Progress in Multi-Wavelength and Multi-Messenger Observations of Blazars and Theoretical Challenges
Abstract
1. Introduction
- What is the matter composition of blazar jets, and what is the dominant particle population responsible for the high-energy emission? Answering this question will allow major progress concerning physics of jet launching and loading, and the mode of acceleration of relativistic particles in jets.
- What is the structure of magnetic fields in the high-energy emission region and their role in the acceleration of relativistic particles? The answer to this question will aid in understanding the physics of jet collimation and stability and provide further clues to the physics of ultra-relativistic particle acceleration (magnetic reconnection vs. shocks vs. shear layers, …)
- Where along the jet is high-energy and very-high-energy -ray emission predominantly produced? Different observational results currently point towards different answers (sub-pc vs. 10s of pc from the central black hole). The confident localization of the blazar -ray emission region will further constrain plausible radiation mechanisms and could possibly hint at beyond-the-standard-model physics (if evidence suggests that absorption in the radiation field of the broad line region is suppressed below standard expectations).
2. Recent Observational Highlights
2.1. Flux Variability
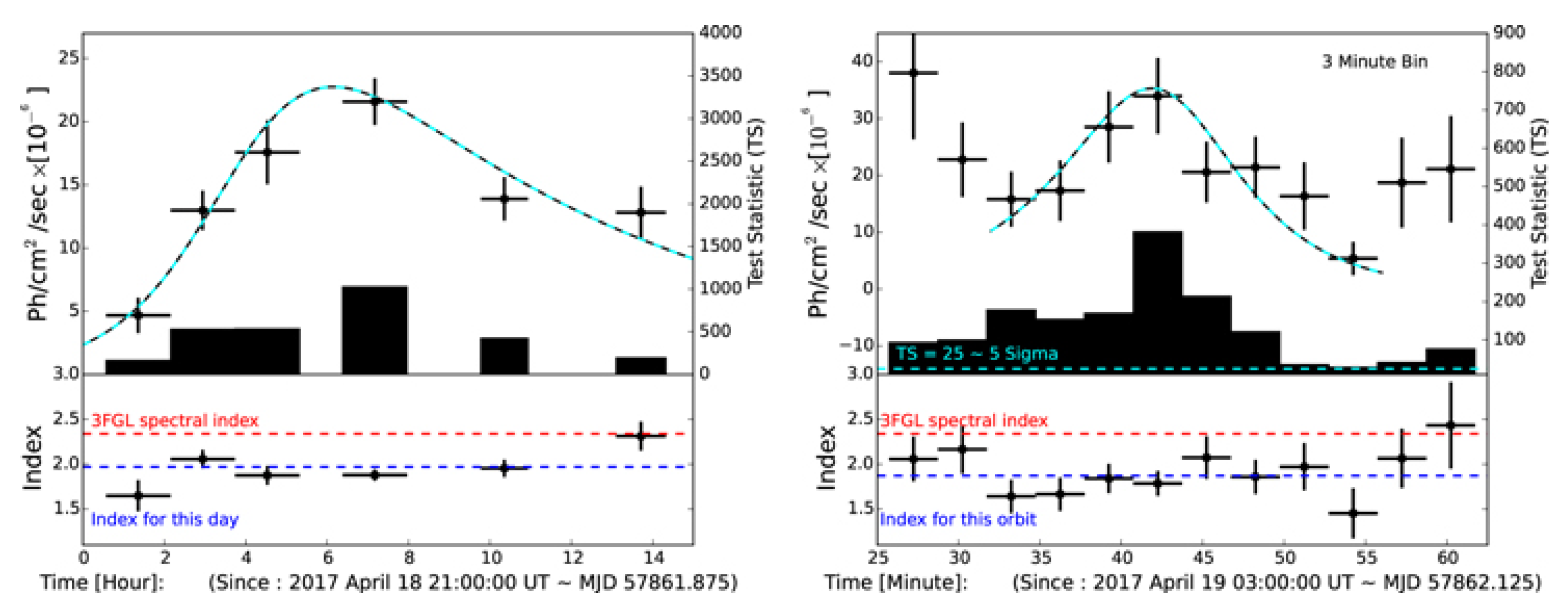
2.1.1. Minute-Scale Variability
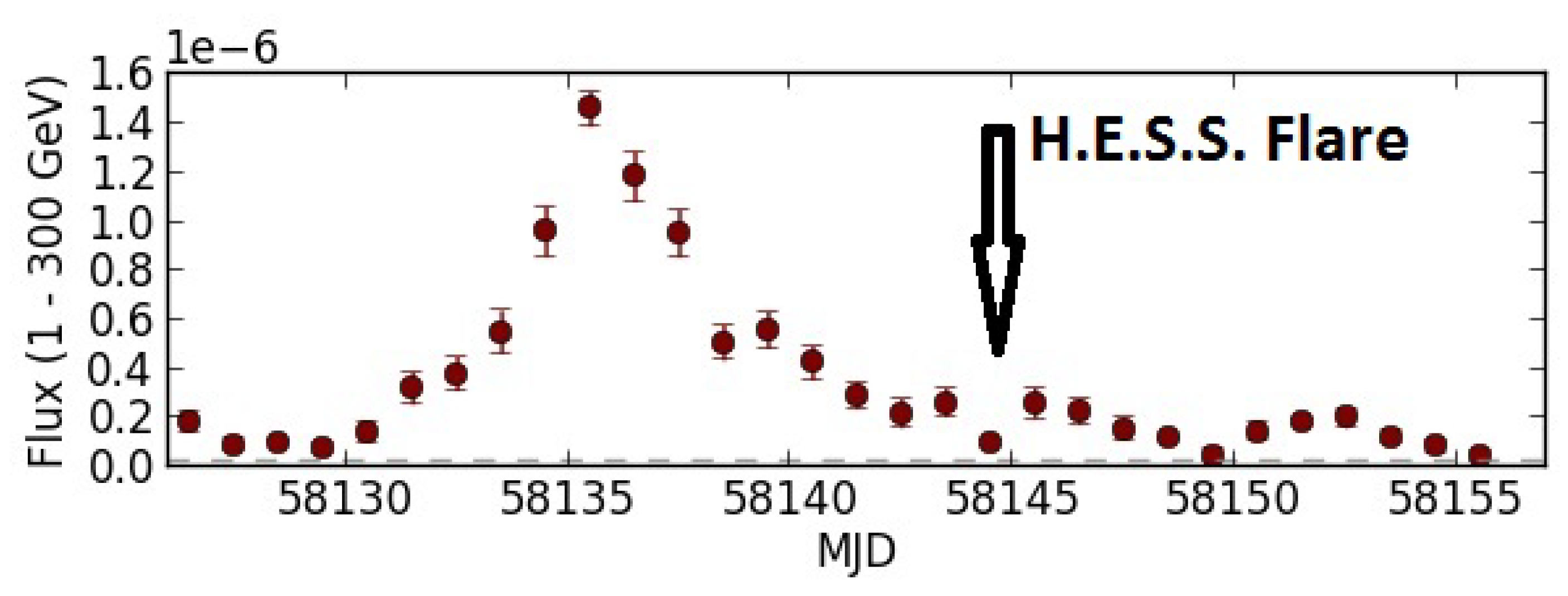
2.1.2. Multiwavelength Correlations
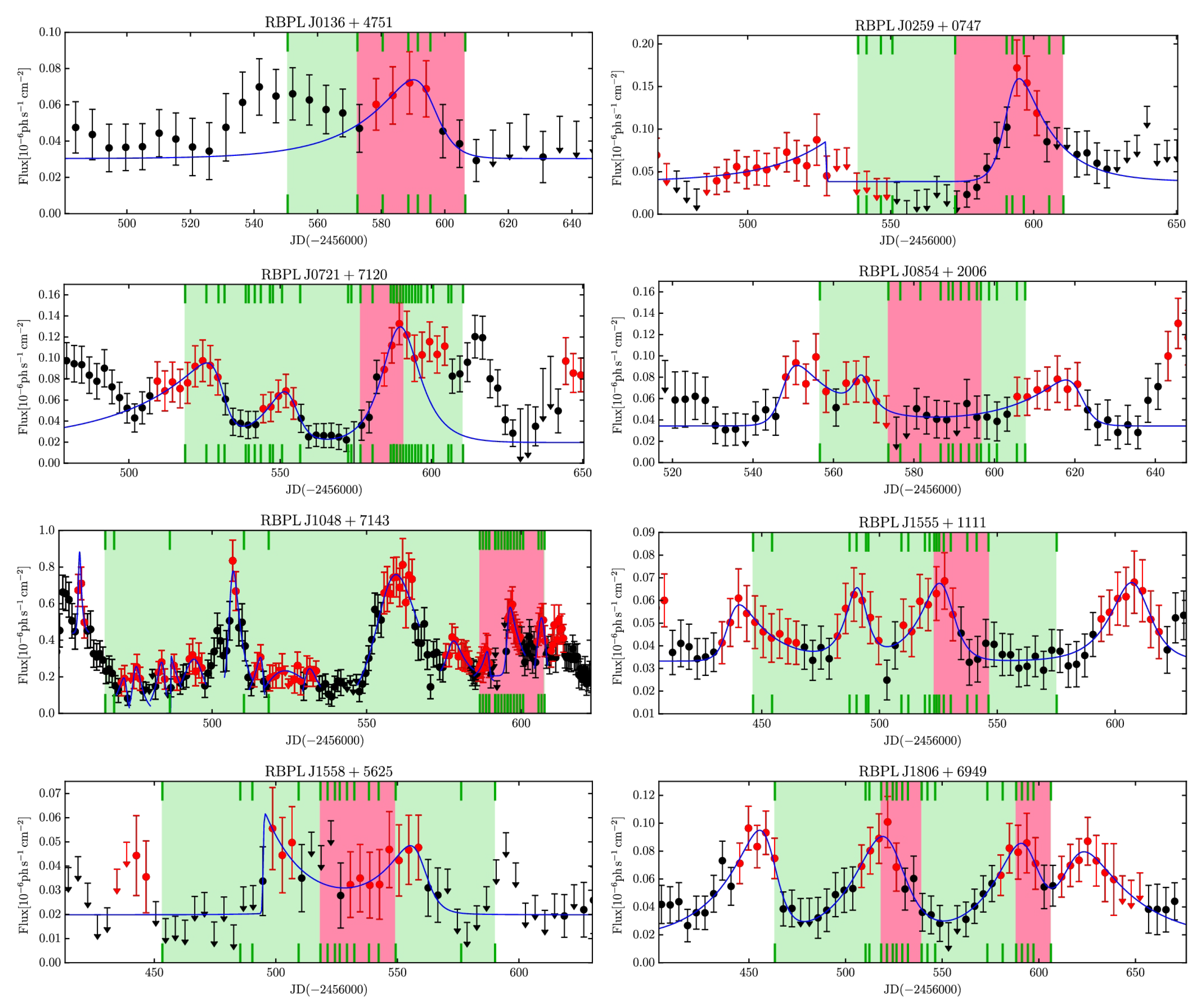
2.1.3. Periodicities?
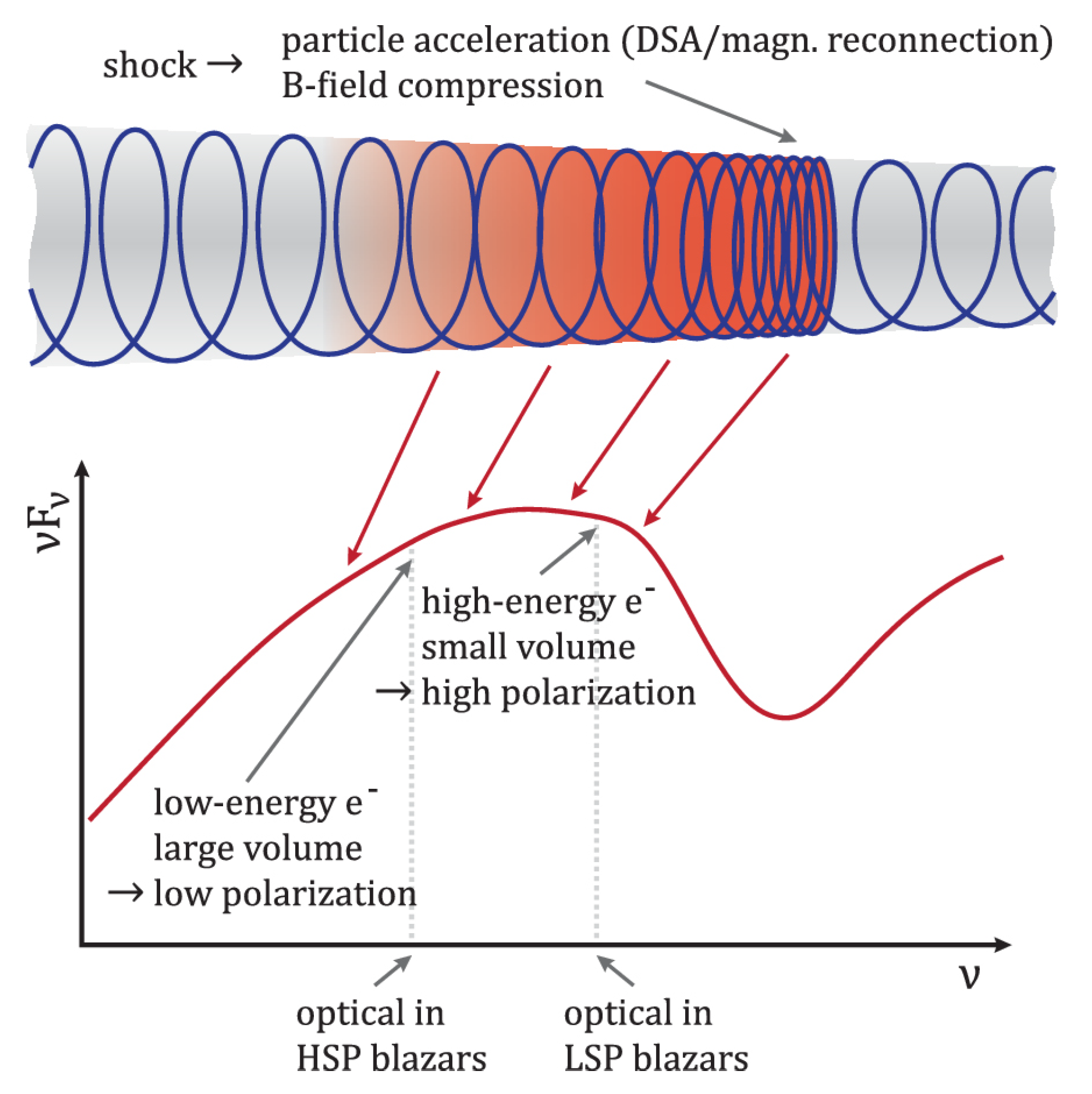
2.2. Polarization—Variability
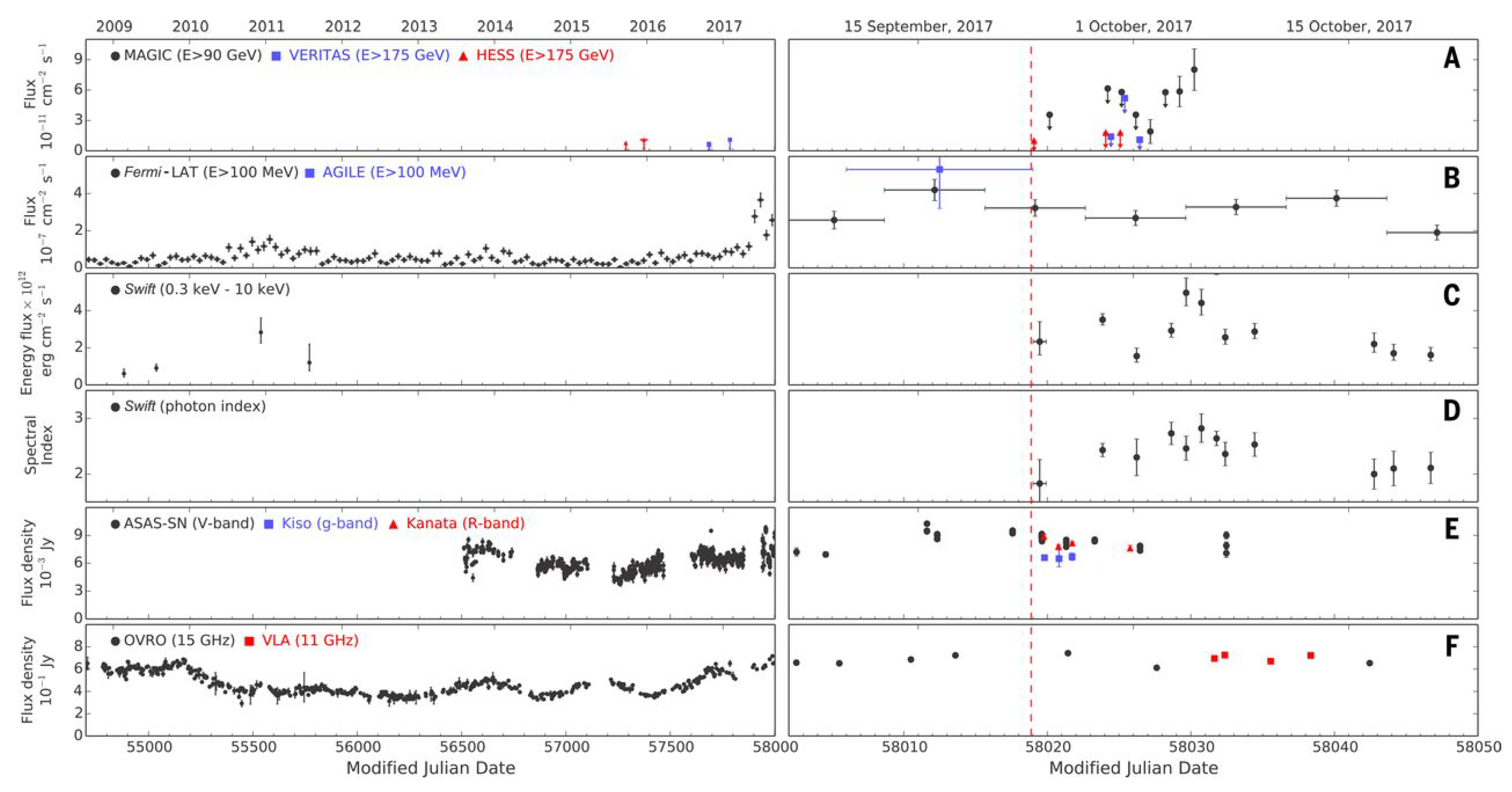
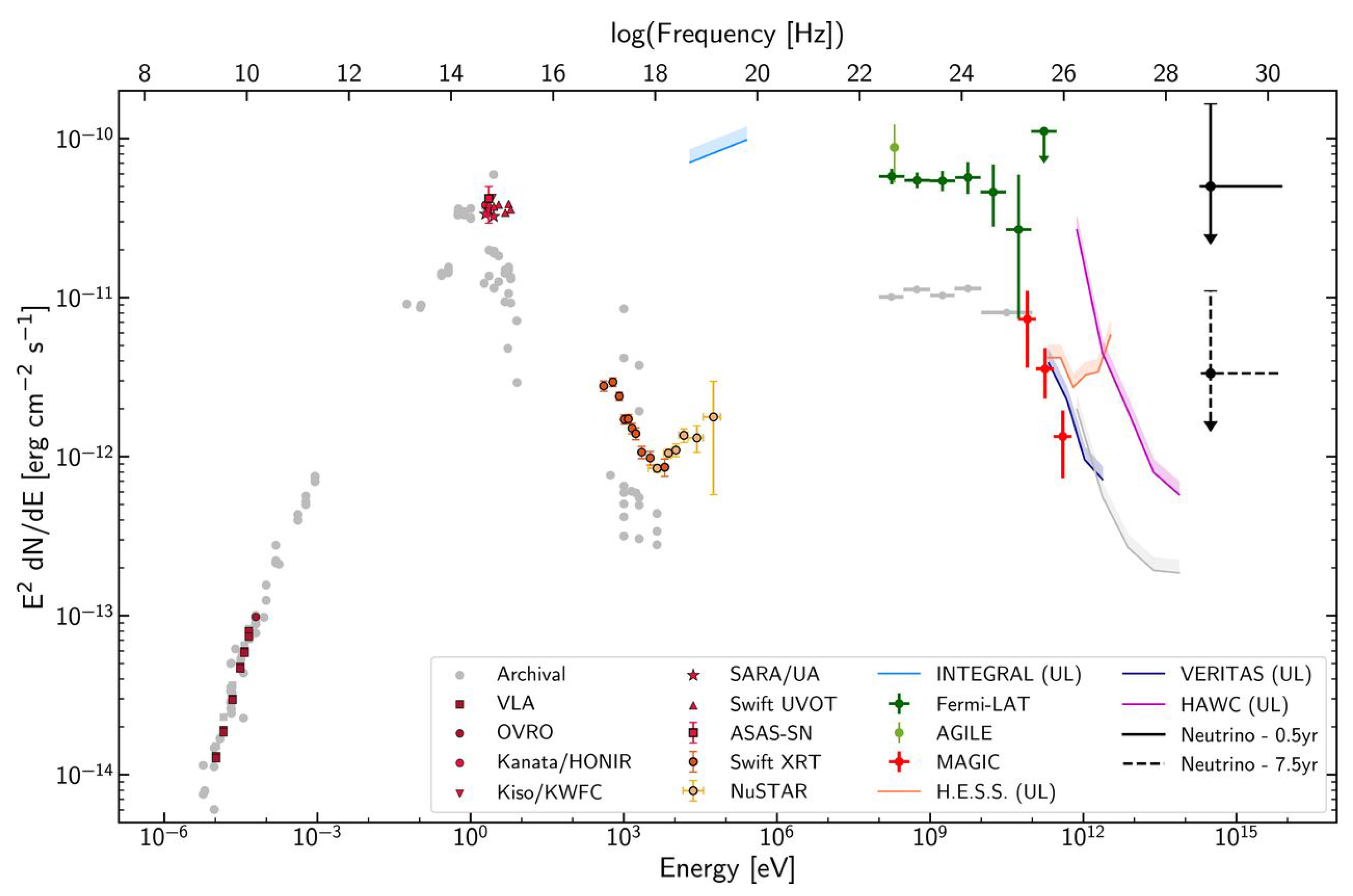
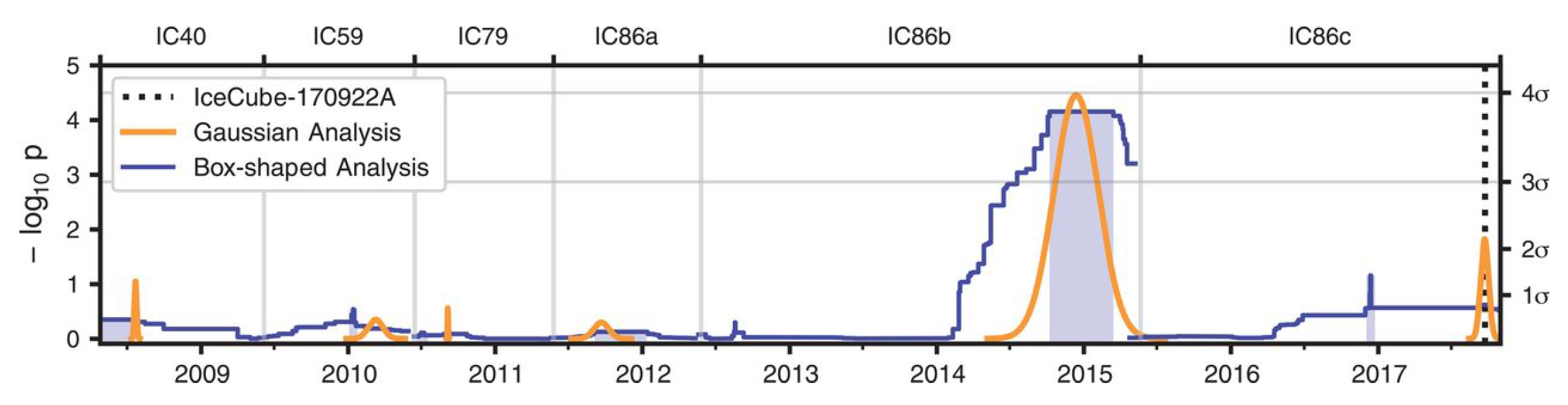
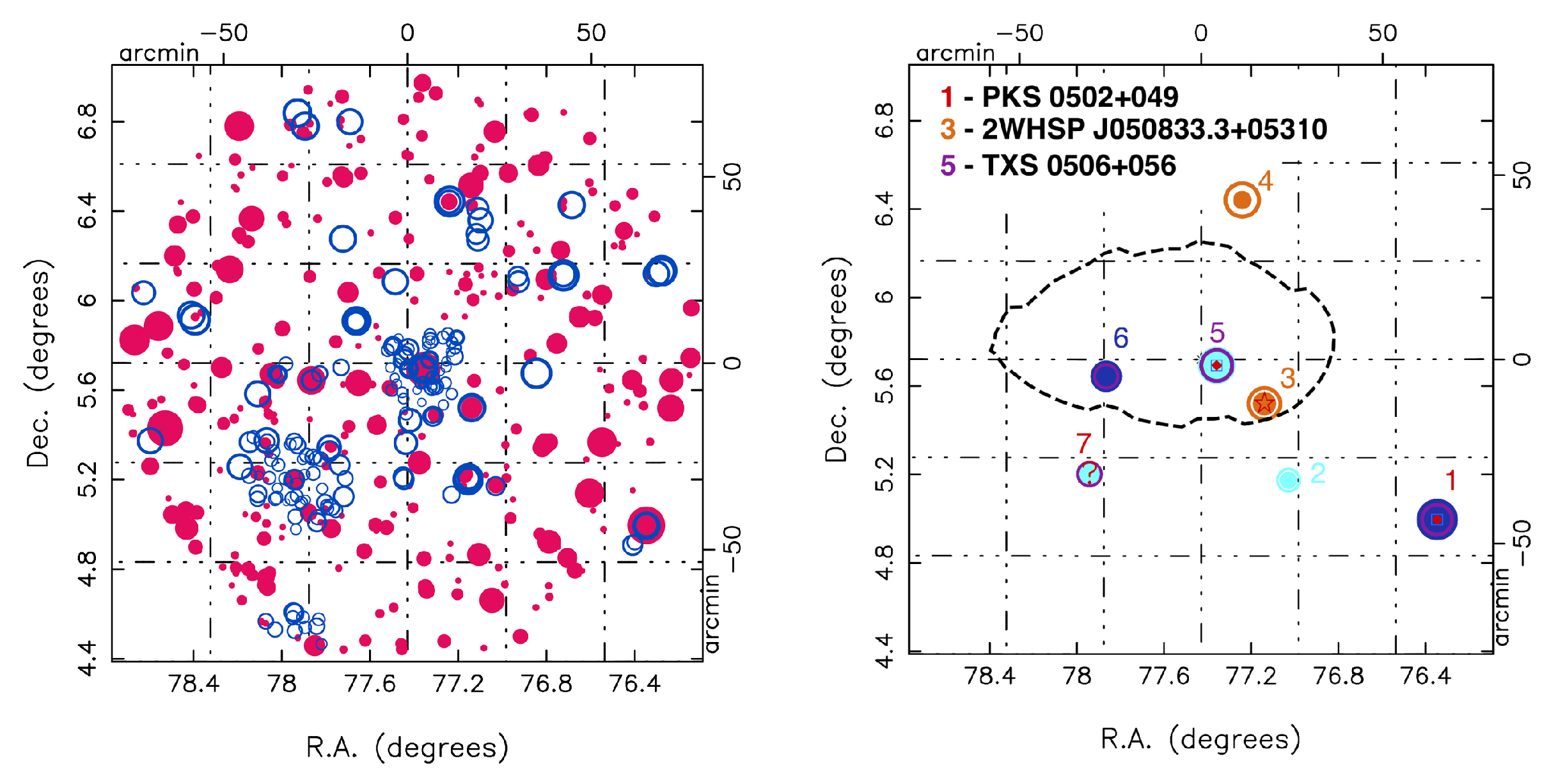
2.3. Multi-Messenger Observations—Neutrinos
3. Theoretical Developments
3.1. Models of Flux Variability
3.1.1. Causes of Variability
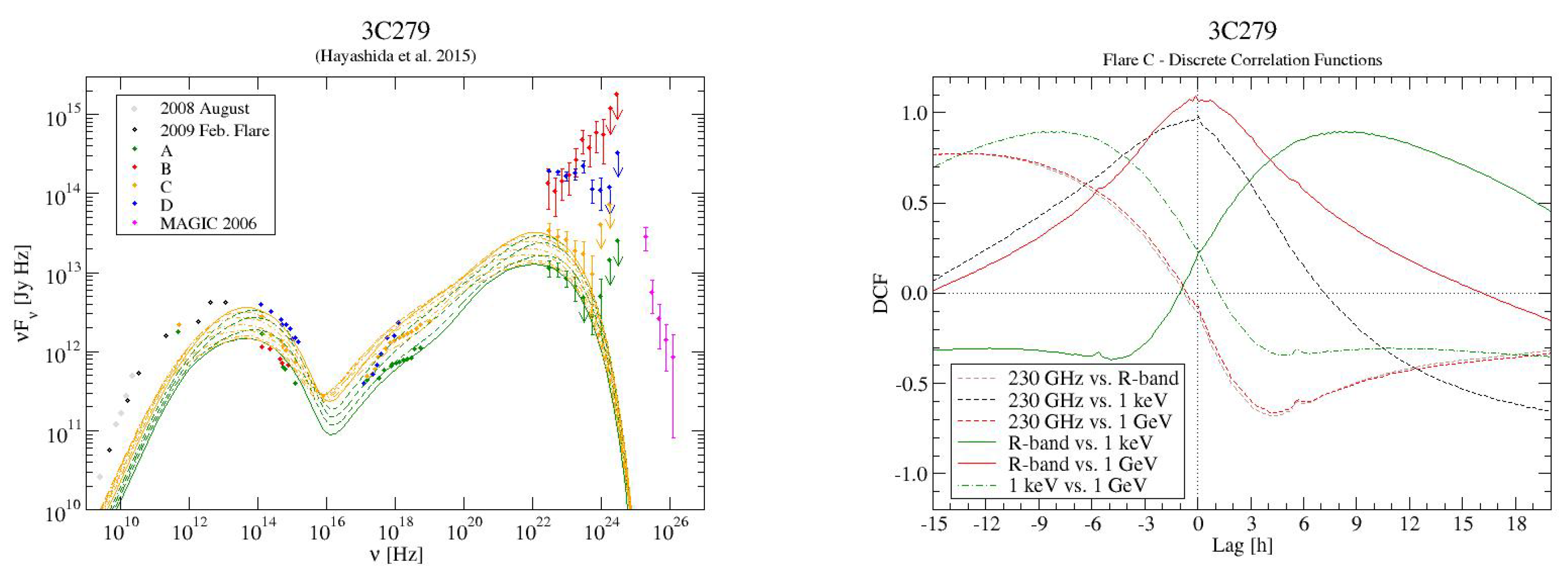
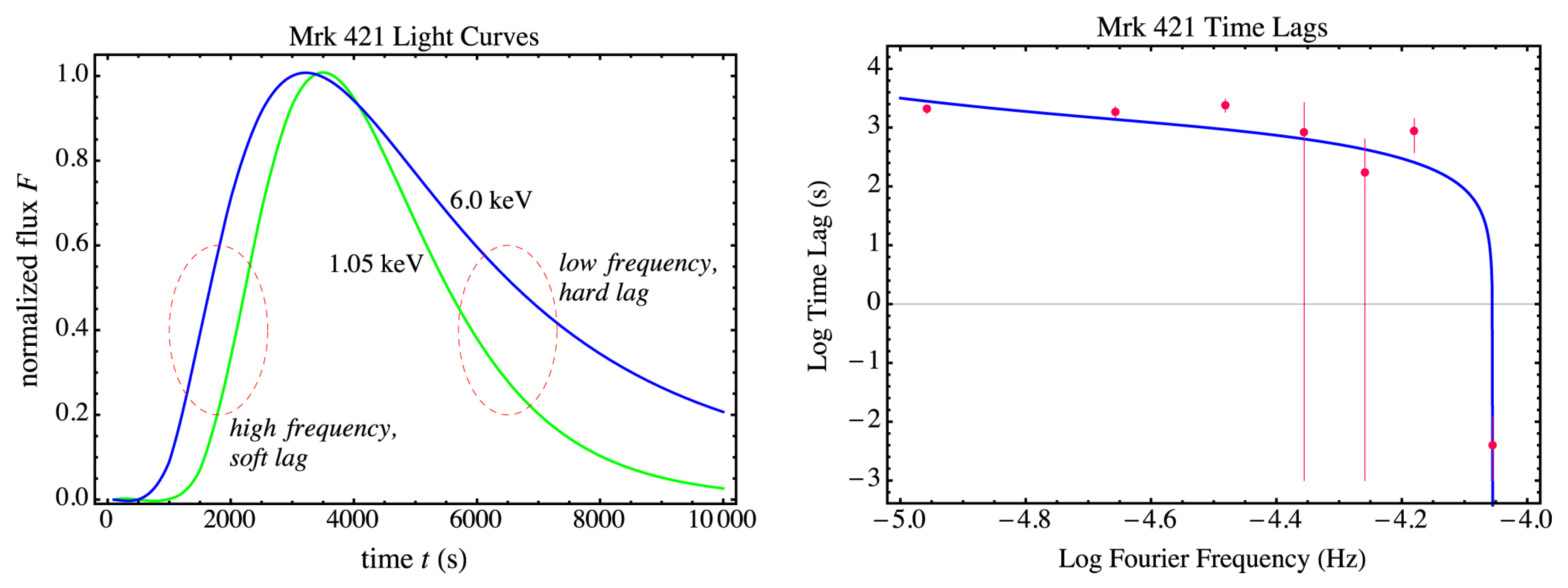
- Shock-in-jet models: In these models (also termed “internal shock models”) inhomogeneities in the jet flow produce mildly relativistic shocks travelling through the (relativistically moving) jet plasma, leading to the acceleration of particles, most plausibly through Diffusive Shock Acceleration (DSA; see, e.g., [81,82,83,84,85]). The shock-in-jet model for blazars was first suggested in the seminal work by Marscher & Gear [86], and subsequently refined in a large number of works, mostly in the framework of leptonic emission scenarios (e.g., [87,88,89,90,91,92,93,94,95,96,97,98]).In shock-in-jet models, particle acceleration occurs in a single region around the shock, equally affecting all radiating particles (leptonic or hadronic). Thus, these models generally predict correlated multi-wavelength variability with inter-band time lags reflecting energy-dependent electron (or proton) cooling (and/or acceleration) time scales (e.g., [87]). In the case of a leptonic emission scenario, for FSRQs, the optical and GeV -ray emissions are produced by electrons of similar energies and therefore are expected to be correlated with close to zero time lag. Radio and X-rays are produced by lower-energy electrons, expected to exhibit a delayed response compared to the optical and -ray emissions. Figure 9 shows an example resulting from a shock-in-jet simulation representing a multiwavelength flare of the FSRQ 3C 279 (flare C from [30]), where the radio and X-ray emissions are expected to lag behind the optical and VHE -ray emissions by ∼10 h. In the case of HSP blazars, the X-ray and -ray emissions are expected to be closely correlated, with GeV -ray and optical emissions lagging behind the X-ray and VHE variations.Uncorrelated variability amongst the two SED components could be achieved, in the framework of shock-in-jet models, with the assumption of the emission from the dominant shock being strongly synchrotron- or high-energy (Compton in leptonic models) dominated, enhancing the quiescent emission from the larger-scale jet only in a narrow frequency band (e.g., [99,100]). Alternatively, in a hadronic shock-in-jet scenario, vastly different acceleration time scales of electrons and protons might give the impression of uncorrelated variability due to the long time delay between the radiation components produced by electrons and protons (e.g., see [101] Figure 10).Shock-in-jet models naturally assume that the shock affects the entire cross section of the jet, with a radius of typically – cm. As discussed in Section 2.1, this constrains the variability time scale to hours, which is very difficult to reconcile with minute-scale variability, unless a very small jet cross section and/or a very large Doppler factor are assumed.It is well known that the formation of strong shocks and efficient particle acceleration at shocks is suppressed in the presence of a dominant magnetic field (e.g., [102]). The low magnetizations (–) typically inferred from broadband SED modeling of blazars (see, e.g., [8,103]) therefore seem to support the hypothesis of shocks being the dominant particle acceleration sites in blazars.
