys. 2012, 537, A37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcolino, W.L.F.; Bouret, J.C.; Martins, F.; Hillier, D.J.; Lanz, T.; Escolano, C. Analysis of Galactic late-type O dwarfs: More constraints on the weak wind problem. Astron. Astrophys. 2009, 498, 837–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassinelli, J.P.; Olson, G.L. The effects of coronal regions on the X-ray flux and ionization conditions in the winds of OB supergiants and Of stars. Astrophys. J. 1979, 229, 304–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouret, J.C.; Hillier, D.J.; Lanz, T.; Fullerton, A.W. Properties of Galactic early-type O-supergiants. A combined FUV-UV and optical analysis. Astron. Astrophys. 2012, 544, A67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zsargó, J.; Hillier, D.J.; Bouret, J.C.; Lanz, T.; Leutenegger, M.A.; Cohen, D.H. On the Importance of the Interclump Medium for Superionization: O VI Formation in the Wind of ζ Puppis. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2008, 685, L149–L152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hearn, A.G. The energy balance and mass loss of stellar coronae. Astron. Astrophys. 1975, 40, 355–364. [Google Scholar]
- Hillier, D.J.; Kudritzki, R.P.; Pauldrach, A.W.; Baade, D.; Cassinelli, J.P.; Puls, J.; Schmitt, J.H.M.M. The 0.1-2.5-KEV X-Ray Spectrum of the O4F-STAR Zeta-Puppis. Astron. Astrophys. 1993, 276, 117. [Google Scholar]
- Cassinelli, J.P.; Miller, N.A.; Waldron, W.L.; MacFarlane, J.J.; Cohen, D.H. Chandra Detection of Doppler-shifted X-Ray Line Profiles from the Wind of ζ Puppis (O4 F). Astrophys. J. Lett. 2001, 554, L55–L58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chlebowski, T. X-ray emission from O-type stars - Parameters which affect it. Astrophys. J. 1989, 342, 1091–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chlebowski, T.; Garmany, C.D. On winds and X-rays of O-type stars. Astrophys. J. 1991, 368, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tramper, F.; Sana, H.; de Koter, A.; Kaper, L. On the Mass-loss Rate of Massive Stars in the Low-metallicity Galaxies IC 1613, WLM, and NGC 3109. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2011, 741, L8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouret, J.C.; Lanz, T.; Hillier, D.J.; Martins, F.; Marcolino, W.L.F.; Depagne, E. No breakdown of the radiatively driven wind theory in low-metallicity environments. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2015, 449, 1545–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, M.; Herrero, A.; Najarro, F.; Lennon, D.J.; Alejandro Urbaneja, M. Winds of Low-metallicity OB-type Stars: HST-COS Spectroscopy in IC 1613. Astrophys. J. 2014, 788, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vink, J.S.; de Koter, A.; Lamers, H.J.G.L.M. Mass-loss predictions for O and B stars as a function of metallicity. Astron. Astrophys. 2001, 369, 574–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucy, L.B. O-star mass-loss rates at low metallicity. Astron. Astrophys. 2012, 543, A18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heap, S.R. Stellar Physics in the Primitive Galaxy, I Zw 18. In Proceedings of the IAU General Assembly, Honolulu, HI, USA, 3–14 August 2015; Volume 29, p. 2257699. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia, M.; Evans, C.J.; Bestenlehner, J.M.; Bouret, J.C.; Castro, N.; Cervi no, M.; Fullerton, A.W.; Gieles, M.; Herrero, A.; de Koter, A.; et al. Massive stars in extremely metal-poor galaxies: A window into the past. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1908.04687. [Google Scholar]
- Abbott, D.C. The theory of radiatively driven stellar winds. II. The line acceleration. Astrophys. J. 1982, 259, 282–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vink, J.S.; de Koter, A.; Lamers, H.J.G.L.M. On the nature of the bi-stability jump in the winds of early-type supergiants. Astron. Astrophys. 1999, 350, 181–196. [Google Scholar]
- Nugis, T.; Lamers, H.J.G.L.M. The mass-loss rates of Wolf–Rayet stars explained by optically thick radiation driven wind models. Astron. Astrophys. 2002, 389, 162–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gräfener, G.; Hamann, W.R. Hydrodynamic model atmospheres for WR stars. Self-consistent modeling of a WC star wind. Astron. Astrophys. 2005, 432, 633–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, F.J.; Iglesias, C.A. Radiative Atomic Rosseland Mean Opacity Tables. Astrophys. J. Suppl. 1992, 79, 507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishii, M.; Ueno, M.; Kato, M. Core-Halo Structure of a Chemically Homogeneous Massive Star and Bending of the Zero-Age Main Sequence. PASJ 1999, 51, 417–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrovic, J.; Pols, O.; Langer, N. Are luminous and metal-rich Wolf–Rayet stars inflated? Astron. Astrophys. 