Evidence for Helical Magnetic Fields Associated with AGN Jets and the Action of a Cosmic Battery
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Observational Evidence for Helical B Fields in AGN Jets
2.1. Linear Polarization Structures
Variety of Observed Structures
- (a), (c) Extended regions of longitudinal or orthogonal B field could be associated with helical jet B fields with comparatively low and high pitch angles (i.e., comparatively “loosely-wound” or “tightly- wound” helical fields), respectively. The pitch angle of the helical field should be due in part to the ratio of the velocities of the rotation and outflow.
- (d) A spine-sheath transverse polarization structure refers to a situation in which the predominant B field is orthogonal near the jet axis and longitudinal at one or both edges of the jet. This configuration could be associated with an overall helical field, with the azimuthal component of the field dominant near the jet axis, where its projection is orthogonal to the jet, and the longitudinal component of the helical field dominant near the jet edges, where its projection is along the jet (e.g., [16,17]). In this case, we would also expect to observe an increase in the degree of polarization from the central axis toward the jet edges.
- (e) Depending on the pitch angle of the helical field and the viewing angle of the jet, situations are possible in which the longitudinal B field predominates on one side of the jet, while the orthogonal B is dominant on the other. If the orthogonal B field is too weak to be detected in a particular image, this may also appear as a region of the longitudinal B field offset toward one side of the jet on its own (see, e.g., [18]).
- (f) The well-ordered longitudinal B field around the outer part of a bend in the jet could come about when the longitudinal component of a helical B field is enhanced by the curvature of the jet, stretching the B field at the outer edge of the bend.
2.2. Faraday Rotation Gradients
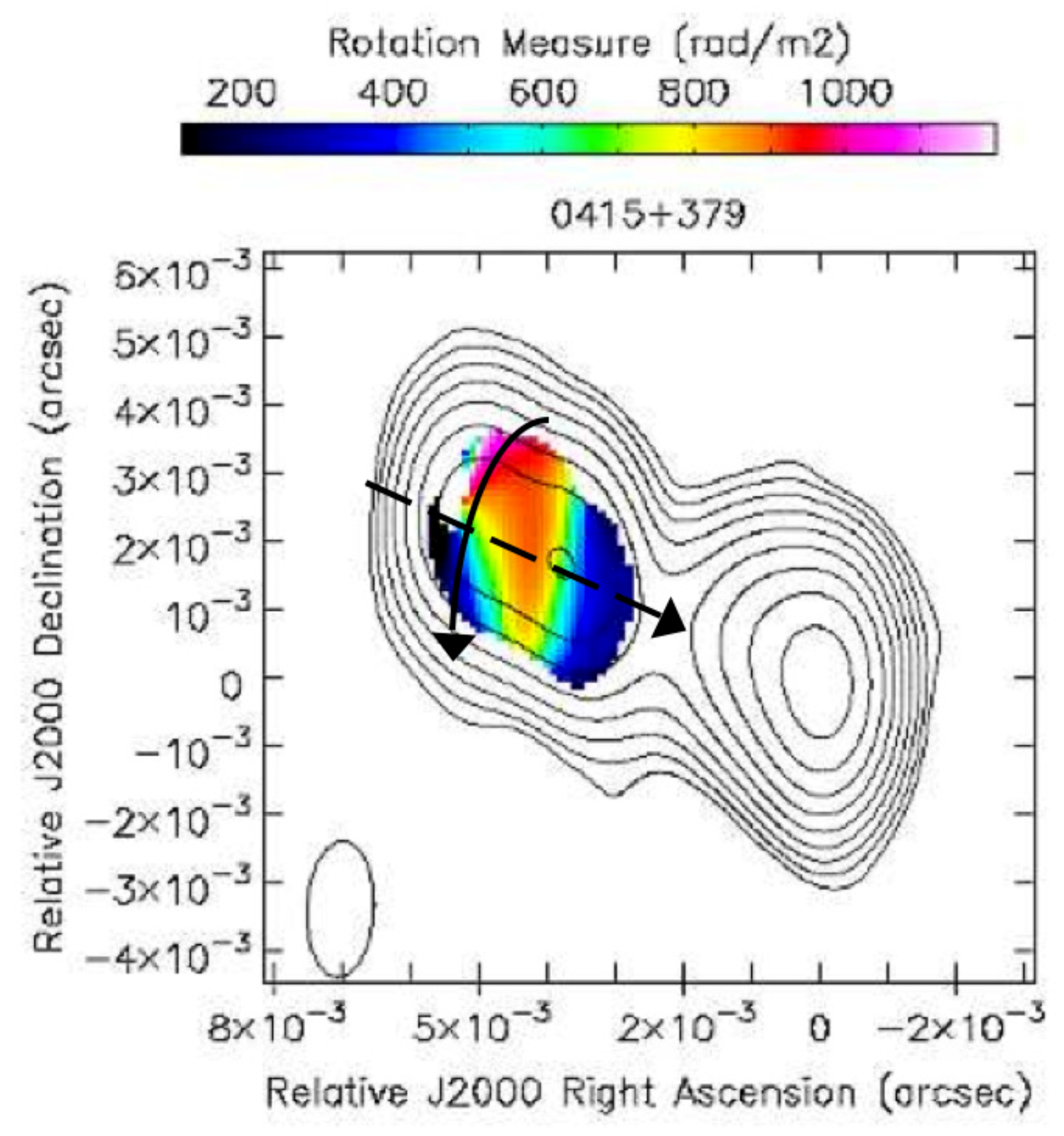
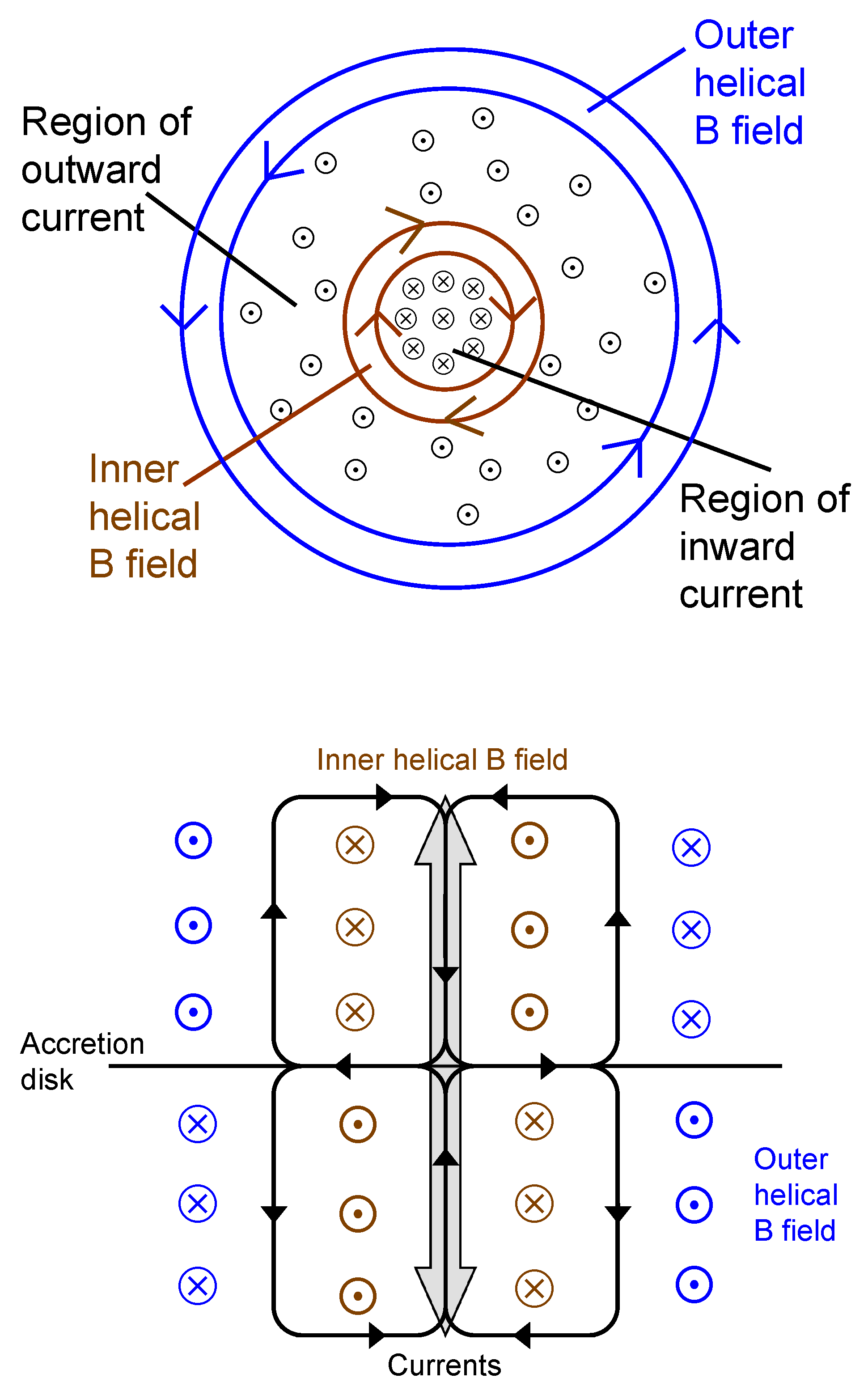
2.2.1. Overall Patterns of the Transverse RM Gradients on pc and kpc Scales: Evidence for the Action of a Cosmic Battery
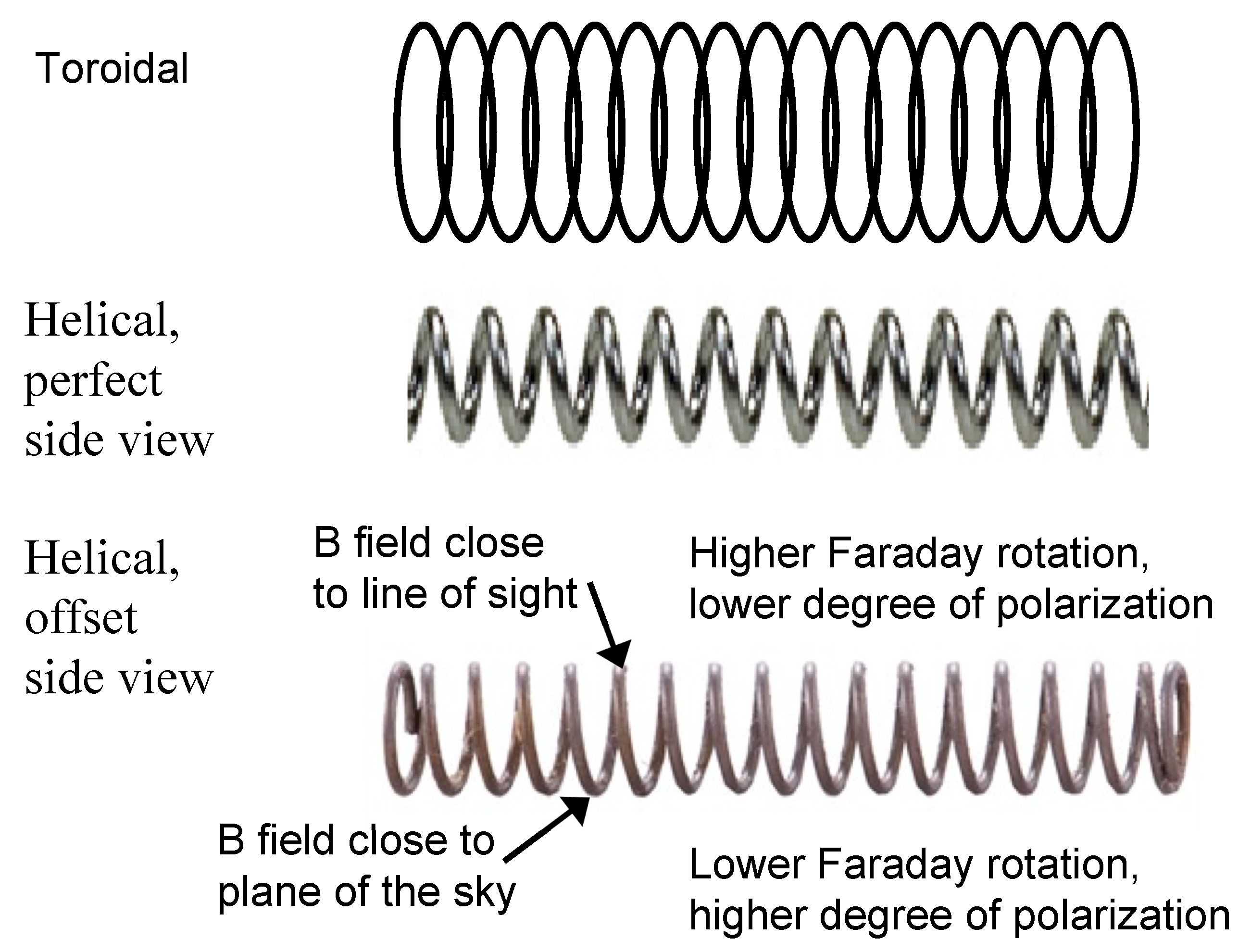