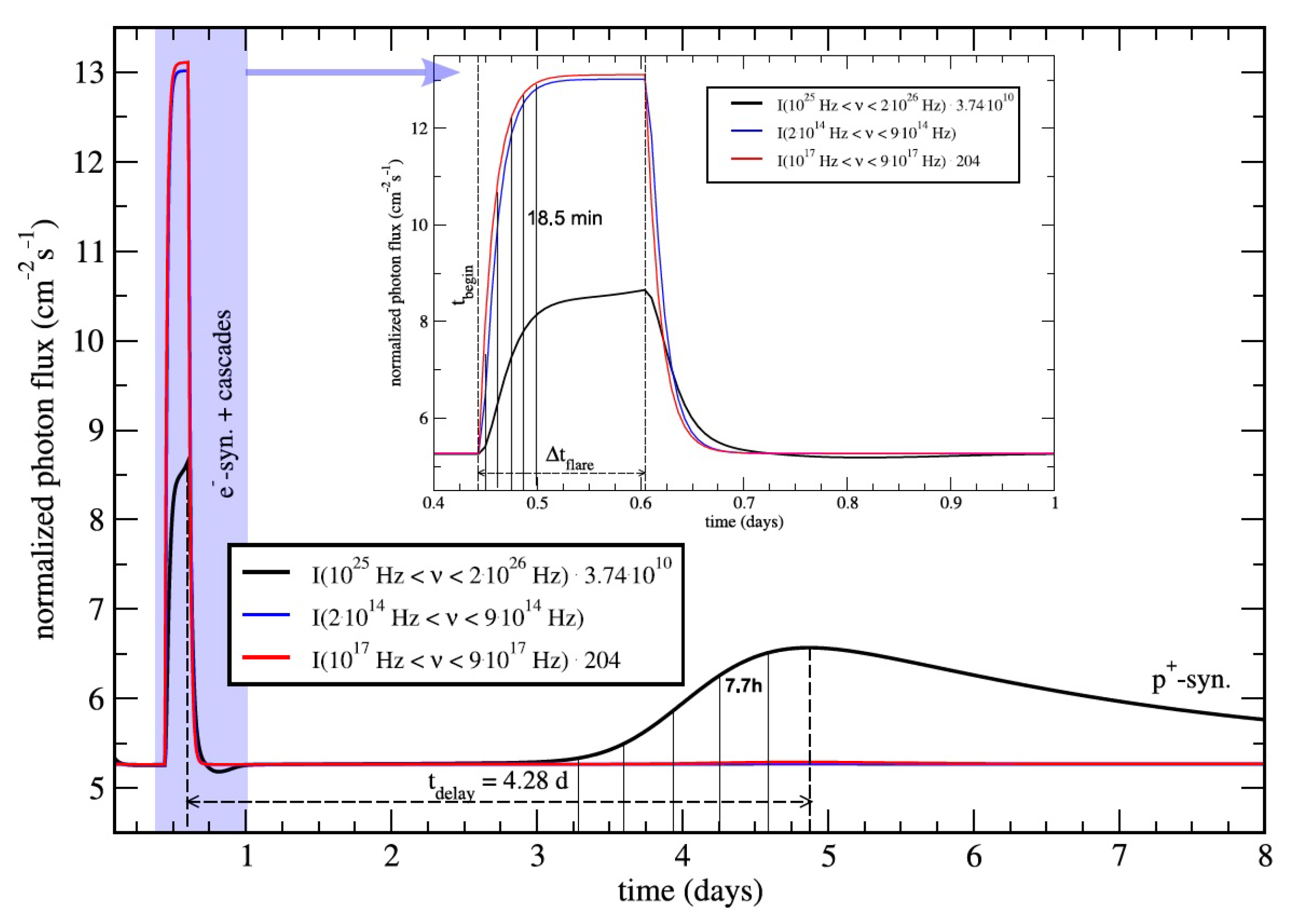
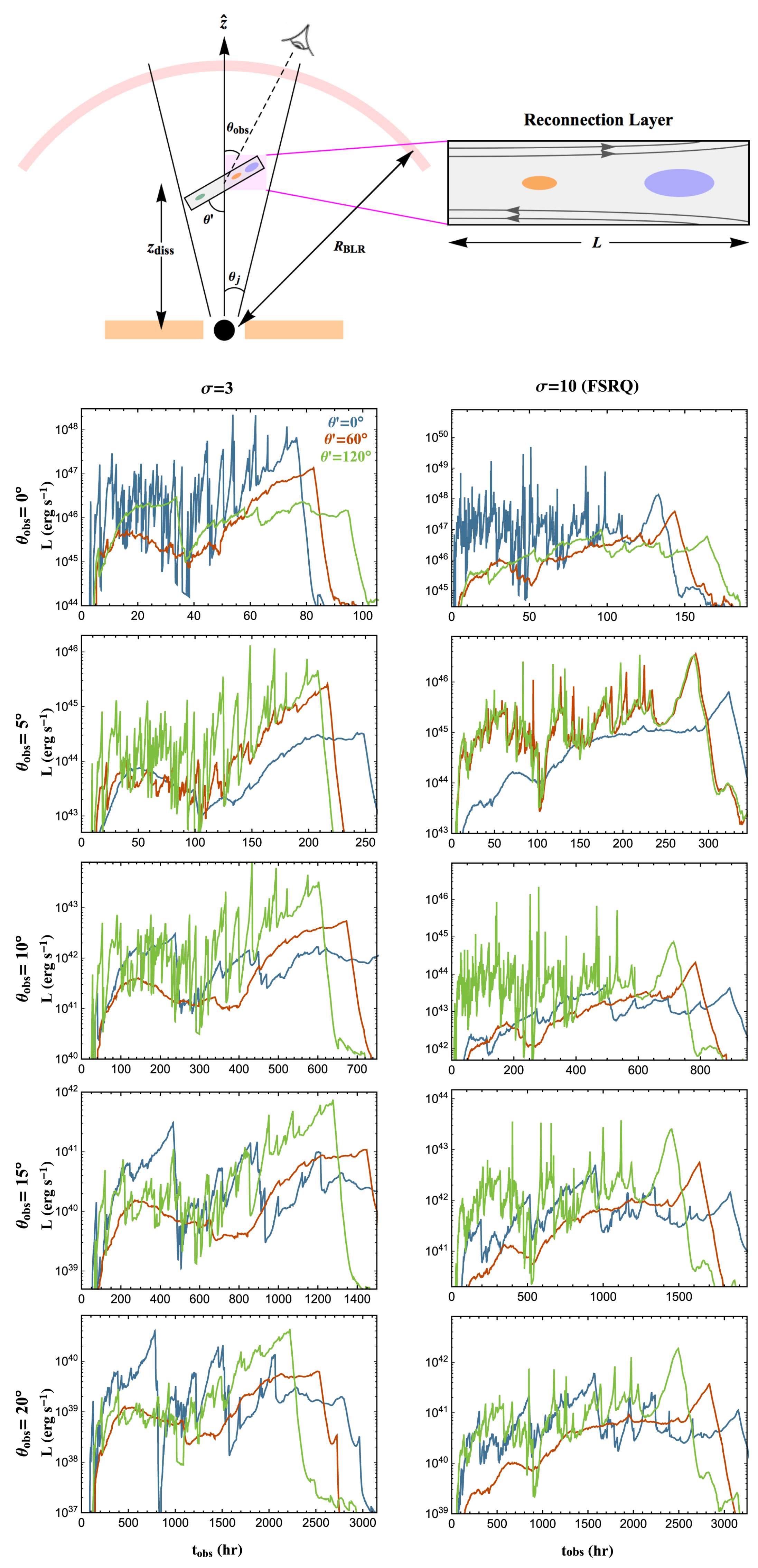
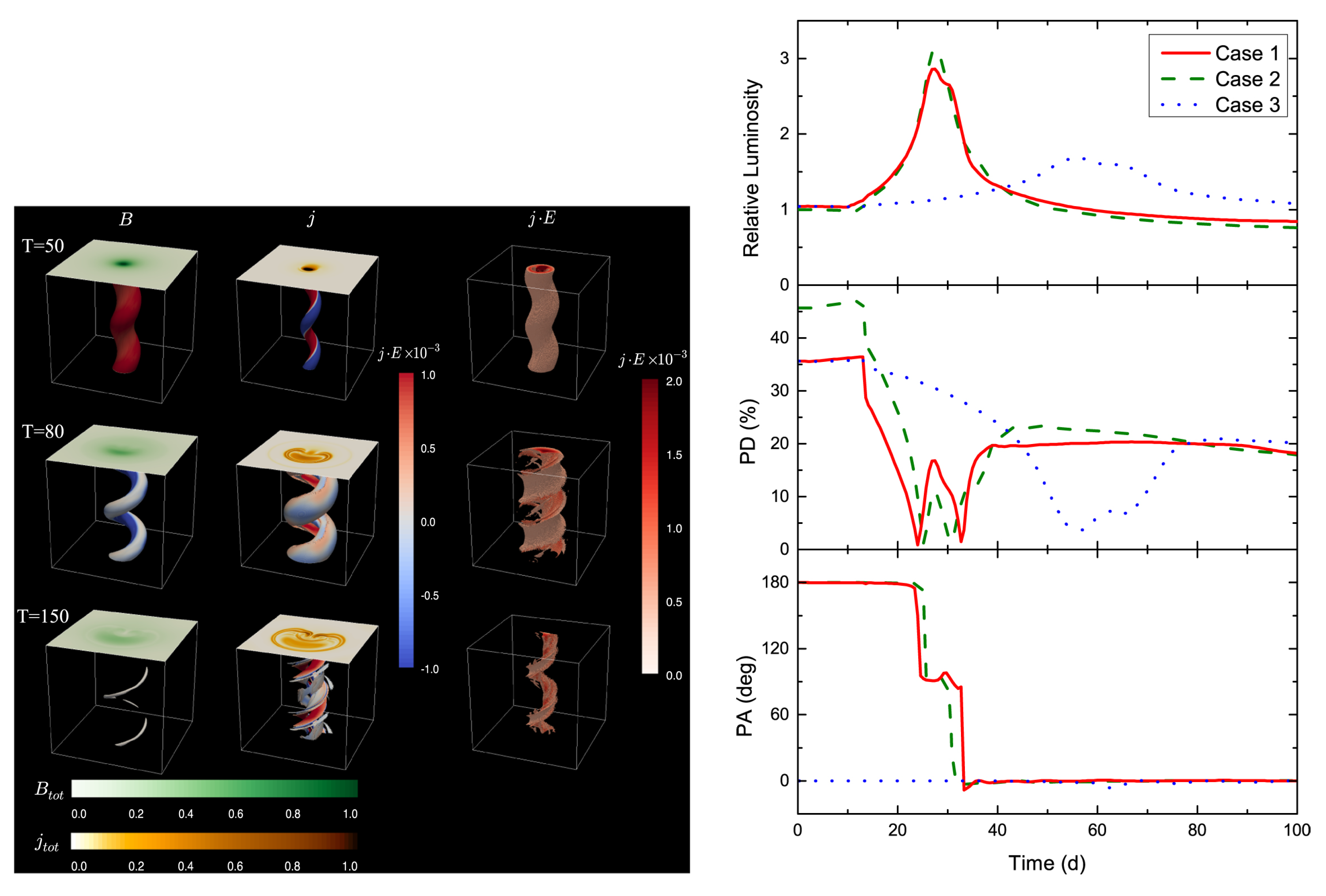
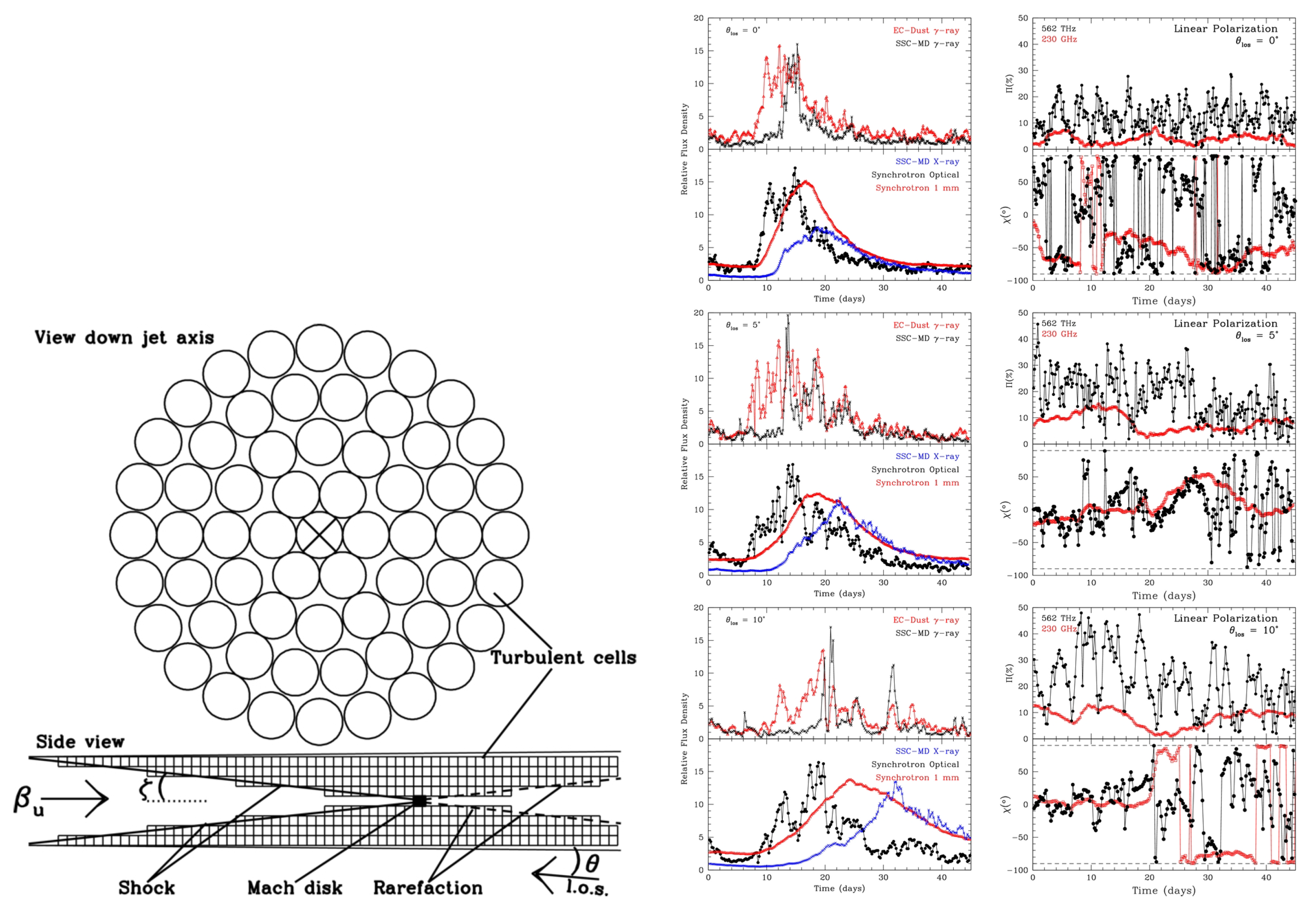
- Turbulence/Magnetic Reconnection: The relativistic flows of AGN jets are likely to develop turbulence, which may trigger magnetic reconnection. This has been studied in a large number of works in recent years (e.g., [104,105,106,107,108]). It has been shown that magnetic reconnection produces hard power-law spectra of relativistic electrons, , including spectral indices approaching a value of 1 (e.g., [109]), which, however, is also achievable with oblique relativistic, but still subluminal shocks [85].In view of the minute-scale variability problem discussed in Section 2.1, magnetic-reconnection models are particularly appealing as they provide the possibility to produce small-scale ultrarelativistic flows within the reconnection region, the so-called “jets-in-a-jet” scenario [110,111,112]. The resulting ultrarelativistic bulk motion of small plasmoids provides additional Doppler boosting, resulting in very short, bright flares. With modest magnetization ( a few), this model is capable of producing the observed fast (minute-scale) variability (see [110,112,113,114,115] Figure 11) without requiring ultrarelativistic () bulk motions of the entire jet material.
