Abstract
The Hubble constant is of paramount importance in astrophysics and cosmology. A large number of methods have been developed with different electromagnetic probes to estimate its value. The most recent results show a tension between values obtained from Cosmic Microwave Background observations and supernovae. The simultaneous detection of gravitational waves and electromagnetic radiation from GW170817 provided a direct estimation of the Hubble constant that did not depend on the astronomical distance ladder. This concise review will present the methods to estimate the Hubble constant with the gravitational observations of compact binary mergers, discussing both bright and dark sirens and reporting the state of the art of the results.
1. Introduction
The model of the Universe envisaged by Einstein was static and required the addition of a cosmological constant [1]. Friedmann found the solution for an expanding Universe [2], whose expansion rate was first estimated by Lemaitre [3]. The landmark observations and the estimated distances of 24 galaxies led Hubble to propose a relation between the recession speed v and the distance d [4], whose proportionality constant H0 was later named the Hubble constant:
The estimated value of the Hubble constant was approximately 500 km s−1 Mpc−1, compared with the currently accepted value of about 70 km s−1 Mpc−1.
The analysis by [5] of the Hubble data found that some stars in the sample were bright HII regions and the population of Cepheid stars was not homogeneous, estimating a value of the Hubble constant of 75 km s−1 Mpc−1.
Presently, there is a broad range of techniques to estimate the Hubble constant. Two reference values are based on electromagnetic observations but in different domains. The Planck Collaboration estimation, H0 = 67.4 ± 0.5 km s−1 Mpc−1, is based in the Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB) temperature and polarization anisotropies [6], while the Supernova H0 for the Equation of State (SH0ES) Collaboration value, H0 = 73.2 ± 1.3 km s−1 Mpc−1, is based in Cepheids and type Ia supernovae [7]. The inconsistence between the two estimates produces the Hubble tension. Due to the relevance of the Hubble constant in distance determinations and its relations with other cosmological parameters, it is of paramount importance to tackle the Hubble tension.
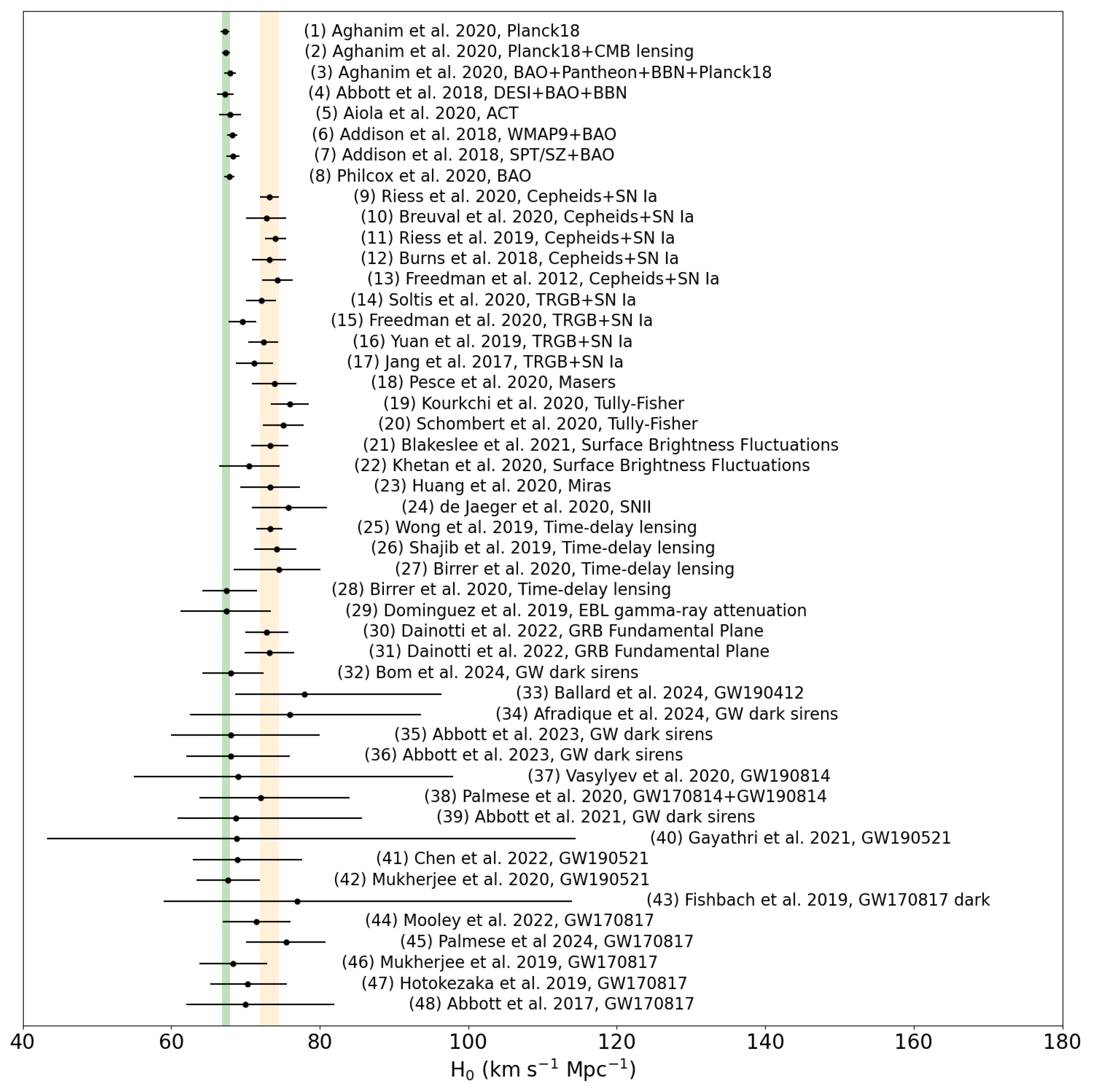
Extensive reviews discussing the methods and the observations to determine the Hubble constant have been presented by [8,9,10,11]. Figure 1 reports an overview of the estimates of the Hubble constant in literature secured using different methods, both in the electromagnetic domain and with gravitational waves, where the green and orange bands are the results by [6] and [7], respectively.
Figure 1.
The value of Hubble measured through different methods in the literature. Planck CMB determinations (1), (2) (3) by [6]; Baryonic Acoustic Oscillations (BAO): (4) by [12]; CMB (5) by [13]; CMB + BAO: (6), (7) by [14]; (8) by [15]; Cepheids+SN IA (9) by [7]; (10) by [16]; (11) by [17]; (12) by [18]; (13) by [19]; Tip of the Red Giant Branch (TRGB)+SN Ia: (14) by [20]; (15) by [21]; (16) by [22]; (17) by [23]; Masers: (18) by [24]; Tully–Fisher: (19) by [25]; (20) by [26]; Surface Brightness Fluctuations (SBF): (21) by [27]; (22) by [28]; Miras: (23) by [29]; SN II: (24) by [30]; Time Delay Lensing (TDL): (25) by [31]; (26) by [32]; (27), (28) by [33]; EBL gamma ray attenuation: (29) by [34]; GRB Fundamental Plane: (30), (31) by [35]. The Hubble constant estimates with gravitational waves from (32) to (48) are discussed in detail in Section 3 and Section 4. The green and orange bands are the CMB results by [6] and the SN Ia/Cepheids results by [7], respectively.
In addition to the CMB/Baryonic Acoustic Oscillations (BAO) estimates [6,12,13,14,15] and SN IA/Cepheids [7,16,17,18,19], a broad range of different methods are used: Tip of the Red Giant Branch (TRGB) with SN Ia [20,21,22,23]; Masers [24]; Tully–Fisher [25,26]; Surface Brightness Fluctuations (SBF) [27,28]; Miras [29]; SN II [30]; Time Delay Lensing (TDL) [31,32,33]; EBL gamma ray attenuation [34]; and GRB Fundamental Plane [35].
Generally, Hubble constant estimates in the electromagnetic domain rely on the observation of low-energy radiation (radio, optical, etc.). The EBL gamma ray attenuation and the GRB Fundamental Plane use high-energy probes as cosmological tools. In particular, the GRB Fundamental Plane uses GRBs as high redshift probes, with the three-dimensional Dainotti relation between the peak prompt luminosity, the rest frame time at the end of the X-ray plateau, and the corresponding X-ray luminosity [35].
With a few exceptions, such as masers, Hubble constant estimates rely on the astronomical distance ladder. Gravitational wave observations [36,37] can provide distance estimates completely independent from the electromagnetic observations, using standard sirens [38], the gravitational equivalent of the standard candles; see also [39].
The method relies on the relation between the strain amplitude h of the gravitational wave and the luminosity distance DL:
where G is the gravitational constant and I is the mass quadrupole moment of the source. The strain h and the frequency evolution of the gravitational signal both depend on the component masses m1, m2 through the chirp mass . The luminosity distance DL is estimated by measuring both the strain and the frequency evolution. Further details about distance measurements in gravitational astronomy can be found in [40].
Standard sirens can be bright, when an electromagnetic counterpart is observed and the host galaxy is identified, or dark. A first gravitational estimate of the Hubble constant [41] was performed using the GW170817 binary neutron star merger associated with the short Gamma-Ray Burst GRB 170817A in the host galaxy NGC 4993 [42]. Other Hubble constant estimates have been performed with dark sirens, relying on galaxy catalogs to provide a list of candidate host galaxies. The standard sirens will be discussed in Section 2; the Hubble constant determinations with bright sirens, in particular with GW170817/GRB 170817A, and with dark sirens will be discussed in Section 3 and Section 4, respectively. Gravitational distance estimates have an impact not only in the context of General Relativity but also in the field of alternative theories of gravity [43,44,45,46,47,48,49]. The comparison of the luminosity distance for gravitational waves and for electromagnetic signals is also relevant for alternative models of gravity and the Universe [50,51].
2. Standard Sirens
The observation of gravitational waves has opened a new window to study the Universe, detecting mergers of binary black holes (BBH) [52], binary neutron stars (BNSs) [42], and neutron star black holes (NSBH) [53]. The most recent gravitational wave transient catalog, GWTC-3 [54], contains 90 compact binary mergers that have been used for population studies [55] and tests of General Relativity [56]. The gravitational observations alone allow a direct measure of the luminosity distance DL of the source, but not of the redshift, which must be separately estimated.