2.2.2. Helical vs. Toroidal Fields
2.3. Variability of the Faraday Rotation Sign
2.4. Inverse Depolarization
2.5. Variability of Jet Ridge Lines
2.6. Large Polarization Angle Rotations Associated with Outbursts
2.7. Double Polarization Angle Rotations
2.8. Circular Polarization
3. Summary
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kellermann, K.I.; Sramek, R.; Schmidt, M.; Shaffer, D.B.; Green, R. VLA observations of objects in the Palomar Bright Quasar Survey. Astron. J. 1989, 98, 1195–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blandford, R.D.; Payne, D.G. Hydromagnetic Flows from Accretion Discs and the Production of Radio Jets. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1982, 199, 883–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blandford, R.D.; Znajek, R.L. Electromagnetic Extraction of Energy from Kerr Black Holes. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1977, 179, 433–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, M.; Uchida, Y.; Hirose, S. Production of Wiggled Structure of AGN Radio Jets in the Wweeping Magnetic Twist Mechanism. New Astron. 2001, 6, 61–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovelace, R.V.E.; Li, H.; Koldoba, A.V.; Ustyugova, G.V.; Romanova, M.M. Poynting Jets from Accretion Disks. Astrophys. J. 2002, 572, 445–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchekhovskoy, A.; Bromberg, O. Three-dimensional Relativistic MHD Simulations of Active Galactic Nuclei Jets: Magnetic Kink Instability and Fanaroff-Riley Dichotomy. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2016, 461, L46–L50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barniol Duran, R.; Tchehovskoy, A.; Giannios, D. Simulations of AGN Jets: Magnetic Kink Instability versus Conical Shocks. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2017, 469, 4957–4978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contopoulos, I.; Christodoulou, D.; Kazanas, D.; Gabuzda, D.C. The Invariant Twist of Magnetic Fields in the Relativistic Jets of Active Galactic Nuclei. Astrophys. J. 2009, 702, L148–L152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christodoulou, D.; Gabuzda, D.; Knuettel, S.; Contopoulos, I.; Kazanas, D.; Coughlan, C. Dominance of Outflowing Electric Currents on Decaparsec to Kiloparsec Scales in Extragalactic Jets. Astron. Astrophys. 2016, 591, A61–A71. [Google Scholar]