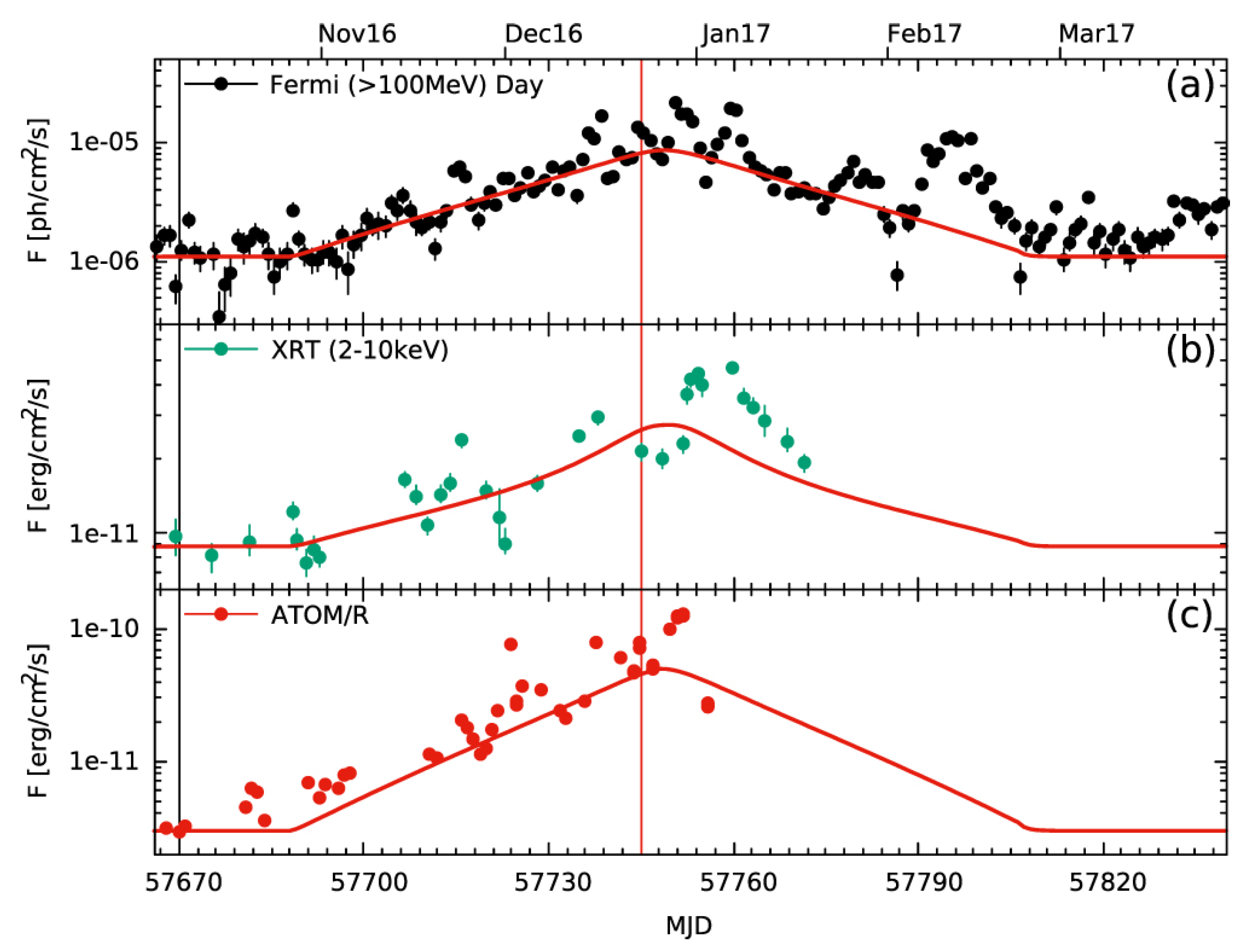
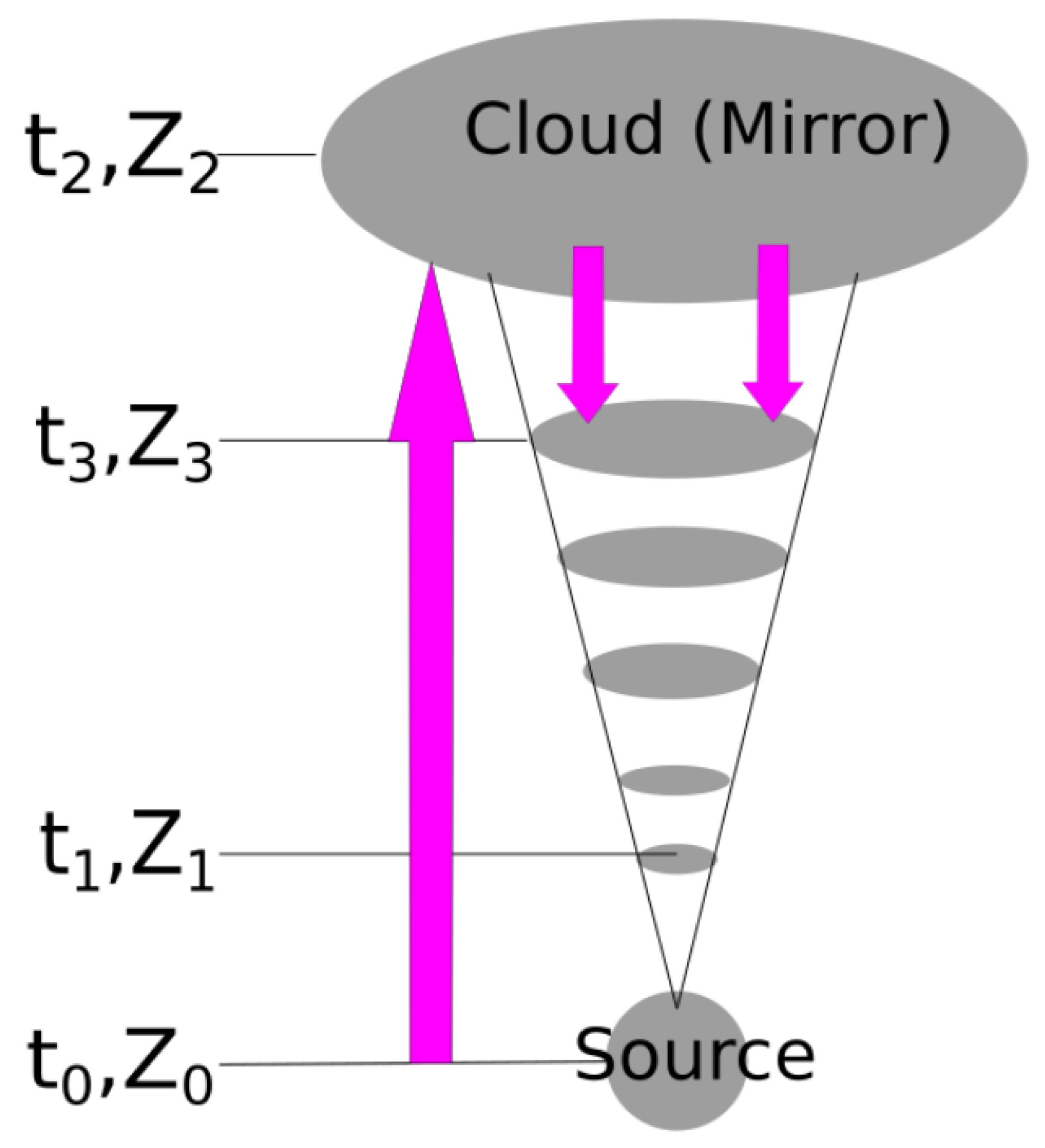
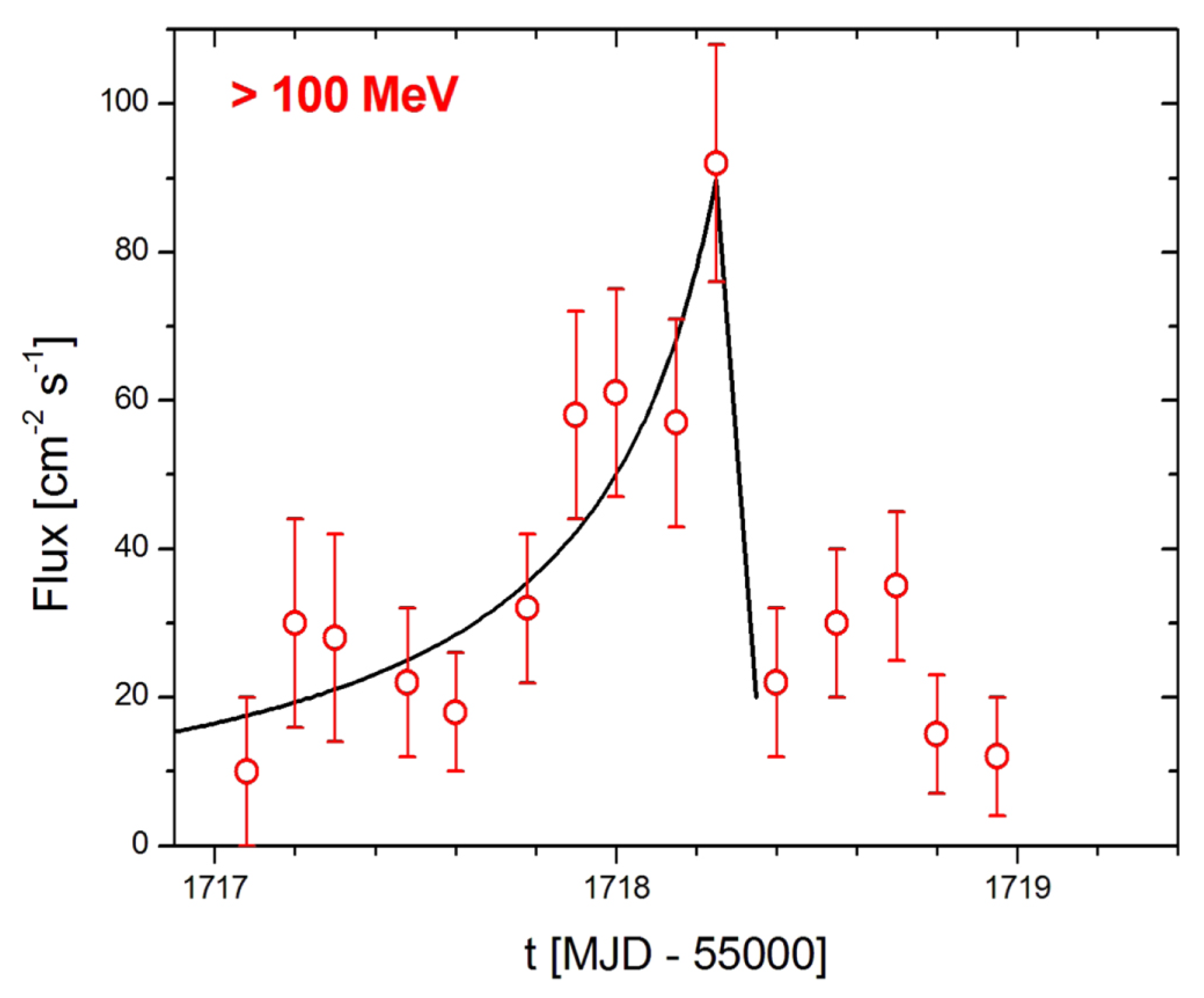
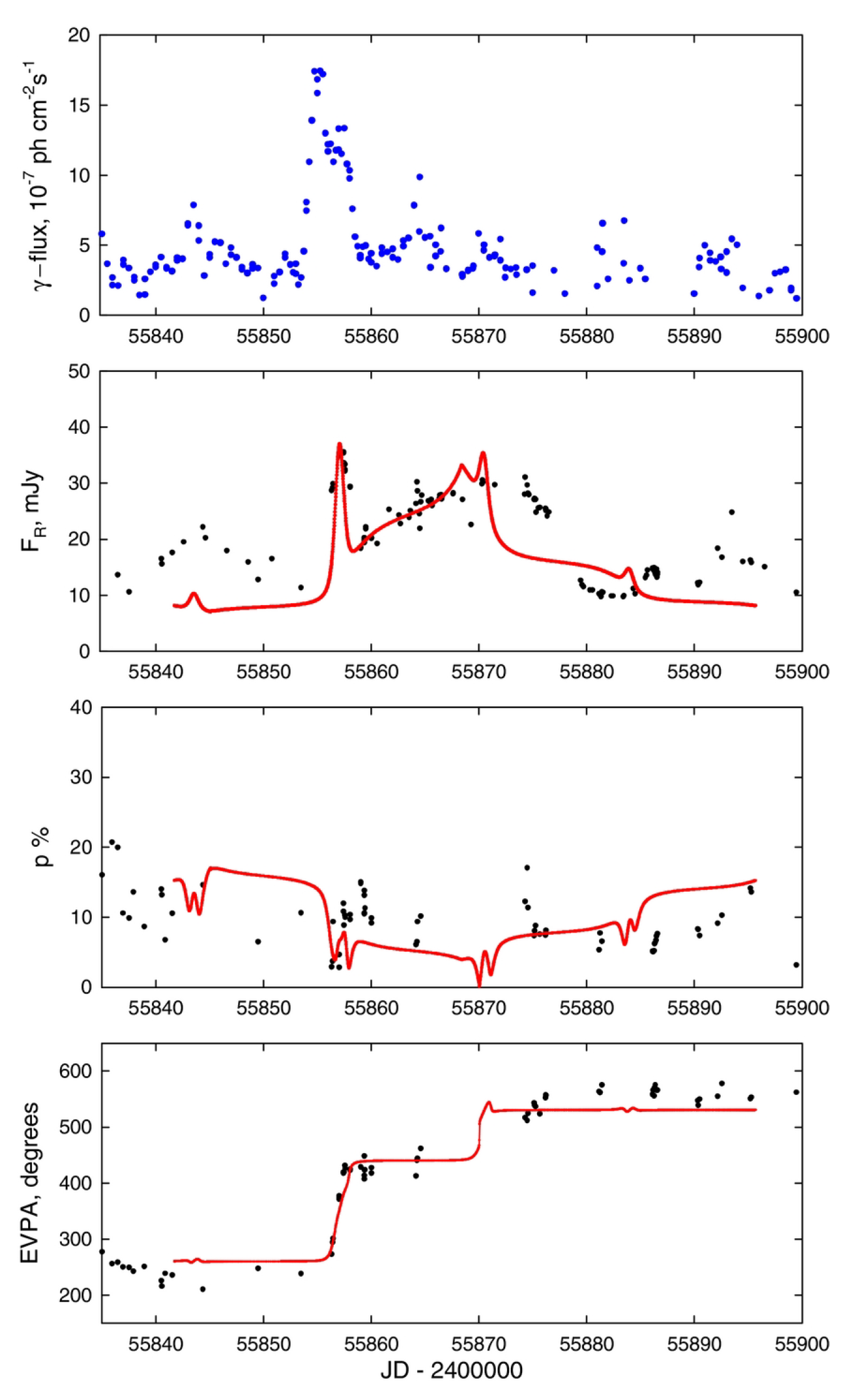
- External Sources of Variability: Another class of models attributes variability to interactions of the jet (or the high-energy emission region within the jet) with matter external to the jet, either by direct collisions or by means of radiative interactions.Examples of the former models include jet–star/cloud collision models (e.g., [116,117,118,119,120]), where the jet interacts with and (at least partially) disrupts a star or a gas cloud, leading to the formation of a strong shock with subsequent particle acceleration. The natural duration of flares in such a scenario is expected to be of the order of the crossing time of the cloud or star through the jet, typically of the order of days to weeks or months. For example, a model of cloud ablation by a blazar jet has recently been proposed by [121] to model the ∼4 months long giant multi-wavelength outburst of the FSRQ CTA 102 in 2016–2017, see Figure 12. Note that [119] argue that a jet-star interaction may also produce rapid, minute-scale variability due to the acceleration of fragments of the stellar envelope to ultra-relativistic bulk speeds.Variability models based on radiative interactions of the jet with external medium include, in particular, synchrotron mirror models, in which the synchrotron emission produced within the jet is reflected off an external obstacle (the “mirror”, which could, e.g., be a cloud of the Broad Line Region or a stationary feature within the jet) (e.g., [122,123] see Figure 13). It thereby appears as an intense target photon field either for Compton scattering (leptonic models—see Figure 14) or p pion producton (hadronic models) for a short time around the passage of the high-energy emission region by the mirror. A hadronic synchrotron mirror model has been proposed by [122] to explain the orphan TeV flare of 1ES 1959+650. The reflected synchrotron X-ray emission in this case would be an inefficient target for Compton scattering due to Klein-Nishina suppression, leaving p interactions off relativistic protons as the dominant signature of the mirror process.