2006, 450, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gräfener, G.; Owocki, S.P.; Vink, J.S. Stellar envelope inflation near the Eddington limit. Implications for the radii of Wolf–Rayet stars and luminous blue variables. Astron. Astrophys. 2012, 538, A40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grassitelli, L.; Chené, A.N.; Sanyal, D.; Langer, N.; St-Louis, N.; Bestenlehner, J.M.; Fossati, L. Diagnostics of the unstable envelopes of Wolf–Rayet stars. Astron. Astrophys. 2016, 590, A12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herald, J.E.; Hillier, D.J.; Schulte-Ladbeck, R.E. Tailored Analyses of the WN 8 Stars WR 40 and WR 16. Astrophys. J. 2001, 548, 932–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sander, A.; Hamann, W.R.; Todt, H. The Galactic WC stars. Stellar parameters from spectral analyses indicate a new evolutionary sequence. Astron. Astrophys. 2012, 540, A144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crowther, P.A.; Dessart, L.; Hillier, D.J.; Abbott, J.B.; Fullerton, A.W. Stellar and wind properties of LMC WC4 stars. A metallicity dependence for Wolf–Rayet mass-loss rates. Astron. Astrophys. 2002, 392, 653–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hainich, R.; Rühling, U.; Todt, H.; Oskinova, L.M.; Liermann, A.; Gräfener, G.; Foellmi, C.; Schnurr, O.; Hamann, W.R. The Wolf–Rayet stars in the Large Magellanic Cloud. A comprehensive analysis of the WN class. Astron. Astrophys. 2014, 565, A27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hainich, R.; Pasemann, D.; Todt, H.; Shenar, T.; Sander, A.; Hamann, W.R. Wolf–Rayet stars in the Small Magellanic Cloud. I. Analysis of the single WN stars. Astron. Astrophys. 2015, 581, A21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neugent, K.F.; Massey, P.; Hillier, D.J.; Morrell, N. The Evolution and Physical Parameters of WN3/O3s: A New Type of Wolf–Rayet Star. Astrophys. J. 2017, 841, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tramper, F.; Gräfener, G.; Hartoog, O.E.; Sana, H.; de Koter, A.; Vink, J.S.; Ellerbroek, L.E.; Langer, N.; Garcia, M.; Kaper, L.; et al. On the nature of WO stars: A quantitative analysis of the WO3 star DR1 in IC 1613. Astron. Astrophys. 2013, 559, A72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bernat, A.P.; Lambert, D.L. Electron scattering in the expanding atmosphere of P Cygni. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 1978, 90, 520–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auer, L.H.; van Blerkom, D. Electron Scattering in Spherically Expanding Envelopes. Astrophys. J. 1972, 178, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillier, D.J. The effects of electron scattering and wind clumping for early emission line stars. Astron. Astrophys. 1991, 247, 455–468. [Google Scholar]
- Najarro, F. Spectroscopy of P Cygni. In P Cygni 2000: 400 Years of Progress; ASP Conf. Ser.; de Groot, M., Sterken, C., Eds.; Astronomical Society of the Pacific: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2001; Volume 233, pp. 133–146. [Google Scholar]
- Groh, J.H.; Hillier, D.J.; Damineli, A.; Whitelock, P.A.; Marang, F.; Rossi, C. On the Nature of the Prototype Luminous Blue Variable Ag Carinae. I. Fundamental Parameters During Visual Minimum Phases and Changes in the Bolometric Luminosity During the S-Dor Cycle. Astrophys. J. 2009, 698, 1698–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koenigsberger, G.; Auer, L.H. IUE observations of phase-dependent variations in WN+O systems. Astrophys. J. 1985, 297, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neugent, K.F.; Massey, P.; Morrell, N. A Modern Search for Wolf–Rayet Stars in the Magellanic Clouds. IV. A Final Census. Astrophys. J. 2018, 863, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, N.; Götberg, Y.; de Mink, S.E. Extreme isolation of WN3/O3 stars and implications for their evolutionary origin as the elusive stripped binaries. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2018, 475, 772–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grunhut, J.H.; Wade, G.A.; Neiner, C.; Oksala, M.E.; Petit, V.; Alecian, E.; Bohlender, D.A.; Bouret, J.C.; Henrichs, H.F.; Hussain, G.A.J.; et al. The MiMeS survey of Magnetism in Massive Stars: Magnetic analysis of the O-type stars. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2017, 465, 2432–2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petit, V.; Wade, G.A.; Schneider, F.R.N.; Fossati, L.; Kamp, K.; Neiner, C.; David-Uraz, A.; Alecian, E.; MiMeS Collaboration. The MiMeS survey of magnetism in massive stars: Magnetic properties of the O-type star population. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2019, 489, 5669–5687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wade, G.A.; Maíz Apellániz, J.; Martins, F.; Petit, V.; Grunhut, J.; Walborn, N.R.; Barbá, R.H.; Gagné, M.; García-Melendo, E.; Jose, J.; et al. NGC 1624-2: A slowly rotating, X-ray luminous Of?cp star with an extraordinarily strong magnetic field. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2012, 425, 1278–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David-Uraz, A.; Erba, C.; Petit, V.; Fullerton, A.W.; Martins, F.; Walborn, N.R.; MacInnis, R.; Barbá, R.H.; Cohen, D.H.; Maíz Apellániz, J.; et al. Extreme resonance line profile variations in the ultraviolet spectra of NGC 1624-2: Probing the giant magnetosphere of the most strongly magnetized known O-type star. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2019, 483, 2814–2824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owocki, S.P.; ud-Doula, A.; Sundqvist, J.O.; Petit, V.; Cohen, D.H.; Townsend, R.H.D. An ‘analytic dynamical magnetosphere’ formalism for X-ray and optical emission from slowly rotating magnetic massive stars. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2016, 462, 3830–3844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, F.; Donati, J.F.; Marcolino, W.L.F.; Bouret, J.C.; Wade, G.A.; Escolano, C.; Howarth, I.D.; Mimes Collaboration. Detection of a magnetic field on HD108: Clues to extreme magnetic braking and the Of?p phenomenon. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2010, 407, 1423–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcolino, W.L.F.; Bouret, J.C.; Walborn, N.R.; Howarth, I.D.; Nazé, Y.; Fullerton, A.W.; Wade, G.A.; Hillier, D.J.; Herrero, A. HST/STIS spectroscopy of the magnetic Of?p star HD 108: The low state at ultraviolet wavelengths. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2012, 422, 2314–2321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundqvist, J.O.; ud-Doula, A.; Owocki, S.P.; Townsend, R.H.D.; Howarth, I.D.; Wade, G.A. A dynamical magnetosphere model for periodic Hα emission from the slowly rotating magnetic O star HD 191612. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2012, 423, L21–L25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howarth, I.D.; Walborn, N.R.; Lennon, D.J.; Puls, J.; Nazé, Y.; Annuk, K.; Antokhin, I.; Bohlender, D.; Bond, H.; Donati, J.F.; et al. Towards an understanding of the Of?p star HD 191612: Optical spectroscopy. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2007, 381, 433–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wade, G.A.; Howarth, I.D.; Townsend, R.H.D.; Grunhut, J.H.; Shultz, M.; Bouret, J.C.; Fullerton, A.; Marcolino, W.; Martins, F.; Nazé, Y.; et al. Confirmation of the magnetic oblique rotator model for the Of?p star HD 191612. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2011, 416, 3160–3169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphreys, R.M.; Davidson, K. The luminous blue variables: Astrophysical geysers. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 1994, 106, 1025–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najarro, F.; Hillier, D.J.; Stahl, O. A spectroscopic investigation of P Cygni. I. H and HeI lines. Astron. Astrophys. 1997, 326, 1117–1134. [Google Scholar]
- Koenigsberger, G.; Morrell, N.; Hillier, D.J.; Gamen, R.; Schneider, F.R.N.; González-Jiménez, N.; Langer, N.; Barbá, R. The HD 5980 Multiple System: Masses and Evolutionary Status. Astron. J. 2014, 148, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgiev, L.; Koenigsberger, G.; Hillier, D.J.; Morrell, N.; Barbá, R.; Gamen, R. Wind Structure and Luminosity Variations in the Wolf–Rayet/Luminous Blue Variable HD 5980. Astron. J. 2011, 142, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shenar, T.; Hainich, R.; Todt, H.; Sander, A.; Hamann, W.R.; Moffat, A.F.J.; Eldridge, J.J.; Pablo, H.; Oskinova, L.M.; Richardson, N.D. Wolf–Rayet stars in the Small Magellanic Cloud. II. Analysis of the binaries. Astron. Astrophys. 2016, 591, A22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobolev, V.V. Moving Envelopes of Stars; Harvard University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1960. [Google Scholar]
- Castor, J.I. Spectral line formation in Wolf–Rayet envelopes. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1970, 149, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prinja, R.K.; Barlow, M.J.; Howarth, I.D. Terminal velocities for a large sample of O stars, B supergiants, and Wolf–Rayet stars. Astrophys. J. 1990, 361, 607–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prinja, R.K.; Barlow, M.J.; Howarth, I.D. Terminal Velocities for a Large Sample of O Stars, B Supergiants, and Wolf–Rayet Stars: Erratum. Astrophys. J. 1991, 383, 466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howarth, I.D.; Phillips, A.P. The ultraviolet spectrum and interstellar environment of HD 50896. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1986, 222, 809–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hillier, D.J. An empirical model for the Wolf–Rayet star HD 50896. Astrophys. J. Suppl. 1987, 63, 965–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catala, C.; Kunasz, P.B.; Praderie, F. Line formation in the wind of AB Aur. Astron. Astrophys. 1984, 134, 402–413. [Google Scholar]