- Gabuzda, D.C.; Roche, N.; Kirwan, A.; Knuettel, S.; Nagle, M.; Houston, C. Parsec Scale Faraday-rotation Structure Across the Jets of Nine Active Galactic Nuclei. Astron. Astrophys. 2017, 472, 1792–1801. [Google Scholar]
- Pacholczyk, A.G. Radio Astrophysics; W. H. Freeman: San Franciso, CA, USA, 1970. [Google Scholar]
- Wardle, J.F.C. The Variable Rotation Measure Distribution in 3C 273 on Parsec Scales. Galaxies 2018, 6, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blandford, R.D.; Königl, A. Relativistic Jets as Compact Radio Sources. Astrophys. J. 1979, 232, 34–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lister, M.L.; Homan, D.C. MOJAVE: Monitoring of Jets in Active Galactic Nuclei with VLBA Experiments. I. First-Epoch 15 GHz Linear Polarization Images. Astron. J. 2005, 130, 1389–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabuzda, D.C. Parsec-Scale Jets in Active Galactic Nuclei. In The Formation and Disruption of Black Hole Jets; Astrophysics and Space Science Library; Springer International: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; Volume 414, pp. 117–148. [Google Scholar]
- Lyutikov, M.; Pariev, V.I.; Gabuzda, D.C. Polarization and Structure of Relativistic Parsec-scale AGN Jets. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2005, 360, 869–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pushkarev, A.B.; Gabuzda, D.C.; Vetukhnovskaya, Y.N.; Yakimov, V.E. Spine-sheath Polarization Structures in Four Active Galactic Nuclei Jets. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2005, 356, 859–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, E.; Cawthorne, T.V.; Gabuzda, D.C. Analysing the Transverse Structure of the Relativistic Jets of Active Galactic Nuclei. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2013, 430, 1504–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, P.A.; Aller, H.D.; Aller, M.A. iPolarized Radio Outbursts in Bl Lacertae—Part Two—The Flux and Polarization of a Piston-Driven Shock. Astrophys. J. 1985, 298, 301–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, P.A.; Aller, H.D.; Aller, M.A. Synchrotron Emission from Shocked Relativistic Jets. II. A Model for the Centimeter Wave Band Quiescent and Burst Emission from BL Lacertae. Astrophys. J. 1989, 341, 68–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laing, R. A Model for the Magnetic-field Structure in Extended Radio Sources. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1980, 193, 439–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marscher, A.P.; Gear, W.K. Models for High-frequency Radio Outbursts in Extragalactic Sources, with Application to the early 1983 Millimeter-to-infrared Flare of 3C 273. Astrophys. J. 1985, 298, 114–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlahakis, N. Disk-Jet Connection. In Blazar Variability Workshop II: Entering the GLAST Era; Astronomical Society of the Pacific: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2006; Volume 350, pp. 169–177. [Google Scholar]
- Marscher, A.P.; Jorstad, S.G.; D’Arcangelo, F.D.; Smith, P.S.; Williams, G.G.; Larionov, V.M.; Oh, H.; Olmstead, A.R.; Aller, M.F.; Aller, H.D.; et al. The Inner Jet of an Active Galactic Nucleus as Revealed by a Radio-to-γ-ray Outburst. Nature 2008, 452, 966–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lobanov, A.; Hardee, P.; Eilek, J. Double Helix in the Kiloparsec-Scale Jet in M 87. In Future Directions in High Resolution Astronomy: The 10th Anniversary of the VLBA; Astronomical Society of the Pacific: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2005; Volume 340, pp. 104–106. [Google Scholar]
- Lobanov, A.P.; Zensus, J.A. A Cosmic Double Helix in the Archetypical Quasar 3C273. Science 2001, 294, 128–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blandford, R.D. Astrophysical Jets; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1993; p. 26. [Google Scholar]
- Perley, R.A.; Bridle, A.H.; Willis, A.G. High-resolution VLA Observations of the Radio Jet in NGC 6251. Astrophys. J. Suppl. 1984, 54, 291–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asada, K.; Inoue, M.; Uchida, Y.; Kameno, S.; Fujisawa, K.; Iguchi, S.; Mutoh, M. A Helical Magnetic Field in the Jet of 3C 273. Publ. Astron. Soc. Jpn. 2002, 54, L39–L43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabuzda, D.C.; Nagle, M.; Roche, N. The Jets of AGN as Giant Coaxial Cables. Astron. Astrophys. 2018, 612, A67–A79. [Google Scholar]