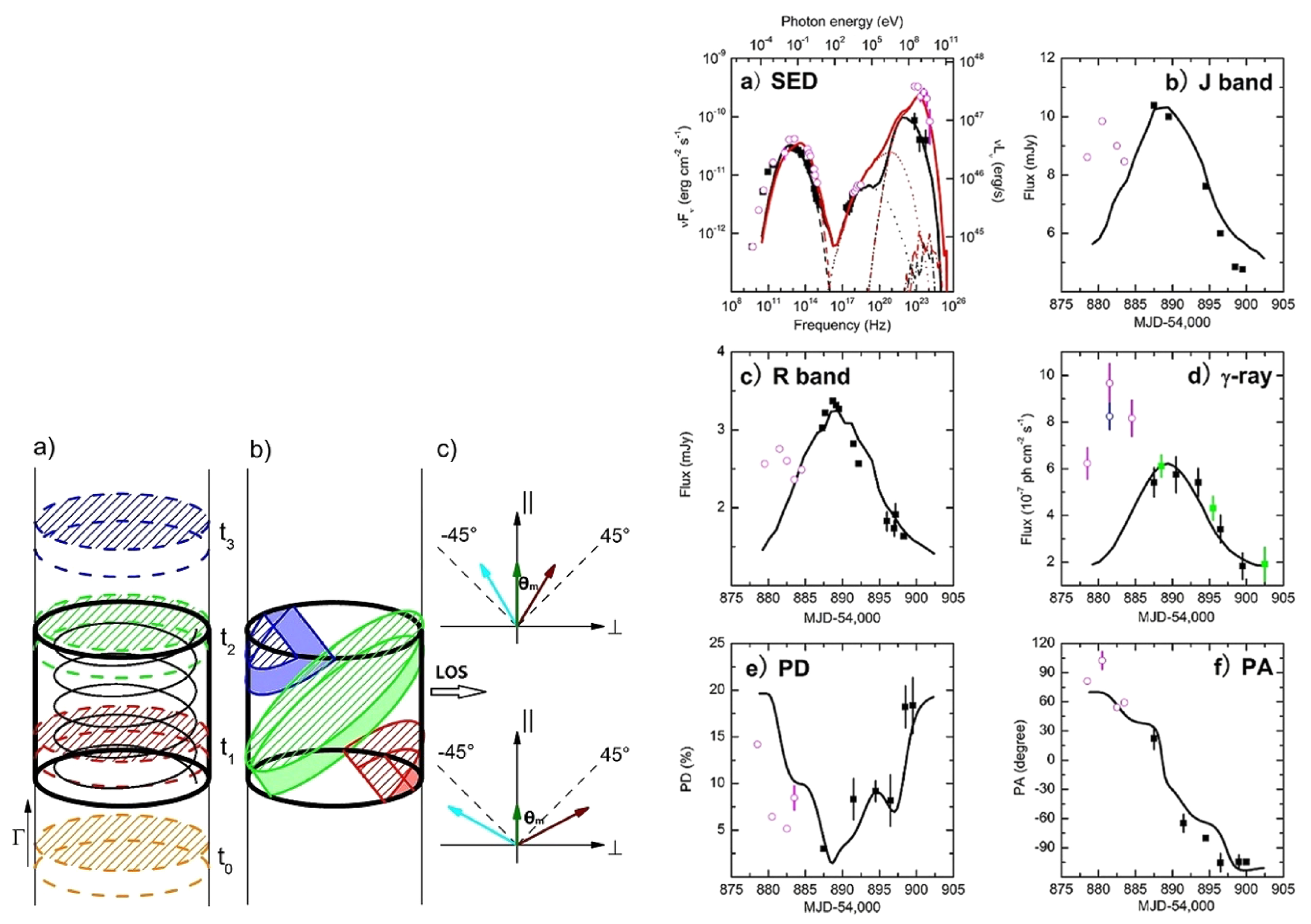
- Geometric Models: Variability models based on bending or helical jets invoke a change of the viewing geometry as the dominant source of variability, due to a change in the Doppler factor (e.g., [126,127,128,129,130]). Bending or helical jet structures are often observed in radio VLBI monitoring (e.g., [131]). Models based on Doppler-factor variability typically predict correlated, almost acromatic variability, except for a small shift in frequency by the changing Doppler factor, unless one assumes that different portions of the electromagnetic spectrum are not produced co-spatially and may be affected by different Doppler-factor variations (e.g., [129]). Such models have also had some success in reproducing optical polarization variability, as discussed further in the next sub-section.Another class of models that may be categorized as geometric invokes particle acceleration triggered by the kink instability in jets (e.g., [132,133]). In these models, variability is caused by particle acceleration due to magnetic energy dissipation in the development of the instability, which is expected to be accompanied by significant changes in the polarization signatures, as discussed further below.
3.1.2. Numerical Approaches
3.2. Multi-Wavelength Polarization Modeling
3.2.1. Optical polarization Angle Swings
3.2.2. High-Energy Polarization
3.3. Models of Neutrino Emission from Blazars
4. Future Prospects
4.1. The Cherenkov Telescope Array
- Short-term variability: The ∼10-fold improved sensitivity of CTA compared to currently operating IACT facilities will allow for the study of blazar variability on short time-scales. In the case of the brightest flares, variability down to sub-minute time-scales could, in principle, be detected, if present. Already the ∼5 min. variability observed in a few cases is severely challenging current blazar models, as discussed in Section 3.1. If blazars do indeed show significant variability on sub-minute time scales, this would call for a profound paradigm shift concerning our understanding of -ray emission from blazars.The detection of minute-scale variability strongly suggests a location of the emission region close to the central black hole, at a distance of the order cm. Even for bulk Lorentz factors of order , this would normally be within the Broad Line Region (BLR) of an FSRQ. Thus, in the case of FSRQs (such as PKS 1222+216, from which sub-hour variability has been seen), it would be very difficult to avoid absorption by the BLR radiation field (e.g., [187,188,189,190]). Thus, such detections either require exotic physics to suppress absorption within the BLR (e.g., [191,192]), or a mechanism to produce very compact emission regions along the jet at ∼ distances from the central black hole.The improved sensitivity will also enable the detection of short-term variability in fainter -ray-detected AGN, including mis-aligned blazars (seen as radio galaxies) and narrow-line Seyfert-1 galaxies, some of which also appear to show blazar-like properties (e.g., [193,194]). Thus, we will be able to study whether sub-hour variability is a property of only a few blazars, or whether it is a common phenomenon among -ray emitting radio-loud AGN.
- Detailed -ray spectral studies: The improved sensitivity and extended energy range of CTA compared to current IACTs will enable detailed -ray spectral studies with substantial overlap in energy with the Fermi-LAT. Potential spectral features due to absorption in the BLR or dust torus radiation fields of the AGN are expected to arise in the ∼10–100 GeV regime (e.g., [190]), i.e., just in the transition region between the energy ranges of Fermi-LAT and IACTs. Currently, the study of spectral features in this regime, beyond simple exponential cut-offs or similar smooth spectral shapes (see, e.g., [195]), is complicated by the fact that a high-quality Fermi-LAT spectrum, for most blazars, typically requires exposures of (at least) several days, during which the source is likely to show substantial variability. On the other hand, IACTs perform short, pointed observations of at most a few hours per night. Thus, any spectral features in this overlap energy range may well be an artifact of the often vastly different integration times in the GeV and TeV regimes. The substantial energy overlap between Fermi-LAT (up to GeV) and CTA ( GeV) will enable to proper flux cross-calibration of the two instruments and allow for a detailed study of spectral features in the overlap region, at least in cases where observations do not indicate significant variability over the course of the joint observations. The identification of BLR absorption features would provide a key diagnostic for the location of the -ray emission region and, thus, the region where relativistic particles are accelerated to >TeV energies. The location of the particle acceleration region would provide strong clues towards the nature of the acceleration mechanism.It has also been suggested (e.g., [196]) that hadronic emission processes might lead to detectable spectral features in the multi-TeV spectra of blazars due to separate spectral components from muon and pion synchrotron emission and photo-pion induced pair cascades. Such features may be detectable, at least for nearby blazars, with the CTA. If they are systematically identified in a sample of blazars, they might provide a “smoking-gun” signature of hadronic processes and point to blazars as sources of high-energy cosmic rays.