The method of bright sirens is based on the identification of the host galaxy of the merger, but the typical localization regions range from hundreds to thousands of deg2, making the identification complicated unless an electromagnetic counterpart is detected. When the host galaxy is identified, its redshift can be determined from spectroscopic observations. An electromagnetic counterpart is expected for BNS and (at least some) NSBH mergers and has been observed in the GW 170817 BNS merger with the associated GRB 170817A [42], as discussed below; on the other hand, no counterpart is expected for BBH mergers, unless surrounding material is present in the merger region [57,58,59,60,61,62,63]. To date, GW170817 is the only merger with an unambiguous detection of an electromagnetic counterpart.
While gravitational wave observations alone do not provide information on the redshift z, they depend on the redshifted mass (1 + z)M, where M is the gravitational mass of the system. Therefore, the redshift can be inferred if an independent mass estimate is provided. The knowledge of either the mass distribution or the merger rate can lift the degeneracy between the mass and the redshift [64,65].
The method can be applied even when the electromagnetic counterpart is missing and has been used in the GWTC-3 estimation of the Hubble constant [66] described below.
When the electromagnetic counterpart of a merger is missing, the Hubble constant can be determined with dark sirens, combining the distance from gravitational wave observations with galaxy surveys to identify a list of candidate hosts within the localization volume, as first proposed by Schutz [38]. The method finds a general application to all types of mergers, including either black holes or neutron stars, BBHs, BNSs, and NSBHs. In addition to the large number of potential candidate galaxies within the large gravitational localization region, the method is limited by the completeness of the catalogs, which are flux-limited [67,68,69]. The dark siren method has been applied to the events detected in the O2 and O3 runs [66,70], as discussed below.
The compilation of estimates of the Hubble constant using bright and dark sirens, which will be discussed below, is reported in Table 1.

Table 1.
Gravitational wave estimates of the Hubble constant.
3. Hubble Constant Measurements with Bright Sirens
3.1. GW170817/GRB 170817A: Gravitational and Multi-Messenger Observations
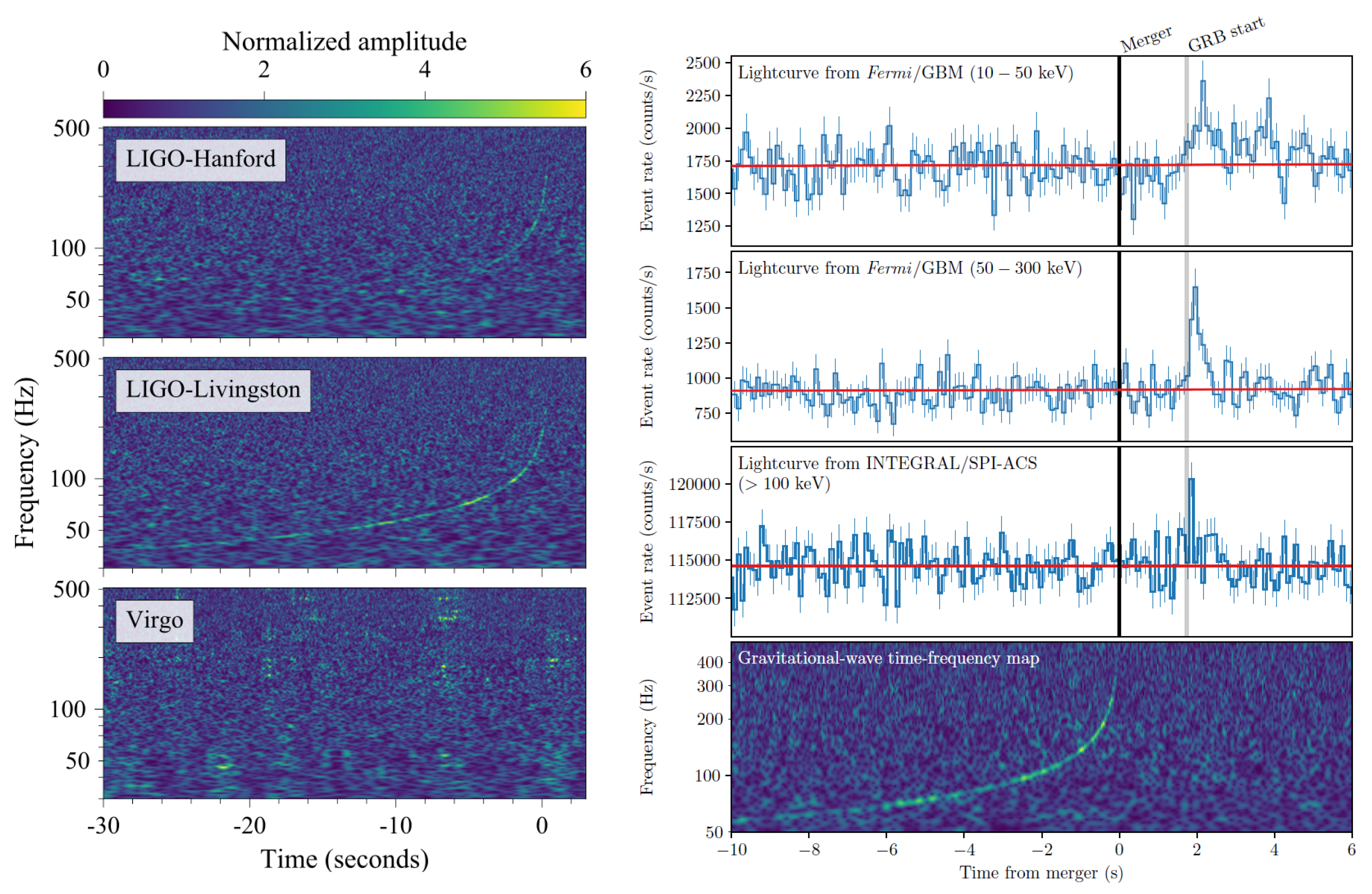
On 17 August 2017, the Advanced LIGO and Advanced Virgo interferometers detected the binary neutron star (BNS) merger GW170817 in the host galaxy NGC 4993 [42] (Figure 2). The luminosity distance of Mpc was consistent with the distance of NGC 4993 estimated with other methods [84,85,86,87,88]. The GBM instrument onboard Fermi and the SPI-ACS instrument onboard INTEGRAL detected the short Gamma-Ray Burst GRB 170817A after about 1.7 s at a position consistent with the merger [89,90]. The merger was detected with a combined signal-to-noise ratio of 32.4 and a false alarm rate smaller than one per 8.0 × 104 years in the LIGO Hanford and LIGO Livingston interferometers [42], and a signal-to-noise ratio of about 2 in the Virgo interferometer, indicating that the sky position of the merger was close to the region of null response [42]. The gravitational observations suggested that the range of the masses of the system components, 0.86 to 2.26 M⊙, and the range of the total mass, 2.72 to 3.29 M⊙, were consistent with the range of masses of neutron stars in binary systems [42].
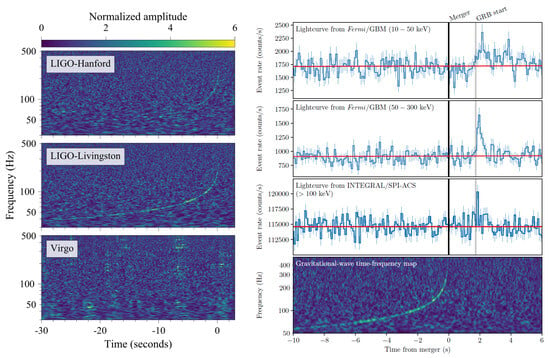
Figure 2.
(Left panel): time−frequency maps of BNS merger GW170817 observed in the LIGO Hanford (top), LIGO Livingston (center), and Virgo (bottom) interferometers. (Right panel): signal of GRB 170817A, associated with GW170817, observed by the Fermi-GBM (10–50 keV, 50–300 keV) and INTEGRAL SPI-ACS instruments (the red line is the background estimate), and the time-frequency map of GW170817. Adapted from [42,91].
The 90% localization region was about 28 deg2 [91], with a list of 54 galaxies obtained by cross-matching a galaxy catalog with the 90% localization volume of the merger; catalog incompleteness should be taken into account [92]. The optical counterpart of GW170817/GRB 170817A, AT2017gfo, was detected in the elliptical galaxy NGC 4993 10.87 h after the BNS merger by the One-Meter Two-Hemispheres collaboration using the Swope telescope [93,94] and quickly confirmed by DLT40 [95], VISTA [96], MASTER [97], DES [98], and LCO [99]. GW170817 was localized at a projected distance of about 2 kpc from the galaxy center [100], an offset consistent with the offsets of short GRBs (sGRBs) in other galaxies [101,102]. The images secured four months before the merger did not show any candidates [95]. The detection of associated electromagnetic radiation and the mass range of both primary and secondary show that at least one of the merging objects was a neutron star. The extensive follow-up multi-messenger observations of GW170817/GRB 170817A around the epoch of the merger and in the first days after have been summarized by [103]. No X-ray or radio counterpart was detected during the first week after the merger [90,104,105,106,107,108]. The X-ray and radio afterglows emerged 9 days [109] and 16 days [106] after the merger, respectively. Additional details about GW170817 and its afterglow can be found in a companion paper in this Special Issue.
3.2. GW170817/GRB 170817A: Hubble Constant Measurement with the Electromagnetic Counterpart
NGC 4993 shows a bulge, concentric shells, and dust lanes, and contains an old stellar population with a low Star Formation Rate [110]. Assuming that the optical counterpart defines the effective sky position of the merger, a re-analysis of gravitational data alone leads to a distance of Mpc [41]. In addition to calibration uncertainties and noise in the interferometers, the uncertainty on the distance is produced by the degeneracy between the luminosity distance DL and the orbital inclination angle i [111]. The distance and the orbital inclination contribute as (1 + )/ and /DL for the two gravitational wave polarizations. A similar signal amplitude can be produced either by a close binary with high inclination or by a distant face off/on merger. Degeneracy occurs when only a single polarization amplitude is measured [111]. The two LIGO interferometers are almost aligned and sensitive to a single polarizations; thus, an additional detector such as Virgo is required to measure both polarizations. The uncertainty has been later removed with the detection of the kilonova [96,112] and the presence of a collimated jet [113], as will be discussed in detail in Section 3.2.