- Knuettel, S.; Gabuzda, D.C.; O’Sullivan, S.P. Evidence for Toroidal B-Field Components in AGN Jets on Kiloparsec Scales. Galaxies 2017, 5, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmud, M.; Coughlan, C.P.; Murphy, E.; Gabuzda, D.C.; Hallahan, D.R. Connecting Magnetic Towers with Faraday Rotation Gradients in Active Galactic Nuclei Jets. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2013, 431, 695–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutsantoniou, L.; Contopoulos, I. Accretion Disk Radiation Dynamics and the Cosmic Battery. Astrophys. J. 2014, 794, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lico, R.; Gomez, J.L.; Asada, K.; Fuentes, A. On the Time Variable Rotation Measure in the Core Region of Markarian 421. Galaxies 2017, 5, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hovatta, T.; Lister, M.L.; Aller, M.F.; Aller, H.D.; Homan, D.C.; Kovalev, Y.Y.; Pushkarev, A.B.; Savolainen, T. MOJAVE: Monitoring of Jets in Active Galactic Nuclei with VLBA Experiments. VIII. Faraday Rotation in Parsec-scale AGN Jets. Astron. J. 2012, 144, 105–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homan, D.C. Inverse Depolarization: A Potential Probe of Internal Faraday Rotation and Helical Magnetic Fields in Extragalactic Radio Jets. Astrophys. J. 2012, 757, L24–L28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, M.H.; Meier, D.L.; Arshakian, T.G.; Clausen-Brown, E.; Homan, D.C.; Hovatta, T.; Kovalev, Y.Y.; Lister, M.L.; Pushkarev, A.B.; Richards, J.L.; et al. Studies of the Jet in Bl Lacertae. II. Superluminal Alfvén Waves. Astrophys. J. 2015, 803, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, M.H.; Aller, H.D.; Aller, M.F.; Hovatta, T.; Kharb, P.; Kovalev, Y.Y.; Lister, M.L.; Meier, D.L.; Pushkarev, A.B.; Savolainen, T. Reversals in the Direction of Polarization Rotation in OJ 287. Astrophys. J. 2018, 862, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, M.; Garofalo, D.; Meier, D.L. A Magnetohydrodynamic Model of the M87 Jet. I. Superluminal Knot Ejections from HST-1 as Trails of Quad Relativistic MHD Shocks. Astrophys. J. 2010, 721, 1783–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, M.; Meier, D.L. A