4.2. High-Energy Polarimetry
4.3. Future Neutrino Detectors
5. Summary and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Acero, F.; Ackermann, M.; Ajello, M.; Albert, A.; Atwood, W.B.; Axelsson, M.; Baldini, L.; Ballet, J.; Barbiellini, G.; Bastieri, D.; et al. Fermi LAT third source catalog. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 2015, 218, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aharonian, F.; Akhperjanian, A.G.; Bazer-Bachi, A.R.; Behera, B.; Beilicke, M.; Benbow, W.; Berge, D.; Bernlöhr, K.; Boisson, C.; Bolz, O.; et al. An Exceptional Very High Energy Gamma-Ray Flare of PKS 2155-304. Astrophys. J. 2007, 644, L71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albert, J.; Aliu, E.; Anderhub, H.; Antoranz, P.; Armada, A.; Baixeras, C.; Barrio, J.A.; Bartko, H.; Bastieri, D.; Becker, J.K.; et al. Variable Very High Energy γ-Ray Emission from Markarian 501. Astrophys. J. 2007, 669, 862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleksić, J.; Antonelli, L.A.; Antoranz, P.; Backes, M.; Barrio, J.A.; Bastieri, D.; González, J.B.; Bednarek, W.; Berdyugin, A.; Berger, K.; et al. MAGIC Discovery of Very High Energy Emission from the FSRQ PKS 1221+21. Astrophys. J. 2011, 730, L8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arlen, T.; Aune, T.; Beilicke, M.; Benbow, W.; Bouvier, A.; Buckley, J.H.; Bugaev, V.; Cesarini, A.; Ciupik, L.; Connolly, M.P.; et al. Rapid TeV Gamma-Ray Flaring of BL Lacertae. Astrophys. J. 2013, 762, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lister, M.; Aller, M.F.; Aller, H.D.; Hodge, M.A.; Homan, D.C.; Kovalev, Y.Y.; Pushkarev, A.B.; Savolainen, T. MOJAVE XV. VLBA 15 GHz Total Intensity and Polarization Maps of 437 Parsec-scale AGN Jets from 1996 to 2017. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 2018, 234, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blinov, D.; Pavlidou, V.; Papadakis, I.E.; Hovatta, T.; Pearson, T.J.; Liodakis, I.; Panopoulou, G.V.; Angelakis, E.; Baloković, M.; Das, H.; et al. RoboPol: Optical polarization-plane rotations and flaring activity in blazas. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2016, 457, 2252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böttcher, M.; Reimer, A.; Sweeney, K.; Prakash, A. Leptonic and Hadronic Modeling of Fermi-Detected Blazars. Astrophys. J. 2013, 768, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, G.E.; Boettcher, M.; Markoff, S.; Tavecchio, F. Relativistic Jets in Active Galactic Nuclei and Microquasars. Space Sci. Rev. 2017, 207, 5–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghisellini, G.; Tavecchio, F.; Foschini, L.; Ghirlanda, G. The transition between BL Lac objects and flat spectrum radio quasars. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2011, 414, 2674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdo, A.A.; Ackermann, M.; Ajello, M.; Axelsson, M.; Baldini, L.; Ballet, J.; Barbiellini, G.; Bastieri, D.; Baughman, B.M.; Bechtol, K.; et al. The Spectral Energy Distribution of Fermi Bright Blazars. Astrophys. J. 2010, 716, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maraschi, L.; Ghisellini, G.; Celotti, A. A jet model for the gamma-ray emitting blazar 3C279. Astrophys. J. 1992, 397, L5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dermer, C.D.; Schlickeiser, R. Model for the High-Energy Emission from Blazars. Astrophys. J. 1993, 416, 458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikora, M.; Begelman, M.C.; Rees, M.J. Comptonization of diffuse ambient radiation by a relativistic jet: The source of gamma-rays from blazars? Astrophys. J. 1994, 421, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Błażejowski, M.; Sikora, M.; Moderski, R.; Madejski, G.M. Comptonization of Infrared Radiation from Hot Dust by Relativistic Jets in Quasars. Astrophys. J. 2000, 545, 107. [Google Scholar]
- Ghisellini, G.; Tavecchio, F.; Chiaberge, M. Structured jets in TeV BL Lac objects and radiogalaxies. Implications for the observed properties. Astron. Astrophys. 2005, 432, 401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georganopoulos, M.; Kazanas, D. Decelerating Flows in TeV Blazars: A Resolution to the BL Lacertae—FR I Unification Problem. Astrophys. J. 2003, 594, L27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikora, M.; Madejski, G. On Pair Content and Variability of Subparsec Jets in Quasars. Astrophys. J. 2000, 534, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aharonian, F.A. TeV gamma-rays from BL Lac objects due to synchrotron radiation of extremely high energy protons. New Astron. 2000, 5, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mücke, A.; Protheroe, R.J. A proton synchrotron blazar model for flaring in Markarian 501. Astrophys. J. 2001, 15, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannheim, K.; Biermann, P.L. Gamma-ray flaring of 3C279—A proton-initiated cascade in the jet? Astron. Astrophys. 1992, 253, L21. [Google Scholar]
- Mannheim, K. The proton blazar. Astron. Astrophys. 1993, 269, 67. [Google Scholar]
- Mücke, A.; Protheroe, R.J.; Engel, R.; Rachen, J.P.; Stanev, T. BL Lac objects in the synchrotron proton blazar model. Astropart. Phys. 2003, 18, 593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aller, M.; Aller, H.; Hughes, P. The University of Michigan Centimeter-Band All Stokes Blazar Monitoring Program: Single-Dish Polarimetry as a Probe of Parsec-Scale Magnetic Fields. Galaxies 2017, 5, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabuzda, D. Parsec-Scale Jets in Active Galactic Nuclei. In The Formation and Disruption of Black Hole Jets; Contopoulos, I., Gabuzda, D., Kylafis, N., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; Volume 414, pp. 117–148. [Google Scholar]
- Jorstad, S.G.; Marscher, A.P.; Morozova, D.A.; Troitsky, I.S.; Agudo, I.; Casadio, C.; Foord, A.; Gómez, J.L.; MacDonald, N.R.; Molina, S.N.; et al. Kinematics of Parsec-scale Jets of Gamma-Ray Blazars at 43 GHz within the VLBA-BU-BLAZAR Program. Astrophys. J. 2017, 846, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lister, M. AGN Jet Kinematics on Parsec-Scales: The MOJAVE Program. Galaxies 2016, 4, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahnen, M.L.; Ansoldi, S.; Antonelli, L.A.; Arcaro, C.; Babić, A.; Banerjee, B.; Bangale, P.; De Almeida, U.B.; Barrio, J.A.; González, J.B.; et al. First multi-wavelength campaign on the gamma-ray loud active galaxy IC 310. Astron. Astrophys. 2017, 603, A25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collaboration, H.E.S.S.; Abdalla, H.; Abramowski, A.; Aharonian, F.; Ait Benkhali, F.; Akhperjanian, A.G.; Andersson, T.; Angüner, E.O.; Arrieta, M.; Aubert, P.; et al. H.E.S.S. discovery of very high energy γ-ray emission from PKS 0625-354. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2018, 476, 4187–4198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashida, M.; Nalewajko, K.; Madejski, G.M.; Sikora, M.; Itoh, R.; Ajello, M.; Blandford, R.D.; Buson, S.; Chiang, J.; Fukazawa, Y.; et al. Rapid Variability of Blazar 3C 279 during Flaring States in 2013–2014 with Joint Fermi-LAT, NuSTAR, Swift, and Ground-Based Multiwavelength Observations. Astrophys. J. 2015, 807, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, S.; Tanaka, Y.T.; Takahashi, T.; Madejski, G.; D’Ammando, F. Very Rapid High-amplitude Gamma-Ray Variability in Luminous Blazar PKS 1510-089 Studied with Fermi-LAT. Astrophys. J. 2013, 766, L11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackermann, M.; Anantua, R.; Asano, K.; Baldini, L.; Barbiellini, G.; Bastieri, D.; Gonzalez, J.B.; Bellazzini, R.; Bissaldi, E.; Blandford, R.D.; et al. Minut-timescale > 100 MeV γ-Ray Variability during the Giant Outburst of Quasar 3C 279 Observed by Fermi-LAT in 2015 June. Astrophys. J. 2016, 824, L20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, A.; Mannheim, K.; Patel, S.R.; Roy, J.; Chitnis, V.R.; Dorner, D.; Rao, A.R.; Anupama, G.C.; Wendel, C. Short-timescale γ-Ray Variability in CTA 102. Astrophys. J. 2018, 854, L26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böttcher, M.; Harris, D.; Krawczynski, H. Relativistic Jets from Active Galactic Nuclei; Wiley-VCH: Berlin, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Dondi, L.; Ghisellini, G. Gamma-ray loud blazars and beaming. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1995, 273, 583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begelman, M.C.; Fabian, A.C.; Rees, M.J. Implications of very rapid TeV variability in blazars. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2008, 384, L19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hovatta, T.; Valtaoja, E.; Tornikoski, M.; Lähteenmäki, A. Doppler factors, Lorentz factors and viewing angles for quasars, BL Lacertae objects and radio galaxies. Astron. Astrophys. 2009, 494, 527–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liodakis, I.; Hovatta, T.; Huppenkothen, D.; Kiehlmann, S.; Max-Moerbeck, W.; Readhead, A.C.S. Constraining the Limiting Brightness Temperature and Doppler Factors for the Largest Sample of Radio-Bright Blazars. Astrophys. J. 2018, 866, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyutikov, M.; Lister, M. Resolving the Doppler-factor Crisis in Active Galactic Nuclei: Non-steady Magnetized Outflows. Astrophys. J. 2010, 722, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, T.; Tashiro, M.; Madejski, G.; Kubo, H.; Kamae, T.; Kataoka, J.; Kii, T.; Makino, F.; Makishima, K.; Yamasaki, N. ASCA Observation of an X-Ray/TeV Flare from the BL Lacertae Object Markarian 421. Astrophys. J. 1996, 470, L89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böttcher, M.; Marscher, A.P.; Ravasio, M.; Villata, M.; Raiteri, C.M.; Aller, H.D.; Aller, M.F.; Teräsranta, H.; Mang, O.; Tagliaferri, G.; et al. Coordinated Multiwavelength Observations of BL Lacertae in 2000. Astrophys. J. 2003, 596, 847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Błażejowski, M.; Blaylock, G.; Bond, I.H.; Bradbury, S.M.; Buckley, J.H.; Carter-Lewis, D.A.; Celik, O.; Cogan, P.; Cui, W.; Daniel, M.; et al. A Multiwavelength View of the TeV Blazar Markarian 421: Correlated Variability, Flaring, and Spectral Evolution. Astrophys. J. 2005, 630, 130. [Google Scholar]
- Krawczynski, H.; Hughes, S.B.; Horan, D.; Aharonian, F.; Aller, M.F.; Aller, H.; Boltwood, P.; Buckley, J.; Coppi, P.; Fossati, G.; et al. Multiwavelength Observations of Strong Flares from the TeV Blazar 1ES 1959+650. Astrophys. J. 2004, 601, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naurois, M.H.E.S.S. Detection of a Strong VHE Activity from the Blazar 3C 279. The Astronomer’s Telegram, No. 11239. 2018. Available online: http://www.astronomerstelegram.org/?read=11239 (accessed on 1 November 2018).
- Capelo, P.R.; Dotti, M.; Volonteri, M.; Mayer, L.; Bellovary, J.M.; Shen, S. A survey of dual active galactic nuclei in simulations of galaxy mergers: Frequency and properties. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2017, 469, 4437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draper, A.R.; Ballantyne, D.R. The Merger-triggered Active Galactic Nucleus Contribution to the Ultraluminous Infrared Galaxy Population. Astrophys. J. 2012, 753, L37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; Wrobel, J.M.; Myers, A.D.; Djorgovski, S.G.; Yan, L. Binary Active Galactic Nuclei in Stripe 82: Constraints on Synchronized Black Hole Accretion in Major Mergers. Astrophys. J. 2015, 815, L6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabala, S.S. Delayed triggering of radio active galactic nuclei in gas-rich minor mergers in the local Universe. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2017, 464, 4706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehto, H.J.; Valtonen, M.J. OJ 287 Outburst Structure and a Binary Black Hole Model. Astrophys. J. 1996, 460, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valtonen, M.J.; Nilsson, K.; Sillanpää, A.; Takalo, L.O.; Lehto, H.J.; Keel, W.C.; Haque, S.; Cornwall, D.; Mattingly, A. The 2005 November Outburst in OJ 287 and the Binary Black Hole Model. Astrophys. J. 2006, 643, L9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valtonen, M.J.; Lehto, H.J.; Sillanpää, A.; Nilsson, K.; Mikkola, S.; Hudec, R.; Basta, M.; Teräsranta, H.; Haque, S.; Rampadarath, H. Pedicting the Next Outbursts of OJ 287 in 2006–2010. Astrophys. J. 2006, 646, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackermann, M.; Ajello, M.; Albert, A.; Atwood, W.B.; Baldini, L.; Ballet, J.; Barbiellini, G.; Bastieri, D.; Gonzalez, J.B.; Bellazzini, R.; et al. Multiwavelength Evidence for Quasi-periodic Modulation in the Gamma-Ray Blazar PG 1553+113. Astrophys. J. 2015, 813, L41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavani, M.; Cavaliere, A.; Munar-Adrover, P.; Argan, A. The Blazar PG 1553+113 as a Binary System of Supermassive Black Holes. Astrophys. J. 2018, 854, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Covino, S.; Sandrinelli, A.; Treves, A. Gamma-ray quasio-periodicities in blazars. A cautious approach. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2018, 482, 1270–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, P.S. Extremely High Optical Polarization Observed in the Blazar PKS 1502+106. The Astronomer’s Telegram, No. 11047. 2017. Available online: http://www.astronomerstelegram.org/?findmsg (accessed on 1 November 2018 ).
- Pavlidou, V.; Angelakis, E.; Myserlis, I.; Blinov, D.; King, O.G.; Papadakis, I.; Tassis, K.; Hovatta, T.; Pazderska, B.; Paleologou, E.; et al. The RoboPol optical polarization survey of gamma-ray loud blazars. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2014, 442, 1693–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelakis, E.; Hovatta, T.; Blinov, D.; Pavlidou, V.; Kiehlmann, S.; Myserlis, I.; Böttcher, M.; Mao, P.; Panopoulou, G.V.; Liodakis, I.; et al. RoboPol: The optical polarization of gamma-ray-loud and gamma-ray-quiet blazars. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2016, 463, 3365–3380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdo, A.A.; Ackermann, M.; Ajello, M.; Axelsson, M.; Baldini, L.; Ballet, J.; Barbiellini, G.; Bastieri, D.; Baughman, B.M.; Bechtol, K.; et al. A change in the optical polarization associated with a γ-ray flare in the blazar 3C279. Nature 2010, 463, 919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marscher, A.P.; Jorstad, S.G.; D’Arcangelo, F.D.; Smith, P.S.; Williams, G.G.; Larionov, V.M.; Oh, H.; Olmstead, A.R.; Aller, M.F.; Aller, H.D.; et al. The inner jet of an active galactic nucleus as revealed by a radio-to-γ-ray outburst. Nature 2008, 452, 7190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marscher, P.; Jorstad, S.G.; Larionov, V.M.; Aller, M.F.; Aller, H.D.; Lähteenmäki, A.; Agudo, I.; Smith, P.S.; Gurwell, M.; Hagen-Thorn, V.A.; et al. Probing the Inner Jet of the Quasar PKS 1510-089 with Multi-Waveband Monitoring During Strong Gamma-Ray Activity. Astrophys. J. 2010, 710, L126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blinov, D.; Pavlidou, V.; Papadakis, I.; Kiehlmann, S.; Panopoulou, G.; Liodakis, I.; King, O.G.; Angelakis, E.; Baloković, M.; Das, H.; et al. RoboPol: Fist season rotations of optical polarization plane in blazars. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2015, 453, 1669–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blinov, D.; Pavlidou, V.; Papadakis, I.; Kiehlmann, S.; Liodakis, I.; Panopoulou, G.V.; Pearson, T.J.; Angelakis, E.; Baloković, M.; Hovatta, T.; et al. RoboPol: Do optical polarization rotations occur in all blazars? Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2016, 462, 1775–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blinov, D.; Pavlidou, V.; Papadakis, I.; Kiehlmann, S.; Liodakis, I.; Panopoulou, G.V.; Angelakis, E.; Baloković, M.; Hovatta, T.; King, O.G.; et al. RoboPol: Connection between optical polarization plane rotations and gamma-ray flares in blazars. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2018, 474, 1296–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hovatta, T.; Lindfors, E.; Blinov, D.; Pavlidou, V.; Nilsson, K.; Kiehlmann, S.; Angelakis, E.; Ramazani, V.F.; Liodakis, I.; Myserlis, I.; et al. Optical polarization of high-energy BL Lacertae objects. Astron. Astrophys. 2016, 596, A78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, B.P.; Abbott, R.; Abbott, T.D.; Abernathy, M.R.; Acernese, F.; Ackley, K.; Adams, C.; Adams, T.; Addesso, P.; Adhikari, R.X.; et al. Observation of Gravitational Waves from a Binary Black Hole Merger. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2016, 116, 061102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbott, B.P.; Abbott, R.; Adhikari, R.X.; Ananyeva, A.; Anderson, S.B.; Appert, S.; Arai, K.; Araya, M.C.; Barayoga, J.C.; Barish, B.C.; et al. Multi-messenger Observations of a Binary Neutron Star Merger. Astrophys. J. 2017, 848, L12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The IceCube; Fermi-LAT; MAGIC; AGILE; ASAS-SN; HAWC; H.E.S.S.; INTEGRAL; Kanata; Kiso; Kapteyn; Liverpool telescope; Subaru; Swift=NuSTAR; VERITAS; VLA/17B-403 teams. Multimessenger observations of a flaring blazar coincident with high-energy neutrino IceCube-170922A. Science 2018, 361, 6398. [Google Scholar]