The detection of the merger and its associated GRB has triggered new measurements of the distance to NGC 4993 using the Fundamental Plane (FP), Surface Brightness Fluctuations (SBFs), and Globular Cluster Luminosity Function (GCLF) [85,86,87,88], as reported in Table 2. Previous measurements were based on the Tully–Fisher method, with distances in the range 31.0 to 41.1 Mpc [84,114,115,116]. The gravitational wave distance estimate is consistent with the distances to NGC 4993 measured with the other methods.

Table 2.
Distance to NGC 4993 using different methods.
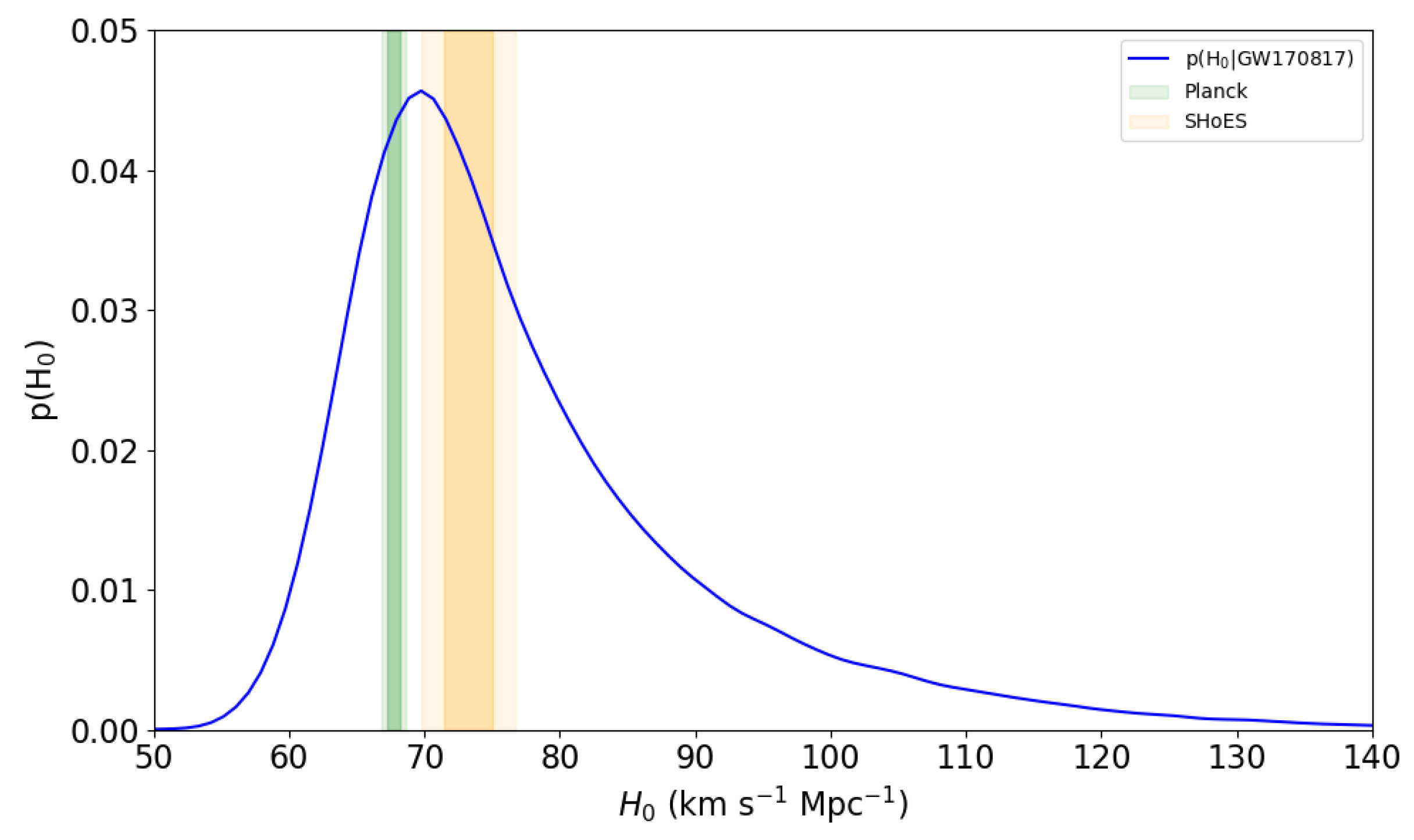
The determination of H0 [41] requires the estimation of the background Hubble flow velocity at the galaxy position. NGC 4993 belongs to a group of galaxies whose center of mass recession velocity relative to the frame of the Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB) is 3327 ± 72 km s−1 [117,118]. The group velocity must be corrected by the peculiar velocity of 310 km s−1 due to the bulk motion toward the Great Attractor [119,120]. A conservative estimate of 150 km s−1 has been assumed as the uncertainty on the peculiar velocity at the location of NGC 4993 [120]. The estimated Hubble velocity is 3017 ± 166 km s−1 [41]. Since the gravitational measurement of the distance is correlated with the inclination of the orbital plane of the binary and on the properties of its components, the uncertainty in these variables is managed by marginalizing over the posterior distribution on system parameters [41], considering a fixed position in the sky at the location of the optical counterpart. A Bayesian analysis to infer a posterior distribution on H0 and system inclination, with marginalization over uncertainties in the peculiar and recessional velocity, produced the marginal posterior for H0 reported in Figure 3.
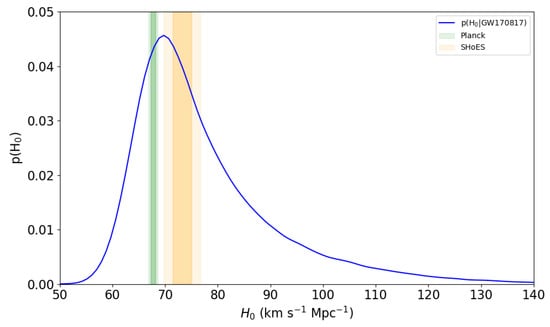
Figure 3.
Hubble constant posterior from GW170817 [41]. The shaded regions are the 1 and 2 contours of the Planck CMB [121] and (SH0ES) supernova [122] estimates. Data credits: https://dcc.ligo.org/LIGO-P1700296, accessed on 22 May 2025.
The inferred value of H0 was km s−1 Mpc−1 [41], consistent with other estimates: the Planck CMB measurements (67.74 ± 0.46 km s−1 Mpc−1) [121]; the type Ia supernova measurements from SH0ES (73.24 ± 1.74 km s−1 Mpc−1) [122]; the Cepheid measurements from the Hubble Space Telescope Key Project [84]; the H0 Lenses in COSMOGRAIL’s Wellspring (H0LiCOW) strong lensing measurements [123]; the SDSS Baryon Acoustic Oscillations measurements [124]; and the SPT high angular multipole CMB measurements from SPT32 [125]. The gravitational estimation of H0 was broadly consistent with both the Planck and SH0ES results but did not resolve the Hubble tension.
The Very Long Baseline Interferometry (VLBI) follow-up of the electromagnetic afterglow of GW170817 provided a tool to resolve the degeneracy of distance and inclination, revealing the presence of a collimated jet [113]. The detection of the jet triggered new estimations of the Hubble constant based on the modeling of the jet afterglow light curve and on the centroid motion. These methods have systematic uncertainties arising from modeling uncertainties in the jet morphology and from the choice of parameter priors. The estimation of the Hubble constant by [71], H0 = km s−1 Mpc−1, used the superluminal motion of the jet and also provided a measurement of the orbital inclination under the assumption of jet emission orthogonal to the orbital plane of the merger. The combination of the VLBI observations with a new estimation of the peculiar velocity produced a revised value of H0 = km s−1 Mpc−1 [72]. The later observations of the GW170817 afterglow have been used for additional Hubble constant estimates. The optical, radio, and X-ray observation of the jet afterglow up to 3.5 years after the merger has produced a measure of the viewing angle of the binary, deg, breaking the distance-angle degeneracy, and an estimation of the Hubble constant as km s−1 Mpc−1 [73]. A more recent determination of the Hubble constant [74], 71.5 ± 4.6 km s−1 Mpc−1, relies on the optical superluminal motion measurements at different epochs.
The GW170817 event has also been analyzed as a dark siren without its electromagnetic counterpart using the Galaxy List for the Advanced Detector Era (GLADE catalog) [75], with an estimated H0 = km s−1 Mpc−1.
The number of bright sirens is expected to increase in the future, allowing us to infer the redshift by observing the electromagnetic counterpart [39,126,127,128]. The initial predicted estimate of the Hubble constant at a level of about two per cent within five years suggested in 2018 by [127] has, however, already been falsified by observations. The number of required mergers can decrease if electromagnetic observations provide constraints on the system inclination as in the observations described above.
3.3. Bright Sirens Other than GW170817?
Among the 90 mergers detected in the first three observing runs [54], there is a second binary neutron star merger, GW190425 [129], with component masses of M⊙ and M⊙ [130]. The large luminosity distance, Gpc, and the extended localization region, 8700 deg2, of GW190425 are less favorable than those of GW170817. Despite an extensive follow-up campaign [131,132,133], there is no accepted counterpart. However, the Anti-Coincidence Shield (ACS) of the SPI gamma-ray spectrometer of INTEGRAL detected GRB 190425 [134], but the observation was not confirmed by Fermi-GBM [135]. The CHIME observatory detected the Fast Radio Burst FRB 20190425A about 2.5 h after the merger [136] at a position consistent with UGC 10667 [137], but the possible association with the merger was ruled out by the lack of a kilonova counterpart [138]. No counterpart was detected for the two neutron-star-black-hole mergers, GW200105 and GW200115 [53].
A special case of the possible bright siren is GW190521, a BBH merger with a total mass of about 150 M⊙ [139,140], that has been associated with the transient ZTF19abanrhr, a flare of the active galactic nucleus J124942.3+344929 [141] produced by the interaction of the remnant black hole with the accretion disk [62]. There is no consensus about the association of the merger with the flare [142,143]. GW190521 has been used alone or by adding the GW170817 posterior to estimate the Hubble constant: km s−1 Mpc−1 [76]; km s−1 Mpc−1 [77]. A value of Hubble constant of km s−1 Mpc−1 has been derived by [78] in the assumption of an eccentric merger.