- Shaviv, N.J. The Porous Atmosphere of η Carinae. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2000, 532, L137–L140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaviv, N.J. The theory of steady-state super-Eddington winds and its application to novae. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2001, 326, 126–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Marle, A.J.; Owocki, S.P.; Shaviv, N.J. Numerical simulations of continuum-driven winds of super-Eddington stars. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2008, 389, 1353–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sander, A.A.C.; Hamann, W.R.; Todt, H.; Hainich, R.; Shenar, T.; Ramachandran, V.; Oskinova, L.M. The Galactic WC and WO stars. The impact of revised distances from Gaia DR2 and their role as massive black hole progenitors. Astron. Astrophys. 2019, 621, A92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rate, G.; Crowther, P.A. Unlocking Galactic Wolf–Rayet stars with Gaia DR2—I. Distances and absolute magnitudes. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2020, 493, 1512–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reimers, D. Circumstellar absorption lines and mass loss from red giants. Mem. Soc. R. Des Sci. De Liege 1975, 8, 369–382. [Google Scholar]
- Nugis, T.; Lamers, H.J.G.L.M. Mass-loss rates of Wolf–Rayet stars as a function of stellar parameters. Astron. Astrophys. 2000, 360, 227–244. [Google Scholar]
- Beasor, E.R.; Davies, B.; Smith, N.; van Loon, J.T.; Gehrz, R.D.; Figer, D.F. A new mass-loss rate prescription for red supergiants. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2020, 492, 5994–6006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paxton, B.; Bildsten, L.; Dotter, A.; Herwig, F.; Lesaffre, P.; Timmes, F. Modules for Experiments in Stellar Astrophysics (MESA). Astrophys. J. Suppl. 2011, 192, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mermilliod, J.C.; Maeder, A. Evolution of massive stars: Comparison of cluster sequences and models with mass loss. Astron. Astrophys. 1986, 158, 45–49. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, N.; Owocki, S.P. On the Role of Continuum-driven Eruptions in the Evolution of Very Massive Stars and Population III Stars. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2006, 645, L45–L48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| 1 | Early observations showed the existence of a strong O vi P Cygni profile in many O stars. Since the effective temperature of the star is too low to produce appreciable O, O is termed a superion. |
| 2 | Because of historical precedents, density variations are often referred to as clumping in the literature, and this is often treated/discussed separately from the effects of porosity and vorosity. |
| 3 | In the optical and UV we can assume that the scattering of a photon by an electron is coherent in the frame of the electron (we can ignore the Compton shift). However, in the observer’s frame the scattered (line) photon will be either blueshifted or redshifted depending on relative motion of the electron relative to the source and the observer. In stars like P Cygni, the random thermal motions of the electrons are larger than the wind speed, and profiles typically show symmetric wings with a characteristic width of order 1000 km s(e.g., [186]). However, in WR stars the outflow velocities are larger than typical thermal speeds, and we preferentially see an electron scattering wing on the red side of the line profile [187]. Recall that in an expanding flow with a monotonic velocity, the source is always receding from the scatterer. |
| 4 | The expression for the radial optical depth is only valid when the Sobolev length is less than the wind scale length (r). |

© 2020 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hillier, D.J. UV Spectroscopy of Massive Stars. Galaxies 2020, 8, 60. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies8030060
Hillier DJ. UV Spectroscopy of Massive Stars. Galaxies. 2020; 8(3):60. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies8030060
Chicago/Turabian StyleHillier, D. John. 2020. "UV Spectroscopy of Massive Stars" Galaxies 8, no. 3: 60. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies8030060
APA StyleHillier, D. J. (2020). UV Spectroscopy of Massive Stars. Galaxies, 8(3), 60. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies8030060