- IceCube Collaboration. Neutrino emission from the direction of the blazar TXS 0506+056 prior to the IceCube-170922A alert. Science 2018, 361, 147. [Google Scholar]
- Aartsen, M.G.; Abraham, K.; Ackermann, M.; Adams, J.; Aguilar, J.A.; Ahlers, M.; Ahrens, M.; Altmann, D.; Anderson, T.; Archinger, M.; et al. Evidence for Astrophysical Muon Neutrinos from the Northern Sky with IceCube. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2015, 115, 081102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aartsen, M.G.; Abraham, K.; Ackermann, M.; Adams, J.; Aguilar, J.A.; Ahlers, M.; Ahrens, M.; Altmann, D.; Andeen, K.; Anderson, T.; et al. Observation and Characterization of a Cosmic Muon Neutrino Flux from he Northern Hemisphere Using Six Years of IceCube Data. Astrophys. J. 2016, 833, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitrakoudis, S.; Mastichiadis, A.; Protheroe, R.J.; Reimer, A. The time-dependent one-zone hadronic model. First principles. Astron. Astrophys. 2012, 546, A120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastichiadis, A. The Hadronic Model of Active Galactic Nuclei. Space Sci. Rev. 1996, 75, 317–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murase, K.; Inoue, Y.; Dermer, C.D. Diffuse neutrino intensity from the inner jets of active galactic nuclei: Impacts of external photon fields and the blazar sequence. Phys. Rev. 2014, 90, 023007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Protheroe, R.J.; Szabo, A.P. High energy cosmic rays from active galactic nuclei. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1992, 69, 2885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stecker, F.W.; Done, C.; Salamon, M.H.; Sommers, P. High-energy neutrinos from active galactic nuclei. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1991, 66, 2697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aartsen, M.G.; Abraham, K.; Ackermann, M.; Adams, J.; Aguilar, J.A.; Ahlers, M.; Ahrens, M.; Altmann, D.; Andeen, K.; Anderson, T.; et al. All-sky Search for Time-integrated Neutrino Emission from Astrophysical Sources with 7 yr of IceCube Data. Astrophys. J. 2017, 835, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adrián-Martínez, S.; Albert, A.; André, M.; Anton, G.; Ardid, M.; Aubert, J.-J.; Baret, B.; Barrios-Martí, J.; Basa, S.; Bertin, V.; et al. The First Combined Search for Neutrino Point-sources in the Southern Hemisphere with the ANTARES and IceCube Neutrino Telescopes. Astrophys. J. 2016, 823, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadler, M.; Krauß, F.; Mannheim, K.; Ojha, R.; Müller, C.; Schulz, R.; Anton, G.; Baumgartner, W.; Beuchert, T.; Buson, S.; et al. Coincidence of a high-fluence blazar outburst with a PeV-energy neutrino event. Nat. Phys. 2016, 12, 807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padovani, P.; Giommi, P.; Resconi, E.; Glauch, T.; Arsioli, B.; Sahakyan, N.; Huber, M. Dissecting the region around IceCube-170922A: The blazar TXS 0506+056 as the first cosmic neutrino source. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2018, 480, 192–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böttcher, M. Modeling the Emission Processes in Blazars; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2007; Volume 309, p. 95. [Google Scholar]
- Baring, M.G.; Böttcher, M.; Summerlin, E.J. Probing acceleration and turbulence at relativistic shocks in blazar jets. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2017, 464, 4875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blandford, R.; Eichler, D. Particle acceleration at astrophysical shocks: A theory of cosmic ray origin. Phys. Rep. 1987, 154, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drury, L. An introduction to the theory of diffusive shock acceleration of energetic particles in tenuous plasmas. Rep. Progr. Phys. 1983, 46, 973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, F.C.; Ellison, D.C. The plasma physics of shock acceleration. Space Sci. Rev. 1991, 58, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Summerlin, E.J.; Baring, M.G. Diffusive Acceleration of Particles at Oblique, Relativistic, Magnetohydrodynamic Shocks. Astrophys. J. 2012, 745, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marscher, A.P.; Gear, W.K. Models for high-frequency radio outbursts in extragalactic sources, with application to the early 1983 millimeter-to-infrared flare of 3C 273. Astrophys. J. 1985, 298, 114–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böttcher, M.; Dermer, C.D. Timing Signatures of the Internal-Shock Model for Blazars. Astrophys. J. 2010, 711, 445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Fossati, G.; Liang, E.P.; Böttcher, M. Time-dependent simulations of multi-wavelength variability of the blazar Mrk 421 with a Monte Carlo multizone code. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2011, 416, 2368–2387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Fossati, G.; Böttcher, M.; Liang, E.P. Time-dependent simulations of emission from the FSRQ PKS 1510-089: Multiwavelength variability of external Compton and synchrotron-self-Compton models. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2012, 424, 789–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graff, P.B.; Georganopoulos, M.; Perlman, E.S.; Kazanas, D. A Multizone Model for Simulating the High-Energy Variability of TeV Blazars. Astrophys. J. 2008, 689, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, M.; Böttcher, M. Time-dependent Radiation Transfer in the Internal Shock Model Scenario for Blazar Jets. Astrophys. J. 2011, 727, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, M.; Marscher, A.P.; Böttcher, M. Seed Photon Fields of Blazars in the Internal Shock Scenario. Astrophys. J. 2014, 785, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokolov, A.; Marscher, A.P.; McHardy, I.M. Synchrotron Self-Compton Model for Rapid Nonthermal Flares in Blazars with Frequency-dependent Time Lags. Astrophys. J. 2004, 613, 725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokolov, A.; Marscher, A.P. External Compton Radiation from Rapid Nonthermal Flares in Blazars. Astrophys. J. 2005, 629, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spada, M.; Ghisellini, G.; Lazzati, D.; Celotti, A. Internal shocks in the jets of radio-loud quasars. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2001, 325, 1559–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Chen, X.; Böttcher, M. Synchrotron Polarization in Blazars. Astrophys. J. 2014, 789, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Chen, X.; Böttcher, M.; Guo, F.; Li, H. Polarization Swings Reveal Magnetic Energy Dissipation in Blazars. Astrophys. J. 2015, 804, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Deng, W.; Li, H.; Böttcher, M. Polarization Signatures of Relativistic Magnetohydrodynamic Shocks in the Blazar Emission Region. I. Force-free Helical Magnetic Fields. Astrophys. J. 2016, 817, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusunose, M.; Takahara, F. A Structured Leptonic Jet Model for the “Orphan” TeV Gamma-Ray Flares in TeV Blazas. Astrophys. J. 2006, 651, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potter, W.J. Modelling blazar flaring using a time-dependent fluid jet emission model—An explanation for orphan flares and radio lags. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2018, 473, 4107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weidinger, M.; Spanier, F. A self-consistent and time-dependent hybrid blazar emission model. Properties and application. Astron. Astrophys. 2015, 573, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sironi, L.; Keshet, U.; Lemoine, M. Relativistic Shocks: Particle Acceleration and Magnetization. Space Sci. Rev. 2015, 191, 519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghisellini, G.; Tavecchio, F.; Foschini, L.; Ghirlanda, G.; Maraschi, L.; Celotti, A. General physical properties of bright Fermi blazars. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2010, 402, 497–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Li, X.; Li, H.; Daughton, W.; Zhang, B.; Lloyd-Ronning, N.; Liu, Y.-H.; Zhang, H.; Deng, W. Efficient Production of High-energy Nonthermal Particles during Magnetic Reconnection in a Magnetically Dominated Ion-Electron Plasma. Astrophys. J. 2016, 818, L9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kagan, D.; Sironi, L.; Cerutti, B.; Giannios, D. Relativistic Magnetic Reconnection in Pair Plasmas and Its Astrophysical Applications. Space Sci. Rev. 2015, 191, 545–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nalewajko, K.; Uzdensky, D.A.; Cerutti, B.; Werner, G.R.; Begelman, M.C. On the Distribution of Particle Acceleration Sites in Plasmoid-dominated Magnetic Reconnection. Astrophys. J. 2015, 815, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sironi, L.; Petropoulou, M.; Giannios, D. Relativistic jets shine through shocks or magnetic reconnection? Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2015, 450, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, G.R.; Uzdensky, D.A.; Cerutti, B.; Nalewajko, K.; Begelman, M.C. The Extent of Power-law Energy Spectra in Collisionless Relativistic Magnetic Reconnection in Pair Plasmas. Astrophys. J. 2016, 816, L8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Li, H.; Daughton, W.; Liu, Y.-H. Formaton of Hard Power Laws in the Energetic Particle Spectra Resulting from Relativistic Magnetic Reconnection. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2014, 113, 155005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giannios, D.; Uzdensky, D.A.; Begelman, M.C. Fast TeV variability in blazars: Jets in a jet. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2009, 395, L29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannos, D.; Uzdensky, D.A.; Begelman, M.C. Fast TeV variability from misaligned minijets in the jet of M87. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2010, 402, 1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannios, D. Reconnection-driven plasmoids in blazars: Fast flares on a slow envelope. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2013, 431, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christie, I.M.; Petropoulou, M.; Sironi, L.; Giannios, D. Radiative signatures of plasmoid-dominated magnetic reconnection in blazar jets. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2019, 482, 65–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghisellini, G.; Tavecchio, F. Rapid variability in TeV blazars: The case of PKS 2155-304. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2008, 386, L28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petropoulou, M.; Giannios, D.; Sironi, L. Blazar flares powered by plasmoids in relativistic reconnection. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2016, 462, 3325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araudo, A.T.; Bosch-Ramon, V.; Romero, G.E. Gamma rays from cloud penetration at the base of AGN jets. Astron. Astrophys. 2010, 552, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araudo, A.T.; Bosch-Ramon, V.; Romero, G.E. Gamma-ray emission from massive stars interacting with active galactic nuclei jets. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2013, 436, 3626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barkov, M.V.; Aharonian, F.A.; Bosch-Ramon, V. Gamma-ray Flares from Red Giant/Jt Interactions in Active Galactic Nuclei. Astrophys. J. 2010, 724, 1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barkov, M.V.; Aharonian, F.A.; Bogovalov, S.V.; Kelner, S.R.; Khangulyan, D. Rapid TeV Variability in Blazars as a Result of Jet-Star Interaction. Astrophys. J. 2012, 749, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khangulyan, D.V.; Barkov, M.V.; Bosch-Ramon, V.; Aharonian, F.A.; Dorodnitsyn, A.V. Star-Jet Interactions and Gamma-Ray Outbursts from 3C454.3. Astrophys. J. 2013, 774, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zacharias, M.; Böttcher, M.; Jankowsky, F.; Lenain, J.-P.; Wagner, S.J.; Wierzcholska, A. Cloud Ablation by a Relativistic Jet and the Extended Flare in CTA 102 in 2016 and 2017. Astrophys. J. 2017, 851, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böttcher, M. A Hadronic Synchrotron Mirror Model for the “Orphan Flare” of 1ES 1959+650. Astrophys. J. 2005, 621, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavani, M.; Vittorini, V.; Cavaliere, A. An Emerging Class of Gamma-ray Flares from Blazars: Beyond One-zone Models. Astrophys. J. 2015, 814, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacDonald, N.R.; Marscher, A.P.; Jorstad, S.G.; Joshi, M. Through the Ring of Fire: Gamma-Ray Variability in Blazars by a Moving Plasmoid Passing a Local Source of Seed Photons. Astrophys. J. 2015, 804, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacDonald, N.R.; Jorstad, S.G.; Marscher, A.P. “Orphan” γ-ray Flares and Stationary Sheaths of Blazar Jets. Astrophys. J. 2017, 850, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larionov, V.M.; Jorstad, S.G.; Marscher, A.P.; Morozova, D.A.; Blinov, D.A.; Hagen-Thorn, V.A.; Konstantinova, T.S.; Kopatskaya, E.N.; Larionova, L.V.; Larionova, E.G.; et al. The Outburst of the Blazar S5 0716+71 in 2011 October: Shock in a Helical Jet. Astrophys. J. 2013, 768, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larionov, V.M.; Villata, M.; Raiteri, C.M.; Jorstad, S.G.; Marscher, A.P.; Agudo, I.; Smith, P.S.; Acosta-Pulido, J.A.; arévalo, M.J.; Arkharov, A.A.; et al. Exceptional outburst of the blazar CTA 102 in 2012: The GASP-WEBT campaign and its extension. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2016, 461, 3047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostorero, L.; Villata, M.; Raiteri, C.M. Helical jets in blazars. Interpretation of the multifrequency long-term variability of AO 0235+16. Astron. Astrophys. 2004, 419, 913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raiteri, C.M.; Villata, M.; Acosta-Pulido, J.A.; Agudo, I.; Arkharov, A.A.; Bachev, R.; Baida, G.V.; Benítez, E.; Borman, G.A.; Boschin, W.; et al. Blazar spectral variability as explained by a twisted inhomogeneous jet. Nature 2017, 552, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villata, M.; Raiteri, C.M. Helical jets in blazars. I. The case of MKN 501. Astron. Astrophys. 1999, 347, 30. [Google Scholar]