4. Hubble Constant Measurements with Dark Sirens
A first estimation of the Hubble constant with dark sirens used BBH mergers detected during the O1 and O2 runs [70] combined with the GLADE catalog of galaxies observed in the B band [144]. The combined estimate using a set of six BBH mergers without a counterpart and the GW170817 estimate produced H0 = km s−1 Mpc−1 [70]. Several recent estimates of the Hubble constant have used the mergers of the O3 run. The estimation based on the GWTC-3 catalog used 47 compact binary coalescences detected during the O1, O2, and O3 runs and the updated GLADE+ catalog, which is complete up to a luminosity distance of Mpc [145]. The majority of mergers routinely detected are at large distances, where the GLADE+ catalog is incomplete. While the dark sirens alone lead to H0 = km s−1 Mpc−1, the inclusion of GW170817 produces an improved value, H0 = km s−1 Mpc−1, also in comparison to the original GW170817 estimation [66].
Additional estimates of the Hubble constant have been performed with one or a selection of dark sirens and catalogs with completeness extending to larger distances than GLADE+. The dark sirens GW170814 and GW190814 have been used together with the Dark Energy Survey (DES) catalog, producing H0 = km s−1 Mpc−1 [146] and km s−1 Mpc−1 [79], while combining GW170814, GW190814, and GW170817 leads to H0 = km s−1 Mpc−1 [79]. GW190814 and the GLADE catalog have been used by [80] to derive H0 = km s−1 Mpc−1 in combination with the GW170817 posterior. An estimation has used the merger GW190412 [147], which is lacking an electromagnetic counterpart but is localized within about 12 deg2 as a dark siren [148]. The estimated Hubble constant is km s−1 Mpc−1, which becomes km s−1 Mpc−1 when the GW170817 posterior is included [82]. Using GW190924_021846 and GW200202154313 as standard sirens and the DECam Local Volume Exploration (DELVE) catalog together with the bright siren GW170817 produces H0 = km s−1 Mpc−1, while using 10 well-localized (within 12 to ∼400 deg2) O3 dark sirens leads to H0 = km s−1 Mpc−1 [81]. The mergers detected during the O4 run have triggered a new determination of Hubble constant, combining 5 new dark sirens with 10 dark sirens from the previous runs [83], with H0 = km s−1 Mpc−1 and km s−1 Mpc−1 when combined with the GW170817 posterior.
All estimates based on dark sirens are broadly consistent and also consistent with the GW170817 estimate. The results suggest that well-localized dark sirens and complete galaxy catalogs can approach the precision of the bright sirens.
When using dark sirens, the modeling of the underlying mass distribution has a strong impact on the Hubble constant, and in principle, it is possible to obtain the BBH mass distribution together with the Hubble constant [149,150]. The Hubble estimation using the analysis of the first two runs used a simple power law model [70]. The Hubble constant determination based on the events in the first three observing runs investigated different distributions, in particular, a power law with one Gaussian over-density at about 35 M⊙ [66]. An analysis not relying on galaxy catalogs provided a joint constraint on the properties of the population of BBHs and the parameters of the cosmological model, with an estimated H0 = km s−1 Mpc−1 [66].
Additional methods have been suggesting to estimate the redshift of dark sirens: redshift distribution of the gravitational sources [151,152]; cross-correlation techniques for deriving the clustering redshift of gravitational mergers [153,154]; Pair-Instability Supernovae mass scale of black holes [65,149]; and tidal distortion of neutron stars [155,156].
5. Conclusions
Gravitational observations of mergers provide a tool to estimate the Hubble constant. The paper has summarized the estimates based on both bright sirens and dark sirens. The results from the bright siren GW170817 and the associated electromagnetic counterpart have provided the first estimation of the Hubble constant independent of the astronomical distance ladder. Other estimates use dark sirens, possibly well localized, and catalogs, whose completeness is a key factor. The number of detected mergers is steadily increasing, with the perspective of detecting a BNS merger as GW170817 in the near future and to estimate the redshift of dark sirens.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Acknowledgments
The author is grateful to the referees for their useful comments that improved the paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Einstein, A. Kosmologische Betrachtungen zur allgemeinen Relativitätstheorie. Sitzungsberichte Königlich Preuss. Akad. Wiss. 1917, 9, 142–152. [Google Scholar]
- Friedmann, A. Über die Krümmung des Raumes. Z. Fur Phys. 1922, 10, 377–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemaître, G. Un Univers homogène de masse constante et de rayon croissant rendant compte de la vitesse radiale des nébuleuses extra-galactiques. Ann. Société Sci. Brux. 1927, 47, 49–59. [Google Scholar]
- Hubble, E. A relation between distance and radial velocity among extra-galactic nebulae. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 1929, 15, 168–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandage, A. Current Problems in the Extragalactic Distance Scale. Astrophys. J. 1958, 127, 513–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghanim, N.; Akrami, Y.; Ashdown, M.; Aumont, J.; Baccigalupi, C.; Ballardini, M.; Banday, A.J.; Barreiro, R.B.; Bartolo, N.; Basak, S.; et al. [Planck Collaboration] Planck 2018 results. VI. Cosmological parameters. Astron. Astrophys. 2020, 641, A6, Erratum in: Astron. Astrophys 2021, 652, C4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riess, A.G.; Casertano, S.; Yuan, W.; Bowers, J.B.; Macri, L.; Zinn, J.C.; Scolnic, D. Cosmic Distances Calibrated to 1% Precision with Gaia EDR3 Parallaxes and Hubble Space Telescope Photometry of 75 Milky Way Cepheids Confirm Tension with ΛCDM. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2021, 908, L6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Valentino, E.; Mena, O.; Pan, S.; Visinelli, L.; Yang, W.; Melchiorri, A.; Mota, D.F.; Riess, A.G.; Silk, J. In the realm of the Hubble tension—A review of solutions. Class. Quant. Grav. 2021, 38, 153001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, P.; Lemos, P.; Lahav, O. A buyer’s guide to the Hubble constant. Astron. Astrophys. Rev. 2021, 29, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freedman, W.L.; Madore, B.F. Progress in direct measurements of the Hubble constant. JCAP 2023, 11, 050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verde, L.; Schöneberg, N.; Gil-Marín, H. A Tale of Many H0. Ann. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 2024, 62, 287–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, T.M.C.; Abdalla, F.B.; Annis, J.; Bechtol, K.; Benson, B.A.; Bernstein, R.A.; Bernstein, G.M.; Bertin, E.; Brooks, D.; Burke, D.L.; et al. [DES Collaboration] Dark Energy Survey Year 1 Results: A Precise H0 Estimate from DES Y1, BAO, and D/H Data. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2018, 480, 3879–3888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiola, S.; Calabrese, E.; Maurin, L.; Naess, S.; Schmitt, B.L.; Abitbol, M.H.; Addison, G.E.; Ade, P.A.R.; Alonso, D.; Amiri, M.; et al. [ACT Collaboration] The Atacama Cosmology Telescope: DR4 Maps and Cosmological Parameters. JCAP 2020, 12, 047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addison, G.E.; Watts, D.J.; Bennett, C.L.; Halpern, M.; Hinshaw, G.; Weiland, J.L. Elucidating ΛCDM: Impact of Baryon Acoustic Oscillation Measurements on the Hubble Constant Discrepancy. Astrophys. J. 2018, 853, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philcox, O.H.E.; Ivanov, M.M.; Simonović, M.; Zaldarriaga, M. Combining Full-Shape and BAO Analyses of Galaxy Power Spectra: A 1.6% CMB-independent constraint on H0. JCAP 2020, 05, 032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breuval, L.; Breuval, L.; Kervella, P.; Anderson, R.I.; Riess, A.G.; Arenou, F.; Trahin, B.; Mérand, A.; Gallenne, A.; Gieren, W.; et al. The Milky Way Cepheid Leavitt law based on Gaia DR2 parallaxes of companion stars and host open cluster populations. Astron. Astrophys. 2020, 643, A115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riess, A.G.; Casertano, S.; Yuan, W.; Macri, L.M.; Scolnic, D. Large Magellanic Cloud Cepheid Standards Provide a 1% Foundation for the Determination of the Hubble Constant and Stronger Evidence for Physics beyond ΛCDM. Astrophys. J. 2019, 876, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, C.R.; Parent, E.; Phillips, M.M.; Stritzinger, M.; Krisciunas, K.; Suntzeff, N.B.; Hsiao, E.Y.; Anais, J.; Boldt, L.; Busta, L.; et al. The Carnegie Supernova Project: Absolute Calibration and the Hubble Constant. Astrophys. J. 2018, 869, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freedman, W.L.; Madore, B.F.; Scowcroft, V.; Burns, C.; Monson, A.; Persson, S.E.; Seibert, M.; Rigby, J. Carnegie Hubble Program: A Mid-Infrared Calibration of the Hubble Constant. Astrophys. J. 2012, 758, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltis, J.; Casertano, S.; Riess, A.G. The Parallax of ω Centauri Measured from Gaia EDR3 and a Direct, Geometric Calibration of the Tip of the Red Giant Branch and the Hubble Constant. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2021, 908, L5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freedman, W.L.; Madore, B.F.; Hatt, D.; Hoyt, T.J.; Jang, I.S.; Beaton, R.L.; Burns, C.R.; Lee, M.G.; Monson, A.J.; Neeley, J.R. The Carnegie-Chicago Hubble Program. VIII. An Independent Determination of the Hubble Constant Based on the Tip of the Red Giant Branch. Astrophys. J. 2019, 882, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, W.; Riess, A.G.; Macri, L.M.; Casertano, S.; Scolnic, D. Consistent Calibration of the Tip of the Red Giant Branch in the Large Magellanic Cloud on the Hubble Space Telescope Photometric System and a Re-determination of the Hubble Constant. Astrophys. J. 2019, 886, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, I.S.; Lee, M.G. The Tip of the Red Giant Branch Distances to Typa Ia Supernova Host Galaxies. V. NGC 3021, NGC 3370, and NGC 1309 and the Value of the Hubble Constant. Astrophys. J. 2017, 836, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesce, D.W.; Braatz, J.A.; Reid, M.J.; Riess, A.G.; Scolnic, D.; Condon, J.J.; Gao, F.; Henkel, C.; Impellizzeri, C.M.V.; Kuo, C.Y.; et al. The Megamaser Cosmology Project. XIII. Combined Hubble constant constraints. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2020, 891, L1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kourkchi, E.; Tully, R.B.; Anand, G.S.; Courtois, H.M.; Dupuy, A.; Neill, J.D.; Rizzi, L.; Seibert, M. Cosmicflows-4: The Calibration of Optical and Infrared Tully–Fisher Relations. Astrophys. J. 2020, 896, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schombert, J.; McGaugh, S.; Lelli, F. Using the Baryonic Tully–Fisher Relation to Measure H o. Astron. J. 2020, 160, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blakeslee, J.P.; Jensen, J.B.; Ma, C.P.; Milne, P.A.; Greene, J.E. The Hubble Constant from Infrared Surface Brightness Fluctuation Distances. Astrophys. J. 2021, 911, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khetan, N.; Izzo, L.; Branchesi, M.; Wojtak, R.; Cantiello, M.; Murugeshan, C.; Agnello, A.; Della Valle, M.; Gall, C.; Hjorth, J.; et al. A new measurement of the Hubble constant using Type Ia supernovae calibrated with surface brightness fluctuations. Astron. Astrophys. 2021, 647, A72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.D.; Riess, A.G.; Yuan, W.; Macri, L.M.; Zakamska, N.L.; Casertano, S.; Whitelock, P.A.; Hoffmann, S.L.; Filippenko, A.V.; Scolnic, D. Hubble Space Telescope Observations of Mira Variables in the SN Ia Host NGC 1559: An Alternative Candle to Measure the Hubble Constant. Astrophys. J. 2020, 889, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Jaeger, T.; Stahl, B.E.; Zheng, W.; Filippenko, A.V.; Riess, A.G.; Galbany, L. A measurement of the Hubble constant from Type II supernovae. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2020, 496, 3402–3411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, K.C.; Suyu, S.H.; Chen, G.C.-F.; Rusu, C.E.; Millon, M.; Sluse, D.; Bonvin, V.; Fassnacht, C.D.; Taubenberger, S.; Auger, M.W.; et al. [H0LiCOW Collaboration] H0LiCOW–XIII. A 2.4 per cent measurement of H0 from lensed quasars: 5.3σ tension between early- and late-Universe probes. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2020, 498, 1420–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shajib, A.J.; Birrer, S.; Treu, T.; Agnello, A.; Buckley-Geer, E.J.; Chan, J.H.H.; Christensen, L.; Lemon, C.; Lin, H.; Millon, M.; et al. STRIDES: A 3.9 per cent measurement of the Hubble constant from the strong lens system DES J0408-5354. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2020, 494, 6072–6102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birrer, S.; Shajib, A.J.; Galan, A.; Millon, M.; Treu, T.; Agnello, A.; Auger, M.; Chen, G.C.-F.; Christensen, L.; Collett, T.; et al. TDCOSMO-IV. Hierarchical time-delay cosmography – joint inference of the Hubble constant and galaxy density profiles. Astron. Astrophys. 2020, 643, A165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domínguez, A.; Wojtak, R.; Finke, J.; Ajello, M.; Helgason, K.; Prada, F.; Desai, A.; Paliya, V.; Marcotulli, L.; Hartmann, D. A new measurement of the Hubble constant and matter content of the Universe using extragalactic background light γ-ray attenuation. Astrophys. J. 2019, 885, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dainotti, M.G.; Lenart, A.L.; Chraya, A.; Sarracino, G.; Nagataki, S.; Fraija, N.; Capozziello, S.; Bogdan, M. The gamma-ray bursts fundamental plane correlation as a cosmological tool. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2023, 518, 2201–2240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggiore, M. Gravitational Waves. Vol. 1: Theory and Experiments; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggiore, M. Gravitational Waves. Vol. 2: Astrophysics and Cosmology; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Schutz, B.F. Determining the Hubble Constant from Gravitational Wave Observations. Nature 1986, 323, 310–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holz, D.E.; Hughes, S.A. Using gravitational-wave standard sirens. Astrophys. J. 2005, 629, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.Y.; Holz, D.E.; Miller, J.; Evans, M.; Vitale, S.; Creighton, J. Distance measures in gravitational-wave astrophysics and cosmology. Class. Quant. Grav. 2021, 38, 055010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, B.P.; Abbott, R.; Abbott, T.D.; Acernese, F.; Ackle; Adams, K.; Adams, T.; Addesso, P.; Adhikari, R.X.; Adya, V.B.; et al. [LIGO Scientific and Virgo and 1M2H and Dark Energy Camera GW-E and DES and DLT40 and Las Cumbres Observatory and VINROUGE and MASTER Collaborations] A gravitational-wave standard siren measurement of the Hubble constant. Nature 2017, 551, 85–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, B.P.; Abbott, R.; Abbott, T.D.; Acernese, F.; Ackley, K.; Adams, C.; Adams, T.; Addesso, P.; Adhikari, R.X.; Adya, V.R.; et al. [LIGO Scientific and Virgo Collaborations] GW170817: Observation of Gravitational Waves from a Binary Neutron Star Inspiral. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2017, 119, 161101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belgacem, E.; Dirian, Y.; Foffa, S.; Maggiore, M. Gravitational-wave luminosity distance in modified gravity theories. Phys. Rev. D 2018, 97, 104066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belgacem, E.; Dirian, Y.; Foffa, S.; Maggiore, M. Modified gravitational-wave propagation and standard sirens. Phys. Rev. D 2018, 98, 023510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belgacem, E.; Dirian, Y.; Finke, A.; Foffa, S.; Maggiore, M. Gravity in the infrared and effective nonlocal models. JCAP 2020, 4, 010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amendola, L.; Sawicki, I.; Kunz, M.; Saltas, I.D. Direct detection of gravitational waves can measure the time variation of the Planck mass. JCAP 2018, 8, 030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalang, C.; Lombriser, L. Limitations on Standard Sirens tests of gravity from screening. JCAP 2019, 10, 013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalang, C.; Fleury, P.; Lombriser, L. Horndeski gravity and standard sirens. Phys. Rev. D 2020, 102, 044036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garoffolo, A.; Tasinato, G.; Carbone, C.; Bertacca, D.; Matarrese, S. Gravitational waves and geometrical optics in scalar-tensor theories. JCAP 2020, 11, 040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanizza, G.; Franchini, G.; Gasperini, M.; Tedesco, L. Comparing the luminosity distance for gravitational waves and electromagnetic signals in a simple model of quadratic gravity. Gen. Relativ. Gravit. 2020, 52, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanizza, G.; Pavone, E.; Tedesco, L. Gravitational wave luminosity distance in viscous cosmological models. JCAP 2022, 08, 064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, B.; Abbott, R.; Abbott, T.D.; Abernathy, M.R.; Acernese, F.; Ackley, K.; Adams, C.; Adams, T.; Addesso, P.; Adhikari, R.X.; et al. [LIGO Scientific and Virgo Collaborations] Observation of Gravitational Waves from a Binary Black Hole Merger. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2016, 116, 061102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, R.; Abbott, T.D.; Abraham, S.; Acernese, F.; Ackley, K.; Adams, K.; Adams, C.; Adhikari, R.X.; Adya, V.B.; Affeldt, C.; et al. [LIGO Scientific and KAGRA and VIRGO Collaborations] Observation of Gravitational Waves from Two Neutron Star–Black Hole Coalescences. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2021, 915, L5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, R.; Abbott, T.D.; Acernese, F.; Ackley, K.; Adams, C.; Adhikari, N.; Adhikari, R.X.; Adya, V.B.; Affeldt, C.; Agarwal, D.; et al. [KAGRA and VIRGO and LIGO Scientific Collaborations] GWTC-3: Compact Binary Coalescences Observed by LIGO and Virgo during the Second Part of the Third Observing Run. Phys. Rev. X 2023, 13, 041039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, R.; Abbott, T.D.; Acernese, F.; Ackley, K.; Adams, C.; Adhikari, N.; Adhikari, R.X.; Adya, V.B.; Affeldt, C.; Agarwal, D.; et al. [KAGRA and VIRGO and LIGO Scientific Collaborations] Population of Merging Compact Binaries Inferred Using Gravitational Waves through GWTC-3. Phys. Rev. X 2023, 13, 011048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, R.; Abe, H.; Acernese, F.; Ackley, K.; Adhikari, N.; Adhikari, R.X.; Adkins, V.K.; Adya, V.B.; Affeldt, C.; Agarwal, D.; et al. [LIGO Scientific and VIRGO and KAGRA Collaborations] Tests of General Relativity with GWTC-3. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2112.06861. [Google Scholar]