Magnetohydrodynamic Model of the M87 Jet. II. Self-consistent Quad-shock Jet Model for Optical Relativistic Motions and Particle Acceleration. Astrophys. J. 2014, 785, 152–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, M.H. OJ 287 as a Rotating Helix. Galaxies 2017, 5, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homan, D.C.; Lister, M.L. iMOJAVE: Monitoring of Jets in Active Galactic Nuclei with VLBA Experiments. II. First-Epoch 15 GHz Circular Polarization Results. Astron. J. 2006, 131, 1262–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, T.W.; O’Dell, S.L. Transfer of Polarized Radiation in Self-absorbed Synchrotron Sources. I. Results for a Homogeneous Source. Astrophys. J. 1977, 214, 522–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ensslin, T.A. Does Circular Polarisation Reveal the Rotation of Quasar Engines? Astron. Astrophys. 2003, 401, 499–504. [Google Scholar]
- Wardle, J.F.C.; Homan, D.A. The Nature of Jets: Evidence from Circular Polarization Observations. In Particles and Fields in Radio Galaxies; Astronomical Society of the Pacific: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2001; pp. 152–163. [Google Scholar]
- Gabuzda, D.C. Determining the Jet Poloidal B Field and Black-Hole Rotation Directions in AGNs. Galaxies 2018, 6, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2018 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gabuzda, D. Evidence for Helical Magnetic Fields Associated with AGN Jets and the Action of a Cosmic Battery. Galaxies 2019, 7, 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies7010005
Gabuzda D. Evidence for Helical Magnetic Fields Associated with AGN Jets and the Action of a Cosmic Battery. Galaxies. 2019; 7(1):5. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies7010005
Chicago/Turabian StyleGabuzda, Denise. 2019. "Evidence for Helical Magnetic Fields Associated with AGN Jets and the Action of a Cosmic Battery" Galaxies 7, no. 1: 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies7010005
APA StyleGabuzda, D. (2019). Evidence for Helical Magnetic Fields Associated with AGN Jets and the Action of a Cosmic Battery. Galaxies, 7(1), 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies7010005