- Lister, M.L.; Aller, M.F.; Aller, H.D.; Homan, D.C.; Kellermann, K.I.; Kovalev, Y.Y.; Pushkarev, A.B.; Richards, J.L.; Ros, E.; Savolainen, T. MOJAVE. X. Parsec-scale Jet Orientation Variations and Superluminal Motion in Active Galactic Nuclei. Astron. J. 2013, 146, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nalewajko, K. A Model of Polarisation Rotations in Blazars from Kink Instabilities in Relativistic Jets. Galaxies 2017, 5, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Li, H.; Guo, F.; Taylor, G. Polarization Signatures of Kink Instabilities in the Blazar Emission Region from Relativistic Magnetohydrodynamic Simulations. Astrophys. J. 2017, 835, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, E.P.; Fu, W.; Böttcher, M.; Roustazadeh, P. Scaling of Relativistic Shear Flows with the Bulk Lorentz Factor. Astrophys. J. 2018, 854, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobacchi, E.; Lyubarsky, Y.E. On the magnetisation and the radiative efficiency of BL Lac jets. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2019. submitted. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asano, K.; Takahara, F.; Kusunose, M.; Toma, K.; Kakuwa, J. Time-dependent Models for Blazar Emission with the Second-order Fermi Acceleration. Astrophys. J. 2014, 780, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böttcher, M.; Chiang, J. X-Ray Spectral Variability Signatures of Flares in BL Lacertae Objects. Astrophys. J. 2000, 581, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diltz, C.; Böttcher, M. Time dependent leptonic modeling of Fermi II processes in the jets of flat spectrum radio quasars. J. High Energy Astrophys. 2014, 1, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirk, J.G.; Rieger, F.M.; Mastichiadis, A. Particle acceleration and synchrotron emission in blazar jets. Astron. Astrophys. 1998, 333, 452. [Google Scholar]
- Kirk, J.G.; Mastichiadis, A. Variability patterns of synchrotron and inverse Compton emission in blazars. Astropart. Phys. 1999, 11, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusunose, M.; Takahara, F.; Li, H. Electron Acceleration and Time Variability of High-Energy Emission from Blazars. Astrophys. J. 2000, 536, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Kusunose, M. Temporal and Spectral Variabilities of High-Energy Emission from Blazars Using Synchrotron Self-Compton Models. Astrophys. J. 2000, 536, 729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastichiadis, A.; Kirk, J.G. Variability in the synchrotron self-Compton model of blazars. Astron. Astrophys. 1997, 320, 19. [Google Scholar]
- Diltz, C.; Böttcher, M.; Fossati, G. Time Dependent Hadronic Modeling of Flat Spectrum Radio Quasars. Astrophys. J. 2015, 802, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petropoulou, M.; Mastichiadis, A. Temporal signatures of leptohadronic feedback mechanisms in compact sources. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2012, 421, 2325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.S.; Cooper, G. A Practical Difference Scheme for Fokker-Planck Equations. J. Comput. Phys. 1970, 6, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potter, W.J.; Cotter, G. Synchrotron and inverse-Compton emission from blazar jets—II. An accelerating jet model with a geometry set by observations of M87. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2012, 429, 1189–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potter, W.J.; Cotter, G. Synchrotron and inverse-Compton emission from blazar jets—I. A uniform conical jet model. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2012, 423, 756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, S.; Spanier, F. A Numerical Model of Parsec-scale SSC Morphologies and Their Radio Emission. Astrophys. J. 2016, 829, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Pohl, M.; Böttcher, M. Particle diffusion and localized acceleration in inhomogeneous AGN Jets—I. Steady-state spectra. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2015, 447, 530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Finke, J.D.; Becker, P.A. Fourier Analysis of Blazar Variability. Astrophys. J. 2014, 791, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finke, J.D.; Becker, P.A. Fourier Analysis of Blazar Variability: Klein-Nishina Effects and the Jet Scattering Environment. Astrophys. J. 2015, 809, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, T.R.; Becker, P.A.; Finke, J.D. Time-dependent Electron Acceleration in Blazar Transients: X-ray Time Lags and Spectral Formation. Astrophys. J. 2016, 824, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.H. Cross-spectral analysis of the X-ray variability of Markarian 421. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2002, 337, 609–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lyutikov, M.; Kravchenko, E.V. Polarization swings in blazars. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2017, 467, 3876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marscher, A.P. Turbulent, Extreme Multi-zone Model for Simulating Flux and Polarization Variability in Blazars. Astrophys. J. 2014, 780, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacDonald, N.R.; Marscher, A.P. Faraday Conversion in Turbulent Blazar Jets. Astrophys. J. 2018, 862, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krawczynski, H. The Polarization Properties of Inverse Compton Emission and Implications for Blazar Observations with the GEMS X-Ray Polarimeter. Astrophys. J. 2012, 744, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonometto, S.; Saggion, A. Polarization in Inverse Compton Scattering of Synchrotron Radiation. Astron. Astrophys. 1974, 23, 9. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Böttcher, M. X-Ray and Gamma-Ray Polarization in Leptonic and Hadronic Jet Models of Blazars. Astrophys. J. 2013, 774, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
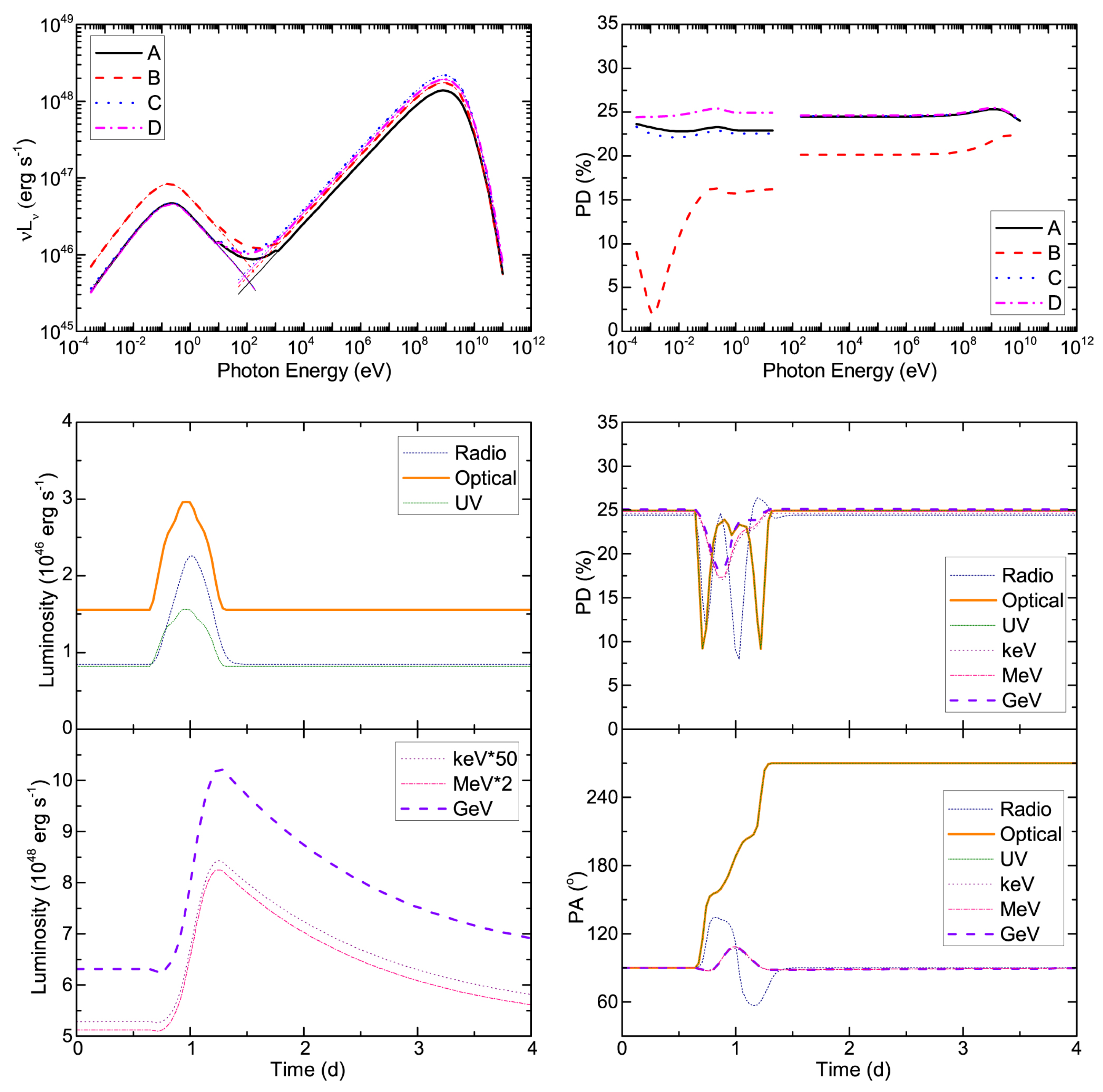
- Zhang, H.; Diltz, C.; Böttcher, M. Radiation and Polarization signatures of the 3D Multizone Time-dependent Hadronic Blazar Model. Astrophys. J. 2016, 829, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petropoulou, M.; Dimitrakoudis, S. Constraints of flat spectrum radio quasars in the hadronic model: The case of 3C 273. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2015, 452, 1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dermer, C.D.; Murase, K.; Inoue, Y. Photopionproduction in black-hole jets and flat-spectrum radio quasars as PeV neutrino sources. J. High Energy Astrophys. 2014, 3, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halzen, F. Pionic photons and neutrinos from cosmic ray accelerators. Astropart. Phys. 2013, 43, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannheim, K.; Biermann, P.L. Photomeson production in active galactic nuclei. Astron. Astrophys. 1989, 221, 211. [Google Scholar]
- Reimer, A.; Böttcher, M.; Postnikov, S. Neutrino Emission in the Hadronic Synchrotron Mirror Model: The “Orphan” TeV Flare from 1ES 1959+650. Astrophys. J. 2005, 630, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petropoulou, M.; Dimitrakoudis, S.; Padovani, P.; Mastichiadis, A.; Resconi, E. Photohadronic origin of γ-ray BL Lac emission: Implications for IceCube neutrinos. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2015, 448, 2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Murase, K.; Inoue, S.; Ge, C.; Wang, X.-Y. Can Winds Driven by Active Galactic Nuclei Account for the Extragalactic Gamma-Ray and Neutrino Backgrounds? Astrophys. J. 2018, 858, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.-Y.; Wang, K.; Xue, R.; Taylor, A.M.; Wang, X.-Y.; Li, Z.; Yan, H. A hadronuclear interpretation of a high-energy neutrino event coincident with a blazar flare. arXiv, 2018; arXiv:1807.05113. [Google Scholar]
- Cerruti, M.; Zech, A.; Boisson, C.; Emery, G.; Inoue, S.; Lenain, J.P. Lepto-hadronic single-zone models for the electromagnetic and neutrino emission of TXS 0506+056. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2018. submitted. [Google Scholar]
- Reimer, A.; Böttcher, M.; Buson, S. Cascading constraints from neutrino emitting blazars: The case of TXS 0506+056. Astrophys. J. 2018. submitted. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, S.; Fedynitch, A.; Winter, W.; Pohl, M. Interpretation of the coincident observation of a high energy neutrino and a bright flare. arXiv, 2018; arXiv:1807.04275. [Google Scholar]
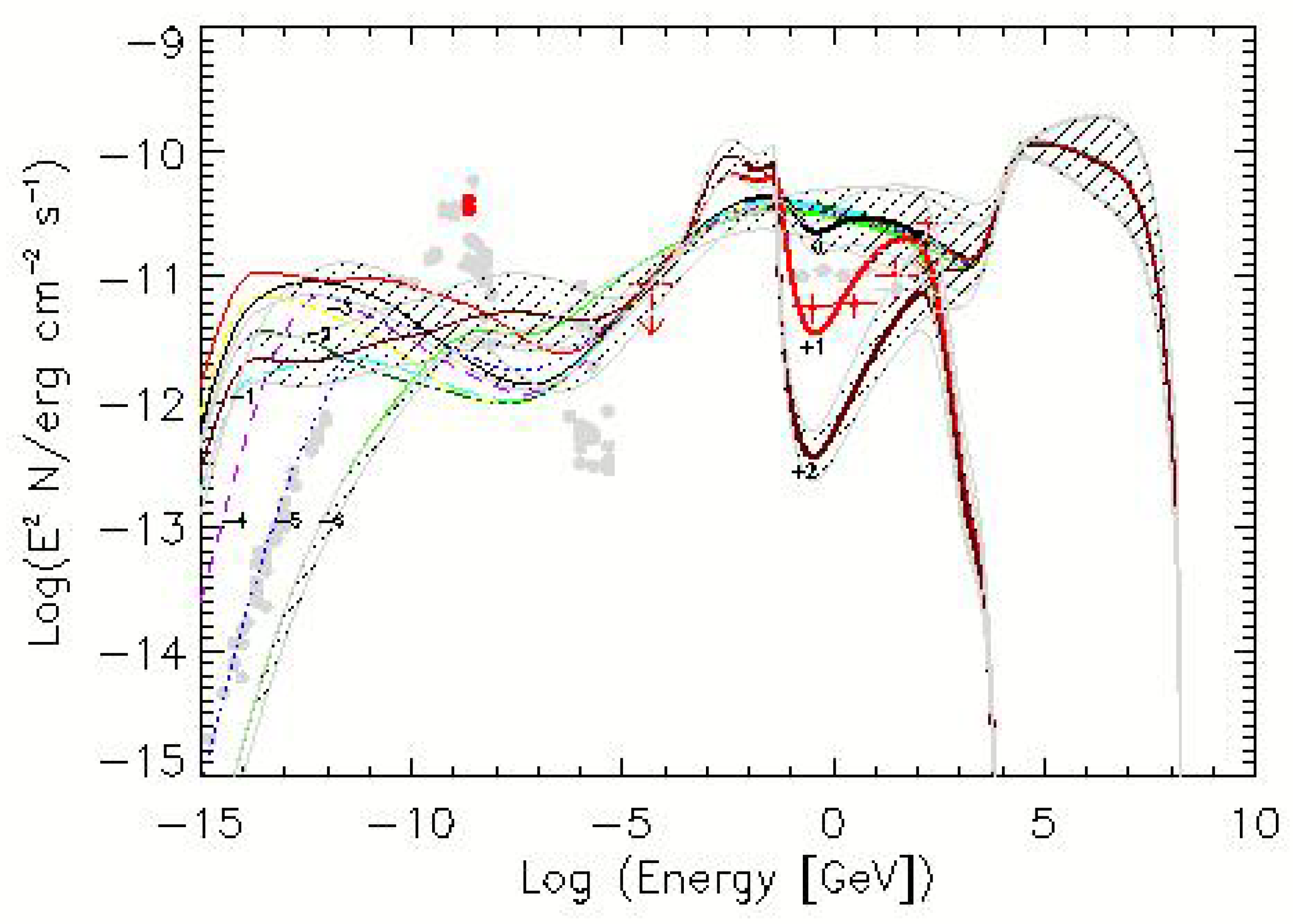
- Keivani, A.; Murase, K.; Petropoulou, M.; Fox, D.B.; Cenko, S.B.; Chaty, S.; Coleiro, A.; DeLaunay, J.J.; Dimitrakoudis, S.; Evans, P.A.; et al. A Mutimessenger Picture of the Flaring Blazar TXS 0506+056: Implications for High-energy Neutrino Emission and Cosmic-Ray Acceleration. Astrophys. J. 2018, 864, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murase, K.; Oikonomou, F.; Petropoulou, M. Blazar Flares as an Origin of High-energy Cosmic Neutrinos? Astrophys. J. 2018, 865, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansoldi, S. The Blazar TXS 0506+056 Associated with a High-energy Neutrino: Insights into Extragalactic Jets and Cosmic-Ray Acceleration. Astrophys. J. 2018, 863, L10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavecchio, F.; Ghisellini, G. Spine-sheath layer radiative interplay in subparsec-scale jets and the TeV emission from M87. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2008, 385, L98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Righi, C.; Tavecchio, F.; Inoue, S. Neutrino emission from BL Lac objects: The role of radiatively inefficient accretion flows. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2018. submitted. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, B.S.; Actis, M.; Aghajani, T.; Agnetta, G.; Aguilar, J.; Aharonian, F.; Ajello, M.; Akhperjanian, A.; Alcubierre, M.; Aleksić, J.; et al. Introducing the CTA Concept. Astropart. Phys. 2013, 43, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisskopf, M.C.; Ramsey, B.; O’Dell, S.L.; Tennant, A.; Elsner, R.; Soffita, P.; Bellazzini, R.; Costa, E.; Kolodziejczak, J.; Kaspi, V.; et al. The Imaging X-ray Polarimetry Explorer (IXPE). Results Phys. 2016, 6, 1179–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margiotta, A. The KM3NeT deep-sea neutrino telescope. Nucl. Inst. Methods Phys. 2014, 766, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adrián-Martínez, S.; Ageron, M.; Aharonian, F.; Aiello, S.; Albert, A.; Ameli, F.; Anassontzis, E.; Andre, M.; Androulakis, G.; Anghinolfi, M.; et al. Letter of intent for KM3NeT 2.0. J. Phys. G 2016, 43, 084001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aartsen, M.G.; Ackermann, M.; Adams, J.; Aguilar, J.A.; Ahlers, M.; Ahrens, M.; Al Samarai, I.; Altmann, D.; Andeen, K.; Anderson, T.; et al. The IceCube Neutrino Observatory—Contributions to ICRC 2017 Part VI: IceCube-Gen2, the Next Generation Neutrino Observatory. arXiv, 2017; arXiv:1710.01207. [Google Scholar]
- Blaufuss, E.; Kopper, C.; Haack, C.; IceCube-Gen2 Collaboration. The IceCube-Gen2 High Energy Array. In Proceedings of the 34th International Cosmic Ray Conference, The Hague, The Netherlands, 30 July–6 August 2015; Volume 236, p. 1146. [Google Scholar]
- Avrorin, A.; Aynutdinov, V.; Belolaptikov, I.; Berezhnev, S.; Bogorodsky, D.; Budnev, N.; Danilchenko, I.; Domogatsky, G.; Doroshenko, A.; Dyachok, A.; et al. The Gigaton Volume Detector in Lake Baikal. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A 2011, 639, 30–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moiseev, A. All-Sky Medium Energy Gamma-Ray Observatory (AMEGO). In Proceedings of the 35th International Cosmic Ray Conference (ICRC2017), Busan, Korea, 12–20 July 2017; Volume 301, p. 798. [Google Scholar]
- Cherenkov Telescope Array Consortium. Science with the Cherenkov Telescope Array. World Sci. 2017, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Böttcher, M.; Els, P. Gamma-Gamma Absorption in the Broad Line Region Radiation Fields of Gamma-Ray Blazars. Astrophys. J. 2016, 821, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finke, J.D. External Compton Scattring in Blazar Jets and the Location of the Location of the Gamma-Ray Emitting Region. Astrophys. J. 2016, 830, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.T.; Bai, J.M. Absorption of 10–200 GeV Gamma-Ray sby Radiation from Broad Line Regions in Blazars. Astrophys. J. 2006, 653, 1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poutanen, J.; Stern, B. GeV Breaks in Blazars as a Result of Gamma-ray Absorption Within the Broad-Line Region. Astrophys. J. 2010, 717, L118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavecchio, F.; Roncadelli, M.; Galanti, G.; Bonnoli, G. Evidence for axion-like particles from PKS 1222+216? Phys. Rev. D 2012, 86, 5036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavecchio, F.; Bonnoli, G. On the detectability of Lorentz invariance violation through anomalies in the multi-TeV γ-ray spectra of blazars. Astron. Astrophys. 2016, 585, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdo, A.A.; Ackermann, M.; Ajello, M.; Baldini, L.; Ballet, J.; Barbiellini, G.; Bastieri, D.; Bechtol, K.; Bellazzini, R.; Berenji, B.; et al. Radio-Loud Narrow-Line Seyfert 1 as a New Class of Gamma-Ray Active Galactic Nuclei. Astrophys. J. 2009, 707, L142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Ammando, F.; Orienti, M.; Finke, J.; Larsson, J.; Giroletti, M.; Raiteri, C.M. A Panchromatic View of Relativistic Jets in Narrow-Line Seyfert 1 Galaxies. Galaxies 2016, 4, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şentürk, G.D.; Errando, M.; Böttcher, M.; Mukherjee, R. Gamma-ray Observational Properties of TeV-detected Blazars. Astrophys. J. 2013, 764, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zech, A.; Cerruti, M.; Mazin, D. Expected signatures from hadronic emission processes in the TeV spectra of BL Lacertae objects. Astron. Astrophys. 2017, 602, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| 1 | |
| 2 | |
| 3 | |
| 4 | |
| 5 | |
| 6 | |
| 7 | |
| 8 | |
| 9 | |
| 10 | Any opinion, finding and conclusion or recommendation expressed in this material is that of the author and the NRF does not accept any liability in this regard. |

© 2019 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Böttcher, M. Progress in Multi-Wavelength and Multi-Messenger Observations of Blazars and Theoretical Challenges. Galaxies 2019, 7, 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies7010020
Böttcher M. Progress in Multi-Wavelength and Multi-Messenger Observations of Blazars and Theoretical Challenges. Galaxies. 2019; 7(1):20. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies7010020
Chicago/Turabian StyleBöttcher, Markus. 2019. "Progress in Multi-Wavelength and Multi-Messenger Observations of Blazars and Theoretical Challenges" Galaxies 7, no. 1: 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies7010020
APA StyleBöttcher, M. (2019). Progress in Multi-Wavelength and Multi-Messenger Observations of Blazars and Theoretical Challenges. Galaxies, 7(1), 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies7010020