- Schnittman, J.D. Electromagnetic Counterparts to Black Hole Mergers. Class. Quant. Grav. 2011, 28, 094021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perna, R.; Lazzati, D.; Giacomazzo, B. Short Gamma-Ray Bursts from the Merger of Two Black Holes. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2016, 821, L18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, N.C.; Metzger, B.D.; Haiman, Z. Assisted inspirals of stellar mass black holes embedded in AGN discs: Solving the ‘final au problem’. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2017, 464, 946–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murase, K.; Kashiyama, K.; Mészáros, P.; Shoemaker, I.; Senno, N. Ultrafast Outflows from Black Hole Mergers with a Minidisk. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2016, 822, L9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mink, S.E.d.; King, A. Electromagnetic signals following stellar-mass black hole mergers. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2017, 839, L7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKernan, B.; Ford, K.E.S.; Bartos, I.; Graham, M.J.; Lyra, W.; Marka, S.; Marka, Z.; Ross, N.P.; Stern, D.; Yang, Y. Ram-pressure stripping of a kicked Hill sphere: Prompt electromagnetic emission from the merger of stellar mass black holes in an AGN accretion disk. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2019, 884, L50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogdanovic, T.; Miller, M.C.; Blecha, L. Electromagnetic counterparts to massive black-hole mergers. Living Rev. Relativ. 2022, 25, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zevin, M.; Bavera, S.S.; Berry, C.P.L.; Kalogera, V.; Fragos, T.; Marchant, P.; Rodriguez, C.L.; Antonini, F.; Holz, D.E.; Pankow, C. One Channel to Rule Them All? Constraining the Origins of Binary Black Holes Using Multiple Formation Pathways. Astrophys. J. 2021, 910, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farr, W.M.; Fishbach, M.; Ye, J.; Holz, D. A Future Percent-Level Measurement of the Hubble Expansion at Redshift 0.8 With Advanced LIGO. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2019, 883, L42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, R.; Abe, H.; Acernese, F.; Ackley, K.; Adhikari, N.; Adhikari, R.X.; Adkins, V.K.; Adya, V.B.; Affeldt, C.; Agarwal, D.; et al. [LIGO Scientific and Virgo and KAGRA Collaborations] Constraints on the Cosmic Expansion History from GWTC–3. Astrophys. J. 2023, 949, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, R.; Magaña Hernandez, I.; Qi, H.; Brady, P.R.; Chen, H.-U.; Farr, W.M.; Fishbach, M.; Gair, J.R.; Ghosh, A.; Holz, D.E.; et al. Cosmological inference using gravitational wave standard sirens: A mock data analysis. Phys. Rev. D 2020, 101, 122001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, R.; Messenger, C.; Veitch, J. A pixelated approach to galaxy catalogue incompleteness: Improving the dark siren measurement of the Hubble constant. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2022, 512, 1127–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, R.; Beirnaert, F.; Karathanasis, C.; Revenu, B.; Chen, A.; Baker, T.; Vallejo, S.; Romano, A.E.; Ghosh, K.; Leyde, K.; et al. Joint cosmological and gravitational-wave population inference using dark sirens and galaxy catalogues. JCAP 2023, 12, 023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, B.P.; Abbott, R.; Abbott, T.D.; Abraham, S.; Acernese, F.; Ackley, K.; Adams, C.; Adhikari, R.X.; Adya, V.B.; Affeldt, C.; et al. [LIGO Scientific and Virgo and VIRGO Collaborations] A Gravitational-wave Measurement of the Hubble Constant Following the Second Observing Run of Advanced LIGO and Virgo. Astrophys. J. 2021, 909, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotokezaka, K.; Nakar, E.; Gottlieb, O.; Nissanke, S.; Masuda, K.; Hallinan, G.; Mooley, K.P.; Deller, A.T. A Hubble constant measurement from superluminal motion of the jet in GW170817. Nat. Astron. 2019, 3, 940–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, S.; Lavaux, G.; Bouchet, F.R.; Jasche, J.; Wandelt, B.D.; Nissanke, S.M.; Leclercq, F.; Hotokezaka, K. Velocity correction for Hubble constant measurements from standard sirens. Astron. Astrophys. 2021, 646, A65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmese, A.; Kaur, R.; Hajela, A.; Margutti, R.; McDowell, A.; MacFadyen, A. Standard siren measurement of the Hubble constant using GW170817 and the latest observations of the electromagnetic counterpart afterglow. Phys. Rev. D 2024, 109, 063508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mooley, K.P.; Anderson, J.; Lu, W. Optical superluminal motion measurement in the neutron-star merger GW170817. Nature 2022, 610, 273–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fishbach, M.; Gray, R.; Magaña Hernandez, I.; Qi, H.; Sur, A.; Acernese, F.; Aiello, L.; Allocca, A.; Aloy, M.A.; Amato, A.; et al. [LIGO Scientific and Virgo Collaborations] A Standard Siren Measurement of the Hubble Constant from GW170817 without the Electromagnetic Counterpart. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2019, 871, L13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, S.; Ghosh, A.; Graham, M.J.; Karathanasis, C.; Kasliwal, M.M.; Magaña Hernandez, I.; Nissanke, S.M.; Silvestri, A.; Wandelt, B.D. First measurement of the Hubble parameter from bright binary black hole GW190521. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2009.14199. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.Y.; Haster, C.J.; Vitale, S.; Farr, W.M.; Isi, M. A standard siren cosmological measurement from the potential GW190521 electromagnetic counterpart ZTF19abanrhr. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2022, 513, 2152–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gayathri, V.; Healy, J.; Lange, J.; O’Brien, B.; Szczepanczyk, M.; Bartos, I.; Campanelli, M.; Klimenko, S.; Lousto, C.O.; O’Shaughnessy, R. Measuring the Hubble Constant with GW190521 as an Eccentric black hole Merger and Its Potential Electromagnetic Counterpart. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2021, 908, L34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmese, A.; deVicente, J.; Pereira, M.E.S.; Annis, J.; Hartley, W.; Herner, K.; Soares-Santos, M.; Crocce, M.; Huterer, D.; Magaña Hernandez, I.; et al. [DES Collaboration] A statistical standard siren measurement of the Hubble constant from the LIGO/Virgo gravitational wave compact object merger GW190814 and Dark Energy Survey galaxies. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2020, 900, L33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasylyev, S.; Filippenko, A. A Measurement of the Hubble Constant using Gravitational Waves from the Binary Merger GW190814. Astrophys. J. 2020, 902, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfradique, V.; Bom, C.R.; Palmese, A.; Teixeira, G.; Santana-Silva, L.; Drlica-Wagner, A.; Riley, A.H.; Martínez-Vázquez, C.E.; Sand, D.J.; Stringfellow, G.S.; et al. A dark siren measurement of the Hubble constant using gravitational wave events from the first three LIGO/Virgo observing runs and DELVE. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2024, 528, 3249–3259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballard, W.; Palmese, A.; Magaña Hernandez, I.; BenZvi, S.; Moon, J.; Ross, A.J.; Rossi, G.; Ahlen, S.; Blum, R.; Brooks, D.; et al. [DESI Collaboration] A Dark Siren Measurement of the Hubble Constant with the LIGO/Virgo Gravitational Wave Event GW190412 and DESI Galaxies. Res. Notes AAS 2023, 7, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bom, C.R.; Alfradique, V.; Palmese, A.; Teixeira, G.; Santana-Silva, L.; Santos, A.; Darc, P. A dark standard siren measurement of the Hubble constant following LIGO/Virgo/KAGRA O4a and previous runs. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2024, 535, 961–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freedman, W.L.; Madore, B.F.; Gibson, B.K.; Ferrarese, L.; Kelson, D.D.; Sakai, S.; Mould, J.R.; Kennicutt, R.C.; Ford, H.C.; Graham, J.A.; et al. [HST Collaboration] Final results from the Hubble Space Telescope key project to measure the Hubble constant. Astrophys. J. 2001, 553, 47–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantiello, M.; Jensen, J.B.; Blakeslee, J.P.; Berger, E.; Levan, A.J.; Tanvir, N.N.; Raimondo, G.; Brocato, E.; Alexander, K.D.; Blanchard, P.K.; et al. A Precise Distance to the Host Galaxy of the Binary Neutron Star Merger GW170817 Using Surface Brightness Fluctuations. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2018, 854, L31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hjorth, J.; Levan, A.J.; Tanvir, N.R.; Lyman, J.D.; Wojtak, R.; Schrøder, S.L.; Mandel, I.; Gall, C.; Bruun, S.H. The Distance to NGC 4993: The Host Galaxy of the Gravitational-wave Event GW170817. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2017, 848, L31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Im, M.; Yoon, Y.; Lee, J.; Lee, H.M.; Kim, J.; Lee, C.-U.; Kim, S.-L.; Troja, E.; Choi, C.; Lim, G.; et al. Distance and Properties of NGC 4993 as the Host Galaxy of the Gravitational-wave Source GW170817. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2017, 849, L16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.G.; Kang, J.; Im, M. A Globular Cluster Luminosity Function Distance to NGC 4993 Hosting a Binary Neutron Star Merger GW170817/GRB 170817A. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2018, 859, L6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, A.; Veres, P.; Burns, E.; Briggs, M.S.; Hamburg, R.; Kocevski, D.; Wilson-Hodge, C.A.; Preece, R.D.; Poolakkil, S.; Roberts, O.J.; et al. An Ordinary Short Gamma-Ray Burst with Extraordinary Implications: Fermi-GBM Detection of GRB 170817A. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2017, 848, L14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savchenko, V.; Ferrigno, C.; Kuulkers, E.; Bazzano, A.; Bozzo, E.; Brandt, S.; Chenevez, J.; Courvoisier, T.J.-L.; Diehl, R.; Domingo, A.; et al. INTEGRAL Detection of the First Prompt Gamma-Ray Signal Coincident with the Gravitational-wave Event GW170817. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2017, 848, L15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, B.P.; Abbott, R.; Abbott, T.D.; Acernese, F.; Ackley, K.; Adams, C.; Adams, T.; Addesso, P.; Adhikari, R.X.; Adya, V.B.; et al. [LIGO Scientific and Virgo and Fermi-GBM and INTEGRAL Collaborations] Gravitational Waves and Gamma-rays from a Binary Neutron Star Merger: GW170817 and GRB 170817A. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2017, 848, L13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, D.P.; Van Sistine, A.; Singer, L.; Kasliwal, M.M. GRB Coordinates Network Circular; 2017; Volume 21519. Available online: https://gcn.nasa.gov/circulars/21519 (accessed on 11 May 2025).
- Coulter, D.A.; Foley, R.J.; Kilpatrick, C.D.; Drout, M.R.; Piro, A.L.; Shappee, B.J.; Siebert, M.R.; Simon, J.D.; Ulloa, N.; Kasen, D.; et al. Swope Supernova Survey 2017a (SSS17a), the Optical Counterpart to a Gravitational Wave Source. Science 2017, 358, 1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siebert, M.R.; Foley, R.J.; Drout, M.R.; Kilpatrick, C.D.; Shappee, B.J.; Coulter, D.A.; Kasen, D.; Madore, B.F.; Murguia-Berthier, A.; Pan, Y.-C.; et al. The Unprecedented Properties of the First Electromagnetic Counterpart to a Gravitational Wave Source. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2017, 848, L26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenti, S.; Sand, D.J.; Yang, S.; Cappellaro, E.; Tartaglia, L.; Corsi, A.; Jha, S.W.; Reichart, D.E.; Haislip, J.; Kouprianov, V. The discovery of the electromagnetic counterpart of GW170817: Kilonova AT 2017gfo/DLT17ck. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2017, 848, L24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanvir, N.R.; Levan, A.J.; González-Fernández, C.; Korobkin, O.; Mandel, I.; Rosswog, S.; Hjorth, J.; D’Avanzo, P.; Fruchter, S.; Fryer, C.L.; et al. The Emergence of a Lanthanide-Rich Kilonova Following the Merger of Two Neutron Stars. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2017, 848, L27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipunov, V.M.; Gorbovskoy, E.; Kornilov, V.G.; Tyurina, N.; Balanutsa, P.; Kuznetsov, A.; Vlasenko, D.; Kuvshinov, D.; Gorbunov, I.; Buckley, D.A.H.; et al. MASTER Optical Detection of the First LIGO/Virgo Neutron Star Binary Merger GW170817. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2017, 850, L1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares-Santos, M.; Holz, D.E.; Annis, J.; Chornock, R.; Herner, K.; Berger, E.; Brout, E.; Chen, H.Y.; Kessler, R.; Sako, M.; et al. [DES and Dark Energy Camera GW-EM Collaborations] The Electromagnetic Counterpart of the Binary Neutron Star Merger LIGO/Virgo GW170817. I. Discovery of the Optical Counterpart Using the Dark Energy Camera. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2017, 848, L16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arcavi, I.; Hosseinzadeh, G.; Howell, D.A.; McCully, C.; Poznanski, D.; Kasen, D.; Barnes, J.; Zaltzman, M.; Vasylyev, S.; Maoz, D.; et al. Optical emission from a kilonova following a gravitational-wave-detected neutron-star merger. Nature 2017, 551, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, B.P.; Abbott, R.; Abbott, T.D.; Acernese, F.; Ackley, K.; Adams, C.; Adams, T.; Addesso, P.; Adhikari, R.X.; Adya, V.B.; et al. [LIGO Scientific and Virgo Collaborations] On the Progenitor of Binary Neutron Star Merger GW170817. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2017, 850, L40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fong, W.F.; Berger, E. The Locations of Short Gamma-ray Bursts as Evidence for Compact Object Binary Progenitors. Astrophys. J. 2013, 776, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, E. Short-Duration Gamma-Ray Bursts. Ann. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 2014, 52, 43–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, B.P.; Abbott, R.; Abbott, T.D.; Acernese, F.; Ackley, K.; Adams, C.; Adams, T.; Addesso, P.; Adhikari, R.X.; Adya, V.B.; et al. [LIGO Scientific and Virgo and Fermi GBM and INTEGRAL and IceCube and IPN and Insight-Hxmt and ANTARES and Swift and Dark Energy Camera GW-EM and DES and DLT40 and GRAWITA and Fermi-LAT and ATCA and ASKAP and OzGrav and DWF (Deeper Wider Faster Program) and AST3 and CAASTRO and VINROUGE and MASTER and J-GEM and GROWTH and JAGWAR and CaltechNRAO and TTU-NRAO and NuSTAR and Pan-STARRS and KU and Nordic Optical Telescope and ePESSTO and GROND and Texas Tech University and TOROS and BOOTES and MWA and CALET and IKI-GW Follow-up and H.E.S.S. and LOFAR and LWA and HAWC and Pierre Auger and ALMA and Pi of Sky and Chandra Team at McGill University and DFN and ATLAS Telescopes and High Time Resolution Universe Survey and RIMAS and RATIR and SKA South Africa/MeerKAT Collaborations and AstroSat Cadmium Zinc Telluride Imager Team and AGILE Team and 1M2H Team and Las Cumbres Observatory Group and MAXI Team and TZAC Consortium and SALT Group and Euro VLBI Team] Multi-messenger Observations of a Binary Neutron Star Merger. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2017, 848, L12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, P.A.; Cenko, S.B.; Kennea, J.A.; Emery, S.W.K.; Kuin, N.P.M.; Korobkin, O.; Wollaeger, R.T.; Fryer, C.L.; Madsen, K.K.; Harrison, F.A.; et al. Swift and NuSTAR observations of GW170817: Detection of a blue kilonova. Science 2017, 358, 1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexander, K.D.; Berger, E.; Fong, W.; Williams, P.K.G.; Guidorzi, C.; Margutti, R.; Metzger, B.D.; Annis, J.; Blanchard, P.K.; Brout, D.; et al. The Electromagnetic Counterpart of the Binary Neutron Star Merger LIGO/VIRGO GW170817. VI. Radio Constraints on a Relativistic Jet and Predictions for Late-Time Emission from the Kilonova Ejecta. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2017, 848, L21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallinan, G.; Corsi, A.; Mooley, K.P.; Hotokezaka, K.; Nakar, E.; Kasliwal, M.M.; Kaplan, D.L.; Frail, D.A.; Myers, S.T.; Murphy, T.; et al. A Radio Counterpart to a Neutron Star Merger. Science 2017, 358, 1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Margutti, R.; Berger, E.; Fong, W.; Guidorzi, C.; Alexander, K.D.; Metzger, B.D.; Blanchard, B.K.; Cowperthwaite, P.S.; Chornock, R.; Eftekhari, T.; et al. The Electromagnetic Counterpart of the Binary Neutron Star Merger LIGO/VIRGO GW170817. V. Rising X-ray Emission from an Off-Axis Jet. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2017, 848, L20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugita, S.; Kawai, N.; Nakahira, S.; Negoro, H.; Serino, M.; Mihara, T.; Yamaoka, K.; Nakajima, M. MAXI upper limits of the electromagnetic counterpart of GW170817. Publ. Astron. Soc. Jpn. 2018, 70, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troja, E.; Piro, L.; van Eerten, H.; Wollaeger, R.T.; Im, M.; Fox, O.D.; Butler, N.R.; Cenko, S.B.; Sakamoto, T.; Fryer, C.L.; et al. The X-ray counterpart to the gravitational wave event GW 170817. Nature 2017, 551, 71–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fong, W.f.; Fong, W.; Blanchard, P.K.; Alexander, K.D.; Strader, J.; Margutti, R.; Hajela, A.; Villar, V.A.; Wu, Y.; Ye, C.S.; et al. The Optical Afterglow of GW170817: An Off-axis Structured Jet and Deep Constraints on a Globular Cluster Origin. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2019, 883, L1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chassande-Mottin, E.; Leyde, K.; Mastrogiovanni, S.; Steer, D.A. Gravitational wave observations, distance measurement uncertainties, and cosmology. Phys. Rev. D 2019, 100, 083514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villar, V.A.; Guillochon, J.; Berger, E.; Metzger, B.D.; Cowperthwaite, P.S.; Nicholl, M.; Alexander, K.D.; Blanchard, P.K.; Chornock, R.; Eftekhari, T.; et al. The Combined Ultraviolet, Optical, and Near-Infrared Light Curves of the Kilonova Associated with the Binary Neutron Star Merger GW170817: Unified Data Set, Analytic Models, and Physical Implications. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2017, 851, L21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mooley, K.P.; Deller, A.T.; Gottlieb, O.; Nakar, E.; Hallinan, G.; Bourke, S.; Frail, D.A.; Horesh, A.; Corsi, A.; Hotokezaka, K. Superluminal motion of a relativistic jet in the neutron-star merger GW170817. Nature 2018, 561, 355–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giovanelli, R.; Haynes, M.; Salzer, J.; Wegner, G.; Costa, L.d.; Freudling, W. The motions of clusters of galaxies and the dipoles of the peculiar velocity field. Astron. J. 1998, 116, 2632–2643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.; Mould, J.R. Peculiar Velocities of Clusters in the Perseus-Pisces Supercluster. Astrphys. J. 1992, 396, 453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, S.; Mould, J.R.; Hughes, S.M.G.; Huchra, J.P.; Macri, L.M.; Kennicutt, R.C.; Gibson, B.K.; Ferrarese, L.; Freedman, W.L.; Han, M.; et al. The Hubble Space Telescope Key Project on the Extragalactic Distance Scale. 24. The Calibration of Tully-Fisher relations and the value of the Hubble Constant. Astrophys. J. 2000, 529, 698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinshaw, G.; Weiland, J.L.; Hill, R.S.; Odegard, N.; Larson, D.; Bennett, C.L.; Gold, B.; Greason, M.R.; Jarosik, N.; Komatsu, E.; et al. [WMAP Collaboration] Five-Year Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe (WMAP) Observations: Data Processing, Sky Maps, and Basic Results. Astrophys. J. Suppl. 2009, 180, 225–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crook, A.C.; Huchra, J.P.; Martimbeau, N.; Masters, K.L.; Jarrett, T.; Macri, L.M. Groups of Galaxies in the Two Micron All-Sky Redshift Survey. Astrophys. J. 2007, 655, 790–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Springob, C.M.; Magoulas, C.; Colless, M.; Mould, J.; Erdogdu, P.; Jones, D.H.; Lucey, J.R.; Campbell, L.; Fluke, C.J. The 6dF Galaxy Survey: Peculiar Velocity Field and Cosmography. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2014, 445, 2677–2697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrick, J.; Turnbull, S.J.; Lavaux, G.; Hudson, M.J. Cosmological parameters from the comparison of peculiar velocities with predictions from the 2M++ density field. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2015, 450, 317–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ade, P.A.R.; Aghanim, N.; Arnaud, M.; Ashdown, M.; Aumont, M.; Baccigalupi, C.; Banday, A.J.; Barreiro, R.B.; Bartlett, J.G.; Bartolo, N.; et al. [Planck Collaboration] Planck 2015 results. XIII. Cosmological parameters. Astron. Astrophys. 2016, 594, A13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riess, A.G.; Macri, L.M.; Hoffmann, S.L.; Scolnic, D.; Casertano, S.; Filippenko, A.V.; Tucker, B.E.; Reid, M.J.; Jones, D.O.; Silverman, J.M.; et al. A 2.4% Determination of the Local Value of the Hubble Constant. Astrophys. J. 2016, 826, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonvin, V.; Courbin, F.; Suyu, S.H.; Marshall, P.J.; Rusu, C.E.; Sluse, D.; Tewes, M.; Wong, K.C.; Collett, T.; Fassnacht, C.D.; et al. [H0LiCOW Collaboration] H0LiCOW – V. New COSMOGRAIL time delays of HE 0435-1223: H0 to 3.8 per cent precision from strong lensing in a flat ΛCDM model. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2017, 465, 4914–4930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aubourg, E.; Bailey, S.; Bautista, J.E.; Beutler, F.; Bhardwaj, V.; Bizyaev, D.; Blanton, M.; Blomqvist, M.; Bolton, A.S.; Bovy, J.; et al. [BOSS Collaboration] Cosmological implications of baryon acoustic oscillation measurements. Phys. Rev. D 2015, 92, 123516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henning, J.W.; Sayre, J.T.; Reichardt, C.L.; Ade, P.A.R.; Anderson, A.J.; Austermann, J.E.; Beall, J.A.; Bender, A.N.; Benson, B.A.; Bleem, L.E.; et al. [SPT Collaboration] Measurements of the Temperature and E-Mode Polarization of the CMB from 500 Square Degrees of SPTpol Data. Astrophys. J. 2018, 852, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nissanke, S.; Holz, D.E.; Hughes, S.A.; Dalal, N.; Sievers, J.L. Exploring short gamma-ray bursts as gravitational-wave standard sirens. Astrophys. J. 2010, 725, 496–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.Y.; Fishbach, M.; Holz, D.E. A two per cent Hubble constant measurement from standard sirens within five years. Nature 2018, 562, 545–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feeney, S.M.; Peiris, H.V.; Williamson, A.R.; Nissanke, S.M.; Mortlock, D.J.; Alsing, J.; Scolnic, D. Prospects for resolving the Hubble constant tension with standard sirens. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2019, 122, 061105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbott, B.P.; Abbott, R.; Abbott, T.D.; Abraham, S.; Acernese, F.; Ackley, K.; Adams, C.; Adhikari, R.X.; Adya, V.B.; Affeldt, C.; et al. GW190425: Observation of a Compact Binary Coalescence with Total Mass ∼3.4M⊙. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2020, 892, L3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, R.; Abbott, T.D.; Acernese, F.; Ackley, K.; Adams, C.; Adhikari, N.; Adhikari, R.X.; Adya, V.B.; Affeldt, C.; Agarwal, D.; et al. [LIGO Scientific and VIRGO Collaborations] GWTC-2.1: Deep extended catalog of compact binary coalescences observed by LIGO and Virgo during the first half of the third observing run. Phys. Rev. D 2024, 109, 022001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boersma, O.; van Leeuwen, J.; Adams, E.A.K.; Adebahr, B.; Kutkin, A.; Oosterloo, T.; de Blok, W.J.G.; van den Brink, R.; Coolen, A.H.W.M.; Connor, L.; et al. A search for radio emission from double-neutron star merger GW190425 using Apertif. Astron. Astrophys. 2021, 650, A131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coughlin, M.W.; Ahumada, T.; Anand, S.; De, K.; Hankins, M.J.; Kasliwal, M.M.; Singer, L.P.; Bellm, E.C.; Andreoni, I.; Cenko, S.B.; et al. GROWTH on S190425z: Searching thousands of square degrees to identify an optical or infrared counterpart to a binary neutron star merger with the Zwicky Transient Facility and Palomar Gattini IR. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2019, 885, L19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseinzadeh, G.; Cowperthwaite, P.S.; Gomez, S.; Villar, V.A.; Nicholl, M.; Margutti, R.; Berger, E.; Chornock, R.; Paterson, K.; Fong, W.; et al. Follow-up of the Neutron Star Bearing Gravitational Wave Candidate Events S190425z and S190426c with MMT and SOAR. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2019, 880, L4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozanenko, A.S.; Minaev, P.Y.; Grebenev, S.A.; Chelovekov, I.V. Observation of the Second LIGO/Virgo Event Connected with a Binary Neutron Star Merger S190425z in the Gamma-Ray Range. Astron. Lett. 2020, arXiv:astro-ph.HE/1912.13112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fletcher, C.; on behalf of the Fermi-GBM Team and the GBM-LIGO/Virgo group. GRB Coordinates Network Circular; 2019; Volume 24185. Available online: https://gcn.nasa.gov/circulars/24185 (accessed on 11 May 2025).
- Moroianu, A.; Wen, L.; James, C.W.; Ai, S.; Kovalam, M.; Panther, F.H.; Zhang, B. An assessment of the association between a fast radio burst and binary neutron star merger. Nat. Astron. 2023, 7, 579–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panther, F.H.; Anderson, G.E.; Bhandari, S.; Goodwin, A.J.; Hurley-Walker, N.; James, C.W.; Kawka, A.; Ai, S.; Kovalam, M.; Moroianu, A.; et al. The most probable host of CHIME FRB 190425A, associated with binary neutron star merger GW190425, and a late-time transient search. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2022, 519, 2235–2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smartt, S.J.; Nicholl, M.; Srivastav, S.; Huber, M.E.; Chambers, K.C.; Smith, K.W.; Young, D.R.; Fulton, M.D.; Tonry, J.L.; Stubbs, C.W.; et al. GW190425: Pan-STARRS and ATLAS coverage of the skymap and limits on optical emission associated with FRB 20190425A. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2024, 528, 2299–2307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, R.; Abbott, T.D.; Abraham, S.; Acernese, F.; Ackley, K.; Adams, C.; Adhikari, R.X.; Adya, V.B.; Affeldt, C.; Agathos, M.; et al. [LIGO Scientific and Virgo Collaborations] GW190521: A Binary Black Hole Merger with a Total Mass of 150M⊙. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2020, 125, 101102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, R.; Abbott, T.D.; Abraham, S.; Acernese, F.; Ackley, K.; Adams, C.; Adhikari, R.X.; Adya, V.B.; Affeldt, C.; Agathos, M.; et al. [LIGO Scientific and Virgo Collaborations] Properties and Astrophysical Implications of the 150 M⊙ Binary Black Hole Merger GW190521. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2020, 900, L13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, M.J.; Ford, K.E.S.; McKernan, B.; Ross, N.P.; Stern, D.; Burdge, K.; Coughlin, M.; Djorgovski, S.G.; Drake, A.J.; Duev, D.; et al. Candidate Electromagnetic Counterpart to the Binary Black Hole Merger Gravitational Wave Event S190521g. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2020, 124, 251102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashton, G.; Ackley, K.; Hernandez, I.M.n.; Piotrzkowski, B. Current observations are insufficient to confidently associate the binary black hole merger GW190521 with AGN J124942.3 + 344929. Class. Quant. Grav. 2021, 38, 235004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmese, A.; Fishbach, M.; Burke, C.J.; Annis, J.T.; Liu, X. Do LIGO/Virgo Black Hole Mergers Produce AGN Flares? The Case of GW190521 and Prospects for Reaching a Confident Association. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2021, 914, L34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dálya, G.; Galgóczi, G.; Dobos, L.; Frei, Z.; Heng, I.S.; Macas, R.; Messenger, C.; Raffai, P.; de Souza, R.S. GLADE: A galaxy catalogue for timessenger searches in the advanced gravitational-wave detector era. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2018, 479, 2374–2381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dálya, G.; Díaz, R.; Bouchet, F.R.; Frei, Z.; Jasche, J.; Lavaux, J.; Macas, R.; Mukherjee, S.; Pálfi, M.; de Souza, R.S.; et al. GLADE+: An Extended Galaxy Catalogue for timessenger Searches with Advanced Gravitational-wave Detectors. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2110.06184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares-Santos, M.; Palmese, A.; Hartley, W.; Annis, J.; Garcia-Bellido, J.; Lahav, O.; Doctor, Z.; Lin, H.; Fishbach, M.; Pereira, M.E.S.; et al. [DES and LIGO Scientific and Virgo Collaborations] First Measurement of the Hubble Constant from a Dark Standard Siren using the Dark Energy Survey Galaxies and the LIGO/Virgo Binary–Black-hole Merger GW170814. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2019, 876, L7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, R.; Abbott, T.D.; Abraham, S.; Acernese, F.; Ackley, K.; Adams, C.; Adhikari, R.X.; Adya, V.B.; Affeldt, C.; Agathos, M.; et al. [LIGO Scientific and Virgo Collaborations] GW190412: Observation of a Binary-Black-Hole Coalescence with Asymmetric Masses. Phys. Rev. D 2020, 102, 043015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmese, A.; Bom, C.R.; Mucesh, S.; Hartley, W.G. A Standard Siren Measurement of the Hubble Constant Using Gravitational-wave Events from the First Three LIGO/Virgo Observing Runs and the DESI Legacy Survey. Astrophys. J. 2023, 943, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastrogiovanni, S.; Leyde, K.; Karathanasis, C.; Chassande-Mottin, E.; Steer, D.A.; Gair, J.; Ghosh, A.; Gray, R.; Mukherjee, S.; Rinaldi, S. On the importance of source population models for gravitational-wave cosmology. Phys. Rev. D 2021, 104, 062009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mali, U.; Essick, R. Striking a Chord with Spectral Sirens: Multiple Features in the Compact Binary Population Correlate with H0. Astrophys. J. 2025, 980, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Biesiada, M.; Zheng, X.; Liao, K.; Li, Z.; Zhu, Z.H. Cosmological inference from standard sirens without redshift measurements. JCAP 2019, 04, 033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, C.; Fishbach, M. Cosmology with standard sirens at cosmic noon. Phys. Rev. D 2021, 104, 043507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bera, S.; Rana, D.; More, S.; Bose, S. Incompleteness Matters Not: Inference of H0 from Binary Black Hole–Galaxy Cross-correlations. Astrophys. J. 2020, 902, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, S.; Wandelt, B.D.; Nissanke, S.M.; Silvestri, A. Accurate precision Cosmology with redshift unknown gravitational wave sources. Phys. Rev. D 2021, 103, 043520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messenger, C.; Read, J. Measuring a cosmological distance-redshift relationship using only gravitational wave observations of binary neutron star coalescences. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2012, 108, 091101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatterjee, D.; Hegade, K.R.A.; Holder, G.; Holz, D.E.; Perkins, S.; Yagi, K.; Yunes, N. Cosmology with Love: Measuring the Hubble constant using neutron star universal relations. Phys. Rev. D 2021, 104, 083528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).